Admiral Cunningham on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Admiral of the Fleet Andrew Browne Cunningham, 1st Viscount Cunningham of Hyndhope, (7 January 1883 – 12 June 1963) was a senior officer of the
 Along with 64 other boys Cunningham joined the
Along with 64 other boys Cunningham joined the
 Cunningham was a highly decorated officer during the First World War, receiving the Distinguished Service Order (DSO) and two bars. In 1911 he was given command of the destroyer , which he commanded throughout the war. In 1914, ''Scorpion'' was involved in the shadowing of the
Cunningham was a highly decorated officer during the First World War, receiving the Distinguished Service Order (DSO) and two bars. In 1911 he was given command of the destroyer , which he commanded throughout the war. In 1914, ''Scorpion'' was involved in the shadowing of the
 In September 1932, Cunningham was promoted to
In September 1932, Cunningham was promoted to
 At the end of March 1941, Hitler wanted the convoys supplying the British Expeditionary force in Greece stopped, and the Italian Navy was the only force able to attempt this. Cunningham stated in his biography: "I myself was inclined to think that the Italians would not try anything. I bet Commander
At the end of March 1941, Hitler wanted the convoys supplying the British Expeditionary force in Greece stopped, and the Italian Navy was the only force able to attempt this. Cunningham stated in his biography: "I myself was inclined to think that the Italians would not try anything. I bet Commander
 On the morning of 20 May 1941,
On the morning of 20 May 1941,
 Cunningham became a Knight Grand Cross of the Order of the Bath (GCB), "in recognition of the recent successful combined operations in the Middle East", in March 1941 and was created a baronet, of Bishop's Waltham in the County of Southampton, in July 1942. From late 1942 to early 1943, he served under
Cunningham became a Knight Grand Cross of the Order of the Bath (GCB), "in recognition of the recent successful combined operations in the Middle East", in March 1941 and was created a baronet, of Bishop's Waltham in the County of Southampton, in July 1942. From late 1942 to early 1943, he served under
 In January 1945 Cunningham was appointed a
In January 1945 Cunningham was appointed a
 Below is a list of awards and titles awarded to Andrew Browne Cunningham during his lifetime.
Below is a list of awards and titles awarded to Andrew Browne Cunningham during his lifetime.
Document piece ADM 196/47
and can be downloaded as a pdf (fee required) fro
Documents Online
Retrieved 2008-08-05
Transcription of Official Service Records on www.admirals.org.uk
1943 bromide print
by
Papers of Viscount Cunningham
held at
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
during the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
. He was widely known by his initials, "ABC".
Cunningham was born in Rathmines
Rathmines () is an affluent inner suburb on the Southside of Dublin in Ireland. It lies three kilometres south of the city centre. It begins at the southern side of the Grand Canal and stretches along the Rathmines Road as far as Rathgar to t ...
in the south side of Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of the Wicklow Mountains range. At the 2016 c ...
on 7 January 1883. After starting his schooling in Dublin and Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian on the southern shore of t ...
, he enrolled at Stubbington House School
Stubbington House School was founded in 1841 as a boys' preparatory school, originally located in the Hampshire village of Stubbington, around from the Solent. Stubbington House School was known by the sobriquet "the cradle of the Navy". The sc ...
, at the age of ten. He entered the Royal Navy in 1897 as a naval cadet in the officers' training ship ''Britannia'', passing out in 1898. He commanded a destroyer during the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
and through most of the interwar period. He was awarded the Distinguished Service Order
The Distinguished Service Order (DSO) is a military decoration of the United Kingdom, as well as formerly of other parts of the Commonwealth, awarded for meritorious or distinguished service by officers of the armed forces during wartime, ty ...
and two Bars, for his performance during this time, specifically for his actions in the Dardanelles
The Dardanelles (; tr, Çanakkale Boğazı, lit=Strait of Çanakkale, el, Δαρδανέλλια, translit=Dardanéllia), also known as the Strait of Gallipoli from the Gallipoli peninsula or from Classical Antiquity as the Hellespont (; ...
and in the Baltics
The Baltic states, et, Balti riigid or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which currently is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, ...
.
In the Second World War, as Commander-in-Chief, Mediterranean Fleet, Cunningham led British naval forces to victory in several critical Mediterranean naval battles. These included the attack on Taranto
The Battle of Taranto took place on the night of 11–12 November 1940 during the Second World War between British naval forces, under Admiral Andrew Cunningham, and Italian naval forces, under Admiral Inigo Campioni. The Royal Navy launched ...
in 1940, the first completely all-aircraft naval attack in history, and the Battle of Cape Matapan
The Battle of Cape Matapan ( el, Ναυμαχία του Ταινάρου) was a naval battle during the Second World War between the Allies, represented by the navies of the United Kingdom and Australia, and the Royal Italian navy, from 27 t ...
in 1941. Cunningham controlled the defence of the Mediterranean supply lines through Alexandria, Gibraltar, and the key chokepoint of Malta. He also directed naval support for the various major Allied landings in the Western Mediterranean littoral
The littoral zone or nearshore is the part of a sea, lake, or river that is close to the shore. In coastal ecology, the littoral zone includes the intertidal zone extending from the high water mark (which is rarely inundated), to coastal a ...
. In autumn 1943, with the incumbent, Sir Dudley Pound, dying, Cunningham was promoted to First Sea Lord
The First Sea Lord and Chief of the Naval Staff (1SL/CNS) is the military head of the Royal Navy and Naval Service of the United Kingdom. The First Sea Lord is usually the highest ranking and most senior admiral to serve in the British Armed Fo ...
, the professional head of the Royal Navy, a position he held until his retirement in 1946. He was ennobled as Baron Cunningham of Hyndhope in 1945 and made Viscount Cunningham of Hyndhope the following year. After his retirement, Cunningham enjoyed several ceremonial positions, including Lord High Steward
The Lord High Steward is the first of the Great Officers of State in England, nominally ranking above the Lord Chancellor.
The office has generally remained vacant since 1421, and is now an ''ad hoc'' office that is primarily ceremonial and ...
at the coronation of Queen Elizabeth II
The coronation of Elizabeth II took place on 2 June 1953 at Westminster Abbey in London. She acceded to the throne at the age of 25 upon the death of her father, George VI, on 6 February 1952, being proclaimed queen by her privy and executive ...
in 1953. He died on 12 June 1963, aged 80.
Childhood
Cunningham was born atRathmines
Rathmines () is an affluent inner suburb on the Southside of Dublin in Ireland. It lies three kilometres south of the city centre. It begins at the southern side of the Grand Canal and stretches along the Rathmines Road as far as Rathgar to t ...
