Ancestry And Health on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''The determinants of health''
Geneva. Accessed 12 May 2011 (which are inter-related with all three, but mostly social factors). The relationship between race and health has been studied from multidisciplinary perspectives, with increasing focus on how racism influences health disparities, and how environmental and
Office of Minority Health
The NIH (National institutes of health) and The WHO are organizations that provide useful links and support research that is targeted at the development of initiatives around minority communities and the health disparities they face. Similarly, In the United Kingdom, the National Health Service established a specialist collection on Ethnicity & Health. This resource was supported by the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) as part of the UK NHS Evidence initiative NHS Evidence. Similarly, there are growing numbers of resource and research centers which are seeking to provide this service for other national settings, such a
Multicultural Mental Health Australia
However, cultural competence has also been criticized for having the potential to create stereotypes. Scientific studies have shown the lack of efficacy of adapting pharmaceutical treatment to racial categories. "Race-based medicine" is the term for medicines that are targeted at specific racial clusters which are shown to have a propensity for a certain disorder. The first example of this in the U.S. was when BiDil, a medication for congestive heart failure, was licensed specifically for use in American patients that self-identify as black. Previous studies had shown that African American patients with congestive heart failure generally respond less effectively to traditional treatments than white patients with similar conditions. After two trials, BiDil was licensed exclusively for use in African American patients. Critics have argued that this particular licensing was unwarranted, since the trials did not in fact show that the drug was more effective in African Americans than in other groups, but merely that it was more effective in African Americans than other similar drugs. It was also only tested in African American males, but not in any other racial groups or among women. This peculiar trial and licensing procedure has prompted suggestions that the licensing was in fact used as a race-based advertising scheme. Critics are concerned that the trend of research on race-specific pharmaceutical treatments will result in inequitable access to pharmaceutical innovation and smaller minority groups may be ignored. This has led to a call for regulatory approaches to be put in place to ensure scientific validity of racial disparity in pharmacological treatment. An alternative to "race-based medicine" is personalized or precision medicine. Precision medicine is a medical model that proposes the customization of
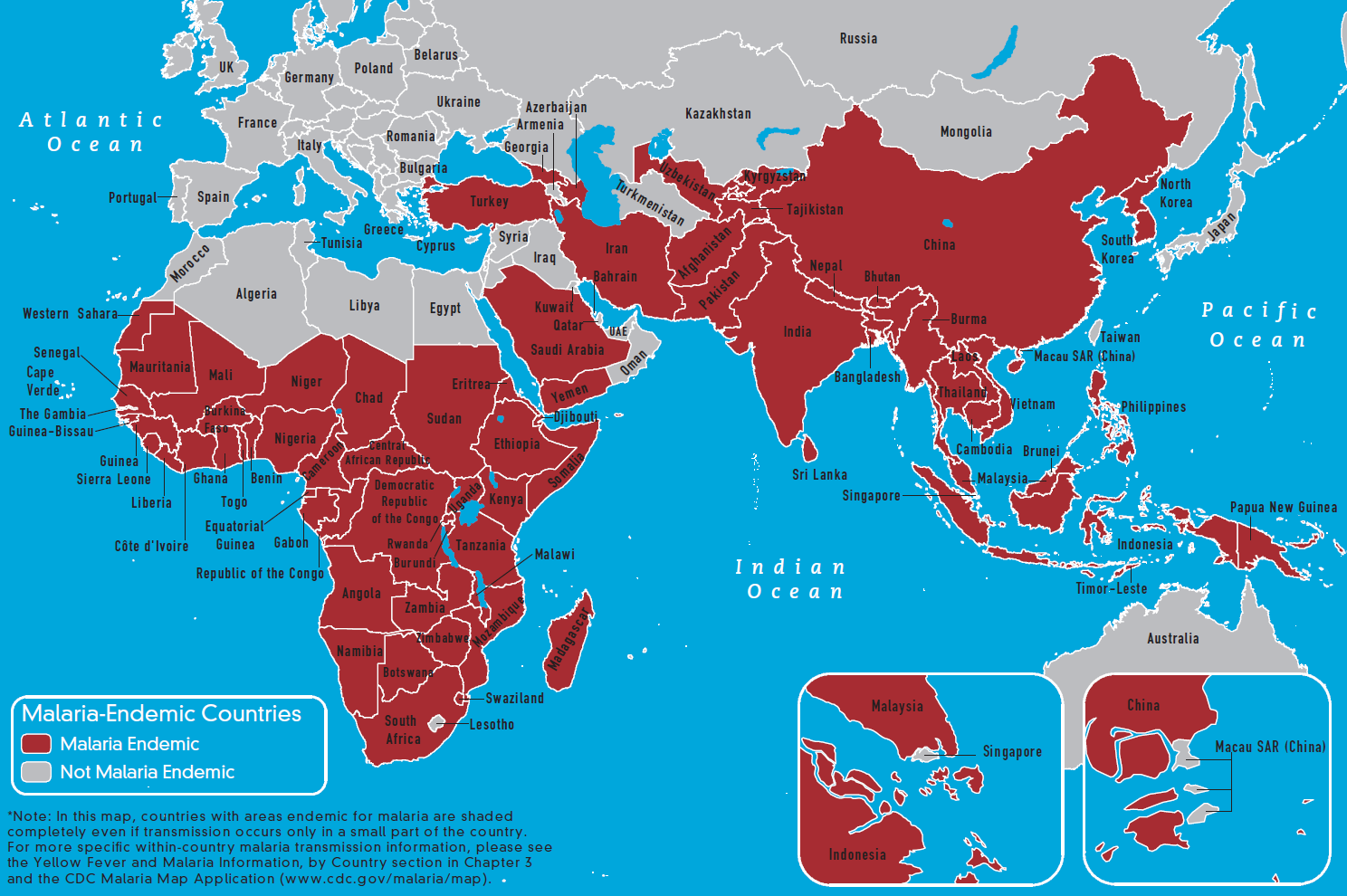
 Genes may be under strong selection in response to local diseases. For example, people who are duffy negative tend to have higher resistance to malaria. Most Africans are duffy negative and most non-Africans are duffy positive due to endemic transmission of malaria in Africa. A number of genetic diseases more prevalent in malaria-affected areas may provide some genetic resistance to malaria including sickle cell disease,
Genes may be under strong selection in response to local diseases. For example, people who are duffy negative tend to have higher resistance to malaria. Most Africans are duffy negative and most non-Africans are duffy positive due to endemic transmission of malaria in Africa. A number of genetic diseases more prevalent in malaria-affected areas may provide some genetic resistance to malaria including sickle cell disease,
What's the Use of Race? Modern Governance and the Biology of Difference
', MIT press. Chapter 9. many doctors consider it useful to take race into account when treating disease because diseases and treatment responses tend to cluster by geographic ancestry. The discovery that more diseases than previously thought correlate with racial identification have further sparked the interest in using race as a proxy for bio-geographical ancestry and genetic buildup. Race in medicine is used as an approximation for more specific genetic and environmental risk factors. Race is thus partly a surrogate for environmental factors such as differences in socioeconomic status that are known to affect health. It is also an imperfect surrogate for ancestral geographic regions and differences in gene frequencies between different ancestral populations and thus differences in genes that can affect health. This can give an approximation of probability for disease or for preferred treatment, although the approximation is less than perfect. Taking the example of sickle-cell disease, in an
