Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq;
Yup'ik
The Yup'ik or Yupiaq (sg & pl) and Yupiit or Yupiat (pl), also Central Alaskan Yup'ik, Central Yup'ik, Alaskan Yup'ik ( own name ''Yup'ik'' sg ''Yupiik'' dual ''Yupiit'' pl; russian: Юпики центральной Аляски), are an I ...
: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a
state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
located in the
Western United States
The Western United States (also called the American West, the Far West, and the West) is the region comprising the westernmost states of the United States. As American settlement in the U.S. expanded westward, the meaning of the term ''the Wes ...
on the northwest extremity of
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
. A
semi-exclave
An enclave is a territory (or a small territory apart of a larger one) that is entirely surrounded by the territory of one other state or entity. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is sometimes used improperly to deno ...
of the U.S., it borders the
Canadian province
Within the geographical areas of Canada, the ten provinces and three territories are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North ...
of
British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ...
and the
Yukon
Yukon (; ; formerly called Yukon Territory and also referred to as the Yukon) is the smallest and westernmost of Canada's three territories. It also is the second-least populated province or territory in Canada, with a population of 43,964 as ...
territory to the east; it also shares a
maritime border
A maritime boundary is a conceptual division of the Earth's water surface areas using physiographic or geopolitical criteria. As such, it usually bounds areas of exclusive national rights over mineral and biological resources,VLIZ Maritime Bound ...
with the
Russian Federation
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
's
Chukotka Autonomous Okrug
Chukotka (russian: Чуко́тка), officially the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug,, ''Čukotkakèn avtonomnykèn okrug'', is the easternmost federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia. It is an autonomous okrug situated in the Russian ...
to the west, just across the
Bering Strait. To the north are the
Chukchi and
Beaufort Beaufort may refer to:
People and titles
* Beaufort (surname)
* House of Beaufort, English nobility
* Duke of Beaufort (England), a title in the peerage of England
* Duke of Beaufort (France), a title in the French nobility
Places Polar regions ...
Seas of the
Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, a ...
, while the
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
lies to the south and southwest.
Alaska is by far the
largest U.S. state by area, comprising more total area than the next three largest states (
Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
,
California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
, and
Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columbi ...
) combined. It represents the
seventh-largest subnational division in the world. It is the
third-least populous and the
most sparsely populated state, but by far the continent's most populous territory located mostly north of the
60th parallel, with a population of 736,081 as of 2020—more than quadruple the combined populations of
Northern Canada
Northern Canada, colloquially the North or the Territories, is the vast northernmost region of Canada variously defined by geography and politics. Politically, the term refers to the three Provinces_and_territories_of_Canada#Territories, territor ...
and
Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is t ...
.
Approximately half of Alaska's residents live within the
Anchorage metropolitan area
The Anchorage Metropolitan Statistical Area, as defined by the United States Census Bureau, is an area consisting of the Municipality of Anchorage and the Matanuska-Susitna Borough in the south central region of Alaska.
As of the 2010 census, ...
. The state capital of
Juneau
The City and Borough of Juneau, more commonly known simply as Juneau ( ; tli, Dzánti K'ihéeni ), is the capital city of the state of Alaska. Located in the Gastineau Channel and the Alaskan panhandle, it is a unified municipality and the se ...
is the second-
largest city in the United States by area, comprising more territory than the states of
Rhode Island
Rhode Island (, like ''road'') is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is the List of U.S. states by area, smallest U.S. state by area and the List of states and territories of the United States ...
and
Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacent Del ...
. The former capital of Alaska,
Sitka
russian: Ситка
, native_name_lang = tli
, settlement_type = Consolidated city-borough
, image_skyline = File:Sitka 84 Elev 135.jpg
, image_caption = Downtown Sitka in 1984
, image_size ...
, is the largest U.S. city by area.
What is now Alaska has been home to various indigenous peoples for thousands of years; it is widely believed that the region served as
the entry point for the initial settlement of North America by way of the
Bering land bridge
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 72 degrees north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip of ...
. The
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
was the first to actively
colonize
Colonization, or colonisation, constitutes large-scale population movements wherein migrants maintain strong links with their, or their ancestors', former country – by such links, gain advantage over other inhabitants of the territory. When ...
the area beginning in the 18th century, eventually establishing
Russian America
Russian America (russian: Русская Америка, Russkaya Amerika) was the name for the Russian Empire's colonial possessions in North America from 1799 to 1867. It consisted mostly of present-day Alaska in the United States, but a ...
, which spanned most of the current state. The expense and logistical difficulty of maintaining this distant possession prompted
its sale to the U.S. in 1867 for
US$
The United States dollar (symbol: $; code: USD; also abbreviated US$ or U.S. Dollar, to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies; referred to as the dollar, U.S. dollar, American dollar, or colloquially buck) is the official ...
7.2 million (equivalent to $ million in ), or approximately two cents per acre ($4.74/km
2). The area went through several administrative changes before becoming organized as a
territory
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, particularly belonging or connected to a country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually either the total area from which a state may extract power resources or a ...
on May 11, 1912. It was admitted as the 49th state of the U.S. on January 3, 1959.
While it has one of the smallest state economies in the country, Alaska's
per capita income is among the highest, owing to a diversified economy dominated by
fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment, but may also be caught from stocked bodies of water such as ponds, canals, park wetlands and reservoirs. Fishing techniques inclu ...
,
natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
, and
oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturated ...
, all of which it has in abundance.
U.S. Armed Forces
The United States Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States. The armed forces consists of six service branches: the Army, Marine Corps, Navy, Air Force, Space Force, and Coast Guard. The president of the United States is the ...
bases and
tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring (disambiguation), touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tour (disambiguation), tours. Th ...
are also a significant part of the
economy
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the ...
; more than half the state is federally owned public land, including a multitude of
national forests,
national parks
A national park is a natural park in use for conservation purposes, created and protected by national governments. Often it is a reserve of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that a sovereign state declares or owns. Although individual ...
, and
wildlife refuges
A nature reserve (also known as a wildlife refuge, wildlife sanctuary, biosphere reserve or bioreserve, natural or nature preserve, or nature conservation area) is a protected area of importance for flora, fauna, or features of geological or ...
.
The
indigenous population
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
of Alaska is proportionally the highest of any U.S. state, at over 15 percent. Close to two dozen native languages are spoken, and Alaskan Natives exercise considerable influence in local and state politics.
Etymology
The name "Alaska" ( rus, Аля́ска, r=Alyáska) was introduced in the
Russian colonial period when it was used to refer to the
Alaska Peninsula
The Alaska Peninsula (also called Aleut Peninsula or Aleutian Peninsula, ale, Alasxix̂; Sugpiaq: ''Aluuwiq'', ''Al'uwiq'') is a peninsula extending about to the southwest from the mainland of Alaska and ending in the Aleutian Islands. The ...
. It was derived from an
Aleut-language idiom
An idiom is a phrase or expression that typically presents a figurative, non-literal meaning attached to the phrase; but some phrases become figurative idioms while retaining the literal meaning of the phrase. Categorized as formulaic language, ...
, , meaning "the mainland" or, more literally, "the object towards which the action of the sea is directed".
[, at pp. 49 (Alaxsxi-x = mainland Alaska), 50 (''alagu-x'' = ''sea''), 508 (''-gi'' = suffix, ''object of its action'').] It is also known as , the "great land", an
Aleut
The Aleuts ( ; russian: Алеуты, Aleuty) are the indigenous people of the Aleutian Islands, which are located between the North Pacific Ocean and the Bering Sea. Both the Aleut people and the islands are politically divided between the U ...
word that was derived from the same root.
History
Pre-colonization

Numerous indigenous peoples occupied Alaska for thousands of years before the arrival of European peoples to the area. Linguistic and DNA studies done here have provided evidence for the settlement of North America by way of the
Bering land bridge
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 72 degrees north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip of ...
. At the
Upward Sun River site
The Upward Sun River site, or Xaasaa Na’, is a Late Pleistocene archaeological site associated with the Paleo-Arctic tradition, located in the Tanana River Valley, Alaska. Dated to around 11,500 BP, Upward Sun River is the site of the oldest ...
in the
Tanana Valley
The Tanana Valley is a lowland region in central Alaska in the United States, on the north side of the Alaska Range, where the Tanana River emerges from the mountains. Traditional inhabitants of the valley are Tanana Athabaskans of Alaskan Athaba ...
in Alaska, remains of a six-week-old infant were found. The baby's DNA showed that she belonged to a population that was genetically separate from other native groups present elsewhere in the
New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. 3 ...
at the end of the
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
. Ben Potter, the
University of Alaska Fairbanks
The University of Alaska Fairbanks (UAF or Alaska) is a public land-grant research university in College, Alaska, a suburb of Fairbanks. It is the flagship campus of the University of Alaska system. UAF was established in 1917 and opened for cla ...
archaeologist who unearthed the remains at the Upward Sun River site in 2013, named this new group
Ancient Beringians.
The
Tlingit people
The Tlingit ( or ; also spelled Tlinkit) are indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast of North America. Their language is the Tlingit language (natively , pronounced ), developed a society with a
matrilineal
Matrilineality is the tracing of kinship through the female line. It may also correlate with a social system in which each person is identified with their matriline – their mother's Lineage (anthropology), lineage – and which can in ...
kinship system of property inheritance and descent in what is today Southeast Alaska, along with parts of
British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ...
and the
Yukon
Yukon (; ; formerly called Yukon Territory and also referred to as the Yukon) is the smallest and westernmost of Canada's three territories. It also is the second-least populated province or territory in Canada, with a population of 43,964 as ...
. Also in Southeast were the
Haida
Haida may refer to:
Places
* Haida, an old name for Nový Bor
* Haida Gwaii, meaning "Islands of the People", formerly called the Queen Charlotte Islands
* Haida Islands, a different archipelago near Bella Bella, British Columbia
Ships
* , a 1 ...
, now well known for their unique arts. The
Tsimshian
The Tsimshian (; tsi, Ts’msyan or Tsm'syen) are an Indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast, Indigenous people of the Pacific Northwest Coast. Their communities are mostly in coastal British Columbia in Terrace, British Columbia, Terr ...
people came to Alaska from British Columbia in 1887, when President
Grover Cleveland
Stephen Grover Cleveland (March 18, 1837June 24, 1908) was an American lawyer and politician who served as the 22nd and 24th president of the United States from 1885 to 1889 and from 1893 to 1897. Cleveland is the only president in American ...
, and later the U.S. Congress, granted them permission to settle on
Annette Island and found the town of
Metlakatla. All three of these peoples, as well as other
indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast
The Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast are composed of many nations and tribal affiliations, each with distinctive cultural and political identities. They share certain beliefs, traditions and prac ...
, experienced
smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) c ...
outbreaks from the late 18th through the mid-19th century, with the most devastating
epidemics
An epidemic (from Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of patients among a given population within an area in a short period of time.
Epidemics of infectious d ...
occurring in the 1830s and 1860s, resulting in high fatalities and social disruption.
The Aleutian Islands are still home to the
Aleut people
The Aleuts ( ; russian: Алеуты, Aleuty) are the indigenous people of the Aleutian Islands, which are located between the North Pacific Ocean and the Bering Sea. Both the Aleut people and the islands are politically divided between the U ...
's seafaring society, although they were the first Native Alaskans to be exploited by the Russians. Western and Southwestern Alaska are home to the
Yup'ik
The Yup'ik or Yupiaq (sg & pl) and Yupiit or Yupiat (pl), also Central Alaskan Yup'ik, Central Yup'ik, Alaskan Yup'ik ( own name ''Yup'ik'' sg ''Yupiik'' dual ''Yupiit'' pl; russian: Юпики центральной Аляски), are an I ...
, while their cousins the
Alutiiq ~ Sugpiaq live in what is now Southcentral Alaska. The
Gwich'in people of the northern Interior region are
Athabaskan
Athabaskan (also spelled ''Athabascan'', ''Athapaskan'' or ''Athapascan'', and also known as Dene) is a large family of indigenous languages of North America, located in western North America in three areal language groups: Northern, Pacific C ...
and primarily known today for their dependence on the caribou within the much-contested
Arctic National Wildlife Refuge
The Arctic National Wildlife Refuge (ANWR or Arctic Refuge) is a national wildlife refuge in northeastern Alaska, United States on traditional Gwich'in lands. It consists of in the Alaska North Slope region. It is the largest national wildlife ...
. The North Slope and
Little Diomede Island
Little Diomede Island or “Yesterday Isle” ( ik, Iŋaliq, formerly known as Krusenstern Island, are occupied by the widespread
Inupiat people.
Colonization


