Altruistic Economic Cluster on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Altruism is the
Altruism is the
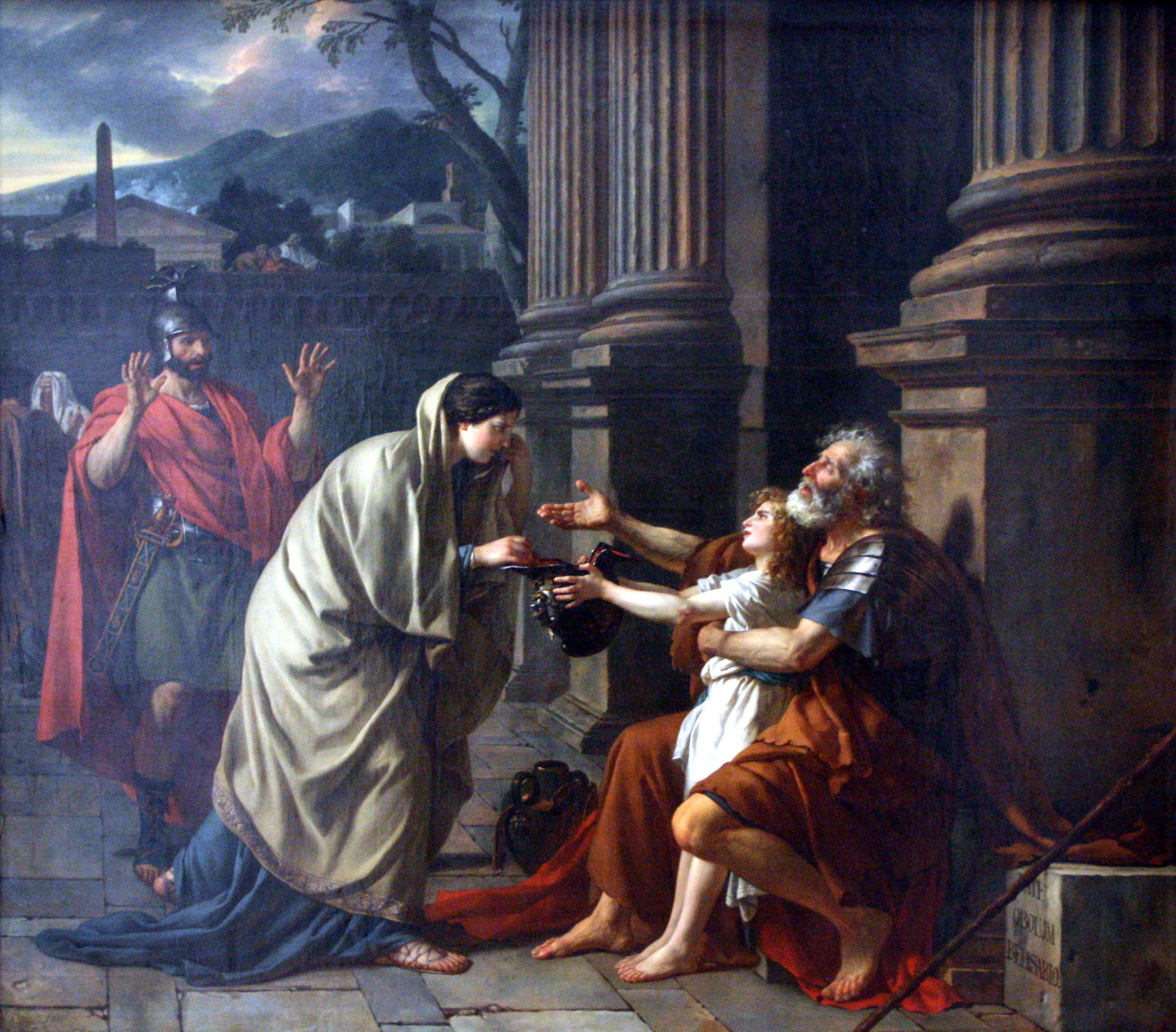
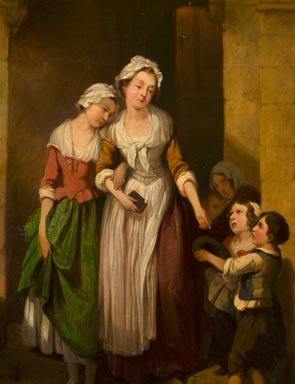 In the science of ethology (the study of animal behaviour), and more generally in the study of social evolution, altruism refers to behaviour by an individual that increases the fitness of another individual while decreasing the fitness of the actor. In evolutionary psychology this may be applied to a wide range of human behaviors such as charity,
In the science of ethology (the study of animal behaviour), and more generally in the study of social evolution, altruism refers to behaviour by an individual that increases the fitness of another individual while decreasing the fitness of the actor. In evolutionary psychology this may be applied to a wide range of human behaviors such as charity,  :Both indirect reciprocity and costly signaling depend on the value of reputation and tend to make similar predictions. One is that people will be more helping when they know that their helping behavior will be communicated to people they will interact with later, is publicly announced, is discussed, or is simply being observed by someone else. This has been documented in many studies. The effect is sensitive to subtle cues such as people being more helpful when there were stylized eyespots instead of a logo on a computer screen. Weak reputational cues such as eyespots may become unimportant if there are stronger cues present and may lose their effect with continued exposure unless reinforced with real reputational effects. Public displays such as public weeping for dead celebrities and participation in demonstrations may be influenced by a desire to be seen as altruistic. People who know that they are publicly monitored sometimes even wastefully donate money they know is not needed by the recipient because of reputational concerns.Wendy Iredal and Mark van Vugt. Altruism as showing off: a signaling perspective on promoting green behaviour and acts of kindness. In
:Women have been found to find altruistic men to be attractive partners. When looking for a long-term partner, altruism may be a preferred trait as it may indicate that he is also willing to share resources with her and her children. It has been shown that men perform altruistic acts in the early stages of a romantic relationship or simply when in the presence of an attractive woman. While both sexes state that kindness is the most preferable trait in a partner there is some evidence that men place less value on this than women and that women may not be more altruistic in presence of an attractive man. Men may even avoid altruistic women in short-term relationships which may be because they expect less success.
:People may compete for social benefit from a burnished reputation, which may cause competitive altruism. On the other hand, in some experiments a proportion of people do not seem to care about reputation and they do not help more even if this is conspicuous. This may possibly be due to reasons such as psychopathy or that they are so attractive that they need not be seen to be altruistic. The reputational benefits of altruism occur in the future as compared to the immediate costs of altruism in the present. While humans and other organisms generally place less value on future costs/benefits as compared to those in the present, some have shorter time horizons than others and these people tend to be less cooperative.
:Explicit extrinsic rewards and punishments have been found to sometimes actually have the opposite effect on behaviors compared to intrinsic rewards. This may be because such extrinsic, top-down incentives may replace (partially or in whole) intrinsic and reputational incentives, motivating the person to focus on obtaining the extrinsic rewards, which overall may make the behaviors less desirable. Another effect is that people would like altruism to be due to a personality characteristic rather than due to overt reputational concerns and simply pointing out that there are reputational benefits of an action may actually reduce them. This may possibly be used as derogatory tactic against altruists, especially by those who are non-cooperators. A counterargument is that doing good due to reputational concerns is better than doing no good at all.
* Group selection. It has controversially been argued by some evolutionary scientists such as David Sloan Wilson that natural selection can act at the level of non-kin groups to produce adaptations that benefit a non-kin group even if these adaptations are detrimental at the individual level. Thus, while altruistic persons may under some circumstances be outcompeted by less altruistic persons at the individual level, according to group selection theory the opposite may occur at the group level where groups consisting of the more altruistic persons may outcompete groups consisting of the less altruistic persons. Such altruism may only extend to ingroup members while directing prejudice and antagonism against outgroup members (see also in-group favoritism). Group selection theory has been criticized by many other evolutionary scientists.
