Alba De Céspedes Y Bertini on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 ''Alba'' ( , ) is the
''Alba'' ( , ) is the
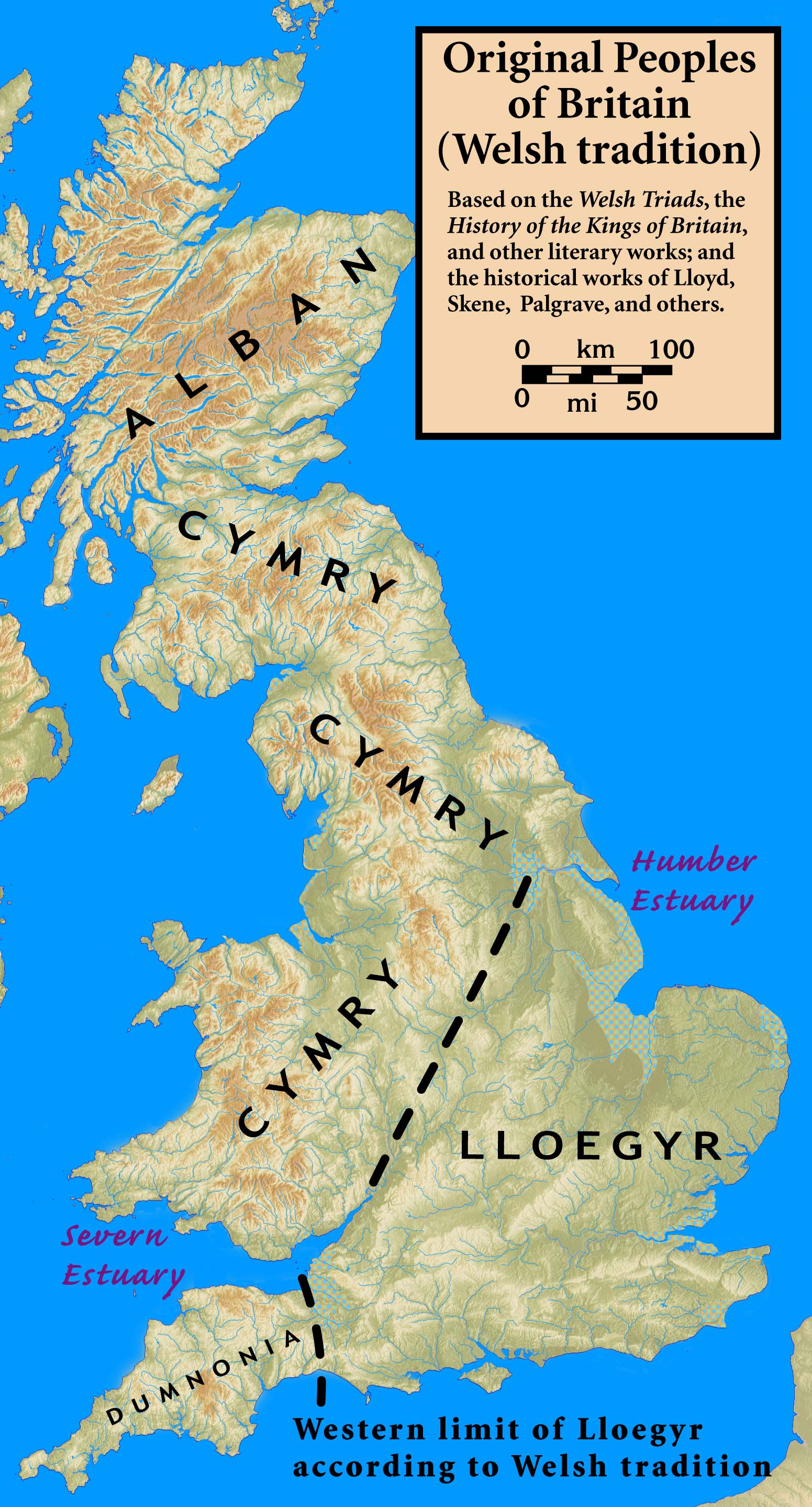 The term first appears in classical texts as ' or ' (in
The term first appears in classical texts as ' or ' (in

Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic ( gd, Gàidhlig ), also known as Scots Gaelic and Gaelic, is a Goidelic language (in the Celtic branch of the Indo-European language family) native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a Goidelic language, Scottish Gaelic, as well as ...
name for Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ...