What's the Use of Race? Modern Governance and the Biology of Difference
', MIT press. Chapter 5. Some of those who are critical of race as a biological concept see race as socially meaningful group that is important to study epidemiologically in order to reduce disparities. For example, some racial groups are less likely than others to receive adequate treatment for osteoporosis, even after risk factors have been assessed. Since the 19th century, blacks have been thought to have thicker bones than whites have and to lose bone mass more slowly with age. In a recent study, African Americans were shown to be substantially less likely to receive prescription osteoporosis medications than Caucasians. Men were also significantly less likely to be treated compared with women. This discrepancy may be due to physicians' knowledge that, on average, African Americans are at lower risk for osteoporosis than Caucasians. It may be possible that these physicians generalize this data to high-risk African-Americans, leading them to fail to appropriately assess and manage these individuals' osteoporosis. On the other hand, some of those who are critical of race as a biological concept see race as socially meaningful group that is important to study epidemiologically in order to reduce disparities. David Williams (1994) argued, after an examination of articles in the journal ''Health Services Research'' during the 1966–90 period, that how race was determined and defined was seldom described. At a minimum, researchers should describe if race was assessed by self-report, proxy report, extraction from records, or direct observation. Race was also often used questionable, such as an indicator of socioeconomic status. Racial genetic explanations may be overemphasized, ignoring the interaction with and the role of the environment.
Cultural Diversity in Healthcare Speaker Series
University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health
Cultural Diversity in Healthcare Research Symposium
University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health
News-Medical.net
Unnatural causes, videos on how racial inequalities influence health
United States Office of Minority Health
United Kingdom National Health Service - Ethnicity & Health
Multicultural Mental Health Australia
{{DEFAULTSORT:Race And Health Health care quality Biomedicine Ethnicity Human population genetics
ancestry
An ancestor, also known as a forefather, fore-elder or a forebear, is a parent or (recursively) the parent of an antecedent (i.e., a grandparent, great-grandparent, great-great-grandparent and so forth). ''Ancestor'' is "any person from whom ...
, social identity
Identity is the qualities, beliefs, personality traits, appearance, and/or expressions that characterize a person or group.Compare ''Collins Dictionary of Sociology'', quoted in
In sociology, emphasis is placed on collective identity, in which ...
, genetic makeup and lived experience. "Race" and ethnicity often remain undifferentiated in health research.
Differences in health status, health outcomes, life expectancy, and many other indicators of health in different racial and ethnic groups are well documented. Epidemiological data indicate that racial groups are unequally affected by diseases, in terms or morbidity and mortality. Some individuals in certain racial groups receive less care, have less access to resources, and live shorter lives in general. Overall, racial health disparities appear to be rooted in social disadvantages associated with race such as implicit stereotyping and average differences in socioeconomic status
Socioeconomic status (SES) is an economic and sociological combined total measure of a person's work experience and of an individual's or family's economic access to resources and social position in relation to others. When analyzing a family's ...
.
Health disparities are defined as "preventable differences in the burden of disease, injury, violence, or opportunities to achieve optimal health that are experienced by socially disadvantaged populations". According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgi ...
, they are intrinsically related to the "historical and current unequal distribution of social, political, economic and environmental resources". World Health Organization''The determinants of health''
Geneva. Accessed 12 May 2011 (which are inter-related with all three, but mostly social factors). The relationship between race and health has been studied from multidisciplinary perspectives, with increasing focus on how racism influences health disparities, and how environmental and
physiological
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical ...
factors respond to one another and to genetics.
