Ahmad I Al-Mansur on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ahmad al-Mansur ( ar, أبو العباس أحمد المنصور, Ahmad Abu al-Abbas al-Mansur, also al-Mansur al-Dahabbi (the Golden), ar, أحمد المنصور الذهبي; and Ahmed al-Mansour; 1549 in
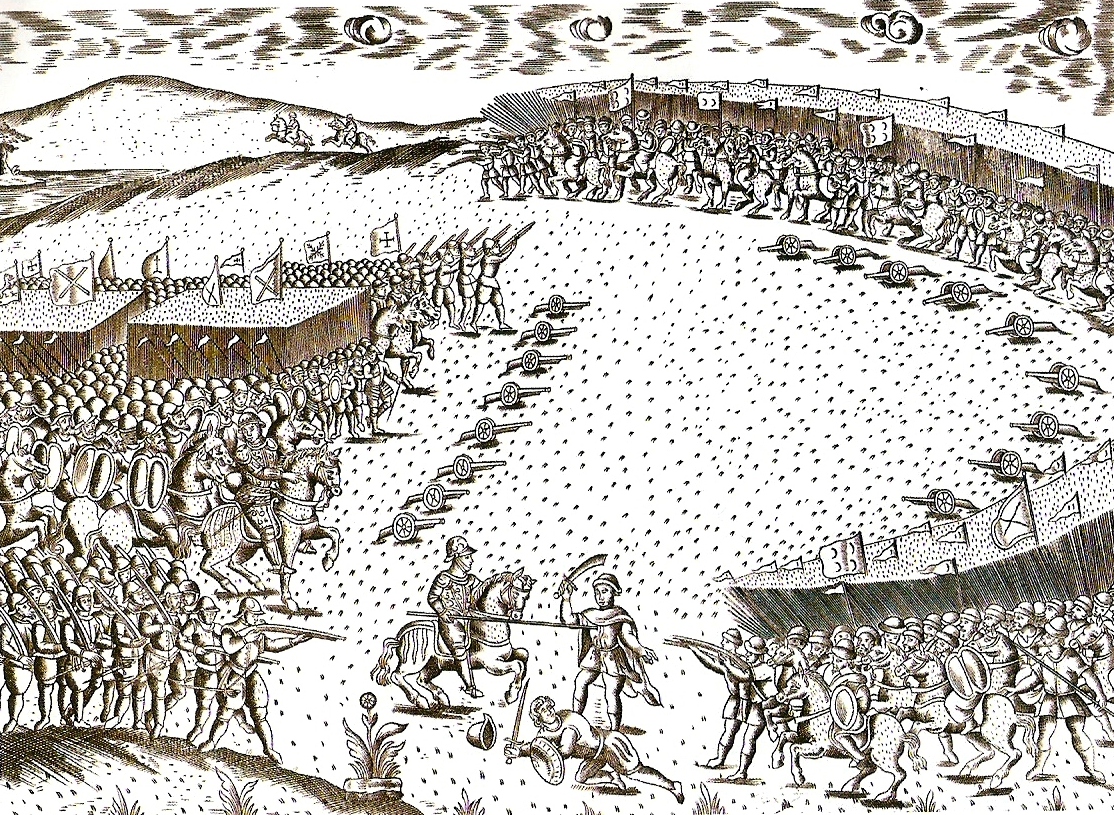

 Al-Mansur had ambivalent relations with the Ottoman Empire. At the very start of his reign he formally recognized the suzerainty of the Ottoman sultan, as
Al-Mansur had ambivalent relations with the Ottoman Empire. At the very start of his reign he formally recognized the suzerainty of the Ottoman sultan, as  In response to the removal of his name from Friday prayers, Murad III began preparations for an attack on Morocco. After getting word of this, al-Mansur rushed to send an ambassador to Istanbul with sizeable gifts and the attack was cancelled. He paid a tribute of over 100,000 gold coins, agreed to show respect to the Ottoman sultan and in return he was left alone. The embassy nearly failed to reach Istanbul due to the opposition of Occhiali, Uluç (later known as Kılıç Ali Paşa), the Ottoman Grand Admiral in Algiers who hoped to have Morocco invaded and incorporated into Ottoman Algeria's sphere of influence.
