Agomelatine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Agomelatine, sold under the brand names Valdoxan and Thymanax, among others, is an
 The
The

atypical antidepressant
An atypical antidepressant is any antidepressant medication that acts in a manner that is different from that of most other antidepressants. Atypical antidepressants include agomelatine, bupropion, iprindole, mianserin, mirtazapine, nefazod ...
most commonly used to treat major depressive disorder
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive low mood, low self-esteem, and loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities. Intro ...
and generalized anxiety disorder
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is a mental and behavioral disorder, specifically an anxiety disorder characterized by excessive, uncontrollable and often irrational worry about events or activities. Worry often interferes with daily function ...
. One review found that it is as effective as other antidepressants with similar discontinuation rates overall but less discontinuations due to side effects. Another review also found it was similarly effective to many other antidepressants.
Common side effects include weight gain, fatigue, liver problems
Liver disease, or hepatic disease, is any of many diseases of the liver. If long-lasting it is termed chronic liver disease. Although the diseases differ in detail, liver diseases often have features in common.
Signs and symptoms
Some of the s ...
, nausea, headaches, and anxiety. Due to potential liver problems ongoing blood tests are recommended. Its use is not recommended in people with dementia
Dementia is a disorder which manifests as a set of related symptoms, which usually surfaces when the brain is damaged by injury or disease. The symptoms involve progressive impairments in memory, thinking, and behavior, which negatively affe ...
or over the age of 75. There is tentative evidence that it may have fewer side effects than some other antidepressants. It acts by blocking certain serotonin receptors and activating melatonin receptors.
Agomelatine was approved for medical use in Europe in 2009 and Australia in 2010. Its use is not approved in the United States and efforts to get approval were ended in 2011. It was developed by the pharmaceutical company Servier
Servier Laboratories (French: Laboratoires Servier, often abbreviated to Servier) is an international pharmaceutical company governed by a non-profit foundation, with its headquarters in France (Suresnes).
The consolidated turnover for the 2018 ...
.
Medical uses
Major depressive disorder
Agomelatine is used for the treatment of major depressive episodes in adults in Europe. Ten placebo controlled trials have been performed to investigate the short term efficacy of agomelatine in major depressive disorder. At the end of treatment, significant efficacy was demonstrated in six of the ten short-term double-blindplacebo-controlled studies
Placebo-controlled studies are a way of testing a medical therapy in which, in addition to a group of subjects that receives the treatment to be evaluated, a separate control group receives a sham "placebo" treatment which is specifically designed ...
. Two were considered "failed" trials, as comparators of established efficacy failed to differentiate from placebo. Efficacy was also observed in more severely depressed patients in all positive placebo-controlled studies. The maintenance of antidepressant efficacy was demonstrated in a relapse prevention study. One meta-analysis found agomelatine to be as effective as standard antidepressants, with an effect size
In statistics, an effect size is a value measuring the strength of the relationship between two variables in a population, or a sample-based estimate of that quantity. It can refer to the value of a statistic calculated from a sample of data, the ...
() of 0.24.
In 2018, a systematic review and network meta-analysis comparing the efficacy and acceptability of 21 antidepressant drugs showed agomelatine to be one of the most effective and one of only two medications found to be more tolerable than placebo.
A meta-analysis
A meta-analysis is a statistical analysis that combines the results of multiple scientific studies. Meta-analyses can be performed when there are multiple scientific studies addressing the same question, with each individual study reporting me ...
found that agomelatine is effective in treating severe depression. Its antidepressant effect is greater for more severe depression. In people with a greater baseline score (>30 on HAMD17 scale), the agomelatine-placebo difference was of 4.53 points. Controlled studies in humans have shown that agomelatine is at least as effective as the SSRI
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are a class of drugs that are typically used as antidepressants in the treatment of major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, and other psychological conditions.
SSRIs increase the extracellul ...
antidepressants paroxetine
Paroxetine, sold under the brand names Paxil and Seroxat among others, is an antidepressant of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class. It is used to treat major depressive disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, panic disorder ...
, sertraline
Sertraline, sold under the brand name Zoloft among others, is an antidepressant of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class. The efficacy of sertraline for depression is similar to that of other antidepressants, and the differ ...
