Aeronautical Engineers on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Aeronautics is the science or art involved with the study,
Aeronautics is the science or art involved with the study,
 Attempts to fly without any real aeronautical understanding have been made from the earliest times, typically by constructing wings and jumping from a tower with crippling or lethal results.
Wiser investigators sought to gain some rational understanding through the study of bird flight. Medieval
Attempts to fly without any real aeronautical understanding have been made from the earliest times, typically by constructing wings and jumping from a tower with crippling or lethal results.
Wiser investigators sought to gain some rational understanding through the study of bird flight. Medieval
 The modern era of lighter-than-air flight began early in the 17th century with
The modern era of lighter-than-air flight began early in the 17th century with  From the mid-18th century the
From the mid-18th century the
Part 1
Part 2
Part 3
''Nicholson's Journal of Natural Philosophy'', 1809–1810. (Via
Raw text
. Retrieved: 30 May 2010. In it he wrote the first scientific statement of the problem, "The whole problem is confined within these limits, viz. to make a surface support a given weight by the application of power to the resistance of air." He identified the four vector forces that influence an aircraft: ''

 Aeronautics may be divided into three main branches comprising
Aeronautics may be divided into three main branches comprising
Aeronautical engineering
, University of Glasgow.
A major part of aeronautical engineering is
 Aeronautics is the science or art involved with the study,
Aeronautics is the science or art involved with the study, design
A design is a plan or specification for the construction of an object or system or for the implementation of an activity or process or the result of that plan or specification in the form of a prototype, product, or process. The verb ''to design'' ...
, and manufacturing of air flight
Flight or flying is the process by which an object moves through a space without contacting any planetary surface, either within an atmosphere (i.e. air flight or aviation) or through the vacuum of outer space (i.e. spaceflight). This can be a ...
–capable machines, and the techniques of operating aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines ...
and rockets within the atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A s ...
. The British Royal Aeronautical Society
The Royal Aeronautical Society, also known as the RAeS, is a British multi-disciplinary professional institution dedicated to the global aerospace community. Founded in 1866, it is the oldest aeronautical society in the world. Members, Fellows ...
identifies the aspects of "aeronautical Art, Science and Engineering" and "The profession of Aeronautics (which expression includes Astronautics)."
While the term originally referred solely to ''operating'' the aircraft, it has since been expanded to include technology, business, and other aspects related to aircraft.
The term "aviation
Aviation includes the activities surrounding mechanical flight and the aircraft industry. ''Aircraft'' includes fixed-wing and rotary-wing types, morphable wings, wing-less lifting bodies, as well as lighter-than-air craft such as hot air ...
" is sometimes used interchangeably with aeronautics, although "aeronautics" includes lighter-than-air
A lifting gas or lighter-than-air gas is a gas that has a density lower than normal atmospheric gases and rises above them as a result. It is required for aerostats to create buoyancy, particularly in lighter-than-air aircraft, which include fre ...
craft such as airship
An airship or dirigible balloon is a type of aerostat or lighter-than-air aircraft that can navigate through the air under its own power. Aerostats gain their lift from a lifting gas that is less dense than the surrounding air.
In early ...
s, and includes ballistic vehicles while "aviation" technically does not.
A significant part of aeronautical science is a branch of dynamics called aerodynamics
Aerodynamics, from grc, ἀήρ ''aero'' (air) + grc, δυναμική (dynamics), is the study of the motion of air, particularly when affected by a solid object, such as an airplane wing. It involves topics covered in the field of fluid dyn ...
, which deals with the motion of air and the way that it interacts with objects in motion, such as an aircraft.
History
Early ideas
 Attempts to fly without any real aeronautical understanding have been made from the earliest times, typically by constructing wings and jumping from a tower with crippling or lethal results.
Wiser investigators sought to gain some rational understanding through the study of bird flight. Medieval
Attempts to fly without any real aeronautical understanding have been made from the earliest times, typically by constructing wings and jumping from a tower with crippling or lethal results.