Racial health disparities
Health disparities refer to gaps in the quality of health andhealth care
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health profe ...
across racial and ethnic groups. The US Health Resources and Services Administration defines health disparities as "population-specific differences in the presence of disease, health outcomes, or access to health care". Health is measured through variables such as life expectancy and incidence of diseases.
For racial and ethnic minorities in the United States, health disparities take on many forms, including higher rates of chronic disease, premature death, and maternal mortality compared to the rates among whites. It is important to note that this pattern is not universal. Some minority groups—most notably, Hispanic immigrants—may have better health outcomes than whites when they arrive in the United States. However this appears to diminish with time spent in the United States. For other indicators, disparities have shrunk, not because of improvements among minorities but because of declines in the health of majority groups.
In the U.S., more than 133 million Americans (45% of the population) have one or more chronic diseases. One study has shown that between the ages of 60 to 70, racial/ethnic minorities are 1.5 to 2.0 times more likely than whites (Hispanic and non Hispanic) to have one of the four major chronic diseases specifically Diabetes, cancer, cardiovascular disease (CVD), and chronic lung disease. However, the greatest differences only occurred among people with single chronic diseases. Racial/ethnic differences were less distinct for some conditions including multiple diseases. Non-Hispanic whites trended toward a high prevalence for dyads of cardiovascular disease (CVD) with cancer or lung disease. Hispanics and African Americans had the greatest prevalence of diabetes, while non-Hispanic blacks had higher odds of having heart disease with cancer or chronic lung disease than non-Hispanic whites. Among non-Hispanic whites the prevalence of multimorbidities
Multimorbidity, also known as multiple long-term conditions (MLTC), means living with two or more chronic illnesses. For example, a person could have diabetes, heart disease and depression at the same time. Multimorbidity can have a significant ...
that include diabetes was low; however, non-Hispanic whites had a very high prevalence of multimorbidities that exclude diabetes. Non-Hispanic whites had the highest prevalence of cancer only or lung disease only.
Between 1960 and 2005 the percentage of children with a chronic disease in the United States quadrupled with minority having higher likelihood for these disease. The most common major chronic biases of youth in the United States are asthma, diabetes mellitus, obesity, hypertension
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high bl ...
, dental disease, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), mental illness
A mental disorder, also referred to as a mental illness or psychiatric disorder, is a behavioral or mental pattern that causes significant distress or impairment of personal functioning. Such features may be persistent, relapsing and remitti ...
, cancers and others. This results in Black and Latinx adult patients facing a disproportionate amount of health concerns, such as asthma, with treatment and management guidelines not developed with studies based on their populations and healthcare needs.
Although individuals from different environmental, continental, socioeconomic, and racial groups etc. have different levels of health, yet not all of these differences are always categorized or defined as health disparities. Some researchers separate definitions of health inequality
Health equity arises from access to the social determinants of health, specifically from wealth, power and prestige. Individuals who have consistently been deprived of these three determinants are significantly disadvantaged from health inequiti ...
from health disparity by preventability. Health inequalities are often categorized as being unavoidable i.e. due to age, while preventable unfair health outcomes are categorized as health inequities. These are seen as preventable because they are usually associated with income, education, race, ethnicity, gender, and more.
Defining race
Definitions of race are ambiguous due to the various paradigms used to discuss race. These definitions are a direct result of biological and social views. Definitions have changed throughout history to yield a modern understanding of race that is complex and fluid. Moreover, there is no one definition that stands, as there are many competing and interlocking ways to look at race. Due to its ambiguity, terms such as race, genetic population, ethnicity, geographic population, and ancestry are used interchangeably in everyday discourse involving race. Some researchers critique this interchangeability noting that the conceptual differences between race and ethnicity are not widely agreed upon. Even though there is a broad scientific agreement that essentialist and typological conceptions of race are untenable, scientists around the world continue to conceptualize race in widely differing ways. Historically, biological definitions of race have encompassed both essentialist and anti-essentialist views. Essentialists have sought to show that racial groups are genetically distinct populations, describing "races as groups of people who share certain innate, inherited biological traits". In contrast, anti-essentialists have used biological evidence to demonstrate that "race groupings do not reflect patterns of human biological variation, countering essentialist claims to the contrary". Over the past 20 years, a consensus has emerged that, while race is partially based on physical similarities within groups, it does not have an inherent physical or biological meaning. In response, researchers and social scientists have begun examining notions of race as constructed. Racial groups are "constructed" from differing historical, political, and economic contexts, rather than corresponding to inherited, biological variations. Proponents of the constructionist view claim that biological definitions have been used to justify racism in the past and still have the potential to be used to encourage racist thinking in the future. Since race is changing and often so loosely characterized on arbitrary phenotypes, and because it has no genetic basis, the only working definition we can assign it is a social construct. This is not to say race is imaginary or non-existent. It is an important social reality. However to say that the concept of race has any scientific merit or has a scientific foundation can lead to many issues in scientific research, and it may also lead to inherent racial bias. Social views also better explain the ambiguity of racial definitions. An individual may self-identify as one race based on one set of determinants (for example, phenotype, culture, ancestry) while society may ascribe the person otherwise based on external forces and discrete racial standards. Dominant racial conceptions influence how individuals label both themselves and others within society. Modern human populations are becoming more difficult to define within traditional racial boundaries due to racial admixture. Most scientific studies, applications, and government documents ask individuals to self-identify race from a limited assortment of common racial categories. The conflict between self-identification and societal ascription further complicates biomedical research and public health policies. However complex its sociological roots, race has real biological ramifications; the intersection of race, science, and society permeates everyday life and influences human health via genetics, access to medical care, diagnosis, and treatment.Race and disease
Diseases affect racial groups differently, especially when they are co-related with class disparities. As socioeconomic factors influence the access to care, the barriers to access healthcare systems can perpetuate different biological effects of diseases among racial groups that are not pre-determined by biology. Some researchers advocate for the use of self-reported race as a way to trace socioeconomic disparities and its effects in health. For instance, a study conducted by the National Health Service checks program in the United Kingdom, which aims to increase diagnosis across demographics, noted that "the reported lower screening in specific black and minority ethnic communities... may increase inequalities in health." In this specific case, the lack of attention to certain demographics can be seen as a cause of increased instances of disease from this lack of proper, equal preventive care. One must consider these external factors when evaluating statistics on the prevalence of disease in populations, even though genetic components can play a role in predispositions to contracting some illnesses. Individuals who share a similar genetic makeup can also share certain propensity or resistance to specific diseases. However, there are confronted positions in relation to the utility of using 'races' to talk about populations sharing a similar genetic makeup. Some geneticists argued that human variation is geographically structured and that genetic differences correlate with general conceptualizations of racial groups. Others claimed that this correlation is too unstable and that the genetic differences are minimal and they are "distributed over the world in a discordant manner". Therefore, race is regarded by some as a useful tool for the assessment of genetic epidemiological risk, while others consider it can lead to an increased underdiagnosis in 'low risk' populations.Single-gene disorders
There are manyautosomal recessive
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and t ...
