Amide synthesis reactions on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
 The lone pair of
The lone pair of  It is estimated that for acetamide, structure A makes a 62% contribution to the structure, while structure B makes a 28% contribution (these figures do not sum to 100% because there are additional less-important resonance forms that are not depicted above). There is also a hydrogen bond present between the hydrogen and nitrogen atoms in the active groups. Resonance is largely prevented in the very strained quinuclidone.
In their IR spectra, amides exhibit a moderately intense ''ν''CO band near 1650 cm−1. The energy of this band is about 60 cm−1 lower than for the ''ν''CO of esters and ketones. This difference reflects the contribution of the zwitterionic resonance structure.
It is estimated that for acetamide, structure A makes a 62% contribution to the structure, while structure B makes a 28% contribution (these figures do not sum to 100% because there are additional less-important resonance forms that are not depicted above). There is also a hydrogen bond present between the hydrogen and nitrogen atoms in the active groups. Resonance is largely prevented in the very strained quinuclidone.
In their IR spectra, amides exhibit a moderately intense ''ν''CO band near 1650 cm−1. The energy of this band is about 60 cm−1 lower than for the ''ν''CO of esters and ketones. This difference reflects the contribution of the zwitterionic resonance structure.
 Here, phenyllithium 1 attacks the carbonyl group of DMF 2, giving tetrahedral intermediate 3. Because the dimethylamide anion is a poor leaving group, the intermediate does not collapse and another nucleophilic addition does not occur. Upon acidic workup, the alkoxide is protonated to give 4, then the amine is protonated to give 5. Elimination of a neutral molecule of
Here, phenyllithium 1 attacks the carbonyl group of DMF 2, giving tetrahedral intermediate 3. Because the dimethylamide anion is a poor leaving group, the intermediate does not collapse and another nucleophilic addition does not occur. Upon acidic workup, the alkoxide is protonated to give 4, then the amine is protonated to give 5. Elimination of a neutral molecule of 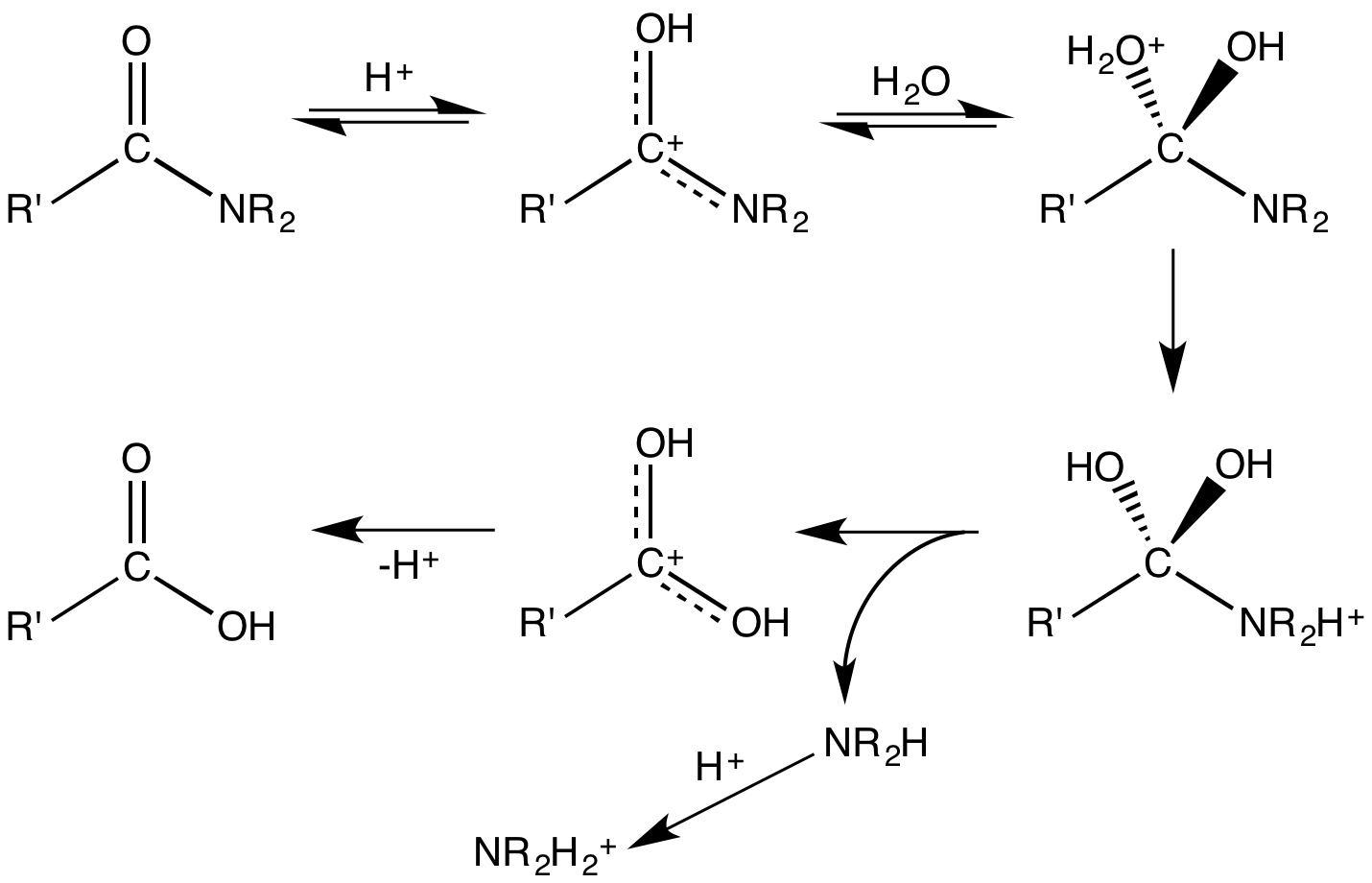
IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology
{{Authority control Functional groups
organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic matter, organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain ...
, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent any group, typically organyl groups or hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond
In organic chemistry, a peptide bond is an amide type of covalent chemical bond linking two consecutive alpha-amino acids from C1 (carbon number one) of one alpha-amino acid and N2 (nitrogen number two) of another, along a peptide or protein cha ...
when it is part of the main chain of a protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
, and an isopeptide bond when it occurs in a side chain
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, a side chain is a substituent, chemical group that is attached to a core part of the molecule called the "main chain" or backbone chain, backbone. The side chain is a hydrocarbon branching element of a mo ...
, as in asparagine and glutamine. It can be viewed as a derivative
In mathematics, the derivative is a fundamental tool that quantifies the sensitivity to change of a function's output with respect to its input. The derivative of a function of a single variable at a chosen input value, when it exists, is t ...
of a carboxylic acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an Substituent, R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as or , sometimes as with R referring to an organyl ...
() with the hydroxyl group () replaced by an amino group (); or, equivalently, an acyl (alkanoyl) group () joined to an amino group.
Common amides are formamide (), acetamide (), benzamide (), and dimethylformamide
Dimethylformamide, DMF is an organic compound with the chemical formula . Its structure is . Commonly abbreviated as DMF (although this initialism is sometimes used for 2,5-dimethylfuran, dimethylfuran, or dimethyl fumarate), this colourless liqui ...
(). Some uncommon examples of amides are ''N''-chloroacetamide () and chloroformamide ().
Amides are qualified as primary, secondary, and tertiary according to the number of acyl groups bounded to the nitrogen atom.
