Ammonium Paratungstate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ammonium paratungstate (or APT) is a white crystalline
 The
The
salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quant ...
with the chemical formula (NH4)10(H2W12O42)┬Ę4H2O. It is described as "the most important raw material for all
other tungsten products."
Production
From tungsten ores
Tungsten
Tungsten, or wolfram, is a chemical element with the symbol W and atomic number 74. Tungsten is a rare metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively as compounds with other elements. It was identified as a new element in 1781 and first isol ...
ores, which are typically oxides, are digested in base to give solutions of tungstate together with many contaminating species. This crude extract is acidified and treated with sulfide to separate molybdenum trisulfide
Molybdenum trisulfide is an inorganic compound with the formula
In science, a formula is a concise way of expressing information symbolically, as in a mathematical formula or a ''chemical formula''. The informal use of the term ''formula'' ...
. Upon further acidification APT eventually crystallizes.
Laboratory methods
If a calcined WO3 is used, refluxing theammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous wa ...
solution is advisable to accelerate its dissolution.
Conversion to tungsten metal
Heating ammonium paratungstate to its decomposition temperature of 600 ┬░C yieldstungsten(VI) oxide
Tungsten(VI) oxide, also known as tungsten trioxide is a chemical compound of oxygen and the transition metal tungsten, with formula WO3. The compound is also called tungstic anhydride, reflecting its relation to tungstic acid . It is a light ...
, as described in this idealized equation:
:(NH4)10(H2W12O42)┬Ę4H2O ŌåÆ 12 WO3 + 10 NH3 + 6 H2O
From there, the trioxide is heated in an atmosphere of hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
, yielding elemental tungsten:
:WO3 + 3 H2 ŌåÆ W + 3 H2O
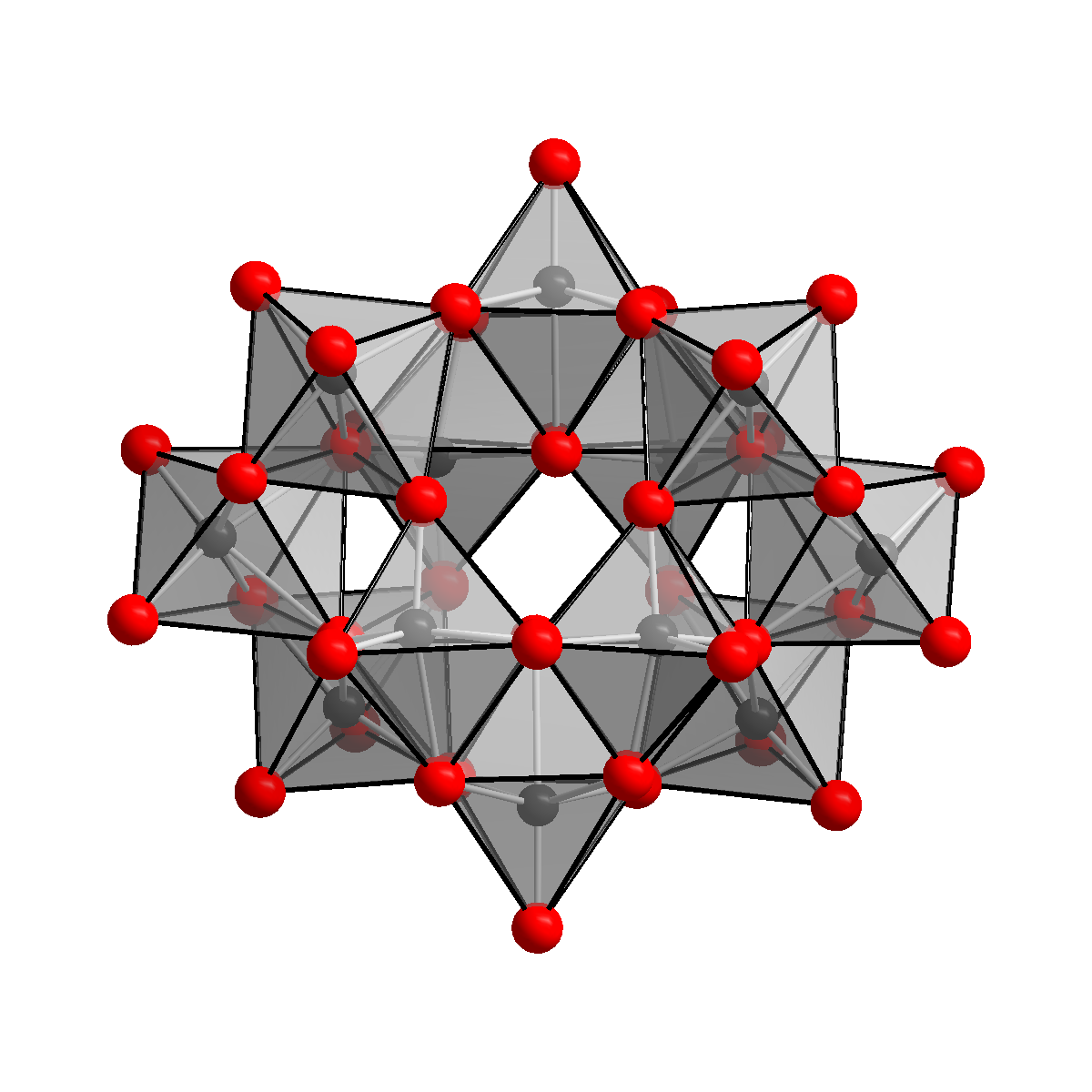
Structure
 The
The anion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conve ...
in (NH4)10(W12O41)┬Ę5H2O has been shown to be 2W12O42sup>10ŌłÆ, containing two hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
atoms, keeping two hydrogen atoms inside the cage. The correct formula notation for ammonium paratungstate is therefore (NH4)10 2W12O42Ę4H2O. The 2W12O42sup>10ŌłÆ ion is known as the paratungstate B ion, as opposed to the paratungstate A ion, that has the formula 7O24sup>6ŌłÆ, similar to the paramolybdate ion. The existence of the paratungstate A ion, could not be confirmed by NMR spectroscopy, however.
Before about 1930, there has been some dispute about the exact composition of the salt, and both (NH4)10W12O41 and (NH4)6W7O24 were proposed. O.W. Gibbs remarked about this:
:"The alkali tungstates are numerous and unusually complex. Salts of essentially different formulae approach so closely in percentage composition, that the differences lie very near the unavoidable errors of analyses. The analyses are hardly sufficiently close to decide the question upon purely analytical grounds."
Other hydrates
When concentrating an ammoniacal solution of tungstic acid (i.e. hydrous WO3), the product obtained is ammonium paratungstate. Below 50 ┬░C, thehexahydrate
In chemistry, a hydrate is a substance that contains water or its constituent elements. The chemical state of the water varies widely between different classes of hydrates, some of which were so labeled before their chemical structure was underst ...
is formed, whereas when the temperature of the solution is above 50 ┬░C, the pentahydrate or heptahydrate is formed. The former crystallizes as triclinic plates or prisms, whereas the latter as pseudorhombic needles. The tetrahydrate is most significant in a commercial sense. Also known:
*decahydrate
*nonahydrate
References
{{Authority control Ammonium compounds Tungstates