African Colonies on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The history of external colonisation of Africa can be dated back from ancient,
 * In ancient times, people from Southern Europe and Western Asia colonised North Africa, while people from Southeast Asia colonised Madagascar
* In the Middle Ages, North and
* In ancient times, people from Southern Europe and Western Asia colonised North Africa, while people from Southeast Asia colonised Madagascar
* In the Middle Ages, North and
 North Africa experienced colonisation from Europe and Western Asia in the early historical period, particularly Greeks and Phoenicians.
Under Egypt's Pharaoh
North Africa experienced colonisation from Europe and Western Asia in the early historical period, particularly Greeks and Phoenicians.
Under Egypt's Pharaoh

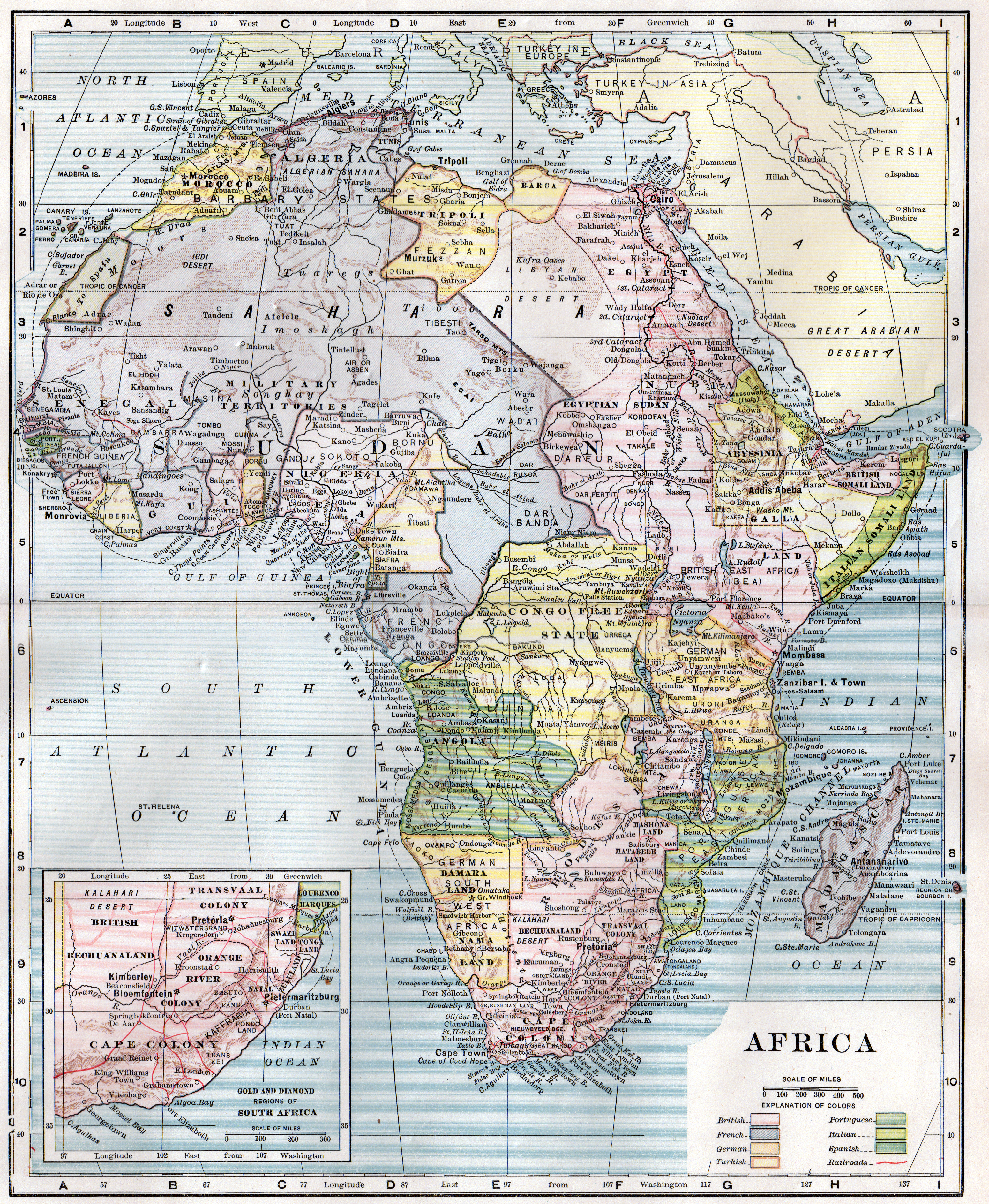
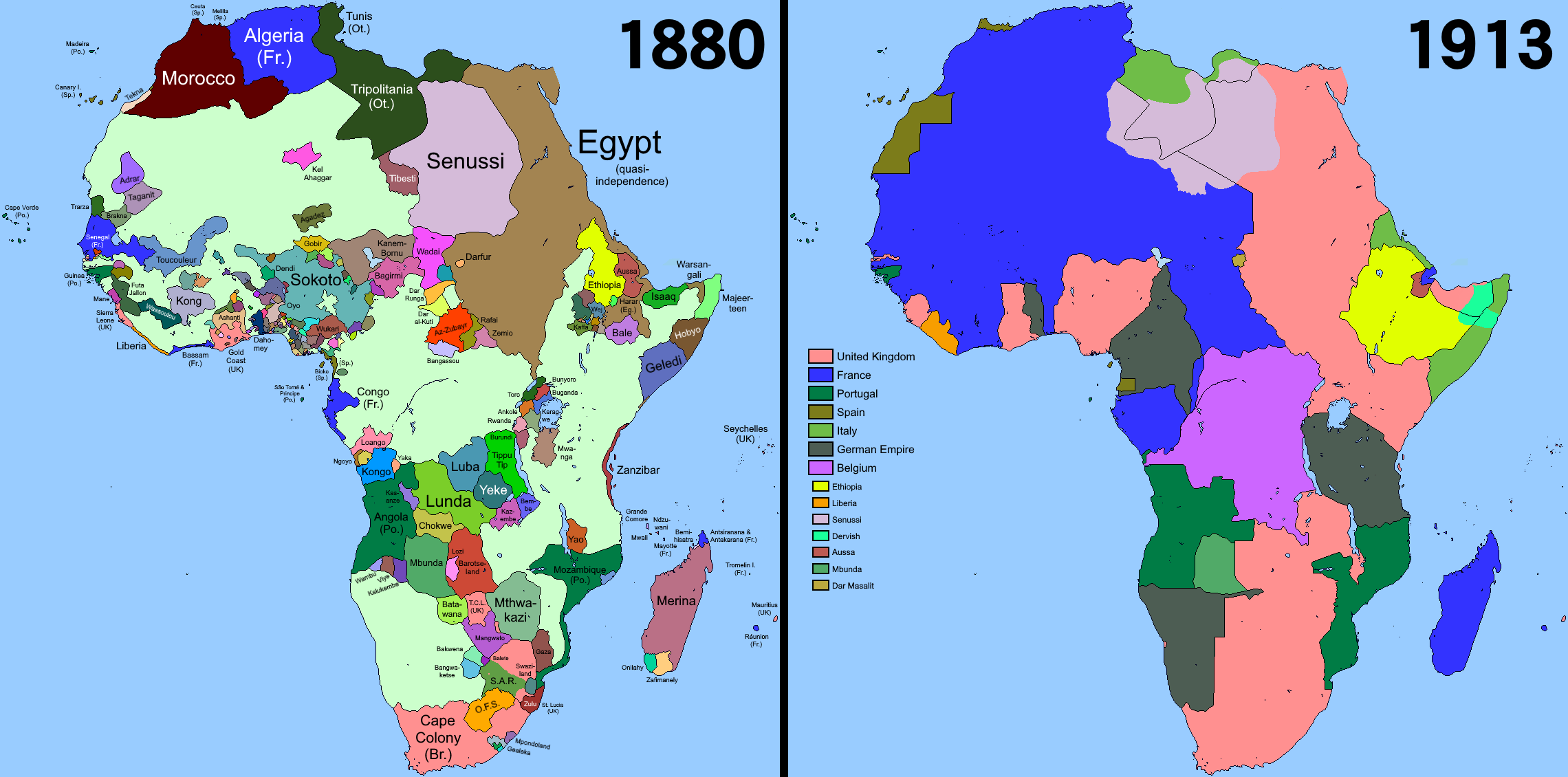 Established empires—notably Britain, France, Spain and Portugal—had already claimed coastal areas but had not penetrated deeply inland. Europeans controlled one tenth of Africa, primarily along the Mediterranean and in the far south. A significant early proponent of colonising inland was King Leopold of Belgium, who oppressed the
Established empires—notably Britain, France, Spain and Portugal—had already claimed coastal areas but had not penetrated deeply inland. Europeans controlled one tenth of Africa, primarily along the Mediterranean and in the far south. A significant early proponent of colonising inland was King Leopold of Belgium, who oppressed the
 Khapoya notes the significant resistance of powers faced to their domination in Africa. Technical superiority enabled conquest and control. Pro-independence Africans recognised the value of European education in dealing with Europeans in Africa. Some Africans established their own churches. Africans also noticed the unequal evidence of gratitude they received for their efforts to support Imperialist countries during the world wars. While European-imposed borders did not correspond to traditional territories, such new territories provided entities to focus efforts by movements for increased political voice up to independence. Among local groups so concerned were professionals such as lawyers and doctors, the petite bourgeoisie (clerks, teachers, small merchants), urban workers, cash crop farmers, peasant farmers, etc. Trade unions and other initially non-political associations evolved into political movements.