single gene genetic disorders that differ in frequency between different populations due to the region and ancestry as well as the founder effect
In population genetics, the founder effect is the loss of genetic variation that occurs when a new population is established by a very small number of individuals from a larger population. It was first fully outlined by Ernst Mayr in 1942, using ...
. Some examples of these disorders include:
* Cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. O ...
, the most common life-limiting autosomal recessive
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and t ...
disease among people of Northern European heritage
* Sickle-cell anemia, most prevalent in populations with sub-Saharan African ancestry but also common among Latin-American, Middle Eastern populations, as well as those people of South European regions such as Turkey, Greece, and Italy
* Thalassemia
Thalassemias are inherited blood disorders characterized by decreased hemoglobin production. Symptoms depend on the type and can vary from none to severe. Often there is mild to severe anemia (low red blood cells or hemoglobin). Anemia can result ...
, most prevalent in populations having Mediterranean ancestry, to the point that the disease's name is derived from Greek ''thalasson'', "sea"
* Tay–Sachs disease, an autosomal recessive disorder most common among Ashkenazi Jews, French Canadians
French Canadians (referred to as Canadiens mainly before the twentieth century; french: Canadiens français, ; feminine form: , ), or Franco-Canadians (french: Franco-Canadiens), refers to either an ethnic group who trace their ancestry to Fren ...
of Saguenay–Lac-Saint-Jean
Saguenay–Lac-Saint-Jean (, ) is a region in Quebec, Canada. It contains the Saguenay Fjord, the estuary of the Saguenay River, stretching through much of the region. It is also known as Sagamie in French, from the first part of "Saguenay" and th ...
, Cajuns of Louisiana and Old Order Amish of Pennsylvania
* Hereditary hemochromatosis, most common among persons having Northern European ancestry, in particular those people of Celtic descent
* Hermansky–Pudlak syndrome, most common among Puerto Ricans
Puerto Ricans ( es, Puertorriqueños; or boricuas) are the people of Puerto Rico, the inhabitants, and citizens of the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico and their descendants.
Overview
The culture held in common by most Puerto Ricans is referred t ...
* Finnish heritage diseases, autosomal recessive diseases that are far more common among Finns
Multifactorial polygenic diseases
Many diseases differ in frequency between different populations. However, complex diseases are affected by multiple factors, including genetic and environmental. There is controversy over the extent to which some of these conditions are influenced by genes, and ongoing research aims to identify which genetic loci, if any, are linked to these diseases. "Risk is the probability that an event will occur. In epidemiology, it is most often used to express the probability that a particular outcome will occur following a particular exposure." Different populations are considered "high-risk" or "low-risk" groups for various diseases due to the probability of that particular population being more exposed to certain risk factors. Beyond genetic factors, history and culture, as well as current environmental and social conditions, influence a certain populations' risk for specific diseases.Disease progression
Racial groups may differ in how a disease progresses. Different access to healthcare services, different living and working conditions influence how a disease progresses within racial groups. However, the reasons for these differences are multiple, and should not be understood a consequence of genetic differences between races, but rather as effects of social and environmental factors affecting.Prevention
Genetics have been proven to be a strong predictor for common diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disease (CVD), diabetes, autoimmune disorders, and psychiatric illnesses. Some geneticists have determined that " human genetic variation is geographically structured" and that different geographic regions correlate with different races. Meanwhile, others have claimed that the human genome is characterized by clinal changes across the globe, in relation with the "Out of Africa" theory and how migration to new environments cause changes in populations' genetics over time. Some diseases are more prevalent in some populations identified as races due to their common ancestry. Thus, people of African and Mediterranean descent are found to be more susceptible to sickle-cell disease whilecystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. O ...
and hemochromatosis are more common among European populations. Some physicians claim that race can be used as a proxy for the risk that the patient may be exposed to in relation to these diseases. However, racial self-identification only provides fragmentary information about the person's ancestry. Thus, racial profiling in medical services would also lead to the risk of underdiagnosis.