, escitalopram
Escitalopram, sold under the brand names Lexapro and Cipralex, among others, is an antidepressant of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class. Escitalopram is mainly used to treat major depressive disorder and generalized anxiet ...
, and fluoxetine in the treatment of major depression
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive low mood, low self-esteem, and loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities. Introdu ...
. A 2018 meta-study comparing 21 antidepressants found agomelatine was one of the more tolerable, yet effective antidepressants.
However, the body of research on agomelatine has been substantially affected by publication bias, prompting analyses which take into account both published and unpublished studies. These have confirmed that agomelatine is approximately as effective as more commonly used antidepressants (e.g. SSRIs), but some qualified this as "marginally clinically relevant", being only slightly above placebo. According to a 2013 review, agomelatine did not seem to provide an advantage in efficacy over other antidepressants for the acute-phase treatment of major depression.
Generalized anxiety disorder
Agomelatine has been found more effective than placebo in the treatment ofgeneralized anxiety disorder
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is a mental and behavioral disorder, specifically an anxiety disorder characterized by excessive, uncontrollable and often irrational worry about events or activities. Worry often interferes with daily function ...
in a number of short-term double-blind placebo-controlled studies
Placebo-controlled studies are a way of testing a medical therapy in which, in addition to a group of subjects that receives the treatment to be evaluated, a separate control group receives a sham "placebo" treatment which is specifically designed ...
and in long term relapse prevention.
Use in special populations
It is not recommended in Europe for use in children andadolescents
Adolescence () is a transitional stage of Developmental biology, physical and psychological Human development (biology), development that generally occurs during the period from puberty to adulthood (typically corresponding to the age of majo ...
below 18 years of age due to a lack of data on safety
Safety is the state of being "safe", the condition of being protected from harm or other danger. Safety can also refer to the control of recognized hazards in order to achieve an acceptable level of risk.
Meanings
There are two slightly dif ...
and efficacy. However, a recent 12 week study first reported in September 2020, and published in 2022 showed greater efficacy vs. placebo for agomelatine 25 mg per day in youth age 7–17 years and an acceptable tolerability profile with similar efficacy to fluoxetine. Only limited data is available on use in elderly people ≥ 75 years old with major depressive episodes.
It is not recommended during pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops (gestation, gestates) inside a woman, woman's uterus (womb). A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occur ...
or breastfeeding
Breastfeeding, or nursing, is the process by which human breast milk is fed to a child. Breast milk may be from the breast, or may be expressed by hand or pumped and fed to the infant. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that br ...
.
Contraindications
Agomelatine is contraindicated in patients with kidney orliver impairment
Liver disease, or hepatic disease, is any of many diseases of the liver. If long-lasting it is termed chronic liver disease. Although the diseases differ in detail, liver diseases often have features in common.
Signs and symptoms
Some of the sig ...
. According to information disclosed by Servier in 2012, guidelines for the follow-up of patients treated with Valdoxan have been modified in concert with the European Medicines Agency. As some patients may experience increased levels of liver enzymes in their blood during treatment with Valdoxan, doctors have to run laboratory tests to check that the liver is working properly at the initiation of the treatment and then periodically during treatment, and subsequently decide whether to pursue the treatment or not. No relevant modification in agomelatine pharmacokinetic parameters in patients with severe renal impairment has been observed. However, only limited clinical data on its use in depressed patients with severe or moderate renal impairment
Kidney failure, also known as end-stage kidney disease, is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as eit ...
with major depressive episodes is available. Therefore, caution should be exercised when prescribing agomelatine to these patients.
Adverse effects
Agomelatine does not alter daytimevigilance
Vigilance may refer to:
* Alertness
* Vigilance, a creature ability in the ''Magic: The Gathering'' collectible card game
* ''Vigilance'' (album), by Threat Signal
* Vigilance (behavioural ecology), the watchfulness of prey for nearby predator ...
and memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered ...
in healthy volunteers. In depressed patients, treatment with the drug increased slow wave sleep without modification of REM ( Rapid Eye Movement) sleep amount or REM latency. Agomelatine also induced an advance of the time of sleep onset and of minimum heart rate. From the first week of treatment, onset of sleep and the quality of sleep were significantly improved without daytime clumsiness as assessed by patients.
Agomelatine appears to cause fewer sexual side effects and discontinuation effects than paroxetine.