Wiser investigators sought to gain some rational understanding through the study of bird flight. Medieval Islamic Golden Age
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of cultural, economic, and scientific flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 14th century. This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign ...
scientists such as Abbas ibn Firnas
Abu al-Qasim Abbas ibn Firnas ibn Wirdas al-Takurini ( ar, أبو القاسم عباس بن فرناس بن ورداس التاكرني; c. 809/810 – 887 A.D.), also known as Abbas ibn Firnas ( ar, عباس ابن فرناس), Latinized Armen ...
also made such studies. Lynn Townsend White, Jr. (Spring, 1961). "Eilmer of Malmesbury, an Eleventh Century Aviator: A Case Study of Technological Innovation, Its Context and Tradition", ''Technology and Culture'' 2 (2), p. 97-111 00f./ref> The founders of modern aeronautics, Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 14522 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, Drawing, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially res ...
in the Renaissance and Cayley in 1799, both began their investigations with studies of bird flight.
Man-carrying kites are believed to have been used extensively in ancient China. In 1282 the Italian explorer Marco Polo
Marco Polo (, , ; 8 January 1324) was a Venetian merchant, explorer and writer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road between 1271 and 1295. His travels are recorded in ''The Travels of Marco Polo'' (also known as ''Book of the Marv ...
described the Chinese techniques then current.Pelham, D.; ''The Penguin book of kites'', Penguin (1976) The Chinese also constructed small hot air balloons, or lanterns, and rotary-wing toys.
An early European to provide any scientific discussion of flight was Roger Bacon
Roger Bacon (; la, Rogerus or ', also '' Rogerus''; ), also known by the scholastic accolade ''Doctor Mirabilis'', was a medieval English philosopher and Franciscan friar who placed considerable emphasis on the study of nature through empiri ...
, who described principles of operation for the lighter-than-air balloon
A balloon is a flexible bag that can be inflated with a gas, such as helium, hydrogen, nitrous oxide, oxygen, and air. For special tasks, balloons can be filled with smoke, liquid water, granular media (e.g. sand, flour or rice), or light so ...
and the flapping-wing ornithopter
An ornithopter (from Greek ''ornis, ornith-'' "bird" and ''pteron'' "wing") is an aircraft that flies by flapping its wings. Designers sought to imitate the flapping-wing flight of birds, bats, and insects. Though machines may differ in form, th ...
, which he envisaged would be constructed in the future. The lifting medium for his balloon would be an "aether" whose composition he did not know.
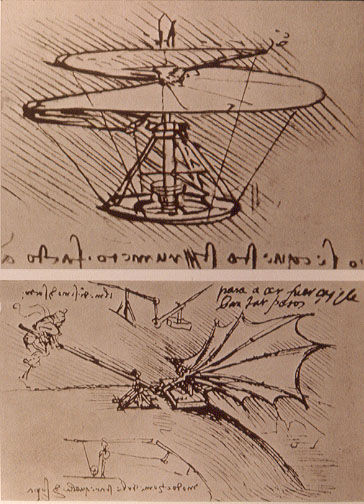
In the late fifteenth century, Leonardo da Vinci followed up his study of birds with designs for some of the earliest flying machines, including the flapping-wing ornithopter
An ornithopter (from Greek ''ornis, ornith-'' "bird" and ''pteron'' "wing") is an aircraft that flies by flapping its wings. Designers sought to imitate the flapping-wing flight of birds, bats, and insects. Though machines may differ in form, th ...
and the rotating-wing helicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attributes ...
. Although his designs were rational, they were not based on particularly good science. Many of his designs, such as a four-person screw-type helicopter, have severe flaws. He did at least understand that "An object offers as much resistance to the air as the air does to the object." (Newton
Newton most commonly refers to:
* Isaac Newton (1642–1726/1727), English scientist
* Newton (unit), SI unit of force named after Isaac Newton
Newton may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Newton'' (film), a 2017 Indian film
* Newton ( ...
would not publish the Third law of motion until 1687.) His analysis led to the realisation that manpower alone was not sufficient for sustained flight, and his later designs included a mechanical power source such as a spring. Da Vinci's work was lost after his death and did not reappear until it had been overtaken by the work of George Cayley
Sir George Cayley, 6th Baronet (27 December 1773 – 15 December 1857) was an English engineer, inventor, and aviator. He is one of the most important people in the history of aeronautics. Many consider him to be the first true scientific aeri ...
.
Balloon flight
 The modern era of lighter-than-air flight began early in the 17th century with
The modern era of lighter-than-air flight began early in the 17th century with Galileo
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642) was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. Commonly referred to as Galileo, his name was pronounced (, ). He was ...
