Adirondacks on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Adirondack Mountains (; a-də-RÄN-dak) form a massif in northeastern New York with boundaries that correspond roughly to those of Adirondack Park. They cover about 5,000 square miles (13,000 km2). The mountains form a roughly circular dome, about in diameter and about high. The current relief owes much to glaciation. There are more than 200 lakes around the mountains, including Lake George, Lake Placid, and Lake Tear of the Clouds, which is the source of the
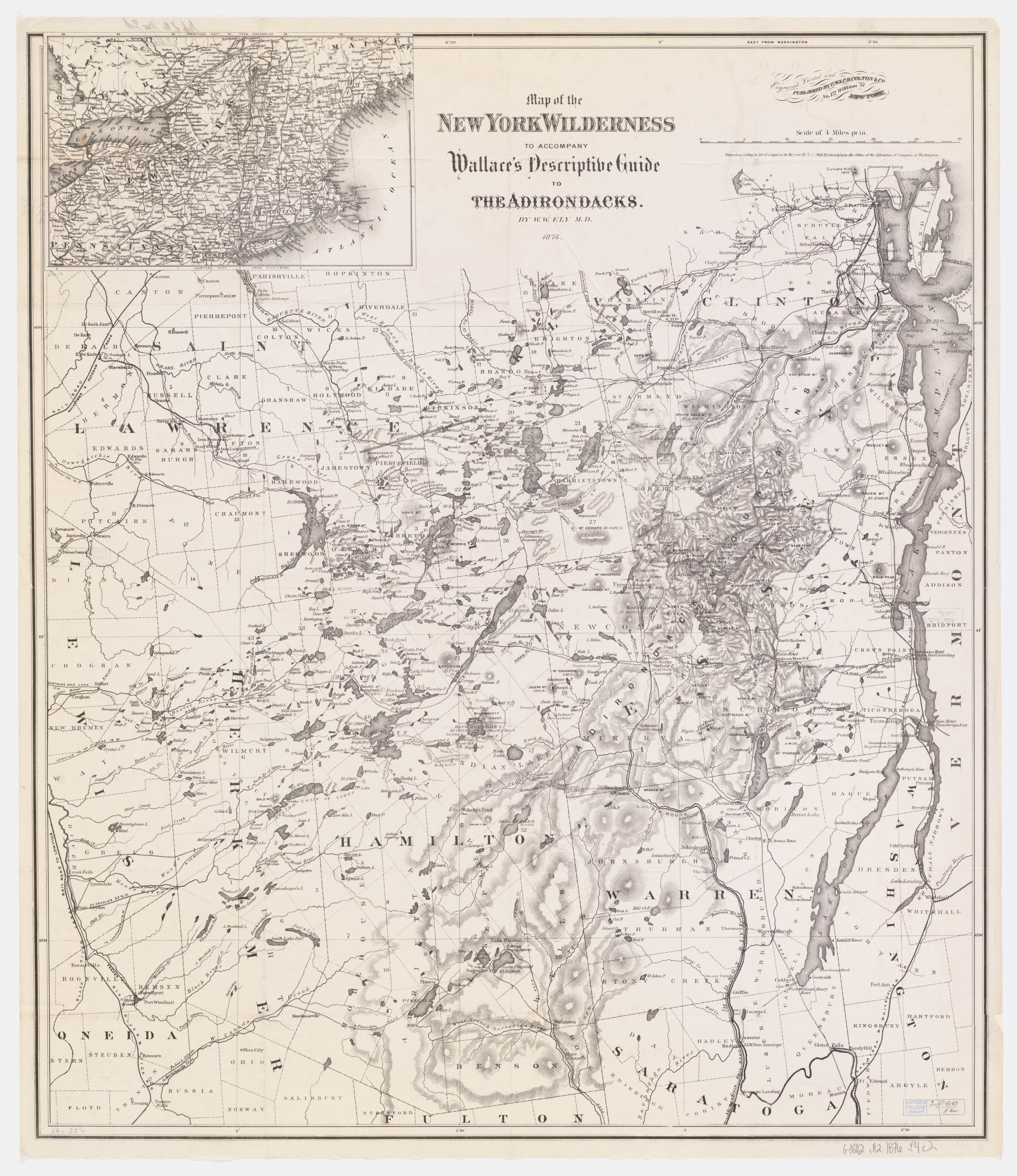 Humans have lived in the region of the Adirondack Mountains since the Paleo-Indian period (15,000 to 7,000 BC), shortly after the last ice age. The first group to move into the area came south from the St. Lawrence River Valley and settled along the shores of the Champlain Sea around 13,000 BC. These Archaic period people, known as the Laurentian culture, were semi-nomadic hunter-gatherers. Evidence for their presence in the Adirondacks includes a projectile point of red-brown
Humans have lived in the region of the Adirondack Mountains since the Paleo-Indian period (15,000 to 7,000 BC), shortly after the last ice age. The first group to move into the area came south from the St. Lawrence River Valley and settled along the shores of the Champlain Sea around 13,000 BC. These Archaic period people, known as the Laurentian culture, were semi-nomadic hunter-gatherers. Evidence for their presence in the Adirondacks includes a projectile point of red-brown
 Starting about 2.5 million years ago, a cycle of
Starting about 2.5 million years ago, a cycle of
 The Adirondack Mountains form the southernmost part of the Eastern forest-boreal transition
The Adirondack Mountains form the southernmost part of the Eastern forest-boreal transition
Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between Ne ...