; Common (1–10% incidence) adverse effects include
* Hyperhidrosis (excess sweating that is not proportionate to the ambient temperature)
* Abdominal pain
* Nausea
* Vomiting
* Diarrhea
* Constipation
* Back pain
* Fatigue
* Increased ALAT and ASAT (liver enzymes)
* Headache
* Dizziness
* Somnolence
* Insomnia
* Migraine
* Anxiety
; Uncommon (0.1–1%) adverse effects include
* Paraesthesia
Paresthesia is an abnormal sensation of the skin (tingling, pricking, chilling, burning, numbness) with no apparent physical cause. Paresthesia may be transient or chronic, and may have any of dozens of possible underlying causes. Paresthesias ar ...
(abnormal sensations .g. itching, burning, tingling, etc.due to malfunctioning of the peripheral nerves)
* Blurred vision
* Eczema
Dermatitis is inflammation of the skin, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened. The area of skin involved can ...
* Pruritus
Itch (also known as pruritus) is a sensation that causes the desire or reflex to scratch. Itch has resisted many attempts to be classified as any one type of sensory experience. Itch has many similarities to pain, and while both are unpleasant ...
(itching)
* Urticaria
Hives, also known as urticaria, is a kind of skin rash with red, raised, itchy bumps. Hives may burn or sting. The patches of rash may appear on different body parts, with variable duration from minutes to days, and does not leave any long-last ...
* Agitation
* Irritability
Irritability (also called as crankiness) is the excitatory ability that living organisms have to respond to changes in their environment. The term is used for both the physiological reaction to stimuli and for the pathological, abnormal or excessi ...
* Restlessness
* Aggression
* Nightmares
* Abnormal dreams
; Rare (0.01–0.1%) adverse effects include
* Mania
* Hypomania
Hypomania (literally "under mania" or "less than mania") is a mental and behavioural disorder, characterised essentially by an apparently non-contextual elevation of mood ( euphoria) that contributes to persistently disinhibited behaviour.
Th ...
* Suicidal ideation
* Suicidal behaviour
* Hallucinations
* Steatohepatitis
Steatohepatitis is a type of fatty liver disease, characterized by inflammation of the liver with concurrent fat accumulation in liver. Mere deposition of fat in the liver is termed steatosis, and together these constitute fatty liver changes.
...
* Increased GGT and/or alkaline phosphatase
* Liver failure
* Jaundice
* Erythematous rash
* Face oedema and angioedema
* Weight gain or loss, which tends to be less significant than with SSRIs
Dependence and withdrawal
No dosage tapering is needed on treatment discontinuation. Agomelatine has noabuse potential
Substance abuse, also known as drug abuse, is the use of a drug in amounts or by methods which are harmful to the individual or others. It is a form of substance-related disorder. Differing definitions of drug abuse are used in public health, ...
as measured in healthy volunteer studies.
Overdose
Agomelatine is expected to be relatively safe in overdose.Interactions
Agomelatine is a substrate ofCYP1A2
Cytochrome P450 1A2 (abbreviated CYP1A2), a member of the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system, is involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics in the human body. In humans, the CYP1A2 enzyme is encoded by the ''CYP1A2'' gene.
Function
...
, CYP2C9
Cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily C member 9 (abbreviated CYP2C9) is an enzyme protein. The enzyme is involved in metabolism, by oxidation, of both xenobiotics, including drugs, and endogenous compounds, including fatty acids. In humans, the prote ...
and CYP2C19
Cytochrome P450 2C19 (abbreviated CYP2C19) is an enzyme protein. It is a member of the CYP2C subfamily of the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system. This subfamily includes enzymes that catalyze metabolism of xenobiotics, including some p ...
. Inhibitors of these enzymes, e.g. the SSRI antidepressant fluvoxamine
Fluvoxamine, sold under the brand name Luvox and Faverin among others, is an antidepressant of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class. It is primarily used to treat major depressive disorder and obsessive–compulsive disorder ...
, reduce its clearance and can therefore lead to an increase in agomelatine exposure. There is also the potential for agomelatine to interact with alcohol to increase the risk of hepatotoxicity
Hepatotoxicity (from ''hepatic toxicity'') implies chemical-driven liver damage. Drug-induced liver injury is a cause of acute and chronic liver disease caused specifically by medications and the most common reason for a drug to be withdrawn fr ...