, County Dublin
"Action to match our speech"
, image_map = Island_of_Ireland_location_map_Dublin.svg
, map_alt = map showing County Dublin as a small area of darker green on the east coast within the lighter green background of ...
, on 7 January 1883, the third of five children born to Professor Daniel John Cunningham
Daniel John Cunningham M.D., D.C.L., LL. D. F.R.S., F.R.S.E. F.R.A.I. (15 April 1850 – 23 July 1909) was a Scottish physician, zoologist, and anatomist, famous for ''Cunningham's Text-book of Anatomy'' and ''Cunningham's Manual of Pra ...
and Elizabeth Cumming Browne, both born in Scotland. General Sir Alan Cunningham was his younger brother. His parents were described as having a "strong intellectual and clerical tradition," both grandfathers having been in the clergy. His father was a Professor of Anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having it ...
at Trinity College Dublin
, name_Latin = Collegium Sanctae et Individuae Trinitatis Reginae Elizabethae juxta Dublin
, motto = ''Perpetuis futuris temporibus duraturam'' (Latin)
, motto_lang = la
, motto_English = It will last i ...
, whilst his mother stayed at home. Elizabeth Browne, with the aid of servants and governesses, oversaw much of his upbringing; as a result he reportedly had a "warm and close" relationship with her.Andrew Cunningham pp. 9–14
After a short introduction to schooling in Dublin he was sent to Edinburgh Academy
The Edinburgh Academy is an independent day school in Edinburgh, Scotland, which was opened in 1824. The original building, on Henderson Row in the city's New Town, is now part of the Senior School. The Junior School is located on Arboretum Ro ...
, where he stayed with his aunts Doodles and Connie May. At the age of ten he received a telegram from his father asking "would you like to go into the Navy?" At the time, the family had no maritime connections, and Cunningham only had a vague interest in the sea. Nevertheless, he replied "Yes, I should like to be an Admiral". He was then sent to a Naval Preparatory School, Stubbington House, which specialised in sending pupils through the entrance examinations. Cunningham passed the exams, showing particular strength in mathematics.
Early naval career
 Along with 64 other boys Cunningham joined the
Along with 64 other boys Cunningham joined the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
as a cadet aboard the training ship ''Britannia'' at Dartmouth on 15 January 1897.Michael Simpson Chap1 p .2 One of his classmates was future Admiral of the Fleet Sir James Somerville. Cunningham was known for his lack of enthusiasm for field sports, although he did enjoy golf and spent most of his spare time "messing around in boats". He said in his memoirs that by the end of his course he was "anxious to seek adventure at sea". Although he committed numerous minor misdemeanours, he still obtained a ''very good'' for conduct. He passed out tenth in April 1898, with first class marks for mathematics and seamanship
Seamanship is the art, knowledge and competence of operating a ship, boat or other craft on water. The'' Oxford Dictionary'' states that seamanship is "The skill, techniques, or practice of handling a ship or boat at sea."
It involves topics a ...
.Dartmouth archives 1897–1899 cited by Michael Simpson in the "References" section, p.283
His first service was as a midshipman on in 1899, serving at the Cape of Good Hope Station
The Commander-in-Chief, Africa was the last title of a Royal Navy's formation commander located in South Africa from 1795 to 1939. Under varying titles, it was one of the longest-lived formations of the Royal Navy. It was also often known as the C ...
when the Second Boer War
The Second Boer War ( af, Tweede Vryheidsoorlog, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, the Anglo–Boer War, or the South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer Republics (the South ...
began.; quote from source cited. By February 1900, he had transferred into the Naval Brigade as he believed "this promised opportunities for bravery and distinction in action." Cunningham then saw action at Pretoria and Diamond Hill
Diamond Hill is a hill in the east of Kowloon, Hong Kong. The name also refers to the area on or adjacent to the hill. It is surrounded by Ngau Chi Wan, San Po Kong, Wong Tai Sin and Tsz Wan Shan. Its northeast is limited by the ridge. It is p ...
as part of the Naval Brigade. He then went back to sea, as midshipman in in December 1901. The following November he joined the protected cruiser
Protected cruisers, a type of naval cruiser of the late-19th century, gained their description because an armoured deck offered protection for vital machine-spaces from fragments caused by shells exploding above them. Protected cruisers re ...
. Beginning in 1902, Cunningham took sub-lieutenant courses at Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most dens ...
and Greenwich
Greenwich ( , ,) is a town in south-east London, England, within the ceremonial county of Greater London. It is situated east-southeast of Charing Cross.
Greenwich is notable for its maritime history and for giving its name to the Greenwich ...
; he served as sub-lieutenant on the battleship , in the Mediterranean, for six months in 1903. In September 1903, he was transferred to to serve as second-in-command. He was promoted to lieutenant
A lieutenant ( , ; abbreviated Lt., Lt, LT, Lieut and similar) is a commissioned officer rank in the armed forces of many nations.
The meaning of lieutenant differs in different militaries (see comparative military ranks), but it is often ...
in 1904, and served on several vessels during the next four years. In 1908, he was awarded his first command, HM Torpedo Boat No. 14.
First World War
 Cunningham was a highly decorated officer during the First World War, receiving the Distinguished Service Order (DSO) and two bars. In 1911 he was given command of the destroyer , which he commanded throughout the war. In 1914, ''Scorpion'' was involved in the shadowing of the
Cunningham was a highly decorated officer during the First World War, receiving the Distinguished Service Order (DSO) and two bars. In 1911 he was given command of the destroyer , which he commanded throughout the war. In 1914, ''Scorpion'' was involved in the shadowing of the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
battlecruiser and cruiser ''Goeben'' and ''Breslau''. This operation was intended to find and destroy the ''Goeben'' and the ''Breslau'' but the German warships evaded the British fleet,Moorehead, Alan pp. 11–28 and passed through the Dardanelles
The Dardanelles (; tr, Çanakkale Boğazı, lit=Strait of Çanakkale, el, Δαρδανέλλια, translit=Dardanéllia), also known as the Strait of Gallipoli from the Gallipoli peninsula or from Classical Antiquity as the Hellespont (; ...
to reach Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya ( Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
. Their arrival contributed to the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
joining the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in ...
in November 1914. Though a bloodless "battle", the failure of the British pursuit had enormous political and military ramifications—in the words of Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from ...
, they brought "more slaughter, more misery and more ruin than has ever before been borne within the compass of a ship."
Cunningham stayed on in the Mediterranean and in 1915 ''Scorpion'' was involved in the attack on the Dardanelles
The Dardanelles (; tr, Çanakkale Boğazı, lit=Strait of Çanakkale, el, Δαρδανέλλια, translit=Dardanéllia), also known as the Strait of Gallipoli from the Gallipoli peninsula or from Classical Antiquity as the Hellespont (; ...