Some researchers believe the first Russian settlement in Alaska was established in the 17th century. According to this hypothesis, in 1648 several
koches of
Semyon Dezhnyov
Semyon Ivanovich Dezhnyov ( rus, Семён Ива́нович Дежнёв, p=sʲɪˈmʲɵn ɪˈvanəvʲɪtɕ dʲɪˈʐnʲɵf; sometimes spelled Dezhnyov; c. 1605 – 1673) was a Russian explorer of Siberia and the first European to sail through t ...
's expedition came ashore in Alaska by storm and founded this settlement. This hypothesis is based on the testimony of
Chukchi geographer Nikolai Daurkin, who had visited Alaska in 1764–1765 and who had reported on a village on the Kheuveren River, populated by "bearded men" who "pray to the
icons
An icon () is a religious work of art, most commonly a painting, in the cultures of the Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, and Catholic churches. They are not simply artworks; "an icon is a sacred image used in religious devotion". The most ...
". Some modern researchers associate Kheuveren with
Koyuk River
The Koyuk River (also spelled, Kuyuk) is a river on the Seward Peninsula of western Alaska, in the United States. The river originates in the interior of the peninsula, at the Lost Jim Lava Flow of the Bering Land Bridge National Preserve, wher ...
.
The first European vessel to reach Alaska is generally held to be the ''St. Gabriel'' under the authority of the surveyor
M. S. Gvozdev and assistant navigator
I. Fyodorov on August 21, 1732, during an expedition of Siberian Cossack A. F. Shestakov and Russian explorer
Dmitry Pavlutsky Dmitry Ivanovich Pavlutsky (russian: Дмитрий Иванович Павлуцкий; died 21 March 1747) was a Russian polar explorer and leader of military expeditions in Chukotka, best known for his campaigns of genocide against the indigenou ...
(1729–1735). Another European contact with Alaska occurred in 1741, when
Vitus Bering
Vitus Jonassen Bering (baptised 5 August 1681 – 19 December 1741),All dates are here given in the Julian calendar, which was in use throughout Russia at the time. also known as Ivan Ivanovich Bering, was a Danish cartographer and explorer in ...
led an
expedition for the Russian Navy aboard the ''St. Peter''. After his crew returned to Russia with
sea otter
The sea otter (''Enhydra lutris'') is a marine mammal native to the coasts of the northern and eastern North Pacific Ocean. Adult sea otters typically weigh between , making them the heaviest members of the weasel family, but among the small ...
pelts judged to be the finest fur in the world, small associations of
fur trade
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals have been the mos ...
rs began to sail from the shores of Siberia toward the Aleutian Islands. The first permanent European settlement was founded in 1784.
Between 1774 and 1800,
Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
sent several
expeditions to Alaska to assert its claim over the Pacific Northwest. In 1789, a Spanish settlement and
fort
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
were built in
Nootka Sound
, image = Morning on Nootka Sound.jpg
, image_size = 250px
, alt =
, caption = Clouds over Nootka Sound
, image_bathymetry =
, alt_bathymetry =
, caption_bathymetry = Map of Nootka So ...
. These expeditions gave names to places such as
Valdez,
Bucareli Sound, and
Cordova. Later, the
Russian-American Company
The Russian-American Company Under the High Patronage of His Imperial Majesty (russian: Под высочайшим Его Императорского Величества покровительством Российская-Американс� ...
carried out an expanded colonization program during the early-to-mid-19th century.
Sitka
russian: Ситка
, native_name_lang = tli
, settlement_type = Consolidated city-borough
, image_skyline = File:Sitka 84 Elev 135.jpg
, image_caption = Downtown Sitka in 1984
, image_size ...
, renamed
New Archangel
russian: Ситка
, native_name_lang = tli
, settlement_type = Consolidated city-borough
, image_skyline = File:Sitka 84 Elev 135.jpg
, image_caption = Downtown Sitka in 1984
, image_size ...
from 1804 to 1867, on
Baranof Island
Baranof Island is an island in the northern Alexander Archipelago in the Alaska Panhandle, in Alaska. The name Baranof was given in 1805 by Imperial Russian Navy captain Yuri Lisyansky, U. F. Lisianski to honor Alexander Andreyevich Baranov. It ...
in the
Alexander Archipelago
The Alexander Archipelago (russian: Архипелаг Александра) is a long archipelago (group of islands) in North America lying off the southeastern coast of Alaska. It contains about 1,100 islands, the tops of submerged coastal m ...
in what is now
Southeast Alaska
Southeast Alaska, colloquially referred to as the Alaska(n) Panhandle, is the southeastern portion of the U.S. state of Alaska, bordered to the east and north by the northern half of the Canadian province of British Columbia (and a small part ...
, became the capital of
Russian America
Russian America (russian: Русская Америка, Russkaya Amerika) was the name for the Russian Empire's colonial possessions in North America from 1799 to 1867. It consisted mostly of present-day Alaska in the United States, but a ...
. It remained the capital after the colony was transferred to the United States. The Russians never fully colonized Alaska, and the colony was never very profitable. Evidence of Russian settlement in names and churches survive throughout southeastern Alaska.
William H. Seward
William Henry Seward (May 16, 1801 – October 10, 1872) was an American politician who served as United States Secretary of State from 1861 to 1869, and earlier served as governor of New York and as a United States Senator. A determined oppon ...
, the 24th
United States Secretary of State
The United States secretary of state is a member of the executive branch of the federal government of the United States and the head of the U.S. Department of State. The office holder is one of the highest ranking members of the president's Ca ...
, negotiated the
Alaska Purchase
The Alaska Purchase (russian: Продажа Аляски, Prodazha Alyaski, Sale of Alaska) was the United States' acquisition of Alaska from the Russian Empire. Alaska was formally transferred to the United States on October 18, 1867, through a ...
(also known as Seward's Folly) with the Russians in 1867 for $7.2 million. Russia's contemporary ruler
Tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East Slavs, East and South Slavs, South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''Caesar (title), caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" i ...
Alexander II, the
Emperor of the Russian Empire
The emperor or empress of all the Russias or All Russia, ''Imperator Vserossiyskiy'', ''Imperatritsa Vserossiyskaya'' (often titled Tsar or Tsarina/Tsaritsa) was the monarch of the Russian Empire.
The title originated in connection with Russia' ...
,
King of Poland
Poland was ruled at various times either by dukes and princes (10th to 14th centuries) or by kings (11th to 18th centuries). During the latter period, a tradition of free election of monarchs made it a uniquely electable position in Europe (16t ...
and
Grand Duke of Finland
Grand Duke of Finland, or, more accurately, the Grand Prince of Finland ( fi, Suomen suuriruhtinas, sv, Storfurste av Finland, rus, Великий князь Финляндский, r=Velikiy knyaz' Finlyandskiy, p=vʲɪˈlʲikɪj knʲæsʲ fʲ ...
, also planned the sale; the purchase was made on March 30, 1867. Six months later the commissioners arrived in Sitka and the formal transfer was arranged; the formal flag-raising took place at Fort Sitka on October 18, 1867. In the ceremony 250 uniformed U.S. soldiers marched to the governor's house at "Castle Hill", where the Russian troops lowered the Russian flag and the U.S. flag was raised. This event is celebrated as
Alaska Day
Alaska Day (russian: День Аляски) is a legal holiday in the U.S. state of Alaska, observed on October 18. It is the anniversary of the formal transfer of territories in present-day Alaska from the Russian Empire to the United States, ...
, a legal holiday on October 18.
Alaska was loosely governed by the military initially, and was administered as a
district
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions o ...
starting in 1884, with a governor appointed by the United States president. A federal
district court was headquartered in Sitka. For most of Alaska's first decade under the United States flag, Sitka was the only community inhabited by American settlers. They organized a "provisional city government", which was Alaska's first municipal government, but not in a legal sense. Legislation allowing Alaskan communities to legally
incorporate as cities did not come about until 1900, and
home rule
Home rule is government of a colony, dependent country, or region by its own citizens. It is thus the power of a part (administrative division) of a state or an external dependent country to exercise such of the state's powers of governance wit ...
for cities was extremely limited or unavailable until statehood took effect in 1959.
Alaska as an incorporated U.S. territory
Starting in the 1890s and stretching in some places to the early 1910s, gold rushes in Alaska and the nearby
Yukon Territory
Yukon (; ; formerly called Yukon Territory and also referred to as the Yukon) is the smallest and westernmost of Canada's three territories. It also is the second-least populated province or territory in Canada, with a population of 43,964 as ...
brought thousands of miners and settlers to Alaska. Alaska was officially incorporated as an organized territory in 1912. Alaska's capital, which had been in
Sitka
russian: Ситка
, native_name_lang = tli
, settlement_type = Consolidated city-borough
, image_skyline = File:Sitka 84 Elev 135.jpg
, image_caption = Downtown Sitka in 1984
, image_size ...
until 1906, was moved north to
Juneau
The City and Borough of Juneau, more commonly known simply as Juneau ( ; tli, Dzánti K'ihéeni ), is the capital city of the state of Alaska. Located in the Gastineau Channel and the Alaskan panhandle, it is a unified municipality and the se ...
. Construction of the
Alaska Governor's Mansion
The Alaska Governor's Mansion, located at 716 Calhoun Avenue in Juneau, Alaska, is the official residence of the governor of Alaska, the first spouse of Alaska, and their families. It was designed by James Knox Taylor. The Governor's Mansion w ...
began that same year. European immigrants from Norway and Sweden also settled in southeast Alaska, where they entered the fishing and logging industries.

During
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, the
Aleutian Islands Campaign focused on
Attu,
Agattu
Agattu ( ale, Angatux̂; russian: Агатту) is an island in Alaska, part of the Near Islands in the western end of the Aleutian Islands. With a land area of Agattu is one of the largest uninhabited islands in the Aleutians. It is the sec ...
and
Kiska
Kiska ( ale, Qisxa, russian: Кыска) is one of the Rat Islands, a group of the Aleutian Islands of Alaska. It is about long and varies in width from . It is part of Aleutian Islands Wilderness and as such, special permission is required ...
, all of which were occupied by the
Empire of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent fo ...
. During the Japanese occupation, a white American civilian and two
United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
personnel were killed at Attu and Kiska respectively, and nearly a total of 50 Aleut civilians and eight sailors were interned in Japan. About half of the Aleuts died during the period of internment.
Unalaska
Unalaska ( ale, Iluulux̂; russian: Уналашка) is the chief center of population in the Aleutian Islands. The city is in the Aleutians West Census Area, a regional component of the Unorganized Borough in the U.S. state of Alaska. Unalaska ...
/
Dutch Harbor
Dutch Harbor is a harbor on Amaknak Island in Unalaska, Alaska. It was the location of the Battle of Dutch Harbor in June 1942, and was one of the few sites in the United States to be subjected to aerial bombardment by a foreign power during Worl ...
and
Adak became significant bases for the
United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cla ...
,
United States Army Air Forces
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II ...
and
United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
. The United States
Lend-Lease
Lend-Lease, formally the Lend-Lease Act and introduced as An Act to Promote the Defense of the United States (), was a policy under which the United States supplied the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union and other Allied nations with food, oil, ...
program involved flying American warplanes through Canada to Fairbanks and then Nome; Soviet pilots took possession of these aircraft, ferrying them to fight the German invasion of the
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
. The construction of military bases contributed to the population growth of some Alaskan cities.
Statehood

Statehood for Alaska was an important cause of
James Wickersham
James Wickersham (August 24, 1857 – October 24, 1939) was a district judge for Alaska, appointed by U.S. President William McKinley to the Third Judicial District in 1900. He resigned his post in 1908 and was subsequently elected as Alaska ...
early in his tenure as a congressional delegate. Decades later, the statehood movement gained its first real momentum following a territorial referendum in 1946. The Alaska Statehood Committee and Alaska's Constitutional Convention would soon follow. Statehood supporters also found themselves fighting major battles against political foes, mostly in the U.S. Congress but also within Alaska. Statehood was approved by the U.S. Congress on July 7, 1958; Alaska was officially proclaimed a state on January 3, 1959.
Good Friday earthquake
On March 27, 1964, the massive
Good Friday earthquake
The 1964 Alaskan earthquake, also known as the Great Alaskan earthquake and Good Friday earthquake, occurred at 5:36 PM AKST on Good Friday, March 27. killed 133 people and destroyed several villages and portions of large coastal communities, mainly by the resultant
tsunamis
A tsunami ( ; from ja, 津波, lit=harbour wave, ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater expl ...
and landslides. It was the
second-most-powerful earthquake in recorded history, with a
moment magnitude
The moment magnitude scale (MMS; denoted explicitly with or Mw, and generally implied with use of a single M for magnitude) is a measure of an earthquake's magnitude ("size" or strength) based on its seismic moment. It was defined in a 1979 pape ...
of 9.2 (more than a thousand times as powerful as the
1989 San Francisco earthquake
The 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake occurred on California's Central Coast on October 17 at local time. The shock was centered in The Forest of Nisene Marks State Park in Santa Cruz County, California, Santa Cruz County, approximately northeast of ...
). The time of day (5:36 pm), time of year (spring) and location of the
epicenter
The epicenter, epicentre () or epicentrum in seismology is the point on the Earth's surface directly above a hypocenter or focus, the point where an earthquake or an underground explosion originates.
Surface damage
Before the instrumental pe ...
were all cited as factors in potentially sparing thousands of lives, particularly in Anchorage.
Lasting four minutes and thirty-eight seconds, the magnitude 9.2
megathrust earthquake
Megathrust earthquakes occur at convergent plate boundaries, where one tectonic plate is forced underneath another. The earthquakes are caused by slip along the thrust fault that forms the contact between the two plates. These interplate earthqua ...
remains the most powerful earthquake recorded in
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
n history, and the second
most powerful earthquake recorded in world history. of fault ruptured at once and moved up to , releasing about 500 years of stress buildup.
Soil liquefaction
Soil liquefaction occurs when a cohesionless saturated or partially saturated soil substantially loses strength and stiffness in response to an applied stress such as shaking during an earthquake or other sudden change in stress condition, in ...
, fissures, landslides, and other ground failures caused major structural damage in several communities and much damage to property.
Anchorage
Anchorage () is the largest city in the U.S. state of Alaska by population. With a population of 291,247 in 2020, it contains nearly 40% of the state's population. The Anchorage metropolitan area, which includes Anchorage and the neighboring Ma ...
sustained great destruction or damage to many inadequately Earthquake engineering, earthquake-engineered houses, buildings, and infrastructure (paved streets, sidewalks, water and sewer mains, electrical systems, and other man-made equipment), particularly in the several landslide zones along Knik Arm. southwest, some areas near Kodiak Island, Kodiak were permanently raised by . Southeast of Anchorage, areas around the head of Turnagain Arm near Girdwood, Anchorage, Girdwood and Portage (Anchorage), Portage dropped as much as , requiring reconstruction and fill to raise the Seward Highway above the new high tide mark.
In Prince William Sound, Port of Valdez, Port Valdez suffered a massive underwater landslide, resulting in the deaths of 32 people between the collapse of the
Valdez city harbor and docks, and inside the ship that was docked there at the time. Nearby, a tsunami destroyed the village of Chenega, Alaska, Chenega, killing 23 of the 68 people who lived there; survivors out-ran the wave, climbing to high ground. Post-quake tsunamis severely affected Whittier, Alaska, Whittier, Seward, Alaska, Seward, Kodiak, Alaska, Kodiak, and other Alaskan communities, as well as people and property in
British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ...
, Washington (state), Washington, Oregon, and
California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
. Tsunamis also caused damage in Hawaii and Japan. Evidence of motion directly related to the earthquake was also reported from Florida and
Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
.
Alaska oil boom
The 1968 discovery of oil at Prudhoe Bay and the 1977 completion of the Trans-Alaska Pipeline System led to an oil boom. Royalty revenues from oil have funded large state budgets from 1980 onward.
In 1989, the ''Exxon Valdez'' hit a reef in the Prince William Sound, Exxon Valdez oil spill, spilling more than of crude oil over of coastline. Today, the battle between philosophies of development and conservation is seen in the contentious debate over oil drilling in the
Arctic National Wildlife Refuge
The Arctic National Wildlife Refuge (ANWR or Arctic Refuge) is a national wildlife refuge in northeastern Alaska, United States on traditional Gwich'in lands. It consists of in the Alaska North Slope region. It is the largest national wildlife ...
and the proposed Pebble Mine.
Geography
Located at the northwest corner of
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
, Alaska is the northernmost and westernmost state in the United States, but also has the most easterly longitude in the United States because the Aleutian Islands extend into the Eastern Hemisphere. Alaska is the only non-Contiguous United States, contiguous U.S. state on continental North America; about of
British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ...
(Canada) separates Alaska from Washington (state), Washington. It is technically part of the Continental United States, continental U.S., but is sometimes not included in colloquial use; Alaska is not part of the Contiguous United States, contiguous U.S., often called Outside (Alaska), "the Lower 48". The capital city, Juneau, is situated on the mainland of the North American continent but is not connected by road to the rest of the North American highway system.
The state is bordered by Canada's
Yukon
Yukon (; ; formerly called Yukon Territory and also referred to as the Yukon) is the smallest and westernmost of Canada's three territories. It also is the second-least populated province or territory in Canada, with a population of 43,964 as ...
and
British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ...
to the east (making it the only state to only border a Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian territory); the Gulf of Alaska and the Pacific Ocean to the south and southwest; the Bering Sea,
Bering Strait, and Chukchi Sea to the west; and the Arctic Ocean to the north. Alaska's territorial waters touch Russia's territorial waters in the Bering Strait, as the Russian Big Diomede Island and Alaskan
Little Diomede Island
Little Diomede Island or “Yesterday Isle” ( ik, Iŋaliq, formerly known as Krusenstern Island, are only apart. Alaska has a longer coastline than all the other U.S. states combined.