. It is also, in English language historiography, used to refer to the polity of Picts
The Picts were a group of peoples who lived in what is now northern and eastern Scotland (north of the Firth of Forth) during Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. Where they lived and what their culture was like can be inferred from ea ...
and Scots united in the ninth century as the Kingdom of Alba
The Kingdom of Alba ( la, Scotia; sga, Alba) was the Kingdom of Scotland between the deaths of Donald II in 900 and of Alexander III in 1286. The latter's death led indirectly to an invasion of Scotland by Edward I of England in 1296 and the ...
, until it developed into the Kingdom of Scotland of the late Middle Ages following the absorption of Strathclyde
Strathclyde ( in Gaelic, meaning "strath (valley) of the River Clyde") was one of nine former local government regions of Scotland created in 1975 by the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1973 and abolished in 1996 by the Local Government et ...
and English-speaking Lothian
Lothian (; sco, Lowden, Loudan, -en, -o(u)n; gd, Lodainn ) is a region of the Scottish Lowlands, lying between the southern shore of the Firth of Forth and the Lammermuir Hills and the Moorfoot Hills. The principal settlement is the Sco ...
in the 12th century. It is cognate
In historical linguistics, cognates or lexical cognates are sets of words in different languages that have been inherited in direct descent from an etymology, etymological ancestor in a proto-language, common parent language. Because language c ...
with the Irish term ' (gen. ', dat. ') and the Manx term ', the two other Goidelic
The Goidelic or Gaelic languages ( ga, teangacha Gaelacha; gd, cànanan Goidhealach; gv, çhengaghyn Gaelgagh) form one of the two groups of Insular Celtic languages, the other being the Brittonic languages.
Goidelic languages historically ...
Insular Celtic languages
Insular Celtic languages are the group of Celtic languages of Brittany, Great Britain, Ireland, and the Isle of Man. All surviving Celtic languages are in the Insular group, including Breton, which is spoken on continental Europe in Brittany, ...
, as well as contemporary words used in Cornish (') and Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peop ...
('), both of which are Brythonic
Brittonic or Brythonic may refer to:
*Common Brittonic, or Brythonic, the Celtic language anciently spoken in Great Britain
*Brittonic languages, a branch of the Celtic languages descended from Common Brittonic
*Britons (Celtic people)
The Br ...
Insular Celtic languages. The third surviving Brythonic language, Breton
Breton most often refers to:
*anything associated with Brittany, and generally
** Breton people
** Breton language, a Southwestern Brittonic Celtic language of the Indo-European language family, spoken in Brittany
** Breton (horse), a breed
**Ga ...
, instead uses ', meaning 'country of the Scots'. In the past, these terms were names for Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
as a whole, related to the Brythonic name Albion
Albion is an alternative name for Great Britain. The oldest attestation of the toponym comes from the Greek language. It is sometimes used poetically and generally to refer to the island, but is less common than 'Britain' today. The name for Scot ...
.
Etymology
 The term first appears in classical texts as ' or ' (in
The term first appears in classical texts as ' or ' (in Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
's writings in Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
), and later as ' in Latin documents. Historically, the term refers to Britain as a whole and is ultimately based on the Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch ...
root for "white". It later came to be used by Gaelic speakers in the form of ' (dative
In grammar, the dative case (abbreviated , or sometimes when it is a core argument) is a grammatical case used in some languages to indicate the recipient or beneficiary of an action, as in "Maria Jacobo potum dedit", Latin for "Maria gave Jacob a ...
', genitive
In grammar, the genitive case (abbreviated ) is the grammatical case that marks a word, usually a noun, as modifying another word, also usually a noun—thus indicating an attributive relationship of one noun to the other noun. A genitive can al ...
', now obsolete) as the name given to the former kingdom of the Picts
The Picts were a group of peoples who lived in what is now northern and eastern Scotland (north of the Firth of Forth) during Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. Where they lived and what their culture was like can be inferred from ea ...
which when first used in this sense (around the time of king Causantín mac Áeda
Causantín mac Áeda ( Modern Gaelic: , anglicised Constantine II; born no later than 879; died 952) was an early King of Scotland, known then by the Gaelic name ''Alba''. The Kingdom of Alba, a name which first appears in Constantine's lifeti ...