. For his performance, Cunningham was rewarded with promotion to commander in July 1915. He was also awarded the Distinguished Service Order, gazetted in March 1916. Cunningham spent much of 1916 on routine patrols. In late 1916, he was engaged in convoy protection, a duty he regarded as mundane.Michael Simpson p. 13 He had no contact with German U-boats during this time, on which he commented; "The immunity of my convoys was probably due to sheer luck". Convinced that the Mediterranean held few offensive possibilities he requested to sail for home. ''Scorpion'' paid off on 21 January 1918. In his seven years as captain of the ''Scorpion'', Cunningham had developed a reputation for first class seamanship. He was transferred by Vice-Admiral Roger Keyes
Admiral of the Fleet Roger John Brownlow Keyes, 1st Baron Keyes, (4 October 1872 – 26 December 1945) was a British naval officer.
As a junior officer he served in a corvette operating from Zanzibar on slavery suppression missions. Ea ...
to , part of Keyes' Dover Patrol
The Dover Patrol and later known as the Dover Patrol Force was a Royal Navy command of the First World War, notable for its involvement in the Zeebrugge Raid on 22 April 1918. The Dover Patrol formed a discrete unit of the Royal Navy based at Dove ...
, in April 1918. For his actions with the Dover Patrol, he was awarded a bar to his DSO the following year.
Interwar years
Association with Cowan
Cunningham saw much action in the interwar years. In 1919, he commanded the S-class destroyer , on duty in theBaltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
* Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originati ...
. The Communists, the White Russians, several varieties of Latvian nationalists and the Germans were trying to control Latvia; the British Government had recognised Latvia's independence after the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Treaty of Brest in Russia) was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Russia and the Central Powers (Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire), that ended Russia's ...
. It was on this voyage that Cunningham first met Admiral Walter Cowan
Admiral Sir Walter Henry Cowan, 1st Baronet, (11 June 1871 – 14 February 1956), known as Tich Cowan, was a Royal Navy officer who saw service in both the First and Second World Wars; in the latter he was one of the oldest British servicemen ...
. Cunningham was impressed by Cowan's methods, specifically his navigation of the potentially dangerous seas, with thick fog and minefields
A land mine is an explosive device concealed under or on the ground and designed to destroy or disable enemy targets, ranging from combatants to vehicles and tanks, as they pass over or near it. Such a device is typically detonated automati ...
threatening the fleet. Throughout several potentially problematic encounters with German forces trying to undermine the Latvian independence movement, Cunningham exhibited "good self control and judgement". Cowan was quoted as saying "Commander Cunningham has on one occasion after another acted with unfailing promptitude and decision, and has proved himself an Officer of exceptional valour and unerring resolution."
He was promoted to the rank of captain, effective 31 December 1919. For his actions in the Baltic, Cunningham was awarded a second bar to his DSO, gazetted in March 1920. His first appointment as a Captain was President of the Naval Inter-Allied Commission of Control in Heligoland
Heligoland (; german: Helgoland, ; Heligolandic Frisian: , , Mooring Frisian: , da, Helgoland) is a small archipelago in the North Sea. A part of the German state of Schleswig-Holstein since 1890, the islands were historically possessions ...
. On his return from the Baltic in 1922, he was appointed captain of the 6th Destroyer Flotilla
The British 6th Destroyer Flotilla, or Sixth Destroyer Flotilla, was a military formation of the Royal Navy from 1911 to 1939 and again from 1947 to 1951
History
The flotilla was formed in 1911 at Portsmouth, with its first commander, Captain Mo ...
. Further commands were to follow; the 1st Destroyer Flotilla
The 1st Destroyer Flotilla, also styled as the First Destroyer Flotilla, was a naval formation of the British Royal Navy from 1909 to 1940 and again from 1947 to 1951.
History
Pre-war history
In May 1906, the First Destroyer Flotilla was at ...
in 1923, and the destroyer base, , at Port Edgar
Port Edgar is a marina on the southern shore of the Firth of Forth, immediately west of the Forth Road Bridge and the town of South Queensferry, in Edinburgh, Scotland. Originally a naval base, HMS Lochinvar (shore establishment), HMS ''Lochinvar ...
in the Firth of Forth, from 1924 to 1926. Cunningham renewed his association with Vice Admiral Cowan between 1926 and 1928, when Cunningham was flag captain and chief staff officer to Cowan while serving on the North America and West Indies Squadron
The North America and West Indies Station was a formation or command of the United Kingdom's Royal Navy stationed in North American waters from 1745 to 1956. The North American Station was separate from the Jamaica Station until 1830 when the t ...
, based at the Royal Naval Dockyard in the Imperial fortress
Imperial fortress was the designation given in the British Empire to four colonies that were located in strategic positions from each of which Royal Navy squadrons could control the surrounding regions and, between them, much of the planet.
His ...
colony
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the '' metropolitan state' ...
of Bermuda
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type = National song
, song = "Hail to Bermuda"
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, mapsize2 =
, map_caption2 =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name =
, es ...
, with shore headquarters at Admiralty House in Pembroke. In his memoirs Cunningham made clear the "high regard"Andrew Cunningham p. 262 in which he held Cowan, and the many lessons he learned from him during their two periods of service together. The late 1920s found Cunningham back in the UK participating in courses at the Army's Senior Officers' School
The Senior Officers' School was a British military establishment established in 1916 by Brigadier-General R.J. Kentish for the training of Commonwealth senior officers of all services in inter-service cooperation. It was established as part of a ...
at Sheerness, as well as at the Imperial Defence College
The Royal College of Defence Studies (RCDS) instructs the most promising senior officers of the British Armed Forces, His Majesty's Diplomatic Service and Civil Service in national defence and international security matters at the highest level ...
. While Cunningham was at the Imperial Defence College, in 1929, he married Nona Byatt (daughter of Horace Byatt, MA; the couple had no children). After a year at the College, Cunningham was given command of his first big ship; the battleship . Eighteen months later, he was appointed commodore
Commodore may refer to:
Ranks
* Commodore (rank), a naval rank
** Commodore (Royal Navy), in the United Kingdom
** Commodore (United States)
** Commodore (Canada)
** Commodore (Finland)
** Commodore (Germany) or ''Kommodore''
* Air commodore ...
of , the Royal Naval Barracks, Chatham
The Royal Naval Barracks, Chatham, also known as HMS ''Pembroke'', was a UK naval barracks that was built between the Victorian Steam Yard and Brompton Barracks from 1897 to 1902. It was built on the site of a prison built in 1853 to house ov ...