:Both indirect reciprocity and costly signaling depend on the value of reputation and tend to make similar predictions. One is that people will be more helping when they know that their helping behavior will be communicated to people they will interact with later, is publicly announced, is discussed, or is simply being observed by someone else. This has been documented in many studies. The effect is sensitive to subtle cues such as people being more helpful when there were stylized eyespots instead of a logo on a computer screen. Weak reputational cues such as eyespots may become unimportant if there are stronger cues present and may lose their effect with continued exposure unless reinforced with real reputational effects. Public displays such as public weeping for dead celebrities and participation in demonstrations may be influenced by a desire to be seen as altruistic. People who know that they are publicly monitored sometimes even wastefully donate money they know is not needed by the recipient because of reputational concerns.Wendy Iredal and Mark van Vugt. Altruism as showing off: a signaling perspective on promoting green behaviour and acts of kindness. In
:Women have been found to find altruistic men to be attractive partners. When looking for a long-term partner, altruism may be a preferred trait as it may indicate that he is also willing to share resources with her and her children. It has been shown that men perform altruistic acts in the early stages of a romantic relationship or simply when in the presence of an attractive woman. While both sexes state that kindness is the most preferable trait in a partner there is some evidence that men place less value on this than women and that women may not be more altruistic in presence of an attractive man. Men may even avoid altruistic women in short-term relationships which may be because they expect less success.
:People may compete for social benefit from a burnished reputation, which may cause competitive altruism. On the other hand, in some experiments a proportion of people do not seem to care about reputation and they do not help more even if this is conspicuous. This may possibly be due to reasons such as psychopathy or that they are so attractive that they need not be seen to be altruistic. The reputational benefits of altruism occur in the future as compared to the immediate costs of altruism in the present. While humans and other organisms generally place less value on future costs/benefits as compared to those in the present, some have shorter time horizons than others and these people tend to be less cooperative.
:Explicit extrinsic rewards and punishments have been found to sometimes actually have the opposite effect on behaviors compared to intrinsic rewards. This may be because such extrinsic, top-down incentives may replace (partially or in whole) intrinsic and reputational incentives, motivating the person to focus on obtaining the extrinsic rewards, which overall may make the behaviors less desirable. Another effect is that people would like altruism to be due to a personality characteristic rather than due to overt reputational concerns and simply pointing out that there are reputational benefits of an action may actually reduce them. This may possibly be used as derogatory tactic against altruists, especially by those who are non-cooperators. A counterargument is that doing good due to reputational concerns is better than doing no good at all.
* Group selection. It has controversially been argued by some evolutionary scientists such as David Sloan Wilson that natural selection can act at the level of non-kin groups to produce adaptations that benefit a non-kin group even if these adaptations are detrimental at the individual level. Thus, while altruistic persons may under some circumstances be outcompeted by less altruistic persons at the individual level, according to group selection theory the opposite may occur at the group level where groups consisting of the more altruistic persons may outcompete groups consisting of the less altruistic persons. Such altruism may only extend to ingroup members while directing prejudice and antagonism against outgroup members (see also in-group favoritism). Group selection theory has been criticized by many other evolutionary scientists.
 Such explanations do not imply that humans are always consciously calculating how to increase their inclusive fitness when they are doing altruistic acts. Instead, evolution has shaped psychological mechanisms, such as emotions, that promote altruistic behaviors.
Not every single instance of altruistic behavior necessarily leads to an increase of inclusive fitness since, if that was the case in the ancestral environment, then altruistic behaviors would have been selected. This also does not imply that on average 50% or more of altruistic acts were beneficial for the altruist in the ancestral environment -- if the benefits from helping the right person were very high it would be beneficial to err on the side of caution and usually be altruistic, even if in most cases there were no benefits.
The benefits for the altruist may be increased and the costs reduced by being more altruistic towards certain groups. Research has found that people are more altruistic to kin than to no-kin, to friends than to strangers, to those attractive than to those unattractive, to non-competitors than to competitors, and to members ingroups than to members of outgroup.
The study of altruism was the initial impetus behind George R. Price's development of the Price equation, which is a mathematical equation used to study genetic evolution. An interesting example of altruism is found in the cellular slime moulds, such as '' Dictyostelium mucoroides''. These protists live as individual amoebae until starved, at which point they aggregate and form a multicellular fruiting body in which some cells sacrifice themselves to promote the survival of other cells in the fruiting body.
Selective investment theory proposes that close social bonds, and associated emotional, cognitive, and neurohormonal mechanisms, evolved in order to facilitate long-term, high-cost altruism between those closely depending on one another for survival and reproductive success.
Such cooperative behaviors have sometimes been seen as arguments for left-wing politics such by the Russian zoologist and
Such explanations do not imply that humans are always consciously calculating how to increase their inclusive fitness when they are doing altruistic acts. Instead, evolution has shaped psychological mechanisms, such as emotions, that promote altruistic behaviors.
Not every single instance of altruistic behavior necessarily leads to an increase of inclusive fitness since, if that was the case in the ancestral environment, then altruistic behaviors would have been selected. This also does not imply that on average 50% or more of altruistic acts were beneficial for the altruist in the ancestral environment -- if the benefits from helping the right person were very high it would be beneficial to err on the side of caution and usually be altruistic, even if in most cases there were no benefits.
The benefits for the altruist may be increased and the costs reduced by being more altruistic towards certain groups. Research has found that people are more altruistic to kin than to no-kin, to friends than to strangers, to those attractive than to those unattractive, to non-competitors than to competitors, and to members ingroups than to members of outgroup.
The study of altruism was the initial impetus behind George R. Price's development of the Price equation, which is a mathematical equation used to study genetic evolution. An interesting example of altruism is found in the cellular slime moulds, such as '' Dictyostelium mucoroides''. These protists live as individual amoebae until starved, at which point they aggregate and form a multicellular fruiting body in which some cells sacrifice themselves to promote the survival of other cells in the fruiting body.
Selective investment theory proposes that close social bonds, and associated emotional, cognitive, and neurohormonal mechanisms, evolved in order to facilitate long-term, high-cost altruism between those closely depending on one another for survival and reproductive success.
Such cooperative behaviors have sometimes been seen as arguments for left-wing politics such by the Russian zoologist and
 In psychological research on altruism, studies often observe altruism as demonstrated through prosocial behaviors such as
In psychological research on altruism, studies often observe altruism as demonstrated through prosocial behaviors such as
 Altruism figures prominently in Buddhism. Love and compassion are components of all forms of Buddhism, and are focused on all beings equally: love is the wish that all beings be happy, and compassion is the wish that all beings be free from suffering. "Many illnesses can be cured by the one medicine of love and compassion. These qualities are the ultimate source of human happiness, and the need for them lies at the very core of our being" ( Dalai Lama).Speech by the Dalai Lama
Altruism figures prominently in Buddhism. Love and compassion are components of all forms of Buddhism, and are focused on all beings equally: love is the wish that all beings be happy, and compassion is the wish that all beings be free from suffering. "Many illnesses can be cured by the one medicine of love and compassion. These qualities are the ultimate source of human happiness, and the need for them lies at the very core of our being" ( Dalai Lama).Speech by the Dalai Lama
The phrase "core of our being" is Freudian; see Still, the notion of altruism is modified in such a world-view, since the belief is that such a practice promotes our own happiness: "The more we care for the happiness of others, the greater our own sense of well-being becomes" (Dalai Lama). In the context of larger ethical discussions on moral action and judgment, Buddhism is characterized by the belief that negative (unhappy) consequences of our actions derive not from punishment or correction based on moral judgment, but from the law of karma, which functions like a natural law of cause and effect. A simple illustration of such cause and effect is the case of experiencing the effects of what one causes: if one causes suffering, then as a natural consequence one would experience suffering; if one causes happiness, then as a natural consequence one would experience happiness.
 The fundamental principles of Jainism revolve around the concept of altruism, not only for humans but for all sentient beings. Jainism preaches the view of ''
The fundamental principles of Jainism revolve around the concept of altruism, not only for humans but for all sentient beings. Jainism preaches the view of ''
Altruism
Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy {{Authority control Auguste Comte Defence mechanisms Morality Moral psychology Philanthropy Social philosophy Interpersonal relationships Virtue
 Altruism is the
Altruism is the principle
A principle is a proposition or value that is a guide for behavior or evaluation. In law, it is a Legal rule, rule that has to be or usually is to be followed. It can be desirably followed, or it can be an inevitable consequence of something, suc ...
and moral practice of concern for the welfare and/or happiness of other human beings or animals, resulting in a quality of life both material and spiritual. It is a traditional virtue in many cultures and a core aspect of various religious and secular worldviews. However, the object(s) of concern vary among cultures and religions. In an extreme case, altruism may become a synonym of selflessness, which is the opposite of selfishness.