(Constantine II, 943–952)) had expanded. The region Breadalbane (', the upper part of "Alba") takes its name from it as well.
As time passed, that kingdom incorporated other territories to its south. It became re-Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
ised in the High Medieval
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the period of European history that lasted from AD 1000 to 1300. The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and were followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended around AD 1500 ...
period as "Albania" (it is unclear whether it may ultimately share the same etymon
Etymology ()The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p. 633 "Etymology /ˌɛtɪˈmɒlədʒi/ the study of the class in words and the way their meanings have changed throughout time". is the study of the history of the form of words and ...
as the modern Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares ...
). This latter word was employed mainly by Celto-Latin writers, and most famously by Geoffrey of Monmouth
Geoffrey of Monmouth ( la, Galfridus Monemutensis, Galfridus Arturus, cy, Gruffudd ap Arthur, Sieffre o Fynwy; 1095 – 1155) was a British cleric from Monmouth, Wales and one of the major figures in the development of British historiograph ...
. It was this word which passed into Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English p ...
as Albany, although very rarely was this used for the Kingdom of Scotland
The Kingdom of Scotland (; , ) was a sovereign state in northwest Europe traditionally said to have been founded in 843. Its territories expanded and shrank, but it came to occupy the northern third of the island of Great Britain, sharing a la ...
, but rather for the notional Duchy of Albany. It is from the latter that Albany, the capital of the US state of New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
, and Albany, Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to th ...
, take their names.
It also appears in the anglicised literary form of ''Albyn'', as in Byron
George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron (22 January 1788 – 19 April 1824), known simply as Lord Byron, was an English romantic poet and Peerage of the United Kingdom, peer. He was one of the leading figures of the Romantic movement, and h ...
's ''Childe Harold
''Childe Harold's Pilgrimage'' is a long narrative poem in four parts written by Lord Byron. The poem was published between 1812 and 1818. Dedicated to " Ianthe", it describes the travels and reflections of a world-weary young man, who is disi ...
'':
:''And wild and high the 'Cameron's gathering' rose,''
::''The war-note of Lochiel, which Albyn's hills''
:''Have heard, and heard, too, have her Saxon foes''
Modern uses

BBC Alba
BBC Alba is a Scottish Gaelic-language free-to-air public broadcast television channel jointly owned by the BBC and MG Alba. The channel was launched on 19 September 2008 and is on-air for up to seven hours a day with BBC Radio nan Gàidheal s ...
, a television channel broadcasting mainly in Scottish Gaelic, was launched in September 2008 as a joint venture between the British Broadcasting Corporation #REDIRECT BBC
Here i going to introduce about the best teacher of my life b BALAJI sir. He is the precious gift that I got befor 2yrs . How has helped and thought all the concept and made my success in the 10th board exam. ...
(BBC) and Gaelic company MG Alba
MG Alba is the operating name of the Gaelic Media Service ( gd, Seirbheis nam Meadhanan Gàidhlig). The organisation's remit, under the Communications Act 2003, is to ensure that a wide and diverse range of high quality Gaelic programmes is ma ...
. A new version of Runrig
Runrig were a Scottish Celtic rock band formed on the Isle of Skye in 1973. From its inception, the band's line-up included songwriters Rory Macdonald and Calum Macdonald. The line-up during most of the 1980s and 1990s (the band's most succe ...
's song (originally on their album, ''The Cutter and the Clan
''The Cutter and the Clan'' is the fifth album by the Scottish Celtic rock band Runrig. It was the band's breakthrough album, taking them from cottage industry to the international stage. It was also the first Runrig album to feature keyboard pl ...
'') was featured on the channel's launch.