. The Adirondack Region is also home to hundreds of mountain summits, with some reaching heights of or more.
Etymology
The word Adirondack is thought to come from the Mohawk word ''ha-de-ron-dah'' meaning "eaters of trees". The earliest written use of the name was in 1635 by Harmen Meyndertsz Van Den Bogaert in his Mohawk to Dutch glossary, found in his ''Journey into Mohawk Country''. He spelled it Adirondakx and said that it stood for Frenchmen, meaning the Algonquians who allied with the French. Another early use of the name, spelled ''Rontaks'', was in 1729 by French missionaryJoseph-François Lafitau
Joseph-François Lafitau (; May 31, 1681 – July 3, 1746) was a French Jesuit missionary, ethnologist, and naturalist who worked in Canada. He is best known for his use of the comparative method in the field of scientific anthropology, the disco ...
. He explained that the word was used by the Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to ...
as a derogatory term for groups of Algonquians who did not practice agriculture and therefore sometimes had to eat tree bark to survive harsh winters.
The Mohawks had no written language, so Europeans used various phonetic spellings of the word, including ''Achkokx'', ''Rondaxe'', and ''Adirondax.'' Such words were strongly associated with the region, but they were not yet considered a place name; an English map from 1761 labels the area simply ''Deer Hunting Country''. In 1837, the mountains were named ''Adirondacks'' by Ebenezer Emmons.
Human history
chert
Chert () is a hard, fine-grained sedimentary rock composed of microcrystalline or cryptocrystalline quartz, the mineral form of silicon dioxide (SiO2). Chert is characteristically of biological origin, but may also occur inorganically as a ...
found in 2007 at the edge of Tupper Lake.
Over the next 11,000 or so years, the region's climate slowly warmed, and forests began to replace the original tundra. Transitioning from the Archaic Period to the Woodland period
In the classification of archaeological cultures of North America, the Woodland period of North American pre-Columbian cultures spanned a period from roughly 1000 BCE to European contact in the eastern part of North America, with some archaeo ...
, multiple different cultures— Sylvan Lake, River, Middlesex, Point Peninsula, and Owasco cultures— replaced the Laurentian culture over time. By the time of the Owasco culture, around 0 AD, maize and beans were being cultivated in the Adirondack uplands.
The first Iroquoian
The Iroquoian languages are a language family of indigenous peoples of North America. They are known for their general lack of labial consonants. The Iroquoian languages are polysynthetic and head-marking.
As of 2020, all surviving Iroquoia ...
peoples, the Mohawk (or Kanyengehaga) and the Oneida (or Oneyotdehaga), arrived in the Adirondack region between 4,000 and 1,200 years ago. Both groups claimed the Adirondack Mountains as hunting grounds. According to Haudenosaunee
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to ...
historian Rick Hill, the region was considered a ' Dish with One Spoon,' symbolizing shared hunting resources between the groups. A group of Algonquian people, known as the Mahicans, also occupied the region, particularly the Hudson River Valley.
These were the groups that the first European explorers of the area encountered. European presence in the area began with a battle between Samuel de Champlain and a group of Mohawks, in what is now Ticonderoga in 1609. The Jesuit missionary Isaac Jogues became the first recorded European to travel through the center of the Adirondacks, as the captive of a Mohawk hunting party, in 1642.