While genetics certainly play a role in determining how susceptible a person is to specific diseases, environmental, structural and cultural factors play a large role as well. For this reason, it is impossible to discern exactly what causes a person to acquire a disease, but it is important to observe how all these factors relate to each other. Each person's health is unique, as they have different genetic compositions and life histories.
Race-based treatment
Racial groups, especially when defined as minorities or ethnic groups, often face structural and cultural barriers to access healthcare services. The development of culturally and structurally competent services and research that meet the specific health care needs of racial groups is still in its infancy. In the United States, thOffice of Minority Health
The NIH (National institutes of health) and The WHO are organizations that provide useful links and support research that is targeted at the development of initiatives around minority communities and the health disparities they face. Similarly, In the United Kingdom, the National Health Service established a specialist collection on Ethnicity & Health. This resource was supported by the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) as part of the UK NHS Evidence initiative NHS Evidence. Similarly, there are growing numbers of resource and research centers which are seeking to provide this service for other national settings, such a
Multicultural Mental Health Australia
However, cultural competence has also been criticized for having the potential to create stereotypes. Scientific studies have shown the lack of efficacy of adapting pharmaceutical treatment to racial categories. "Race-based medicine" is the term for medicines that are targeted at specific racial clusters which are shown to have a propensity for a certain disorder. The first example of this in the U.S. was when BiDil, a medication for congestive heart failure, was licensed specifically for use in American patients that self-identify as black. Previous studies had shown that African American patients with congestive heart failure generally respond less effectively to traditional treatments than white patients with similar conditions. After two trials, BiDil was licensed exclusively for use in African American patients. Critics have argued that this particular licensing was unwarranted, since the trials did not in fact show that the drug was more effective in African Americans than in other groups, but merely that it was more effective in African Americans than other similar drugs. It was also only tested in African American males, but not in any other racial groups or among women. This peculiar trial and licensing procedure has prompted suggestions that the licensing was in fact used as a race-based advertising scheme. Critics are concerned that the trend of research on race-specific pharmaceutical treatments will result in inequitable access to pharmaceutical innovation and smaller minority groups may be ignored. This has led to a call for regulatory approaches to be put in place to ensure scientific validity of racial disparity in pharmacological treatment. An alternative to "race-based medicine" is personalized or precision medicine. Precision medicine is a medical model that proposes the customization of
healthcare
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health profe ...
, with medical decisions, treatments, practices, or products being tailored to the individual patient. It involves identifying genetic, genomic (i.e., genomic sequencing), and clinical information—as opposed to using race as a proxy for these data—to better predict a patient's predisposition to certain diseases.
Environmental factors
A positive correlation between minorities and asocioeconomic status
Socioeconomic status (SES) is an economic and sociological combined total measure of a person's work experience and of an individual's or family's economic access to resources and social position in relation to others. When analyzing a family's ...
of being low-income in industrialized and rural regions of the U.S. depict how low-income communities tend to include more individuals that have a lower educational background, most importantly in health. Income status, diet, and education all construct a higher burden for low-income minorities, to be conscious about their health. Research conducted by medical departments at universities in San Diego, Miami, Pennsylvania, and North Carolina suggested that minorities in regions where lower socioeconomic status is common, there was a direct relationship with unhealthy diets and greater distance of supermarkets. Therefore, in areas where supermarkets are less accessible ( food deserts) to impoverished areas, the more likely these groups are to purchase inexpensive fast food or just follow an unhealthy diet. As a result, because food deserts are more prevalent in low income communities, minorities that reside in these areas are more prone to obesity, which can lead to diseases such as chronic kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a type of kidney disease in which a gradual loss of kidney function occurs over a period of months to years. Initially generally no symptoms are seen, but later symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vo ...
, hypertension
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high bl ...
, or diabetes.
Furthermore, this can also occur when minorities living in rural areas undergoing urbanization, are introduced to fast food
Fast food is a type of mass-produced food designed for commercial resale, with a strong priority placed on speed of service. It is a commercial term, limited to food sold in a restaurant or store with frozen, preheated or precooked ingredien ...
. A study done in Thailand focused on urbanized metropolitan areas, the students who participated in this study as were diagnosed as "non-obese" in their early life according to their BMI, however were increasingly at risk of developing Type 2 Diabetes, or obesity as adults, as opposed to young adults who lived in more rural areas during their early life. Therefore, early exposure to urbanized regions can encourage unhealthy eating due to widespread presence of inexpensive fast food. Different racial populations that originate from more rural areas and then immigrate to the urbanized metropolitan areas can develop a fixation for a more westernized diet; this change in lifestyle typically occurs due to loss of traditional values when adapting to a new environment. For example, a 2009 study named CYKIDS was based on children from Cyprus, a country east of the Mediterranean Sea, who were evaluated by the KIDMED index to test their adherence to a Mediterranean diet after changing from rural residence to an urban residence. It was found that children in urban areas swapped their traditional dietary patterns for a diet favoring fast food.
