Adam ḳadmon on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
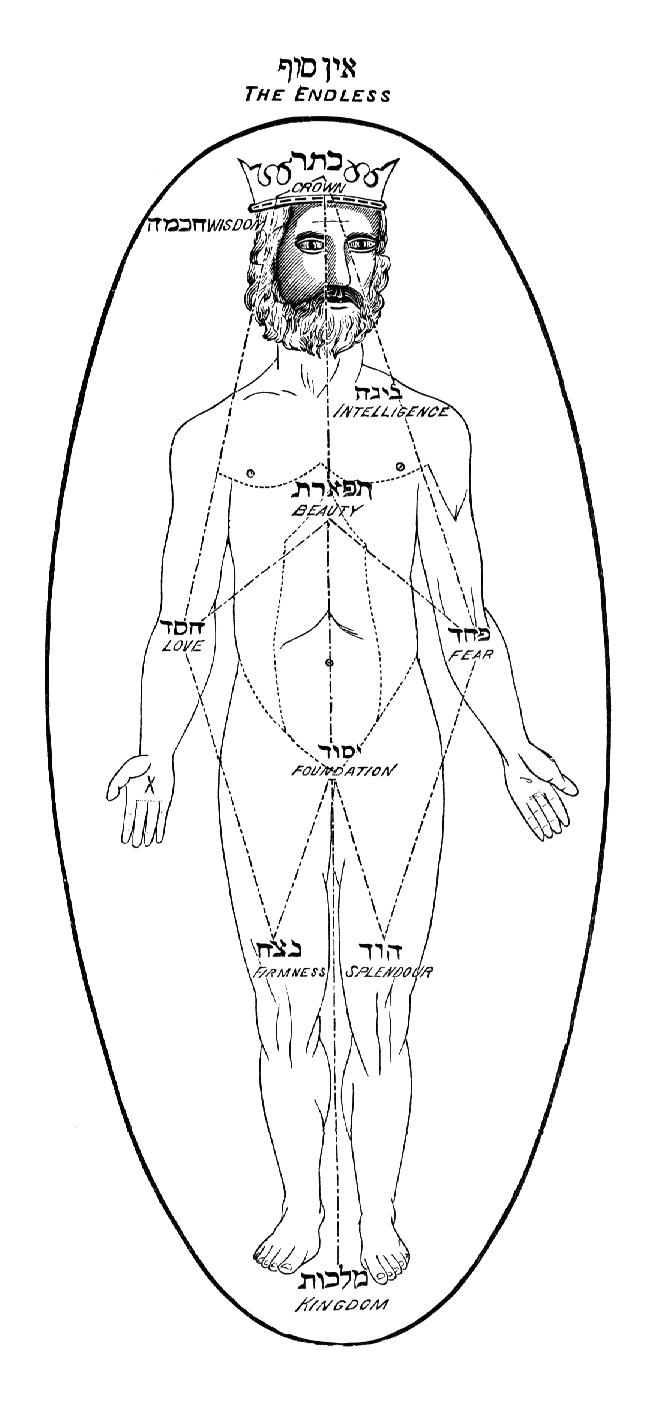 In Kabbalah, before creation began, all that existed was God's Infinite Light. The first stage of creation began when God contracted His Infinite Light to create the vacuum. Then a ray of divine light penetrated the vacuum and the
In Kabbalah, before creation began, all that existed was God's Infinite Light. The first stage of creation began when God contracted His Infinite Light to create the vacuum. Then a ray of divine light penetrated the vacuum and the
Adam Kadmon—The Divine Names
{{Webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20031013172723/http://www.kheper.net/topics/Kabbalah/Lurianic-AdamKadmon.htm , date=13 October 2003
Jewish mysticism Kabbalah Kabbalistic words and phrases Elcesaites Adam and Eve Mythological first humans
Kabbalah
Kabbalah or Qabalah ( ; , ; ) is an esoteric method, discipline and school of thought in Jewish mysticism. It forms the foundation of Mysticism, mystical religious interpretations within Judaism. A traditional Kabbalist is called a Mekubbal ...
, Adam Kadmon (, ''ʾāḏām qaḏmōn'', "Primordial Man") also called Adam Elyon
Elyon or El Elyon ( ''ʼĒl ʻElyōn''), is an epithet that appears in the Hebrew Bible. ' is usually rendered in English as "God Most High", and similarly in the Septuagint as ("God the highest"). The title ' is a common topic of scholarly de ...