In the mid-1990s, the Celtic League
The Celtic League is a pan-Celtic organisation, founded in 1961, that aims to promote modern Celtic identity and culture in Ireland, Scotland, Wales, Brittany, Cornwall and the Isle of Man – referred to as the Celtic nations; it places part ...
started a campaign to have the word "Alba" on the Scottish football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly c ...
and rugby
Rugby may refer to:
Sport
* Rugby football in many forms:
** Rugby league: 13 players per side
*** Masters Rugby League
*** Mod league
*** Rugby league nines
*** Rugby league sevens
*** Touch (sport)
*** Wheelchair rugby league
** Rugby union: 1 ...
tops. Since 2005, the SFA have supported the use of Scottish Gaelic by adding on the back of the official team strip. However, as of 2008, the SRU SRU may refer to:
Organizations
* Salve Regina University, Newport, Rhode Island, US
* Scottish Rugby Union
* Shri Rawatpura Sarkar University, Chhattisgarh, India
* Slippery Rock University of Pennsylvania, US
* Sri Ramachandra University, Chennai ...
is still being lobbied to have added to the national rugby union strip.
In 2007, the then Scottish Executive re-branded itself as "The Scottish Government" and started to use a bilingual logo with the Gaelic name . However, the Gaelic version from the outset had always been . The Scottish Parliament
The Scottish Parliament ( gd, Pàrlamaid na h-Alba ; sco, Scots Pairlament) is the devolved, unicameral legislature of Scotland. Located in the Holyrood area of the capital city, Edinburgh, it is frequently referred to by the metonym Holyro ...
, likewise, uses the Gaelic name .
A new welcome sign on the historic A7 route into Scotland was erected in 2009, with the text .
Phrases such as may be used as a catch-phrase or rallying cry. It was used in the movie ''Braveheart
''Braveheart'' is a 1995 American historical drama film directed and produced by, and starring Mel Gibson. Gibson portrays Sir William Wallace, a late-13th century Scottish warrior who led the Scots in the First War of Scottish Independence ag ...
'' as William Wallace
Sir William Wallace ( gd, Uilleam Uallas, ; Norman French: ; 23 August 1305) was a Scottish knight who became one of the main leaders during the First War of Scottish Independence.
Along with Andrew Moray, Wallace defeated an English army a ...
encouraged the troops at the Battle of Stirling Bridge
The Battle of Stirling Bridge ( gd, Blàr Drochaid Shruighlea) was a battle of the First War of Scottish Independence. On 11 September 1297, the forces of Andrew Moray and William Wallace defeated the combined English forces of John de Warenne ...
.
In March 2021, former first minister of Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ...
and leader of the SNP Alex Salmond
Alexander Elliot Anderson Salmond (; born 31 December 1954) is a Scottish politician and economist who served as First Minister of Scotland from 2007 to 2014. A prominent figure on the Scottish nationalist movement, he has served as leader ...
launched the pro-independence Alba Party
The Alba Party is a Scottish nationalist and pro-independence political party in Scotland. The party was founded in February 2021, with Alex Salmond (a former first minister of Scotland) announced as party leader shortly thereafter. Salmond lau ...
, set to contest the 2021 Scottish Parliament election
The 2021 Scottish Parliament election took place on 6 May 2021, under the provisions of the Scotland Act 1998. All 129 Members of the Scottish Parliament were elected in the sixth election since the parliament was re-established in 1999. The ele ...
s.
See also
*Albanactus
Albanactus, according to Geoffrey of Monmouth, was the founding king of Albania or Albany. He is in effect Geoffrey's eponym for Scotland. His territory was that north of the River Humber. This myth was then taken up by Giraldus Cambrensis.
Lege ...
* Caledonia
Caledonia (; ) was the Latin name used by the Roman Empire to refer to the part of Great Britain () that lies north of the River Forth, which includes most of the land area of Scotland. Today, it is used as a romantic or poetic name for all ...
* Kingdom of Alba
The Kingdom of Alba ( la, Scotia; sga, Alba) was the Kingdom of Scotland between the deaths of Donald II in 900 and of Alexander III in 1286. The latter's death led indirectly to an invasion of Scotland by Edward I of England in 1296 and the ...
* Scotia
Scotia is a Latin placename derived from ''Scoti'', a Latin name for the Gaels, first attested in the late 3rd century.Duffy, Seán. ''Medieval Ireland: An Encyclopedia''. Routledge, 2005. p.698 The Romans referred to Ireland as "Scotia" around ...
References
{{British Isles Medieval Scotland Terminology of the British Isles Scottish words and phrases