Amazon EC2 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) is a part of
 , Amazon charged about $0.0058 per hour ($4.176 per month) for the smallest "Nano Instance" (t2.nano) virtual machine running Linux or Windows. Storage-optimized instances cost as much as $4.992 per hour (i3.16xlarge). "Reserved" instances can go as low as $2.50 per month for a three-year prepaid plan. The data transfer charge ranges from free to $0.12 per gigabyte, depending on the direction and monthly volume (inbound data transfer is free on all AWS services).
EC2 costs can be analyzed using the Amazon Cost and Usage Report. There are many different cost categories for EC2 including: hourly Instance Charges, Data Transfer, EBS Volumes, EBS Volume Snapshots, and Nat Gateway.
, Amazon charged about $0.0058 per hour ($4.176 per month) for the smallest "Nano Instance" (t2.nano) virtual machine running Linux or Windows. Storage-optimized instances cost as much as $4.992 per hour (i3.16xlarge). "Reserved" instances can go as low as $2.50 per month for a three-year prepaid plan. The data transfer charge ranges from free to $0.12 per gigabyte, depending on the direction and monthly volume (inbound data transfer is free on all AWS services).
EC2 costs can be analyzed using the Amazon Cost and Usage Report. There are many different cost categories for EC2 including: hourly Instance Charges, Data Transfer, EBS Volumes, EBS Volume Snapshots, and Nat Gateway.
 EBS volumes provide persistent storage independent of the lifetime of the EC2 instance, and act much like hard drives on a real server. More accurately, they appear as block devices to the operating system that are backed by Amazon's disk arrays. The OS is free to use the device however it wants. In the most common case, a file system is loaded and the volume acts as a hard drive. Another possible use is the creation of RAID arrays by combining two or more EBS volumes. RAID allows increases of speed and/or reliability of EBS. Users can set up and manage storage volumes of sizes from 1 GB to 16 TB. The volumes support snapshots, which can be taken from a GUI tool or the API. EBS volumes can be attached or detached from instances while they are running, and moved from one instance to another.
Simple Storage Service (S3) is a storage system in which data is accessible to EC2 instances, or directly over the network to suitably authenticated callers (all communication is over HTTP). Amazon does not charge for the bandwidth for communications between EC2 instances and S3 storage "in the same region." Accessing S3 data stored in a different region (for example, data stored in Europe from a US East Coast EC2 instance) will be billed at Amazon's normal rates.
S3-based storage is priced per gigabyte per month. Applications access S3 through an API. For example,
EBS volumes provide persistent storage independent of the lifetime of the EC2 instance, and act much like hard drives on a real server. More accurately, they appear as block devices to the operating system that are backed by Amazon's disk arrays. The OS is free to use the device however it wants. In the most common case, a file system is loaded and the volume acts as a hard drive. Another possible use is the creation of RAID arrays by combining two or more EBS volumes. RAID allows increases of speed and/or reliability of EBS. Users can set up and manage storage volumes of sizes from 1 GB to 16 TB. The volumes support snapshots, which can be taken from a GUI tool or the API. EBS volumes can be attached or detached from instances while they are running, and moved from one instance to another.
Simple Storage Service (S3) is a storage system in which data is accessible to EC2 instances, or directly over the network to suitably authenticated callers (all communication is over HTTP). Amazon does not charge for the bandwidth for communications between EC2 instances and S3 storage "in the same region." Accessing S3 data stored in a different region (for example, data stored in Europe from a US East Coast EC2 instance) will be billed at Amazon's normal rates.
S3-based storage is priced per gigabyte per month. Applications access S3 through an API. For example,
 Amazon's elastic IP address feature is similar to static IP address in traditional data centers, with one key difference. A user can programmatically map an elastic IP address to any virtual machine instance without a network administrator's help and without having to wait for DNS to propagate the binding. In this sense an Elastic IP Address belongs to the account and not to a virtual machine instance. It exists until it is explicitly removed, and remains associated with the account even while it is associated with no instance.
Amazon's elastic IP address feature is similar to static IP address in traditional data centers, with one key difference. A user can programmatically map an elastic IP address to any virtual machine instance without a network administrator's help and without having to wait for DNS to propagate the binding. In this sense an Elastic IP Address belongs to the account and not to a virtual machine instance. It exists until it is explicitly removed, and remains associated with the account even while it is associated with no instance.