.
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Agomelatine is amelatonin receptor agonist
Melatonin receptor agonists are analogues of melatonin that bind to and activate the melatonin receptor. Agonists of the melatonin receptor have a number of therapeutic applications including treatment of sleep disorders and depression. The disc ...
( MT1 (''K''i 0.1 nM) and MT2 (''K''i = 0.12 nM)) and serotonin 5-HT2C (''K''i = 631 nM) and 5-HT2B receptor (''K''i = 660 nM) antagonist. Binding studies indicate that it has no effect on monoamine
Monoamine neurotransmitters are neurotransmitters and neuromodulators that contain one amino group connected to an aromatic ring by a two-carbon chain (such as -CH2-CH2-). Examples are dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin.
All monoamines ar ...
uptake and no affinity
Affinity may refer to:
Commerce, finance and law
* Affinity (law), kinship by marriage
* Affinity analysis, a market research and business management technique
* Affinity Credit Union, a Saskatchewan-based credit union
* Affinity Equity Par ...
for adrenergic
Adrenergic means "working on adrenaline (epinephrine) or noradrenaline (norepinephrine)" (or on their receptors). When not further qualified, it is usually used in the sense of enhancing or mimicking the effects of epinephrine and norepinephrine ...
, histamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogenous compound involved in local immune responses, as well as regulating physiological functions in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter for the brain, spinal cord, and uterus. Since histamine was discovered ...
, cholinergic
Cholinergic agents are compounds which mimic the action of acetylcholine and/or butyrylcholine. In general, the word " choline" describes the various quaternary ammonium salts containing the ''N'',''N'',''N''-trimethylethanolammonium cati ...
, dopamine, and benzodiazepine receptors, nor other serotonin receptors.
Agomelatine resynchronizes circadian rhythms in animal models of delayed sleep phase syndrome
Delayed sleep phase disorder (DSPD), more often known as delayed sleep phase syndrome and also as delayed sleep–wake phase disorder, is a delaying of a person's circadian rhythm (biological clock) compared to those of societal norms. The diso ...
. By antagonizing 5-HT2C, it disinhibits/increases noradrenaline
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and body as both a hormone and neurotransmitter. The name "noradrenaline" (from Latin '' ad'', ...
and dopamine release specifically in the frontal cortex. Therefore, it is sometimes classified as a norepinephrine–dopamine disinhibitor. It has no influence on the extracellular levels of serotonin. Agomelatine has shown an antidepressant-like effect in animal models of depression
Animal models of depression are research tools used to investigate depression and action of antidepressants as a simulation to investigate the symptomatology and pathophysiology of depressive illness or used to screen novel antidepressants.
In ...
(learned helplessness test, despair test, chronic mild stress) as well as in models with circadian rhythm desynchronisation and in models related to stress and anxiety. In humans, agomelatine has positive phase-shifting properties; it induces a phase advance of sleep, body temperature decline, and melatonin onset.
Antagonism of 5-HT2B is putatively an antidepressant property agomelatine shares with several atypical antipsychotics
The atypical antipsychotics (AAP), also known as second generation antipsychotics (SGAs) and serotonin–dopamine antagonists (SDAs), are a group of antipsychotic drugs (antipsychotic drugs in general are also known as major tranquilizers and ne ...
, such as aripiprazole
Aripiprazole, sold under the brand names Abilify and Aristada among others, is an atypical antipsychotic. It is primarily used in the treatment of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Other uses include as an add-on treatment in major depressiv ...
, which are themselves used as atypical antidepressants. 5-HT2B antagonists are currently being investigated for their usefulness in reducing cardiotoxicity
Cardiotoxicity is the occurrence of heart dysfunction as electric or muscle damage, resulting in heart toxicity. The heart becomes weaker and is not as efficient in pumping blood. Cardiotoxicity may be caused by chemotherapy (a usual example is th ...
of drugs as well as being effective in reducing headache. Hence this particular receptor antagonism of agomelatine is useful for its antidepressant effectiveness
Effectiveness is the capability of producing a desired result or the ability to produce desired output. When something is deemed effective, it means it has an intended or expected outcome, or produces a deep, vivid impression.