(, ''ʾāḏām ʿelyōn'', "Most High Man"), or Adam Ila'ah (, ''ʾāḏām ʿīllāʾā'' "Most High Adam" in Aramaic
Aramaic (; ) is a Northwest Semitic language that originated in the ancient region of Syria and quickly spread to Mesopotamia, the southern Levant, Sinai, southeastern Anatolia, and Eastern Arabia, where it has been continually written a ...
), sometimes abbreviated as A"K (, ''ʾA.Q.''), is the first of Four Worlds
The Four Worlds ( ''ʿOlāmot'', singular: ''ʿOlām'' ), sometimes counted with a primordial world, Adam Kadmon, and called the Five Worlds, are the comprehensive categories of spiritual realms in Kabbalah in a descending chain of existence ...
that came into being after the contraction
Contraction may refer to:
Linguistics
* Contraction (grammar), a shortened word
* Poetic contraction, omission of letters for poetic reasons
* Elision, omission of sounds
** Syncope (phonology), omission of sounds in a word
* Synalepha, merged ...
of God's infinite light. ''Adam Kadmon'' is not the same as the physical ''Adam Ha-Rishon'' (אָדָם הָרִאשׁוֹן).
In Lurianic Kabbalah
Lurianic Kabbalah is a school of Kabbalah named after Isaac Luria (1534–1572), the Jewish rabbi who developed it. Lurianic Kabbalah gave a seminal new account of Kabbalistic thought that its followers synthesised with, and read into, the earli ...
, the description of ''Adam Kadmon'' is anthropomorphic
Anthropomorphism is the attribution of human traits, emotions, or intentions to non-human entities. It is considered to be an innate tendency of human psychology. Personification is the related attribution of human form and characteristics to ...
. Nonetheless, ''Adam Kadmon'' is divine light
In theology, divine light (also called divine radiance or divine refulgence) is an aspect of divine presence perceived as light during a theophany or vision, or represented as such in allegory or metaphor.
Light has always been associated wit ...
without vessels, i.e., pure potential. In the human psyche, ''Adam Kadmon'' corresponds to the yechidah
The soul is the purported immaterial aspect or essence of a living being. It is typically believed to be immortal and to exist apart from the material world. The three main theories that describe the relationship between the soul and the bod ...
, the collective essence of the soul.
In Judaism
Philo
The first to use the expression "original man," or "heavenly man," wasPhilo
Philo of Alexandria (; ; ; ), also called , was a Hellenistic Jewish philosopher who lived in Alexandria, in the Roman province of Egypt.
The only event in Philo's life that can be decisively dated is his representation of the Alexandrian J ...
, in whose view this or , "as being born in the image of God
In monotheistic belief systems, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. In polytheistic belief systems, a god is "a spirit or being believed to have created, or for controlling some part of the un ...
, has no participation in any corruptible or earthlike essence; whereas the earthly man is made of loose material, called a lump of clay." The heavenly man, as the perfect image of the ''Logos
''Logos'' (, ; ) is a term used in Western philosophy, psychology and rhetoric, as well as religion (notably Logos (Christianity), Christianity); among its connotations is that of a rationality, rational form of discourse that relies on inducti ...
'', is neither man nor woman, but an incorporeal intelligence purely an idea; while the earthly man, who was created by God later, is perceptible to the senses and partakes of earthly qualities. Philo is evidently combining philosophy and Midrash
''Midrash'' (;"midrash"
. ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. ; or ''midrashot' ...
, . ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. ; or ''midrashot' ...
Plato
Plato ( ; Greek language, Greek: , ; born BC, died 348/347 BC) was an ancient Greek philosopher of the Classical Greece, Classical period who is considered a foundational thinker in Western philosophy and an innovator of the writte ...
and the rabbis.
Setting out from the duplicate biblical account of Adam
Adam is the name given in Genesis 1–5 to the first human. Adam is the first human-being aware of God, and features as such in various belief systems (including Judaism, Christianity, Gnosticism and Islam).
According to Christianity, Adam ...
, who was formed in the image of God (), and of the first man, whose body God formed from the earth (), he combines with it the Platonic theory of forms; taking the primordial Adam as the idea, and the created man of flesh and blood as the "image." That Philo's philosophic views are grounded on the Midrash, and not vice versa, is evident from his seemingly senseless statement that the "heavenly man," the οὐράνιος ἄνθρωπος (who is merely an idea), is "neither man nor woman." This doctrine, however, becomes quite intelligible in view of the following ancient Midrash.
