Activation Of Cyclopropanes By Transition Metals on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In organometallic chemistry, the activation of cyclopropanes by transition metals is a research theme with implications for
In organometallic chemistry, the activation of cyclopropanes by transition metals is a research theme with implications for 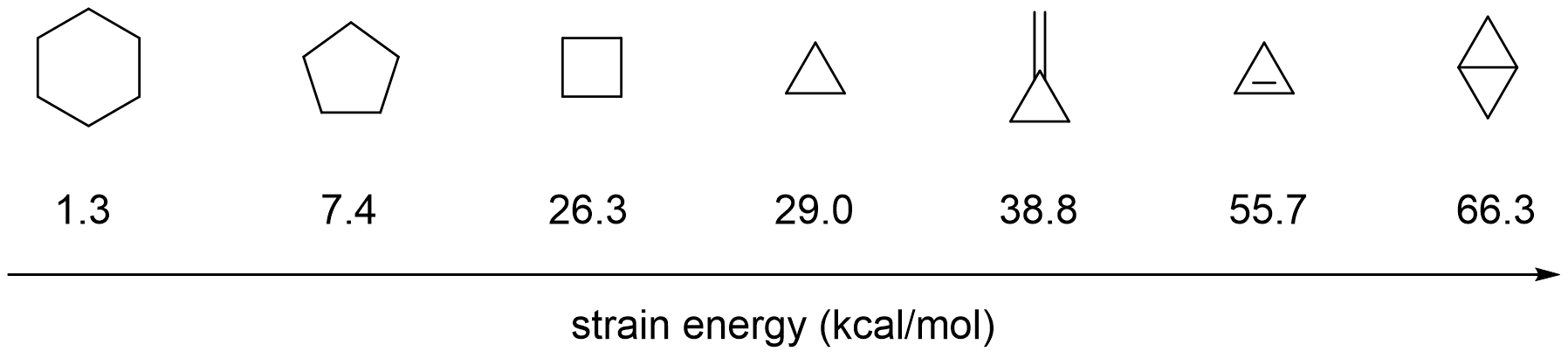 Two main approaches achieve C-C bond activation using a transition metal. One strategy is to increase the
Two main approaches achieve C-C bond activation using a transition metal. One strategy is to increase the

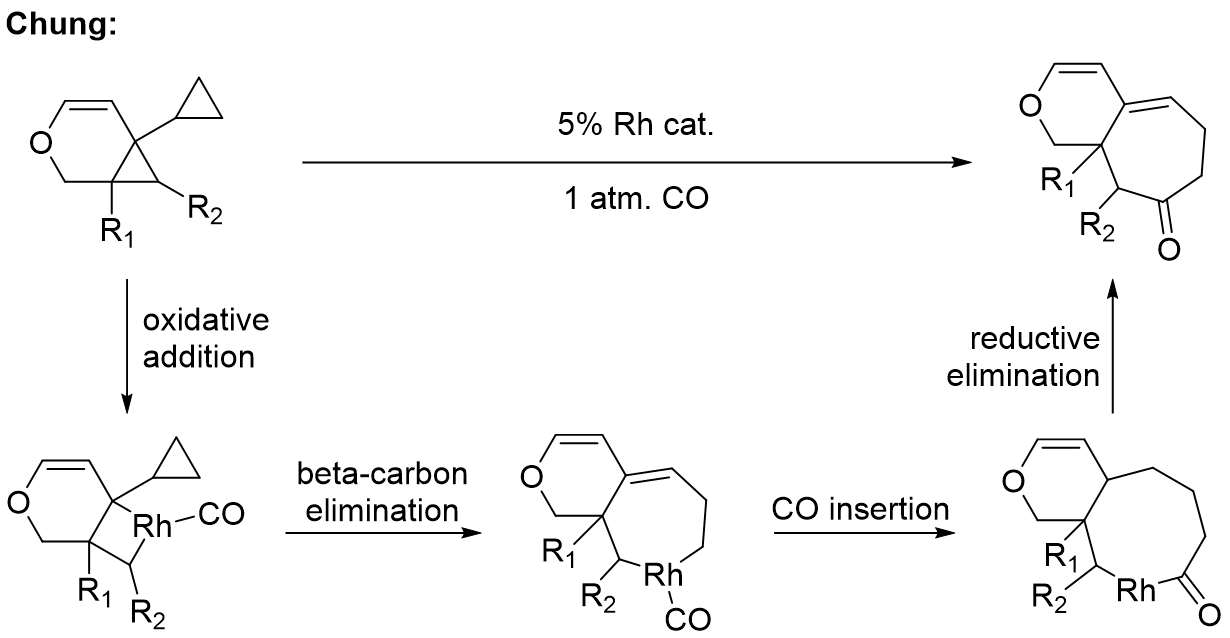
 Using the same rhodium(I) catalyst and C-C bond activation strategy one can access compounds with fused rings. Once again the reaction involves oxidative addition to give a rhodacyclobutane eventually affording a rhodacycloheptene intermediate. Insertion of carbon monoxide into one of the carbon-rhodium bonds form a rhodacyclooctenone intermediate that can reductively eliminate to yield a 6,7-fused ring system. The authors propose that the regioselectivity of the initial oxidative addition is controlled by coordination of the endocyclic double bond to the rhodium catalyst.