In 1582, al-Mansur was also forced to agree to a special Ottoman “protection” over Morocco and to pay a certain tribute in order to stop the attacks from Barbary pirates, Algerian corsairs on the Moroccan coast and on Moroccan ships. In 1583, the Saadian and Ottoman sultans even tentatively discussed a joint military operation against the Spanish in Oran. Al-Mansur enjoyed peaceful relations with the Ottoman Empire afterwards and respected its sovereignty, but also played the Ottomans and European powers against each other and issued propaganda that undermined the Ottoman sultan's claim as leader of all Muslims. He continued to send a payment to Istanbul every year, which the Saadians interpreted as a "gift" to the Ottomans while the Ottomans considered it a "tribute".
In 1587 Uluç died and a change in the Ottoman administration in Algiers limited the power of its governors. After this, tensions between the two states further decreased, while the Saadian government further stabilized and its independence became more entrenched. Al-Mansur even felt confident enough after 1587 to drop his regular payments to Murad III. Despite the limits of his power, he officially proclaimed himself Caliphate, caliph in the later part of his reign, seeing himself as rival, rather than subordinate, of the Ottomans, and even as the rightful leader of the Muslim world.
In response to the removal of his name from Friday prayers, Murad III began preparations for an attack on Morocco. After getting word of this, al-Mansur rushed to send an ambassador to Istanbul with sizeable gifts and the attack was cancelled. He paid a tribute of over 100,000 gold coins, agreed to show respect to the Ottoman sultan and in return he was left alone. The embassy nearly failed to reach Istanbul due to the opposition of Occhiali, Uluç (later known as Kılıç Ali Paşa), the Ottoman Grand Admiral in Algiers who hoped to have Morocco invaded and incorporated into Ottoman Algeria's sphere of influence.
In 1582, al-Mansur was also forced to agree to a special Ottoman “protection” over Morocco and to pay a certain tribute in order to stop the attacks from Barbary pirates, Algerian corsairs on the Moroccan coast and on Moroccan ships. In 1583, the Saadian and Ottoman sultans even tentatively discussed a joint military operation against the Spanish in Oran. Al-Mansur enjoyed peaceful relations with the Ottoman Empire afterwards and respected its sovereignty, but also played the Ottomans and European powers against each other and issued propaganda that undermined the Ottoman sultan's claim as leader of all Muslims. He continued to send a payment to Istanbul every year, which the Saadians interpreted as a "gift" to the Ottomans while the Ottomans considered it a "tribute".
In 1587 Uluç died and a change in the Ottoman administration in Algiers limited the power of its governors. After this, tensions between the two states further decreased, while the Saadian government further stabilized and its independence became more entrenched. Al-Mansur even felt confident enough after 1587 to drop his regular payments to Murad III. Despite the limits of his power, he officially proclaimed himself Caliphate, caliph in the later part of his reign, seeing himself as rival, rather than subordinate, of the Ottomans, and even as the rightful leader of the Muslim world.

 Ahmad al-Mansur died in 1603 and was succeeded by his son Zidan Abu Maali, Zidan al-Nasir, who was based in Marrakech, and by Abou Fares Abdallah, who was based in Fes who had only local power. He was buried in the mausoleum of the Saadian Tombs in Marrakech. Well-known writers at his court were Ahmed Mohammed al-Maqqari, Abd al-Aziz al-Fishtali, Ahmad Ibn al-Qadi and Al-Masfiwi.
Through astute diplomacy al-Mansur resisted the demands of the Ottoman sultan, to preserve Moroccan independence. By playing the Europeans and Ottomans against one another, al-Mansur excelled in the art of the balancing of power through diplomacy. Eventually he spent far more than he collected in revenue. He attempted to expand his holdings through conquest, and although initially successful in their military campaign against the Songhai Empire, the Moroccans found it increasingly difficult to maintain control over the conquered locals as time went on. Meanwhile, as the Moroccans continued to struggle in Songhai, their power and prestige on the world stage declined significantly.
Al-Mansur was one of the first authorities to take action on smoking in 1602 towards the end of his reign. The ruler of the Saadi dynasty used the religious tool of fatwa, ''fatwas'' (Islamic legal pronouncements) to discourage the use of tobacco.