The word "altruism" was popularized (and possibly coined) by the French philosopher Auguste Comte
Isidore Marie Auguste François Xavier Comte (; 19 January 1798 – 5 September 1857) was a French philosopher and writer who formulated the doctrine of positivism. He is often regarded as the first philosopher of science in the modern sense ...
in French, as ''altruisme'', for an antonym
In lexical semantics, opposites are words lying in an inherently incompatible binary relationship. For example, something that is ''long'' entails that it is not ''short''. It is referred to as a 'binary' relationship because there are two members ...
of egoism. He derived it from the Italian ''altrui'', which in turn was derived from Latin ''alteri'', meaning " other people" or "somebody else".
Altruism in biological
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary in ...
observations in field populations of the day organisms is an individual performing an action which is at a cost to themselves (e.g., pleasure and quality of life, time, probability of survival or reproduction), but benefits, either directly or indirectly, another individual, without the expectation of reciprocity or compensation for that action. Steinberg suggests a definition for altruism in the clinical setting, that is "intentional and voluntary actions that aim to enhance the welfare of another person in the absence of any quid pro quo external rewards". In one sense, the opposite of altruism is spite; a spiteful action harms another with no self-benefit.
Altruism can be distinguished from feelings of loyalty
Loyalty, in general use, is a devotion and faithfulness to a nation, cause, philosophy, country, group, or person. Philosophers disagree on what can be an object of loyalty, as some argue that loyalty is strictly interpersonal and only another h ...
or concern for the common good. The latter are predicated upon social relationships, whilst altruism does not consider relationships. Much debate exists as to whether ''"true"'' altruism is possible in human psychology. The theory of psychological egoism suggests that no act of sharing, helping or sacrificing can be described as truly altruistic, as the actor may receive an intrinsic reward in the form of personal gratification. The validity of this argument depends on whether intrinsic rewards qualify as "benefits".
The term ''altruism
Altruism is the principle and moral practice of concern for the welfare and/or happiness of other human beings or animals, resulting in a quality of life both material and spiritual. It is a traditional virtue in many cultures and a core as ...
'' may also refer to an ethical doctrine that claims that individuals are morally obliged to benefit others. Used in this sense, it is usually contrasted with egoism, which claims individuals are morally obligated to serve themselves first. Effective altruism
Effective altruism is a philosophical and social movement that advocates "using evidence and reason to figure out how to benefit others as much as possible, and taking action on that basis". People who pursue the goals of effective altruism, c ...
is the use of evidence and reason to determine the most effective ways to benefit others.
The notion of altruism
The concept has a long history in philosophical and ethical thought. The term was originally coined in the 19th century by the founding sociologist and philosopher of science,Auguste Comte
Isidore Marie Auguste François Xavier Comte (; 19 January 1798 – 5 September 1857) was a French philosopher and writer who formulated the doctrine of positivism. He is often regarded as the first philosopher of science in the modern sense ...
, and has become a major topic for psychologists (especially evolutionary psychology researchers), evolutionary biologists, and ethologists. Whilst ideas about altruism from one field can affect the other fields, the different methods and focuses of these fields always lead to different perspectives on altruism. In simple terms, altruism is caring about the welfare of other people and acting to help them.
Scientific viewpoints
Anthropology
Marcel Mauss's essay '' The Gift'' contains a passage called "Note on alms". This note describes the evolution of the notion of alms (and by extension of altruism) from the notion of sacrifice. In it, he writes:Evolutionary explanations
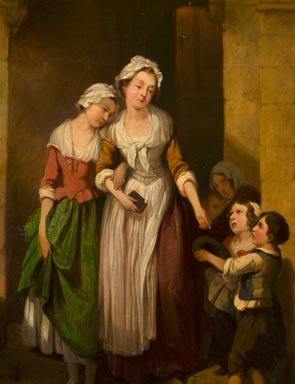 In the science of ethology (the study of animal behaviour), and more generally in the study of social evolution, altruism refers to behaviour by an individual that increases the fitness of another individual while decreasing the fitness of the actor. In evolutionary psychology this may be applied to a wide range of human behaviors such as charity,
In the science of ethology (the study of animal behaviour), and more generally in the study of social evolution, altruism refers to behaviour by an individual that increases the fitness of another individual while decreasing the fitness of the actor. In evolutionary psychology this may be applied to a wide range of human behaviors such as charity, emergency aid
Emergency management or disaster management is the managerial function charged with creating the framework within which communities reduce vulnerability to hazards and cope with disasters. Emergency management, despite its name, does not actuall ...
, help to coalition partners, tipping, courtship gifts, production of public good Public good may refer to:
* Public good (economics), an economic good that is both non-excludable and non-rivalrous
* The common good, outcomes that are beneficial for all or most members of a community
See also
* Digital public goods
Digital pu ...
s, and environmentalism.Pat Barcaly. The evolution of charitable behaviour and the power of reputation. In
Theories of apparently altruistic behavior were accelerated by the need to produce theories compatible with evolutionary origins. Two related strands of research on altruism have emerged from traditional evolutionary analyses and from evolutionary game theory a mathematical model and analysis of behavioural strategies.
Some of the proposed mechanisms are:
* Kin selection. That animals and humans are more altruistic towards close kin than to distant kin and non-kin has been confirmed in numerous studies across many different cultures. Even subtle cues indicating kinship may unconsciously increase altruistic behavior. One kinship cue is facial resemblance. One study found that slightly altering photographs so that they more closely resembled the faces of study participants increased the trust the participants expressed regarding depicted persons. Another cue is having the same family name, especially if rare, and this has been found to increase helpful behavior. Another study found more cooperative behavior the greater the number of perceived kin in a group. Using kinship terms in political speeches increased audience agreement with the speaker in one study. This effect was especially strong for firstborns, who are typically close to their families.
* Vested interests. People are likely to suffer if their friends, allies, and similar social ingroups suffer or even disappear. Helping such group members may therefore eventually benefit the altruist. Making ingroup membership more noticeable increases cooperativeness. Extreme self-sacrifice towards the ingroup may be adaptive if a hostile outgroup Outgroup may refer to:
* Outgroup (cladistics), an evolutionary-history concept
* Outgroup (sociology), a social group
{{disambig ...
threatens to kill the entire ingroup.
* Reciprocal altruism. See also Reciprocity (evolution).
** Direct reciprocity
Reciprocity may refer to:
Law and trade
* Reciprocity (Canadian politics), free trade with the United States of America
** Reciprocal trade agreement, entered into in order to reduce (or eliminate) tariffs, quotas and other trade restrictions on ...
. Research shows that it can be beneficial to help others if there is a chance that they can and will reciprocate the help. The effective tit for tat strategy is one game theoretic example. Many people seem to be following a similar strategy by cooperating if and only if others cooperate in return.
**:One consequence is that people are more cooperative if it is more likely that individuals will interact again in the future. People tend to be less cooperative if they perceive that the frequency of helpers in the population is lower. They tend to help less if they see non-cooperativeness by others and this effect tend to be stronger than the opposite effect of seeing cooperative behaviors. Simply changing the cooperative framing of a proposal may increase cooperativeness such as calling it a "Community Game" instead of a "Wall Street Game".
**:A tendency towards reciprocity implies that people will feel obligated to respond if someone helps them. This has been used by charities that give small gifts to potential donors hoping thereby to induce reciprocity. Another method is to announce publicly that someone has given a large donation. The tendency to reciprocate can even generalize so people become more helpful toward others in general after being helped. On the other hand, people will avoid or even retaliate against those perceived not to be cooperating. People sometimes mistakenly fail to help when they intended to, or their helping may not be noticed, which may cause unintended conflicts. As such, it may be an optimal strategy to be slightly forgiving of and have a slightly generous interpretation of non-cooperation.
**:People are more likely to cooperate on a task if they can communicate with one another first. This may be due to better assessments of cooperativeness or due to exchange of promises. They are more cooperative if they can gradually build trust, instead of being asked to give extensive help immediately. Direct reciprocity and cooperation in a group can be increased by changing the focus and incentives from intra-group competition to larger scale competitions such as between groups or against the general population. Thus, giving grades and promotions based only on an individual's performance relative to a small local group, as is common, may reduce cooperative behaviors in the group.
** Indirect reciprocity. The avoidance of poor reciprocators and cheaters causes a person's reputation to become very important. A person with a good reputation for reciprocity has a higher chance of receiving help even from persons they have had no direct interactions with previously.
