Alcatraz Recreation Yard, NW View on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Alcatraz Island () is a small island in
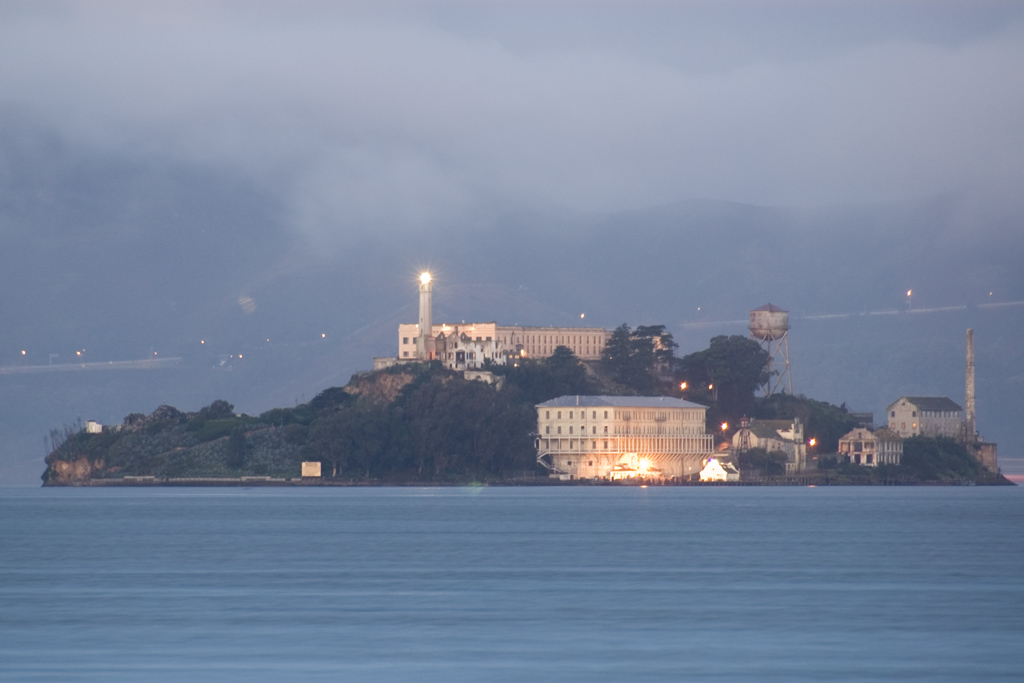
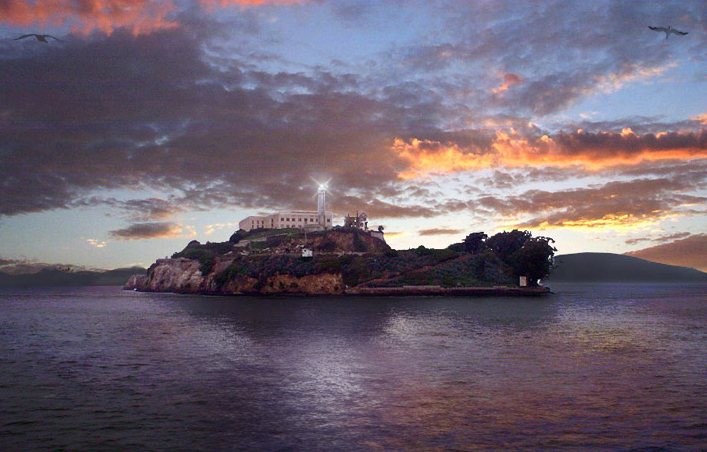





 The first European to document the islands of San Francisco Bay was
The first European to document the islands of San Francisco Bay was
 Following the acquisition of California by the United States as a result of the
Following the acquisition of California by the United States as a result of the  Starting in 1863, the military also held private citizens accused of treason, after the writ of
Starting in 1863, the military also held private citizens accused of treason, after the writ of
 The United States Disciplinary Barracks on Alcatraz were acquired by the
The United States Disciplinary Barracks on Alcatraz were acquired by the  During the 29 years it was in use, the prison held some of the most notorious criminals in American history, including gangsters such as
During the 29 years it was in use, the prison held some of the most notorious criminals in American history, including gangsters such as
 Alcatraz Island was occupied by Native American activists for the first time on March 8, 1964. The protest, proposed by Lakota Sioux activist
Alcatraz Island was occupied by Native American activists for the first time on March 8, 1964. The protest, proposed by Lakota Sioux activist  The Native Americans demanded reparations for the many treaties broken by the US government and for the lands that were taken from so many tribes.
During the nineteen months and nine days of occupation by the American Indians, several buildings at Alcatraz were damaged or destroyed by fire, including the lighthouse keeper's home, the warden's home, the Officers' Club, the recreation hall, and the Coast Guard quarters. The origin of the fires is disputed. The US government demolished a number of other buildings (mostly apartments) after the occupation had ended. Graffiti from the period of Native American occupation is still visible at many locations on the island.
During the occupation, President Richard Nixon rescinded the Indian termination policy, designed by earlier administrations to end federal recognition of many tribes and their special relationship with the US government. He established a new Native American self-determination, policy of self-determination, in part as a result of the publicity and awareness created by the occupation. The occupation ended on June 11, 1971.
The Native Americans demanded reparations for the many treaties broken by the US government and for the lands that were taken from so many tribes.
During the nineteen months and nine days of occupation by the American Indians, several buildings at Alcatraz were damaged or destroyed by fire, including the lighthouse keeper's home, the warden's home, the Officers' Club, the recreation hall, and the Coast Guard quarters. The origin of the fires is disputed. The US government demolished a number of other buildings (mostly apartments) after the occupation had ended. Graffiti from the period of Native American occupation is still visible at many locations on the island.
During the occupation, President Richard Nixon rescinded the Indian termination policy, designed by earlier administrations to end federal recognition of many tribes and their special relationship with the US government. He established a new Native American self-determination, policy of self-determination, in part as a result of the publicity and awareness created by the occupation. The occupation ended on June 11, 1971.
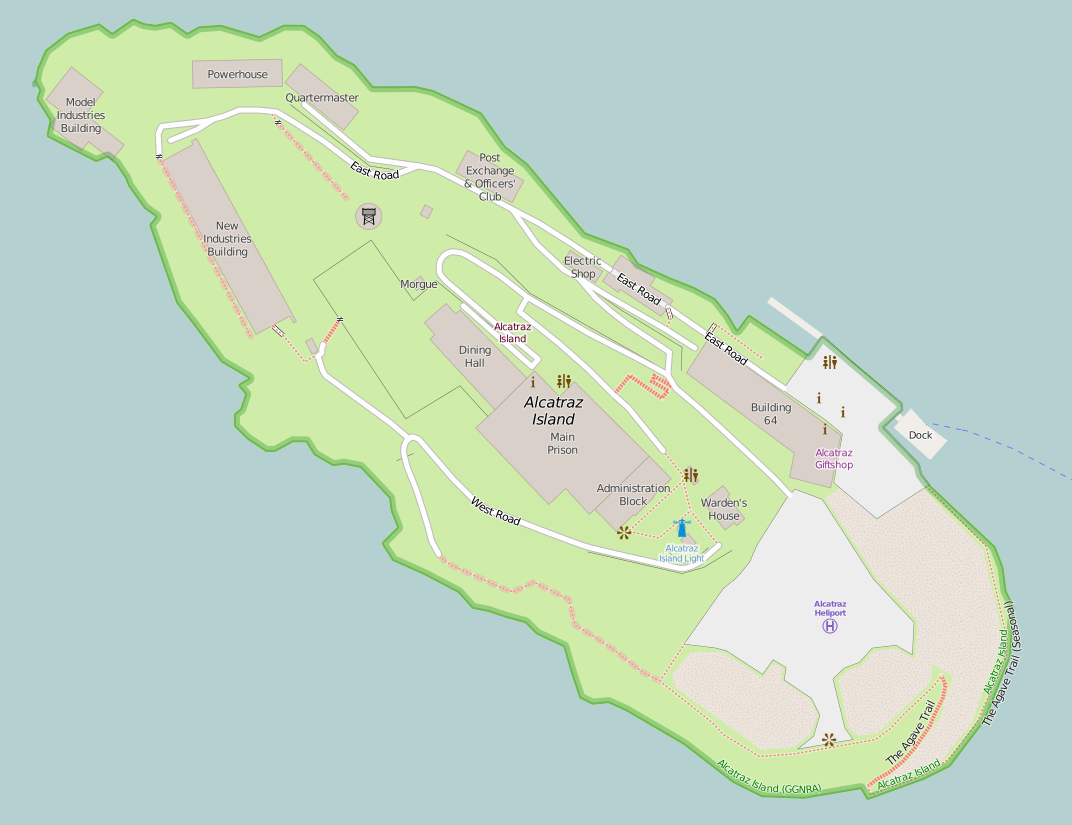 Major sites in the cultural landscape include:
* Barker Beach
* Boat Dock, Alcatraz, Boat Dock
*
Major sites in the cultural landscape include:
* Barker Beach
* Boat Dock, Alcatraz, Boat Dock
*
 Now one of San Francisco's major tourist attractions, Alcatraz drew some 1.7 million visitors annually according to a 2018 report. Visitors arrive by ferry, operated under contract by Alcatraz Cruises LLC at Pier 33.