While the British sought to follow a process of gradual transfer of power and thus independence, the French policy of assimilation faced some resentment, especially in North Africa. The granting of independence in March 1956 to Morocco and Tunisia allowed a concentration on Algeria where there was a long ( 1954–62) and bloody armed struggle to achieve independence. When President
Khapoya notes the significant resistance of powers faced to their domination in Africa. Technical superiority enabled conquest and control. Pro-independence Africans recognised the value of European education in dealing with Europeans in Africa. Some Africans established their own churches. Africans also noticed the unequal evidence of gratitude they received for their efforts to support Imperialist countries during the world wars. While European-imposed borders did not correspond to traditional territories, such new territories provided entities to focus efforts by movements for increased political voice up to independence. Among local groups so concerned were professionals such as lawyers and doctors, the petite bourgeoisie (clerks, teachers, small merchants), urban workers, cash crop farmers, peasant farmers, etc. Trade unions and other initially non-political associations evolved into political movements.
While the British sought to follow a process of gradual transfer of power and thus independence, the French policy of assimilation faced some resentment, especially in North Africa. The granting of independence in March 1956 to Morocco and Tunisia allowed a concentration on Algeria where there was a long ( 1954–62) and bloody armed struggle to achieve independence. When President
 Mahmood Mamdani wrote his book ''Citizen and Subject'' in 1996. The main point of his argument is that the colonial state in Africa took the form of a bifurcated state, "two forms of power under a single hegemonic authority". The colonial state in Africa was divided into two. One state for the colonial European population and one state for the indigenous population. The colonial power was mainly in urban towns and cities and were served by elected governments. The indigenous power was found in rural villages and were ruled by tribal authority, which seemed to be more in keeping with their history and tradition. Mamdani mentions that in urban areas, native institutions were not recognised. The natives, who were portrayed as uncivilised by the
Mahmood Mamdani wrote his book ''Citizen and Subject'' in 1996. The main point of his argument is that the colonial state in Africa took the form of a bifurcated state, "two forms of power under a single hegemonic authority". The colonial state in Africa was divided into two. One state for the colonial European population and one state for the indigenous population. The colonial power was mainly in urban towns and cities and were served by elected governments. The indigenous power was found in rural villages and were ruled by tribal authority, which seemed to be more in keeping with their history and tradition. Mamdani mentions that in urban areas, native institutions were not recognised. The natives, who were portrayed as uncivilised by the
 Achille Mbembe is a Cameroonian historian, political theorist, and philosopher who has written and theorized extensively on life in the colony and postcolony. His 2000 book ''
Achille Mbembe is a Cameroonian historian, political theorist, and philosopher who has written and theorized extensively on life in the colony and postcolony. His 2000 book ''
Online
* * Hoskins, H.L. ''European imperialism in Africa'' (1967
online
*Michalopoulos, Stelios; Papaioannou, Elias (2020-03-01).