.
Promoted to flag rank
 In September 1932, Cunningham was promoted to
In September 1932, Cunningham was promoted to flag rank
A flag officer is a commissioned officer in a nation's armed forces senior enough to be entitled to fly a flag to mark the position from which the officer exercises command.
The term is used differently in different countries:
*In many countries ...
, and aide-de-camp to the King
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen, which title is also given to the consort of a king.
*In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the tit ...
. He was appointed Rear Admiral (Destroyers) in the Mediterranean in December 1933 and was made a Companion of the Bath
The Most Honourable Order of the Bath is a British order of chivalry founded by George I on 18 May 1725. The name derives from the elaborate medieval ceremony for appointing a knight, which involved bathing (as a symbol of purification) as on ...
in 1934. Having hoisted his flag in the light cruiser , Cunningham used his time to practice fleet
Fleet may refer to:
Vehicles
*Fishing fleet
*Naval fleet
*Fleet vehicles, a pool of motor vehicles
*Fleet Aircraft, the aircraft manufacturing company
Places
Canada
* Fleet, Alberta, Canada, a hamlet
England
* The Fleet Lagoon, at Chesil Beach ...
handling for which he was to receive much praise in the Second World War.Cunningham, Andrew p. 158 There were also fleet exercises in the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
in which he learnt the skills and values of night actions that he would also use to great effect in years to come.
On his promotion to vice admiral in July 1936, due to the interwar naval policy, further active employment seemed remote. However, a year later due to the illness of Sir Geoffrey Blake, Cunningham assumed the combined appointment of commander of the Battlecruiser Squadron and second-in-command of the Mediterranean Fleet, with as his flagship.Andrew Cunningham ch.7 After his long service in small ships, Cunningham considered his accommodation aboard ''Hood'' to be almost palatial, even surpassing his previous big ship experience on ''Rodney''.
He retained command until September 1938, when he was appointed to the Admiralty
Admiralty most often refers to:
*Admiralty, Hong Kong
*Admiralty (United Kingdom), military department in command of the Royal Navy from 1707 to 1964
*The rank of admiral
*Admiralty law
Admiralty can also refer to:
Buildings
* Admiralty, Traf ...
as Deputy Chief of the Naval Staff, although he did not actually take up this post until December 1938. He accepted this shore job with reluctance since he loathed administration, but the Board of Admiralty's high regard of him was evident. For six months during an illness of Admiral Sir Roger Backhouse
Admiral of the Fleet Sir Roger Roland Charles Backhouse, (24 November 1878 – 15 July 1939) was a Royal Navy officer. He served in the First World War as a cruiser commander and after the war became a battle squadron commander and later Com ...
, the then First Sea Lord
The First Sea Lord and Chief of the Naval Staff (1SL/CNS) is the military head of the Royal Navy and Naval Service of the United Kingdom. The First Sea Lord is usually the highest ranking and most senior admiral to serve in the British Armed Fo ...
, he deputised for Backhouse on the Committee of Imperial Defence and on the Admiralty Board
The Admiralty Board is the body established under the Defence Council of the United Kingdom for the administration of the Naval Service of the United Kingdom. It meets formally only once a year, and the day-to-day running of the Royal Navy is ...
. In 1939 he was made a Knight Commander of the Order of the Bath
The Most Honourable Order of the Bath is a British order of chivalry founded by George I on 18 May 1725. The name derives from the elaborate medieval ceremony for appointing a knight, which involved bathing (as a symbol of purification) as o ...
(KCB), becoming known as Sir Andrew Cunningham.
Second World War
Cunningham described the command of the Mediterranean Fleet as "The finest command the Royal Navy has to offer"Michael Simpson, Chapter 5 p. 42 and he remarked in his memoirs that "I probably knew the Mediterranean as well as any Naval Officer of my generation". Cunningham was made Commander-in-Chief, Mediterranean, hoisting his flag in on 6 June 1939, one day after arriving inAlexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
on 5 June 1939. As Commander-in-Chief, Cunningham's main concern was for the safety of convoys heading for Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
and Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
. These convoys were highly significant in that they were desperately needed to keep Malta, a small British colony and naval base, in the war. Malta was a strategic strongpoint and Cunningham fully appreciated this. Cunningham believed that the main threat to British Sea Power in the Mediterranean would come from the Italian Fleet. As such Cunningham had his fleet at a heightened state of readiness, so that when Italy did choose to enter into hostilities the British Fleet would be ready.
French Surrender (June 1940)
In his role as Commander-in-Chief, Mediterranean, Cunningham had to negotiate with the French Admiral René-Émile Godfroy for the demilitarisation and internment of theForce X The Force X was a squadron of the French Navy, assembled on 29 April 1940, after the outbreak of the Second World War, to deter Italy from striking in the Levantine Sea. It was constituted of the old battleship ''Lorraine'', of the three modern hea ...
, the French squadron at Alexandria, in June 1940, following the Fall of France. Churchill had ordered Cunningham to prevent the French warships from leaving port, and to ensure that French warships did not pass into enemy hands. Stationed at the time at Alexandria, Cunningham entered into delicate negotiations with Godfroy to ensure his fleet, which consisted of the battleship ''Lorraine'', four cruisers, three destroyers and a submarine, posed no threat.Oliver Warner p. 97 The Admiralty ordered Cunningham to complete the negotiations on 3 July. Just as an agreement seemed imminent Godfroy heard of the British action against the French at Mers el Kebir
Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) is a viral respiratory infection caused by ''Middle East respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus'' (MERS-CoV). Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. Typical symptoms include fever, cough, ...
and, for a while, Cunningham feared a battle between French and British warships in the confines of Alexandria harbour. The deadline was overrun but negotiations ended well, after Cunningham put them on a more personal level and had the British ships appeal to their French opposite numbers. Cunningham's negotiations succeeded and the French emptied their fuel bunkers and removed the firing mechanisms from their guns.Oliver Warner p. 100 Cunningham in turn promised to repatriate the ships' crews.