's experiments in which he showed that air has weight. Around 1650 Cyrano de Bergerac
Savinien de Cyrano de Bergerac ( , ; 6 March 1619 – 28 July 1655) was a French novelist, playwright, epistolarian, and duelist.
A bold and innovative author, his work was part of the libertine literature of the first half of the 17th cen ...
wrote some fantasy novels in which he described the principle of ascent using a substance (dew) he supposed to be lighter than air, and descending by releasing a controlled amount of the substance. Francesco Lana de Terzi
Francesco Lana de Terzi (1631 in Brescia, Lombardy – 22 February 1687, in Brescia, Lombardy) was an Italian Jesuit priest, mathematician, naturalist and aeronautics pioneer. Having been professor of physics and mathematics at Brescia, he first ...
measured the pressure of air at sea level and in 1670 proposed the first scientifically credible lifting medium in the form of hollow metal spheres from which all the air had been pumped out. These would be lighter than the displaced air and able to lift an airship
An airship or dirigible balloon is a type of aerostat or lighter-than-air aircraft that can navigate through the air under its own power. Aerostats gain their lift from a lifting gas that is less dense than the surrounding air.
In early ...
. His proposed methods of controlling height are still in use today; by carrying ballast which may be dropped overboard to gain height, and by venting the lifting containers to lose height. In practice de Terzi's spheres would have collapsed under air pressure, and further developments had to wait for more practicable lifting gases.
 From the mid-18th century the
From the mid-18th century the Montgolfier brothers
The Montgolfier brothers – Joseph-Michel Montgolfier (; 26 August 1740 – 26 June 1810) and Jacques-Étienne Montgolfier (; 6 January 1745 – 2 August 1799) – were aviation pioneers, balloonists and paper manufacturers from the commune A ...
in France began experimenting with balloons. Their balloons were made of paper, and early experiments using steam as the lifting gas were short-lived due to its effect on the paper as it condensed. Mistaking smoke for a kind of steam, they began filling their balloons with hot smoky air which they called "electric smoke" and, despite not fully understanding the principles at work, made some successful launches and in 1783 were invited to give a demonstration to the French ''Académie des Sciences''.
Meanwhile, the discovery of hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, an ...
led Joseph Black
Joseph Black (16 April 1728 – 6 December 1799) was a Scottish physicist and chemist, known for his discoveries of magnesium, latent heat, specific heat, and carbon dioxide. He was Professor of Anatomy and Chemistry at the University of Glas ...
in to propose its use as a lifting gas, though practical demonstration awaited a gas tight balloon material. On hearing of the Montgolfier Brothers' invitation, the French Academy member Jacques Charles
Jacques Alexandre César Charles (November 12, 1746 – April 7, 1823) was a French inventor, scientist, mathematician, and balloonist.
Charles wrote almost nothing about mathematics, and most of what has been credited to him was due to mistaking ...
offered a similar demonstration of a hydrogen balloon. Charles and two craftsmen, the Robert brothers, developed a gas tight material of rubberised silk for the envelope. The hydrogen gas was to be generated by chemical reaction during the filling process.
The Montgolfier designs had several shortcomings, not least the need for dry weather and a tendency for sparks from the fire to set light to the paper balloon. The manned design had a gallery around the base of the balloon rather than the hanging basket of the first, unmanned design, which brought the paper closer to the fire. On their free flight, De Rozier and d'Arlandes took buckets of water and sponges to douse these fires as they arose. On the other hand, the manned design of Charles was essentially modern. As a result of these exploits, the hot-air balloon became known as the ''Montgolfière'' type and the hydrogen balloon the ''Charlière''.
Charles and the Robert brothers' next balloon, '' La Caroline'', was a Charlière that followed Jean Baptiste Meusnier
Jean Baptiste Marie Charles Meusnier de la Place (Tours, 19 June 1754 — le Pont de Cassel, near Mainz, 13 June 1793) was a French mathematician, engineer and Revolutionary general. He is best known for Meusnier's theorem on the curvature o ...
's proposals for an elongated dirigible balloon, and was notable for having an outer envelope with the gas contained in a second, inner ballonet. On 19 September 1784, it completed the first flight of over 100 km, between Paris and Beuvry, despite the man-powered propulsive devices proving useless.