 Amazon CloudWatch is a web service that provides real-time monitoring to Amazon's EC2 customers on their resource utilization such as CPU, disk, network and replica lag for RDS Database replicas. CloudWatch does not provide any memory, disk space, or load average metrics without running additional software on the instance. Since December 2017 Amazon provides a CloudWatch Agent for Windows and Linux operating systems included disk and previously not available memory information, previously Amazon provided example scripts for Linux instances to collect OS information. The data is aggregated and provided through AWS management console. It can also be accessed through command line tools and Web APIs, if the customer desires to monitor their EC2 resources through their enterprise monitoring software. Amazon provides an API which allows clients to operate on CloudWatch alarms.
The metrics collected by Amazon CloudWatch enables the auto-scaling feature to dynamically add or remove EC2 instances. The customers are charged by the number of monitoring instances.
Since May 2011, Amazon CloudWatch accepts custom metrics that can be submitted programmatically via Web Services API and then monitored the same way as all other internal metrics, including setting up the alarms for them, and since July 2014 Cloudwatch Logs service is also available.
Basic Amazon CloudWatch is included in Amazon Free Tier service.
Amazon CloudWatch is a web service that provides real-time monitoring to Amazon's EC2 customers on their resource utilization such as CPU, disk, network and replica lag for RDS Database replicas. CloudWatch does not provide any memory, disk space, or load average metrics without running additional software on the instance. Since December 2017 Amazon provides a CloudWatch Agent for Windows and Linux operating systems included disk and previously not available memory information, previously Amazon provided example scripts for Linux instances to collect OS information. The data is aggregated and provided through AWS management console. It can also be accessed through command line tools and Web APIs, if the customer desires to monitor their EC2 resources through their enterprise monitoring software. Amazon provides an API which allows clients to operate on CloudWatch alarms.
The metrics collected by Amazon CloudWatch enables the auto-scaling feature to dynamically add or remove EC2 instances. The customers are charged by the number of monitoring instances.
Since May 2011, Amazon CloudWatch accepts custom metrics that can be submitted programmatically via Web Services API and then monitored the same way as all other internal metrics, including setting up the alarms for them, and since July 2014 Cloudwatch Logs service is also available.
Basic Amazon CloudWatch is included in Amazon Free Tier service.
 Amazon's auto-scaling feature of EC2 allows it to automatically adapt computing capacity to site traffic. The schedule-based (e.g. time-of-the-day) and rule-based (e.g. CPU utilization thresholds) auto scaling mechanisms are easy to use and efficient for simple applications. However, one potential problem is that VMs may take up to several minutes to be ready to use, which are not suitable for time critical applications. The VM startup time is dependent on image size, VM type, data center locations, etc. The convenience of using EC2 enables you to dynamically increase capacity in accordance with demand and access resources rapidly.
Amazon's auto-scaling feature of EC2 allows it to automatically adapt computing capacity to site traffic. The schedule-based (e.g. time-of-the-day) and rule-based (e.g. CPU utilization thresholds) auto scaling mechanisms are easy to use and efficient for simple applications. However, one potential problem is that VMs may take up to several minutes to be ready to use, which are not suitable for time critical applications. The VM startup time is dependent on image size, VM type, data center locations, etc. The convenience of using EC2 enables you to dynamically increase capacity in accordance with demand and access resources rapidly.