Ahmad al-Mansur died in 1603 and was succeeded by his son Zidan Abu Maali, Zidan al-Nasir, who was based in Marrakech, and by Abou Fares Abdallah, who was based in Fes who had only local power. He was buried in the mausoleum of the Saadian Tombs in Marrakech. Well-known writers at his court were Ahmed Mohammed al-Maqqari, Abd al-Aziz al-Fishtali, Ahmad Ibn al-Qadi and Al-Masfiwi.
Through astute diplomacy al-Mansur resisted the demands of the Ottoman sultan, to preserve Moroccan independence. By playing the Europeans and Ottomans against one another, al-Mansur excelled in the art of the balancing of power through diplomacy. Eventually he spent far more than he collected in revenue. He attempted to expand his holdings through conquest, and although initially successful in their military campaign against the Songhai Empire, the Moroccans found it increasingly difficult to maintain control over the conquered locals as time went on. Meanwhile, as the Moroccans continued to struggle in Songhai, their power and prestige on the world stage declined significantly.
Al-Mansur was one of the first authorities to take action on smoking in 1602 towards the end of his reign. The ruler of the Saadi dynasty used the religious tool of fatwa, ''fatwas'' (Islamic legal pronouncements) to discourage the use of tobacco.
Fes
Fez or Fes (; ar, فاس, fās; zgh, ⴼⵉⵣⴰⵣ, fizaz; french: Fès) is a city in northern inland Morocco and the capital of the Fès-Meknès administrative region. It is the second largest city in Morocco, with a population of 1.11 mi ...
– 25 August 1603, Fes
Fez or Fes (; ar, فاس, fās; zgh, ⴼⵉⵣⴰⵣ, fizaz; french: Fès) is a city in northern inland Morocco and the capital of the Fès-Meknès administrative region. It is the second largest city in Morocco, with a population of 1.11 mi ...
) was the Saadi Sultan
Sultan (; ar, سلطان ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it ...
of Morocco from 1578 to his death in 1603, the sixth and most famous of all rulers of the Saadis. Ahmad al-Mansur was an important figure in both Europe and Africa in the sixteenth century. His powerful army and strategic location made him an important power player in the late Renaissance period. He has been described as "a man of profound Islamic learning, a lover of books, calligraphy and mathematics, as well as a connoisseur of mystical texts and a lover of scholarly discussions."
Early life
Ahmad was the fifth son of Mohammed ash-Sheikh who was the first Saadi sultan of Morocco. His mother wasLalla Masuda
Mas'uda al-Wizkitiya (; died 1591), known popularly in Morocco as Lala 'Auda () and in Western sources as Lalla Masuda, was a Moroccan political figure in the Saadi Dynasty. She is remembered for her humanitarian, charity, political, and developmen ...
. After the murder of their father, Mohammed in 1557 and the following struggle for power, the two brothers Ahmad al-Mansur and Abd al-Malik
Abdul Malik ( ar, عبد الملك) is an Arabic (Muslim or Christian) male given name and, in modern usage, surname. It is built from the Arabic words '' Abd'', ''al-'' and '' Malik''. The name means "servant of the King", in the Christian insta ...
had to flee their elder brother Abdallah al-Ghalib (1557–1574), leave Morocco and stay abroad until 1576. The two brothers spent 17 years among the Ottomans
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
between the Regency of Algiers and Constantinople, and benefited from Ottoman training and contacts with Ottoman culture. More generally, he "received an extensive education in Islamic religious and secular sciences, including theology, law, poetry, grammar, lexicography, exegesis, geometry, arithmetics and algebra, and astronomy."
Battle of Ksar el Kebir
In 1578, Ahmad's brother, SultanAbu Marwan Abd al-Malik I
Abu Marwan Abd al-Malik I ( ar, أبو مروان عبد الملك الغازي), often simply Abd al-Malik or Mulay Abdelmalek, (b. 1541 – d. 4 August 1578) was the Saadian Sultan of Morocco from 1576 until his death right after the Battle o ...
, died in battle against the Portuguese army at Ksar-el-Kebir. Ahmad was named his brother's successor and began his reign amid newly won prestige and wealth from the ransom of Portuguese captives.