The 2018 report indicated that "former prison buildings are being conserved and seismically upgraded and additional areas of the Island are opened to the public as safety hazards are removed". During the COVID-19 pandemic in California, COVID-19 pandemic, the buildings and the island remained closed to the public for more than a year (and ferry services were suspended), reopening in March 2021.
Now one of San Francisco's major tourist attractions, Alcatraz drew some 1.7 million visitors annually according to a 2018 report. Visitors arrive by ferry, operated under contract by Alcatraz Cruises LLC at Pier 33.
The 2018 report indicated that "former prison buildings are being conserved and seismically upgraded and additional areas of the Island are opened to the public as safety hazards are removed". During the COVID-19 pandemic in California, COVID-19 pandemic, the buildings and the island remained closed to the public for more than a year (and ferry services were suspended), reopening in March 2021.
 * Cisterns. A bluff that, because of its moist crevices, is believed to be an important site for California slender salamanders.
* Cliff tops at the island's north end. Containing a onetime manufacturing building and a plaza, the area is listed as important to nesting and roosting birds.
* The power station, powerhouse area. A steep embankment where native grassland and creeping Elymus (plant), wild rye support a habitat for deer mice.
* Tide pools. One of the only complexes in the San Francisco Bay, the island's tide pools were created by quarrying activities, and contain a variety of typical invertebrate species.
* Western cliffs and cliff tops. Rising to heights of nearly , they provide nesting and roosting sites for seabirds including pigeon guillemots,
* Cisterns. A bluff that, because of its moist crevices, is believed to be an important site for California slender salamanders.
* Cliff tops at the island's north end. Containing a onetime manufacturing building and a plaza, the area is listed as important to nesting and roosting birds.
* The power station, powerhouse area. A steep embankment where native grassland and creeping Elymus (plant), wild rye support a habitat for deer mice.
* Tide pools. One of the only complexes in the San Francisco Bay, the island's tide pools were created by quarrying activities, and contain a variety of typical invertebrate species.
* Western cliffs and cliff tops. Rising to heights of nearly , they provide nesting and roosting sites for seabirds including pigeon guillemots,
 Gardens planted by families of the original Army post, and later by families of the prison guards, fell into neglect after the prison closure in 1963. After 40 years, they are being restored by a paid staff member and many volunteers, thanks to funding by the Garden Conservancy and the Golden Gate National Parks Conservancy. The untended gardens had become severely overgrown and had developed into a nesting habitat and sanctuary for numerous birds. Now, areas of bird habitat are being preserved and protected, while many of the gardens are being restored to their original state.
In clearing out the overgrowth, workers found that many of the original plants were growing where they had been planted – some more than 100 years ago. Numerous heirloom rose hybrids, including a Welsh rose (Bardou Job) that had been believed to be extinct, have been discovered and propagated. Many species of roses, succulents, and geraniums are growing among apple and fig trees, banks of sweet peas, manicured gardens of cutting flowers, and wildly overgrown sections of native grasses with blackberry and honeysuckle.
Gardens planted by families of the original Army post, and later by families of the prison guards, fell into neglect after the prison closure in 1963. After 40 years, they are being restored by a paid staff member and many volunteers, thanks to funding by the Garden Conservancy and the Golden Gate National Parks Conservancy. The untended gardens had become severely overgrown and had developed into a nesting habitat and sanctuary for numerous birds. Now, areas of bird habitat are being preserved and protected, while many of the gardens are being restored to their original state.
In clearing out the overgrowth, workers found that many of the original plants were growing where they had been planted – some more than 100 years ago. Numerous heirloom rose hybrids, including a Welsh rose (Bardou Job) that had been believed to be extinct, have been discovered and propagated. Many species of roses, succulents, and geraniums are growing among apple and fig trees, banks of sweet peas, manicured gardens of cutting flowers, and wildly overgrown sections of native grasses with blackberry and honeysuckle.
File:Alcatraz03182006.jpg, A panorama of Alcatraz as viewed from San Francisco Bay, facing east. Sather Tower and UC Berkeley are visible in the background on the right. (Drag image left and right to show full panorama.)
File:San Francisco-Alcatraz-Water Tower-1940.jpg, Different view of the Water Tower built in 1940.
File:San Francisco-Alcatraz-Utility House-Power Plant Chimney-1930.jpg, Alcatraz Utility House and Power Plant Chimney, built in 1939.
File:San Francisco-Alcatraz-School and Electric Repair Shop-1930.jpg, School House (two story building in the middle) and the Electric Repair shop (foreground) built in 1930s.
File:Alcatraz outside (2012).jpg, Alcatraz, outside (2012)
File:Alcatraz hallway (2013).jpg, Alcatraz, hallway (2013)
File:Alcatraz - unione vista due lati - agosto 2011.jpg, Views of both long sides of the island.
File:Alcatraz island 2.jpg, Alcatraz Island harbor guards tower.
File:Alcatraz Island aerial view.jpg, Alcatraz Island view from the west. Image shot from an altitude of approximately .
File:Alcatraz August 2016.jpg, Alcatraz view from tour boat.
File:Alcatraz Basement.jpg, Basement of Alcatraz
AlcatrazHistory.com: Alcatraz History website – homepage
Alcatraz Tour and Tickets
American Devils Island Holds Toughest Prisoners
– ''Popular Science'' (February 1935).
Federal Bureau of Prisons.gov: "A Brief History of Alcatraz"
* [http://www.kdrt.org/node/8655 2012 KDRTradio.org: Interview with former Alcatraz convict Robert Luke]
Report on the 1962 Alcatraz escape incident
– ''(from the FBI United States FOIA, FOIA electronic reading room)''.
Mapicurious.com: Map of Alcatraz
– ''with marker pictures''.
Alcatraz: A Prison as Disneyland
Chris Hedges (December 2014).
Alcatraz Island, Part of Golden Gate National Recreation Area, National Park Service at Google Cultural Institute
{{authority control Alcatraz Island, Islands of San Francisco Islands of San Francisco Bay Islands of Northern California Golden Gate National Recreation Area Parks in San Francisco Forts in California National Historic Landmarks in the San Francisco Bay Area National Register of Historic Places in San Francisco National Park Service areas in California 1850 establishments in California Protected areas established in 1972 1972 establishments in California Tourist attractions in the San Francisco Bay Area Historic districts on the National Register of Historic Places in California Prison islands
San Francisco Bay
San Francisco Bay is a large tidal estuary in the U.S. state of California, and gives its name to the San Francisco Bay Area. It is dominated by the big cities of San Francisco, San Jose, and Oakland.
San Francisco Bay drains water from a ...
, offshore from San Francisco, California
San Francisco (; Spanish for " Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the fourth most populous in California and 17th ...
, United States. The island was developed in the mid-19th century with facilities for a lighthouse
A lighthouse is a tower, building, or other type of physical structure designed to emit light from a system of lamps and lenses and to serve as a beacon for navigational aid, for maritime pilots at sea or on inland waterways.
Lighthouses mar ...
, a military fortification, and a military prison. In 1934, the island was converted into a federal prison, Alcatraz Federal Penitentiary
United States Penitentiary, Alcatraz Island, also known simply as Alcatraz (, ''"the gannet"'') or The Rock was a maximum security federal prison on Alcatraz Island, off the coast of San Francisco, California, United States, the site of a for ...
. The strong currents around the island and cold water temperatures made escape nearly impossible, and the prison became one of the most notorious in American history. The prison closed in 1963, and the island is now a major tourist attraction.
Beginning in November 1969, the island was occupied
' (Norwegian: ') is a Norwegian political thriller TV series that premiered on TV2 on 5 October 2015. Based on an original idea by Jo Nesbø, the series is co-created with Karianne Lund and Erik Skjoldbjærg. Season 2 premiered on 10 October ...
for more than 19 months by a group of Native Americans, initially primarily from San Francisco, who were later joined by AIM and other urban Indians from other parts of the country, who were part of a wave of Native American activists
Native may refer to:
People
* Jus soli, citizenship by right of birth
* Indigenous peoples, peoples with a set of specific rights based on their historical ties to a particular territory
** Native Americans (disambiguation)
In arts and enterta ...
organizing public protests across the US through the 1970s. In 1972, Alcatraz was transferred to the Department of Interior to become part of Golden Gate National Recreation Area
The Golden Gate National Recreation Area (GGNRA) is a U.S. National Recreation Area protecting of ecologically and historically significant landscapes surrounding the San Francisco Bay Area. Much of the park is land formerly used by the United ...