Using the same rhodium(I) catalyst and C-C bond activation strategy one can access compounds with fused rings. Once again the reaction involves oxidative addition to give a rhodacyclobutane eventually affording a rhodacycloheptene intermediate. Insertion of carbon monoxide into one of the carbon-rhodium bonds form a rhodacyclooctenone intermediate that can reductively eliminate to yield a 6,7-fused ring system. The authors propose that the regioselectivity of the initial oxidative addition is controlled by coordination of the endocyclic double bond to the rhodium catalyst.
 With the metallacyclobutane intermediate, 1,2-migratory insertion into an
With the metallacyclobutane intermediate, 1,2-migratory insertion into an 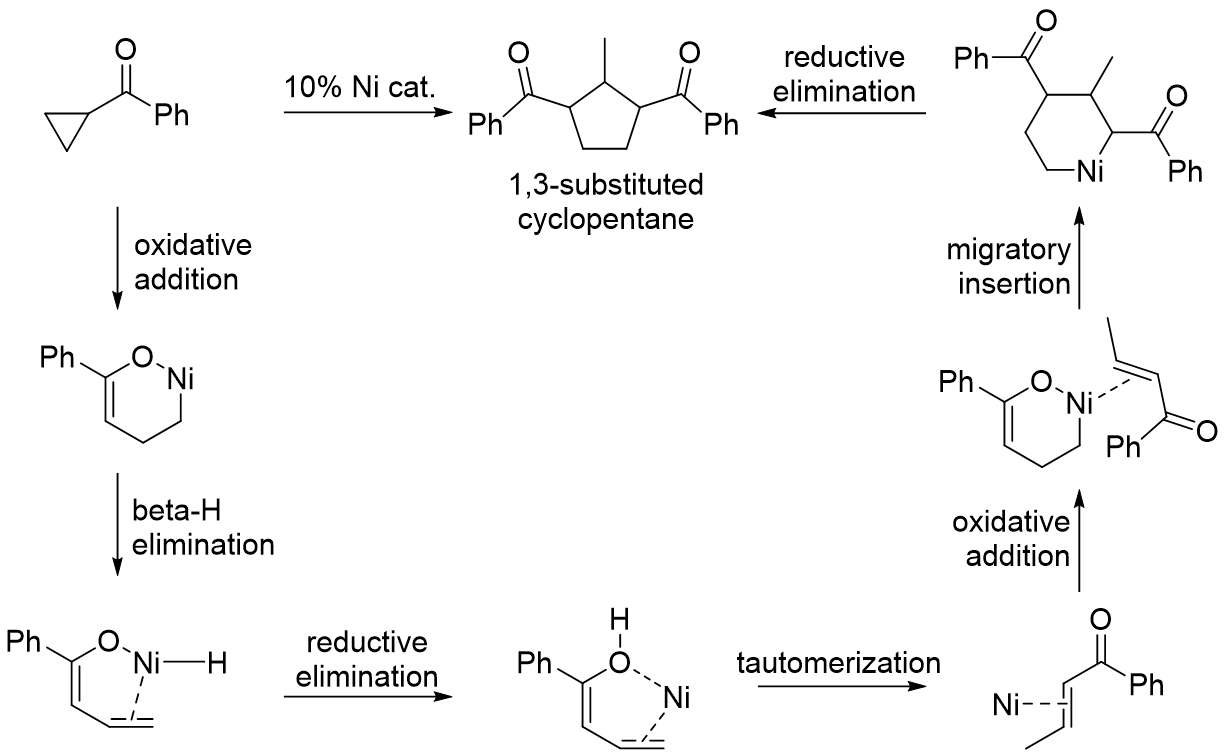






 In organometallic chemistry, the activation of cyclopropanes by transition metals is a research theme with implications for
In organometallic chemistry, the activation of cyclopropanes by transition metals is a research theme with implications for organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the intentional construction of organic compounds. Organic molecules are often more complex than inorganic compounds, and their synthesis has developed into one o ...
and homogeneous catalysis
In chemistry, homogeneous catalysis is catalysis by a soluble catalyst in a solution. Homogeneous catalysis refers to reactions where the catalyst is in the same phase as the reactants, principally in solution. In contrast, heterogeneous catalysi ...