Rule (1578–1603)
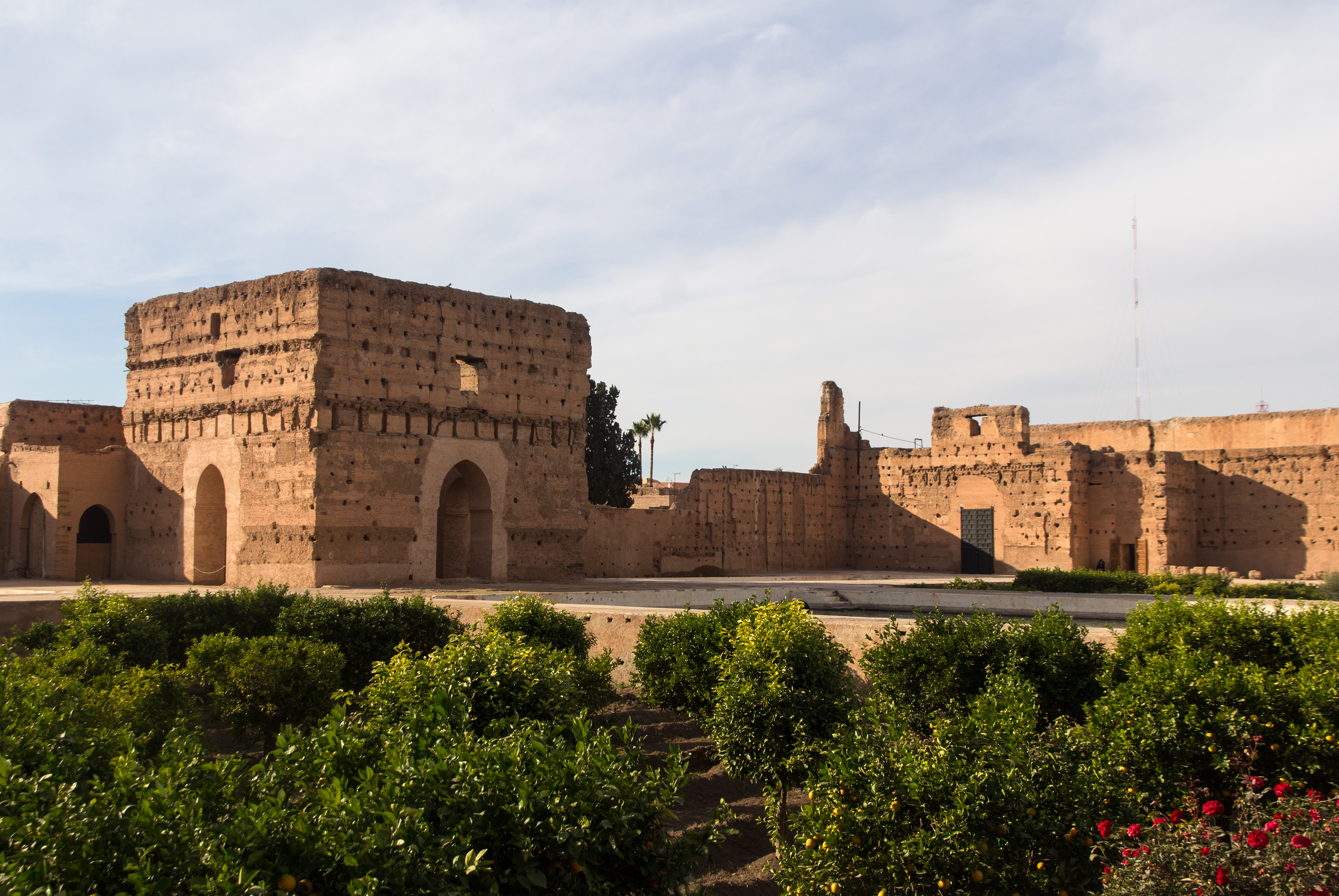
Al-Mansur began his reign by leveraging his dominant position with the vanquished Portuguese during prisoner ransom talks, the collection of which filled the Moroccan royal coffers. Shortly after, he commissioned the great architectural symbol of this new birth of Moroccan power, theEl Badi Palace
El Badi Palace ( ar, قصر البديع, lit=Palace of Wonder/Brilliance, also frequently translated as the "Incomparable Palace") or Badi' Palace is a ruined palace located in Marrakesh, Morocco. It was commissioned by the sultan Ahmad al-Mans ...
in Marrakesh
Marrakesh or Marrakech ( or ; ar, مراكش, murrākuš, ; ber, ⵎⵕⵕⴰⴽⵛ, translit=mṛṛakc}) is the fourth largest city in the Kingdom of Morocco. It is one of the four Imperial cities of Morocco and is the capital of the Marrakes ...