Battle of Taranto (November 1940)
Although the threat from the French Fleet had been neutralised, Cunningham was still aware of the threat posed by the Italian Fleet to British North African operations, based in Egypt. Although the Royal Navy had won in several actions in the Mediterranean, considerably upsetting the balance of power, the Italians who were following the theory of afleet in being
In naval warfare, a "fleet in being" is a naval force that extends a controlling influence without ever leaving port. Were the fleet to leave port and face the enemy, it might lose in battle and no longer influence the enemy's actions, but while ...
had left their ships in harbour. This made the threat of a sortie against the British Fleet a serious problem. At the time the harbour at Taranto contained six battleships (five of them battle-worthy), seven heavy cruiser
The heavy cruiser was a type of cruiser, a naval warship designed for long range and high speed, armed generally with naval guns of roughly 203 mm (8 inches) in caliber, whose design parameters were dictated by the Washington Naval T ...
s, two light cruiser
A light cruiser is a type of small or medium-sized warship. The term is a shortening of the phrase "light armored cruiser", describing a small ship that carried armor in the same way as an armored cruiser: a protective belt and deck. Prior to th ...
s, and eight destroyers. The Admiralty, concerned with the potential for an attack, had drawn up Operation ''Judgement''; a surprise attack on Taranto Harbour. To carry out the attack, the Admiralty sent the new aircraft carrier , commanded by Lumley Lyster
Vice-Admiral Sir Arthur Lumley St George Lyster, (27 April 1888 – 4 August 1957) was a Royal Navy officer during the Second World War.
Naval career
After leaving Berkhamsted School, in 1902 Lyster joined HMS ''Britannia'' to train for a nav ...
, to join in Cunningham's fleet.
The attack started at 21:00, 11 November 1940, when the first of two waves of Fairey Swordfish
The Fairey Swordfish is a biplane torpedo bomber, designed by the Fairey Aviation Company. Originating in the early 1930s, the Swordfish, nicknamed "Stringbag", was principally operated by the Fleet Air Arm of the Royal Navy. It was also us ...
torpedo bombers
A torpedo bomber is a military aircraft designed primarily to attack ships with aerial torpedoes. Torpedo bombers came into existence just before the First World War almost as soon as aircraft were built that were capable of carrying the weight ...
took off from ''Illustrious'', followed by the second wave an hour later. The attack was a great success: the Italian fleet lost half its strength in one night. The "fleet-in-being" diminished in importance and the threat to the Royal Navy's control of the Mediterranean had been considerably reduced. Cunningham said of the victory: "Taranto, and the night of 11–12 November 1940, should be remembered for ever as having shown once and for all that in the Fleet Air Arm
The Fleet Air Arm (FAA) is one of the five fighting arms of the Royal Navy and is responsible for the delivery of naval air power both from land and at sea. The Fleet Air Arm operates the F-35 Lightning II for maritime strike, the AW159 Wil ...
the Navy has its most devastating weapon." The Royal Navy had launched the first all-aircraft naval attack in history, flying a small number of aircraft from an aircraft carrier. This, and other aspects of the raid, were important facts in the planning of the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor in 1941: the Japanese planning staff were thought to have studied it intensively.
Cunningham's official reaction at the time was memorably terse. After landing the last of the attacking aircraft, ''Illustrious'' signalled "Operation Judgement executed". After seeing aerial reconnaissance photographs the next day which showed several Italian ships sunk or out of action, Cunningham replied with the two-letter code group which signified, "Manoeuvre well executed".
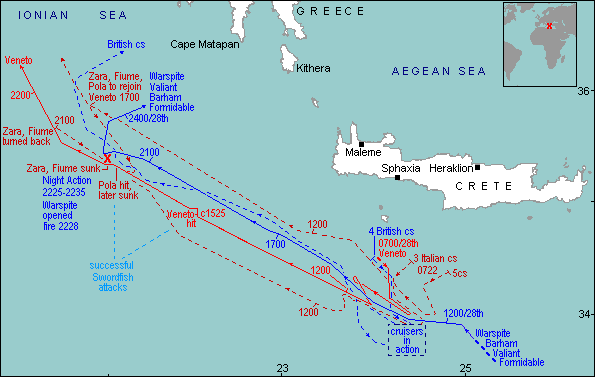
Battle of Cape Matapan (March 1941)
 At the end of March 1941, Hitler wanted the convoys supplying the British Expeditionary force in Greece stopped, and the Italian Navy was the only force able to attempt this. Cunningham stated in his biography: "I myself was inclined to think that the Italians would not try anything. I bet Commander
At the end of March 1941, Hitler wanted the convoys supplying the British Expeditionary force in Greece stopped, and the Italian Navy was the only force able to attempt this. Cunningham stated in his biography: "I myself was inclined to think that the Italians would not try anything. I bet Commander Power
Power most often refers to:
* Power (physics), meaning "rate of doing work"
** Engine power, the power put out by an engine
** Electric power
* Power (social and political), the ability to influence people or events
** Abusive power
Power may a ...
, the Staff Officer, Operations, the sum of ten shillings that we would see nothing of the enemy."
Under pressure from Germany, the Italian Fleet planned to launch an attack on the British Fleet on 28 March 1941. The Italian commander, Admiral Angelo Iachino, intended to carry out a surprise attack on the British Cruiser Squadron in the area (commanded by Vice-Admiral Sir Henry Pridham-Wippell), executing a pincer movement
The pincer movement, or double envelopment, is a military maneuver in which forces simultaneously attack both flanks (sides) of an enemy formation. This classic maneuver holds an important foothold throughout the history of warfare.
The pin ...
with the battleship ''Vittorio Veneto''.Bernard Edwards, Chapter 11, Cape Matapan Cunningham though, was aware of Italian naval activity through intercepts of Italian Enigma
Enigma may refer to:
*Riddle, someone or something that is mysterious or puzzling
Biology
*ENIGMA, a class of gene in the LIM domain
Computing and technology
* Enigma (company), a New York-based data-technology startup
* Enigma machine, a family ...
messages. Although Italian intentions were unclear, Cunningham's staff believed an attack upon British troop convoys was likely and orders were issued to spoil the enemy plan and, if possible, intercept their fleet. Cunningham wished, however, to disguise his own activity and arranged for a game of golf and a fictitious evening gathering to mislead enemy agents (he was, in fact, overheard by the local Japanese Consul).
After sunset, he boarded HMS ''Warspite'' and left Alexandria. Cunningham, realising that an air attack could weaken the Italians, ordered an attack by the 's Albacore
The albacore (''Thunnus alalunga''), known also as the longfin tuna, is a species of tuna of the order Perciformes. It is found in temperate and tropical waters across the globe in the epipelagic and mesopelagic zones. There are six distinct s ...
torpedo-bombers. A hit on the ''Vittorio Veneto'' slowed her temporarily and Iachino, realising his fleet was vulnerable without air cover, ordered his forces to retire. Cunningham gave the order to pursue the Italian Fleet.