Historical Legacies and African Development
" ''Journal of Economic Literature''. 58 (1): 53–128. * * Nabudere, D. Wadada. ''Imperialism in East Africa'' (2 vol 1981
online
* Olson, James S., ed. ''Historical Dictionary of the British Empire'' (1996
Online
* Olson, James S., ed. '' Historical Dictionary of European Imperialism'' (1991
online
* Pakenham, Thomas (1992). ''The Scramble for Africa: the White Man's Conquest of the Dark Continent from 1876 to 1912'' (13th ed.). London: Abacus. . * Phillips, Anne. ''The enigma of colonialism : British policy in West Africa'' (1989
Online
Economic Impact of Colonialism
Germany Refuses to Apologize for Herero Holocaust
– from Africana.com * Andre Osborn
"Belgium exhumes its colonial demons"
''The Guardian'', 12 July 2002 {{Colonization
medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the Post-classical, post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with t ...
, or modern history, depending on how the term colonisation is defined.
Ancient Greeks, Romans, Arabs and Malays all established colonies on the African continent, some of which endured centuries. In popular parlance, discussions of colonialism
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their relig ...
in Africa usually focus on the European conquests of the New Imperialism
In historical contexts, New Imperialism characterizes a period of colonial expansion by European powers, the United States, and Japan during the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
Com
The period featured an unprecedented pursuit of ove ...
and the Scramble for Africa
The Scramble for Africa, also called the Partition of Africa, or Conquest of Africa, was the invasion, annexation, division, and colonisation of Africa, colonization of most of Africa by seven Western Europe, Western European powers during a ...
(1884-1914) era, followed by gradual decolonisation
Decolonization or decolonisation is the undoing of colonialism, the latter being the process whereby imperial nations establish and dominate foreign territories, often overseas. Some scholars of decolonization focus especially on separatism, in ...
after World War II. The principal powers involved in the modern colonisation of Africa are Britain, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, Portugal, Spain and Italy. In nearly all African countries today, the language used in government and media is the one imposed by a recent colonial power, though most people speak their native African languages.
Background
 * In ancient times, people from Southern Europe and Western Asia colonised North Africa, while people from Southeast Asia colonised Madagascar
* In the Middle Ages, North and
* In ancient times, people from Southern Europe and Western Asia colonised North Africa, while people from Southeast Asia colonised Madagascar
* In the Middle Ages, North and East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historical ...
was further colonised by people from Western Asia.
* In the Modern Era
The term modern period or modern era (sometimes also called modern history or modern times) is the period of history that succeeds the Middle Ages (which ended approximately 1500 AD). This terminology is a historical periodization that is applie ...
, Western Europeans colonised all parts of the continent, culminating in the Scramble for Africa
The Scramble for Africa, also called the Partition of Africa, or Conquest of Africa, was the invasion, annexation, division, and colonisation of Africa, colonization of most of Africa by seven Western Europe, Western European powers during a ...
in the late 19th century.
Ancient and Medieval colonisation
 North Africa experienced colonisation from Europe and Western Asia in the early historical period, particularly Greeks and Phoenicians.
Under Egypt's Pharaoh
North Africa experienced colonisation from Europe and Western Asia in the early historical period, particularly Greeks and Phoenicians.
Under Egypt's Pharaoh Amasis Amasis may refer to:
* Amasis I, Pharaoh of Egypt in 1550–1525 BC
* Amasis II, Pharaoh of Egypt in 570–526 BC
* Amasis (Persian general), Achaemenid military commander in Egypt in ca. 525 BC
* Amasis Painter, ancient Greek vase painter of the ...
(570–526 BC) a Greek mercantile colony was established at Naucratis, some 50 miles from the later Alexandria. Greeks colonised Cyrenaica around the same time. There was an attempt in 513 BC to establish a Greek colony between Cyrene and Carthage, which resulted in the combined local and Carthaginian expulsion two years later of the Greek colonists. Alexander the Great (356–323 BC) founded Alexandria during his conquest of Egypt. This became one of the major cities of Hellenistic and Roman times, a trading and cultural centre as well as a military headquarters and communications hub.
Phoenicians established several colonies along the coast of North Africa. Some of these were founded relatively early. Utica, for example, was founded c. 1100 BC. Carthage, which means New City, has a traditional foundation date of 814 BC. It was established in what is now Tunisia and became a major power in the Mediterranean by the 4th century BC. The Carthaginians sent out expeditions to explore and establish colonies along Africa's Atlantic coast. A surviving account of such is that of Hanno, around 425 BC.
