Anatolian Hunter-gatherers on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Anatolian hunter-gatherers (AHG) were a human
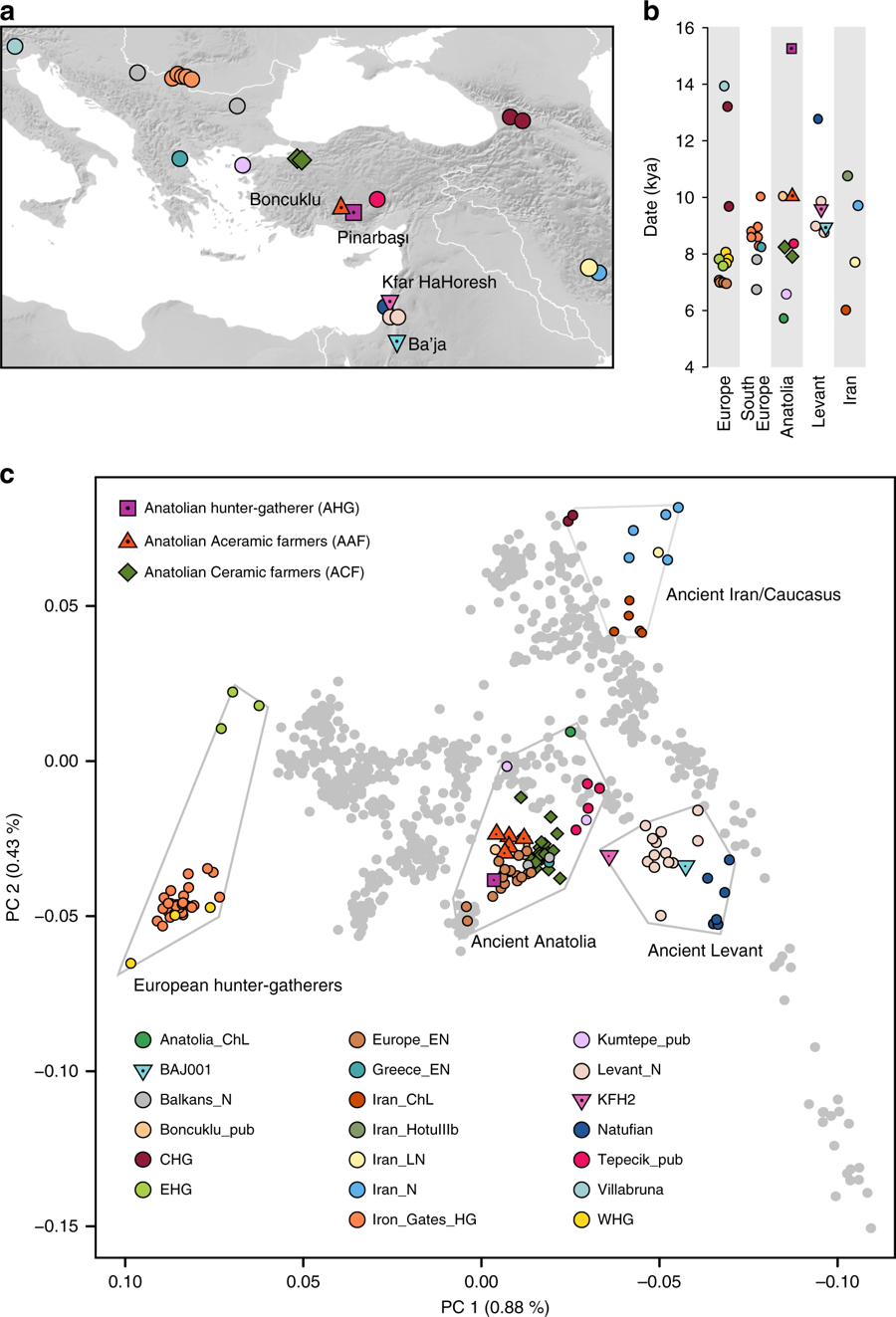
 The existence of this ancient population has been inferred through the genetic analysis of the remains of a male individual from the site of Pınarbaşı (37 ° 29'N, 33 ° 02'E), in central
The existence of this ancient population has been inferred through the genetic analysis of the remains of a male individual from the site of Pınarbaşı (37 ° 29'N, 33 ° 02'E), in central
 At the
At the
Epipaleolithic
In archaeology, the Epipalaeolithic or Epipaleolithic (sometimes Epi-paleolithic etc.) is a period occurring between the Upper Paleolithic and Neolithic during the Stone Age. Mesolithic also falls between these two periods, and the two are someti ...