An air attack from the ''Formidable'' had disabled the cruiser , and Iachino, unaware of Cunningham's pursuing battlefleet, ordered a squadron of cruisers and destroyers to return and protect the ''Pola''. Cunningham, meanwhile, was joining up with Pridham-Wippell's cruiser squadron. Throughout the day several chases and sorties occurred with no overall victor. None of the Italian ships were equipped for night fighting, and when night fell, they made to return to Taranto. The British battlefleet equipped with radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, we ...
detected the Italians shortly after 22:00. In a pivotal moment in naval warfare during the Second World War, the battleships , and ''Warspite'' opened fire on two Italian cruisers at only 3,800 yards (3.5 km), destroying them in only five minutes.
Although the ''Vittorio Veneto'' escaped from the battle by returning to Taranto, there were many accolades given to Cunningham for continuing the pursuit at night, against the advice of his staff. After the previous defeat at Taranto, the defeat at Cape Matapan dealt another strategic blow to the Italian Navy. Five ships—three heavy cruisers and two destroyers—were sunk, and around 2,400 Italian sailors were killed, missing or captured. The British lost only three aircrew when one torpedo bomber was shot down. Cunningham had lost his bet with Commander Power but he had won a strategic victory in the war in the Mediterranean. The defeats at Taranto and Cape Matapan meant that the Italian Navy did not intervene in the heavily contested evacuations of Greece and Crete, later in 1941. It also ensured that, for the remainder of the war, the Regia Marina
The ''Regia Marina'' (; ) was the navy of the Kingdom of Italy (''Regno d'Italia'') from 1861 to 1946. In 1946, with the birth of the Italian Republic (''Repubblica Italiana''), the ''Regia Marina'' changed its name to ''Marina Militare'' ("M ...
conceded the Eastern Mediterranean to the Allied Fleet, and did not leave port for the remainder of the war.
Battle of Crete (May 1941)
 On the morning of 20 May 1941,
On the morning of 20 May 1941, Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
launched an airborne invasion of Crete, under the code-name ''Unternehmen Merkur'' (Operation Mercury). Despite initial heavy casualties, Maleme
Maleme ( el, Μάλεμε) is a small village and military airport to the west of Chania, in north western Crete, Greece. It is located in Platanias municipality, in Chania regional unit.
History
Bronze Age
A Late Minoan tholos tomb has been ...
airfield in western Crete fell to the Germans and enabled them to fly in heavy reinforcements and overwhelm the Allied forces.
After a week of heavy fighting, British commanders decided that the situation was hopeless and ordered a withdrawal from Sfakia
Sfakiá ( el, Σφακιά) is a mountainous area in the southwestern part of the island of Crete, in the Chania regional unit. It is considered to be one of the few places in Greece that have never been fully occupied by foreign powers. With a ...
. During the next four nights, 16,000 troops were evacuated to Egypt by ships (including of Battle of the River Plate
The Battle of the River Plate was fought in the South Atlantic on 13 December 1939 as the first naval battle of the Second World War. The Kriegsmarine heavy cruiser , commanded by Captain Hans Langsdorff, engaged a Royal Navy squadron, command ...
fame). A smaller number of ships were to withdraw troops on a separate mission from Heraklion
Heraklion or Iraklion ( ; el, Ηράκλειο, , ) is the largest city and the administrative capital of the island of Crete and capital of Heraklion regional unit. It is the fourth largest city in Greece with a population of 211,370 (Urban Ar ...
, but these ships were attacked en route by Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German ''Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the ''Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabtei ...
dive bombers. Without air cover, Cunningham's ships suffered serious losses. Cunningham was determined, though, that the "navy must not let the army down", and when army generals feared he would lose too many ships, Cunningham said,
The "never say die" attitude of Cunningham and the men under his command meant that of 22,000 men on Crete, 16,500 were rescued but at the loss of three cruisers and six destroyers. Fifteen other major warships were damaged.
Allied Expeditionary Force (1942–43)

 Cunningham became a Knight Grand Cross of the Order of the Bath (GCB), "in recognition of the recent successful combined operations in the Middle East", in March 1941 and was created a baronet, of Bishop's Waltham in the County of Southampton, in July 1942. From late 1942 to early 1943, he served under
Cunningham became a Knight Grand Cross of the Order of the Bath (GCB), "in recognition of the recent successful combined operations in the Middle East", in March 1941 and was created a baronet, of Bishop's Waltham in the County of Southampton, in July 1942. From late 1942 to early 1943, he served under General
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry.
In some usages the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED ...
Dwight D. Eisenhower
Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower (born David Dwight Eisenhower; ; October 14, 1890 – March 28, 1969) was an American military officer and statesman who served as the 34th president of the United States from 1953 to 1961. During World War II, ...
, who made him Naval Commander, Allied Expeditionary Force. In this role Cunningham commanded the large fleet that covered the Anglo-American landings in North Africa ( Operation Torch). General Eisenhower said of him in his diary:
On 21 January 1943, Cunningham was promoted to Admiral of the Fleet. February 1943 saw him return to his post as Commander-in-Chief, Mediterranean Fleet. Three months later, when Axis forces in North Africa were on the verge of surrender, he ordered that none should be allowed to escape. Entirely in keeping with his fiery character he signalled the fleet "Sink, burn and destroy: Let nothing pass". He oversaw the naval forces used in the joint Anglo-American amphibious invasions of Sicily, during Operation Husky
Operation or Operations may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media
* ''Operation'' (game), a battery-operated board game that challenges dexterity
* Operation (music), a term used in musical set theory
* ''Operations'' (magazine), Multi-Ma ...
, Operation Baytown
Operation Baytown was an Allied amphibious landing on the mainland of Italy that took place on 3 September 1943, part of the Allied invasion of Italy, itself part of the Italian Campaign, during the Second World War.
Planning
The attack was ...
and Operation Avalanche
Operation Avalanche was the codename for the Allied landings near the port of Salerno, executed on 9 September 1943, part of the Allied invasion of Italy during World War II. The Italians withdrew from the war the day before the invasion, but ...
. On the morning of 11 September 1943, Cunningham was present at Malta when the Italian Fleet surrendered. Cunningham informed the Admiralty with a telegram; "Be pleased to inform their Lordships that the Italian battle fleet now lies at anchor under the guns of the fortress of Malta."
First Sea Lord (1943-46)
In October 1943, Cunningham becameFirst Sea Lord
The First Sea Lord and Chief of the Naval Staff (1SL/CNS) is the military head of the Royal Navy and Naval Service of the United Kingdom. The First Sea Lord is usually the highest ranking and most senior admiral to serve in the British Armed Fo ...
and Chief of the Naval Staff, after the death of Sir Dudley Pound
Admiral of the Fleet Sir Alfred Dudley Pickman Rogers Pound, (29 August 1877 – 21 October 1943) was a British senior officer of the Royal Navy. He served in the First World War as a battleship commander, taking part in the Battle of Jutland ...