Carthage encountered and struggled with the Romans. After the third and final war between them, the Third Punic War (150–146 BC), Rome completely destroyed Carthage. Scullard mentions plans by such as Gaius Gracchus in the late 2nd century BC, Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and ...
and Augustus in the mid- and late 1st century BC to establish a new Roman colony near the same site. This was established and under Augustus served as the capital city of African continent Roman province of Africa. Gothic Vandals briefly established a kingdom there in the 5th century, which shortly thereafter fell to the Romans again, this time the Byzantines. The whole of Roman/Byzantine North Africa eventually fell to the Arabs in the 7th century. Arabs introduced the Arabic language and Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
in the early Medieval period, while the Malay people introduced varieties of their language to Madagascar even earlier.
The oldest modern city founded by Europeans on the African continent is Cape Town, which was founded by the Dutch East India Company in 1652, as a halfway stop for passing European ships sailing to the east.
Early modern period
Early European expeditions by the Portuguese concentrated on colonising previously uninhabited islands such as theCape Verde
, national_anthem = ()
, official_languages = Portuguese
, national_languages = Cape Verdean Creole
, capital = Praia
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, demonym ...
Islands and São Tomé Island, or establishing coastal forts as a base for trade. The Spanish also established possessions of the Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are west of Morocc ...
off the West African Coast, and Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea ( es, Guinea Ecuatorial; french: Guinée équatoriale; pt, Guiné Equatorial), officially the Republic of Equatorial Guinea ( es, link=no, República de Guinea Ecuatorial, french: link=no, République de Guinée équatoria ...
, Ceuta and Melilla
Melilla ( , ; ; rif, Mřič ; ar, مليلية ) is an autonomous city of Spain located in north Africa. It lies on the eastern side of the Cape Three Forks, bordering Morocco and facing the Mediterranean Sea. It has an area of . It was par ...
on the African mainland before 1830.
Scramble for Africa
 Established empires—notably Britain, France, Spain and Portugal—had already claimed coastal areas but had not penetrated deeply inland. Europeans controlled one tenth of Africa, primarily along the Mediterranean and in the far south. A significant early proponent of colonising inland was King Leopold of Belgium, who oppressed the
Established empires—notably Britain, France, Spain and Portugal—had already claimed coastal areas but had not penetrated deeply inland. Europeans controlled one tenth of Africa, primarily along the Mediterranean and in the far south. A significant early proponent of colonising inland was King Leopold of Belgium, who oppressed the Congo Basin
The Congo Basin (french: Bassin du Congo) is the sedimentary basin of the Congo River. The Congo Basin is located in Central Africa, in a region known as west equatorial Africa. The Congo Basin region is sometimes known simply as the Congo. It con ...
as his own private domain until 1908. The 1885 Berlin Conference, initiated by Otto von Bismarck
Otto, Prince of Bismarck, Count of Bismarck-Schönhausen, Duke of Lauenburg (, ; 1 April 1815 – 30 July 1898), born Otto Eduard Leopold von Bismarck, was a conservative German statesman and diplomat. From his origins in the upper class of J ...
to establish international guidelines and avoiding violent disputes among European Powers, formalized the "New Imperialism
In historical contexts, New Imperialism characterizes a period of colonial expansion by European powers, the United States, and Japan during the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
Com
The period featured an unprecedented pursuit of ove ...
". This allowed the imperialists to move inland, with relatively few disputes among themselves. The only serious threat of inter-Imperial violence came in the Fashoda Incident of 1898 between Britain and France; It was settled without significant military violence between the colonising countries. Between 1870 and 1914 Europe acquired almost 23,000,000 sq. km —one-fifth of the land area of the globe—to its overseas colonial possessions.
Imperialism generated self-esteem across Europe. The Allies of World War I and World War II made extensive use of African labour and soldiers during the wars. In terms of administrative styles, " e French, the Portuguese, the Germans and the Belgians exercised a highly centralised type of administration called 'direct rule.'" The British by contrast sought to rule by identifying local power holders and encouraging or forcing them to administer for the British Empire. This was indirect rule. France ruled from Paris, appointing chiefs individually without considering traditional criteria, but rather loyalty to France. France established two large colonial federations in Africa, French West Africa
French West Africa (french: Afrique-Occidentale française, ) was a federation of eight French colonial territories in West Africa: Mauritania, Senegal, French Sudan (now Mali), French Guinea (now Guinea), Ivory Coast, Upper Volta (now Burki ...
and French Equatorial Africa. France appointed the state officials, passed laws and had to approve any measures passed by colonial assemblies.