, a huge and lavish riad Riad or Riyad may refer to:
* Riyadh, the capital city of Saudi Arabia
* Riyad, Mauritania
* Riad (name), a given name and surname (including a list of people with the name, also Riyad or Riyadh)
* Riad (architecture), a traditional Moroccan house ...
-style palace which he used to receive ambassadors and to host celebrations. Construction began in December 1578 and was only finished in 1593 or 1594.
Eventually the coffers began to run dry due to the great expense of supporting the military, extensive spy services, the palace and other urban building projects, a royal lifestyle and a propaganda campaign aimed at building support for his controversial claim to the Caliphate.

Relations with Europe
Morocco's standing with the Christian states was still in flux. The Spaniards and the Portuguese were seen as theinfidel
An infidel (literally "unfaithful") is a person accused of disbelief in the central tenets of one's own religion, such as members of another religion, or the irreligious.
Infidel is an ecclesiastical term in Christianity around which the Church ...
, but al-Mansur knew that the only way his sultanate would thrive was to continue to benefit from alliances with other Christian economies. To do that, Morocco had to control sizeable gold resources of its own. Accordingly, al-Mansur was drawn irresistibly to the trans-Saharan gold trade of the Songhai in hopes of solving Morocco's economic deficit with Europe.
Al-Mansur developed friendly relations with England in view of an Anglo-Moroccan alliance
The Anglo-Moroccan alliance''Britain and Morocco during the embassy of John Drummond Hay, 1845-1886'' Khalid Ben Srhir, Malcolm Williams, Gavin Waterson p.13-1/ref> was established at the end of the 16th century and the early 17th century between t ...
. In 1600 he sent his Secretary Abd el-Ouahed ben Messaoud as ambassador to the Court of Queen Elizabeth I of England to negotiate an alliance against Spain.
Al-Mansur also wrote about reconquering al-Andalus for Islam back from the Christian Spanish. In a letter of 1 May 1601 he wrote that he also had ambitions to colonize the New World and settle it with Moroccans. He envisioned that Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
would prevail in the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
and the Mahdi would be proclaimed from the two sides of the oceans.
Al-Mansur had French physicians at his court. Arnoult de Lisle was physician to the sultan from 1588 to 1598. He was then succeeded by Étienne Hubert d'Orléans from 1598 to 1600. Both in turn returned to France to become professors of Arabic at the Collège de France, and continued with their diplomatic endeavours.
Relations with Ottoman Empire
 Al-Mansur had ambivalent relations with the Ottoman Empire. At the very start of his reign he formally recognized the suzerainty of the Ottoman sultan, as
Al-Mansur had ambivalent relations with the Ottoman Empire. At the very start of his reign he formally recognized the suzerainty of the Ottoman sultan, as Abd al-Malik
Abdul Malik ( ar, عبد الملك) is an Arabic (Muslim or Christian) male given name and, in modern usage, surname. It is built from the Arabic words '' Abd'', ''al-'' and '' Malik''. The name means "servant of the King", in the Christian insta ...
had done, while still remaining de facto independent. However he quickly alienated the Ottoman sultan when he favorably received the Spanish embassy in 1579, who brought him lavish gifts, and then reportedly trampled the symbol of Ottoman suzerainty before a Spanish embassy in 1581. He also suspected that the Ottomans were involved in the first rebellions against him in his early reign. As a result, he minted coins in his own name and had Friday prayers and the '' khutba'' delivered in his name instead of in the name of Murad III
Murad III ( ota, مراد ثالث, Murād-i sālis; tr, III. Murad; 4 July 1546 – 16 January 1595) was Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1574 until his death in 1595. His rule saw battles with the Habsburgs and exhausting wars with the Saf ...
, the Ottoman sultan.