. This promotion meant that he had to relinquish his coveted post of Commander-in-Chief, Mediterranean, recommending his namesake Admiral John H. D. Cunningham
Admiral of the Fleet Sir John Henry Dacres Cunningham (13 April 1885 – 13 December 1962) was a Royal Navy officer. A qualified senior navigator, he became Director of Plans at the Admiralty in 1930. He saw action as Commander-in-Chief of the ...
as his successor. In the position of First Sea Lord, and as a member of the Chiefs of Staff committee, Cunningham was responsible for the overall strategic direction of the navy for the remainder of the war. He attended the major conferences at Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the Capital city, capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, List of ...
, Tehran
Tehran (; fa, تهران ) is the largest city in Tehran Province and the capital of Iran. With a population of around 9 million in the city and around 16 million in the larger metropolitan area of Greater Tehran, Tehran is the most popul ...
, Yalta
Yalta (: Я́лта) is a resort city on the south coast of the Crimean Peninsula surrounded by the Black Sea. It serves as the administrative center of Yalta Municipality, one of the regions within Crimea. Yalta, along with the rest of Cri ...
and Potsdam
Potsdam () is the capital and, with around 183,000 inhabitants, largest city of the German state of Brandenburg. It is part of the Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region. Potsdam sits on the River Havel, a tributary of the Elbe, downstream o ...
, at which the Allies discussed future strategy, including the invasion of Normandy and the deployment of a British fleet
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
to the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contin ...
.
While the port of Antwerp was vital for the Allies after D-Day, Admirals Cunningham and Ramsay warned SHAEF and Montgomery that the port was of no use while the Germans held the approaches. But Montgomery postponed the Battle of the Scheldt
The Battle of the Scheldt in World War II was a series of military operations led by the First Canadian Army, with Polish and British units attached, to open up the shipping route to Antwerp so that its port could be used to supply the Alli ...
, and the delay in opening the port was a grave blow to the Allied build-up before winter approached.
Retirement
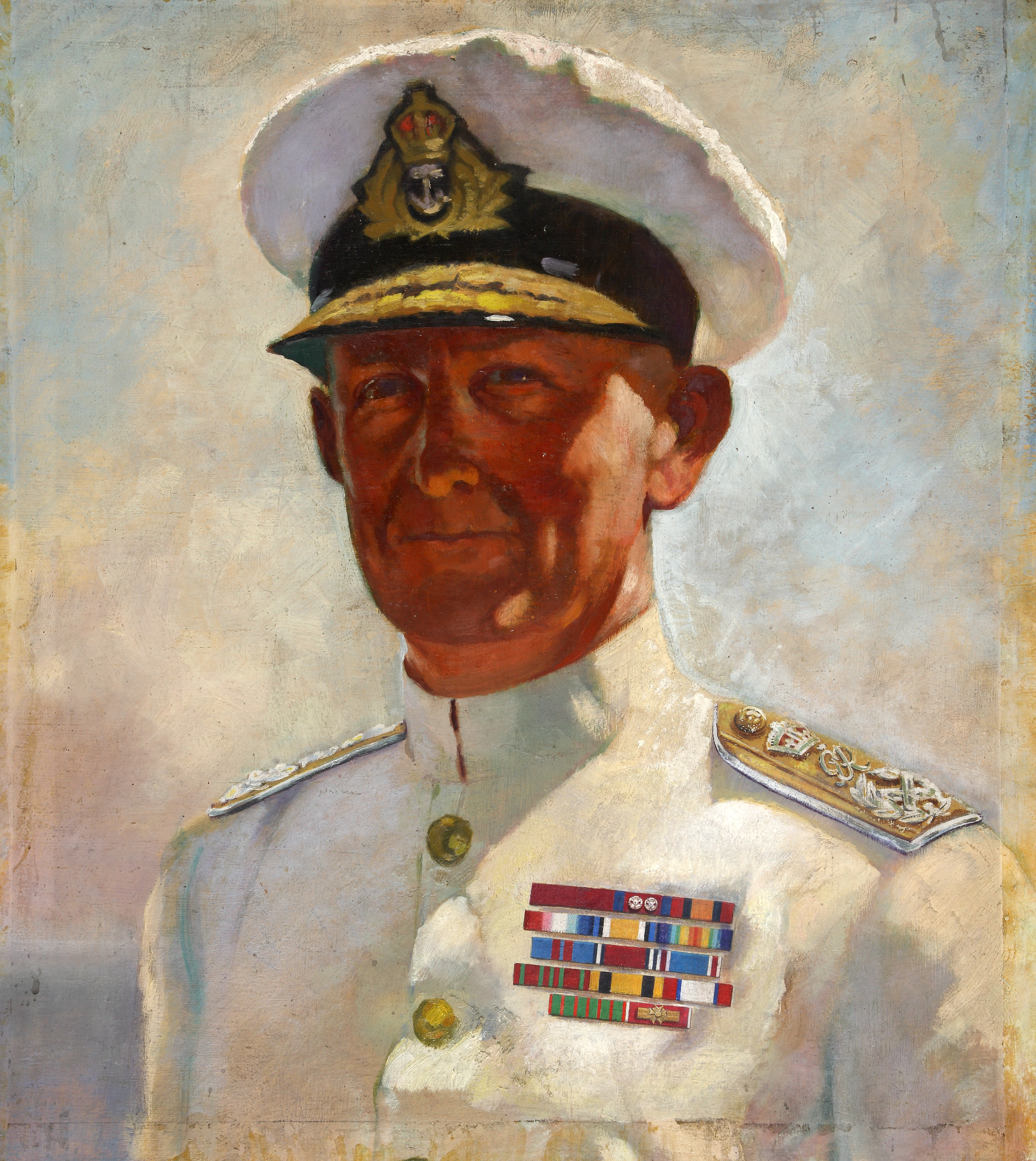
 In January 1945 Cunningham was appointed a
In January 1945 Cunningham was appointed a Knight of the Thistle
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of knighthood by a head of state (including the Pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church or the country, especially in a military capacity. Knighthood finds origins in the Gr ...
and raised to the peerage as Baron Cunningham of Hyndhope, of Kirkhope in the County of Selkirk. He was entitled to retire at the end of the war in 1945 but he resolved to pilot the Navy through the transition to peace before retiring. With the election of Clement Attlee as British Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister i ...
in 1945, and the implementation of his Post-war consensus
The post-war consensus, sometimes called the post-war compromise, was the economic order and social model of which the major political parties in post-war Britain shared a consensus supporting view, from the end of World War II in 1945 to the ...