** Strong reciprocity. A form of reciprocity where some individuals seem to spend more resources on cooperating and punishing than would be most beneficial as predicted by several established theories of altruism. A number of theories have been proposed as explanations as well as criticisms regarding its existence.
** Pseudo-reciprocity. An organism behaves altruistically and the recipient does not reciprocate but has an increased chance of acting in a way that is selfish but also as a byproduct benefits the altruist.
* Costly signaling and the handicap principle. Since altruism takes away resources from the altruist it can be an "honest signal" of resource availability and the abilities needed to gather resources. This may signal to others that the altruist is a valuable potential partner. It may also be a signal of interactive and cooperative intentions since those not interacting further in the future gain nothing from the costly signaling. It is unclear if costly signaling can indicate a long-term cooperative personality but people have increased trust for those who help. Costly signaling is pointless if everyone has the same traits, resources, and cooperative intentions, but becomes potentially more important if the population increasingly varies on these characteristics.
:Hunters widely sharing the meat has been seen as a costly signal of ability and research has found that good hunters have higher reproductive success and more adulterous relations even if they themselves receive no more of the hunted meat than anyone else. Similarly, holding large feasts and giving large donations has been seen as ways of demonstrating one's resources. Heroic risk-taking has also been interpreted as a costly signal of ability.
 :Both indirect reciprocity and costly signaling depend on the value of reputation and tend to make similar predictions. One is that people will be more helping when they know that their helping behavior will be communicated to people they will interact with later, is publicly announced, is discussed, or is simply being observed by someone else. This has been documented in many studies. The effect is sensitive to subtle cues such as people being more helpful when there were stylized eyespots instead of a logo on a computer screen. Weak reputational cues such as eyespots may become unimportant if there are stronger cues present and may lose their effect with continued exposure unless reinforced with real reputational effects. Public displays such as public weeping for dead celebrities and participation in demonstrations may be influenced by a desire to be seen as altruistic. People who know that they are publicly monitored sometimes even wastefully donate money they know is not needed by the recipient because of reputational concerns.Wendy Iredal and Mark van Vugt. Altruism as showing off: a signaling perspective on promoting green behaviour and acts of kindness. In
:Women have been found to find altruistic men to be attractive partners. When looking for a long-term partner, altruism may be a preferred trait as it may indicate that he is also willing to share resources with her and her children. It has been shown that men perform altruistic acts in the early stages of a romantic relationship or simply when in the presence of an attractive woman. While both sexes state that kindness is the most preferable trait in a partner there is some evidence that men place less value on this than women and that women may not be more altruistic in presence of an attractive man. Men may even avoid altruistic women in short-term relationships which may be because they expect less success.
:People may compete for social benefit from a burnished reputation, which may cause competitive altruism. On the other hand, in some experiments a proportion of people do not seem to care about reputation and they do not help more even if this is conspicuous. This may possibly be due to reasons such as psychopathy or that they are so attractive that they need not be seen to be altruistic. The reputational benefits of altruism occur in the future as compared to the immediate costs of altruism in the present. While humans and other organisms generally place less value on future costs/benefits as compared to those in the present, some have shorter time horizons than others and these people tend to be less cooperative.
:Explicit extrinsic rewards and punishments have been found to sometimes actually have the opposite effect on behaviors compared to intrinsic rewards. This may be because such extrinsic, top-down incentives may replace (partially or in whole) intrinsic and reputational incentives, motivating the person to focus on obtaining the extrinsic rewards, which overall may make the behaviors less desirable. Another effect is that people would like altruism to be due to a personality characteristic rather than due to overt reputational concerns and simply pointing out that there are reputational benefits of an action may actually reduce them. This may possibly be used as derogatory tactic against altruists, especially by those who are non-cooperators. A counterargument is that doing good due to reputational concerns is better than doing no good at all.
* Group selection. It has controversially been argued by some evolutionary scientists such as David Sloan Wilson that natural selection can act at the level of non-kin groups to produce adaptations that benefit a non-kin group even if these adaptations are detrimental at the individual level. Thus, while altruistic persons may under some circumstances be outcompeted by less altruistic persons at the individual level, according to group selection theory the opposite may occur at the group level where groups consisting of the more altruistic persons may outcompete groups consisting of the less altruistic persons. Such altruism may only extend to ingroup members while directing prejudice and antagonism against outgroup members (see also in-group favoritism). Group selection theory has been criticized by many other evolutionary scientists.
:Both indirect reciprocity and costly signaling depend on the value of reputation and tend to make similar predictions. One is that people will be more helping when they know that their helping behavior will be communicated to people they will interact with later, is publicly announced, is discussed, or is simply being observed by someone else. This has been documented in many studies. The effect is sensitive to subtle cues such as people being more helpful when there were stylized eyespots instead of a logo on a computer screen. Weak reputational cues such as eyespots may become unimportant if there are stronger cues present and may lose their effect with continued exposure unless reinforced with real reputational effects. Public displays such as public weeping for dead celebrities and participation in demonstrations may be influenced by a desire to be seen as altruistic. People who know that they are publicly monitored sometimes even wastefully donate money they know is not needed by the recipient because of reputational concerns.Wendy Iredal and Mark van Vugt. Altruism as showing off: a signaling perspective on promoting green behaviour and acts of kindness. In
:Women have been found to find altruistic men to be attractive partners. When looking for a long-term partner, altruism may be a preferred trait as it may indicate that he is also willing to share resources with her and her children. It has been shown that men perform altruistic acts in the early stages of a romantic relationship or simply when in the presence of an attractive woman. While both sexes state that kindness is the most preferable trait in a partner there is some evidence that men place less value on this than women and that women may not be more altruistic in presence of an attractive man. Men may even avoid altruistic women in short-term relationships which may be because they expect less success.
:People may compete for social benefit from a burnished reputation, which may cause competitive altruism. On the other hand, in some experiments a proportion of people do not seem to care about reputation and they do not help more even if this is conspicuous. This may possibly be due to reasons such as psychopathy or that they are so attractive that they need not be seen to be altruistic. The reputational benefits of altruism occur in the future as compared to the immediate costs of altruism in the present. While humans and other organisms generally place less value on future costs/benefits as compared to those in the present, some have shorter time horizons than others and these people tend to be less cooperative.
:Explicit extrinsic rewards and punishments have been found to sometimes actually have the opposite effect on behaviors compared to intrinsic rewards. This may be because such extrinsic, top-down incentives may replace (partially or in whole) intrinsic and reputational incentives, motivating the person to focus on obtaining the extrinsic rewards, which overall may make the behaviors less desirable. Another effect is that people would like altruism to be due to a personality characteristic rather than due to overt reputational concerns and simply pointing out that there are reputational benefits of an action may actually reduce them. This may possibly be used as derogatory tactic against altruists, especially by those who are non-cooperators. A counterargument is that doing good due to reputational concerns is better than doing no good at all.
* Group selection. It has controversially been argued by some evolutionary scientists such as David Sloan Wilson that natural selection can act at the level of non-kin groups to produce adaptations that benefit a non-kin group even if these adaptations are detrimental at the individual level. Thus, while altruistic persons may under some circumstances be outcompeted by less altruistic persons at the individual level, according to group selection theory the opposite may occur at the group level where groups consisting of the more altruistic persons may outcompete groups consisting of the less altruistic persons. Such altruism may only extend to ingroup members while directing prejudice and antagonism against outgroup members (see also in-group favoritism). Group selection theory has been criticized by many other evolutionary scientists.
 Such explanations do not imply that humans are always consciously calculating how to increase their inclusive fitness when they are doing altruistic acts. Instead, evolution has shaped psychological mechanisms, such as emotions, that promote altruistic behaviors.
Not every single instance of altruistic behavior necessarily leads to an increase of inclusive fitness since, if that was the case in the ancestral environment, then altruistic behaviors would have been selected. This also does not imply that on average 50% or more of altruistic acts were beneficial for the altruist in the ancestral environment -- if the benefits from helping the right person were very high it would be beneficial to err on the side of caution and usually be altruistic, even if in most cases there were no benefits.
The benefits for the altruist may be increased and the costs reduced by being more altruistic towards certain groups. Research has found that people are more altruistic to kin than to no-kin, to friends than to strangers, to those attractive than to those unattractive, to non-competitors than to competitors, and to members ingroups than to members of outgroup.