Local groups in German East Africa
German East Africa (GEA; german: Deutsch-Ostafrika) was a German colony in the African Great Lakes region, which included present-day Burundi, Rwanda, the Tanzania mainland, and the Kionga Triangle, a small region later incorporated into Mozam ...
resisted German enforced labour and taxation. In the Abushiri revolt, the Germans were almost driven out of the area in 1888. A decade later the colony seemed conquered, though, "It had been a long-drawn-out struggle and inland administration centres were in reality little more than a series of small military fortresses." In 1905, the Germans were astonished by the widely supported Maji Maji Rebellion. This resistance was at first successful. However, within a year, the insurrection was suppressed by reinforcing troops armed with machine guns. German attempts to seize control in Southwest Africa also produced ardent resistance, which was very forcefully repressed leading to the Herero and Namaqua Genocide.
King Leopold II of Belgium called his vast private colony the Congo Free State
''(Work and Progress)
, national_anthem = Vers l'avenir
, capital = Vivi Boma
, currency = Congo Free State franc
, religion = Catholicism (''de facto'')
, leader1 = Leopo ...
. His barbaric treatment of the Africans sparked a strong international protest and the European powers forced him to relinquish control of the colony to the Belgian Parliament.
Vincent Khapoya notes the significant attention colonial powers paid to the economics of colonisation. This included: acquisition of land, often enforced labour, the introduction of cash crops, sometimes even to the neglect of food crops, changing inter-African trading patterns of pre-colonial times, the introduction of labourers from India, etc. and the continuation of Africa as a source of raw materials for European industry. Colonial powers later focused on abolishing slavery, developing infrastructure, and improving health and education.
Decolonisation
Charles de Gaulle
Charles André Joseph Marie de Gaulle (; ; (commonly abbreviated as CDG) 22 November 18909 November 1970) was a French army officer and statesman who led Free France against Nazi Germany in World War II and chaired the Provisional Government ...
held a referendum in 1958 on the issue, only Guinea voted for outright independence. Nevertheless, in 1959 France amended the constitution to allow other colonies this option.
Farmers in British East Africa were upset by attempts to take their land and to impose agricultural methods against their wishes and experience. In Tanganyika, Julius Nyerere exerted influence not only among Africans, united by the common Swahili language
Swahili, also known by its local name , is the native language of the Swahili people, who are found primarily in Tanzania, Kenya and Mozambique (along the East African coast and adjacent litoral islands). It is a Bantu language, though Swahili ...
, but also on some white leaders whose disproportionate voice under a racially weighted constitution was significant. He became the leader of an independent Tanganyika in 1961. In Kenya, whites had evicted African tenant farmers in the 1930s; since the 1940s there has been conflict, which intensified in 1952. By 1955, Britain had suppressed the revolt, and by 1960 Britain accepted the principle of African majority rule. Kenya became independent three years later.
The main period of decolonisation in Africa began after World War II. Growing independence movements, indigenous political parties and trade unions coupled with pressure from within the imperialist powers and from the United States and the Soviet Union ensured the decolonisation of the majority of the continent by 1980. Some areas (in particular South Africa and Namibia) retain a large population of European descent. Only the Spanish enclave
An enclave is a territory (or a small territory apart of a larger one) that is entirely surrounded by the territory of one other state or entity. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is sometimes used improperly to deno ...
s of Ceuta and Melilla
Melilla ( , ; ; rif, Mřič ; ar, مليلية ) is an autonomous city of Spain located in north Africa. It lies on the eastern side of the Cape Three Forks, bordering Morocco and facing the Mediterranean Sea. It has an area of . It was par ...
are still governed by a European country. While the islands of Réunion
Réunion (; french: La Réunion, ; previously ''Île Bourbon''; rcf, label= Reunionese Creole, La Rényon) is an island in the Indian Ocean that is an overseas department and region of France. It is located approximately east of the island ...
and Mayotte, Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan Da Cunha
Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha is a British Overseas Territory located in the South Atlantic and consisting of the island of Saint Helena, Ascension Island and the archipelago of Tristan da Cunha including Gough Island. Its name wa ...