The early European perception of the Adirondacks was of a vast, inhospitable wilderness. One map of the area from 1771 shows the region as a blank space in the northeastern corner of New York. In 1784, Thomas Pownhall wrote that the Native Americans referred to the area as "the Dismal Wilderness, or the Habitation of Winter," and that the area was "either not much known to them, or, if known, very wisely by them kept from the Knowledge of the Europeans." He clearly had the impression that native people did not live within the Adirondack mountains.
Because local Iroquoian
The Iroquoian languages are a language family of indigenous peoples of North America. They are known for their general lack of labial consonants. The Iroquoian languages are polysynthetic and head-marking.
As of 2020, all surviving Iroquoia ...
and Algonquian tribes had been decimated first by smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) ce ...
and measles in the 1600s, then by wars with encroaching European settlers, there likely were very few people living in the region by the time Pownhall wrote his description. It is only relatively recently that numerous archaeological finds have definitively shown that Native Americans were indeed very present in the Adirondacks before European contact, hunting, making pottery, and practicing agriculture.
The European impression of a wild region devoid of human connection set up a narrative about wilderness that would persist through the next 200-some years of the region's history. While society's perception of the Adirondacks' value changed, they were always seen as a land of natural resources and physical beauty, not of human history. First the area was an inhospitable tangle, then a lucrative store of lumber. After the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of ...
, New York State gained ownership of most of the land in the region.
Needing money to discharge war debts, the government sold nearly all the original public acreage about 7 million acres for pennies an acre. Lumbermen were welcomed to the interior, with few restraints, resulting in massive deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then land conversion, converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban area, urban ...
. Later, the wilderness character of the region became popular with the rise of the Romantic movement, and the Adirondacks became a destination for those wishing to escape the evils of city life. Rising concern over water quality and deforestation led to the creation of the Adirondack Park in 1885. In 1989, part of the Adirondack region was designated by UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. I ...
as the Champlain-Adirondack Biosphere Reserve
The Champlain-Adirondack Biosphere Network (formerly Champlain-Adirondack Biosphere Reserve) is a UNESCO-designated biosphere reserve. The Champlain-Adirondack Biosphere Network is part of a global network of 727 biosphere reserves in 131 countries ...
.
For the more recent human history of the Adirondack region, see the page Adirondack Park.
Geology
The rocks of the Adirondack mountains originated about two billion years ago as 50,000 feet (ca. 15,240 m) thick sediments at the bottom of a sea located near theequator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can al ...
. Because of plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label= Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large t ...
these collided with Laurentia (the precursor of modern North America) in a mountain building episode known as the Grenville orogeny. During this time the sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particle ...
was changed into metamorphic rock
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock ( protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, cau ...
. It is these Proterozoic
The Proterozoic () is a geological eon spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8million years ago. It is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon". It is also the longest eon of the Earth's geologic time scale, and it is subdivided ...
minerals and lithologies that make up the core of the massif. Minerals of interest include:
* wollastonite, mined near Harrisville
* magnetite
Magnetite is a mineral and one of the main iron ores, with the chemical formula Fe2+Fe3+2O4. It is one of the oxides of iron, and is ferrimagnetic; it is attracted to a magnet and can be magnetized to become a permanent magnet itself. With ...
and hematite
Hematite (), also spelled as haematite, is a common iron oxide compound with the formula, Fe2O3 and is widely found in rocks and soils. Hematite crystals belong to the rhombohedral lattice system which is designated the alpha polymorph of ...
, formerly mined at the Benson Mines, Lyon Mountain, Mineville, Tahawus, and Witherbee.
* graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on la ...
, mined near Hague and Ticonderoga.
* garnet
Garnets () are a group of silicate minerals that have been used since the Bronze Age as gemstones and abrasives.
All species of garnets possess similar physical properties and crystal forms, but differ in chemical composition. The different ...
, mined at the Barton Mine, north of Gore Mountain.
* anorthosite, visible in road cuts on the New York State Route 3 between Saranac Lake Saranac Lake may refer to:
* Saranac Lake, New York, a village in the northern Adirondacks
*One of the three nearby Saranac Lakes, part of the Saranac River:
**Upper Saranac Lake
**Middle Saranac Lake
**Lower Saranac Lake
Note: There is no lake nam ...
and Tupper Lake.
* marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or dolomite. Marble is typically not foliated (layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the term ''marble'' refers to metamorpho ...
* zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic t ...
: The Balmat-Edwards district on the northwest flank of the massif also in St. Lawrence County was a major zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic t ...
ore deposit
* titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resista ...
was mined at Tahawus.