. It was designated as a National Historic Landmark
A National Historic Landmark (NHL) is a building, district, object, site, or structure that is officially recognized by the United States government for its outstanding historical significance. Only some 2,500 (~3%) of over 90,000 places listed ...
in 1986.
Today, the island's facilities are managed by the National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an agency of the United States federal government within the U.S. Department of the Interior that manages all national parks, most national monuments, and other natural, historical, and recreational propertie ...
as part of Golden Gate National Recreation Area. Visitors can reach the island in less than 15 minutes by ferry
A ferry is a ship, watercraft or amphibious vehicle used to carry passengers, and sometimes vehicles and cargo, across a body of water. A passenger ferry with many stops, such as in Venice, Italy, is sometimes called a water bus or water taxi ...
ride from Pier 33, located between the San Francisco Ferry Building
The San Francisco Ferry Building is a terminal for ferries that travel across the San Francisco Bay, a food hall and an office building. It is located on The Embarcadero in San Francisco, California and is served by Golden Gate Ferry and San ...
and Fisherman's Wharf, San Francisco
Fisherman's Wharf is a neighborhood and popular tourist attraction in San Francisco, California. It roughly encompasses the northern waterfront area of San Francisco from Ghirardelli Square or Van Ness Avenue east to Pier 35 or Kearny Street. Th ...
. Hornblower Cruises
Hornblower Cruises & Events NOW City Experiences is a San Francisco-based charter yacht, dining cruise and ferry service company.
History
The company began in 1974 in Berkeley, California with two ships. In 1980 the original owner, Ward Proes ...
, operating under the name Alcatraz Cruises, is the official ferry provider to and from the island.
Alcatraz Island is the site of the abandoned federal prison, the oldest operating lighthouse
A lighthouse is a tower, building, or other type of physical structure designed to emit light from a system of lamps and lenses and to serve as a beacon for navigational aid, for maritime pilots at sea or on inland waterways.
Lighthouses mar ...
on the West Coast of the United States
The West Coast of the United States, also known as the Pacific Coast, Pacific states, and the western seaboard, is the coastline along which the Western United States meets the North Pacific Ocean. The term typically refers to the contiguous U.S ...
, early military fortification
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
s, and natural features such as rock pool
A tide pool or rock pool is a shallow pool of seawater that forms on the rocky intertidal shore. Many of these pools exist as separate bodies of water only at low tide.
Many tide pool habitats are home to especially adaptable animals that ...
s and a seabird
Seabirds (also known as marine birds) are birds that are adapted to life within the marine environment. While seabirds vary greatly in lifestyle, behaviour and physiology, they often exhibit striking convergent evolution, as the same enviro ...
colony (mostly western gull
The western gull (''Larus occidentalis'') is a large white-headed gull that lives on the west coast of North America. It was previously considered conspecific with the yellow-footed gull (''Larus livens'') of the Gulf of California. The western g ...
s, cormorant
Phalacrocoracidae is a family of approximately 40 species of aquatic birds commonly known as cormorants and shags. Several different classifications of the family have been proposed, but in 2021 the IOC adopted a consensus taxonomy of seven ge ...
s, and egret
Egrets ( ) are herons, generally long-legged wading birds, that have white or buff plumage, developing fine plumes (usually milky white) during the breeding season. Egrets are not a biologically distinct group from herons and have the same build ...
s). According to a 1971 documentary on the history of Alcatraz, the island measures by and is at highest point during mean tide. The total area of the island is reported to be .
Landmarks on the island include the Main Cellhouse, Dining Hall
A cafeteria, sometimes called a canteen outside the U.S., is a type of food service location in which there is little or no waiting staff table service, whether a restaurant or within an institution such as a large office building or school ...
, Lighthouse
A lighthouse is a tower, building, or other type of physical structure designed to emit light from a system of lamps and lenses and to serve as a beacon for navigational aid, for maritime pilots at sea or on inland waterways.
Lighthouses mar ...
, the ruins of the Warden's House and Social Hall, Parade Grounds, Building 64
Building 64, also known as the Building #64 or the Building 64 Residential Apartments, was the first building constructed on the island of Alcatraz off the coast of San Francisco, USA, entirely for the purpose of accommodating the military officers ...
, Water Tower
A water tower is an elevated structure supporting a water tank constructed at a height sufficient to pressurize a water distribution system, distribution system for potable water, and to provide emergency storage for fire protection. Water towe ...
, New Industries Building
The New Industries Building is a building on the western end of Alcatraz Island off the coast of San Francisco, United States. It was constructed in 1939 for $186,000 as part of a $1.1 million modernization scheme which also included the water to ...
, Model Industries Building
The Model Industries building or Industries Building is a three/four-story building on the northwest corner of Alcatraz Island off the coast of San Francisco, USA. This building was originally built by the U.S. military and was used as a laundry bu ...
, and the Recreation Yard.
History




 The first European to document the islands of San Francisco Bay was
The first European to document the islands of San Francisco Bay was Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Cana ...
naval officer and explorer Juan Manuel de Ayala
Juan Manuel de Ayala y Aranza (28 December 1745 – 30 December 1797) was a Spanish naval officer who played a significant role in the European exploration of California, since he and the crew of his ship the ''San Carlos'' are the first European ...
during Spanish rule of California; he charted San Francisco Bay in 1775. He named today's Yerba Buena Island
Yerba Buena Island (Spanish: ''Isla Yerba Buena'') sits in San Francisco Bay within the borders of the City and County of San Francisco. The Yerba Buena Tunnel runs through its center and connects the western and eastern spans of the San Francis ...
as ''"La Isla de los Alcatraces"'', which translates as "The Island of the Gannets
Gannets are seabirds comprising the genus ''Morus'' in the family Sulidae, closely related to boobies.
Gannets are large white birds with yellowish heads; black-tipped wings; and long bills. Northern gannets are the largest seabirds in the Nor ...
" but is commonly believed to translate as "The Island of the Pelican
Pelicans (genus ''Pelecanus'') are a genus of large water birds that make up the family Pelecanidae. They are characterized by a long beak and a large throat pouch used for catching prey and draining water from the scooped-up contents before s ...
s" (the modern Spanish word for 'pelican' is ''pelícano''), from the archaic Spanish ' ("pelican"). There are no gannets native to the Pacific coast, making the older Spanish usage more likely.
Yerba Buena Island was labeled on Ayala
Ayala may refer to:
Places
* Ciudad Ayala, Morelos, Mexico
* Ayala Alabang, a barangay in Muntinlupa, Philippines
* Ayala Avenue, a major thoroughfare in the Makati Central Business District, Philippines
* Ayala, Magalang, a barrio in Magalang ...
's 1775 chart of San Francisco Bay as "Isla de Alcatraces". The name was later applied to the rock now known as Alcatraz Island by Captain Frederick W. Beechey, an English naval officer and explorer.
Over the years, the Spanish version "Alcatraz" became popular and is now widely used. In August 1827, for instance, French Captain Auguste Bernard Duhaut-Cilly wrote "... running past Alcatraze's (Pelicans) Island ... covered with a countless number of these birds. A gun fired over the feathered legions caused them to fly up in a great cloud and with a noise like a hurricane." The California brown pelican
The brown pelican (''Pelecanus occidentalis'') is a bird of the pelican family, Pelecanidae, one of three species found in the Americas and one of two that feed by diving into water. It is found on the Atlantic Coast from New Jersey to the mout ...
(''Pelecanus occidentalis californicus'') is not known to nest on the island today. The Spanish built several small buildings on the island and other minor structures.
Fort Alcatraz
The earliest recorded private owner of the island of Alcatraz is Julian Workman, to whom it was given byMexican
Mexican may refer to:
Mexico and its culture
*Being related to, from, or connected to the country of Mexico, in North America
** People
*** Mexicans, inhabitants of the country Mexico and their descendants
*** Mexica, ancient indigenous people ...
governor Pio Pico
Pio may refer to:
Places
* Pio Lake, Italy
* Pio Island, Solomon Islands
* Pio Point, Bird Island, south Atlantic Ocean
People
* Pio (given name)
* Pio (surname)
* Pio (footballer, born 1986), Brazilian footballer
* Pio (footballer, born 1988), B ...
in June 1846, with the understanding that Workman would build a lighthouse on it. Julian Workman is the baptismal name of William Workman, co-owner of Rancho La Puente
Rancho La Puente was a ranch in the southern San Gabriel Valley that measured just under , and remained intact from its establishment in the late 1700s as an outpost of Mission San Gabriel until about 1870. By modern landmarks, the ranch extended ...
and a personal friend of Pio Pico. Later in 1846, acting in his capacity as Military Governor of California, John C. Frémont
John Charles Frémont or Fremont (January 21, 1813July 13, 1890) was an American explorer, military officer, and politician. He was a U.S. Senator from California and was the first Republican nominee for president of the United States in 1856 ...
bought the island for $5,000 in the name of the United States government
The federal government of the United States (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the national government of the United States, a federal republic located primarily in North America, composed of 50 states, a city within a fede ...
from Francis Temple.