Genetic factors
The fact that every human has a unique genetic code is the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. Versions of genetic markers, known as alleles, occur at different frequencies in different human populations; populations that are more geographically and ancestrally remote tend to differ more. A phenotype is the "outward, physical manifestation" of an organism." For humans, phenotypic differences are most readily seen via skin color, eye color, hair color, or height; however, any observable structure, function, or behavior can be considered part of a phenotype. A genotype is the "internally coded, inheritable information" carried by all living organisms. The human genome is encoded in DNA. For any trait of interest, observed differences among individuals "may be due to differences in the genes" coding for a trait and "the result of variation in environmental condition". This variability is due to gene-environment interactions that influence genetic expression patterns and trait heritability. For humans, there is "more genetic variation among individual people than between larger racial groups". In general, an average of 80% of genetic variation exists within local populations, around 10% is between local populations within the same continent, and approximately 8% of variation occurs between large groups living on different continents. Studies have found evidence of genetic differences between populations, but the distribution of genetic variants within and among human populations is impossible to describe succinctly because of the difficulty of defining a "population", the clinal nature of variation, and heterogeneity across the genome. Thus, the racialization of science and medicine can lead to controversy when the term population and race are used interchangeably.Evolutionary factors

 Genes may be under strong selection in response to local diseases. For example, people who are duffy negative tend to have higher resistance to malaria. Most Africans are duffy negative and most non-Africans are duffy positive due to endemic transmission of malaria in Africa. A number of genetic diseases more prevalent in malaria-affected areas may provide some genetic resistance to malaria including sickle cell disease,
Genes may be under strong selection in response to local diseases. For example, people who are duffy negative tend to have higher resistance to malaria. Most Africans are duffy negative and most non-Africans are duffy positive due to endemic transmission of malaria in Africa. A number of genetic diseases more prevalent in malaria-affected areas may provide some genetic resistance to malaria including sickle cell disease, thalassaemias
Thalassemias are inherited blood disorders characterized by decreased hemoglobin production. Symptoms depend on the type and can vary from none to severe. Often there is mild to severe anemia (low red blood cells or hemoglobin). Anemia can result ...
, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, and possibly others.
Many theories about the origin of the cystic fibrosis have suggested that it provides a heterozygote advantage by giving resistance to diseases earlier common in Europe.
In earlier research, a common theory was the " common disease-common variant" model. It argues that for common illnesses, the genetic contribution comes from the additive or multiplicative effects of gene variants that each one is common in the population. Each such gene variant is argued to cause only a small risk of disease and no single variant is sufficient or necessary to cause the disease. An individual must have many of these common gene variants in order for the risk of disease to be substantial.
More recent research indicates that the "common disease-rare variant" may be a better explanation for many common diseases. In this model, rare but higher-risk gene variants cause common diseases. This model may be relevant for diseases that reduces fertility. In contrast, for common genes associated with common disease to persist they must either have little effect during the reproductive period of life (like Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegeneration, neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in short-term me ...
) or provide some advantage in the original environment (like genes causing autoimmune diseases also providing resistance against infections). In either case varying frequencies of genes variants in different populations may be an explanation for health disparities. Genetic variants associated with Alzheimer's disease, deep venous thrombosis, Crohn disease, and type 2 diabetes appear to adhere to "common disease-common variant" model.
Gene flow
Gene flow
In population genetics, gene flow (also known as gene migration or geneflow and allele flow) is the transfer of genetic material from one population to another. If the rate of gene flow is high enough, then two populations will have equivalent a ...
and admixture
Admixture may refer to:
* Genetic admixture, the result of interbreeding between two or more previously isolated populations within a species
* Racial admixture, admixture between humans, also referred to as miscegenation
* Hybrid
* Mixture, the ch ...
can also have an effect on relationships between race and race-linked disorders. Multiple sclerosis, for example, is typically associated with people of European descent, but due to admixture African Americans have elevated levels of the disorder relative to Africans.
Some diseases and physiological variables vary depending upon their admixture ratios. Examples include measures of insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism o ...
functioning and obesity.
Gene interactions
The same gene variant, or group of gene variants, may produce different effects in different populations depending on differences in the gene variants, or groups of gene variants, they interact with. One example is the rate of progression toAIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual m ...
and death in HIV–infected patients. In Caucasians and Hispanics, HHC haplotype
A haplotype ( haploid genotype) is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent.
Many organisms contain genetic material ( DNA) which is inherited from two parents. Normally these organisms have their DNA or ...
s were associated with disease retardation, particularly a delayed progression to death, while for African Americans, possession of HHC haplotypes was associated with disease acceleration. In contrast, while the disease-retarding effects of the CCR2-641 allele were found in African Americans, they were not found in Caucasians.
Theoretical approaches in addressing health and race disparities
Public health researchers and policy makers are working to reduce health disparities. Health effects of racism are now a major area of research. In fact, these seem to be the primary research focus in biological and social sciences. Interdisciplinary methods have been used to address how race affects health. according to published studies, many factors combine to affect the health of individuals and communities. Whether people are healthy or not, is determined by their circumstances and environment. Factors that need to be addressed when looking at health and race include income and social status, education, physical environment, social support networks, genetics, health services, targeted instruction, and gender. These determinants are often cited in public health, anthropology, and other social science disciplines. The WHO categorizes these determinants into three broader topics: the social and economic environment, the physical environment, and the person's individual characteristics and behaviors. Due to the diversity of factors that often attribute to health disparities outcomes, interdisciplinary approaches are often implemented. Interdisciplinarity or interdisciplinary studies involves the combining of two or more academic disciplines into one activity (e.g., a research project) The term ''interdisciplinary'' is applied within education and training pedagogies to describe studies that use methods and insights of several established disciplines or traditional fields of study. Interdisciplinarity involves researchers, students, and teachers in the goals of connecting and integrating several academic schools of thought, professions, or technologies—along with their specific perspectives—in the pursuit of a common task.Biocultural approach
Biocultural evolution was introduced and first used in the 1970s. Biocultural methods focus on the interactions between humans and their environment to understand human biologicaladaptation
In biology, adaptation has three related meanings. Firstly, it is the dynamic evolutionary process of natural selection that fits organisms to their environment, enhancing their evolutionary fitness. Secondly, it is a state reached by the po ...
and variation
Variation or Variations may refer to:
Science and mathematics
* Variation (astronomy), any perturbation of the mean motion or orbit of a planet or satellite, particularly of the moon
* Genetic variation, the difference in DNA among individual ...