, there was a large reduction in the Defence Budget. The extensive reorganisation was a challenge for Cunningham. "We very soon came to realise how much easier it was to make war than to reorganise for peace." Due to pressures on the budget from all three services, the Navy embarked on a reduction programme that was larger than Cunningham had envisaged.
In October 1945 he was elected Rector of the University of Edinburgh
The Lord Rector of The University of Edinburgh is elected every three years by the students and staff at The University of Edinburgh. Seldom referred to as ''Lord Rector'', the incumbent is more commonly known just as the ''Rector''.
Role
Th ...
. He was made Viscount Cunningham of Hyndhope, of Kirkhope in the County of Selkirk, in the 1946 New Year Honours
The 1946 New Year Honours were appointments by many of the Commonwealth Realms of King George VI to various orders and honours to reward and highlight good works by citizens of those countries, and to celebrate the passing of 1945 and the beginni ...
, and appointed to the Order of Merit in June of that year. At the end of May 1946, after overseeing the transition through to peacetime, Cunningham retired from his post as First Sea Lord.The Cunningham Papers Cunningham retreated to the "little house in the country", 'Palace House', at Bishop's Waltham
Bishop's Waltham (or Bishops Waltham) is a medieval market town situated at the source of the River Hamble in Hampshire, England. It has a foot in the South Downs National Park and is located at the midpoint of a long-established route betw ...
in Hampshire, which he and Lady Cunningham had acquired before the war. They both had a busy retirement. He attended the House of Lords irregularly and occasionally lent his name to press statements about the Royal Navy, particularly those relating to Admiral Dudley North, who had been relieved of his command of Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = " Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gib ...
in 1940. Cunningham, and several of the surviving admirals of the fleet, set about securing justice for North, and they succeeded with a partial vindication in 1957. He also busied himself with various appointments; he was Lord High Commissioner to the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland
The Lord High Commissioner to the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland is the Scottish monarch's personal representative to the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland (the Kirk), reflecting the Church's role as the national church of ...
in 1950 and 1952, and in 1953 he acted as Lord High Steward
The Lord High Steward is the first of the Great Officers of State in England, nominally ranking above the Lord Chancellor.
The office has generally remained vacant since 1421, and is now an ''ad hoc'' office that is primarily ceremonial and ...
—the most recent one to date—at the coronation of Queen Elizabeth II
The coronation of Elizabeth II took place on 2 June 1953 at Westminster Abbey in London. She acceded to the throne at the age of 25 upon the death of her father, George VI, on 6 February 1952, being proclaimed queen by her privy and executive ...
. Throughout this time Cunningham and his wife entertained family and friends, including his own great nephew, Jock Slater
Jock may refer to:
Common meanings
* Jock (stereotype), a North American term for a stereotypical male athlete
* Jock, a derogatory term for Scottish people mostly used by the English
* Short for jockstrap, an item of male protective undergarme ...
, in their extensive gardens. Cunningham died in London on 12 June 1963, and was buried at sea off Portsmouth. There were no children from his marriage and his titles consequently became extinct on his death.
A bust of Cunningham by Franta Belsky
František Bělský (also known as Franta Belsky; 6 April 1921 – 5 July 2000) was a Czech sculptor.
He was known for large-scale abstract works of public art as well as more iconographic statues and busts of noted 20th-century figures such ...
was unveiled in Trafalgar Square
Trafalgar Square ( ) is a public square in the City of Westminster, Central London, laid out in the early 19th century around the area formerly known as Charing Cross. At its centre is a high column bearing a statue of Admiral Nelson comm ...
in London on 2 April 1967 by Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh
Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh (born Prince Philip of Greece and Denmark, later Philip Mountbatten; 10 June 1921 – 9 April 2021) was the husband of Queen Elizabeth II. As such, he served as the consort of the British monarch from E ...
. The April 2010 UK naval operation to ship British military personnel and air passengers stranded in continental Europe by the air travel disruption after the 2010 Eyjafjallajökull eruption
In response to concerns that volcanic ash ejected during the 2010 eruptions of Eyjafjallajökull in Iceland would damage aircraft engines, the controlled airspace of many European countries was closed to instrument flight rules traffic, resulti ...
back to the UK was named Operation Cunningham after him.
Honours and arms
 Below is a list of awards and titles awarded to Andrew Browne Cunningham during his lifetime.
Below is a list of awards and titles awarded to Andrew Browne Cunningham during his lifetime.
United Kingdom
Awards from other countries
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * Most of Cunningham's service record is iDocument piece ADM 196/47
and can be downloaded as a pdf (fee required) fro
Documents Online
Retrieved 2008-08-05
Further reading
* * * * *External links
Transcription of Official Service Records on www.admirals.org.uk
1943 bromide print
by
Yousuf Karsh
Yousuf Karsh, FRPS (December 23, 1908 – July 13, 2002) was a Canadian-Armenian photographer known for his portraits of notable individuals. He has been described as one of the greatest portrait photographers of the 20th century.
An Armenian ...
at the National Portrait Gallery, London
*
* Papers of Viscount Cunningham
held at
Churchill Archives Centre
The Churchill Archives Centre (CAC) at Churchill College at the University of Cambridge is one of the largest repositories in the United Kingdom for the preservation and study of modern personal papers. It is best known for housing the papers of ...
, -
, -
, -
, -
, -
, -
, -
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cunningham, Andrew, 1st Viscount Cunningham Of Hyndhope
1963 deaths
Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War
Chief Commanders of the Legion of Merit
Commandeurs of the Légion d'honneur
Companions of the Distinguished Service Order
Crete in World War II
First Sea Lords and Chiefs of the Naval Staff
Foreign recipients of the Distinguished Service Medal (United States)
Graduates of Britannia Royal Naval College
Graduates of the Royal Naval College, Greenwich
Grand Crosses of the Order of George I
Irish Presbyterians
Knights Grand Cross of the Order of the Bath
Knights of the Thistle
Lord High Stewards
Lords High Commissioner to the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland
Lords of the Admiralty
Members of the Order of Merit
Naval history of World War II
People educated at Edinburgh Academy
People educated at Stubbington House School
People from Rathmines
Recipients of the Croix de Guerre 1939–1945 (France)
Recipients of the Croix de guerre (Belgium)
Recipients of the Medal of Military Merit (Greece)
Rectors of the University of Edinburgh
Royal Navy admirals of the fleet
Royal Navy admirals of World War II
Royal Navy officers of World War I
Royal Navy personnel of the Second Boer War
Admiralty personnel of World War II
Alumni of the Royal College of Defence Studies
Recipients of the Navy Distinguished Service Medal
Recipients of the Distinguished Service Medal (US Army)
1883 births
Barons created by George VI
Viscounts created by George VI
British people of Scottish descent
Military personnel from Dublin (city)