Etymology
The ori ...
as well as reducing the drug's adverse effect
An adverse effect is an undesired harmful effect resulting from a medication or other intervention, such as surgery. An adverse effect may be termed a " side effect", when judged to be secondary to a main or therapeutic effect. The term compl ...
s.
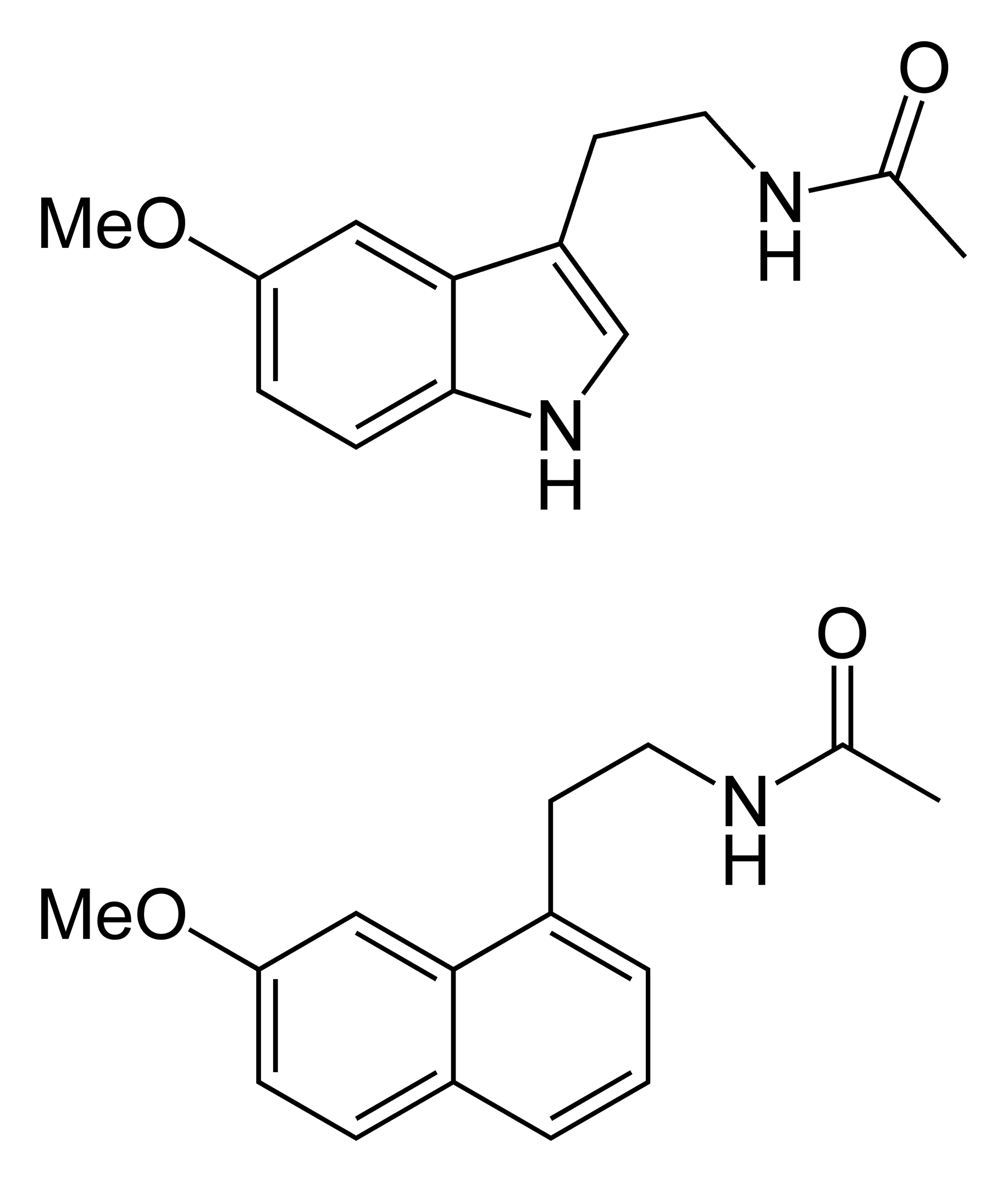
Chemistry
Structure
 The
The chemical structure
A chemical structure determination includes a chemist's specifying the molecular geometry and, when feasible and necessary, the electronic structure of the target molecule or other solid. Molecular geometry refers to the spatial arrangement of ...
of agomelatine is very similar to that of melatonin. Where melatonin has an indole ring system, agomelatine has a naphthalene bioisostere
In medicinal chemistry, bioisosteres are chemical substituents or groups with similar physical or chemical properties which produce broadly similar biological properties to another chemical compound. In drug design, the purpose of exchanging one bi ...
instead.