The study of altruism was the initial impetus behind George R. Price's development of the Price equation, which is a mathematical equation used to study genetic evolution. An interesting example of altruism is found in the cellular slime moulds, such as '' Dictyostelium mucoroides''. These protists live as individual amoebae until starved, at which point they aggregate and form a multicellular fruiting body in which some cells sacrifice themselves to promote the survival of other cells in the fruiting body.
Selective investment theory proposes that close social bonds, and associated emotional, cognitive, and neurohormonal mechanisms, evolved in order to facilitate long-term, high-cost altruism between those closely depending on one another for survival and reproductive success.
Such cooperative behaviors have sometimes been seen as arguments for left-wing politics such by the Russian zoologist and
Such explanations do not imply that humans are always consciously calculating how to increase their inclusive fitness when they are doing altruistic acts. Instead, evolution has shaped psychological mechanisms, such as emotions, that promote altruistic behaviors.
Not every single instance of altruistic behavior necessarily leads to an increase of inclusive fitness since, if that was the case in the ancestral environment, then altruistic behaviors would have been selected. This also does not imply that on average 50% or more of altruistic acts were beneficial for the altruist in the ancestral environment -- if the benefits from helping the right person were very high it would be beneficial to err on the side of caution and usually be altruistic, even if in most cases there were no benefits.
The benefits for the altruist may be increased and the costs reduced by being more altruistic towards certain groups. Research has found that people are more altruistic to kin than to no-kin, to friends than to strangers, to those attractive than to those unattractive, to non-competitors than to competitors, and to members ingroups than to members of outgroup.
The study of altruism was the initial impetus behind George R. Price's development of the Price equation, which is a mathematical equation used to study genetic evolution. An interesting example of altruism is found in the cellular slime moulds, such as '' Dictyostelium mucoroides''. These protists live as individual amoebae until starved, at which point they aggregate and form a multicellular fruiting body in which some cells sacrifice themselves to promote the survival of other cells in the fruiting body.
Selective investment theory proposes that close social bonds, and associated emotional, cognitive, and neurohormonal mechanisms, evolved in order to facilitate long-term, high-cost altruism between those closely depending on one another for survival and reproductive success.
Such cooperative behaviors have sometimes been seen as arguments for left-wing politics such by the Russian zoologist and anarchist
Anarchism is a political philosophy and movement that is skeptical of all justifications for authority and seeks to abolish the institutions it claims maintain unnecessary coercion and hierarchy, typically including, though not neces ...
Peter Kropotkin
Pyotr Alexeyevich Kropotkin (; russian: link=no, Пётр Алексе́евич Кропо́ткин ; 9 December 1842 – 8 February 1921) was a Russian anarchist, socialist, revolutionary, historian, scientist, philosopher, and activis ...
in his 1902 book '' Mutual Aid: A Factor of Evolution'' and Moral Philosopher Peter Singer in his book '' A Darwinian Left''.
Neurobiology
Jorge Moll andJordan Grafman
Jordan Henry Grafman (born December 21, 1950) is an American neuropsychologist who serves as Professor of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation in the Feinberg School of Medicine at Northwestern University. He is also the Director of Brain Injury ...
, neuroscientists at the National Institutes of Health and LABS-D'Or Hospital Network (J.M.) provided the first evidence for the neural bases of altruistic giving in normal healthy volunteers, using functional magnetic resonance imaging
Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI (fMRI) measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow. This technique relies on the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled. When an area o ...
. In their research, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA in October 2006, they showed that both pure monetary rewards and charitable donations activated the mesolimbic reward pathway, a primitive part of the brain that usually responds to food and sex. However, when volunteers generously placed the interests of others before their own by making charitable donations, another brain circuit was selectively activated: the subgenual cortex/septal region
The septal area (medial olfactory area), consisting of the lateral septum and medial septum, is an area in the lower, posterior part of the medial surface of the frontal lobe, and refers to the nearby septum pellucidum.
The septal nuclei are loca ...
. These structures are intimately related to social attachment and bonding in other species. Altruism, the experiment suggested, was not a superior moral faculty that suppresses basic selfish urges but rather was basic to the brain, hard-wired and pleasurable. One brain region, the subgenual anterior cingulate
In the human brain, the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) is the frontal part of the cingulate cortex that resembles a "collar" surrounding the frontal part of the corpus callosum. It consists of Brodmann areas 24, 32, and 33.
It is involved i ...
cortex/ basal forebrain, contributes to learning altruistic behavior, especially in those with trait empathy.
* The same study has shown a connection between giving to charity and the promotion of social bonding.
In fact, in an experiment published in March 2007 at the University of Southern California neuroscientist Antonio R. Damasio
Antonio Damasio ( pt, António Damásio) is a Portuguese-American neuroscientist. He is currently the David Dornsife Chair in Neuroscience, as well as Professor of Psychology, Philosophy, and Neurology, at the University of Southern California, ...
and his colleagues showed that subjects with damage to the ventromedial prefrontal cortex lack the ability to empathically feel their way to moral answers, and that when confronted with moral dilemmas, these brain-damaged patients coldly came up with "end-justifies-the-means" answers, leading Damasio to conclude that the point was not that they reached immoral conclusions, but that when they were confronted by a difficult issue – in this case as whether to shoot down a passenger plane hijacked by terrorists before it hits a major city – these patients appear to reach decisions without the anguish that afflicts those with normally functioning brains. According to Adrian Raine
Adrian Raine (born 27 January 1954) is a British psychologist. He currently holds the chair of Richard Perry University Professor of Criminology & Psychiatry in the Department of Criminology of the School of Arts and Sciences and in the Departmen ...
, a clinical neuroscientist also at the University of Southern California, one of this study's implications is that society may have to rethink how it judges immoral people: "Psychopaths often feel no empathy or remorse. Without that awareness, people relying exclusively on reasoning seem to find it harder to sort their way through moral thickets. Does that mean they should be held to different standards of accountability?"
In another study, in the 1990s, Dr. Bill Harbaugh, a University of Oregon economist, concluded people are motivated to give for reasons of personal prestige and in a similar fMRI scanner test in 2007 with his psychologist colleague Dr. Ulrich Mayr, reached the same conclusions of Jorge Moll and Jordan Grafman about giving to charity, although they were able to divide the study group into two groups: "egoists" and "altruists". One of their discoveries was that, though rarely, even some of the considered "egoists" sometimes gave more than expected because that would help others, leading to the conclusion that there are other factors in cause in charity, such as a person's environment and values.
Psychology
The International Encyclopedia of the Social Sciences defines ''psychological altruism'' as "a motivational state with the goal of increasing another's welfare". Psychological altruism is contrasted with ''psychological egoism'', which refers to the motivation to increase one's own welfare. There has been some debate on whether or not humans are truly capable of psychological altruism. atson, C. (2011). Altruism in humans. New York, NY US: Oxford University Press./ref> Some definitions specify a self-sacrificial nature to altruism and a lack of external rewards for altruistic behaviors. However, because altruism ultimately benefits the self in many cases, the selflessness of altruistic acts is brought to question. The social exchange theory postulates that altruism only exists when benefits to the self outweigh costs to the self. Daniel Batson is a psychologist who examined this question and argues against the social exchange theory. He identified four major motives: to ultimately benefit the self (egoism), to ultimately benefit the other person (altruism), to benefit a group (collectivism), or to uphold a moral principle ( principlism). Altruism that ultimately serves selfish gains is thus differentiated from selfless altruism, but the general conclusion has been that empathy-induced altruism can be genuinely selfless. The '' empathy-altruism hypothesis'' basically states that psychological altruism does exist and is evoked by the empathic desire to help someone who is suffering. Feelings of empathic concern are contrasted with feelings of personal distress, which compel people to reduce their own unpleasant emotions and increase their own positive ones through helping someone in need. Empathy is thus not selfless, since altruism works either as the way to avoid those negative, unpleasant feelings and have positive, pleasant feelings triggered by others' need for help, or as the way to incentive the gain of social reward or through fear to avoid social punishment by helping. People with empathic concern help others in distress even when exposure to the situation could be easily avoided, whereas those lacking in empathic concern avoid helping unless it is difficult or impossible to avoid exposure to another's suffering. Helping behavior is seen in humans at about two years old, when a toddler is capable of understanding subtle emotional cues. In psychological research on altruism, studies often observe altruism as demonstrated through prosocial behaviors such as
In psychological research on altruism, studies often observe altruism as demonstrated through prosocial behaviors such as helping
Helping behavior refers to voluntary actions intended to help the others, with reward regarded or disregarded. It is a type of prosocial behavior (voluntary action intended to help or benefit another individual or group of individuals, such as shar ...