In 1850, President Millard Fillmore
Millard Fillmore (January 7, 1800March 8, 1874) was the 13th president of the United States, serving from 1850 to 1853; he was the last to be a member of the Whig Party while in the White House. A former member of the U.S. House of Represen ...
ordered that Alcatraz Island be set aside specifically as a United States military reservation, for military purposes based upon the U.S. acquisition of California from Mexico following the Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the (''United States intervention in Mexico''), was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the 1 ...
. Frémont had expected a large compensation for his initiative in purchasing and securing Alcatraz Island for the U.S. government, but the U.S. government later invalidated the sale and paid Frémont nothing. Frémont and his heirs sued for compensation during protracted but unsuccessful legal battles that extended into the 1890s.
 Following the acquisition of California by the United States as a result of the
Following the acquisition of California by the United States as a result of the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo ( es, Tratado de Guadalupe Hidalgo), officially the Treaty of Peace, Friendship, Limits, and Settlement between the United States of America and the United Mexican States, is the peace treaty that was signed on 2 ...
(1848), which ended the Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the (''United States intervention in Mexico''), was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the 1 ...
, and the onset of the California Gold Rush
The California Gold Rush (1848–1855) was a gold rush that began on January 24, 1848, when gold was found by James W. Marshall at Sutter's Mill in Coloma, California. The news of gold brought approximately 300,000 people to California fro ...
the following year, the U.S. Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cl ...
began studying the suitability of Alcatraz Island for the positioning of coastal batteries to protect the approaches to San Francisco Bay. In 1853, under the direction of Zealous B. Tower
Zealous Bates Tower (January 12, 1819 – March 20, 1900) was an American soldier and civil engineer who served as a general in the Union Army during the American Civil War. He was most noted for constructing the solid defenses of Federal-occupie ...
, the United States Army Corps of Engineers
, colors =
, anniversaries = 16 June (Organization Day)
, battles =
, battles_label = Wars
, website =
, commander1 = ...
began fortifying the island, work which continued until 1858, when the initial version of Fort Alcatraz
Fort Alcatraz was a United States Army coastal fortification on Alcatraz Island near the mouth of San Francisco Bay in California, part of the Third System of fixed fortifications, although very different from most other Third System works. Initi ...
was complete. The island's first garrison, numbering about 200 soldiers, arrived at the end of that year.
When the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
broke out in 1861, the island mounted 85 cannons (increased to 105 cannons by 1866) in casemates around its perimeter, though the small size of the garrison meant only a fraction of the guns could be used at one time. At this time it also served as the San Francisco Arsenal for storage of firearms to prevent them falling into the hands of Confederate sympathizers
In the 1860s, the Copperheads, also known as Peace Democrats, were a faction of Democrats in the Union who opposed the American Civil War and wanted an immediate peace settlement with the Confederates.
Republicans started calling anti-war D ...
. Alcatraz, built as a "heavily fortified military site on the West Coast", was to form a "triangle of defense" with Fort Point and Lime Point, but the contemplated work on Lime Point was never built. The first operational lighthouse on the West Coast of the United States
The West Coast of the United States, also known as the Pacific Coast, Pacific states, and the western seaboard, is the coastline along which the Western United States meets the North Pacific Ocean. The term typically refers to the contiguous U.S ...
was also built on Alcatraz. During the war, Fort Alcatraz was used to imprison Confederate
Confederacy or confederate may refer to:
States or communities
* Confederate state or confederation, a union of sovereign groups or communities
* Confederate States of America, a confederation of secessionist American states that existed between 1 ...
sympathizers and privateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or deleg ...
s on the west coast, but its guns were never fired at an enemy.
Studies of the island and its fortifications have included archeological surveys relying on contemporary technology. In 2019 "Binghamton University archaeologist Timothy de Smet and colleagues located historical remains beneath the former recreation yard of the Alcatraz Federal Penitentiary." Using ground-penetrating radar
Ground-penetrating radar (GPR) is a geophysical method that uses radar pulses to image the subsurface. It is a non-intrusive method of surveying the sub-surface to investigate underground utilities such as concrete, asphalt, metals, pipes, cables o ...
(GPR) data and georectifications, Smet and colleagues discovered structures, including "a 'bombproof' earthwork traverse along with its underlying vaulted brick masonry tunnel and ventilation ducts," in surprisingly good condition. Archaeologists also found the remains of ammunition magazines, and tunnels below the penitentiary that was built later.
Because of the isolation created by the cold, strong currents of the waters of San Francisco Bay, as early as 1859, Alcatraz was used to house soldiers convicted of crimes. By 1861, the fort was the military prison for the Department of the Pacific
The Department of the Pacific or Pacific Department was a major command ( Department) of the United States Army from 1853 to 1858. It replaced the Pacific Division, and was itself replaced by the Department of California and the Department of O ...
. It housed Civil War prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held Captivity, captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold priso ...
(POWs) as early as that year.
 Starting in 1863, the military also held private citizens accused of treason, after the writ of
Starting in 1863, the military also held private citizens accused of treason, after the writ of habeas corpus in the United States
In United States law, ''habeas corpus'' () is a recourse challenging the reasons or conditions of a person's confinement under color of law. A petition for ''habeas corpus'' is filed with a court that has jurisdiction over the custodian, and i ...
was suspended. Hundreds of troops were trained on the island, with more than 350 military personnel in place by April 1861. As enlistees were assigned to units, new green troops reported for training. In early 1865, the number of men reached 433, the peak of the war.
During the Civil War-era, rapid changes in artillery and fortification were generated. Alcatraz's defenses were obsolete by the postwar years. Modernization efforts, including an ambitious plan to level the entire island and construct shell-proof underground magazines and tunnels, were undertaken between 1870 and 1876 but never completed (the so-called "parade ground" on the southern tip of the island represents the extent of the flattening effort). Instead, the army switched the focus of its plans for Alcatraz from coastal defense to detention, a task for which it was well suited because of its isolation.
In 1867, a brick jailhouse was built (previously inmates had been kept in the basement of the guardhouse), and in 1868, Alcatraz was officially designated as a long-term detention facility for military prisoners. The facility was later discontinued for Prisoners of War in 1846. Among those incarcerated at Alcatraz were Confederates caught on the West Coast West Coast or west coast may refer to:
Geography Australia
* Western Australia
*Regions of South Australia#Weather forecasting, West Coast of South Australia
* West Coast, Tasmania
**West Coast Range, mountain range in the region
Canada
* Britis ...
and some Hopi
The Hopi are a Native American ethnic group who primarily live on the Hopi Reservation in northeastern Arizona, United States. As of the 2010 census, there are 19,338 Hopi in the country. The Hopi Tribe is a sovereign nation within the Unite ...
Native American men in the 1870s, who refused orders to send their children away from their families to Indian boarding schools
American Indian boarding schools, also known more recently as American Indian residential schools, were established in the United States from the mid 17th to the early 20th centuries with a primary objective of "civilizing" or assimilating Nat ...
.
In 1898, due to the Spanish–American War
, partof = the Philippine Revolution, the decolonization of the Americas, and the Cuban War of Independence
, image = Collage infobox for Spanish-American War.jpg
, image_size = 300px
, caption = (clock ...
, the prison population rose from 26 to over 450. From 1905 to 1907 it was commanded by U.S. Army General George W. McIver
Brigadier general (United States), Brigadier General George Willcox McIver (February 22, 1858 – May 9, 1947) was a United States Army officer who served as acting Chief of the National Guard Bureau, Chief of the Militia Bureau and commanded the ...
. After the 1906 San Francisco earthquake
At 05:12 Pacific Standard Time on Wednesday, April 18, 1906, the coast of Northern California was struck by a major earthquake with an estimated moment magnitude of 7.9 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of XI (''Extreme''). High-intensity sha ...
, civilian prisoners were transferred to Alcatraz for safe confinement. On March 21, 1907, Alcatraz was officially designated as the Western U.S. Military Prison, later Pacific Branch, U.S. Disciplinary Barracks, 1915.