Nomenclature
The core of amides is called the amide group (specifically, carboxamide group). In the usual nomenclature, one adds the term "amide" to the stem of the parent acid's name. For instance, the amide derived fromacetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main compone ...
is named acetamide (CH3CONH2). IUPAC recommends ethanamide, but this and related formal names are rarely encountered. When the amide is derived from a primary or secondary amine, the substituents on nitrogen are indicated first in the name. Thus, the amide formed from dimethylamine
Dimethylamine is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2NH. This secondary amine is a colorless, flammable gas with an ammonia-like odor. Dimethylamine is commonly encountered commercially as a solution in water at concentrations up to around ...
and acetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main compone ...
is ''N'',''N''-dimethylacetamide (CH3CONMe2, where Me = CH3). Usually even this name is simplified to dimethylacetamide. Cyclic amides are called lactam
A lactam is a Cyclic compound, cyclic amide, formally derived from an amino alkanoic acid through cyclization reactions. The term is a portmanteau of the words ''lactone'' + ''amide''.
Nomenclature
Greek_alphabet#Letters, Greek prefixes in alpha ...
s; they are necessarily secondary or tertiary amides.
Applications
Amides are pervasive in nature and technology.Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s and important plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic polymers, synthetic or Semisynthesis, semisynthetic materials composed primarily of Polymer, polymers. Their defining characteristic, Plasticity (physics), plasticity, allows them to be Injection moulding ...
s like nylon
Nylon is a family of synthetic polymers characterised by amide linkages, typically connecting aliphatic or Polyamide#Classification, semi-aromatic groups.
Nylons are generally brownish in color and can possess a soft texture, with some varieti ...
s, aramids, Twaron, and Kevlar
Kevlar (para-aramid) is a strong, heat-resistant synthetic fiber, related to other aramids such as Nomex and Technora. Developed by Stephanie Kwolek at DuPont in 1965, the high-strength material was first used commercially in the early 1970s as ...
are polymer
A polymer () is a chemical substance, substance or material that consists of very large molecules, or macromolecules, that are constituted by many repeat unit, repeating subunits derived from one or more species of monomers. Due to their br ...
s whose units are connected by amide groups (polyamide
A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds.
Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk. Artificially made polyamides can be made throug ...
s); these linkages are easily formed, confer structural rigidity, and resist hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water ...
. Amides include many other important biological compounds, as well as many drug
A drug is any chemical substance other than a nutrient or an essential dietary ingredient, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. Consumption of drugs can be via insufflation (medicine), inhalation, drug i ...
s like paracetamol
Paracetamol, or acetaminophen, is a non-opioid analgesic and antipyretic agent used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. It is a widely available over-the-counter drug sold under various brand names, including Tylenol and Panadol.
Parac ...
, penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of beta-lactam antibiotic, β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' Mold (fungus), moulds, principally ''Penicillium chrysogenum, P. chrysogenum'' and ''Penicillium rubens, P. ru ...
and LSD. Low-molecular-weight amides, such as dimethylformamide, are common solvents.
Structure and bonding
 The lone pair of
The lone pair of electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
s on the nitrogen atom is delocalized into the Carbonyl group, thus forming a partial double bond
In chemistry, a double bond is a covalent bond between two atoms involving four bonding electrons as opposed to two in a single bond. Double bonds occur most commonly between two carbon atoms, for example in alkenes. Many double bonds exist betw ...
between nitrogen and carbon. In fact the O, C and N atoms have molecular orbitals occupied by delocalized electron
In chemistry, delocalized electrons are electrons in a molecule, ion or solid metal that are not associated with a single atom or a covalent bond.IUPAC Gold Boo''delocalization''/ref>
The term delocalization is general and can have slightly dif ...
s, forming a conjugated system
In physical organic chemistry, a conjugated system is a system of connected p-orbitals with delocalized electrons in a molecule, which in general lowers the overall energy of the molecule and increases Chemical stability, stability. It is Reson ...
. Consequently, the three bonds of the nitrogen in amides is not pyramidal (as in the amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are organic compounds that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. Amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom in an amine possesses a lone pair of elec ...
s) but planar. This planar restriction prevents rotations about the N linkage and thus has important consequences for the mechanical properties of bulk material of such molecules, and also for the configurational properties of macromolecules built by such bonds. The inability to rotate distinguishes amide groups from ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid (either organic or inorganic) in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group () of that acid is replaced by an organyl group (R). These compounds contain a distin ...
groups which allow rotation and thus create more flexible bulk material.
The C-C(O)NR2 core of amides is planar. The C=O distance is shorter than the C-N distance by almost 10%. The structure of an amide can be described also as a resonance
Resonance is a phenomenon that occurs when an object or system is subjected to an external force or vibration whose frequency matches a resonant frequency (or resonance frequency) of the system, defined as a frequency that generates a maximu ...
between two alternative structures: neutral (A) and zwitterionic (B).
:Basicity
Compared toamine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are organic compounds that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. Amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom in an amine possesses a lone pair of elec ...
s, amides are very weak bases. While the conjugate acid
A conjugate acid, within the Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, is a chemical compound formed when an acid gives a proton () to a base—in other words, it is a base with a hydrogen ion added to it, as it loses a hydrogen ion in the rever ...
of an amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are organic compounds that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. Amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom in an amine possesses a lone pair of elec ...
has a p''K''a of about 9.5, the conjugate acid
A conjugate acid, within the Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, is a chemical compound formed when an acid gives a proton () to a base—in other words, it is a base with a hydrogen ion added to it, as it loses a hydrogen ion in the rever ...
of an amide has a p''K''a around −0.5. Therefore, compared to amines, amides do not have acid–base properties that are as noticeable in water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
. This relative lack of basicity is explained by the withdrawing of electrons from the amine by the carbonyl. On the other hand, amides are much stronger bases than carboxylic acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an Substituent, R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as or , sometimes as with R referring to an organyl ...
s, ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid (either organic or inorganic) in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group () of that acid is replaced by an organyl group (R). These compounds contain a distin ...
s, aldehydes, and ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure , where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group (a carbon-oxygen double bond C=O). The simplest ketone is acetone ( ...
s (their conjugate acids' p''K''as are between −6 and −10).
The proton of a primary or secondary amide does not dissociate readily; its p''K''a is usually well above 15. Conversely, under extremely acidic conditions, the carbonyl oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
can become protonated with a p''K''a of roughly −1. It is not only because of the positive charge on the nitrogen but also because of the negative charge on the oxygen gained through resonance.
Hydrogen bonding and solubility
Because of the greater electronegativity of oxygen than nitrogen, the carbonyl (C=O) is a stronger dipole than the N–C dipole. The presence of a C=O dipole and, to a lesser extent a N–C dipole, allows amides to act as H-bond acceptors. In primary and secondary amides, the presence of N–H dipoles allows amides to function as H-bond donors as well. Thus amides can participate inhydrogen bonding
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (H-bond) is a specific type of molecular interaction that exhibits partial covalent character and cannot be described as a purely electrostatic force. It occurs when a hydrogen (H) atom, Covalent bond, covalently b ...
with water and other protic solvents; the oxygen atom can accept hydrogen bonds from water and the N–H hydrogen atoms can donate H-bonds. As a result of interactions such as these, the water solubility of amides is greater than that of corresponding hydrocarbons. These hydrogen bonds also have an important role in the secondary structure
Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains. The two most common Protein structure#Secondary structure, secondary structural elements are alpha helix, alpha helices and beta ...
of proteins.
The solubilities of amides and esters are roughly comparable. Typically amides are less soluble than comparable amines and carboxylic acids since these compounds can both donate and accept hydrogen bonds. Tertiary amides, with the important exception of ''N'',''N''-dimethylformamide, exhibit low solubility in water.
Reactions
Amides do not readily participate in nucleophilic substitution reactions. Amides are stable to water, and are roughly 100 times more stable towardshydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water ...
than esters. Amides can, however, be hydrolyzed to carboxylic acids in the presence of acid or base. The stability of amide bonds has biological implications, since the amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
s that make up protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s are linked with amide bonds. Amide bonds are resistant enough to hydrolysis to maintain protein structure in aqueous
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, also known as sodium chloride (NaCl), in wat ...
environments but are susceptible to catalyzed hydrolysis.
Primary and secondary amides do not react usefully with carbon nucleophiles. Instead, Grignard reagents and organolithiums deprotonate an amide N-H bond. Tertiary amides do not experience this problem, and react with carbon nucleophiles to give ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure , where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group (a carbon-oxygen double bond C=O). The simplest ketone is acetone ( ...
s; the amide
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a chemical compound, compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent any group, typically organyl functional group, groups or hydrogen at ...
anion (NR2−) is a very strong base and thus a very poor leaving group, so nucleophilic attack only occurs once. When reacted with carbon nucleophiles, ''N'',''N''-dimethylformamide (DMF) can be used to introduce a formyl group.
 Here, phenyllithium 1 attacks the carbonyl group of DMF 2, giving tetrahedral intermediate 3. Because the dimethylamide anion is a poor leaving group, the intermediate does not collapse and another nucleophilic addition does not occur. Upon acidic workup, the alkoxide is protonated to give 4, then the amine is protonated to give 5. Elimination of a neutral molecule of
Here, phenyllithium 1 attacks the carbonyl group of DMF 2, giving tetrahedral intermediate 3. Because the dimethylamide anion is a poor leaving group, the intermediate does not collapse and another nucleophilic addition does not occur. Upon acidic workup, the alkoxide is protonated to give 4, then the amine is protonated to give 5. Elimination of a neutral molecule of dimethylamine
Dimethylamine is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2NH. This secondary amine is a colorless, flammable gas with an ammonia-like odor. Dimethylamine is commonly encountered commercially as a solution in water at concentrations up to around ...
and loss of a proton give benzaldehyde, 6.
:
Hydrolysis
Amides hydrolyse in hotalkali
In chemistry, an alkali (; from the Arabic word , ) is a basic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7.0. The a ...
as well as in strong acid
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis ...
ic conditions. Acidic conditions yield the carboxylic acid and the ammonium ion while basic hydrolysis yield the carboxylate ion and ammonia. The protonation of the initially generated amine under acidic conditions and the deprotonation of the initially generated carboxylic acid under basic conditions render these processes non-catalytic and irreversible. Electrophiles other than protons react with the carbonyl oxygen. This step often precedes hydrolysis, which is catalyzed by both Brønsted acids and Lewis acid
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any ...
s. Peptidase enzymes and some synthetic catalysts often operate by attachment of electrophiles to the carbonyl oxygen.
Synthesis
From carboxylic acids and related compounds
Amides are usually prepared by coupling acarboxylic acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an Substituent, R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as or , sometimes as with R referring to an organyl ...
with an amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are organic compounds that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. Amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom in an amine possesses a lone pair of elec ...
. The direct reaction generally requires high temperatures to drive off the water:
:
:
Ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid (either organic or inorganic) in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group () of that acid is replaced by an organyl group (R). These compounds contain a distin ...
s are far superior substrates relative to carboxylic acids.
Further "activating" both acid chloride
In organic chemistry, an acyl chloride (or acid chloride) is an organic compound with the functional group . Their formula is usually written , where R is a side chain. They are reactive derivatives of carboxylic acids (). A specific example o ...
s ( Schotten-Baumann reaction) and anhydride
An acid anhydride is a type of chemical compound derived by the removal of water molecules from an acid (chemistry), acid.
In organic chemistry, organic acid anhydrides contain the functional group . Organic acid anhydrides often form when one ...
s ( Lumière–Barbier method) react with amines to give amides:
:
:
:
Peptide synthesis use coupling agents such as HATU, HOBt, or PyBOP.
From nitriles
The hydrolysis of nitriles is conducted on an industrial scale to produce fatty amides. Laboratory procedures are also available.Specialty routes
Many specialized methods also yield amides. A variety of reagents, e.g. tris(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl) borate have been developed for specialized applications.See also
* Amidogen * Amino radical * Amidicity * Imidic acid * Metal amidesReferences
External links
IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology
{{Authority control Functional groups