Actomyosin Ring on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
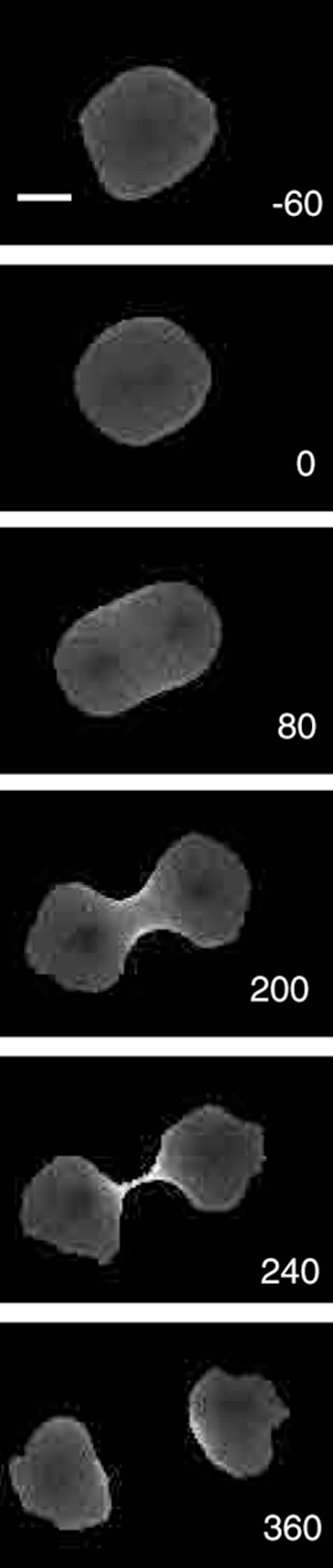 In animals, the ring forms along the
In animals, the ring forms along the
 In
In molecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. The study of chemical and physi ...
, an actomyosin contractile ring is a prominent structure during cytokinesis
Cytokinesis () is the part of the cell division process during which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell divides into two daughter cells. Cytoplasmic division begins during or after the late stages of nuclear division in mitosis and meios ...
.Cheffings TH, Burroughs NJ, Balasubramanian MK. (2016). Actomyosin Ring Formation and Tension Generation in Eukaryotic Cytokinesis. Curr Biol. 26(15):719-737. It forms perpendicular to the axis of the spindle apparatus
In cell biology, the spindle apparatus refers to the cytoskeletal structure of eukaryotic cells that forms during cell division to separate sister chromatids between daughter cells. It is referred to as the mitotic spindle during mitosis, a pr ...
towards the end of telophase
Telophase () is the final stage in both meiosis and mitosis in a eukaryotic cell. During telophase, the effects of prophase and prometaphase (the nucleolus and nuclear membrane disintegrating) are reversed. As chromosomes reach the cell poles, a ...
, in which sister chromatids are identically separated at the opposite sides of the spindle forming nuclei (Figure 1). The actomyosin ring follows an orderly sequence of events: identification of the active division site, formation of the ring, constriction of the ring, and disassembly of the ring. It is composed of actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of over ...
and myosin II
Myosins () are a superfamily of motor proteins best known for their roles in muscle contraction and in a wide range of other motility processes in eukaryotes. They are ATP-dependent and responsible for actin-based motility.
The first myosin (M2 ...
bundles, thus the term actomyosin. The actomyosin ring operates in contractile motion, although the mechanism on how or what triggers the constriction is still an evolving topic. Other cytoskeletal
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is compo ...
proteins are also involved in maintaining the stability of the ring and driving its constriction. Apart from cytokinesis, in which the ring constricts as the cells divide (Figure 2), actomyosin ring constriction has also been found to activate during wound closure
A wound is a rapid onset of injury that involves lacerated or punctured skin (an ''open'' wound), or a contusion (a ''closed'' wound) from blunt force trauma or compression. In pathology, a ''wound'' is an acute injury that damages the epiderm ...
. During this process, actin filaments are degraded, preserving the thickness of the ring. After cytokinesis is complete, one of the two daughter cells inherits a remnant known as the midbody ring.
Activation of the cell-cycle kinase (e.g. Rho-kinases) during telophase initiates constriction of the actomyosin ring by creating a groove that migrates in an inward motion. Rho-kinases such as ROCK1
ROCK1 is a protein serine/threonine kinase also known as rho-associated, coiled-coil-containing protein kinase 1. Other common names are ROKβ and P160ROCK. ROCK1 is a major downstream effecter of the small GTPase RhoA and is a regulator of the a ...
has been found to regulate actomyosin contraction through phosphorylation
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, wh ...
of the myosin light chain
A myosin light chain is a light chain (small polypeptide subunit) of myosin. Myosin light chains were discovered by Chinese biochemist Cao Tianqin (Tien-chin Tsao) when he was a graduate student at the University of Cambridge in England.
Struct ...
(MLC). This mechanism promotes cell-cell contacts and integrity leading to adhesion
Adhesion is the tendency of dissimilar particles or surfaces to cling to one another ( cohesion refers to the tendency of similar or identical particles/surfaces to cling to one another).
The forces that cause adhesion and cohesion can be ...
formation.
Variation between kingdoms
 In animals, the ring forms along the
In animals, the ring forms along the cleavage furrow
In cell biology, the cleavage furrow is the indentation of the cell's surface that begins the progression of cleavage, by which animal and some algal cells undergo cytokinesis, the final splitting of the membrane, in the process of cell division. ...
on the inside of the plasma membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (t ...
then splits by abscission. In fungi, it forms at the mother-bud neck before mitosis. Septin
Septins are a group of guanosine triphosphate, GTP-molecular binding, binding proteins gene expression, expressed in all eukaryote, eukaryotic cells except plants. Different septins form protein complexes with each other. These complexes can furt ...
is heavily involved in the formation of the fungal AMR. In most bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
and many archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebac ...
a homologous structure called the z-ring forms out of FtsZ
FtsZ is a protein encoded by the ''ftsZ'' gene that assembles into a ring at the future site of bacterial cell division (also called the Z ring). FtsZ is a prokaryotic homologue of the eukaryotic protein tubulin. The initials FtsZ mean "Filamen ...
, a homolog of tubulin
Tubulin in molecular biology can refer either to the tubulin protein superfamily of globular proteins, or one of the member proteins of that superfamily. α- and β-tubulins polymerize into microtubules, a major component of the eukaryotic cytoske ...
. Chloroplasts
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant cell, plant and algae, algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, ...
form an analogous structure out of FtsZ. These structures are not made out of actomyosin, but serve a similar role in constricting and permitting cytokinesis. In plant cells, there is no actomyosin ring. Instead, a cell plate
image:Phragmoplast.png, 300px, Phragmoplast and cell plate formation in a plant cell during cytokinesis. Left side: Phragmoplast forms and cell plate starts to assemble in the center of the cell. Towards the right: Phragmoplast enlarges in a donut ...
grows centrifugally outwards from the center of the plane of division until it fuses with the existing cell wall
A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. It provides the cell with both structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mech ...
.Bi, E., P. Maddox, D. Lew, E. Salmon, J. McMillan, E. Yeh, and J. Pringle. (1998). Involvement of an Actomyosin Contractile Ring in ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' Cytokinesis. Journal Of Cell Biology. 142(5):1301–1312.
See also
*References
{{Reflist Mitosis Protein complexes