In 1909 construction began on the huge concrete main cell block, designed by Major Reuben Turner, which remains the island's dominant feature. It was completed in 1912. To accommodate the new cell block, the Citadel, a three-story barracks, was demolished down to the first floor, which was below ground level. The building had been constructed in an excavated pit, creating a defensive dry moat
A moat is a deep, broad ditch, either dry or filled with water, that is dug and surrounds a castle, fortification, building or town, historically to provide it with a preliminary line of defence. In some places moats evolved into more extensive ...
. The first floor was incorporated as a basement to the new cell block, giving rise to the popular legend of "dungeons" below the main cell block. The US Disciplinary Barracks was deactivated in October 1933 and transferred to the Bureau of Prisons
The Federal Bureau of Prisons (BOP) is a United States federal law enforcement agency under the Department of Justice that is responsible for the care, custody, and control of incarcerated individuals who have committed federal crimes; that i ...
.
During World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, the prison was used to hold conscientious objectors
A conscientious objector (often shortened to conchie) is an "individual who has claimed the right to refuse to perform military service" on the grounds of freedom of thought, conscience, or religion. The term has also been extended to object ...
, including Philip Grosser
Philip Grosser (1890 in Slavuta – October 3, 1933 in Boston) was an anarchist and anti-militarist, hailed by fellow anarchist, Alexander Berkman, as "one of yfinest comrades".
He was imprisoned at the Federal Military Prison on Alcatraz Island ...
, who wrote a pamphlet entitled ''Uncle Sam's Devil's Island'' about his experiences.
Alcatraz Federal Penitentiary
United States Department of Justice
The United States Department of Justice (DOJ), also known as the Justice Department, is a federal executive department of the United States government tasked with the enforcement of federal law and administration of justice in the United State ...
on October 12, 1933, and the island was designated as a federal prison
A federal prison is operated under the jurisdiction of a federal government as opposed to a state or provincial body. Federal prisons are used for convicts who violated federal law (U.S., Mexico), inmates considered dangerous (Brazil), or those s ...
in August 1934. Alcatraz was designed to hold prisoners who continuously caused trouble at other federal prisons. At 9:40 am on August 11, 1934, the first batch of 137 prisoners arrived at Alcatraz, arriving by railroad from the United States Penitentiary in Leavenworth, Kansas
Leavenworth () is the county seat and largest city of Leavenworth County, Kansas, United States and is part of the Kansas City metropolitan area. As of the 2020 census, the population of the city was 37,351. It is located on the west bank of t ...
, to Santa Venetia, California
Santa Venetia is a census-designated place (CDP) in Marin County, California, United States. It is located north of downtown San Rafael, at an elevation of . The population was 4,289 at the 2020 census.
Geography
Santa Venetia is located in eas ...
. They were escorted to Alcatraz, while handcuffed in high security coaches and guarded by 60 special FBI agents
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic intelligence and security service of the United States and its principal federal law enforcement agency. Operating under the jurisdiction of the United States Department of Justice, t ...
, U.S. Marshals
The United States Marshals Service (USMS) is a federal law enforcement agency in the United States. The USMS is a bureau within the U.S. Department of Justice, operating under the direction of the Attorney General, but serves as the enforce ...
and railway security officials.
Most of the prisoners were notorious bank robbers and murderers. The prison initially had a staff of 155, including the first warden James A. Johnston and associate warden J. E. Shuttleworth, both considered to be "iron men". The staff were highly trained in security, but not rehabilitation.
 During the 29 years it was in use, the prison held some of the most notorious criminals in American history, including gangsters such as
During the 29 years it was in use, the prison held some of the most notorious criminals in American history, including gangsters such as Al Capone
Alphonse Gabriel Capone (; January 17, 1899 – January 25, 1947), sometimes known by the nickname "Scarface", was an American gangster and businessman who attained notoriety during the Prohibition era as the co-founder and boss of the ...
, Robert Franklin Stroud
Robert Franklin Stroud (January 28, 1890 – November 21, 1963), known as the "Birdman of Alcatraz", was a convicted murderer, American federal prisoner and author who has been cited as one of the most notorious criminals in the United S ...
(the "Birdman of Alcatraz"), George "Machine Gun" Kelly Machine Gun Kelly most often refers to:
* Machine Gun Kelly (gangster) (1900–1954), American gangster.
* Machine Gun Kelly (musician) (born 1990), American rapper.
Machine Gun Kelly may also refer to:
* ''Machine-Gun Kelly'' (film), 1958 film a ...
and Bumpy Johnson
Ellsworth Raymond "Bumpy" Johnson (October 31, 1905 – July 7, 1968) was an American crime boss in the Harlem neighborhood of New York City.
Early life
Ellsworth Raymond "Bumpy" Johnson was born in Charleston, South Carolina, on October 31, 1905 ...
, and political terrorists such as Rafael Cancel Miranda
Rafael Cancel Miranda (July 18, 1930 – March 2, 2020) was a poet, political activist, member of the Puerto Rican Nationalist Party and an advocate of Puerto Rican independence. On March 1, 1954, Cancel Miranda and three other Nationalists (L ...
, a member of the Puerto Rican Nationalist Party
The Nationalist Party of Puerto Rico ( es, Partido Nacionalista de Puerto Rico, PNPR) is a Puerto Rican political party founded on September 17, 1922, in San Juan, Puerto Rico. Its primary goal is to work for Puerto Rico's independence. The P ...
who attacked the United States Capitol
The United States Capitol, often called The Capitol or the Capitol Building, is the seat of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, which is formally known as the United States Congress. It is located on Capitol Hill ...
building in 1954."Former Alcatraz inmate speaks about his time", ''San Francisco Examiner'', by D. Morita; October 9, 2009 Others included Mickey Cohen
Meyer Harris "Mickey" Cohen (September 4, 1913 – July 29, 1976) was an American gangster, boxer and entrepreneur based in Los Angeles during the mid-20th century.
Early life
Mickey Cohen was born on September 4, 1913, in New York City to Je ...
, Arthur R. "Doc" Barker, and Alvin "Creepy" Karpis, who served more time at Alcatraz than any other inmate. It also provided housing for the Bureau of Prisons staff and their families.
Contrary to popular belief, it was possible to escape and swim all of the way to shore. However, during its 29 years of operation, the penitentiary claimed that no prisoner successfully escaped. A total of 36 prisoners made 14 escape attempts, two men trying twice. 23 were caught alive, six were shot and killed during their escape, two drowned, and five are listed as "missing and presumed drowned". The most violent incident occurred on May 2, 1946, when a failed escape attempt by six prisoners led to the Battle of Alcatraz
The Battle of Alcatraz, which lasted from May 2 to 4, 1946, was the result of an escape attempt at Alcatraz Federal Penitentiary by armed convicts. Two Federal Bureau of Prisons officers—William A. Miller and Harold Stites—were killed (Mille ...
. Perhaps the most famous is the intricate escape, carried out on June 11, 1962, by Frank Morris, John Anglin, and Clarence Anglin
In June 1962, inmates Clarence Anglin, John Anglin, and Frank Morris escaped from Alcatraz Federal Penitentiary, a maximum-security prison located on Alcatraz Island in San Francisco Bay. Late on the night of June 11 or early morning o ...
. The three men are believed to have drowned in their attempt.
Although most escapees were caught or drowned, in 1962, prisoner John Paul Scott
John Paul Scott (January 3, 1927 – February 22, 1987) was an American criminal who is noted as the only escapee from Alcatraz Federal Penitentiary known to have reached the San Francisco shore by swimming. He was recaptured almost immediately ...
made it to the shore. However, he was so weary that police found him unconscious and in hypothermic
Hypothermia is defined as a body core temperature below in humans. Symptoms depend on the temperature. In mild hypothermia, there is shivering and mental confusion. In moderate hypothermia, shivering stops and confusion increases. In severe h ...
shock. The annual Escape from Alcatraz Triathlon
Escape from Alcatraz is the name for two different triathlons held in the San Francisco Bay Area of California. The Escape from Alcatraz originated in 1981 as a private club event, beginning in San Francisco and ending in Marin County. The race ...
includes a required swim from the island to the bay shore.
Post-prison years
Closing of the prison
There are several reasons that Alcatraz closed as a penitentiary in 1963. The penitentiary cost much more to operate than other prisons (nearly $10 per prisoner per day, as opposed to $3 per prisoner per day at Atlanta). Half a century of saltwater saturation
Water content or moisture content is the quantity of water contained in a material, such as soil (called soil moisture), rock, ceramics, crops, or wood. Water content is used in a wide range of scientific and technical areas, and is expressed as ...
had severely eroded the buildings and three people had escaped in 1962. After its closure, George Moscone
George Richard Moscone (; November 24, 1929 – November 27, 1978) was an American attorney and Democratic politician. He was the 37th mayor of San Francisco, California from January 1976 until his assassination in November 1978. He was known ...
received public proposals to repurpose Alcatraz Island.
Native American occupation
 Alcatraz Island was occupied by Native American activists for the first time on March 8, 1964. The protest, proposed by Lakota Sioux activist
Alcatraz Island was occupied by Native American activists for the first time on March 8, 1964. The protest, proposed by Lakota Sioux activist Belva Cottier
Belva Cottier (June 27, 1920May 2, 2000) was an American Rosebud Sioux activist and social worker. She proposed the idea of occupying Alcatraz Island in 1964 and was one of the activists who led the protest for return of the island to Native A ...
and joined by about 35 others, was reported by, among others, the ''San Francisco Chronicle
The ''San Francisco Chronicle'' is a newspaper serving primarily the San Francisco Bay Area of Northern California. It was founded in 1865 as ''The Daily Dramatic Chronicle'' by teenage brothers Charles de Young and M. H. de Young, Michael H. de ...
'' and the ''San Francisco Examiner
The ''San Francisco Examiner'' is a newspaper distributed in and around San Francisco, California, and published since 1863.
Once self-dubbed the "Monarch of the Dailies" by then-owner William Randolph Hearst, and flagship of the Hearst Corporat ...
''.
Beginning on November 20, 1969, a group of Native Americans called United Indians of All Tribes
United Indians of All Tribes (also known as the United Indians of All Tribes Foundation, or UIATF) is a non-profit foundation that provides social and educational services to Native Americans in the Seattle metropolitan area and aims to promot ...
, mostly college students from San Francisco, occupied the island to protest federal policies related to American Indians. Some of them were children of Native Americans who had relocated in the city as part of the Bureau of Indian Affairs
The Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA), also known as Indian Affairs (IA), is a United States federal agency within the Department of the Interior. It is responsible for implementing federal laws and policies related to American Indians and A ...
' (BIA) Indian termination policy
Indian termination is a phrase describing United States policies relating to Native Americans from the mid-1940s to the mid-1960s. It was shaped by a series of laws and practices with the intent of assimilating Native Americans into mainstream ...
, which was a series of laws and policies aimed at the assimilation of Native Americans into mainstream US society. It encouraged Native Americans to move away from the Indian reservations
An Indian reservation is an area of land held and governed by a federally recognized Native American tribal nation whose government is accountable to the United States Bureau of Indian Affairs and not to the state government in which it ...
and into cities to take advantage of health, educational and employment opportunities. A number of employees of the Bureau of Indian Affairs also occupied Alcatraz at that time, including Doris Purdy, an amateur photographer, who later produced footage of her stay on the island.
The occupiers, who stayed on the island for nearly two years, demanded that the island's facilities be adapted and new structures built for an Indian education center, ecology center, and cultural center. The American Indians claimed the island by provisions of the Treaty of Fort Laramie (1868)
The Treaty of Fort Laramie (also the Sioux Treaty of 1868) is an agreement between the United States and the Oglala, Miniconjou, and Brulé bands of Lakota people, Yanktonai Dakota and Arapaho Nation, following the failure of the first F ...
between the US and the Sioux; they said the treaty promised to return all retired, abandoned, or out-of-use federal lands to the native peoples from whom they were acquired. Indians of All Tribes claimed Alcatraz Island by the " Right of Discovery"; as historian Troy R. Johnson states in ''The Occupation of Alcatraz Island'', generations of indigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
knew about Alcatraz at least 10,000 years before any European knew about any part of North America. Begun by urban Indians of San Francisco, the occupation attracted other Native Americans from across the country, including American Indian Movement
The American Indian Movement (AIM) is a Native American grassroots movement which was founded in Minneapolis, Minnesota in July 1968, initially centered in urban areas in order to address systemic issues of poverty, discrimination, and police ...
(AIM) urban activists from Minneapolis.
 The Native Americans demanded reparations for the many treaties broken by the US government and for the lands that were taken from so many tribes.
During the nineteen months and nine days of occupation by the American Indians, several buildings at Alcatraz were damaged or destroyed by fire, including the lighthouse keeper's home, the warden's home, the Officers' Club, the recreation hall, and the Coast Guard quarters. The origin of the fires is disputed. The US government demolished a number of other buildings (mostly apartments) after the occupation had ended. Graffiti from the period of Native American occupation is still visible at many locations on the island.
During the occupation, President Richard Nixon rescinded the Indian termination policy, designed by earlier administrations to end federal recognition of many tribes and their special relationship with the US government. He established a new Native American self-determination, policy of self-determination, in part as a result of the publicity and awareness created by the occupation. The occupation ended on June 11, 1971.
The Native Americans demanded reparations for the many treaties broken by the US government and for the lands that were taken from so many tribes.
During the nineteen months and nine days of occupation by the American Indians, several buildings at Alcatraz were damaged or destroyed by fire, including the lighthouse keeper's home, the warden's home, the Officers' Club, the recreation hall, and the Coast Guard quarters. The origin of the fires is disputed. The US government demolished a number of other buildings (mostly apartments) after the occupation had ended. Graffiti from the period of Native American occupation is still visible at many locations on the island.
During the occupation, President Richard Nixon rescinded the Indian termination policy, designed by earlier administrations to end federal recognition of many tribes and their special relationship with the US government. He established a new Native American self-determination, policy of self-determination, in part as a result of the publicity and awareness created by the occupation. The occupation ended on June 11, 1971.
Alcatraz under the National Park Service
In 1972, the National Park Service purchased Alcatraz along with Fort Mason from the U.S. Army to establish the Golden Gate National Recreation Area. Under "An Act to Establish the Golden Gate National Recreation Area" President Richard Nixon allocated $120 million for land acquisition and development of the area. It has since been under the direction of the Golden Gate National Recreation Area and now operates as a tourist site and museum dedicated to its time as a federal penitentiary. Operating costs still remain one of its biggest challenges today.Landmarks
Part of the Golden Gate National Recreation Area since 1972, the entire Alcatraz Island was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1976. In 1986 it was designated as aNational Historic Landmark
A National Historic Landmark (NHL) is a building, district, object, site, or structure that is officially recognized by the United States government for its outstanding historical significance. Only some 2,500 (~3%) of over 90,000 places listed ...
, the highest recognition. and
In 1993, the National Park Service published a plan entitled ''Alcatraz Development Concept and Environmental Assessment.'' This plan, approved in 1980, doubled the area of Alcatraz accessible to the public, in order to enable visitors to enjoy its scenery and bird, marine, and animal life.
 Major sites in the cultural landscape include:
* Barker Beach
* Boat Dock, Alcatraz, Boat Dock
*
Major sites in the cultural landscape include:
* Barker Beach
* Boat Dock, Alcatraz, Boat Dock
* Building 64
Building 64, also known as the Building #64 or the Building 64 Residential Apartments, was the first building constructed on the island of Alcatraz off the coast of San Francisco, USA, entirely for the purpose of accommodating the military officers ...
* Alcatraz Citadel, Citadel
* Dining Hall
A cafeteria, sometimes called a canteen outside the U.S., is a type of food service location in which there is little or no waiting staff table service, whether a restaurant or within an institution such as a large office building or school ...
* Former Military Chapel (Bachelor Quarters)
* Helipad
* Alcatraz Library, Library
* Lighthouse
A lighthouse is a tower, building, or other type of physical structure designed to emit light from a system of lamps and lenses and to serve as a beacon for navigational aid, for maritime pilots at sea or on inland waterways.
Lighthouses mar ...
* Main Cellhouse
* Model Industries Building
The Model Industries building or Industries Building is a three/four-story building on the northwest corner of Alcatraz Island off the coast of San Francisco, USA. This building was originally built by the U.S. military and was used as a laundry bu ...
* Alcatraz Morgue, Morgue
* New Industries Building
The New Industries Building is a building on the western end of Alcatraz Island off the coast of San Francisco, United States. It was constructed in 1939 for $186,000 as part of a $1.1 million modernization scheme which also included the water to ...
* Social Hall (Alcatraz), Officers' Club
* Parade Grounds
* Power House (Alcatraz), Power House
* Recreation Yard
* Warden's House (Alcatraz Island), Wardens House
* Water Tower
A water tower is an elevated structure supporting a water tank constructed at a height sufficient to pressurize a water distribution system, distribution system for potable water, and to provide emergency storage for fire protection. Water towe ...