Synthesis
History
Agomelatine was discovered and developed by theEurope
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
an pharmaceutical
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field an ...
company Servier Laboratories Ltd. Servier continued to develop the drug and conduct phase III trials
The phases of clinical research are the stages in which scientists conduct experiments with a health intervention to obtain sufficient evidence for a process considered effective as a medical treatment. For drug development, the clinical phases ...
in the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
.
In March 2005, Servier submitted agomelatine to the European Medicines Agency (EMA) under the trade names Valdoxan and Thymanax. On 27 July 2006, the Committee for Medical Products for Human Use (CHMP) of the EMA recommended a refusal of the marketing authorisation. The major concern was that efficacy had not been sufficiently shown, while there were no special concerns about side effects
In medicine, a side effect is an effect, whether therapeutic or adverse, that is secondary to the one intended; although the term is predominantly employed to describe adverse effects, it can also apply to beneficial, but unintended, consequence ...
. In September 2007, Servier submitted a new marketing application to the EMA.
In March 2006, Servier
Servier Laboratories (French: Laboratoires Servier, often abbreviated to Servier) is an international pharmaceutical company governed by a non-profit foundation, with its headquarters in France (Suresnes).
The consolidated turnover for the 2018 ...
announced it had sold the rights to market agomelatine in the United States to Novartis
Novartis AG is a Swiss-American multinational pharmaceutical corporation based in Basel, Switzerland and
Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States (global research).name="novartis.com">https://www.novartis.com/research-development/research-loc ...
. It was undergoing several phase III clinical trials in the US, and until October 2011 Novartis listed the drug as scheduled for submission to the FDA no earlier than 2012. However, the development for the US market was discontinued in October 2011, when the results from the last of those trials became available.
It received approval from the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for marketing in the European Union in February 2009 and approval from the Therapeutic Goods Administration
The Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) is the medicine and therapeutic regulatory agency of the Australian Government. As part of the Department of Health and Aged Care, the TGA regulates the quality, supply and advertising of medicines, p ...
(TGA) for marketing in Australia in August 2010.
Research
Circadian rhythm sleep disorders
Agomelatine has been investigated for its effects onsleep regulation
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural, internal process that regulates the sleep–wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours. It can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., endogenous) and responds to ...
due its actions as a melatonin receptor agonist
Melatonin receptor agonists are analogues of melatonin that bind to and activate the melatonin receptor. Agonists of the melatonin receptor have a number of therapeutic applications including treatment of sleep disorders and depression. The disc ...
. Studies report various improvements in general quality of sleep metrics, as well as benefits in circadian rhythm sleep disorders. However, research is very limited (e.g., case report In medicine, a case report is a detailed report of the symptoms, signs, diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of an individual patient. Case reports may contain a demographic profile of the patient, but usually describe an unusual or novel occurrenc ...
s) and agomelatine is not approved for use in the treatment of sleep disorder
A sleep disorder, or somnipathy, is a medical disorder of an individual's sleep patterns. Some sleep disorders are severe enough to interfere with normal physical, mental, social and emotional functioning. Polysomnography and actigraphy are tests ...
s.
Seasonal affective disorder
A 2019Cochrane review
Cochrane (previously known as the Cochrane Collaboration) is a British international charitable organisation formed to organise medical research findings to facilitate evidence-based choices about health interventions involving health profes ...
suggested no recommendations of agomelatine in support of, or against, its use to treat individuals with seasonal affective disorder
Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) is a mood disorder subset, in which people who have normal mental health throughout most of the year exhibit depressive symptoms at the same time each year.
Common symptoms include sleeping too much, having li ...
.
References
External links
* * Genf interaction table- https://www.hug.ch/sites/interhug/files/structures/pharmacologie_et_toxicologie_cliniques/carte_cytochromes_2016_final.pdf {{Portal bar , Medicine 5-HT2C antagonists Acetamides Antidepressants Laboratoires Servier Melatonin receptor agonists Naphthol ethers Phenethylamines Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate