amide reduction on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Amide reduction is a reaction in
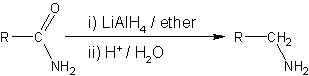
Amide reduction @ organic-chemistry.org
Organic redox reactions
organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the intentional construction of organic compounds. Organic molecules are often more complex than inorganic compounds, and their synthesis has developed into one o ...
where an amide
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent organic groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it is ...
is reduced to either an amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituen ...
or an aldehyde
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl grou ...
functional group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the rest ...
.
Catalytic hydrogenation
Catalytichydrogenation
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a Catalysis, catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to redox, reduce or S ...
can be used to reduce amides to amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituen ...
s; however, the process often requires high hydrogenation pressures and reaction temperatures to be effective (i.e. often requiring pressures above 197 atm and temperatures exceeding 200 °C). Selective catalysts for the reaction include copper chromite
Copper chromite is an inorganic compound with the formula Cu2Cr2O5. It is a black solid that is used to catalyze reactions in organic synthesis.
History
The material was first described in 1908. The catalyst was developed in North America by Home ...
, rhenium trioxide
Rhenium trioxide or rhenium(VI) oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula ReO3. It is a red solid with a metallic lustre that resembles copper in appearance. It is the only stable trioxide of the Group 7 elements ( Mn, Tc, Re).
Prepara ...
and rhenium(VII) oxide
Rhenium(VII) oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Re2 O7. This yellowish solid is the anhydride of HOReO3. Perrhenic acid, Re2O7·2H2O, is closely related to Re2O7. Re2O7 is the raw material for all rhenium compounds, being the volat ...
or bimetallic catalyst.
Non-catalytic routes to amines
Reducing agent
In chemistry, a reducing agent (also known as a reductant, reducer, or electron donor) is a chemical species that "donates" an electron to an (called the , , , or ).
Examples of substances that are commonly reducing agents include the Earth meta ...
s able to effect this reaction include metal hydride
In chemistry, a hydride is formally the anion of hydrogen( H−). The term is applied loosely. At one extreme, all compounds containing covalently bound H atoms are called hydrides: water (H2O) is a hydride of oxygen, ammonia is a hydride of ...
s such as lithium aluminium hydride
Lithium aluminium hydride, commonly abbreviated to LAH, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Li Al H4. It is a white solid, discovered by Finholt, Bond and Schlesinger in 1947. This compound is used as a reducing agent in organic ...
, or lithium borohydride
Lithium borohydride (LiBH4) is a borohydride and known in organic synthesis as a reducing agent for esters. Although less common than the related sodium borohydride, the lithium salt offers some advantages, being a stronger reducing agent and ...
in mixed solvents of tetrahydrofuran
Tetrahydrofuran (THF), or oxolane, is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4O. The compound is classified as heterocyclic compound, specifically a cyclic ether. It is a colorless, water-miscible organic liquid with low viscosity. It is ma ...
and methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical and the simplest aliphatic alcohol, with the formula C H3 O H (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often abbreviated as MeOH). It is a ...
.
: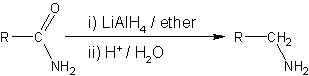
Noncatalytic routes to aldehydes
N,N-disubstituted amides can be reduced to aldehydes by using an excess of the amide: :R(CO)NRR' + LiAlH4 → RCHO + HNRR' With further reduction thealcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
is obtained.
Some amides can be reduced to aldehydes in the Sonn-Müller method.
Hydrosilylation
A well known method for amide reduction ishydrosilylation Hydrosilylation, also called catalytic hydrosilation, describes the addition of Si-H bonds across unsaturated bonds."Hydrosilylation A Comprehensive Review on Recent Advances" B. Marciniec (ed.), Advances in Silicon Science, Springer Science, 2009 ...
with silyl hydrides and a suitable catalyst based on Rh, Ru, Pt, Pd, Ir, Os, Re, Mn, Mo, In, or Ti.
Iron catalysis by triiron dodecacarbonyl
Triiron dodecarbonyl is the organoiron compound with the formula Fe3(CO)12. It is a dark green solid that sublimes under vacuum. It is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents to give intensely green solutions. Most low-nuclearity clusters are pale ...
in combination with polymethylhydrosiloxane
Polymethylhydrosiloxane (PMHS) is a polymer with the general structure -(CH3(H)Si-O)-. It is used in organic chemistry as a mild and stable reducing agent easily transferring hydrides to metal centers and a number of other reducible functional gr ...
has been reported.
References
{{Reflist, 30emExternal links
Amide reduction @ organic-chemistry.org
Organic redox reactions