Midrash
The remarkable contradiction between Genesis 1:27 and Genesis 2:7 could not escape the attention of thePharisees
The Pharisees (; ) were a Jews, Jewish social movement and school of thought in the Levant during the time of Second Temple Judaism. Following the Siege of Jerusalem (AD 70), destruction of the Second Temple in 70 AD, Pharisaic beliefs became ...
, for whom the Bible was a subject of close study. In explaining the various views concerning Eve's creation, they taught that Adam was created as a man-woman (androgynos
In Jewish tradition, the term ''androgynos'' ( in Hebrew, transliterated: "ʾandərôg̲înôs",literally: man-woman, translation: "intersex") refers to someone who possesses both male and female sexual characteristics. Due to the ambiguous nature ...
), explaining "" () as "male and female" instead of "man and woman," and that the separation of the sexes arose from the subsequent operation upon Adam's body, as related in the Scripture. This explains Philo's statement that the original man was neither man nor woman.
This doctrine concerning the Logos, as also that of man made "in the likeness," although tinged with true Philonic coloring, is also based on the theology of the Pharisees. Genesis Rabbah
Genesis Rabbah (, also known as Bereshit Rabbah and abbreviated as GenR) is a religious text from Judaism's classical period, probably written between 300 and 500 CE with some later additions. It is an expository midrash comprising a collection of ...
:
This contains the kernel of Philo's philosophical doctrine of the creation of the original man. He calls him the idea of the earthly Adam, while with the rabbis the spirit () of Adam not only existed before the creation of the earthly Adam, but was preexistent to the whole of creation. From the preexisting Adam, or Messiah, to the Logos is merely a step.
Kabbalah
 In Kabbalah, before creation began, all that existed was God's Infinite Light. The first stage of creation began when God contracted His Infinite Light to create the vacuum. Then a ray of divine light penetrated the vacuum and the
In Kabbalah, before creation began, all that existed was God's Infinite Light. The first stage of creation began when God contracted His Infinite Light to create the vacuum. Then a ray of divine light penetrated the vacuum and the persona
A persona (plural personae or personas) is a strategic mask of identity in public, the public image of one's personality, the social role that one adopts, or simply a fictional Character (arts), character. It is also considered "an intermediary ...
of Adam Kadmon was projected into the vacuum. The first stage of Adam Kadmon was in the form of ten concentric circles ( ''igulim''), which emanated from the ray. The ray of light was then enclothed by the anthropomorphic form of Adam Kadmon ( ), which is a realm of infinite divine light without vessels, constrained by its potential to create future Existence. Adam Kadmon is sometimes referred to as ''Adam Ila'a'' (Aramaic: "upper man") or ''Adam Elyon'' (Hebrew: "upper man").
The soul of Adam HaRishon ("the first man") was the supreme essence of mankind. It contained within it all subsequent souls. In the midrash
''Midrash'' (;"midrash"
. ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. ; or ''midrashot' ...
, he is sometimes referred to as ''Adam HaKadmoni'' ("the ancient man"), ''Adam Tata'a'' (Aramaic: "lower man") or ''Adam Tachton'' (Hebrew: "lower man").
The . ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. ; or ''midrashot' ...
anthropomorphic
Anthropomorphism is the attribution of human traits, emotions, or intentions to non-human entities. It is considered to be an innate tendency of human psychology. Personification is the related attribution of human form and characteristics to ...
name of Adam Kadmon denotes that it contains both the ultimate divine purpose for creation, i.e., mankind, as well as an embodiment of the Sefirot
Sefirot (; , plural of ), meaning '' emanations'', are the 10 attributes/emanations in Kabbalah, through which Ein Sof ("infinite space") reveals itself and continuously creates both the physical realm and the seder hishtalshelut (the chained ...
(divine attributes). Adam Kadmon is paradoxically both "Adam" and divine ("Kadmon-Primary").
Adam Kadmon preceded the manifestation of the Four Worlds
The Four Worlds ( ''ʿOlāmot'', singular: ''ʿOlām'' ), sometimes counted with a primordial world, Adam Kadmon, and called the Five Worlds, are the comprehensive categories of spiritual realms in Kabbalah in a descending chain of existence ...
, Atzilut
Atziluth or Atzilut (also ''Olam Atsiluth'', עוֹלָם אֲצִילוּת, literally "the World of Emanation") is the highest of four worlds in which exists the Kabbalistic Tree of Life. It is also known as "near to God."MEIJERS, L. D., and J. ...
("emanation"), Beriah ("creation"), Yetzirah
Yetzirah (also known as ''Olam Yetsirah'', עוֹלָם יְצִירָה in Hebrew) is the third of four worlds in the Kabbalistic Tree of Life, following Atziluth and Beri'ah and preceding Assiah. It is known as the "World of Formation".
"Y ...
("formation") and Asiyah ("action"). Whereas each of the Four Worlds is represented by one letter of the divine four-lettered name of God, Adam Kadmon is represented by the transcendental cusp of the first letter Yud.
In the system of the sefirot
Sefirot (; , plural of ), meaning '' emanations'', are the 10 attributes/emanations in Kabbalah, through which Ein Sof ("infinite space") reveals itself and continuously creates both the physical realm and the seder hishtalshelut (the chained ...
, Adam Kadmon corresponds to Keter
Keter or Kether (; ) is the first of the ten sefirot in the Kabbalistic Tree of Life, symbolizing the divine will and the initial impulse towards creation from the '' Ein Sof'', or infinite source. It represents pure consciousness and transce ...
("crown"), the divine will that motivated creation.
The two versions of Kabbalistic theosophy, the "medieval/classic/Zoharic" (systemised by Moshe Cordovero
Moses ben Jacob Cordovero ( ''Moshe Kordovero'' ; 1522–1570) was a central figure in the historical development of Kabbalah, leader of a mystical school in the Ottoman Empire in 16th-century Safed, located in the modern State of Israel. H ...
) and the more comprehensive Lurianic, describe the process of descending worlds differently. For Cordovero, the sefirot, Adam Kadmon and the Four Worlds evolve sequentially from the Ein Sof
Ein Sof, or Eyn Sof (, '; meaning "infinite", ), in Kabbalah, is understood as God before any self-manifestation in the production of any spiritual realm, probably derived from Solomon ibn Gabirol's (1021–1070) term, "the Endless One" ( ''še ...
(divine infinity). For Luria, creation is a dynamic process of divine exile-rectification enclothement, where Adam Kadmon is preceded by the Tzimtzum
The ''tzimtzum'' or ''tsimtsum'' () is a term used in Lurianic Kabbalah to explain Isaac Luria's doctrine that God began the process of creation by limiting the Ohr Ein Sof (infinite light) of the Godhead in order to allow for a conceptual spa ...
(Divine "contraction") and followed by Shevira (the "shattering" of the sefirot).
Closely related to the Philonic doctrine of the heavenly Adam is the Adam Ḳadmon (called also Adam 'Ilaya, the "high man," the "heavenly man") of the Zohar
The ''Zohar'' (, ''Zōhar'', lit. "Splendor" or "Radiance") is a foundational work of Kabbalistic literature. It is a group of books including commentary on the mystical aspects of the Torah and scriptural interpretations as well as material o ...
, whose conception of the original man can be deduced from the following passages: "The form of man is the image of everything that is above n heavenand below pon earth therefore did the Holy Ancient odselect it for His own form."
As with Philo the Logos is the original image of man, or the original man, so in the Zohar the heavenly man is the embodiment of all divine manifestations: the ten Sefirot
Sefirot (; , plural of ), meaning '' emanations'', are the 10 attributes/emanations in Kabbalah, through which Ein Sof ("infinite space") reveals itself and continuously creates both the physical realm and the seder hishtalshelut (the chained ...
, the original image of man. The heavenly Adam, stepping forth out of the highest original darkness, created the earthly Adam. In other words, the activity of the original essence manifested itself in the creation of man, who at the same time is the image of the heavenly man and of the universe, just as with Plato and Philo the idea of man, as microcosm, embraces the idea of the universe or macrocosm.
The conception of Adam Ḳadmon becomes an important factor in the later Kabbalah of Isaac Luria
Isaac ben Solomon Ashkenazi Luria (; #FINE_2003, Fine 2003, p24/ref>July 25, 1572), commonly known in Jewish religious circles as Ha'ari, Ha'ari Hakadosh or Arizal, was a leading rabbi and Jewish mysticism, Jewish mystic in the community of Saf ...