population that inhabited central Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
around 13,642-13,073 BCE. This population constitutes one of the three currently known ancestral genetic contributions of the present-day Europeans: Western Hunter Gatherers (WHG), Anatolian Neolithic Farmers (AHG) and Ancient North Eurasians
In archaeogenetics, the term Ancient North Eurasian (generally abbreviated as ANE) is the name given to an ancestral component that represents a lineage ancestral to the people of the Mal'ta–Buret' culture and populations closely related to the ...
(via Western Steppe Herders
In archaeogenetics, the term Western Steppe Herders (WSH), or Western Steppe Pastoralists, is the name given to a distinct ancestral component first identified in individuals from the Eneolithic steppe around the turn of the 5th millennium BCE, ...
.)
Introduction
 The existence of this ancient population has been inferred through the genetic analysis of the remains of a male individual from the site of Pınarbaşı (37 ° 29'N, 33 ° 02'E), in central
The existence of this ancient population has been inferred through the genetic analysis of the remains of a male individual from the site of Pınarbaşı (37 ° 29'N, 33 ° 02'E), in central Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
, which has been dated at 13,642-13,073 cal BCE. This population is genetically differentiated from the rest of the known Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
populations.
It has been discovered that populations of the Anatolian Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
derive a significant portion of their ancestry from the AHG, suggesting that agriculture was adopted in situ by these hunter-gatherers and not spread by demic diffusion
Demic diffusion, as opposed to trans-cultural diffusion, is a demographic term referring to a migratory model, developed by Luigi Luca Cavalli-Sforza, of population diffusion into and across an area that had been previously uninhabited by that gro ...
into the region.
Genetics
 At the
At the autosomal
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosome, allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in au ...
level, in the Principal component analysis (PCA) the analyzed AHG individual turns out to be close to two later Anatolian populations, the Anatolian Aceramic Farmers (AAF) dating from 8300-7800 BCE, and the Anatolian Ceramic Farmers (ACF) dating from 7000-6000 BCE. These early Anatolian farmers later replaced the European hunter-gatherers populations in Europe to a large extent, ultimately becoming the main genetic contribution to current European populations, especially those of the Mediterranean. In addition, their position in this analysis is intermediate between Natufian
The Natufian culture () is a Late Epipaleolithic archaeological culture of the Levant, dating to around 15,000 to 11,500 years ago. The culture was unusual in that it supported a sedentary or semi-sedentary population even before the introduction ...
farmers and Western Hunter-Gatherers (WHG). This last point is confirmed by the ''ADMIXTURE'' and ''qp-Adm'' analysis and confirms the presence of hunter-gatherers of both European and Near-Eastern origins in Central Anatolia in the late Pleistocene
The Late Pleistocene is an unofficial Age (geology), age in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, also known as Upper Pleistocene from a Stratigraphy, stratigraphic perspective. It is intended to be the fourth division of ...
. Regarding their genetic proximity to the WHG, it has been proven that this proximity is greater with the so-called Villabruna cluster, which lived in Europe 14,000 years ago, and in particular with the individual known as Iron Gates HG, from the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
. The detailed study of these results suggests that this affinity is not due to a genetic flow from the AHG to the ancestors of the Villabruna cluster, but on the contrary: there was a genetic flow from the ancestors of the Villabruna cluster to the ancestors of the AHG.
Uniparental markers
The individual analyzed belongs to Y-chromosomal haplogroup C1a2 (C-V20), which has been found in some of the early WHGs, and mitochondrial haplogroup K2b. Both paternal and maternal lineages are rare in modern Eurasian populations.See also
*Early European Farmer
Early European Farmers (EEF), First European Farmers (FEF), Neolithic European Farmers, Ancient Aegean Farmers, or Anatolian Neolithic Farmers (ANF) are names used to describe a distinct group of early Neolithic farmers who brought agriculture to E ...
s
References
{{reflist Archaeogenetic lineages Prehistoric Anatolia Population genetics Epipalaeolithic Hunter-gatherers of Asia