. These studies:
"research on questions of human biology and medical ecology that specifically includes social, cultural, or behavioral variables in the research design, offer valuable models for studying the interface between biological and cultural factors affecting human well-being"
This approach is useful in generating holistic viewpoints on human biological variation. There are two biocultural approach models. The first approach fuses biological, environmental, and cultural data. The second approach treats biological data as primary data and culture and environmental data as secondary.
The salt sensitivity hypothesis is an example of implementing biocultural approaches in order to understand cardiovascular health disparities among African American populations. This theory, founded by Wilson and Grim, stems from the disproportional rates of salt sensitive high blood pressure seen between U.S. African American and White populations and between U.S. African American and West Africans as well. The researchers hypothesized that the patterns were in response to two events. One the trans-Atlantic slave trade, which resulted in massive death totals of Africans who were forced over, those who survived and made to the United States were more likely able to withstand the harsh conditions because they retained salt and water better. The selection continued once they were in the United States. African Americans who were able to withstand hard working conditions had better survival rates due to high water and salt retention. Second, today, because of different environmental conditions and increased salt intake with diets, water and salt retention are disadvantageous, leaving U.S. African Americans at disproportional risks because of their biological descent and culture.
Bio social inheritance model
Similar to the biocultural approach, the bio social inheritance model also looks at biological and social methods in examining health disparities. Hoke et al. define Biosocial inheritance as "the process whereby social adversity in one generation is transmitted to the next through reinforcing biological and social mechanisms that impair health, exacerbating social and health disparities."Controversy
There is a controversy regarding race as a method for classifying humans. Different sources argue it is purely social construct or a biological reality reflecting average genetic group differences. New interest in human biological variation has resulted in a resurgence of the use of race in biomedicine. The main impetus for this development is the possibility of improving the prevention and treatment of certain diseases by predicting hard-to-ascertain factors, such as genetically conditioned health factors, based on more easily ascertained characteristics such as phenotype and racial self-identification. Since medical judgment often involves decision making under uncertain conditions,Ian Whitmarsh and David S. Jones, 2010,What's the Use of Race? Modern Governance and the Biology of Difference
', MIT press. Chapter 9. many doctors consider it useful to take race into account when treating disease because diseases and treatment responses tend to cluster by geographic ancestry. The discovery that more diseases than previously thought correlate with racial identification have further sparked the interest in using race as a proxy for bio-geographical ancestry and genetic buildup. Race in medicine is used as an approximation for more specific genetic and environmental risk factors. Race is thus partly a surrogate for environmental factors such as differences in socioeconomic status that are known to affect health. It is also an imperfect surrogate for ancestral geographic regions and differences in gene frequencies between different ancestral populations and thus differences in genes that can affect health. This can give an approximation of probability for disease or for preferred treatment, although the approximation is less than perfect. Taking the example of sickle-cell disease, in an
emergency room
An emergency department (ED), also known as an accident and emergency department (A&E), emergency room (ER), emergency ward (EW) or casualty department, is a medical treatment facility specializing in emergency medicine, the acute care of pati ...
, knowing the geographic origin of a patient may help a doctor doing an initial diagnosis if a patient presents with symptoms compatible with this disease. This is unreliable evidence with the disease being present in many different groups as noted above with the trait also present in some Mediterranean European populations. Definitive diagnosis comes from examining the blood of the patient. In the US, screening for sickle cell anemia is done on all newborns regardless of race.
The continued use of racial categories has been criticized. Apart from the general controversy regarding race, some argue that the continued use of racial categories in health care and as risk factors could result in increased stereotyping and discrimination in society and health services.Ian Whitmarsh and David S. Jones, 2010, What's the Use of Race? Modern Governance and the Biology of Difference
', MIT press. Chapter 5. Some of those who are critical of race as a biological concept see race as socially meaningful group that is important to study epidemiologically in order to reduce disparities. For example, some racial groups are less likely than others to receive adequate treatment for osteoporosis, even after risk factors have been assessed. Since the 19th century, blacks have been thought to have thicker bones than whites have and to lose bone mass more slowly with age. In a recent study, African Americans were shown to be substantially less likely to receive prescription osteoporosis medications than Caucasians. Men were also significantly less likely to be treated compared with women. This discrepancy may be due to physicians' knowledge that, on average, African Americans are at lower risk for osteoporosis than Caucasians. It may be possible that these physicians generalize this data to high-risk African-Americans, leading them to fail to appropriately assess and manage these individuals' osteoporosis. On the other hand, some of those who are critical of race as a biological concept see race as socially meaningful group that is important to study epidemiologically in order to reduce disparities. David Williams (1994) argued, after an examination of articles in the journal ''Health Services Research'' during the 1966–90 period, that how race was determined and defined was seldom described. At a minimum, researchers should describe if race was assessed by self-report, proxy report, extraction from records, or direct observation. Race was also often used questionable, such as an indicator of socioeconomic status. Racial genetic explanations may be overemphasized, ignoring the interaction with and the role of the environment.