, the Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are west of Morocc ...
and Madeira
)
, anthem = ( en, "Anthem of the Autonomous Region of Madeira")
, song_type = Regional anthem
, image_map=EU-Portugal_with_Madeira_circled.svg
, map_alt=Location of Madeira
, map_caption=Location of Madeira
, subdivision_type=Sovereign st ...
all remain under either French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
, British, Spanish, or Portuguese control, the latter two of which were never part of any African polity and have overwhelmingly European populations.
Theoretical frameworks
The theory of colonialism addresses the problems and consequences of the colonisation of a country, and there has been much research conducted exploring these concepts.Walter Rodney
Guyanese historian and activist Walter Rodney proposes in his book '' How Europe Underdeveloped Africa'' that Africa was pillaged and plundered by the West through economic exploitation. Using a Marxist analysis, he opines that as Europe was being developed, Africa was being underdeveloped via resource extraction. He concludes that the structure of present-day Africa and Europe can, through a comparative analysis be traced to theAtlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and i ...
and colonialism. He includes a gendered analysis and states the rights of African women were further diminished during colonialism.
Mahmood Mamdani
 Mahmood Mamdani wrote his book ''Citizen and Subject'' in 1996. The main point of his argument is that the colonial state in Africa took the form of a bifurcated state, "two forms of power under a single hegemonic authority". The colonial state in Africa was divided into two. One state for the colonial European population and one state for the indigenous population. The colonial power was mainly in urban towns and cities and were served by elected governments. The indigenous power was found in rural villages and were ruled by tribal authority, which seemed to be more in keeping with their history and tradition. Mamdani mentions that in urban areas, native institutions were not recognised. The natives, who were portrayed as uncivilised by the
Mahmood Mamdani wrote his book ''Citizen and Subject'' in 1996. The main point of his argument is that the colonial state in Africa took the form of a bifurcated state, "two forms of power under a single hegemonic authority". The colonial state in Africa was divided into two. One state for the colonial European population and one state for the indigenous population. The colonial power was mainly in urban towns and cities and were served by elected governments. The indigenous power was found in rural villages and were ruled by tribal authority, which seemed to be more in keeping with their history and tradition. Mamdani mentions that in urban areas, native institutions were not recognised. The natives, who were portrayed as uncivilised by the Europeans
Europeans are the focus of European ethnology, the field of anthropology related to the various ethnic groups that reside in the states of Europe. Groups may be defined by common genetic ancestry, common language, or both. Pan and Pfeil (2004) ...
, were excluded from the rights of citizenship. The division of the colonial state created a racial segregation between the European 'citizen' and African 'subject', and a division between institutions of government.
Achille Mbembe
On the Postcolony
''On the Postcolony'' is a collection of critical essays by Cameroonian philosopher and political theorist Achille Mbembe. The book is Mbembe's most well-known work and explores questions of power and subjectivity in postcolonial Africa. The book ...
'' critically examines postcolonial life in Africa and is a prolific work within the field of postcolonialism
Postcolonialism is the critical academic study of the cultural, political and economic legacy of colonialism and imperialism, focusing on the impact of human control and exploitation of colonized people and their lands. More specifically, it is a ...
. It is through this examination of the postcolony that Mbembe reveals the modes through which power was exerted in colonial Africa. He reminds the reader that colonial powers demanded use of African bodies in particularly violent ways for the purpose of labor as well as the shaping of subservient colonised identities.
By comparing power in the colony and postcolony, Mbembe demonstrates that violence in the colony was exerted on African bodies largely for labor and submission. European colonial powers sought natural resources in African colonies and needed the requisite labor force to extract them and simultaneously build the colonial city around these industries. Because Europeans viewed native bodies as degenerate and in need of taming, violence was necessary to create a submissive laborer. Colonisers viewed this violence as necessary and good because it shaped the African into a productive worker. They had the simultaneous goals of utilizing the raw labor and shaping the identity and character of the African. By beating into the African a docile nature, colonisers ultimately shaped and enforced the way Africans could move through colonial spaces. The African’s day-to-day life then became a show of submission done through exercises like public works projects and military conscription.