Development
American Indigenous groups, such as the International Indian Treaty Council, occasionally hold ceremonies on the island, most notably, their "Sunrise Gatherings" every Columbus Day and Thanksgiving Day. Around 2007, the Global Peace Foundation proposed to raze the prison and build a peace center in its place. Supporters collected 10,350 signatures – sufficient to have it placed as a proposition on the presidential primary ballots in San Francisco for February 5, 2008. The proposed plan was estimated at US$1 billion. For the plan to pass, United States Congress, Congress would have to have taken Alcatraz out of the National Park Service. Critics of the plan said that Alcatraz is too rich in history to be destroyed. On February 6, 2008, the Alcatraz Island Global Peace Center Proposition C failed to pass, with 72% of voters rejecting the proposition. The coastal environment of the San Francisco Bay Area has caused deterioration and corrosion of building materials throughout Alcatraz. Beginning in 2011, theNational Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an agency of the United States federal government within the U.S. Department of the Interior that manages all national parks, most national monuments, and other natural, historical, and recreational propertie ...
began major renovations on the island, including the installation of solar panels on the cell house roof, slope stabilization near the Warden's House, and the stabilization and rehabilitation of the outer cell house walls.
 Now one of San Francisco's major tourist attractions, Alcatraz drew some 1.7 million visitors annually according to a 2018 report. Visitors arrive by ferry, operated under contract by Alcatraz Cruises LLC at Pier 33.
The 2018 report indicated that "former prison buildings are being conserved and seismically upgraded and additional areas of the Island are opened to the public as safety hazards are removed". During the COVID-19 pandemic in California, COVID-19 pandemic, the buildings and the island remained closed to the public for more than a year (and ferry services were suspended), reopening in March 2021.
Now one of San Francisco's major tourist attractions, Alcatraz drew some 1.7 million visitors annually according to a 2018 report. Visitors arrive by ferry, operated under contract by Alcatraz Cruises LLC at Pier 33.
The 2018 report indicated that "former prison buildings are being conserved and seismically upgraded and additional areas of the Island are opened to the public as safety hazards are removed". During the COVID-19 pandemic in California, COVID-19 pandemic, the buildings and the island remained closed to the public for more than a year (and ferry services were suspended), reopening in March 2021.
Art
Alcatraz has been home to several art installations. In 2014, Chinese artist/dissident Ai Weiwei staged an exhibition which explored "questions about human rights and freedom of expression" called @Large. This exhibition included Lego portraits of famous political prisoners. The creation of the exhibition was featured in a 2019 documentary film, ''Yours Truly (2019 film), Yours Truly''. In 2016, Nelson Saiers used Mathematics, math and prison slang as central elements in a six-month installation that called attention to the imposition of long prison sentences.Fauna and flora
Habitat
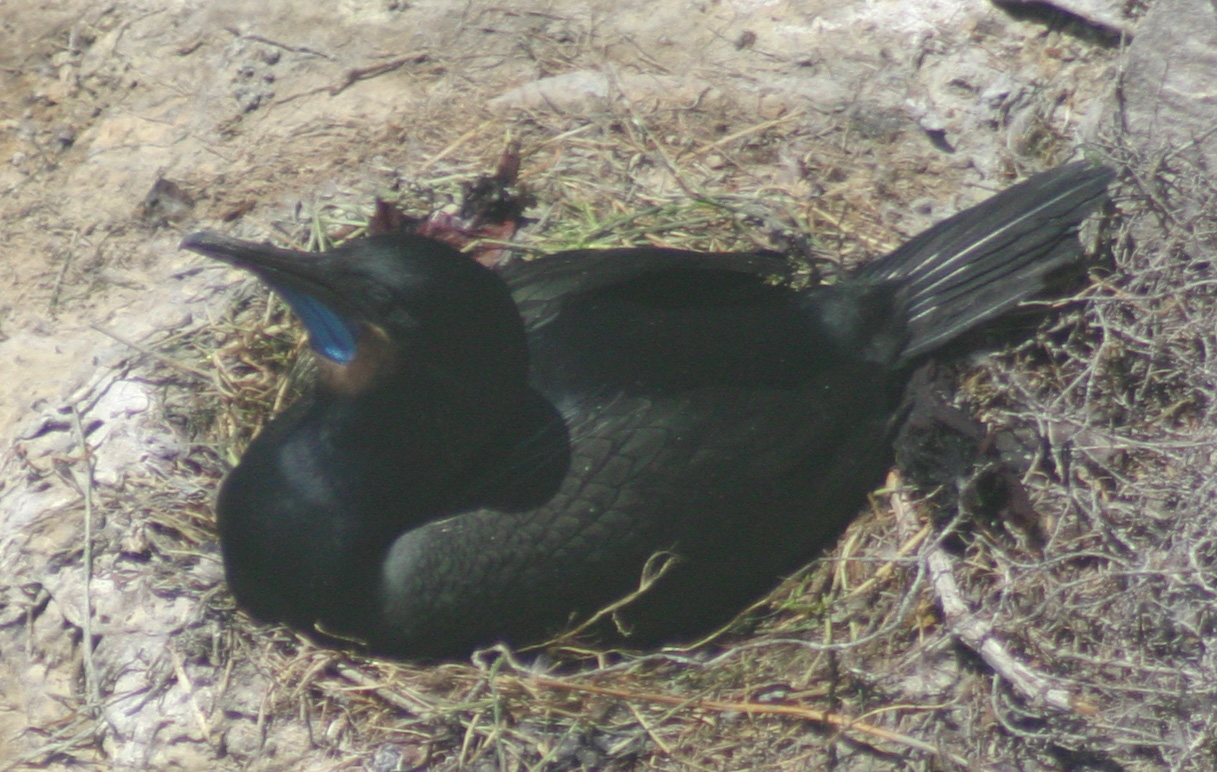
 * Cisterns. A bluff that, because of its moist crevices, is believed to be an important site for California slender salamanders.
* Cliff tops at the island's north end. Containing a onetime manufacturing building and a plaza, the area is listed as important to nesting and roosting birds.
* The power station, powerhouse area. A steep embankment where native grassland and creeping Elymus (plant), wild rye support a habitat for deer mice.
* Tide pools. One of the only complexes in the San Francisco Bay, the island's tide pools were created by quarrying activities, and contain a variety of typical invertebrate species.
* Western cliffs and cliff tops. Rising to heights of nearly , they provide nesting and roosting sites for seabirds including pigeon guillemots,
* Cisterns. A bluff that, because of its moist crevices, is believed to be an important site for California slender salamanders.
* Cliff tops at the island's north end. Containing a onetime manufacturing building and a plaza, the area is listed as important to nesting and roosting birds.
* The power station, powerhouse area. A steep embankment where native grassland and creeping Elymus (plant), wild rye support a habitat for deer mice.
* Tide pools. One of the only complexes in the San Francisco Bay, the island's tide pools were created by quarrying activities, and contain a variety of typical invertebrate species.
* Western cliffs and cliff tops. Rising to heights of nearly , they provide nesting and roosting sites for seabirds including pigeon guillemots, cormorant
Phalacrocoracidae is a family of approximately 40 species of aquatic birds commonly known as cormorants and shags. Several different classifications of the family have been proposed, but in 2021 the IOC adopted a consensus taxonomy of seven ge ...
s, Heermann's gulls, and western gull
The western gull (''Larus occidentalis'') is a large white-headed gull that lives on the west coast of North America. It was previously considered conspecific with the yellow-footed gull (''Larus livens'') of the Gulf of California. The western g ...
s. Harbor seals can occasionally be seen on a small beach at the base.
* The parade grounds. Carved from the hillside during the late 19th century and covered with rubble since the government demolished Corrections officer, guard housing in 1971, the area has become a habitat and breeding ground for black-crowned night herons, western gull
The western gull (''Larus occidentalis'') is a large white-headed gull that lives on the west coast of North America. It was previously considered conspecific with the yellow-footed gull (''Larus livens'') of the Gulf of California. The western g ...
s, slender salamanders, and deer mice.
* The Agave Path, a trail named for its dense growth of agave. Located atop a shoreline bulkhead on the south side, it provides a nesting habitat for night herons.