In an attempt the next year to provide both endurance and controllability, de Rozier developed a balloon having both hot air and hydrogen gas bags, a design which was soon named after him as the ''Rozière.'' The principle was to use the hydrogen section for constant lift and to navigate vertically by heating and allowing to cool the hot air section, in order to catch the most favourable wind at whatever altitude it was blowing. The balloon envelope was made of goldbeater's skin
Goldbeater's skin is the processed outer membrane of the intestine of an animal, typically cattle, which is valued for its strength against tearing. The term derives from its traditional use as durable layers interleaved between sheets of gold st ...
. The first flight ended in disaster and the approach has seldom been used since.
Cayley and the foundation of modern aeronautics
Sir George Cayley
Sir George Cayley, 6th Baronet (27 December 1773 – 15 December 1857) was an English engineer, inventor, and aviator. He is one of the most important people in the history of aeronautics. Many consider him to be the first true scientific aer ...
(1773–1857) is widely acknowledged as the founder of modern aeronautics. He was first called the "father of the aeroplane" in 1846 and Henson called him the "father of aerial navigation." He was the first true scientific aerial investigator to publish his work, which included for the first time the underlying principles and forces of flight.
In 1809 he began the publication of a landmark three-part treatise titled "On Aerial Navigation" (1809–1810).''Cayley, George''. "On Aerial NavigationPart 1
Part 2
Part 3
''Nicholson's Journal of Natural Philosophy'', 1809–1810. (Via
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeeding t ...
)Raw text
. Retrieved: 30 May 2010. In it he wrote the first scientific statement of the problem, "The whole problem is confined within these limits, viz. to make a surface support a given weight by the application of power to the resistance of air." He identified the four vector forces that influence an aircraft: ''
thrust
Thrust is a reaction force described quantitatively by Newton's third law. When a system expels or accelerates mass in one direction, the accelerated mass will cause a force of equal magnitude but opposite direction to be applied to that syst ...
'', ''lift
Lift or LIFT may refer to:
Physical devices
* Elevator, or lift, a device used for raising and lowering people or goods
** Paternoster lift, a type of lift using a continuous chain of cars which do not stop
** Patient lift, or Hoyer lift, mobil ...
'', '' drag'' and ''weight
In science and engineering, the weight of an object is the force acting on the object due to gravity.
Some standard textbooks define weight as a Euclidean vector, vector quantity, the gravitational force acting on the object. Others define weigh ...
'' and distinguished stability and control in his designs.
He developed the modern conventional form of the fixed-wing aeroplane having a stabilising tail with both horizontal and vertical surfaces, flying gliders both unmanned and manned.
He introduced the use of the whirling arm test rig to investigate the aerodynamics of flight, using it to discover the benefits of the curved or cambered aerofoil
An airfoil (American English) or aerofoil (British English) is the cross-sectional shape of an object whose motion through a gas is capable of generating significant lift, such as a wing, a sail, or the blades of propeller, rotor, or turbine.
...
over the flat wing he had used for his first glider. He also identified and described the importance of dihedral, diagonal bracing and drag reduction, and contributed to the understanding and design of ornithopter
An ornithopter (from Greek ''ornis, ornith-'' "bird" and ''pteron'' "wing") is an aircraft that flies by flapping its wings. Designers sought to imitate the flapping-wing flight of birds, bats, and insects. Though machines may differ in form, th ...
s and parachute
A parachute is a device used to slow the motion of an object through an atmosphere by creating drag or, in a ram-air parachute, aerodynamic lift. A major application is to support people, for recreation or as a safety device for aviators, who ...
s.
Another significant invention was the tension-spoked wheel, which he devised in order to create a light, strong wheel for aircraft undercarriage.
The 19th century
During the 19th century Cayley's ideas were refined, proved and expanded on, culminating in the works ofOtto Lilienthal
Karl Wilhelm Otto Lilienthal (23 May 1848 – 10 August 1896) was a German pioneer of aviation who became known as the "flying man". He was the first person to make well-documented, repeated, successful flights with gliders, therefore making ...
.