At in total area, Alaska is by far the largest state in the United States. Alaska is more than twice the size of the second-largest U.S. state (Texas), and it is larger than the next three largest states (Texas, California, and Montana) combined. Alaska is the seventh List of the largest country subdivisions by area, largest subnational division in the world, and if it was an independent nation would be the 16th largest country in the world, as it is larger than Iran.
With its myriad islands, Alaska has nearly of tidal shoreline. The Aleutian Islands chain extends west from the southern tip of the
Alaska Peninsula
The Alaska Peninsula (also called Aleut Peninsula or Aleutian Peninsula, ale, Alasxix̂; Sugpiaq: ''Aluuwiq'', ''Al'uwiq'') is a peninsula extending about to the southwest from the mainland of Alaska and ending in the Aleutian Islands. The ...
. Many active volcanoes are found in the Aleutians and in coastal regions. Unimak Island, for example, is home to Mount Shishaldin, which is an occasionally smoldering volcano that rises to above the North Pacific. The chain of volcanoes extends to Mount Spurr, west of Anchorage on the mainland. Geologists have identified Alaska as part of Wrangellia, a large region consisting of multiple states and Canadian provinces in the Pacific Northwest, which is actively undergoing plate tectonics, continent building.
One of the world's largest tides occurs in Turnagain Arm, just south of Anchorage, where tidal differences can be more than .
Alaska has more than three million lakes. Marshlands and wetland permafrost cover (mostly in northern, western and southwest flatlands). Glacier ice covers about of Alaska. The Bering Glacier is the largest glacier in North America, covering alone.
Regions
There are no officially defined borders demarcating the various regions of Alaska, but there are six widely accepted regions:
South Central
The most populous region of Alaska, containing Anchorage, the Matanuska-Susitna Valley and the Kenai Peninsula. Rural, mostly unpopulated areas south of the Alaska Range and west of the Wrangell Mountains also fall within the definition of South Central, as do the Prince William Sound area and the communities of
Cordova and
Valdez.
Southeast
Also referred to as the Panhandle or Inside Passage, this is the region of Alaska closest to the contiguous states. As such, this was where most of the initial non-indigenous settlement occurred in the years following the
Alaska Purchase
The Alaska Purchase (russian: Продажа Аляски, Prodazha Alyaski, Sale of Alaska) was the United States' acquisition of Alaska from the Russian Empire. Alaska was formally transferred to the United States on October 18, 1867, through a ...
. The region is dominated by the
Alexander Archipelago
The Alexander Archipelago (russian: Архипелаг Александра) is a long archipelago (group of islands) in North America lying off the southeastern coast of Alaska. It contains about 1,100 islands, the tops of submerged coastal m ...
as well as the Tongass National Forest, the largest national forest in the United States. It contains the state capital Juneau, the former capital
Sitka
russian: Ситка
, native_name_lang = tli
, settlement_type = Consolidated city-borough
, image_skyline = File:Sitka 84 Elev 135.jpg
, image_caption = Downtown Sitka in 1984
, image_size ...
, and Ketchikan, at one time Alaska's largest city. The Alaska Marine Highway provides a vital surface transportation link throughout the area and country, as only three communities (Haines, Alaska, Haines, Hyder, Alaska, Hyder and Skagway, Alaska, Skagway) enjoy direct connections to the contiguous North American road system.
Interior

The Interior is the largest region of Alaska; much of it is uninhabited wilderness. Fairbanks, Alaska, Fairbanks is the only large city in the region. Denali National Park and Preserve is located here. Denali, formerly Mount McKinley, is the highest mountain in North America, and is also located here.
Southwest
Southwest Alaska is a sparsely inhabited region stretching some inland from the Bering Sea. Most of the population lives along the coast. Kodiak Island is also located in Southwest. The massive Yukon–Kuskokwim Delta, one of the largest river deltas in the world, is here. Portions of the
Alaska Peninsula
The Alaska Peninsula (also called Aleut Peninsula or Aleutian Peninsula, ale, Alasxix̂; Sugpiaq: ''Aluuwiq'', ''Al'uwiq'') is a peninsula extending about to the southwest from the mainland of Alaska and ending in the Aleutian Islands. The ...
are considered part of Southwest, with the remaining portions included with the Aleutian Islands (see below).
North Slope
The North Slope is mostly tundra peppered with small villages. The area is known for its massive reserves of crude oil and contains both the National Petroleum Reserve–Alaska and the Prudhoe Bay Oil Field. The city of Utqiaġvik, Alaska, Utqiaġvik, formerly known as Barrow, is the northernmost city in the United States and is located here. The Northwest Arctic Borough, Alaska, Northwest Arctic area, anchored by Kotzebue, Alaska, Kotzebue and also containing the Kobuk River valley, is often regarded as being part of this region. However, the respective Inupiat people, Inupiat of the North Slope and of the Northwest Arctic seldom consider themselves to be one people.
Aleutian Islands

More than 300 small volcanic islands make up this chain, which stretches more than into the Pacific Ocean. Some of these islands fall in the Eastern Hemisphere, but the International Date Line was drawn west of 180th meridian, 180° to keep the whole state, and thus the entire North American continent, within the same legal day. Two of the islands,
Attu and Kiska, were occupied by Japanese forces during World War II.
Land ownership
According to an October 1998 report by the United States Bureau of Land Management, approximately 65% of Alaska is owned and managed by the Federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government as public lands, including a multitude of
national forests, national parks, and national wildlife refuges. Of these, the Bureau of Land Management manages , or 23.8% of the state. The
Arctic National Wildlife Refuge
The Arctic National Wildlife Refuge (ANWR or Arctic Refuge) is a national wildlife refuge in northeastern Alaska, United States on traditional Gwich'in lands. It consists of in the Alaska North Slope region. It is the largest national wildlife ...
is managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service. It is the world's largest wildlife refuge, comprising .
Of the remaining land area, the state of Alaska owns , its entitlement under the Alaska Statehood Act. A portion of that acreage is occasionally ceded to the organized boroughs presented above, under the statutory provisions pertaining to newly formed boroughs. Smaller portions are set aside for rural subdivisions and other homesteading-related opportunities. These are not very popular due to the often remote and roadless locations. The University of Alaska, as a land grant university, also owns substantial acreage which it manages independently.
Another are owned by 12 regional, and scores of local, Native corporations created under the Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act (ANCSA) of 1971. Alaska Native Regional Corporation, Regional Native corporation Doyon, Limited often promotes itself as the largest private landowner in Alaska in advertisements and other communications. Provisions of ANCSA allowing the corporations' land holdings to be sold on the open market starting in 1991 were repealed before they could take effect. Effectively, the corporations hold title (including subsurface title in many cases, a privilege denied to individual Alaskans) but cannot sell the land. Alaska Native Allotment Act, Individual Native allotments can be and are sold on the open market, however.
Various private interests own the remaining land, totaling about one percent of the state. Alaska is, by a large margin, the state with the smallest percentage of private land ownership when Native corporation holdings are excluded.
Alaska Heritage Resources Survey
The Alaska Heritage Resources Survey (AHRS) is a restricted inventory of all reported historic site, historic and prehistoric sites within the U.S. state of Alaska; it is maintained by the Office of History and Archaeology. The survey's inventory of cultural resources includes objects, structures, buildings, sites, districts, and travel ways, with a general provision that they are more than fifty years old. , more than 35,000 sites have been reported.
Cities, towns and boroughs
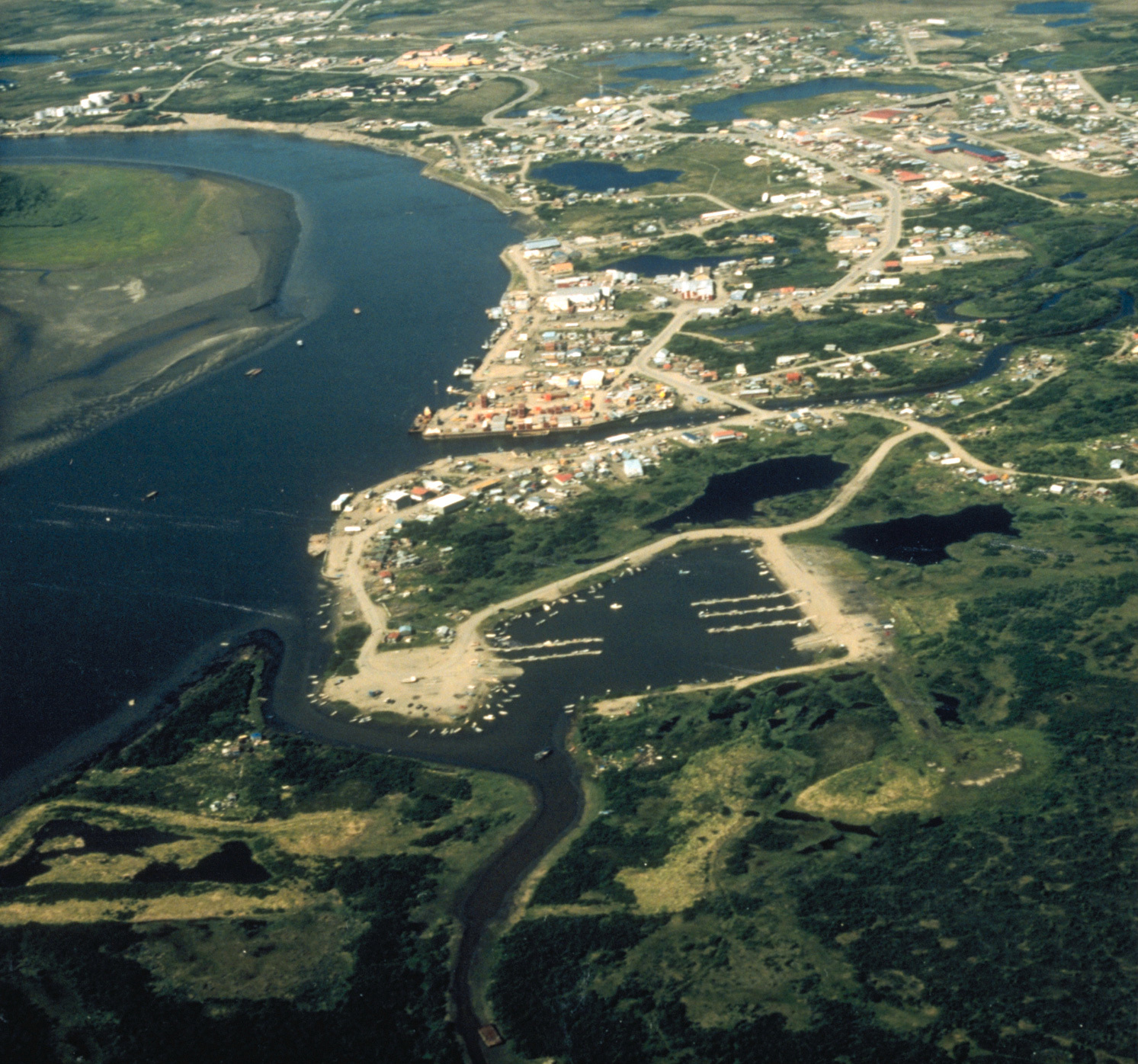
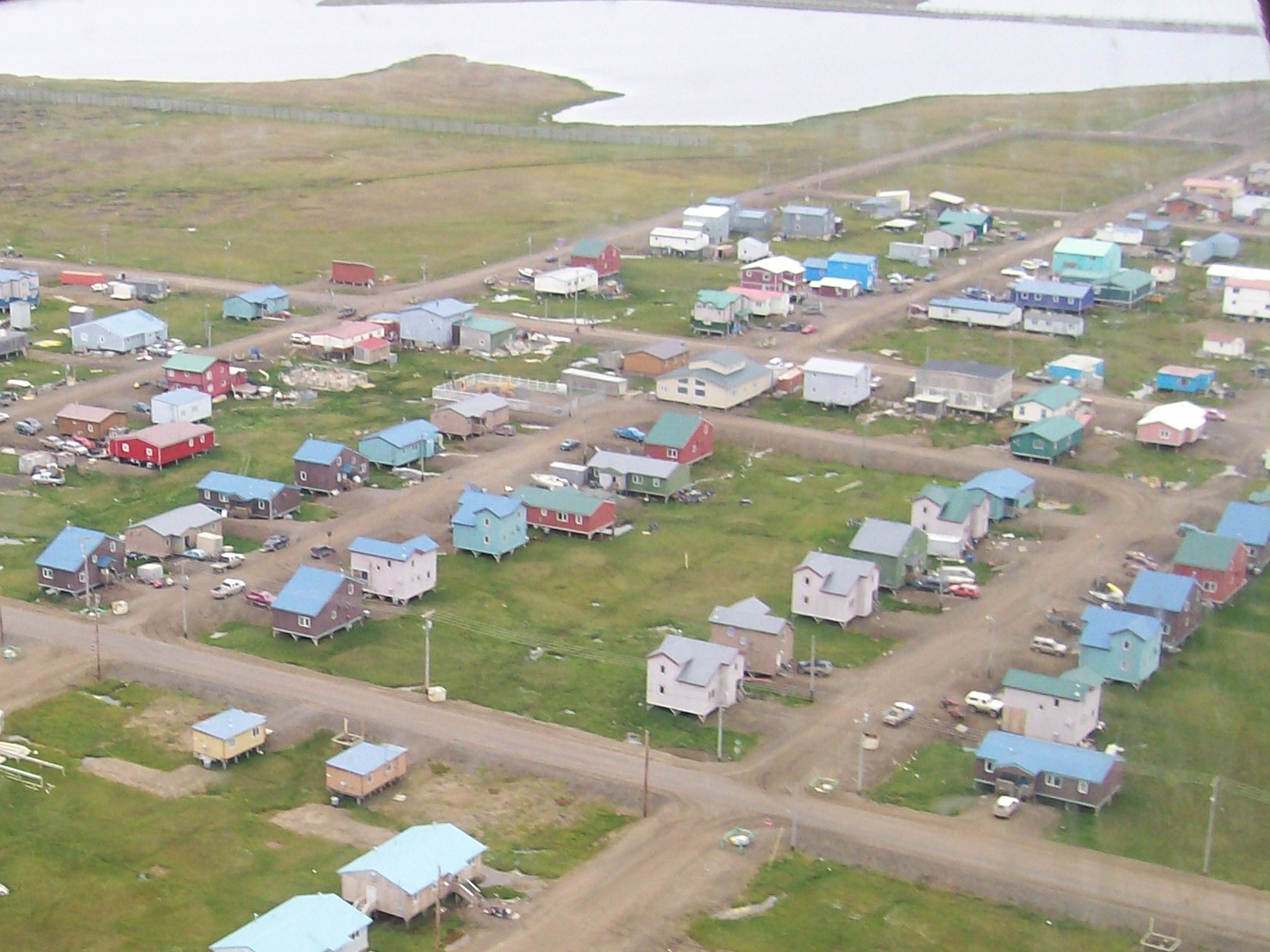







Alaska is not divided into County (United States), counties, as most of the other U.S. states, but it is divided into ''List of boroughs and census areas in Alaska, boroughs''. Delegates to the Alaska Constitutional Convention wanted to avoid the pitfalls of the traditional county system and adopted their own unique model. Many of the more densely populated parts of the state are part of Alaska's 16 boroughs, which function somewhat similarly to counties in other states. However, unlike county-equivalents in the other 49 states, the boroughs do not cover the entire land area of the state. The area not part of any borough is referred to as the Unorganized Borough, Alaska, Unorganized Borough.
The Unorganized Borough has no government of its own, but the U.S. Census Bureau in cooperation with the state divided the Unorganized Borough into 11 census areas solely for the purposes of statistical analysis and presentation. A ''recording district'' is a mechanism for management of the public record in Alaska. The state is divided into 34 recording districts which are centrally administered under a state recorder of deeds, recorder. All recording districts use the same acceptance criteria, fee schedule, etc., for accepting documents into the public record.
Whereas many U.S. states use a three-tiered system of decentralization—state/county/township—most of Alaska uses only two tiers—state/borough. Owing to the low population density, most of the land is located in the Unorganized Borough. As the name implies, it has no intermediate borough government but is administered directly by the state government. In 2000, 57.71% of Alaska's area has this status, with 13.05% of the population.
Anchorage merged the city government with the Greater Anchorage Area Borough in 1975 to form the Municipality of Anchorage, containing the city proper and the communities of Eagle River, Chugiak, Peters Creek, Girdwood, Bird, and Indian. Fairbanks has a separate borough (the Fairbanks North Star Borough) and municipality (the City of Fairbanks).
The state's most populous city is
Anchorage
Anchorage () is the largest city in the U.S. state of Alaska by population. With a population of 291,247 in 2020, it contains nearly 40% of the state's population. The Anchorage metropolitan area, which includes Anchorage and the neighboring Ma ...
, home to 291,247 people in 2020.
The richest Alaska locations by per capita income, location in Alaska by per capita income is Denali Borough, Alaska, Denali ($42,245). Yakutat City, Sitka, Juneau, and Anchorage are the four List of U.S. cities by area, largest cities in the U.S. by area.
Cities and census-designated places (by population)
As reflected in the 2020 United States census, Alaska has a total of 355 incorporated cities and census-designated places (CDPs).
[
] The tally of cities includes four unified municipalities, essentially the equivalent of a consolidated city–county. The majority of these communities are located in the rural expanse of Alaska known as "The Bush (Alaska), The Bush" and are unconnected to that contiguous North American road network. The table at the bottom of this section lists about the 100 largest cities and census-designated places in Alaska, in population order.
Of Alaska's 2020 U.S. census population figure of 733,391, 16,655 people, or 2.27% of the population, did not live in an incorporated city or census-designated place.
Approximately three-quarters of that figure were people who live in urban and suburban neighborhoods on the outskirts of the city limits of Ketchikan, Kodiak, Palmer and Wasilla. CDPs have not been established for these areas by the United States Census Bureau, except that seven CDPs were established for the Ketchikan-area neighborhoods in the 1980 United States Census, 1980 Census (Clover Pass, Herring Cove, Ketchikan East, Mountain Point, North Tongass Highway, Pennock Island and Saxman, Alaska, Saxman East), but have not been used since. The remaining population was scattered throughout Alaska, both within organized boroughs and in the Unorganized Borough, in largely remote areas.
Climate

The climate in south and southeastern Alaska is a mid-latitude oceanic climate (Köppen climate classification: ''Cfb''), and a subarctic oceanic climate (Köppen ''Cfc'') in the northern parts. On an annual basis, the southeast is both the wettest and warmest part of Alaska with milder temperatures in the winter and high precipitation throughout the year. Juneau averages over of precipitation a year, and Ketchikan, Alaska, Ketchikan averages over . This is also the only region in Alaska in which the average daytime high temperature is above freezing during the winter months.