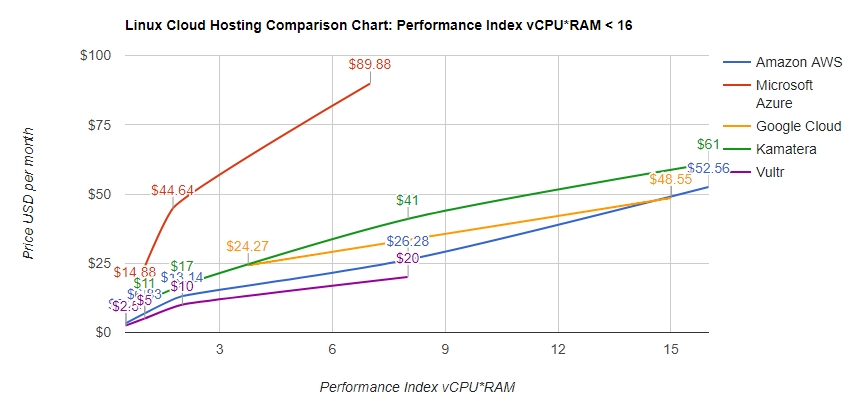
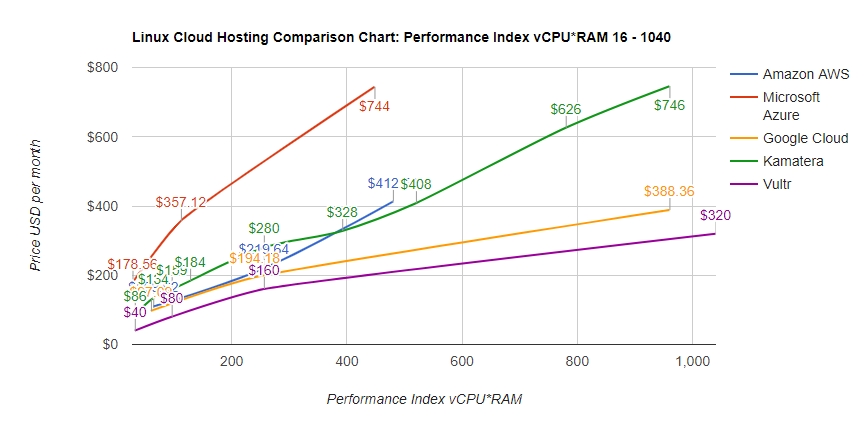
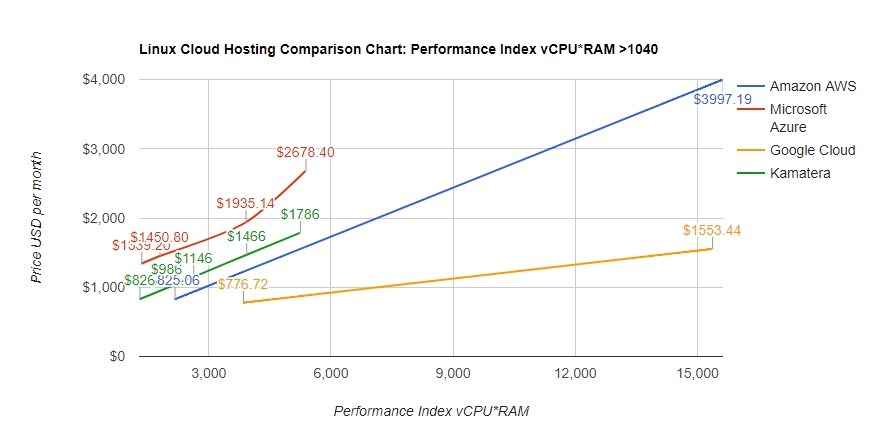 On Demand EC2 instances are priced per hour. An example of this pricing would be $0.096 per hour for a Linux, m5.large, EC2 instance in the us-east-1 region. Pricing will vary based on the instance type, region, and operating system of the instance. Public on-demand pricing for EC2 can be found on th
On Demand EC2 instances are priced per hour. An example of this pricing would be $0.096 per hour for a Linux, m5.large, EC2 instance in the us-east-1 region. Pricing will vary based on the instance type, region, and operating system of the instance. Public on-demand pricing for EC2 can be found on th
AWS website
The other pricing models for EC2 have different pricing models. Spot instances also have a cost per instance hour, but the cost will change on a regular basis based on the supply of EC2 spot capacity. Reserved Instances and Compute Savings plans are priced per hour. Each of these reservation tools has its own price per hour based on the payment option, term and reservation product being used. These prices are locked in for either a 1-year or 3-year term. Amazon EC2 price varies from $2.5 per month for "nano" instance with 1 vCPU and 0.5 GB RAM on board to "xlarge" type of instances with 32 vCPU and 488 GB RAM billed up to $3997.19 per month. The charts above show how Amazon EC2 pricing is compared to similar Cloud Computing services: Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, Kamatera, and Vultr.
 To make EC2 more fault-tolerant, Amazon engineered ''Availability Zones'' that are designed to be insulated from failures in other availability zones. Availability zones do not share the same infrastructure. Applications running in more than one availability zone can achieve higher availability.
EC2 provides users with control over the geographical location of instances that allows for latency optimization and high levels of redundancy. For example, to minimize downtime, a user can set up server instances in multiple zones that are insulated from each other for most causes of failure such that one backs up the other.
Higher-availability database services, like Amazon Relational Database Service run separately from EC2 instances.
To make EC2 more fault-tolerant, Amazon engineered ''Availability Zones'' that are designed to be insulated from failures in other availability zones. Availability zones do not share the same infrastructure. Applications running in more than one availability zone can achieve higher availability.