. Adam Ḳadmon is with him no longer the concentrated manifestation of the Sefirot, but a mediator between the En-Sof ("infinite") and the Sefirot
Sefirot (; , plural of ), meaning '' emanations'', are the 10 attributes/emanations in Kabbalah, through which Ein Sof ("infinite space") reveals itself and continuously creates both the physical realm and the seder hishtalshelut (the chained ...
. The En-Sof, according to Luria, is so utterly incomprehensible that the older Kabbalistic doctrine of the manifestation of the En-Sof in the Sefirot must be abandoned. Hence he teaches that only the Adam Ḳadmon, who arose in the way of self-limitation by the En-Sof, can be said to manifest himself in the Sefirot. This theory of Luria is treated by Ḥayyim Vital
Hayyim ben Joseph Vital (; Safed, October 23, 1542 (Old Style and New Style dates, Julian calendar) / October 11, 1542 (Gregorian Calendar) – Damascus, 23 April 1620) was a rabbi in Safed and the foremost disciple of Isaac Luria. He record ...
in "'Eẓ Ḥayyim; Derush 'Agulim we-Yosher" (Treatise on Circles and the Straight Line).
Gnosticism
The Primeval Man (''Protanthropos'', Adam) occupies a prominent place in severalGnostic
Gnosticism (from Ancient Greek: , romanized: ''gnōstikós'', Koine Greek: �nostiˈkos 'having knowledge') is a collection of religious ideas and systems that coalesced in the late 1st century AD among early Christian sects. These diverse g ...
systems. In the Coptic Nag Hammadi texts, the archetypical Adam is known as Pigeradamas or Geradamas. According to Irenaeus
Irenaeus ( or ; ; ) was a Greeks, Greek bishop noted for his role in guiding and expanding Christianity, Christian communities in the southern regions of present-day France and, more widely, for the development of Christian theology by oppos ...
the Aeon
The word aeon , also spelled eon (in American and Australian English), originally meant "life", "vital force" or "being", "generation" or "a period of time", though it tended to be translated as "age" in the sense of "ages", "forever", "timele ...
Autogenes emits the true and perfect Anthrôpos, also called Adamas; he has a helpmate, "Perfect Knowledge", and receives an irresistible force, so that all things rest in him. Others say there is a blessed and incorruptible and endless light in the power of Bythos; this is the Father of all things who is invoked as the First Man, who, with his Ennoia, emits "the Son of Man", or Euteranthrôpos.
According to Valentinus
Valentinus is a Roman masculine given name derived from the Latin word "valens" meaning "healthy, strong". It may refer to:
People Churchmen
*Pope Valentine (died 827)
*Saint Valentine, 3rd century Christian saint
*Valentinus (Gnostic) (died c. 1 ...
, Adam was created in the name of Anthrôpos and overawes the demons by the fear of the pre-existent man ('). In the Valentinian syzygies and in the Marcosian system, we meet in the fourth (originally the third) place Anthrôpos and Ecclesia.
In the ''Pistis Sophia
''Pistis Sophia'' () is a Gnostic text discovered in 1773, possibly written between the 3rd and 4th centuries AD. The existing manuscript, which some scholars place in the late 4th century, relates one Gnostic group's teachings of the transfigu ...
'', the Aeon Jeu is called the First Man, he is the overseer of the Light, messenger of the First Precept, and constitutes the forces of the Heimarmene. In the ''Books of Jeu
The Books of Jeu are two Gnostic texts. Though independent works, both the First Book of Jeu and the Second Book of Jeu appear, in Sahidic Coptic, in the Bruce Codex. They are a combination of a gospel and an esoteric revelation; the work profes ...
'' this "great Man" is the King of the Light-treasure, he is enthroned above all things and is the goal of all souls.
According to the Naassenes
The Naassenes (Greek ''Naasseni,'' possibly from Hebrew נָחָשׁ ''naḥaš'', snake) were a Christian Gnosticism, Christian Gnostic sect known only through the accounts in the books known as the ''Philosophumena'' or the ''Refutation of all H ...
, the Protanthropos is the first element; the fundamental being before its differentiation into individuals. "The Son of Man" is the same being after it has been individualized into existing things and thus sunk into matter.