Note: the Adirondacks are uplifted by a hot spot in the Canadian Shield in contrast to other mountain ranges in New York which are a part of the Appalachian chain (not to be confused with the cultural region of Appalachia).
Around 600 million years ago, as Laurentia drifted away from Baltica (European Craton), the area began to be pulled apart forming the Iapetus Ocean. Faults developed, running north to northeast which formed valleys and deep lakes. Examples visible today include the grabens Lake George and Schroon Lake. By this time the Grenville mountains had been eroded away and the area was covered by a shallow sea. Several thousand feet of sediment accumulated on the sea bed. Trilobites were the principal life-form of the sea bed, and fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
tracks can be seen in the Potsdam sandstone floor of the Paul Smiths Visitor Interpretive Center.
About 10 million years ago, the region began to be uplifted. It has been lifted about 7000 feet (ca. 2,134 meters) and is continuing at about 2 millimeters per year, which is greater than the rate of denudation. The cause of the uplift is unknown, but geologists theorize that it is caused by a hot spot
Hotspot, Hot Spot or Hot spot may refer to:
Places
* Hot Spot, Kentucky, a community in the United States
Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities
* Hot Spot (comics), a name for the DC Comics character Isaiah Crockett
* Hot Spot (Tra ...
in the earth's crust. A recent study has revealed a column of seismically slow materials about 50–80 km deep beneath the Adirondack Mountains, which was interpreted to be the upwelling asthenosphere contributing to the uplift of the mountains. The occurrence of earthquake swarms near the center of the massif at Blue Mountain Lake may be evidence of this. Some of the earthquakes have exceeded 5 on the Richter magnitude scale
The Richter scale —also called the Richter magnitude scale, Richter's magnitude scale, and the Gutenberg–Richter scale—is a measure of the strength of earthquakes, developed by Charles Francis Richter and presented in his landmark 1935 p ...
.
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the '' Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed ...
glacial and interglacial
An interglacial period (or alternatively interglacial, interglaciation) is a geological interval of warmer global average temperature lasting thousands of years that separates consecutive glacial periods within an ice age. The current Holocene ...
periods began which covered the area in ice. During the most recent episode, the Laurentide Ice Sheet covered most of northern North America between about 95,000 and c. 20,000 years ago. After this the climate warmed, but it took nearly 10,000 years for a 10,000 feet (ca. 3,048 m) thick layer of ice to completely melt. Evidence of this period includes:
* Eskers
An esker, eskar, eschar, or os, sometimes called an ''asar'', ''osar'', or ''serpent kame'', is a long, winding ridge of stratified sand and gravel, examples of which occur in glaciated and formerly glaciated regions of Europe and North Ameri ...
: the Rainbow Lake esker bisects the eponymous lake and extends discontinuously for 85 miles (ca. 137 km). Another long discontinuous esker extends from Mountain Pond through Keese Mill, passing between Upper St. Regis Lake and the Spectacle Ponds, and continuing to Ochre, Fish, and Lydia Ponds in the St. Regis Canoe Area. A 150-foot-high esker bisects the Five Ponds Wilderness Area.
* Glacial erratics: there is a large one at the Newcomb Visitor Information Center next to the Rich Lake Trail.
* Kames
* Moraines
* The cirques that characterize the Whiteface Mountain.
* Outwash plains: St. Regis Canoe Area is an outwash plain pitted with kettle holes
A kettle (also known as a kettle lake, kettle hole, or pothole) is a depression/hole in an outwash plain formed by retreating glaciers or draining floodwaters. The kettles are formed as a result of blocks of dead ice left behind by retreating gla ...
.
Soils in the area are generally thin, sandy, acidic, and infertile, having developed since the glacial retreat.
Climate
The climate is strongly continental, with highhumidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Humidity dep ...
and precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hai ...
year-round. The Adirondacks typically experience pleasantly warm, rainy weather in the summer (June-August), with temperatures in the range of , cooler than the rest of New York State due to the higher elevation. Summer evenings in the Adirondacks are chilly, with temperatures ranging on average between . Winters (December-March) are long, cold, snowy and harsh, with temperatures ranging from . Winter nights are frigid, with temperatures between . Spring (April-May) and fall (September-November) are short transitional seasons.
Ecology
 The Adirondack Mountains form the southernmost part of the Eastern forest-boreal transition
The Adirondack Mountains form the southernmost part of the Eastern forest-boreal transition ecoregion
An ecoregion (ecological region) or ecozone (ecological zone) is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than a bioregion, which in turn is smaller than a biogeographic realm. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas o ...