Lilienthal was a German engineer and businessman who became known as the "flying man". He was the first person to make well-documented, repeated, successful flights with glider
Glider may refer to:
Aircraft and transport Aircraft
* Glider (aircraft), heavier-than-air aircraft primarily intended for unpowered flight
** Glider (sailplane), a rigid-winged glider aircraft with an undercarriage, used in the sport of glidin ...
s, therefore making the idea of "heavier than air
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to flight, fly by gaining support from the Atmosphere of Earth, air. It counters the force of gravity by using either Buoyancy, static lift or by using the Lift (force), dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in ...
" a reality. Newspapers and magazines published photographs of Lilienthal gliding, favourably influencing public and scientific opinion about the possibility of flying machines becoming practical.
His work lead to him developing the concept of the modern wing. His flight attempts in the year 1891 are seen as the beginning of human flight and the "Lilienthal Normalsegelapparat
The Lilienthal ''Normalsegelapparat'' (German: "Normal soaring apparatus") is a Glider aircraft, glider designed by Otto Lilienthal in Germany in the late 19th century. It is considered to be the first aeroplane to be serially produced, exampl ...
" is considered to be the first air plane in series production, making the ''Maschinenfabrik Otto Lilienthal'' the first air plane production company in the world.
Otto Lilienthal
Karl Wilhelm Otto Lilienthal (23 May 1848 – 10 August 1896) was a German pioneer of aviation who became known as the "flying man". He was the first person to make well-documented, repeated, successful flights with gliders, therefore making ...
is often referred to as either the "father of aviation" or "father of flight".
Other important investigators included Horatio Phillips
Horatio Frederick Phillips (1845 – 1924) was an English aviation pioneer, born in Streatham, Surrey. He was famous for building multiplane flying machines with many more sets of lifting surfaces than are normal on modern aircraft. However he ...
.
Branches

 Aeronautics may be divided into three main branches comprising
Aeronautics may be divided into three main branches comprising Aviation
Aviation includes the activities surrounding mechanical flight and the aircraft industry. ''Aircraft'' includes fixed-wing and rotary-wing types, morphable wings, wing-less lifting bodies, as well as lighter-than-air craft such as hot air ...
, Aeronautical science
Aeronautics is the science or art involved with the study, design process, design, and manufacturing of air flight–capable machines, and the techniques of operating aircraft and rockets within the atmosphere. The British Royal Aeronautical So ...
and Aeronautical engineering
Aerospace engineering is the primary field of engineering concerned with the development of aircraft and spacecraft. It has two major and overlapping branches: Aeronautics, aeronautical engineering and Astronautics, astronautical engineering. A ...
.
Aviation
Aviation is the art or practice of aeronautics. Historically aviation meant only heavier-than-air flight, but nowadays it includes flying in balloons and airships.Aeronautical engineering
Aeronautical engineering covers the design and construction of aircraft, including how they are powered, how they are used and how they are controlled for safe operation., University of Glasgow.
aerodynamics
Aerodynamics, from grc, ἀήρ ''aero'' (air) + grc, δυναμική (dynamics), is the study of the motion of air, particularly when affected by a solid object, such as an airplane wing. It involves topics covered in the field of fluid dyn ...
, the science of passing through the air.
With the increasing activity in space flight, nowadays aeronautics and astronautics are often combined as aerospace engineering
Aerospace engineering is the primary field of engineering concerned with the development of aircraft and spacecraft. It has two major and overlapping branches: aeronautical engineering and astronautical engineering. Avionics engineering is si ...
.
Aerodynamics
The science of aerodynamics deals with the motion of air and the way that it interacts with objects in motion, such as an aircraft. The study of aerodynamics falls broadly into three areas: ''Incompressible flow
In fluid mechanics or more generally continuum mechanics, incompressible flow ( isochoric flow) refers to a flow in which the material density is constant within a fluid parcel—an infinitesimal volume that moves with the flow velocity. An e ...
'' occurs where the air simply moves to avoid objects, typically at subsonic speeds below that of sound (Mach 1).
''Compressible flow
Compressible flow (or gas dynamics) is the branch of fluid mechanics that deals with flows having significant changes in fluid density. While all flows are compressible, flows are usually treated as being incompressible when the Mach number (the r ...
'' occurs where shock waves appear at points where the air becomes compressed, typically at speeds above Mach 1.
''Transonic flow
Transonic (or transsonic) flow is air flowing around an object at a speed that generates regions of both subsonic and supersonic airflow around that object. The exact range of speeds depends on the object's critical Mach number, but transoni ...