The Gnostic Anthrôpos, therefore, or ''Adamas'', as it is sometimes called, is a cosmogonic element, pure mind as distinct from matter, mind conceived hypostatically as emanating from God and not yet darkened by contact with matter. This mind is considered as the reason of humanity, or humanity itself, as a personified idea, a category without corporeality, the human reason conceived as the World-Soul. The same idea, somewhat modified, occurs in Hermetic literature, especially the '' Poimandres''.
In Manichaeism
A portion of these Gnostic teachings, when combined withZoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism ( ), also called Mazdayasnā () or Beh-dīn (), is an Iranian religions, Iranian religion centred on the Avesta and the teachings of Zoroaster, Zarathushtra Spitama, who is more commonly referred to by the Greek translation, ...
, furnished Mani
Mani may refer to:
People
* Mani (name), (), a given name and surname (including a list of people with the name)
** Mani (prophet) (c. 216–274), a 3rd century Iranian prophet who founded Manichaeism
** Mani (musician) (born 1962), an English ...
with his particular doctrine of the original man. He even retains the Jewish designations "Adam Kadmon" (= ) and "Nakhash Kadmon" (= ), as may be seen in ''Al-Fihrist
The () (''The Book Catalogue'') is a compendium of the knowledge and literature of tenth-century Islam compiled by Ibn al-Nadim (d. 998). It references approx. 10,000 books and 2,000 authors.''The Biographical Dictionary of the Society for the ...
''. But, according to Mani, the original man is fundamentally distinct from the first father of the human race. He is a creation of the King of Light, and is therefore endowed with five elements of the kingdom of light; whereas Adam really owes his existence to the kingdom of darkness, and only escapes belonging altogether to the number of demons through the fact that he bears the likeness of the original man in the elements of light contained within him. The Gnostic doctrine of the identity of Adam, as the original man, with the Messiah appears in Mani in his teaching of the "Redeeming Christ," who has his abode in the sun and moon, but is identical with the original man. It also appears in this theory that Adam was the first of the sevenfold series of true prophets, comprising Adam
Adam is the name given in Genesis 1–5 to the first human. Adam is the first human-being aware of God, and features as such in various belief systems (including Judaism, Christianity, Gnosticism and Islam).
According to Christianity, Adam ...
, Seth
Seth, in the Abrahamic religions, was the third son of Adam and Eve. The Hebrew Bible names two of his siblings (although it also states that he had others): his brothers Cain and Abel. According to , Seth was born after Abel's murder by Cain, ...
, Noah
Noah (; , also Noach) appears as the last of the Antediluvian Patriarchs (Bible), patriarchs in the traditions of Abrahamic religions. His story appears in the Hebrew Bible (Book of Genesis, chapters 5–9), the Quran and Baháʼí literature, ...
, Abraham
Abraham (originally Abram) is the common Hebrews, Hebrew Patriarchs (Bible), patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father who began the Covenant (biblical), covenanta ...
, Zoroaster
Zarathushtra Spitama, more commonly known as Zoroaster or Zarathustra, was an Iranian peoples, Iranian religious reformer who challenged the tenets of the contemporary Ancient Iranian religion, becoming the spiritual founder of Zoroastrianism ...
, Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha (),*
*
*
was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism. According to Buddhist legends, he was ...
, and Jesus
Jesus (AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many Names and titles of Jesus in the New Testament, other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the Jesus in Chris ...
. The stepping-stone from the Gnostic original man to Manichaeism
Manichaeism (; in ; ) is an endangered former major world religion currently only practiced in China around Cao'an,R. van den Broek, Wouter J. Hanegraaff ''Gnosis and Hermeticism from Antiquity to Modern Times''. SUNY Press, 1998 p. 37 found ...
was probably the older Mandaean conception, which may have exercised great influence. Of this conception, however, there remains in the later Mandaean writings little more than the expression "Gabra Ḳadmaya" (Adam Ḳadmon).
In Mandaeism
'' Adam Kasia'', also referred to using the portmanteau ''Adakas'' in the ''Ginza Rabba
The Ginza Rabba (), Ginza Rba, or Sidra Rabba (), and formerly the Codex Nasaraeus, is the longest and the most important holy scripture of Mandaeism.
The Ginza Rabba is composed of two parts: the Right Ginza (GR) and the Left Ginza (GL). T ...
'', means "the hidden Adam" in Mandaic Mandaic may refer to:
* Mandaic language
* Mandaic alphabet
The Mandaic alphabet is a writing system primarily used to write the Mandaic language. It is thought to have evolved between the second and seventh century CE from either a cursive fo ...