EC2 provides users with control over the geographical location of instances that allows for latency optimization and high levels of redundancy. For example, to minimize downtime, a user can set up server instances in multiple zones that are insulated from each other for most causes of failure such that one backs up the other.
Higher-availability database services, like Amazon Relational Database Service run separately from EC2 instances.
Amazon
Amazon most often refers to:
* Amazon River, in South America
* Amazon rainforest, a rainforest covering most of the Amazon basin
* Amazon (company), an American multinational technology company
* Amazons, a tribe of female warriors in Greek myth ...
's cloud-computing platform, Amazon Web Services
Amazon Web Services, Inc. (AWS) is a subsidiary of Amazon.com, Amazon that provides Software as a service, on-demand cloud computing computing platform, platforms and Application programming interface, APIs to individuals, companies, and gover ...
(AWS), that allows users to rent virtual computers on which to run their own computer applications. EC2 encourages scalable deployment of applications by providing a web service
A web service (WS) is either:
* a service offered by an electronic device to another electronic device, communicating with each other via the Internet, or
* a server running on a computer device, listening for requests at a particular port over a n ...
through which a user can boot an Amazon Machine Image (AMI) to configure a virtual machine
In computing, a virtual machine (VM) is the virtualization or emulator, emulation of a computer system. Virtual machines are based on computer architectures and provide the functionality of a physical computer. Their implementations may involve ...
, which Amazon calls an "instance", containing any software desired. A user can create, launch, and terminate server-instances as needed, paying by the second for active servershence the term "elastic". EC2 provides users with control over the geographical location of instances that allows for latency optimization and high levels of redundancy. In November 2010, Amazon switched its own retail website platform to EC2 and AWS.
History
Amazon announced a limited public beta test of EC2 on August 25, 2006, offering access on a first-come, first-served basis. Amazon added two new instance types (Large and Extra-Large) on October 16, 2007. On May 29, 2008, two more types were added, High-CPU Medium and High-CPU Extra Large. There were twelve types of instances available. Amazon added three new features on March 27, 2008, static IP addresses, availability zones, and user selectable kernels. On August 20, 2008, Amazon added Elastic Block Store (EBS) This provides persistent storage, a feature that had been lacking since the service was introduced. Amazon EC2 went into full production when it dropped the beta label on October 23, 2008. On the same day, Amazon announced the following features: * a service level agreement for EC2, *Microsoft Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
in beta form on EC2,
* Microsoft SQL Server
Microsoft SQL Server is a proprietary relational database management system developed by Microsoft using Structured Query Language (SQL, often pronounced "sequel"). As a database server, it is a software product with the primary function of ...
in beta form on EC2,
* plans for an AWS management console, and
* plans for load balancing, autoscaling, and cloud monitoring services.
These features were subsequently added on May 18, 2009.
Amazon EC2 was developed mostly by a team in Cape Town, South Africa led by Chris Pinkham. Pinkham provided the initial architecture guidance for EC2 and then built the team and led the development of the project along with Willem van Biljon.
Instance types
Initially, EC2 used Xen virtualization exclusively. However, on November 6, 2017, Amazon announced the new C5 family of instances that were based on a custom architecture around the KVM hypervisor, called Nitro. Each virtual machine, called an "instance", functions as a virtual private server. Amazon sizes instances based on "Elastic Compute Units". The performance of otherwise identical virtual machines may vary. On November 28, 2017, AWS announced a bare-metal instance, a departure from exclusively offering virtualized instance types. As of January 2019, the following instance types were offered: * General Purpose: A1, T3, T2, M5, M5a, M4, T3a * Compute Optimized: C5, C5n, C4 * Memory Optimized: R5, R5a, R4, X1e, X1, High Memory, z1d * Accelerated Computing: P3, P2, G3, F1 * Storage Optimized: H1, I3, D2 , the following payment methods by instance were offered: * On-demand: pay by the hour without commitment. * Reserved: rent instances with one-time payment receiving discounts on the hourly charge. * Spot: bid-based service: runs the jobs only if the spot price is below the bid specified by bidder. The spot price is claimed to be supply-demand based, however a 2011 study concluded that the price was generally not set to clear the market, but was dominated by an undisclosed reserve price.Cost
 , Amazon charged about $0.0058 per hour ($4.176 per month) for the smallest "Nano Instance" (t2.nano) virtual machine running Linux or Windows. Storage-optimized instances cost as much as $4.992 per hour (i3.16xlarge). "Reserved" instances can go as low as $2.50 per month for a three-year prepaid plan. The data transfer charge ranges from free to $0.12 per gigabyte, depending on the direction and monthly volume (inbound data transfer is free on all AWS services).
EC2 costs can be analyzed using the Amazon Cost and Usage Report. There are many different cost categories for EC2 including: hourly Instance Charges, Data Transfer, EBS Volumes, EBS Volume Snapshots, and Nat Gateway.
, Amazon charged about $0.0058 per hour ($4.176 per month) for the smallest "Nano Instance" (t2.nano) virtual machine running Linux or Windows. Storage-optimized instances cost as much as $4.992 per hour (i3.16xlarge). "Reserved" instances can go as low as $2.50 per month for a three-year prepaid plan. The data transfer charge ranges from free to $0.12 per gigabyte, depending on the direction and monthly volume (inbound data transfer is free on all AWS services).
EC2 costs can be analyzed using the Amazon Cost and Usage Report. There are many different cost categories for EC2 including: hourly Instance Charges, Data Transfer, EBS Volumes, EBS Volume Snapshots, and Nat Gateway.
Free tier
Amazon offered a bundle of free resource credits to new account holders. The credits are designed to run a "micro" sized server, storage (EBS), and bandwidth for one year. Unused credits cannot be carried over from one month to the next.Reserved instances
Reserved instances enable EC2 or RDS service users to reserve an instance for one or three years. The corresponding hourly rate charged by Amazon to operate the instance is 35 to 75% lower than the rate charged for on-demand instances. Reserved instances can be purchased with three different payment options: All Upfront, Partial Upfront and No Upfront. The different purchase options allow for different structuring of payment models, with a larger discount given to customers that pay their reservation upfront. Reserved Instances are purchased based on a resource commitment. These reservations are made based on an instance type and a count of that instance type. For example, you could reserve 100 i3.large instances for a 3-year term. In September 2016, AWS announced several enhancements to Reserved instances, introducing a new feature called scope and a new reservation type called a Convertible. In October 2017, AWS announced the allowance to subdivide the instances purchased for more flexibility.Spot instances
Cloud providers maintain large amounts of excess capacity they have to sell or risk incurring losses. Amazon EC2 Spot instances are spare compute capacity in the AWS cloud available at up to 90% discount compared to On-Demand prices. As a trade-off, AWS offers no SLA on these instances and customers take the risk that it can be interrupted with only two minutes of notification when Amazon needs the capacity back. Researchers from the Israeli Institute of Technology found that "they (Spot instances) are typically generated at random from within a tight price interval via a dynamic hidden reserve price". Some companies, like Spotinst, are using machine learning to predict spot interruptions up to 15 minutes in advance.Savings Plans
In November 2019, Amazon announced Savings Plans. Savings Plans are an alternative to Reserved Instances that come in two different plan types: Compute Savings Plans and EC2 Instances Savings Plans. Compute Savings Plans allow an organization to commit to EC2 and Fargate usage with the freedom to change region, family, size, availability zone, OS and tenancy inside the lifespan of the commitment. EC2 Instance Savings plans provide a larger discount than Compute Savings Plans but are less flexible meaning a user must commit to individual instance families within a region to take advantage, but with the freedom to change instances within the family in that region. AWS uses the Cost Explorer to automatically calculate recommendations for the commitments you should make how that commitment will look like as a monthly charge on your AWS bill. AWS Savings Plans are purchased based on hourly spend commitment. This hourly commitment is made using the discounted pricing of the savings plan you are purchasing. For example, you could commit to spending $5 per hour, on a Compute Savings Plan, for a 3-year term.Features
Operating systems
When it launched in August 2006, the EC2 service offeredLinux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
and later Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems, Inc., often known as Sun for short, was an American technology company that existed from 1982 to 2010 which developed and sold computers, computer components, software, and information technology services. Sun contributed sig ...
' OpenSolaris
OpenSolaris () is a discontinued open-source computer operating system for SPARC and x86 based systems, created by Sun Microsystems and based on Solaris. Its development began in the mid 2000s and ended in 2010.
OpenSolaris was developed as ...
and Solaris Express Community Edition. In October 2008, EC2 added the Windows Server 2003
Windows Server 2003, codenamed "Whistler Server", is the sixth major version of the Windows NT operating system produced by Microsoft and the first server version to be released under the Windows Server brand name. It is part of the Windows NT ...
and Windows Server 2008
Windows Server 2008, codenamed "Longhorn Server" (alternatives: "Windows Vista Server" or "Windows Server Vista"), is the seventh major version of the Windows NT operating system produced by Microsoft to be released under the Windows Server b ...
operating systems to the list of available operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
s.
In March 2011, NetBSD
NetBSD is a free and open-source Unix-like operating system based on the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). It was the first open-source BSD descendant officially released after 386BSD was fork (software development), forked. It continues to ...
AMIs became available. In November 2012, Windows Server 2012
Windows Server 2012, codenamed "Windows Server 8", is the ninth major version of the Windows NT operating system produced by Microsoft to be released under the Windows Server brand name. It is the server version of Windows based on Windows ...
support was added.
Since 2006, Colin Percival
Colin A. Percival (born 1980) is a Canadian computer scientist and computer security researcher. He completed his undergraduate education at Simon Fraser University and a doctorate at the University of Oxford. While at university he joined the F ...
, a FreeBSD developer and Security Officer, solicited Amazon to add FreeBSD. In November 2012, Amazon officially supported running FreeBSD
FreeBSD is a free-software Unix-like operating system descended from the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). The first version was released in 1993 developed from 386BSD, one of the first fully functional and free Unix clones on affordable ...
in EC2. The FreeBSD/EC2 platform is maintained by Percival who also developed the secure deduplicating Amazon S3-cloud based backup service Tarsnap.
Amazon has their own Linux distribution based on Fedora and Red Hat Enterprise Linux
Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) is a commercial Linux distribution developed by Red Hat. Red Hat Enterprise Linux is released in server versions for x86-64, Power ISA, ARM64, and IBM Z and a desktop version for x86-64. Fedora Linux and ...
as a low cost offering known as the Amazon Linux AMI. Version 2013.03 included: Linux kernel
The Linux kernel is a Free and open-source software, free and open source Unix-like kernel (operating system), kernel that is used in many computer systems worldwide. The kernel was created by Linus Torvalds in 1991 and was soon adopted as the k ...
, Java OpenJDK
OpenJDK (Open Java Development Kit) is a free and open-source implementation of the Java Platform, Standard Edition (Java SE). It is the result of an effort Sun Microsystems began in 2006, four years before the company was acquired by Oracle Corp ...
Runtime Environment and GNU Compiler Collection
The GNU Compiler Collection (GCC) is a collection of compilers from the GNU Project that support various programming languages, Computer architecture, hardware architectures, and operating systems. The Free Software Foundation (FSF) distributes ...
.
On November 30, 2020, Amazon announced that it would be adding macOS to the EC2 service. Initial support was announced for macOS Mojave
macOS Mojave ( ; version 10.14) is the fifteenth major release of macOS, Apple Inc.'s desktop operating system for Macintosh computers. Mojave was announced at Apple's Worldwide Developers Conference on June 4, 2018, and was released to the ...
and macOS Catalina
macOS Catalina (version 10.15) is the sixteenth software versioning, major release of macOS, Apple Inc.'s desktop operating system for Macintosh computers. It is the successor to macOS Mojave and was announced at WWDC 2019 on June 3, 2019 and ...
running on Mac Mini
Mac Mini (stylized as Mac mini) is a small form factor (desktop and motherboard), small form factor desktop computer developed and marketed by Apple Inc. It is one of the company's four current Mac (computer), Mac desktop computers, positioned ...
.
Managed Container and Kubernetes Services
Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR) is a Docker registry service for Amazon EC2 instances to access repositories and images. Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) a managed Kubernetes service running on top of EC2 without needing to provision or manage instances.Persistent storage
An EC2 instance may be launched with a choice of two types of storage for its boot disk or "root device." The first option is a local "instance-store" disk as a root device (originally the only choice). The second option is to use an EBS volume as a root device. Instance-store volumes are temporary storage, which survive rebooting an EC2 instance, but when the instance is stopped or terminated (e.g., by an API call, or due to a failure), this store is lost. The Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) provides raw block devices that can be attached to Amazon EC2 instances. These block devices can then be used like any raw block device. In a typical use case, this would include formatting the device with a filesystem and mounting it. In addition, EBS supports a number of advanced storage features, including snapshotting and cloning. EBS volumes can be up to 16 TB in size. EBS volumes are built on replicated storage, so that the failure of a single component will not cause data loss. EBS was introduced to the general public by Amazon in August 2008.Apache Hadoop
Apache Hadoop () is a collection of open-source software utilities for reliable, scalable, distributed computing. It provides a software framework for distributed storage and processing of big data using the MapReduce programming model. Hadoop wa ...
supports a special s3: filesystem to support reading from and writing to S3 storage during a MapReduce
MapReduce is a programming model and an associated implementation for processing and generating big data sets with a parallel and distributed algorithm on a cluster.
A MapReduce program is composed of a ''map'' procedure, which performs filte ...
job. There are also S3 filesystems for Linux, which mount a remote S3 filestore on an EC2 image, as if it were local storage. As S3 is not a full POSIX
The Portable Operating System Interface (POSIX; ) is a family of standards specified by the IEEE Computer Society for maintaining compatibility between operating systems. POSIX defines application programming interfaces (APIs), along with comm ...
filesystem, things may not behave the same as on a local disk (e.g., no locking support).
Elastic IP addresses
Amazon CloudWatch
Automated scaling
Pricing
NOTE: the examples, figures and comparison charts in this section are from 2018 in the best case; please bear this in mind, as the situation has changed a lot from then.

 On Demand EC2 instances are priced per hour. An example of this pricing would be $0.096 per hour for a Linux, m5.large, EC2 instance in the us-east-1 region. Pricing will vary based on the instance type, region, and operating system of the instance. Public on-demand pricing for EC2 can be found on th
On Demand EC2 instances are priced per hour. An example of this pricing would be $0.096 per hour for a Linux, m5.large, EC2 instance in the us-east-1 region. Pricing will vary based on the instance type, region, and operating system of the instance. Public on-demand pricing for EC2 can be found on thAWS website
The other pricing models for EC2 have different pricing models. Spot instances also have a cost per instance hour, but the cost will change on a regular basis based on the supply of EC2 spot capacity. Reserved Instances and Compute Savings plans are priced per hour. Each of these reservation tools has its own price per hour based on the payment option, term and reservation product being used. These prices are locked in for either a 1-year or 3-year term. Amazon EC2 price varies from $2.5 per month for "nano" instance with 1 vCPU and 0.5 GB RAM on board to "xlarge" type of instances with 32 vCPU and 488 GB RAM billed up to $3997.19 per month. The charts above show how Amazon EC2 pricing is compared to similar Cloud Computing services: Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, Kamatera, and Vultr.
Reliability
 To make EC2 more fault-tolerant, Amazon engineered ''Availability Zones'' that are designed to be insulated from failures in other availability zones. Availability zones do not share the same infrastructure. Applications running in more than one availability zone can achieve higher availability.
EC2 provides users with control over the geographical location of instances that allows for latency optimization and high levels of redundancy. For example, to minimize downtime, a user can set up server instances in multiple zones that are insulated from each other for most causes of failure such that one backs up the other.
Higher-availability database services, like Amazon Relational Database Service run separately from EC2 instances.
To make EC2 more fault-tolerant, Amazon engineered ''Availability Zones'' that are designed to be insulated from failures in other availability zones. Availability zones do not share the same infrastructure. Applications running in more than one availability zone can achieve higher availability.
EC2 provides users with control over the geographical location of instances that allows for latency optimization and high levels of redundancy. For example, to minimize downtime, a user can set up server instances in multiple zones that are insulated from each other for most causes of failure such that one backs up the other.
Higher-availability database services, like Amazon Relational Database Service run separately from EC2 instances.
Issues
In early July 2008, the anti-spam organizations Outblaze and Spamhaus.org began blocking Amazon's EC2 address pool due to problems with the distribution ofspam
Spam most often refers to:
* Spam (food), a consumer brand product of canned processed pork of the Hormel Foods Corporation
* Spamming, unsolicited or undesired electronic messages
** Email spam, unsolicited, undesired, or illegal email messages
...
and malware
Malware (a portmanteau of ''malicious software'')Tahir, R. (2018)A study on malware and malware detection techniques . ''International Journal of Education and Management Engineering'', ''8''(2), 20. is any software intentionally designed to caus ...
.
On December 1, 2010, Amazon pulled its service to WikiLeaks
WikiLeaks () is a non-profit media organisation and publisher of leaked documents. It is funded by donations and media partnerships. It has published classified documents and other media provided by anonymous sources. It was founded in 2006 by ...
after coming under political pressure in the US. Assange said that WikiLeaks chose Amazon knowing it would probably be kicked off the service "in order to separate rhetoric from reality". The Internet group Anonymous
Anonymous may refer to:
* Anonymity, the state of an individual's identity, or personally identifiable information, being publicly unknown
** Anonymous work, a work of art or literature that has an unnamed or unknown creator or author
* Anonym ...
attempted to attack EC2 in revenge; however, Amazon was not affected by the attack.
Amazon's websites were temporarily offline on December 12, 2010, although it was initially unclear if this was due to attacks or a hardware failure. An Amazon official later stated that it was due to a hardware failure.
Shortly before 5 am ET on April 21, 2011, an outage started at EC2's Northern Virginia
Northern Virginia, locally referred to as NOVA or NoVA, comprises several County (United States), counties and independent city (United States), independent cities in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. ...
data center that brought down several websites, including Foursquare, Springpad, Reddit
Reddit ( ) is an American Proprietary software, proprietary social news news aggregator, aggregation and Internet forum, forum Social media, social media platform. Registered users (commonly referred to as "redditors") submit content to the ...
, Quora
Quora is an American social question-and-answer website and online knowledge market headquartered in Mountain View, California. It was founded on June 25, 2009, and made available to the public on June 21, 2010. Users can post questions, answ ...
, and Hootsuite
Hootsuite is a Online presence management, social media management platform, created by Ryan Holmes in 2008. The system's user interface takes the form of a dashboard (web administration), dashboard, and supports social network integrations for T ...
. Specifically, attempts to use Amazon's elastic-disk and database services hung, failed, or were slow. Service was restored to some parts of the data center (three of four "availability zones" in Amazon's terms) by late afternoon Eastern time that day; problems for at least some customers were continuing as of April 25. 0.07% of EBS volumes in one zone have also been lost; EBS failures were a part of normal operation even before this outage and were a risk documented by Amazon, though the number of failures and the number of ''simultaneous'' failures may find some EC2 users unprepared.
On Sunday August 6, 2011, Amazon suffered a power outage in one of their Ireland availability zones. Lightning was originally blamed for the outage; however, on August 11, Irish energy supplier ESB Networks dismissed this as a cause, but at time of writing, could not confirm what the cause of the problem was. The power outage raised multiple questions regarding Amazon's EBS infrastructure, which caused several bugs in their software to be exposed. The bugs resulted in some customers' data being deleted when recovering EBS volumes in a mid-write operation during the crash.
August 8, 2011, saw another network connectivity outage of Amazon's Northern Virginia data center, knocking out the likes of Reddit, Quora, Netflix and FourSquare. The outage lasted around 25 minutes.
Another Northern Virginia data center outage occurred on October 22, 2012, from approximately 10 am to 4 pm PT. Edmodo, Airbnb, Flipboard, Reddit, and other customers were affected. Anonymous claimed responsibility, but Amazon denied this assertion.
See also
* Amazon Virtual Private Cloud * Alibaba Cloud * AppScale *Bitnami
Bitnami is a library of installers or software packages for web applications and software stacks as well as virtual appliances. Bitnami is sponsored by Bitrock, a company founded in 2003 in Seville, Spain by Daniel Lopez Ridruejo and Erica Bre ...
* CopperEgg
* ElasticHosts
* Eucalyptus (software)
* FlexiScale
* FUJITSU Cloud IaaS Trusted Public S5
* GoGrid
* Google App Engine
* Google Cloud Platform
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is a suite of cloud computing services offered by Google that provides a series of modular cloud services including computing, Computer data storage, data storage, Data analysis, data analytics, and machine learnin ...
* GreenQloud
* Internap
* Linode
* Lunacloud
* Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure, or just Azure ( /ˈæʒər, ˈeɪʒər/ ''AZH-ər, AY-zhər'', UK also /ˈæzjʊər, ˈeɪzjʊər/ ''AZ-ure, AY-zure''), is the cloud computing platform developed by Microsoft. It has management, access and development of ...
* Nimbula
* OpenShift
* Oracle Cloud
Oracle Cloud is a cloud computing service offered by Oracle Corporation providing servers, storage, network, applications and services through a global network of Oracle Corporation managed data centers. The company allows th ...
* OrionVM
* OVHcloud
OVH, legally OVH Groupe SA, is a French cloud computing company which offers VPS, dedicated servers, and other web services. The company was founded in 1999 by the Klaba family and is headquartered in Roubaix, France. In 2019 OVH adopted OVHcl ...
* Rackspace Cloud
* RightScale
* Savvis
* TurnKey Linux Virtual Appliance Library
* Zadara
Notes
References
External links
* {{Cloud computing Amazon Web Services Cloud computing Cloud computing providers Cloud infrastructure Cloud platforms Web services