'' occurs in the intermediate speed range around Mach 1, where the airflow over an object may be locally subsonic at one point and locally supersonic at another.
Rocketry
Arocket
A rocket (from it, rocchetto, , bobbin/spool) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using the surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely fr ...
or rocket vehicle is a missile
In military terminology, a missile is a guided airborne ranged weapon capable of self-propelled flight usually by a jet engine or rocket motor. Missiles are thus also called guided missiles or guided rockets (when a previously unguided rocket i ...
, spacecraft, aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines ...
or other vehicle
A vehicle (from la, vehiculum) is a machine that transports people or cargo. Vehicles include wagons, bicycles, motor vehicles (motorcycles, cars, trucks, buses, mobility scooters for disabled people), railed vehicles (trains, trams), wa ...
which obtains thrust
Thrust is a reaction force described quantitatively by Newton's third law. When a system expels or accelerates mass in one direction, the accelerated mass will cause a force of equal magnitude but opposite direction to be applied to that syst ...
from a rocket engine
A rocket engine uses stored rocket propellants as the reaction mass for forming a high-speed propulsive jet of fluid, usually high-temperature gas. Rocket engines are reaction engines, producing thrust by ejecting mass rearward, in accordanc ...
. In all rockets, the exhaust is formed entirely from propellant
A propellant (or propellent) is a mass that is expelled or expanded in such a way as to create a thrust or other motive force in accordance with Newton's third law of motion, and "propel" a vehicle, projectile, or fluid payload. In vehicles, the e ...
s carried within the rocket before use. Rocket engines work by action and reaction As described by the third of Newton's laws of motion of classical mechanics, all forces occur in pairs such that if one object exerts a force on another object, then the second object exerts an equal and opposite reaction force on the first. The t ...
. Rocket engines push rockets forwards simply by throwing their exhaust backwards extremely fast.
Rockets for military and recreational uses date back to at least 13th-century China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. Significant scientific, interplanetary and industrial use did not occur until the 20th century, when rocketry was the enabling technology of the Space Age
The Space Age is a period encompassing the activities related to the Space Race, space exploration, space technology, and the cultural developments influenced by these events, beginning with the Sputnik_1#Launch_and_mission, launch of Sputnik 1 ...
, including setting foot on the moon.
Rockets are used for fireworks
Fireworks are a class of Explosive, low explosive Pyrotechnics, pyrotechnic devices used for aesthetic and entertainment purposes. They are most commonly used in fireworks displays (also called a fireworks show or pyrotechnics), combining a l ...
, weaponry, ejection seat
In aircraft, an ejection seat or ejector seat is a system designed to rescue the aircraft pilot, pilot or other aircrew, crew of an aircraft (usually military) in an emergency. In most designs, the seat is propelled out of the aircraft by an ex ...
s, launch vehicle
A launch vehicle or carrier rocket is a rocket designed to carry a payload (spacecraft or satellites) from the Earth's surface to outer space. Most launch vehicles operate from a launch pad, launch pads, supported by a missile launch contro ...
s for artificial satellite
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioisoto ...
s, human spaceflight
Human spaceflight (also referred to as manned spaceflight or crewed spaceflight) is spaceflight with a crew or passengers aboard a spacecraft, often with the spacecraft being operated directly by the onboard human crew. Spacecraft can also be ...
and exploration
Exploration refers to the historical practice of discovering remote lands. It is studied by geographers and historians.
Two major eras of exploration occurred in human history: one of convergence, and one of divergence. The first, covering most ...
of other planets. While comparatively inefficient for low speed use, they are very lightweight and powerful, capable of generating large accelerations and of attaining extremely high speeds with reasonable efficiency.
Chemical rockets are the most common type of rocket and they typically create their exhaust by the combustion of rocket propellant
Rocket propellant is the reaction mass of a rocket. This reaction mass is ejected at the highest achievable velocity from a rocket engine
A rocket engine uses stored rocket propellants as the reaction mass for forming a high-speed propuls ...
. Chemical rockets store a large amount of energy in an easily released form, and can be very dangerous. However, careful design, testing, construction and use minimizes risks.
See also
References
Citations
Sources
* * *External links
Courses
* * * *Research
* * * {{Authority control + Vehicle operation Articles containing video clips