. The hidden Adam is also called ''Adam Qadmaiia'' ("First Adam") or ''Gabra Qadmaiia '' ("First Man"). In Mandaeism
Mandaeism (Mandaic language, Classical Mandaic: ),https://qadaha.wordpress.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/nhura-dictionary-mandaic-english-mandaic.pdf sometimes also known as Nasoraeanism or Sabianism, is a Gnosticism, Gnostic, Monotheism, ...
, it means the soul
The soul is the purported Mind–body dualism, immaterial aspect or essence of a Outline of life forms, living being. It is typically believed to be Immortality, immortal and to exist apart from the material world. The three main theories that ...
of the first man and the soul of every human. ''Adam Kasia'' shows many similarities with the Jewish idea of Adam Kadmon.
In other traditions
Outside of anAbrahamic
The term Abrahamic religions is used to group together monotheistic religions revering the Biblical figure Abraham, namely Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. The religions share doctrinal, historical, and geographic overlap that contrasts them wit ...
context, the Cosmic Man is also an archetypical figure that appears in creation myths of a wide variety of cultures. Generally he is described as bestowing life upon all things, and is also frequently the physical basis of the world, such that after death parts of his body became physical parts of the universe. He also represents the oneness of human existence, or the universe.
For instance, in the Purusha sukta
Purusha Sukta (, ) is a hymn in the Rigveda, dedicated to the Purusha, the "Cosmic Being". It is considered to have been a relatively late addition to the scripture — probably, to accord theological sanction to an increasingly unequal Kuru po ...
of the Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' (, , from wikt:ऋच्, ऋच्, "praise" and wikt:वेद, वेद, "knowledge") is an ancient Indian Miscellany, collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canoni ...
, Purusha
''Purusha'' (, ʊɾʊʂᵊ ) is a complex concept whose meaning evolved in Vedic and Upanishadic times. Depending on source and historical timeline, it means the cosmic being or self, awareness, and universal principle.Karl Potter, Presupposit ...
(Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
'', ''पुरुष "man," or "Cosmic Man") is sacrificed by the devas from the foundation of the world—his mind is the Moon, his eyes are the Sun, and his breath is the wind. He is described as having a thousand heads and a thousand feet.
In popular culture
One tradition associates Adam Kadmon or the biblical Adam and the figure ofCadmus
In Greek mythology, Cadmus (; ) was the legendary Phoenician founder of Boeotian Thebes, Greece, Thebes. He was, alongside Perseus and Bellerophon, the greatest hero and slayer of monsters before the days of Heracles. Commonly stated to be a ...
in Greek mythology, both associated with dragon
A dragon is a Magic (supernatural), magical legendary creature that appears in the folklore of multiple cultures worldwide. Beliefs about dragons vary considerably through regions, but European dragon, dragons in Western cultures since the Hi ...
s/ serpents.
The Marvel Comics character Eternity
Eternity, in common parlance, is an Infinity, infinite amount of time that never ends or the quality, condition or fact of being everlasting or eternal. Classical philosophy, however, defines eternity as what is timeless or exists outside tim ...
has called himself Adam Qadmon.
In ''Persona 5 Royal
is a 2016 role-playing video game developed by P-Studio and published by Atlus. The game is the sixth installment in the ''Persona'' series, itself a part of the larger ''Megami Tensei'' franchise. It was released for PlayStation 3 and PlayStat ...
'', the ultimate Persona of the antagonist Takuto Maruki is named Adam Kadmon.
See also
*Adam and Eve
Adam and Eve, according to the creation myth of the Abrahamic religions, were the first man and woman. They are central to the belief that humanity is in essence a single family, with everyone descended from a single pair of original ancestors. ...
* Adam-God Doctrine
* Original Sin
Original sin () in Christian theology refers to the condition of sinfulness that all humans share, which is inherited from Adam and Eve due to the Fall of man, Fall, involving the loss of original righteousness and the distortion of the Image ...
References
Attribution
*External links
Adam Kadmon—The Divine Names
{{Webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20031013172723/http://www.kheper.net/topics/Kabbalah/Lurianic-AdamKadmon.htm , date=13 October 2003
Jewish mysticism Kabbalah Kabbalistic words and phrases Elcesaites Adam and Eve Mythological first humans