 In response to the removal of his name from Friday prayers, Murad III began preparations for an attack on Morocco. After getting word of this, al-Mansur rushed to send an ambassador to Istanbul with sizeable gifts and the attack was cancelled. He paid a tribute of over 100,000 gold coins, agreed to show respect to the Ottoman sultan and in return he was left alone. The embassy nearly failed to reach Istanbul due to the opposition of Occhiali, Uluç (later known as Kılıç Ali Paşa), the Ottoman Grand Admiral in Algiers who hoped to have Morocco invaded and incorporated into Ottoman Algeria's sphere of influence.
In 1582, al-Mansur was also forced to agree to a special Ottoman “protection” over Morocco and to pay a certain tribute in order to stop the attacks from Barbary pirates, Algerian corsairs on the Moroccan coast and on Moroccan ships. In 1583, the Saadian and Ottoman sultans even tentatively discussed a joint military operation against the Spanish in Oran. Al-Mansur enjoyed peaceful relations with the Ottoman Empire afterwards and respected its sovereignty, but also played the Ottomans and European powers against each other and issued propaganda that undermined the Ottoman sultan's claim as leader of all Muslims. He continued to send a payment to Istanbul every year, which the Saadians interpreted as a "gift" to the Ottomans while the Ottomans considered it a "tribute".
In 1587 Uluç died and a change in the Ottoman administration in Algiers limited the power of its governors. After this, tensions between the two states further decreased, while the Saadian government further stabilized and its independence became more entrenched. Al-Mansur even felt confident enough after 1587 to drop his regular payments to Murad III. Despite the limits of his power, he officially proclaimed himself Caliphate, caliph in the later part of his reign, seeing himself as rival, rather than subordinate, of the Ottomans, and even as the rightful leader of the Muslim world.
In response to the removal of his name from Friday prayers, Murad III began preparations for an attack on Morocco. After getting word of this, al-Mansur rushed to send an ambassador to Istanbul with sizeable gifts and the attack was cancelled. He paid a tribute of over 100,000 gold coins, agreed to show respect to the Ottoman sultan and in return he was left alone. The embassy nearly failed to reach Istanbul due to the opposition of Occhiali, Uluç (later known as Kılıç Ali Paşa), the Ottoman Grand Admiral in Algiers who hoped to have Morocco invaded and incorporated into Ottoman Algeria's sphere of influence.
In 1582, al-Mansur was also forced to agree to a special Ottoman “protection” over Morocco and to pay a certain tribute in order to stop the attacks from Barbary pirates, Algerian corsairs on the Moroccan coast and on Moroccan ships. In 1583, the Saadian and Ottoman sultans even tentatively discussed a joint military operation against the Spanish in Oran. Al-Mansur enjoyed peaceful relations with the Ottoman Empire afterwards and respected its sovereignty, but also played the Ottomans and European powers against each other and issued propaganda that undermined the Ottoman sultan's claim as leader of all Muslims. He continued to send a payment to Istanbul every year, which the Saadians interpreted as a "gift" to the Ottomans while the Ottomans considered it a "tribute".
In 1587 Uluç died and a change in the Ottoman administration in Algiers limited the power of its governors. After this, tensions between the two states further decreased, while the Saadian government further stabilized and its independence became more entrenched. Al-Mansur even felt confident enough after 1587 to drop his regular payments to Murad III. Despite the limits of his power, he officially proclaimed himself Caliphate, caliph in the later part of his reign, seeing himself as rival, rather than subordinate, of the Ottomans, and even as the rightful leader of the Muslim world.
Conquests
Annexation of Saharan oases
In 1583 after the dispatch of al-Mansur led by the commander Abu Abdullah Muhammad bin Baraka and Abu Al-Abbas Ahmed Ibn Al-Haddad Al-Omari. The march of the army began fromMarrakesh
Marrakesh or Marrakech ( or ; ar, مراكش, murrākuš, ; ber, ⵎⵕⵕⴰⴽⵛ, translit=mṛṛakc}) is the fourth largest city in the Kingdom of Morocco. It is one of the four Imperial cities of Morocco and is the capital of the Marrakes ...
, and they arrived after 70 days, where they initially called for obedience and warning, after the tribal elders refused to comply, the war began. The annexed territories contained Tuat, Jouda, Tamentit, Tamantit, Tabelbala, Ouargla, Ourgla, Tsabit, Tekorareen, and others.