. They are heavily forested, and contain one of the southernmost distributions of the taiga
Taiga (; rus, тайга́, p=tɐjˈɡa; relates to Mongolic and Turkic languages), generally referred to in North America as a boreal forest or snow forest, is a biome characterized by coniferous forests consisting mostly of pines, spruces ...
ecotype in North America. The forests of the Adirondacks include spruce
A spruce is a tree of the genus ''Picea'' (), a genus of about 35 species of coniferous evergreen trees in the family Pinaceae, found in the northern temperate and boreal ( taiga) regions of the Earth. ''Picea'' is the sole genus in the sub ...
, pine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family (biology), family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The World Flora Online created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanic ...
and deciduous
In the fields of horticulture and Botany, the term ''deciduous'' () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, a ...
trees. Lumbering, once an important industry, has been much restricted by the creation of state forest preserve.
The mountains include many wetland
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in the soils. The ...
s, of which there are three kinds:
* swamps, any wetland including trees and shrubs.
* marsh
A marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous rather than woody plant species.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p Marshes can often be found a ...
es, wetlands with water stagnation. These may support bullfrogs, spring peepers, spotted salamander
The spotted salamander or yellow-spotted salamander (''Ambystoma maculatum'') is a mole salamander common in eastern United States and Canada. The spotted salamander is the state amphibian of Ohio and South Carolina. This salamander ranges from ...
s, great blue heron
The great blue heron (''Ardea herodias'') is a large wading bird in the heron family Ardeidae, common near the shores of open water and in wetlands over most of North America and Central America, as well as the Caribbean and the Galápagos ...
s, American bittern
The American bittern (''Botaurus lentiginosus'') is a species of wading bird in the heron family. It has a Nearctic distribution, breeding in Canada and the northern and central parts of the United States, and wintering in the U.S. Gulf Coast ...
s, and painted turtles
The painted turtle (''Chrysemys picta'') is the most widespread native turtle of North America. It lives in slow-moving fresh waters, from southern Canada to northern Mexico, and from the Atlantic to the Pacific. They have been shown to prefer l ...
. Pickerel weed often forms large colonies.
* bog
A bog or bogland is a wetland that accumulates peat as a deposit of dead plant materials often mosses, typically sphagnum moss. It is one of the four main types of wetlands. Other names for bogs include mire, mosses, quagmire, and muskeg; a ...
s, characterized by plants like sphagnum moss, orchid
Orchids are plants that belong to the family Orchidaceae (), a diverse and widespread group of flowering plants with blooms that are often colourful and fragrant.
Along with the Asteraceae, they are one of the two largest families of flowering ...
s, and pitcher plants.
Breeding birds include northern forest specialists not found anywhere else in the state, such as boreal chickadees, Canada jay
The Canada jay (''Perisoreus canadensis''), also known as the gray jay, grey jay, camp robber, or whisky jack, is a passerine bird of the family Corvidae. It is found in boreal forests of North America north to the tree line, and in the ...
s, spruce grouse, black-backed woodpeckers, common loon
The common loon or great northern diver (''Gavia immer'') is a large member of the loon, or diver, family of birds. Breeding adults have a plumage that includes a broad black head and neck with a greenish, purplish, or bluish sheen, blackish ...
s and crossbills. Mammals include raccoon
The raccoon ( or , ''Procyon lotor''), sometimes called the common raccoon to distinguish it from other species, is a mammal native to North America. It is the largest of the procyonid family, having a body length of , and a body weight o ...
s, beaver
Beavers are large, semiaquatic rodents in the genus ''Castor'' native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. There are two extant species: the North American beaver (''Castor canadensis'') and the Eurasian beaver (''C. fiber''). Beavers a ...
s, river otters, bobcats, moose
The moose (in North America) or elk (in Eurasia) (''Alces alces'') is a member of the New World deer subfamily and is the only species in the genus ''Alces''. It is the largest and heaviest extant species in the deer family. Most adult ma ...
, black bears, and coyotes. Extirpated or extinct mammals that formerly roamed the Adirondacks include the eastern cougar, eastern elk, wolverine, caribou, eastern wolf, and the Canada lynx. Attempted reintroductions of elk and lynx in the 20th century failed for numerous reasons, including poaching, vehicle collisions, and conservation incompetence.
Nearly 60 percent of the park is covered with