Mbembe contrasts colonial violence with that of the postcolony. Mbembe demonstrates that violence in the postcolony is cruder and more generally for the purpose of demonstrating raw power. Expressions of excess and exaggeration characterize this violence. Mbembe's theorization of violence in the colony illuminates the unequal relationship between the coloniser and colonised and reminds us of the violence inflicted on African bodies throughout the process of colonisation. It cannot be understood nor should be taught without the context of this violence.
Stephanie Terreni Brown
Stephanie Terreni Brown is an academic in the field of colonialism. In her 2014 paper she examines how sanitation and dirt is used in colonial narratives through the example of Kampala. Brown describesabjection
Abjection is a concept in critical theory referring to becoming cast off and separated from norms and rules, especially on the scale of society and morality. The term has been explored in post-structuralism as that which inherently disturbs conven ...
as the process whereby one group others or dehumanizes another. Those who are deemed abject are often avoided by others and seen as inferior. Abjectivication is continually used as a mechanism to dominate a group of people and control them. In the case of colonialism, she argues that it is used by the west to dominate over and control the indigenous population of Africa.
Abjectivication through discourses of dirt and sanitation are used to draw distinctions between the Western governing figures and the local population. Dirt being seen as something out of place, whilst cleanliness being attributed to the “in group”, the colonisers, and dirt being paralleled with the indigenous people. The reactions of disgust and displeasure to dirt and uncleanliness are often linked social norms and the wider cultural context, shaping the way in which Africa is still thought of today.
Brown discusses how the colonial authorities were only concerned with constructing a working sewage system to cater for the colonials and were not concerned with the Ugandan population. This rhetoric of sanitation is important because it is seen as a key part of modernity and being civilised. The lack of sanitation and proper sewage systems symbolize that Africans are savages and uncivilised, playing a central role in how the west justified the case of the civilising process. Brown refers to this process of abjectification using discourses of dirt as a physical and material legacy of colonialism that is still very much present in Kampala and other African cities today.
Critique
Critical theory on the colonisation of Africa is largely unified in a condemnation of imperial activities. Postcolonial theory has been derived from this anti-colonial/anti-imperial concept and writers such as Mbembe, Mamdani and Brown, and many more, have used it as a narrative for their work on the colonisation of Africa. Postcolonial geographers are consistent with the notion that colonialism, although maybe not in such clear-cut forms, is still concurrent today. Both Mbembe, Mamdani and Brown’s theories have a consistent theme of the indigenous Africans having been treated as uncivilised, second class citizens and that in many former colonial cities this has continued into the present day with a switch from race to wealth divide. ''On the Postcolony
''On the Postcolony'' is a collection of critical essays by Cameroonian philosopher and political theorist Achille Mbembe. The book is Mbembe's most well-known work and explores questions of power and subjectivity in postcolonial Africa. The book ...
'' has faced criticism from academics such as Meredith Terreta for focusing too much on specific African nations such as Cameroon. Echoes of this criticism can also be found when looking at the work of Mamdani with his theories questioned for generalising across an Africa that, in reality, was colonised in very different ways, by fundamentally different European imperial ideologies.
See also
*Economic history of Africa
The earliest humans were hunter gatherers who were living in small, family groupings. Even then there was considerable trade that could cover long distances. Archaeologists have found that evidence of trade in luxury items lik ...
* Neocolonialism
* Third world
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * Gann, Lewis H. ''Colonialism in Africa, 1870-1960'' (1969Online
* * Hoskins, H.L. ''European imperialism in Africa'' (1967
online
*Michalopoulos, Stelios; Papaioannou, Elias (2020-03-01).
Historical Legacies and African Development
" ''Journal of Economic Literature''. 58 (1): 53–128. * * Nabudere, D. Wadada. ''Imperialism in East Africa'' (2 vol 1981
online
* Olson, James S., ed. ''Historical Dictionary of the British Empire'' (1996
Online
* Olson, James S., ed. '' Historical Dictionary of European Imperialism'' (1991
online
* Pakenham, Thomas (1992). ''The Scramble for Africa: the White Man's Conquest of the Dark Continent from 1876 to 1912'' (13th ed.). London: Abacus. . * Phillips, Anne. ''The enigma of colonialism : British policy in West Africa'' (1989
Online
External links
Economic Impact of Colonialism
Germany Refuses to Apologize for Herero Holocaust
– from Africana.com * Andre Osborn
"Belgium exhumes its colonial demons"
''The Guardian'', 12 July 2002 {{Colonization