, comforting, sharing, cooperation, philanthropy
Philanthropy is a form of altruism that consists of "private initiatives, for the Public good (economics), public good, focusing on quality of life". Philanthropy contrasts with business initiatives, which are private initiatives for private goo ...
, and community service. Research has found that people are most likely to help if they recognize that a person is in need and feel personal responsibility for reducing the person's distress. Research also suggests that the number of bystanders witnessing distress or suffering affects the likelihood of helping (the '' Bystander effect''). Greater numbers of bystanders decrease individual feelings of responsibility. However, a witness with a high level of empathic concern is likely to assume personal responsibility entirely regardless of the number of bystanders.
Many studies have observed the effects of volunteerism (as a form of altruism) on happiness and health and have consistently found a strong connection between volunteerism and current and future health and well-being. In a study of older adults, those who volunteered were higher on life satisfaction and will to live, and lower in depression, anxiety, and somatization. Volunteerism and helping behavior have not only been shown to improve mental health, but physical health and longevity as well, attributable to the activity and social integration it encourages. One study examined the physical health of mothers who volunteered over a 30-year period and found that 52% of those who did not belong to a volunteer organization experienced a major illness while only 36% of those who did volunteer experienced one. A study on adults ages 55+ found that during the four-year study period, people who volunteered for two or more organizations had a 63% lower likelihood of dying. After controlling for prior health status, it was determined that volunteerism accounted for a 44% reduction in mortality. Merely being aware of kindness in oneself and others is also associated with greater well-being. A study that asked participants to count each act of kindness they performed for one week significantly enhanced their subjective happiness. It is important to note that, while research supports the idea that altruistic acts bring about happiness, it has also been found to work in the opposite direction—that happier people are also kinder. The relationship between altruistic behavior and happiness is bidirectional. Studies have found that generosity increases linearly from sad to happy affective states.
Studies have also been careful to note that feeling over-taxed by the needs of others has conversely negative effects on health and happiness. For example, one study on volunteerism found that feeling overwhelmed by others' demands had an even stronger negative effect on mental health than helping had a positive one (although positive effects were still significant). Additionally, while generous acts make people feel good about themselves, it is also important for people to appreciate the kindness they receive from others. Studies suggest that gratitude goes hand-in-hand with kindness and is also very important for our well-being. A study on the relationship happiness to various character strengths showed that "a conscious focus on gratitude led to reductions in negative affect and increases in optimistic appraisals, positive affect, offering emotional support, sleep quality, and well-being".
=Pathological altruism
= Pathological altruism is when altruism is taken to an unhealthy extreme, and either harms the altruistic person, or well-intentioned actions cause more harm than good. The term "pathological altruism" was popularised by the book ''Pathological Altruism
''Pathological Altruism'' is a book edited by Barbara Oakley, Ariel Knafo, Guruprasad Madhavan, and David Sloan Wilson. It was published on 5 January 2012 by Oxford University Press, and contains 31 academic papers. Oakley defines pathological ...
''.
Examples include depression and burnout seen in healthcare professionals, an unhealthy focus on others to the detriment of one's own needs, hoarding of animals, and ineffective philanthropic and social programs that ultimately worsen the situations they are meant to aid.
Sociology
"Sociologists have long been concerned with how to build the good society". The structure of our societies and how individuals come to exhibit charitable, philanthropic, and other pro-social, altruistic actions for the common good is a largely researched topic within the field. The American Sociology Association (ASA) acknowledges public sociology saying, "The intrinsic scientific, policy, and public relevance of this field of investigation in helping to construct 'good societies' is unquestionable". This type of sociology seeks contributions that aid grassroots and theoretical understandings of what motivates altruism and how it is organized, and promotes an altruistic focus in order to benefit the world and people it studies. How altruism is framed, organized, carried out, and what motivates it at the group level is an area of focus that sociologists seek to investigate in order to contribute back to the groups it studies and "build the good society". The motivation of altruism is also the focus of study; some publications link the occurrence of moral outrage to the punishment of perpetrators and compensation of victims. Studies have shown that generosity in laboratory and in online experiments is contagious – people imitate observed generosity of others.Religious viewpoints
Most, if not all, of the world's religions promote altruism as a very important moral value. Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism,Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
, Jainism, Judaism, and Sikhism, etc., place particular emphasis on altruistic morality.
Buddhism
The phrase "core of our being" is Freudian; see Still, the notion of altruism is modified in such a world-view, since the belief is that such a practice promotes our own happiness: "The more we care for the happiness of others, the greater our own sense of well-being becomes" (Dalai Lama). In the context of larger ethical discussions on moral action and judgment, Buddhism is characterized by the belief that negative (unhappy) consequences of our actions derive not from punishment or correction based on moral judgment, but from the law of karma, which functions like a natural law of cause and effect. A simple illustration of such cause and effect is the case of experiencing the effects of what one causes: if one causes suffering, then as a natural consequence one would experience suffering; if one causes happiness, then as a natural consequence one would experience happiness.
Jainism
 The fundamental principles of Jainism revolve around the concept of altruism, not only for humans but for all sentient beings. Jainism preaches the view of ''
The fundamental principles of Jainism revolve around the concept of altruism, not only for humans but for all sentient beings. Jainism preaches the view of ''Ahimsa
Ahimsa (, IAST: ''ahiṃsā'', ) is the ancient Indian principle of nonviolence which applies to all living beings. It is a key virtue in most Indian religions: Jainism, Buddhism, and Hinduism.Bajpai, Shiva (2011). The History of India � ...
'' – to live and let live, thereby not harming sentient beings, i.e. uncompromising reverence for all life. It also considers all living things to be equal. The first Tirthankara, Rishabhdev
Rishabhanatha, also ( sa, ऋषभदेव), Rishabhadeva, or Ikshvaku is the first (Supreme preacher) of Jainism and establisher of Ikshvaku dynasty. He was the first of twenty-four teachers in the present half-cycle of time in Jain co ...
, introduced the concept of altruism for all living beings, from extending knowledge and experience to others to donation, giving oneself up for others, non-violence and compassion for all living things.
Jainism prescribes a path of non-violence to progress the soul to this ultimate goal. A major characteristic of Jain belief is the emphasis on the consequences of not only physical but also mental behaviors. One's unconquered mind with anger, pride (ego), deceit, greed and uncontrolled sense organs are the powerful enemies of humans. Anger spoils good relations, pride destroys humility, deceit destroys peace and greed destroys everything. Jainism recommends conquering anger by forgiveness, pride by humility, deceit by straightforwardness and greed by contentment.
Jains believe that to attain enlightenment and ultimately liberation, one must practice the following ethical principles (major vows) in thought, speech and action. The degree to which these principles are practiced is different for householders and monks. They are:
# Non-violence (Ahimsa);
# Truthfulness (Satya);
# Non-stealing (Asteya);
# Celibacy (Brahmacharya
''Brahmacharya'' (; sa, ब्रह्मचर्य ) is a concept within Indian religions that literally means to stay in conduct within one's own Self. In Yoga, Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism it generally refers to a lifestyle charac ...
);
# Non-possession or non-materialism (Aparigraha);
The "great vows" ( Mahavrata) are prescribed for monks and "limited vows" ( Anuvrata) are prescribed for householders. The house-holders are encouraged to practice the above-mentioned five vows. The monks have to observe them very strictly. With consistent practice, it will be possible to overcome the limitations gradually, accelerating the spiritual progress.
The principle of nonviolence seeks to minimize karmas which limit the capabilities of the soul. Jainism views every soul as worthy of respect because it has the potential to become ''Siddha'' ( God in Jainism). Because all living beings possess a soul, great care and awareness is essential in one's actions. Jainism emphasizes the equality of all life, advocating harmlessness towards all, whether the creatures are great or small. This policy extends even to microscopic organisms. Jainism acknowledges that every person has different capabilities and capacities to practice and therefore accepts different levels of compliance for ascetics and householders.
Christianity
St Thomas Aquinas interprets 'You should love your neighbour as yourself' as meaning that love for ourselves is the exemplar of love for others. Considering that "the love with which a man loves himself is the form and root of friendship" and quotes Aristotle that "the origin of friendly relations with others lies in our relations to ourselves", he concluded that though we are not bound to love others more than ourselves, we naturally seek the common good, the good of the whole, more than any private good, the good of a part. However, he thinks we should love God more than ourselves and our neighbours, and more than our bodily life—since the ultimate purpose of loving our neighbour is to share in eternal beatitude: a more desirable thing than bodily well-being. In coining the word Altruism, as stated above,Comte
''Comte'' is the French, Catalan and Occitan form of the word 'count' (Latin: ''comes''); ''comté'' is the Gallo-Romance form of the word 'county' (Latin: ''comitatus'').
Comte or Comté may refer to:
* A count in French, from Latin ''comes''
* A ...
was probably opposing this Thomistic doctrine, which is present in some theological schools within Catholicism.
Many biblical authors draw a strong connection between love of others and love of God. 1 John 4 states that for one to love God one must love his fellowman, and that hatred of one's fellowman is the same as hatred of God. Thomas Jay Oord has argued in several books that altruism is but one possible form of love. An altruistic action is not always a loving action. Oord defines altruism as acting for the other's good, and he agrees with feminists who note that sometimes love requires acting for one's own good when the other's demands undermine overall well-being.
German philosopher Max Scheler distinguishes two ways in which the strong can help the weak. One way is a sincere expression of Christian love, "motivated by a powerful feeling of security, strength, and inner salvation, of the invincible fullness of one's own life and existence". Another way is merely "one of the many modern substitutes for love, ... nothing but the urge to turn away from oneself and to lose oneself in other people's business". At its worst, Scheler says, "love for the small, the poor, the weak, and the oppressed is really disguised hatred, repressed envy, an impulse to detract, etc., directed against the opposite phenomena: wealth, strength, power, largesse."
Islam
InIslam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
, the concept "''īthār''" (إيثار) (altruism) is the notion of "preferring others to oneself". For Sufis, this means devotion to others through complete forgetfulness of one's own concerns, where concern for others is deemed as a demand made by Allah
Allah (; ar, الله, translit=Allāh, ) is the common Arabic word for God. In the English language, the word generally refers to God in Islam. The word is thought to be derived by contraction from '' al- ilāh'', which means "the god", an ...
(i.e. God) on the human body, considered to be property of Allah alone. The importance of ''īthār'' lies in sacrifice for the sake of the greater good; Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
considers those practicing ''īthār'' as abiding by the highest degree of nobility.
This is similar to the notion of chivalry, but unlike that European concept, in ''īthār'' attention is focused on everything in existence. A constant concern for Allah results in a careful attitude towards people, animals, and other things in this world.
Judaism
Judaism defines altruism as the desired goal of creation. The famous RabbiAbraham Isaac Kook
Abraham Isaac Kook (; 7 September 1865 – 1 September 1935), known as Rav Kook, and also known by the acronym HaRaAYaH (), was an Orthodox rabbi, and the first Ashkenazi Chief Rabbi of British Mandatory Palestine. He is considered to be one of ...
stated that love is the most important attribute in humanity. This is defined as bestowal, or giving, which is the intention of altruism. This can be altruism towards humanity that leads to altruism towards the creator or God. Kabbalah defines God as the force of giving in existence. Rabbi Moshe Chaim Luzzatto in particular focused on the 'purpose of creation' and how the will of God was to bring creation into perfection and adhesion with this upper force.
Modern Kabbalah developed by Rabbi Yehuda Ashlag, in his writings about the future generation, focuses on how society could achieve an altruistic social framework. Ashlag proposed that such a framework is the purpose of creation, and everything that happens is to raise humanity to the level of altruism, love for one another. Ashlag focused on society and its relation to divinity.
Sikhism
Altruism is essential to theSikh
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism, Sikhism (Sikhi), a Monotheism, monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Gu ...
religion. The central faith in Sikhism is that the greatest deed any one can do is to imbibe and live the godly qualities like love, affection, sacrifice, patience, harmony, truthfulness. The concept of ''seva'', or selfless service to the community for its own sake, is an important concept in Sikhism.
The fifth Guru, Arjun Dev
Guru Arjan (Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਅਰਜਨ, pronunciation: ; 15 April 1563 – 30 May 1606) was the first of the two Gurus martyred in the Sikh faith and the fifth of the ten total Sikh Gurus. He compiled the first official edition of th ...
, sacrificed his life to uphold "22 carats of pure truth, the greatest gift to humanity", the Guru Granth
The Guru Granth Sahib ( pa, ਗੁਰੂ ਗ੍ਰੰਥ ਸਾਹਿਬ, ) is the central holy religious scripture of Sikhism, regarded by Sikhs as the final, sovereign and eternal Guru following the lineage of the ten human gurus of the rel ...
. The ninth Guru, Tegh Bahadur, sacrificed his head to protect weak and defenseless people against atrocity.
In the late seventeenth century, Guru Gobind Singh
Guru Gobind Singh (; 22 December 1666 – 7 October 1708), born Gobind Das or Gobind Rai the tenth Sikh Guru, a spiritual master, warrior, poet and philosopher. When his father, Guru Tegh Bahadur, was executed by Aurangzeb, Guru Gobind Sing ...
(the tenth Guru in Sikhism), was at war with the Mughal
Mughal or Moghul may refer to:
Related to the Mughal Empire
* Mughal Empire of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries
* Mughal dynasty
* Mughal emperors
* Mughal people, a social group of Central and South Asia
* Mughal architecture
* Mug ...
rulers to protect the people of different faiths when a fellow Sikh, Bhai Kanhaiya
Bhai Kanhaiya (1648–1718) was a Sikh of Guru Tegh Bahadur Ji and was requested to establish the Sevapanthi or Addanshahi order of the Sikhs by Guru Gobind Singh Ji. He was known for pouring water for all the wounded members of the battlefield no ...
, attended the troops of the enemy. He gave water to both friends and foes who were wounded on the battlefield. Some of the enemy began to fight again and some Sikh warriors were annoyed by Bhai Kanhaiya as he was helping their enemy. Sikh soldiers brought Bhai Kanhaiya before Guru Gobind Singh, and complained of his action that they considered counterproductive to their struggle on the battlefield. "What were you doing, and why?" asked the Guru. "I was giving water to the wounded because I saw your face in all of them", replied Bhai Kanhaiya. The Guru responded, "Then you should also give them ointment to heal their wounds. You were practicing what you were coached in the house of the Guru."
Under the tutelage of the Guru, Bhai Kanhaiya subsequently founded a volunteer corps for altruism, which is still engaged today in doing good to others and in training new recruits for this service.
Hinduism
In Hinduism Selflessness (Atmatyag), Love (Prema), Kindness (Daya) and Forgiveness (Kshama) are considered as the highest acts of humanity or "Manushyattva". Giving alms to the beggars or poor people is considered as a divine act or "Punya" and Hindus believe it will free their souls from guilt or "Paapa" and will led them to heaven or "Swarga" in afterlife. Altruism is also the central act of various Hindu mythology and religious poems and songs. The founder of warkari samprdaya the great saint "Dhnyaneshwar Maharaj" (1275-1296) in his "Pasaydan" pray to the supreme lord "Vitthal" for the wellbeing of all living organisms of the universe.Swami Vivekananda
Swami Vivekananda (; ; 12 January 1863 – 4 July 1902), born Narendranath Datta (), was an Indian Hindu monk, philosopher, author, religious teacher, and the chief disciple of the Indian mystic Ramakrishna. He was a key figure in the intro ...
, the legendary Hindu monk, has said -"Jive prem kare jeijon, Seijon sebiche Iswar" (Whoever loves any living being, is serving god.). Mass donation of clothes to poor people (Vastraseva), or blood donation camp or mass food donation (Annaseva) for poor people is common in various Hindu religious ceremonies.
Swami Sivananda
Sivananda Saraswati (or Swami Sivananda; 8 September 1887 – 14 July 1963) was a yoga guru, a Hindu spiritual teacher, and a proponent of Vedanta. Sivananda was born Kuppuswami in Pattamadai, in the Tirunelveli district of Tamil Nadu. He stu ...
, an Advaita scholar, reiterates the views in his commentary synthesising Vedanta views on the Brahma Sutras, a Vedantic text. In his commentary on Chapter 3 of the Brahma Sutras, Sivananda notes that karma is insentient and short-lived, and ceases to exist as soon as a deed is executed. Hence, karma cannot bestow the fruits of actions at a future date according to one's merit. Furthermore, one cannot argue that karma generates apurva or punya, which gives fruit. Since apurva is non-sentient, it cannot act unless moved by an intelligent being such as a god. It cannot independently bestow reward or punishment.
However the very well known and popular text, the Bhagavad Gita
The Bhagavad Gita (; sa, श्रीमद्भगवद्गीता, lit=The Song by God, translit=śrīmadbhagavadgītā;), often referred to as the Gita (), is a 700- verse Hindu scripture that is part of the epic ''Mahabharata'' (c ...
supports the doctrine of karma yoga (achieving oneness with God through action) & " Nishkam Karma" or action without expectation / desire for personal gain which can be said to encompass altruism. Altruistic acts are generally celebrated and very well received in Hindu literature and is central to Hindu morality.
Philosophy
There exists a wide range of philosophical views on humans' obligations or motivations to act altruistically. Proponents of ethical altruism maintain that individuals are morally obligated to act altruistically. The opposing view isethical egoism
In ethical philosophy, ethical egoism is the normative position that moral agents ''ought'' to act in their own self-interest. It differs from psychological egoism, which claims that people ''can only'' act in their self-interest. Ethical egoism ...
, which maintains that moral agents should always act in their own self-interest. Both ethical altruism and ethical egoism contrast with utilitarianism, which maintains that each agent should act in order to maximise the efficacy of their function and the benefit to both themselves and their co-inhabitants.
A related concept in descriptive ethics
Descriptive ethics, also known as comparative ethics, is the study of people's beliefs about morality. It contrasts with prescriptive or normative ethics, which is the study of ethical theories that prescribe how people ought to act, and with meta- ...
is psychological egoism, the thesis that humans always act in their own self-interest and that true altruism is impossible. Rational egoism is the view that rationality
Rationality is the quality of being guided by or based on reasons. In this regard, a person acts rationally if they have a good reason for what they do or a belief is rational if it is based on strong evidence. This quality can apply to an abil ...
consists in acting in one's self-interest (without specifying how this affects one's moral obligations).
Effective altruism
Effective altruism
Effective altruism is a philosophical and social movement that advocates "using evidence and reason to figure out how to benefit others as much as possible, and taking action on that basis". People who pursue the goals of effective altruism, c ...
is a philosophy
Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, knowledge, values, mind, and language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. Some ...
and social movement
A social movement is a loosely organized effort by a large group of people to achieve a particular goal, typically a social or political one. This may be to carry out a social change, or to resist or undo one. It is a type of group action and may ...
that uses evidence and reasoning to determine the most effective ways to benefit others. Effective altruism encourages individuals to consider all causes and actions and to act in the way that brings about the greatest positive impact, based upon their values. It is the broad, evidence-based and cause-neutral approach that distinguishes effective altruism from traditional altruism or charity. Effective altruism is part of the larger movement towards evidence-based practices.
While a substantial proportion of effective altruists have focused on the nonprofit sector
The voluntary sector, independent sector, or civic sector is the realm of social activity undertaken by organizations that are non-governmental nonprofit organizations. This sector is also called the third sector, community sector, and nonprofit s ...
, the philosophy of effective altruism applies more broadly to prioritizing the scientific projects, companies, and policy initiatives which can be estimated to save lives, help people, or otherwise have the biggest benefit. People associated with the movement include philosopher Peter Singer, Facebook co founder Dustin Moskovitz, Cari Tuna
Cari Tuna is an American nonprofit businessperson. Formerly a reporter for ''The Wall Street Journal'', she co-founded and works for the organizations Open Philanthropy and Good Ventures.
Education and career
Tuna was born in Minnesota. The el ...
, Ben Delo, Oxford-based researchers William MacAskill and Toby Ord, and professional poker player Liv Boeree.
Genetics
The genes OXTR,CD38
CD38 (cluster of differentiation 38), also known as cyclic ADP ribose hydrolase is a glycoprotein found on the surface of many immune cells (white blood cells), including CD4+, CD8+, B lymphocytes and natural killer cells. CD38 also functions in ...
, COMT, DRD4, DRD5
Dopamine receptor D5, also known as D1BR, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DRD5'' gene. It belongs to the D1-like receptor family along with the D1 receptor subtype.
Function
D5 receptor is a subtype of the dopamine receptor ...
, IGF2, and GABRB2
The GABAA beta-2 subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GABRB2 gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or '' ...
have been found to be candidate genes for altruism.
Digital altruism
Digital altruism is the notion that some are willing to freely share information based on the principle ofreciprocity
Reciprocity may refer to:
Law and trade
* Reciprocity (Canadian politics), free trade with the United States of America
** Reciprocal trade agreement, entered into in order to reduce (or eliminate) tariffs, quotas and other trade restrictions on ...
and in the belief that in the end, everyone benefits from sharing information via the Internet.
This term is coined by Dr. Dana Klisanin, the founder and CEO of Evolutionary Guidance Media R&D Inc., and is a recipient of the Early Career Award An Early Career Award is an award recognizing individuals for notable contributions to their fields, companies, or organizations towards the beginning of an individual's career. Early Career Awards are typically bestowed on recipients early in thei ...
for Scientific Achievement in Media Psychology from the American Psychological Association's Division of Media Psychology.
According to Klisanin, "the notion that some are willing to freely reveal what they know" is interesting.
Types of digital altruism
There are three types of digital altruism: (1) "everyday digital altruism," involving expedience, ease, moral engagement, and conformity; (2) "creative digital altruism," involving creativity, heightened moral engagement, and cooperation; and (3) "co-creative digital altruism" involving creativity, moral engagement, and meta cooperative efforts.See also
*Altruria, California Altruria was a short-lived utopian commune in Sonoma County, California , based on Christian socialist principles and inspired by William Dean Howells's 1894 novel, ''A Traveler from Altruria''.
History
Founded by the Unitarian minister Edward ...
* Charitable organization
* Consideration
Consideration is a concept of English common law and is a necessity for simple contracts but not for special contracts (contracts by deed). The concept has been adopted by other common law jurisdictions.
The court in ''Currie v Misa'' declared ...
* Egotism
* Family economics
* Golden Rule
* Gene-centered view of evolution
* Humanity (virtue)
Humanity is a virtue linked with basic ethics of altruism derived from the human condition. It also symbolises human love and compassion towards each other.
Humanity differs from mere justice in that there is a level of altruism towards individu ...
* Misanthropy
* Mutual aid
* '' Non nobis solum''
* Prisoner's dilemma
* Philanthropy
Philanthropy is a form of altruism that consists of "private initiatives, for the Public good (economics), public good, focusing on quality of life". Philanthropy contrasts with business initiatives, which are private initiatives for private goo ...
* Random act of kindness
* Social preferences
* Social psychology
* Solidarity (sociology)
''Solidarity'' is an awareness of shared interests, objectives, standards, and sympathies creating a psychological sense of unity of groups or classes. It is based on class collaboration.''Merriam Webster'', http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictio ...
* Spite (game theory)
* Tragedy of the commons
Notes
References
* * * * * * Comte, Auguste, ''Catechisme positiviste'' (1852) or ''Catechism of Positivism'', tr. R. Congreve, (London: Kegan Paul, 1891) * * Kropotkin, Peter, '' Mutual Aid: A Factor of Evolution'' (1902) * *Nietzsche, Friedrich
Friedrich Wilhelm Nietzsche (; or ; 15 October 1844 – 25 August 1900) was a German philosopher, Prose poetry, prose poet, cultural critic, Philology, philologist, and composer whose work has exerted a profound influence on contemporary philo ...
, '' Beyond Good and Evil''
* Pierre-Joseph Proudhon, ''The Philosophy of Poverty'' (1847)
* Lysander Spooner, ''Natural Law''
* Matt Ridley, '' The Origins of Virtue''
* Oliner, Samuel P. and Pearl M. Towards a Caring Society: Ideas into Action. West Port, CT: Praeger, 1995.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
* * * * *Richard Kraut (2016Altruism
Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy {{Authority control Auguste Comte Defence mechanisms Morality Moral psychology Philanthropy Social philosophy Interpersonal relationships Virtue