The climate of
Anchorage
Anchorage () is the largest city in the U.S. state of Alaska by population. With a population of 291,247 in 2020, it contains nearly 40% of the state's population. The Anchorage metropolitan area, which includes Anchorage and the neighboring Ma ...
and south central Alaska is mild by Alaskan standards due to the region's proximity to the seacoast. While the area gets less rain than southeast Alaska, it gets more snow, and days tend to be clearer. On average,
Anchorage
Anchorage () is the largest city in the U.S. state of Alaska by population. With a population of 291,247 in 2020, it contains nearly 40% of the state's population. The Anchorage metropolitan area, which includes Anchorage and the neighboring Ma ...
receives of precipitation a year, with around of snow, although there are areas in the south central which receive far more snow. It is a subarctic climate (Köppen climate classification#GROUP D: Continental/microthermal climate, Köppen: ''Dfc'') due to its brief, cool summers.
The climate of Southwest Alaska, western Alaska is determined in large part by the Bering Sea and the Gulf of Alaska. It is a subarctic oceanic climate in the southwest and a continental subarctic climate farther north. The temperature is somewhat moderate considering how far north the area is. This region has a tremendous amount of variety in precipitation. An area stretching from the northern side of the Seward Peninsula to the Kobuk River valley (i.e., the region around Kotzebue Sound) is technically a desert, with portions receiving less than of precipitation annually. On the other extreme, some locations between Dillingham, Alaska, Dillingham and Bethel, Alaska, Bethel average around of precipitation.
The climate of the interior of Alaska is subarctic. Some of the highest and lowest temperatures in Alaska occur around the area near Fairbanks, Alaska, Fairbanks. The summers may have temperatures reaching into the 90s °F (the low-to-mid 30s °C), while in the winter, the temperature can fall below . Precipitation is sparse in the Interior, often less than a year, but what precipitation falls in the winter tends to stay the entire winter.
The highest and lowest recorded temperatures in Alaska are both in the Interior. The highest is in Fort Yukon, Alaska, Fort Yukon (which is just inside the arctic circle) on June 27, 1915,
making Alaska tied with Hawaii as the state with the lowest high temperature in the United States. The lowest official Alaska temperature is in Prospect Creek, Alaska, Prospect Creek on January 23, 1971,
one degree above the lowest temperature recorded in continental North America (in Snag, Yukon, Snag, Yukon, Canada).
The climate in the extreme north of Alaska is polar climate, Arctic (Köppen climate classification#GROUP E: Polar climates, Köppen: ''ET'') with long, very cold winters and short, cool summers. Even in July, the average low temperature in Utqiaġvik, Alaska, Utqiaġvik is . Precipitation is light in this part of Alaska, with many places averaging less than per year, mostly as snow which stays on the ground almost the entire year.
Demographics
The United States Census Bureau found in the 2020 United States census that the population of Alaska was 736,081 on April 1, 2020, a 3.6% increase since the 2010 United States census.
According to the 2010 United States census, the U.S. state of Alaska had a population of 710,231, increasing from 626,932 at the 2000 U.S. census.
In 2010, Alaska ranked as the 47th state by population, ahead of North Dakota, Vermont, and Wyoming (and Washington, D.C.). Estimates show North Dakota ahead . Alaska is the least densely populated state, and one of the most sparsely populated areas in the world, at , with the next state, Wyoming, at . Alaska is by far the largest U.S. state by List of U.S. states and territories by area, area, and the tenth wealthiest (per capita income). due to its population size, it is one of 14 U.S. states that still have only one telephone Telephone numbering plan, area code.
Race and ethnicity

The 2019 American Community Survey estimated 60.2% of the population was Non-Hispanic whites, non-Hispanic white, 3.7% African Americans, black or African American, 15.6% Native Americans in the United States, American Indian or Alaska Native, 6.5% Asian Americans, Asian, 1.4% Pacific Islander Americans, Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islander, 7.5% two or more races, and 7.3% Hispanic and Latino Americans, Hispanic or Latin American of any race. At the survey estimates, 7.8% of the total population was foreign-born from 2015 to 2019. In 2015, 61.3% was non-Hispanic white, 3.4% black or African American, 13.3% American Indian or Alaska Native, 6.2% Asian, 0.9% Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islander, 0.3% some other race, and 7.7% multiracial. Hispanics and Latin Americans were 7% of the state population in 2015. From 2015 to 2019, the largest Hispanic and Latin American groups were Mexican Americans, Puerto Ricans, and Cuban Americans. The largest Asian groups living in the state were Filipino Americans, Filipinos, Korean Americans, and Japanese Americans, Japanese and Chinese Americans.
The state was 66.7% white (64.1% non-Hispanic white), 14.8% American Indian and Alaska Native, 5.4% Asian, 3.3% black or African American, 1.0% Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islander, 1.6% from some other race, and 7.3% from two or more races in 2010. Hispanics or Latin Americans of any race made up 5.5% of the population in 2010. , 50.7% of Alaska's population younger than one year of age belonged to minority groups (i.e., did not have two parents of non-Hispanic white ancestry). In 1960, the United States Census Bureau reported Alaska's population as 77.2% white, 3% black, and 18.8% American Indian and Alaska Native.
Languages
According to the 2011 American Community Survey, 83.4% of people over the age of five spoke only English at home. About 3.5% spoke Spanish at home, 2.2% spoke another Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, about 4.3% spoke an Languages of Asia, Asian language (including Tagalog language, Tagalog), and about 5.3% spoke other languages at home. In 2019, the American Community Survey determined 83.7% spoke only English, and 16.3% spoke another language other than English. The most spoken European language after English was Spanish, spoken by approximately 4.0% of the state population. Collectively, Asian and Pacific Islander languages were spoken by 5.6% of Alaskans. Since 2010, a total of 5.2% of Alaskans speak one of the state's 20 Indigenous languages of the Americas, indigenous languages, known locally as "native languages".
The Alaska Native Language Center at the
University of Alaska Fairbanks
The University of Alaska Fairbanks (UAF or Alaska) is a public land-grant research university in College, Alaska, a suburb of Fairbanks. It is the flagship campus of the University of Alaska system. UAF was established in 1917 and opened for cla ...
claims that at least 20 Alaska Native languages, Alaskan native languages exist and there are also some languages with different dialects.
Most of Alaska's native languages belong to either the Eskimo–Aleut languages, Eskimo–Aleut or Na-Dene languages, Na-Dene language families; however, some languages are thought to be Language isolate, isolates (e.g. Haida language, Haida) or have not yet been classified (e.g. Tsimshianic languages, Tsimshianic).
nearly all of Alaska's native languages were classified as either threatened, shifting, moribund, nearly extinct, or dormant languages.
In October 2014, the governor of Alaska signed a bill declaring the state's 20 indigenous languages to have official status. This bill gave them symbolic recognition as official languages, though they have not been adopted for official use within the government. The 20 languages that were included in the bill are:
# Inupiat language, Inupiaq
# Central Siberian Yupik language, Siberian Yupik
# Central Alaskan Yup'ik language, Central Alaskan Yup'ik
# Alutiiq language, Alutiiq
# Aleut language, Unangax
# Dena'ina language, Dena'ina
# Deg Xinag language, Deg Xinag
# Holikachuk language, Holikachuk
# Koyukon language, Koyukon
# Upper Kuskokwim language, Upper Kuskokwim
# Gwich'in language, Gwich'in
# Lower Tanana language, Tanana
# Upper Tanana language, Upper Tanana
# Tanacross language, Tanacross
# Hän language, Hän
# Ahtna language, Ahtna
# Eyak language, Eyak
# Tlingit language, Tlingit
# Haida language, Haida
# Coast Tsimshian dialect, Tsimshian
Religion


According to statistics collected by the Association of Religion Data Archives from 2010, about 34% of Alaska residents were members of religious congregations. Of the religious population, 100,960 people identified as evangelical Protestants; 50,866 as Roman Catholic; and 32,550 as mainline Protestants.
Roughly 4% were Mormon, 0.5% Judaism, Jewish, 0.5% Muslim, 1% Buddhist, 0.2% Baháʼí, and 0.5% Hindu. The largest religious denominations in Alaska was the Catholic Church, Roman Catholic Church with 50,866 adherents; non-denominational Evangelicals with 38,070 adherents; The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints with 32,170 adherents; and the Southern Baptist Convention with 19,891 adherents. Alaska has been identified, along with Washington and Oregon in the Pacific Northwest, as being Unchurched Belt, the least religious states in the United States, in terms of church membership.
The Pew Research Center in 2014 determined 62% of the adult population practiced Christianity. Protestantism was the largest Christian tradition, dominated by Evangelicalism. Mainline Protestants were the second largest Protestant Christian group, followed by black church, predominantly African American churches. The Roman Catholic Church remained the largest single Christian tradition practiced in Alaska. Of the unaffiliated population, they made up the largest non-Christian religious affiliation. Atheism, Atheists made up 5% of the population and the largest non-Christian religion was Buddhism. In 2020, the Public Religion Research Institute determined 57% of adults were Christian.
In 1795, the first Russian Orthodox Church was established in Kodiak Island Borough, Alaska, Kodiak. Intermarriage with Alaskan Natives helped the Russian immigrants integrate into society. As a result, an increasing number of Russian Orthodox churches gradually became established within Alaska. Alaska also has the largest Quaker population (by percentage) of any state. In 2009, there were 6,000 Jews in Alaska (for whom observance of halakha Jewish law in the polar regions, may pose special problems). Alaskan Hindus often share venues and celebrations with members of other Asian religious communities, including Sikhism, Sikhs and Jainism, Jains. In 2010, Alaskan Hindus established the Sri Ganesha Temple of Alaska, making it the first Hindu Temple in Alaska and the northernmost Hindu Temple in the world. There are an estimated 2,000–3,000 Hindus in Alaska. The vast majority of Hindus live in Anchorage or Fairbanks.
Estimates for the number of Muslims in Alaska range from 2,000 to 5,000. The Islamic Community Center of Anchorage, Alaska, Islamic Community Center of Anchorage began efforts in the late 1990s to construct a mosque in Anchorage. They broke ground on a building in south Anchorage in 2010 and were nearing completion in late 2014. When completed, the mosque will be the first in the state and one of the northernmost mosques in the world. There's also a Baháʼí Faith, Baháʼí center.
Economy

As of October 2022, Alaska had a total employment of 316,900. The number of employer establishments was 21,077.
The 2018 gross state product was $55 billion, 48th in the U.S. Its List of U.S. states by GDP per capita (nominal), per capita personal income for 2018 was $73,000, ranking 7th in the nation. According to a 2013 study by Phoenix Marketing International, Alaska had the fifth-largest number of millionaires per capita in the United States, with a ratio of 6.75 percent. The oil and gas industry dominates the Alaskan economy, with more than 80% of the state's revenues derived from petroleum extraction. Alaska's main export product (excluding oil and natural gas) is seafood, primarily salmon, cod, pollock and crab.
Agriculture represents a very small fraction of the Alaskan economy. Agricultural production is primarily for consumption within the state and includes nursery stock, dairy products, vegetables, and livestock. Manufacturing is limited, with most foodstuffs and general goods imported from elsewhere.
Employment is primarily in government and industries such as natural resource extraction, shipping, and transportation. Military bases are a significant component of the economy in the Fairbanks North Star, Anchorage and Kodiak Island boroughs, as well as Kodiak. Federal subsidies are also an important part of the economy, allowing the state to keep taxes low. Its industrial outputs are crude petroleum, natural gas, coal, gold, precious metals, zinc and other mining, seafood processing, timber and wood products. There is also a growing service and tourism sector. Tourists have contributed to the economy by supporting local lodging.
Energy