Flora
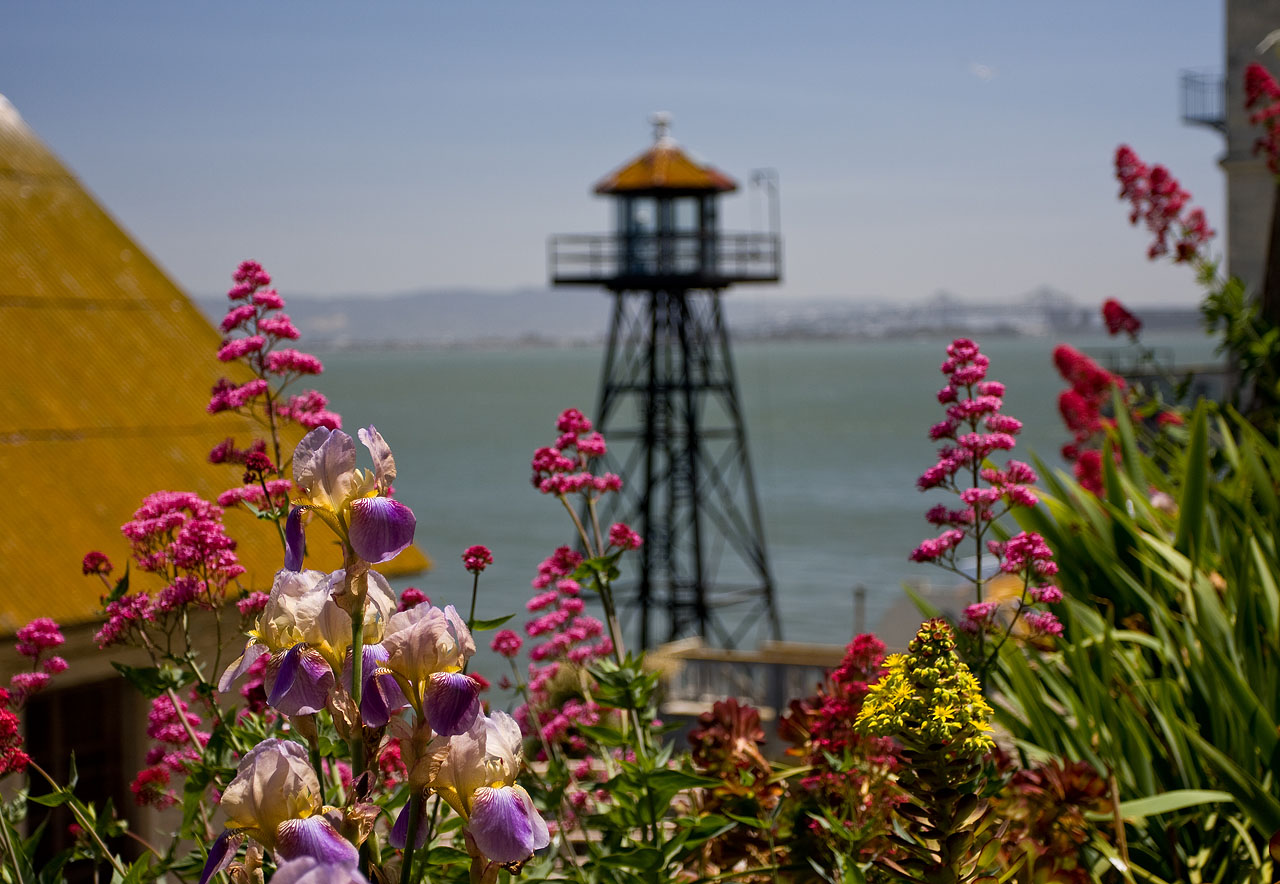
 Gardens planted by families of the original Army post, and later by families of the prison guards, fell into neglect after the prison closure in 1963. After 40 years, they are being restored by a paid staff member and many volunteers, thanks to funding by the Garden Conservancy and the Golden Gate National Parks Conservancy. The untended gardens had become severely overgrown and had developed into a nesting habitat and sanctuary for numerous birds. Now, areas of bird habitat are being preserved and protected, while many of the gardens are being restored to their original state.
In clearing out the overgrowth, workers found that many of the original plants were growing where they had been planted – some more than 100 years ago. Numerous heirloom rose hybrids, including a Welsh rose (Bardou Job) that had been believed to be extinct, have been discovered and propagated. Many species of roses, succulents, and geraniums are growing among apple and fig trees, banks of sweet peas, manicured gardens of cutting flowers, and wildly overgrown sections of native grasses with blackberry and honeysuckle.
Gardens planted by families of the original Army post, and later by families of the prison guards, fell into neglect after the prison closure in 1963. After 40 years, they are being restored by a paid staff member and many volunteers, thanks to funding by the Garden Conservancy and the Golden Gate National Parks Conservancy. The untended gardens had become severely overgrown and had developed into a nesting habitat and sanctuary for numerous birds. Now, areas of bird habitat are being preserved and protected, while many of the gardens are being restored to their original state.
In clearing out the overgrowth, workers found that many of the original plants were growing where they had been planted – some more than 100 years ago. Numerous heirloom rose hybrids, including a Welsh rose (Bardou Job) that had been believed to be extinct, have been discovered and propagated. Many species of roses, succulents, and geraniums are growing among apple and fig trees, banks of sweet peas, manicured gardens of cutting flowers, and wildly overgrown sections of native grasses with blackberry and honeysuckle.
In popular culture
Alcatraz Island appears often in media and popular culture, including films dating from 1962: ''The Book of Eli'' (2010), ''X-Men: The Last Stand'' (2006), ''Catch Me If You Can'' (2002), ''The Rock (film), The Rock'' (1996), ''Murder in the First (film), Murder in the First'' (1995), ''Escape from Alcatraz (film), Escape from Alcatraz'' (1979), ''The Enforcer (1976 film), The Enforcer'' (1976), ''Point Blank (1967 film), Point Blank'' (1967) '', Birdman of Alcatraz (film), Birdman of Alcatraz'' (1962) and J. J. Abrams' 2012 television series ''Alcatraz (TV series), Alcatraz''. It also was featured in the ''Yu-Gi-Oh!, Yu-Gi-Oh! Duel Monsters'' anime, in the book ''Al Capone Does My Shirts'', in the video game ''Tony Hawk's Pro Skater 4'' as a playable level. It is also showcased as a playable racetrack in the 1997 arcade racing video game ''San Francisco Rush: Extreme Racing, San Francisco Rush the Rock: Alcatraz Edition''. Alcatraz has also been portrayed often as a safe haven or headquarters, base of operations in many apocalyptic and post-apocalyptic fiction, post-apocalyptic movies, such as ''The Book of Eli''. Alcatraz was featured in the video game ''Call of Duty: Black Ops II'' in a downloadable zombie survival map called "Mob of the Dead" in which players could explore the Main Cellhouse, the Boat Dock, and a fictional area called the Catacombs which runs through the island. A segment of Alcatraz' Cellhouse makes a cameo appearance in ''Call of Duty: Black Ops III'' in the downloadable zombies survival map "Revelations". The map was then remastered in ''Call of Duty: Black Ops IIII, Call of Duty: Black Ops 4's'' zombie mode as "Blood of the Dead" in which the playable area of the map was expanded to include the Model Industries Building, New Industries Building, and the Warden's House. ''Call of Duty: Mobile'' also has a seasonal game mode in Alcatraz Island. ''Call of Duty: Warzones Rebirth Island is also based on Alcatraz Island. Alcatraz even appears in ''The Alchemyst'' and ''The Sorceress: The Secrets of the Immortal Nicholas Flamel, The Sorceress'' by author Michael Scott (Irish author), Michael Scott and is depicted as a prison for the immortal Perenelle Flamel. Alcatraz is featured in the episode "Bird Mummy of Alcatraz" in the children's program, ''Mummies Alive!'' and was also featured in a mission in the video game ''Watch Dogs 2''. Alcatraz is also featured as a Downloadable content, downloadable map in the video game ''The Escapists.'' Escape from Alcatraz (film), ''Escape from Alcatraz'' and ''The Rock'' are two films that show how inescapable the island is. ''Escape from Alcatraz'' is based on the true story of a few inmates trying to flee the island. The Rock (film), ''The Rock'' on the other hand, just depicts life in Alcatraz. In the 2003 video game ''Hulk (video game), Hulk'', Alcatraz is the location of a secret base of operations called ''Freehold'' for the supervillain Leader (character), Leader.Gallery
See also
* Asinara * Cellular Jail * Château d'If * Devil's Island * Fort Denison * List of islands of California * Robben Island * San Lucas IslandReferences
Further reading
* * *AlcatrazHistory.com: Alcatraz History website – homepage
Alcatraz Tour and Tickets
American Devils Island Holds Toughest Prisoners
– ''Popular Science'' (February 1935).
Federal Bureau of Prisons.gov: "A Brief History of Alcatraz"
* [http://www.kdrt.org/node/8655 2012 KDRTradio.org: Interview with former Alcatraz convict Robert Luke]
Report on the 1962 Alcatraz escape incident
– ''(from the FBI United States FOIA, FOIA electronic reading room)''.
Mapicurious.com: Map of Alcatraz
– ''with marker pictures''.
Alcatraz: A Prison as Disneyland
Chris Hedges (December 2014).
Alcatraz Island, Part of Golden Gate National Recreation Area, National Park Service at Google Cultural Institute
{{authority control Alcatraz Island, Islands of San Francisco Islands of San Francisco Bay Islands of Northern California Golden Gate National Recreation Area Parks in San Francisco Forts in California National Historic Landmarks in the San Francisco Bay Area National Register of Historic Places in San Francisco National Park Service areas in California 1850 establishments in California Protected areas established in 1972 1972 establishments in California Tourist attractions in the San Francisco Bay Area Historic districts on the National Register of Historic Places in California Prison islands