From concepts of race to ethnogenetic layering
There is general agreement that a goal of health-related genetics should be to move past the weak surrogate relationships of racial health disparity and get to the root causes of health and disease. This includes research which strives to analyze human genetic variation in smaller groups than races across the world. One such method is called ethnogenetic layering. It works by focusing on geographically identified microethnic groups. For example, in the Mississippi Delta region ethnogenetic layering might include such microethnic groups as the Cajun (as a subset of European Americans), the Creole and Black groups ith African origins in Senegambia, Central Africa and Bight of Benin(as a subset of African Americans), and Choctaw, Houmas, Chickasaw, Coushatta, Caddo, Atakapa, Karankawa and Chitimacha peoples (as subsets of Native Americans). Better still may be individual genetic assessment of relevant genes. As genotyping and sequencing have become more accessible and affordable, avenues for determining individual genetic makeup have opened dramatically. Even when such methods become commonly available, race will continue to be important when looking at groups instead of individuals such as in epidemiologic research. Some doctors and scientists such as geneticist Neil Risch argue that using self-identified race as a proxy for ancestry is necessary to be able to get a sufficiently broad sample of different ancestral populations, and in turn to be able to provide health care that is tailored to the needs of minority groups.Association studies
One area in which population categories can be important considerations in genetics research is in controlling for confounding between population genetic substructure, environmental exposures, and health outcomes. Association studies can produce spurious results if cases and controls have differing allele frequencies for genes that are not related to the disease being studied, although the magnitude of its problem in genetic association studies is subject to debate. Various techniques detect and account for population substructure, but these methods can be difficult to apply in practice. Population genetic substructure also can aid genetic association studies. For example, populations that represent recent mixtures of separated ancestral groups can exhibit longer-range linkage disequilibrium between susceptibility alleles and genetic markers than is the case for other populations. Genetic studies can use this disequilibrium to search for disease alleles with fewer markers than would be needed otherwise. Association studies also can take advantage of the contrasting experiences of racial or ethnic groups, including migrant groups, to search for interactions between particular alleles and environmental factors that might influence health.Human genome projects
The Human Genome Diversity Project has collected genetic samples from 52 indigenous populations.Sources of racial disparities in care
In a report by theInstitute of Medicine
The National Academy of Medicine (NAM), formerly called the Institute of Medicine (IoM) until 2015, is an American nonprofit, non-governmental organization. The National Academy of Medicine is a part of the National Academies of Sciences, E ...
called Unequal Treatment, three major source categories are put forth as potential explanations for disparities in health care: patient-level variables, healthcare system-level factors, and care process-level variables.
Patient-level variables
There are many individual factors that could explain the established differences in health care between different racial and ethnic groups. First, attitudes and behaviors of minority patients are different. They are more likely to refuse recommended services, adhere poorly to treatment regimens, and delay seeking care, yet despite this, these behaviors and attitudes are unlikely to explain the differences in health care. In addition to behaviors and attitudes, biological based racial differences have been documented, but these also seem unlikely to explain the majority of observed disparities in care.Health system-level factors
Health system-level factors include any aspects of health systems that can have different effects on patient outcomes. Some of these factors include different access to services, access to insurance or other means to pay for services, access to adequate language and interpretation services, and geographic availability of different services. Many studies assert that these factors explain portions of the existing disparities in health of racial and ethnic minorities in the United States when compared to their white counterparts.Care process-level variables
Three major mechanisms are suggested by the Institute of Medicine that may contribute to healthcare disparities from the provider's side: bias (or prejudice) against racial and ethnic minorities; greater clinical uncertainty when interacting with minority patients; and beliefs held by the provider about the behavior or health of minorities. While research in this area is ongoing, some exclusions within clinical trials themselves are also present. A recent systematic review of the literature relating to hearing loss in adults demonstrated that many studies fail to include aspects of racial or ethnic diversity, resulting in studies that do not necessarily represent the US population.See also
* * * HapMap * * List of countries by life expectancy * Ethnic bioweapon * Environmental racism in Europe * Racial Minorities in STEM Fields * Psychological impact of discrimination on health *Social determinants of health
The social determinants of health (SDOH) are the economic and social conditions that influence individual and group differences in health status. They are the health promoting factors found in one's living and working conditions (such as the d ...
*
* Ethnopsychopharmacology
* '' :Human genome projects''
* Cystic fibrosis and race
United States:
* Race and health in the United States
* Center for Minority Health
The School of Public Health (sometimes shortened to Pitt Public Health) is one of 17 schools at the University of Pittsburgh. The school, founded in 1948, was first led by Thomas Parran, surgeon general of the U.S. Public Health Service. It is ...
, US.
* Environmental racism
* Environmental Racism in the United States
General:
* Health disparities
* Pharmacogenomics
* Medical genetics
* Personal genomics
References
External links
Cultural Diversity in Healthcare Speaker Series
University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health
Cultural Diversity in Healthcare Research Symposium
University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health
News-Medical.net
Unnatural causes, videos on how racial inequalities influence health
Governmental
United States Office of Minority Health
United Kingdom National Health Service - Ethnicity & Health
Multicultural Mental Health Australia
{{DEFAULTSORT:Race And Health Health care quality Biomedicine Ethnicity Human population genetics