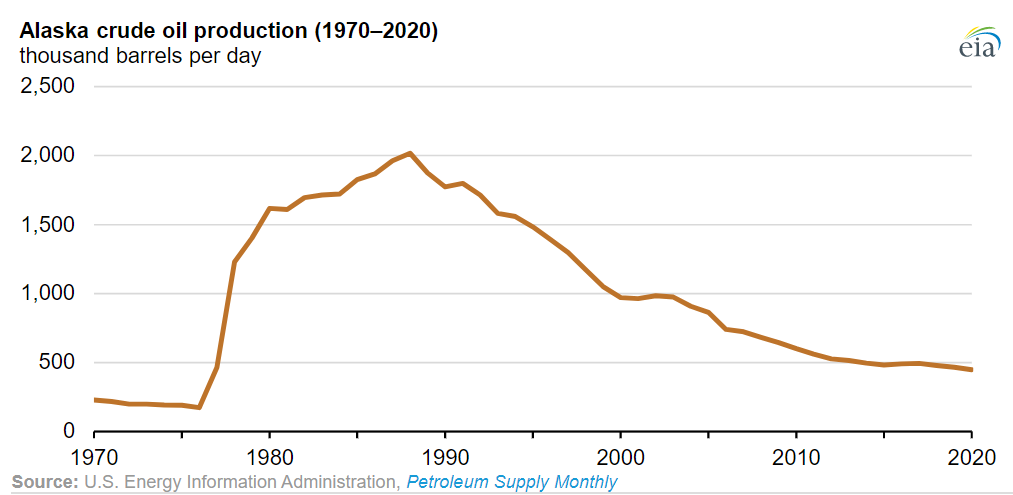
Alaska has vast energy resources, although its oil reserves have been largely depleted. Major oil and gas reserves were found in the Alaska North Slope (ANS) and Cook Inlet basins, but according to the Energy Information Administration, by February 2014 Alaska had fallen to fourth place in the nation in crude oil production after Texas, North Dakota, and California. Prudhoe Bay on Alaska's North Slope is still the second highest-yielding oil field in the United States, typically producing about , although by early 2014 North Dakota's Bakken Formation was producing over . Prudhoe Bay was the largest conventional oil field ever discovered in North America, but was much smaller than Canada's enormous Athabasca oil sands field, which by 2014 was producing about of unconventional oil, and had hundreds of years of producible reserves at that rate.
The Trans-Alaska Pipeline can transport and pump up to of crude oil per day, more than any other crude oil pipeline in the United States. Additionally, substantial coal deposits are found in Alaska's bituminous, sub-bituminous, and lignite coal basins. The United States Geological Survey estimates that there are of undiscovered, technically recoverable gas from natural gas hydrates on the Alaskan North Slope. Alaska also offers some of the highest hydroelectric power potential in the country from its numerous rivers. Large swaths of the Alaskan coastline offer wind and geothermal energy potential as well.
Alaska's economy depends heavily on increasingly expensive diesel fuel for heating, transportation, electric power and light. Although wind and hydroelectric power are abundant and underdeveloped, proposals for statewide energy systems (e.g. with special single-wire earth return#Use in interties, low-cost electric interties) were judged uneconomical (at the time of the report, 2001) due to low (less than 50¢/gal) fuel prices, long distances and low population. The cost of a gallon of gas in urban Alaska today is usually thirty to sixty cents higher than the national average; prices in rural areas are generally significantly higher but vary widely depending on transportation costs, seasonal usage peaks, nearby petroleum development infrastructure and many other factors.
Permanent Fund
The Alaska Permanent Fund is a constitutionally authorized appropriation of oil revenues, established by voters in 1976 to manage a surplus in state petroleum revenues from oil, largely in anticipation of the then recently constructed Trans-Alaska Pipeline System. The fund was originally proposed by Governor Keith Harvey Miller, Keith Miller on the eve of the 1969 Prudhoe Bay lease sale, out of fear that the legislature would spend the entire proceeds of the sale (which amounted to $900 million) at once. It was later championed by Governor Jay Hammond and Kenai, Alaska, Kenai Alaska House of Representatives, state representative Hugh Malone. It has served as an attractive political prospect ever since, diverting revenues which would normally be deposited into the general fund.
The Alaska Constitution was written so as to discourage dedicating state funds for a particular purpose. The Permanent Fund has become the rare exception to this, mostly due to the political climate of distrust existing during the time of its creation. From its initial principal of $734,000, the fund has grown to $50 billion as a result of oil royalties and capital investment programs. Most if not all the principal is invested conservatively outside Alaska. This has led to frequent calls by Alaskan politicians for the Fund to make investments within Alaska, though such a stance has never gained momentum.
Starting in 1982, dividends from the fund's annual growth have been paid out each year to eligible Alaskans, ranging from an initial $1,000 in 1982 (equal to three years' payout, as the distribution of payments was held up in a lawsuit over the distribution scheme) to $3,269 in 2008 (which included a one-time $1,200 "Resource Rebate"). Every year, the state legislature takes out 8% from the earnings, puts 3% back into the principal for inflation proofing, and the remaining 5% is distributed to all qualifying Alaskans. To qualify for the Permanent Fund Dividend, one must have lived in the state for a minimum of 12 months, maintain constant residency subject to allowable absences, and not be subject to court judgments or criminal convictions which fall under various disqualifying classifications or may subject the payment amount to civil garnishment.
The Permanent Fund is often considered to be one of the leading examples of a basic income policy in the world.
Cost of living
The cost of goods in Alaska has long been higher than in the contiguous 48 states. Federal government employees, particularly United States Postal Service (USPS) workers and active-duty military members, receive a Cost of Living Allowance usually set at 25% of base pay because, while the cost of living has gone down, it is still one of the highest in the country.
Rural Alaska suffers from extremely high prices for food and consumer goods compared to the rest of the country, due to the relatively limited transportation infrastructure.
Agriculture and fishing

Due to the northern climate and short growing season, relatively little farming occurs in Alaska. Most farms are in either the Matanuska Valley, about northeast of Anchorage, or on the Kenai Peninsula, about southwest of Anchorage. The short 100-day growing season limits the crops that can be grown, but the long sunny summer days make for productive growing seasons. The primary crops are potatoes, carrots, lettuce, and cabbage.
The
Tanana Valley
The Tanana Valley is a lowland region in central Alaska in the United States, on the north side of the Alaska Range, where the Tanana River emerges from the mountains. Traditional inhabitants of the valley are Tanana Athabaskans of Alaskan Athaba ...
is another notable agricultural locus, especially the Delta Junction, Alaska, Delta Junction area, about southeast of Fairbanks, with a sizable concentration of farms growing agronomic crops; these farms mostly lie north and east of Fort Greely. This area was largely set aside and developed under a state program spearheaded by Hammond during his second term as governor. Delta-area crops consist predominantly of barley and hay. West of Fairbanks lies another concentration of small farms catering to restaurants, the hotel and tourist industry, and community-supported agriculture.
Alaskan agriculture has experienced a surge in growth of market gardeners, small farms and farmers' markets in recent years, with the highest percentage increase (46%) in the nation in growth in farmers' markets in 2011, compared to 17% nationwide. The peony industry has also taken off, as the growing season allows farmers to harvest during a gap in supply elsewhere in the world, thereby filling a niche in the flower market.
Alaska, with no counties, lacks county fairs. However, a small assortment of state and local fairs (with the Alaska State Fair in Palmer, Alaska, Palmer the largest), are held mostly in the late summer. The fairs are mostly located in communities with historic or current agricultural activity, and feature local farmers exhibiting produce in addition to more high-profile commercial activities such as carnival rides, concerts and food. "Alaska Grown" is used as an agricultural slogan.
Alaska has an abundance of seafood, with the primary fisheries in the Bering Sea and the North Pacific. Seafood is one of the few food items that is often cheaper within the state than outside it. Many Alaskans take advantage of salmon seasons to harvest portions of their household diet while fishing for subsistence, as well as sport. This includes fish taken by hook, net or Fish wheel, wheel.
Hunting for subsistence, primarily caribou, moose, and Dall sheep is still common in the state, particularly in remote The Bush (Alaska), Bush communities. An example of a traditional native food is Akutaq, the Eskimo ice cream, which can consist of reindeer fat, seal oil, dried fish meat and local berries.
Alaska's reindeer herding is concentrated on Seward Peninsula, where wild caribou can be prevented from mingling and migrating with the domesticated reindeer.
Most food in Alaska is transported into the state from Outside (Alaska), "Outside" (the other 49 US states), and shipping costs make food in the cities relatively expensive. In rural areas, subsistence hunting and gathering is an essential activity because imported food is prohibitively expensive. Although most small towns and villages in Alaska lie along the coastline, the cost of importing food to remote villages can be high, because of the terrain and difficult road conditions, which change dramatically, due to varying climate and precipitation changes. The cost of transport can reach as high as 50¢ per pound ($1.10/kg) or more in some remote areas, during the most difficult times, if these locations can be reached at all during such inclement weather and terrain conditions. The cost of delivering a of milk is about $3.50 in many villages where per capita income can be $20,000 or less. Fuel cost per gallon is routinely twenty to thirty cents higher than the contiguous United States average, with only Hawaii having higher prices.
Culture


Some of Alaska's popular annual events are the Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race from Anchorage to Nome, World Ice Art Championships in Fairbanks, the Blueberry Festival and Alaska Hummingbird Festival in Ketchikan, Alaska, Ketchikan, the Sitka Whale Fest, and the Stikine River Garnet Fest in Wrangell, Alaska, Wrangell. The Stikine River attracts the largest springtime concentration of American bald eagles in the world.
The Alaska Native Heritage Center celebrates the rich heritage of Alaska's 11 cultural groups. Their purpose is to encourage cross-cultural exchanges among all people and enhance self-esteem among Native people. The Alaska Native Arts Foundation promotes and markets Native art from all regions and cultures in the State, using the internet.
Music
Influences on music in Alaska include the traditional music of Alaska Natives as well as folk music brought by later immigrants from Russia and Europe. Prominent musicians from Alaska include singer Jewel (singer), Jewel, traditional Aleut flautist Mary Youngblood, folk singer-songwriter Libby Roderick, Christian music singer-songwriter Lincoln Brewster, metal/post hardcore band 36 Crazyfists and the groups Pamyua and Portugal. The Man.
There are many established music festivals in Alaska, including the Alaska Folk Festival, the Fairbanks Summer Arts Festival the Anchorage Folk Festival, the Athabascan Old-Time Fiddling Festival, the Sitka Jazz Festival, and the Sitka Summer Music Festival. The most prominent orchestra in Alaska is the Anchorage Symphony Orchestra, though the Fairbanks Symphony Orchestra and Juneau Symphony are also notable. The Anchorage Opera is currently the state's only professional opera company, though there are several volunteer and semi-professional organizations in the state as well.
The official List of U.S. state songs, state song of Alaska is "Alaska's Flag", which was adopted in 1955; it celebrates the flag of Alaska.
Alaska in film/television/videogames

Alaska's first independent picture entirely made in Alaska was ''The Chechahcos'', produced by Alaskan businessman Austin E. Lathrop and filmed in and around Anchorage. Released in 1924 by the Alaska Moving Picture Corporation, it was the only film the company made.
One of the most prominent movies filmed in Alaska is Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer, MGM's ''Eskimo/Mala The Magnificent'', starring Alaska Native Ray Mala. In 1932, an expedition set out from MGM's studios in Hollywood to Alaska to film what was then billed as "The Biggest Picture Ever Made". Upon arriving in Alaska, they set up "Camp Hollywood" in Northwest Alaska, where they lived during the duration of the filming. Louis B. Mayer spared no expense in spite of the remote location, going so far as to hire the chef from the Roosevelt Hotel (Hollywood), Hotel Roosevelt in Hollywood to prepare meals.
When ''Eskimo'' premiered at the Astor Theatre, New York City, Astor Theatre in New York City, the studio received the largest amount of feedback in its history. ''Eskimo'' was critically acclaimed and released worldwide; as a result, Mala became an international movie star. ''Eskimo'' won the first Oscar for Academy Award for Best Film Editing, Best Film Editing at the Academy Awards, and showcased and preserved aspects of Inupiat people, Inupiat culture on film.
The 1983 Disney movie ''Never Cry Wolf (film), Never Cry Wolf'' was at least partially shot in Alaska. The 1991 film ''White Fang (1991 film), White Fang'', based on Jack London's 1906 novel and starring Ethan Hawke, was filmed in and around Haines, Alaska, Haines. Steven Seagal's 1994 ''On Deadly Ground'', starring Michael Caine, was filmed in part at the Worthington Glacier near
Valdez. The 1999 John Sayles film ''Limbo (1999 film), Limbo'', starring David Strathairn, Mary Elizabeth Mastrantonio, and Kris Kristofferson, was filmed in Juneau.
The psychological thriller ''Insomnia (2002 film), Insomnia'', starring Al Pacino and Robin Williams, was shot in Canada, but was set in Alaska. The 2007 film directed by Sean Penn, ''Into the Wild (film), Into The Wild'', was partially filmed and set in Alaska. The film, which is based on the novel of the same name, follows the adventures of Christopher McCandless, who died in a remote abandoned bus along the Stampede Trail west of Healy, Alaska, Healy in 1992.
Many films and television shows set in Alaska are not filmed there; for example, ''Northern Exposure'', set in the fictional town of Cicely, Alaska, was filmed in Roslyn, Washington. The 2007 horror feature ''30 Days of Night (film), 30 Days of Night'' is set in Utqiaġvik, Alaska, Barrow, Alaska, but was filmed in New Zealand.
Many reality television shows are filmed in Alaska. In 2011, the ''Anchorage Daily News'' found ten set in the state.
The 2020 videogame Tell Me Why (video game), ''Tell Me Why'' (video game) takes place around Southern Alaska and includes representation of Tlingit culture.
Sports
Public health and public safety
The Alaska State Troopers are Alaska's statewide police force. They have a long and storied history, but were not an official organization until 1941. Before the force was officially organized, law enforcement in Alaska was handled by various federal agencies. Larger towns usually have their own local police and some villages rely on "Public Safety Officers" who have police training but do not carry firearms. In much of the state, the troopers serve as the only police force available. In addition to enforcing traffic and criminal law, wildlife Troopers enforce hunting and fishing regulations. Due to the varied terrain and wide scope of the Troopers' duties, they employ a wide variety of land, air, and water patrol vehicles.
Many rural communities in Alaska are considered "dry", having outlawed the importation of alcoholic beverages. Suicide rates for rural residents are higher than urban.
Domestic abuse and other violent crimes are also at high levels in the state; this is in part linked to alcohol abuse. Alaska has the highest rate of sexual assault in the nation, especially in rural areas. The average age of sexually assaulted victims is 16 years old. In four out of five cases, the suspects were relatives, friends or acquaintances.
Education

The Alaska Department of Education and Early Development administers many List of school districts in Alaska, school districts in Alaska. In addition, the state operates a boarding school, Mt. Edgecumbe High School in
Sitka
russian: Ситка
, native_name_lang = tli
, settlement_type = Consolidated city-borough
, image_skyline = File:Sitka 84 Elev 135.jpg
, image_caption = Downtown Sitka in 1984
, image_size ...
, and provides partial funding for other boarding schools, including Nenana Student Living Center in Nenana, Alaska, Nenana and The Galena Interior Learning Academy in Galena, Alaska, Galena.
There are more than a dozen List of colleges and universities in Alaska, colleges and universities in Alaska. Accredited universities in Alaska include the University of Alaska Anchorage,
University of Alaska Fairbanks
The University of Alaska Fairbanks (UAF or Alaska) is a public land-grant research university in College, Alaska, a suburb of Fairbanks. It is the flagship campus of the University of Alaska system. UAF was established in 1917 and opened for cla ...
, University of Alaska Southeast, and Alaska Pacific University. Alaska is the only state that has no collegiate athletic programs that are members of NCAA Division I, although both Alaska-Fairbanks and Alaska-Anchorage maintain single sport membership in Division I for college ice hockey, men's ice hockey.
The Alaska Department of Labor and Workforce Development operates AVTEC, Alaska's Institute of Technology. Campuses in Seward and Anchorage offer one-week to 11-month training programs in areas as diverse as Information Technology, Welding, Nursing, and Mechanics.
Alaska has had a problem with a "brain drain". Many of its young people, including most of the highest academic achievers, leave the state after high school graduation and do not return. , Alaska did not have a Legal education in Alaska, law school or medical school. The University of Alaska has attempted to combat this by offering partial four-year scholarships to the top 10% of Alaska high school graduates, via the Alaska Scholars Program.
Beginning in 1998, schools in rural Alaska must have at least 10 students to retain funding from the state, and campuses not meeting the number close. This was due to the loss in oil revenues that previously propped up smaller rural schools. In 2015, there was a proposal to raise that minimum to 25, but legislators in the state largely did not agree.
Transportation
Roads
Alaska has few road connections compared to the rest of the U.S. The state's road system, covering a relatively small area of the state, linking the central population centers and the Alaska Highway, the principal route out of the state through Canada. The state capital, Juneau, is not accessible by road, only a car ferry; this has spurred debate over decades about moving the capital to a city on the road system, or building a road connection from Haines, Alaska, Haines. The western part of Alaska has no road system connecting the communities with the rest of Alaska.
The Interstate Highways in Alaska consists of a total of . One unique feature of the Alaska Highway system is the Anton Anderson Memorial Tunnel, an active Alaska Railroad tunnel recently upgraded to provide a paved roadway link with the isolated community of Whittier, Alaska, Whittier on Prince William Sound to the Seward Highway about southeast of Anchorage at Portage, Alaska, Portage. At , the tunnel was the longest road tunnel in North America until 2007. The tunnel is the longest combination List of road-rail tunnels, road and rail tunnel in North America.
File:Sterling Highway.jpg, The Sterling Highway, near its intersection with the Seward Highway
File:Susitnabridge.JPG, The Susitna River bridge on the Denali Highway is long.
File:Interstate Routes in Alaska.svg, List of Interstate Highways in Alaska, Alaska Interstate Highways
File:AlaskaSign.jpg, Alaska welcome sign on the Klondike Highway
Rail
Built around 1915, the Alaska Railroad (ARR) played a key role in the development of Alaska through the 20th century. It links north Pacific shipping through providing critical infrastructure with tracks that run from Seward, Alaska, Seward to Interior Alaska by way of South Central Alaska, passing through Anchorage, Eklutna, Wasilla, Talkeetna, Alaska, Talkeetna, Denali, and Fairbanks, with spurs to Whittier, Alaska, Whittier, Palmer, Alaska, Palmer and North Pole, Alaska, North Pole. The cities, towns, villages, and region served by ARR tracks are known statewide as "The Railbelt". In recent years, the ever-improving paved highway system began to eclipse the railroad's importance in Alaska's economy.
The railroad played a vital role in Alaska's development, moving freight into Alaska while transporting natural resources southward, such as coal from the Usibelli coal mine near Healy, Alaska, Healy to Seward and gravel from the Matanuska Valley to Anchorage. It is well known for its summertime tour passenger service.
The Alaska Railroad was one of the last railroads in North America to use cabooses in regular service and still uses them on some gravel trains. It continues to offer one of the last Request stop, flag stop routes in the country. A stretch of about of track along an area north of Talkeetna remains inaccessible by road; the railroad provides the only transportation to rural homes and cabins in the area. Until construction of the Parks Highway in the 1970s, the railroad provided the only land access to most of the region along its entire route.
In northern Southeast Alaska, the White Pass and Yukon Route also partly runs through the state from Skagway, Alaska, Skagway northwards into Canada (British Columbia and Yukon Territory), crossing the border at White Pass Summit. This line is now mainly used by tourists, often arriving by cruise liner at Skagway. It was featured in the 1983 BBC television series ''Great Little Railways.''
The Alaska Rail network is not connected to Outside. (The nearest link to the North American railway network is the northwest terminus of the Canadian National Railway at Prince Rupert, British Columbia, several hundred miles to the southeast.) In 2000, the U.S. Congress authorized $6 million to study the feasibility of a rail link between Alaska, Canada, and the lower 48.
Some private companies provides car float service between Whittier, Alaska, Whittier and Seattle.
File:Alaska Railroad, Girdwood, Alaska, Estados Unidos, 2017-08-31, DD 40.jpg, An Alaska Railroad locomotive over a bridge in Girdwood approaching Anchorage (2007)
File:Skagway-Hoonah-Angoon Census Area, In to the Tunnel.jpg, The White Pass and Yukon Route traverses rugged terrain north of Skagway near the Canada–United States border, Canada–US border.
Marine transport
Many cities, towns and villages in the state do not have road or highway access; the only modes of access involve travel by air, river, or the sea.

Alaska's well-developed state-owned ferry system (known as the Alaska Marine Highway) serves the cities of Southeast Alaska, southeast, the Gulf Coast and the Alaska Peninsula. The ferries transport vehicles as well as passengers. The system also operates a ferry service from Bellingham, Washington and Prince Rupert, British Columbia, in Canada through the Inside Passage to Skagway, Alaska, Skagway. The Inter-Island Ferry Authority also serves as an important marine link for many communities in the Prince of Wales Island (Alaska), Prince of Wales Island region of Southeast and works in concert with the Alaska Marine Highway.
In recent years, cruise lines have created a summertime tourism market, mainly connecting the Pacific Northwest to Southeast Alaska and, to a lesser degree, towns along Alaska's gulf coast. The population of Ketchikan, Alaska, Ketchikan for example fluctuates dramatically on many days—up to four large cruise ships can dock there at the same time.
Air transport
Cities not served by road, sea, or river can be reached only by air, foot, dogsled, or Continuous track#Snow vehicles, snowmachine, accounting for Alaska's extremely well developed Alaskan Bush, bush air services—an Alaskan novelty. Anchorage and, to a lesser extent Fairbanks, is served by Ted Stevens Anchorage International Airport#Airlines and destinations, many major airlines. Because of limited highway access, air travel remains the most efficient form of transportation in and out of the state. Anchorage recently completed extensive remodeling and construction at Ted Stevens Anchorage International Airport to help accommodate the upsurge in tourism (in 2012–2013, Alaska received almost two million visitors).
Regular flights to most villages and towns within the state that are commercially viable are challenging to provide, so they are heavily subsidized by the federal government through the Essential Air Service program. Alaska Airlines is the only major airline offering in-state travel with jet service (sometimes in combination cargo and passenger Boeing 737-400s) from Anchorage and Fairbanks International Airport, Fairbanks to regional hubs like Bethel, Alaska, Bethel, Nome, Alaska, Nome, Kotzebue, Alaska, Kotzebue, Dillingham, Alaska, Dillingham, Kodiak, Alaska, Kodiak, and other larger communities as well as to major Southeast and Alaska Peninsula communities.

The bulk of remaining commercial flight offerings come from small regional commuter airlines such as Ravn Alaska, PenAir, and Frontier Flying Service. The smallest towns and villages must rely on scheduled or chartered bush flying services using general aviation aircraft such as the Cessna Caravan, the most popular aircraft in use in the state. Much of this service can be attributed to the Alaska bypass mail program which subsidizes bulk mail delivery to Alaskan rural communities. The program requires 70% of that subsidy to go to carriers who offer passenger service to the communities.
Many communities have small air taxi services. These operations originated from the demand for customized transport to remote areas. Perhaps the most quintessentially Alaskan plane is the bush seaplane. The world's busiest seaplane base is Lake Hood Seaplane Base, Lake Hood, located next to Ted Stevens Anchorage International Airport, where flights bound for remote villages without an airstrip carry passengers, cargo, and many items from stores and warehouse clubs.
In 2006, Alaska had the highest number of pilots per capita of any U.S. state. In Alaska there are 8,795 active pilot certificates as of 2020.
Of these, there are 2,507 Private, 1,496 Commercial, 2,180 Airline Transport, and 2,239 student pilots. There are also 3,987 pilots with an Instrument rating and 1,511 Flight Instructors.
Other transport
Another Alaskan transportation method is the dogsled. In modern times (that is, any time after the mid-late 1920s), dog mushing is more of a sport than a true means of transportation. Various races are held around the state, but the best known is the Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race, a trail from Anchorage to Nome (although the distance varies from year to year, the official distance is set at ). The race commemorates the famous 1925 serum run to Nome in which mushers and dogs like Togo (dog), Togo and Balto took much-needed medicine to the diphtheria-stricken community of Nome, Alaska, Nome when all other means of transportation had failed. Mushers from all over the world come to Anchorage each March to compete for cash, prizes, and prestige. The "Serum Run" is another sled dog race that more accurately follows the route of the famous 1925 relay, leaving from the community of Nenana, Alaska, Nenana (southwest of Fairbanks) to Nome.
In areas not served by road or rail, primary transportation in summer is by all-terrain vehicle and in winter by snowmobile or "snow machine", as it is commonly referred to in Alaska.
Data transport
Alaska's internet and other data transport systems are provided largely through the two major telecommunications companies: GCI (company), GCI and Alaska Communications. GCI owns and operates what it calls the Alaska United Fiber Optic system and, as of late 2011, Alaska Communications advertised that it has "two fiber optic paths to the lower 48 and two more across Alaska. In January 2011, it was reported that a $1 billion project to connect Asia and rural Alaska was being planned, aided in part by $350 million in stimulus from the federal government.
Law and government
State government

Like all other U.S. states, Alaska is governed as a republic, with three separation of powers, branches of government: an executive branch consisting of the governor of Alaska and their appointees which head executive departments; a legislative branch consisting of the Alaska House of Representatives and Alaska Senate; and a judicial branch consisting of the Alaska Supreme Court and lower courts.
The state of Alaska employs approximately 16,000 people statewide.
The Alaska Legislature consists of a 40-member Alaska House of Representatives, House of Representatives and a 20-member Alaska Senate, Senate. Senators serve four-year terms and House members two. The governor of Alaska serves four-year terms. The List of Lieutenant Governors of Alaska, lieutenant governor runs separately from the governor in the Primary election, primaries, but during the general election, the nominee for governor and nominee for lieutenant governor run together on the same ticket.
Alaska's court system has four levels: the Alaska Supreme Court, the Alaska Court of Appeals, the superior courts and the district courts.
The superior and district courts are trial courts. Superior courts are courts of general jurisdiction, while district courts hear only certain types of cases, including misdemeanor criminal cases and civil cases valued up to $100,000.
The Supreme Court and the Court of Appeals are appellate courts. The Court of Appeals is required to hear appeals from certain lower-court decisions, including those regarding criminal prosecutions, juvenile delinquency, and habeas corpus.
The Supreme Court hears civil appeals and may in its discretion hear criminal appeals.
State politics
Although in its early years of statehood Alaska was a Democratic Party (United States), Democratic state, since the early 1970s it has been characterized as Republican Party (United States), Republican-leaning. Local political communities have often worked on issues related to land use development, fishing, tourism, and individual rights. Alaska Natives, while organized in and around their communities, have been active within the Alaska Native Regional Corporations, Native corporations. These have been given ownership over large tracts of land, which require stewardship.
Alaska was formerly the only state in which possession of one ounce or less of marijuana in one's home was completely legal under state law, though the federal law remains in force.
The state has an independence movement favoring a vote on secession from the United States, with the Alaskan Independence Party.
Six Republican Party (United States), Republicans and four Democratic Party (United States), Democrats have served as governor of Alaska. In addition, Republican governor Wally Hickel was elected to the office for a second term in 1990 after leaving the Republican party and briefly joining the Alaskan Independence Party ticket just long enough to be reelected. He officially rejoined the Republican party in 1994.
Alaska's 2014 Alaska Measure 2, voter initiative making marijuana legal took effect on February 24, 2015, placing Alaska alongside Colorado and Washington as the first three U.S. states where recreational marijuana is legal. The new law means people over 21 can consume small amounts of cannabis. The first legal marijuana store opened in Valdez in October 2016.
Voter registration
Taxes
To finance state government operations, Alaska depends primarily on petroleum revenues and federal subsidies. This allows it to have the lowest individual tax burden in the United States. It is one of five states with no sales tax, one of seven states with no individual income tax, and—along with New Hampshire—one of two that has neither. The Department of Revenue Tax Division reports regularly on the state's revenue sources. The department also issues an annual summary of its operations, including new state laws that directly affect the tax division. In 2014, the Tax Foundation ranked Alaska as having the fourth most "business friendly" tax policy, behind only Wyoming, South Dakota, and Nevada.
While Alaska has no state sales tax, 89 municipalities collect a local sales tax, from 1.0 to 7.5%, typically 3–5%. Other local taxes levied include raw fish taxes, hotel, motel, and bed-and-breakfast 'bed' taxes, severance taxes, liquor and tobacco taxes, gaming (pull tabs) taxes, tire taxes and fuel transfer taxes. A part of the revenue collected from certain state taxes and license fees (such as petroleum, aviation motor fuel, telephone cooperative) is shared with municipalities in Alaska.
The fall in oil prices after the Hydraulic fracturing in the United States, fracking boom in the early 2010s has decimated Alaska's state treasury, which has historically received about 85 percent of its revenue from taxes and fees imposed on oil and gas companies. The state government has had to drastically reduce its budget, and has brought its budget shortfall from over $2 billion in 2016 to under $500 million by 2018. In 2020, Alaska's state government budget was $4.8 billion, while projected government revenues were only $4.5 billion.
Federal politics

Alaska regularly supports Republican Party (United States), Republicans in presidential elections and has done so since statehood. Republicans have won the state's Electoral College (United States), electoral college votes in all but one election that it has participated in (1964 United States presidential election, 1964). No state has voted for a Democratic Party (United States), Democratic presidential candidate fewer times. Alaska was carried by Democratic nominee Lyndon B. Johnson during his landslide election in 1964 United States presidential election, 1964, while the 1960 United States presidential election, 1960 and 1968 United States presidential election, 1968 elections were close. Since 1972 United States presidential election, 1972, however, Republicans have carried the state by large margins. In 2008 United States presidential election, 2008, Republican John McCain defeated Democrat Barack Obama in Alaska, 59.49% to 37.83%. McCain's running mate was Sarah Palin, the state's governor and the first Alaskan on a major party ticket. Obama lost Alaska again in 2012 United States presidential election, 2012, but he captured 40% of the state's vote in that election, making him the first Democrat to do so since 1968. In 2020 United States presidential election, 2020, Joe Biden received 42.77% of the vote for president, marking the high point for a Democratic presidential candidate since Johnson's 1964 victory.
The The Bush (Alaska), Alaska Bush, central Juneau, midtown and downtown Anchorage, and the areas surrounding the
University of Alaska Fairbanks
The University of Alaska Fairbanks (UAF or Alaska) is a public land-grant research university in College, Alaska, a suburb of Fairbanks. It is the flagship campus of the University of Alaska system. UAF was established in 1917 and opened for cla ...
campus and Ester have been strongholds of the Democratic Party. The Matanuska-Susitna Borough, the majority of Fairbanks (including North Pole and the military base), and South Anchorage typically have the strongest Republican showing.
Elections
Alaska has had a long history of primary defeats for incumbent U.S. Senators, with Ernest Gruening, Mike Gravel and Lisa Murkowski all being defeated for the nomination to their re-election. However, Murkowski 2010 United States Senate election in Alaska, won re-election with a write-in campaign. Despite this, Alaska has had some long-serving congressmen, with Ted Stevens serving as U.S. Senator for 40 years, and Don Young serving as the at-large representative for 49 years.

In a 2020 study, Alaska was ranked as the 15th hardest state for citizens to vote in.
In the 2020 Alaska elections, 2020 election cycle, Alaskan voters approved Ballot Measure 2.
The measure passed by a margin of 1.1%, or about 4,000 votes.
The measure requires campaigns to disclose the original source and any intermediaries for campaign contributions over $2,000. The measure also establishes Nonpartisan blanket primary, non-partisan blanket primaries for statewide elections (like in Washington (state)#Elections, Washington state and California#Government and politics, California) and Instant-runoff voting, ranked-choice voting (like in Maine#Politics, Maine).
Measure 2 makes Alaska the third state with Jungle primary, jungle primaries for all statewide races, the second state with ranked voting, ranked choice voting, and the only state with both.
The first race to use the new system of elections was the 2022 Alaska's at-large congressional district special election, 2022 special election to fill Alaska's only U.S. House seat, left vacant by the death of Don Young, won by Mary Peltola, the first Democrat to win the House seat since 1972 United States House of Representatives election in Alaska, 1972, and the first Alaska Natives, Alaskan Native to be elected to the United States Congress in history.
File:Mike Dunleavy official photo (cropped).jpg, Mike Dunleavy (politician), Mike Dunleavy, List of Governors of Alaska, Governor
File:Senator Kevin Meyer (cropped).jpg, Kevin Meyer (politician), Kevin Meyer, List of lieutenant governors of Alaska, Lieutenant governor
File:Lisa Murkowski official photo.jpg, Lisa Murkowski, senior List of United States senators from Alaska, United States senator
File:Senator Dan Sullivan official.jpg, Dan Sullivan (U.S. senator), Dan Sullivan, junior United States senator
File:U.S. Representative Mary Peltola, 117th Congress.jpg, Mary Peltola, United States Alaska's at-large congressional district, congresswoman
See also
* Index of Alaska-related articles
* Outline of Alaska
Notes
References
External links
*
Alaska's Digital ArchivesAlaska Inter-Tribal Council*
*
Who Owns/Manages Alaska?(map)
Carl J. Sacarlasen Diary Extractsat Dartmouth College Library
M.E. Diemer Alaska Photographsat Dartmouth College Library
* hdl:10079/fa/beinecke.brooksah, Alfred Hulse Brooks Photographs and Papers. Yale Collection of Western Americana, Beinecke Rare Book and Manuscript Library.
U.S. federal government
Alaska State Guide from the Library of CongressEnergy & Environmental Data for AlaskaUSGS real-time, geographic, and other scientific resources of Alaska
Alaska State FactsAlaska Statehood Subject Guide from the Eisenhower Presidential Library
Alaska state government
State of Alaska websiteAlaska State DatabasesAlaska Department of Natural Resources, Recorder's Office
{{coord, 64, -152, dim:2000000_region:US-AK_type:adm1st, name=State of Alaska, display=title
Alaska,
Arctic Ocean
Former Russian colonies
States and territories established in 1959
States of the United States
States of the West Coast of the United States
U.S. states with multiple time zones
1959 establishments in the United States
Western United States
Northern America
Enclaves and exclaves
Beringia
Exclaves in the United States
 Numerous indigenous peoples occupied Alaska for thousands of years before the arrival of European peoples to the area. Linguistic and DNA studies done here have provided evidence for the settlement of North America by way of the
Numerous indigenous peoples occupied Alaska for thousands of years before the arrival of European peoples to the area. Linguistic and DNA studies done here have provided evidence for the settlement of North America by way of the 
 Some researchers believe the first Russian settlement in Alaska was established in the 17th century. According to this hypothesis, in 1648 several koches of
Some researchers believe the first Russian settlement in Alaska was established in the 17th century. According to this hypothesis, in 1648 several koches of  During
During  Statehood for Alaska was an important cause of
Statehood for Alaska was an important cause of  The Interior is the largest region of Alaska; much of it is uninhabited wilderness. Fairbanks, Alaska, Fairbanks is the only large city in the region. Denali National Park and Preserve is located here. Denali, formerly Mount McKinley, is the highest mountain in North America, and is also located here.
The Interior is the largest region of Alaska; much of it is uninhabited wilderness. Fairbanks, Alaska, Fairbanks is the only large city in the region. Denali National Park and Preserve is located here. Denali, formerly Mount McKinley, is the highest mountain in North America, and is also located here.
 More than 300 small volcanic islands make up this chain, which stretches more than into the Pacific Ocean. Some of these islands fall in the Eastern Hemisphere, but the International Date Line was drawn west of 180th meridian, 180° to keep the whole state, and thus the entire North American continent, within the same legal day. Two of the islands, Attu and Kiska, were occupied by Japanese forces during World War II.
More than 300 small volcanic islands make up this chain, which stretches more than into the Pacific Ocean. Some of these islands fall in the Eastern Hemisphere, but the International Date Line was drawn west of 180th meridian, 180° to keep the whole state, and thus the entire North American continent, within the same legal day. Two of the islands, Attu and Kiska, were occupied by Japanese forces during World War II.






 Alaska is not divided into County (United States), counties, as most of the other U.S. states, but it is divided into ''List of boroughs and census areas in Alaska, boroughs''. Delegates to the Alaska Constitutional Convention wanted to avoid the pitfalls of the traditional county system and adopted their own unique model. Many of the more densely populated parts of the state are part of Alaska's 16 boroughs, which function somewhat similarly to counties in other states. However, unlike county-equivalents in the other 49 states, the boroughs do not cover the entire land area of the state. The area not part of any borough is referred to as the Unorganized Borough, Alaska, Unorganized Borough.
The Unorganized Borough has no government of its own, but the U.S. Census Bureau in cooperation with the state divided the Unorganized Borough into 11 census areas solely for the purposes of statistical analysis and presentation. A ''recording district'' is a mechanism for management of the public record in Alaska. The state is divided into 34 recording districts which are centrally administered under a state recorder of deeds, recorder. All recording districts use the same acceptance criteria, fee schedule, etc., for accepting documents into the public record.
Whereas many U.S. states use a three-tiered system of decentralization—state/county/township—most of Alaska uses only two tiers—state/borough. Owing to the low population density, most of the land is located in the Unorganized Borough. As the name implies, it has no intermediate borough government but is administered directly by the state government. In 2000, 57.71% of Alaska's area has this status, with 13.05% of the population.
Anchorage merged the city government with the Greater Anchorage Area Borough in 1975 to form the Municipality of Anchorage, containing the city proper and the communities of Eagle River, Chugiak, Peters Creek, Girdwood, Bird, and Indian. Fairbanks has a separate borough (the Fairbanks North Star Borough) and municipality (the City of Fairbanks).
The state's most populous city is
Alaska is not divided into County (United States), counties, as most of the other U.S. states, but it is divided into ''List of boroughs and census areas in Alaska, boroughs''. Delegates to the Alaska Constitutional Convention wanted to avoid the pitfalls of the traditional county system and adopted their own unique model. Many of the more densely populated parts of the state are part of Alaska's 16 boroughs, which function somewhat similarly to counties in other states. However, unlike county-equivalents in the other 49 states, the boroughs do not cover the entire land area of the state. The area not part of any borough is referred to as the Unorganized Borough, Alaska, Unorganized Borough.
The Unorganized Borough has no government of its own, but the U.S. Census Bureau in cooperation with the state divided the Unorganized Borough into 11 census areas solely for the purposes of statistical analysis and presentation. A ''recording district'' is a mechanism for management of the public record in Alaska. The state is divided into 34 recording districts which are centrally administered under a state recorder of deeds, recorder. All recording districts use the same acceptance criteria, fee schedule, etc., for accepting documents into the public record.
Whereas many U.S. states use a three-tiered system of decentralization—state/county/township—most of Alaska uses only two tiers—state/borough. Owing to the low population density, most of the land is located in the Unorganized Borough. As the name implies, it has no intermediate borough government but is administered directly by the state government. In 2000, 57.71% of Alaska's area has this status, with 13.05% of the population.
Anchorage merged the city government with the Greater Anchorage Area Borough in 1975 to form the Municipality of Anchorage, containing the city proper and the communities of Eagle River, Chugiak, Peters Creek, Girdwood, Bird, and Indian. Fairbanks has a separate borough (the Fairbanks North Star Borough) and municipality (the City of Fairbanks).
The state's most populous city is 
 As of October 2022, Alaska had a total employment of 316,900. The number of employer establishments was 21,077.
The 2018 gross state product was $55 billion, 48th in the U.S. Its List of U.S. states by GDP per capita (nominal), per capita personal income for 2018 was $73,000, ranking 7th in the nation. According to a 2013 study by Phoenix Marketing International, Alaska had the fifth-largest number of millionaires per capita in the United States, with a ratio of 6.75 percent. The oil and gas industry dominates the Alaskan economy, with more than 80% of the state's revenues derived from petroleum extraction. Alaska's main export product (excluding oil and natural gas) is seafood, primarily salmon, cod, pollock and crab.
Agriculture represents a very small fraction of the Alaskan economy. Agricultural production is primarily for consumption within the state and includes nursery stock, dairy products, vegetables, and livestock. Manufacturing is limited, with most foodstuffs and general goods imported from elsewhere.
Employment is primarily in government and industries such as natural resource extraction, shipping, and transportation. Military bases are a significant component of the economy in the Fairbanks North Star, Anchorage and Kodiak Island boroughs, as well as Kodiak. Federal subsidies are also an important part of the economy, allowing the state to keep taxes low. Its industrial outputs are crude petroleum, natural gas, coal, gold, precious metals, zinc and other mining, seafood processing, timber and wood products. There is also a growing service and tourism sector. Tourists have contributed to the economy by supporting local lodging.
As of October 2022, Alaska had a total employment of 316,900. The number of employer establishments was 21,077.
The 2018 gross state product was $55 billion, 48th in the U.S. Its List of U.S. states by GDP per capita (nominal), per capita personal income for 2018 was $73,000, ranking 7th in the nation. According to a 2013 study by Phoenix Marketing International, Alaska had the fifth-largest number of millionaires per capita in the United States, with a ratio of 6.75 percent. The oil and gas industry dominates the Alaskan economy, with more than 80% of the state's revenues derived from petroleum extraction. Alaska's main export product (excluding oil and natural gas) is seafood, primarily salmon, cod, pollock and crab.
Agriculture represents a very small fraction of the Alaskan economy. Agricultural production is primarily for consumption within the state and includes nursery stock, dairy products, vegetables, and livestock. Manufacturing is limited, with most foodstuffs and general goods imported from elsewhere.
Employment is primarily in government and industries such as natural resource extraction, shipping, and transportation. Military bases are a significant component of the economy in the Fairbanks North Star, Anchorage and Kodiak Island boroughs, as well as Kodiak. Federal subsidies are also an important part of the economy, allowing the state to keep taxes low. Its industrial outputs are crude petroleum, natural gas, coal, gold, precious metals, zinc and other mining, seafood processing, timber and wood products. There is also a growing service and tourism sector. Tourists have contributed to the economy by supporting local lodging.

 Alaska has vast energy resources, although its oil reserves have been largely depleted. Major oil and gas reserves were found in the Alaska North Slope (ANS) and Cook Inlet basins, but according to the Energy Information Administration, by February 2014 Alaska had fallen to fourth place in the nation in crude oil production after Texas, North Dakota, and California. Prudhoe Bay on Alaska's North Slope is still the second highest-yielding oil field in the United States, typically producing about , although by early 2014 North Dakota's Bakken Formation was producing over . Prudhoe Bay was the largest conventional oil field ever discovered in North America, but was much smaller than Canada's enormous Athabasca oil sands field, which by 2014 was producing about of unconventional oil, and had hundreds of years of producible reserves at that rate.
The Trans-Alaska Pipeline can transport and pump up to of crude oil per day, more than any other crude oil pipeline in the United States. Additionally, substantial coal deposits are found in Alaska's bituminous, sub-bituminous, and lignite coal basins. The United States Geological Survey estimates that there are of undiscovered, technically recoverable gas from natural gas hydrates on the Alaskan North Slope. Alaska also offers some of the highest hydroelectric power potential in the country from its numerous rivers. Large swaths of the Alaskan coastline offer wind and geothermal energy potential as well.
Alaska's economy depends heavily on increasingly expensive diesel fuel for heating, transportation, electric power and light. Although wind and hydroelectric power are abundant and underdeveloped, proposals for statewide energy systems (e.g. with special single-wire earth return#Use in interties, low-cost electric interties) were judged uneconomical (at the time of the report, 2001) due to low (less than 50¢/gal) fuel prices, long distances and low population. The cost of a gallon of gas in urban Alaska today is usually thirty to sixty cents higher than the national average; prices in rural areas are generally significantly higher but vary widely depending on transportation costs, seasonal usage peaks, nearby petroleum development infrastructure and many other factors.
Alaska has vast energy resources, although its oil reserves have been largely depleted. Major oil and gas reserves were found in the Alaska North Slope (ANS) and Cook Inlet basins, but according to the Energy Information Administration, by February 2014 Alaska had fallen to fourth place in the nation in crude oil production after Texas, North Dakota, and California. Prudhoe Bay on Alaska's North Slope is still the second highest-yielding oil field in the United States, typically producing about , although by early 2014 North Dakota's Bakken Formation was producing over . Prudhoe Bay was the largest conventional oil field ever discovered in North America, but was much smaller than Canada's enormous Athabasca oil sands field, which by 2014 was producing about of unconventional oil, and had hundreds of years of producible reserves at that rate.
The Trans-Alaska Pipeline can transport and pump up to of crude oil per day, more than any other crude oil pipeline in the United States. Additionally, substantial coal deposits are found in Alaska's bituminous, sub-bituminous, and lignite coal basins. The United States Geological Survey estimates that there are of undiscovered, technically recoverable gas from natural gas hydrates on the Alaskan North Slope. Alaska also offers some of the highest hydroelectric power potential in the country from its numerous rivers. Large swaths of the Alaskan coastline offer wind and geothermal energy potential as well.
Alaska's economy depends heavily on increasingly expensive diesel fuel for heating, transportation, electric power and light. Although wind and hydroelectric power are abundant and underdeveloped, proposals for statewide energy systems (e.g. with special single-wire earth return#Use in interties, low-cost electric interties) were judged uneconomical (at the time of the report, 2001) due to low (less than 50¢/gal) fuel prices, long distances and low population. The cost of a gallon of gas in urban Alaska today is usually thirty to sixty cents higher than the national average; prices in rural areas are generally significantly higher but vary widely depending on transportation costs, seasonal usage peaks, nearby petroleum development infrastructure and many other factors.

 Some of Alaska's popular annual events are the Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race from Anchorage to Nome, World Ice Art Championships in Fairbanks, the Blueberry Festival and Alaska Hummingbird Festival in Ketchikan, Alaska, Ketchikan, the Sitka Whale Fest, and the Stikine River Garnet Fest in Wrangell, Alaska, Wrangell. The Stikine River attracts the largest springtime concentration of American bald eagles in the world.
The Alaska Native Heritage Center celebrates the rich heritage of Alaska's 11 cultural groups. Their purpose is to encourage cross-cultural exchanges among all people and enhance self-esteem among Native people. The Alaska Native Arts Foundation promotes and markets Native art from all regions and cultures in the State, using the internet.
Some of Alaska's popular annual events are the Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race from Anchorage to Nome, World Ice Art Championships in Fairbanks, the Blueberry Festival and Alaska Hummingbird Festival in Ketchikan, Alaska, Ketchikan, the Sitka Whale Fest, and the Stikine River Garnet Fest in Wrangell, Alaska, Wrangell. The Stikine River attracts the largest springtime concentration of American bald eagles in the world.
The Alaska Native Heritage Center celebrates the rich heritage of Alaska's 11 cultural groups. Their purpose is to encourage cross-cultural exchanges among all people and enhance self-esteem among Native people. The Alaska Native Arts Foundation promotes and markets Native art from all regions and cultures in the State, using the internet.
 Alaska's first independent picture entirely made in Alaska was ''The Chechahcos'', produced by Alaskan businessman Austin E. Lathrop and filmed in and around Anchorage. Released in 1924 by the Alaska Moving Picture Corporation, it was the only film the company made.
One of the most prominent movies filmed in Alaska is Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer, MGM's ''Eskimo/Mala The Magnificent'', starring Alaska Native Ray Mala. In 1932, an expedition set out from MGM's studios in Hollywood to Alaska to film what was then billed as "The Biggest Picture Ever Made". Upon arriving in Alaska, they set up "Camp Hollywood" in Northwest Alaska, where they lived during the duration of the filming. Louis B. Mayer spared no expense in spite of the remote location, going so far as to hire the chef from the Roosevelt Hotel (Hollywood), Hotel Roosevelt in Hollywood to prepare meals.
When ''Eskimo'' premiered at the Astor Theatre, New York City, Astor Theatre in New York City, the studio received the largest amount of feedback in its history. ''Eskimo'' was critically acclaimed and released worldwide; as a result, Mala became an international movie star. ''Eskimo'' won the first Oscar for Academy Award for Best Film Editing, Best Film Editing at the Academy Awards, and showcased and preserved aspects of Inupiat people, Inupiat culture on film.
The 1983 Disney movie ''Never Cry Wolf (film), Never Cry Wolf'' was at least partially shot in Alaska. The 1991 film ''White Fang (1991 film), White Fang'', based on Jack London's 1906 novel and starring Ethan Hawke, was filmed in and around Haines, Alaska, Haines. Steven Seagal's 1994 ''On Deadly Ground'', starring Michael Caine, was filmed in part at the Worthington Glacier near Valdez. The 1999 John Sayles film ''Limbo (1999 film), Limbo'', starring David Strathairn, Mary Elizabeth Mastrantonio, and Kris Kristofferson, was filmed in Juneau.
The psychological thriller ''Insomnia (2002 film), Insomnia'', starring Al Pacino and Robin Williams, was shot in Canada, but was set in Alaska. The 2007 film directed by Sean Penn, ''Into the Wild (film), Into The Wild'', was partially filmed and set in Alaska. The film, which is based on the novel of the same name, follows the adventures of Christopher McCandless, who died in a remote abandoned bus along the Stampede Trail west of Healy, Alaska, Healy in 1992.
Many films and television shows set in Alaska are not filmed there; for example, ''Northern Exposure'', set in the fictional town of Cicely, Alaska, was filmed in Roslyn, Washington. The 2007 horror feature ''30 Days of Night (film), 30 Days of Night'' is set in Utqiaġvik, Alaska, Barrow, Alaska, but was filmed in New Zealand.
Many reality television shows are filmed in Alaska. In 2011, the ''Anchorage Daily News'' found ten set in the state.
The 2020 videogame Tell Me Why (video game), ''Tell Me Why'' (video game) takes place around Southern Alaska and includes representation of Tlingit culture.
Alaska's first independent picture entirely made in Alaska was ''The Chechahcos'', produced by Alaskan businessman Austin E. Lathrop and filmed in and around Anchorage. Released in 1924 by the Alaska Moving Picture Corporation, it was the only film the company made.
One of the most prominent movies filmed in Alaska is Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer, MGM's ''Eskimo/Mala The Magnificent'', starring Alaska Native Ray Mala. In 1932, an expedition set out from MGM's studios in Hollywood to Alaska to film what was then billed as "The Biggest Picture Ever Made". Upon arriving in Alaska, they set up "Camp Hollywood" in Northwest Alaska, where they lived during the duration of the filming. Louis B. Mayer spared no expense in spite of the remote location, going so far as to hire the chef from the Roosevelt Hotel (Hollywood), Hotel Roosevelt in Hollywood to prepare meals.
When ''Eskimo'' premiered at the Astor Theatre, New York City, Astor Theatre in New York City, the studio received the largest amount of feedback in its history. ''Eskimo'' was critically acclaimed and released worldwide; as a result, Mala became an international movie star. ''Eskimo'' won the first Oscar for Academy Award for Best Film Editing, Best Film Editing at the Academy Awards, and showcased and preserved aspects of Inupiat people, Inupiat culture on film.
The 1983 Disney movie ''Never Cry Wolf (film), Never Cry Wolf'' was at least partially shot in Alaska. The 1991 film ''White Fang (1991 film), White Fang'', based on Jack London's 1906 novel and starring Ethan Hawke, was filmed in and around Haines, Alaska, Haines. Steven Seagal's 1994 ''On Deadly Ground'', starring Michael Caine, was filmed in part at the Worthington Glacier near Valdez. The 1999 John Sayles film ''Limbo (1999 film), Limbo'', starring David Strathairn, Mary Elizabeth Mastrantonio, and Kris Kristofferson, was filmed in Juneau.
The psychological thriller ''Insomnia (2002 film), Insomnia'', starring Al Pacino and Robin Williams, was shot in Canada, but was set in Alaska. The 2007 film directed by Sean Penn, ''Into the Wild (film), Into The Wild'', was partially filmed and set in Alaska. The film, which is based on the novel of the same name, follows the adventures of Christopher McCandless, who died in a remote abandoned bus along the Stampede Trail west of Healy, Alaska, Healy in 1992.
Many films and television shows set in Alaska are not filmed there; for example, ''Northern Exposure'', set in the fictional town of Cicely, Alaska, was filmed in Roslyn, Washington. The 2007 horror feature ''30 Days of Night (film), 30 Days of Night'' is set in Utqiaġvik, Alaska, Barrow, Alaska, but was filmed in New Zealand.
Many reality television shows are filmed in Alaska. In 2011, the ''Anchorage Daily News'' found ten set in the state.
The 2020 videogame Tell Me Why (video game), ''Tell Me Why'' (video game) takes place around Southern Alaska and includes representation of Tlingit culture.
 The Alaska Department of Education and Early Development administers many List of school districts in Alaska, school districts in Alaska. In addition, the state operates a boarding school, Mt. Edgecumbe High School in
The Alaska Department of Education and Early Development administers many List of school districts in Alaska, school districts in Alaska. In addition, the state operates a boarding school, Mt. Edgecumbe High School in  Alaska's well-developed state-owned ferry system (known as the Alaska Marine Highway) serves the cities of Southeast Alaska, southeast, the Gulf Coast and the Alaska Peninsula. The ferries transport vehicles as well as passengers. The system also operates a ferry service from Bellingham, Washington and Prince Rupert, British Columbia, in Canada through the Inside Passage to Skagway, Alaska, Skagway. The Inter-Island Ferry Authority also serves as an important marine link for many communities in the Prince of Wales Island (Alaska), Prince of Wales Island region of Southeast and works in concert with the Alaska Marine Highway.
In recent years, cruise lines have created a summertime tourism market, mainly connecting the Pacific Northwest to Southeast Alaska and, to a lesser degree, towns along Alaska's gulf coast. The population of Ketchikan, Alaska, Ketchikan for example fluctuates dramatically on many days—up to four large cruise ships can dock there at the same time.
Alaska's well-developed state-owned ferry system (known as the Alaska Marine Highway) serves the cities of Southeast Alaska, southeast, the Gulf Coast and the Alaska Peninsula. The ferries transport vehicles as well as passengers. The system also operates a ferry service from Bellingham, Washington and Prince Rupert, British Columbia, in Canada through the Inside Passage to Skagway, Alaska, Skagway. The Inter-Island Ferry Authority also serves as an important marine link for many communities in the Prince of Wales Island (Alaska), Prince of Wales Island region of Southeast and works in concert with the Alaska Marine Highway.
In recent years, cruise lines have created a summertime tourism market, mainly connecting the Pacific Northwest to Southeast Alaska and, to a lesser degree, towns along Alaska's gulf coast. The population of Ketchikan, Alaska, Ketchikan for example fluctuates dramatically on many days—up to four large cruise ships can dock there at the same time.
 The bulk of remaining commercial flight offerings come from small regional commuter airlines such as Ravn Alaska, PenAir, and Frontier Flying Service. The smallest towns and villages must rely on scheduled or chartered bush flying services using general aviation aircraft such as the Cessna Caravan, the most popular aircraft in use in the state. Much of this service can be attributed to the Alaska bypass mail program which subsidizes bulk mail delivery to Alaskan rural communities. The program requires 70% of that subsidy to go to carriers who offer passenger service to the communities.
Many communities have small air taxi services. These operations originated from the demand for customized transport to remote areas. Perhaps the most quintessentially Alaskan plane is the bush seaplane. The world's busiest seaplane base is Lake Hood Seaplane Base, Lake Hood, located next to Ted Stevens Anchorage International Airport, where flights bound for remote villages without an airstrip carry passengers, cargo, and many items from stores and warehouse clubs.
In 2006, Alaska had the highest number of pilots per capita of any U.S. state. In Alaska there are 8,795 active pilot certificates as of 2020.
Of these, there are 2,507 Private, 1,496 Commercial, 2,180 Airline Transport, and 2,239 student pilots. There are also 3,987 pilots with an Instrument rating and 1,511 Flight Instructors.
The bulk of remaining commercial flight offerings come from small regional commuter airlines such as Ravn Alaska, PenAir, and Frontier Flying Service. The smallest towns and villages must rely on scheduled or chartered bush flying services using general aviation aircraft such as the Cessna Caravan, the most popular aircraft in use in the state. Much of this service can be attributed to the Alaska bypass mail program which subsidizes bulk mail delivery to Alaskan rural communities. The program requires 70% of that subsidy to go to carriers who offer passenger service to the communities.
Many communities have small air taxi services. These operations originated from the demand for customized transport to remote areas. Perhaps the most quintessentially Alaskan plane is the bush seaplane. The world's busiest seaplane base is Lake Hood Seaplane Base, Lake Hood, located next to Ted Stevens Anchorage International Airport, where flights bound for remote villages without an airstrip carry passengers, cargo, and many items from stores and warehouse clubs.
In 2006, Alaska had the highest number of pilots per capita of any U.S. state. In Alaska there are 8,795 active pilot certificates as of 2020.
Of these, there are 2,507 Private, 1,496 Commercial, 2,180 Airline Transport, and 2,239 student pilots. There are also 3,987 pilots with an Instrument rating and 1,511 Flight Instructors.
 Like all other U.S. states, Alaska is governed as a republic, with three separation of powers, branches of government: an executive branch consisting of the governor of Alaska and their appointees which head executive departments; a legislative branch consisting of the Alaska House of Representatives and Alaska Senate; and a judicial branch consisting of the Alaska Supreme Court and lower courts.
The state of Alaska employs approximately 16,000 people statewide.
The Alaska Legislature consists of a 40-member Alaska House of Representatives, House of Representatives and a 20-member Alaska Senate, Senate. Senators serve four-year terms and House members two. The governor of Alaska serves four-year terms. The List of Lieutenant Governors of Alaska, lieutenant governor runs separately from the governor in the Primary election, primaries, but during the general election, the nominee for governor and nominee for lieutenant governor run together on the same ticket.
Alaska's court system has four levels: the Alaska Supreme Court, the Alaska Court of Appeals, the superior courts and the district courts. The superior and district courts are trial courts. Superior courts are courts of general jurisdiction, while district courts hear only certain types of cases, including misdemeanor criminal cases and civil cases valued up to $100,000.
The Supreme Court and the Court of Appeals are appellate courts. The Court of Appeals is required to hear appeals from certain lower-court decisions, including those regarding criminal prosecutions, juvenile delinquency, and habeas corpus. The Supreme Court hears civil appeals and may in its discretion hear criminal appeals.
Like all other U.S. states, Alaska is governed as a republic, with three separation of powers, branches of government: an executive branch consisting of the governor of Alaska and their appointees which head executive departments; a legislative branch consisting of the Alaska House of Representatives and Alaska Senate; and a judicial branch consisting of the Alaska Supreme Court and lower courts.
The state of Alaska employs approximately 16,000 people statewide.
The Alaska Legislature consists of a 40-member Alaska House of Representatives, House of Representatives and a 20-member Alaska Senate, Senate. Senators serve four-year terms and House members two. The governor of Alaska serves four-year terms. The List of Lieutenant Governors of Alaska, lieutenant governor runs separately from the governor in the Primary election, primaries, but during the general election, the nominee for governor and nominee for lieutenant governor run together on the same ticket.
Alaska's court system has four levels: the Alaska Supreme Court, the Alaska Court of Appeals, the superior courts and the district courts. The superior and district courts are trial courts. Superior courts are courts of general jurisdiction, while district courts hear only certain types of cases, including misdemeanor criminal cases and civil cases valued up to $100,000.
The Supreme Court and the Court of Appeals are appellate courts. The Court of Appeals is required to hear appeals from certain lower-court decisions, including those regarding criminal prosecutions, juvenile delinquency, and habeas corpus. The Supreme Court hears civil appeals and may in its discretion hear criminal appeals.
 Alaska regularly supports Republican Party (United States), Republicans in presidential elections and has done so since statehood. Republicans have won the state's Electoral College (United States), electoral college votes in all but one election that it has participated in (1964 United States presidential election, 1964). No state has voted for a Democratic Party (United States), Democratic presidential candidate fewer times. Alaska was carried by Democratic nominee Lyndon B. Johnson during his landslide election in 1964 United States presidential election, 1964, while the 1960 United States presidential election, 1960 and 1968 United States presidential election, 1968 elections were close. Since 1972 United States presidential election, 1972, however, Republicans have carried the state by large margins. In 2008 United States presidential election, 2008, Republican John McCain defeated Democrat Barack Obama in Alaska, 59.49% to 37.83%. McCain's running mate was Sarah Palin, the state's governor and the first Alaskan on a major party ticket. Obama lost Alaska again in 2012 United States presidential election, 2012, but he captured 40% of the state's vote in that election, making him the first Democrat to do so since 1968. In 2020 United States presidential election, 2020, Joe Biden received 42.77% of the vote for president, marking the high point for a Democratic presidential candidate since Johnson's 1964 victory.
The The Bush (Alaska), Alaska Bush, central Juneau, midtown and downtown Anchorage, and the areas surrounding the
Alaska regularly supports Republican Party (United States), Republicans in presidential elections and has done so since statehood. Republicans have won the state's Electoral College (United States), electoral college votes in all but one election that it has participated in (1964 United States presidential election, 1964). No state has voted for a Democratic Party (United States), Democratic presidential candidate fewer times. Alaska was carried by Democratic nominee Lyndon B. Johnson during his landslide election in 1964 United States presidential election, 1964, while the 1960 United States presidential election, 1960 and 1968 United States presidential election, 1968 elections were close. Since 1972 United States presidential election, 1972, however, Republicans have carried the state by large margins. In 2008 United States presidential election, 2008, Republican John McCain defeated Democrat Barack Obama in Alaska, 59.49% to 37.83%. McCain's running mate was Sarah Palin, the state's governor and the first Alaskan on a major party ticket. Obama lost Alaska again in 2012 United States presidential election, 2012, but he captured 40% of the state's vote in that election, making him the first Democrat to do so since 1968. In 2020 United States presidential election, 2020, Joe Biden received 42.77% of the vote for president, marking the high point for a Democratic presidential candidate since Johnson's 1964 victory.
The The Bush (Alaska), Alaska Bush, central Juneau, midtown and downtown Anchorage, and the areas surrounding the  In a 2020 study, Alaska was ranked as the 15th hardest state for citizens to vote in.
In the 2020 Alaska elections, 2020 election cycle, Alaskan voters approved Ballot Measure 2. The measure passed by a margin of 1.1%, or about 4,000 votes. The measure requires campaigns to disclose the original source and any intermediaries for campaign contributions over $2,000. The measure also establishes Nonpartisan blanket primary, non-partisan blanket primaries for statewide elections (like in Washington (state)#Elections, Washington state and California#Government and politics, California) and Instant-runoff voting, ranked-choice voting (like in Maine#Politics, Maine). Measure 2 makes Alaska the third state with Jungle primary, jungle primaries for all statewide races, the second state with ranked voting, ranked choice voting, and the only state with both.
The first race to use the new system of elections was the 2022 Alaska's at-large congressional district special election, 2022 special election to fill Alaska's only U.S. House seat, left vacant by the death of Don Young, won by Mary Peltola, the first Democrat to win the House seat since 1972 United States House of Representatives election in Alaska, 1972, and the first Alaska Natives, Alaskan Native to be elected to the United States Congress in history.
In a 2020 study, Alaska was ranked as the 15th hardest state for citizens to vote in.
In the 2020 Alaska elections, 2020 election cycle, Alaskan voters approved Ballot Measure 2. The measure passed by a margin of 1.1%, or about 4,000 votes. The measure requires campaigns to disclose the original source and any intermediaries for campaign contributions over $2,000. The measure also establishes Nonpartisan blanket primary, non-partisan blanket primaries for statewide elections (like in Washington (state)#Elections, Washington state and California#Government and politics, California) and Instant-runoff voting, ranked-choice voting (like in Maine#Politics, Maine). Measure 2 makes Alaska the third state with Jungle primary, jungle primaries for all statewide races, the second state with ranked voting, ranked choice voting, and the only state with both.
The first race to use the new system of elections was the 2022 Alaska's at-large congressional district special election, 2022 special election to fill Alaska's only U.S. House seat, left vacant by the death of Don Young, won by Mary Peltola, the first Democrat to win the House seat since 1972 United States House of Representatives election in Alaska, 1972, and the first Alaska Natives, Alaskan Native to be elected to the United States Congress in history.