Annexation of Chinguetti
The Saadi Sultanate, Saadians repeatedly tried to control Chinguetti, and the most prominent attempts were made during the reign of Sultan Mohammed al-Shaykh, Muhammad al-Shaykh, but control of it did not come until the reign of Ahmed al-Mansur, who stripped a campaign in 1584 led by Muhammad bin Salem in which he managed to seize control of Chinguetti, modern day Mauritania.Songhai campaign
The Songhai Empire was a West Africa, West African state centered in eastern Mali. From the early 15th to the late 16th century, it was one of the List of largest empires, largest African empires in history. On October 16, 1590, Ahmad took advantage of the recent civil strife in the empire and dispatched an army of 4,000 men across the Sahara desert under the command of converted Spain, Spaniard Judar Pasha.. Though the Songhai met them at the Battle of Tondibi with a force of 40,000, they lacked the Moroccan's gunpowder weapons and quickly fled. Ahmad advanced, sacking the Songhai cities of Timbuktu and Djenné, as well as the capital Gao. Despite these initial successes, the logistics of controlling a territory across the Sahara soon grew too difficult, and the Saadians lost control of the cities not long after 1620.Legacy

 Ahmad al-Mansur died in 1603 and was succeeded by his son Zidan Abu Maali, Zidan al-Nasir, who was based in Marrakech, and by Abou Fares Abdallah, who was based in Fes who had only local power. He was buried in the mausoleum of the Saadian Tombs in Marrakech. Well-known writers at his court were Ahmed Mohammed al-Maqqari, Abd al-Aziz al-Fishtali, Ahmad Ibn al-Qadi and Al-Masfiwi.
Through astute diplomacy al-Mansur resisted the demands of the Ottoman sultan, to preserve Moroccan independence. By playing the Europeans and Ottomans against one another, al-Mansur excelled in the art of the balancing of power through diplomacy. Eventually he spent far more than he collected in revenue. He attempted to expand his holdings through conquest, and although initially successful in their military campaign against the Songhai Empire, the Moroccans found it increasingly difficult to maintain control over the conquered locals as time went on. Meanwhile, as the Moroccans continued to struggle in Songhai, their power and prestige on the world stage declined significantly.
Al-Mansur was one of the first authorities to take action on smoking in 1602 towards the end of his reign. The ruler of the Saadi dynasty used the religious tool of fatwa, ''fatwas'' (Islamic legal pronouncements) to discourage the use of tobacco.
Ahmad al-Mansur died in 1603 and was succeeded by his son Zidan Abu Maali, Zidan al-Nasir, who was based in Marrakech, and by Abou Fares Abdallah, who was based in Fes who had only local power. He was buried in the mausoleum of the Saadian Tombs in Marrakech. Well-known writers at his court were Ahmed Mohammed al-Maqqari, Abd al-Aziz al-Fishtali, Ahmad Ibn al-Qadi and Al-Masfiwi.
Through astute diplomacy al-Mansur resisted the demands of the Ottoman sultan, to preserve Moroccan independence. By playing the Europeans and Ottomans against one another, al-Mansur excelled in the art of the balancing of power through diplomacy. Eventually he spent far more than he collected in revenue. He attempted to expand his holdings through conquest, and although initially successful in their military campaign against the Songhai Empire, the Moroccans found it increasingly difficult to maintain control over the conquered locals as time went on. Meanwhile, as the Moroccans continued to struggle in Songhai, their power and prestige on the world stage declined significantly.
Al-Mansur was one of the first authorities to take action on smoking in 1602 towards the end of his reign. The ruler of the Saadi dynasty used the religious tool of fatwa, ''fatwas'' (Islamic legal pronouncements) to discourage the use of tobacco.
Popular culture
* He is featured as the playable leader of the Moroccan civilization in the 2013 computer strategy game ''Civilization V: Brave New World''References
Bibliography
*. *. *. {{DEFAULTSORT:Ahmad Al-Mansur 1549 births 1603 deaths 16th-century Arabs 17th-century Arabs Sultans of Morocco Saadi dynasty People from Marrakesh 17th-century Moroccan people 16th-century Moroccan people People from Fez, Morocco 16th-century monarchs in Africa 17th-century monarchs in Africa