. Being highly strained, cyclopropanes are prone to oxidative addition
Oxidative addition and reductive elimination are two important and related classes of reactions in organometallic chemistry. Oxidative addition is a process that increases both the oxidation state and coordination number of a metal centre. Oxid ...
to transition metal
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. They are the elements that c ...
complexes. The resulting metallacycle
In organometallic chemistry, a metallacycle is a derivative of a carbocyclic compound wherein a metal has replaced at least one carbon center; this is to some extent similar to heterocycles. Metallacycles appear frequently as reactive intermediate ...
s are susceptible to a variety of reactions. These reactions are rare examples of C-C bond activation. The rarity of C-C activation processes has been attributed to Steric effects
Steric effects arise from the spatial arrangement of atoms. When atoms come close together there is a rise in the energy of the molecule. Steric effects are nonbonding interactions that influence the shape ( conformation) and reactivity of ions ...
that protect C-C bonds. Furthermore, the directionality of C-C bonds as compared to C-H bonds makes orbital
Orbital may refer to:
Sciences Chemistry and physics
* Atomic orbital
* Molecular orbital
* Hybrid orbital Astronomy and space flight
* Orbit
** Earth orbit
Medicine and physiology
* Orbit (anatomy), also known as the ''orbital bone''
* Orbito ...
interaction with transition metals less favorable. Thermodynamically, C-C bond activation is more favored than C-H bond activation as the strength
Strength may refer to:
Physical strength
*Physical strength, as in people or animals
*Hysterical strength, extreme strength occurring when people are in life-and-death situations
*Superhuman strength, great physical strength far above human ca ...
of a typical C-C bond is around 90 kcal per mole while the strength of a typical unactivated C-H bond is around 104 kcal per mole.
 Two main approaches achieve C-C bond activation using a transition metal. One strategy is to increase the
Two main approaches achieve C-C bond activation using a transition metal. One strategy is to increase the ring strain
In organic chemistry, ring strain is a type of instability that exists when bonds in a molecule form angles that are abnormal. Strain is most commonly discussed for small rings such as cyclopropanes and cyclobutanes, whose internal angles are s ...
and the other is to stabilize the resulting cleaved C-C bond complex (e.g. through aromatization
Aromatization is a chemical reaction in which an aromatic system is formed from a single nonaromatic precursor. Typically aromatization is achieved by dehydrogenation of existing cyclic compounds, illustrated by the conversion of cyclohexane into ...
or chelation
Chelation is a type of bonding of ions and molecules to metal ions. It involves the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand and a single central metal atom. These ligands are ...
). Because of the large ring strain energy of cyclopropanes (29.0 kcal per mole), they are often used as substrates for C-C activation through oxidative addition of a transition metal into one of the three C-C bonds leading to a metallacyclobutane intermediate.
Substituents on the cyclopropane affect the course of its activation.
Reaction scope
Cyclopropane
The first example of cyclopropane being activated by a metal complex was reported in 1955, involving the reaction of cyclopropane and hexachloroplatinic acid. This reaction produces the polymeric platinacyclobutane complex Pt(C3H6)Cl2. The bis(pyridine) adduct of this complex was characterized byX-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angle ...
.
The electrophile Cp*Ir(PMe3)(Me)OTf reacts with cyclopropane to give the allyl complex:
:Cp*Ir(PMe3)(Me)OTf + C3H6 → p*Ir(PMe3)(η3-C3H5)Tf + CH4

Fused and spiro-cyclopropanes
Rhodium
Rhodium is a chemical element with the symbol Rh and atomic number 45. It is a very rare, silvery-white, hard, corrosion-resistant transition metal. It is a noble metal and a member of the platinum group. It has only one naturally occurring ...
-catalyzed C-C bondactivation of strained spiropentane
Spiropentane is a hydrocarbon with formula . It is the simplest spiro-connected cycloalkane, a triangulane.
It took several years after the discovery in 1887 until the structure of the molecule was determined. According to the nomenclature rules ...
s leads to a cyclopentenone
2-Cyclopentenone is a ketone with chemical formula and CAS number 930-30-3. It is structurally similar to cyclopentanone, with the additional feature of α-β unsaturation in the ring system. 2-Cyclopentenone contains two functional groups, a ...
s. In terms of mechanism, the reaction proceeds by apparent oxidative addition of the 4-5 carbon-carbon bond, leading to a rhodacyclobutane intermediate. In the presence of carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide ( chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the si ...
, migratory insertion
In organometallic chemistry, a migratory insertion is a type of reaction wherein two ligands on a metal complex combine. It is a subset of reactions that very closely resembles the insertion reactions, and both are differentiated by the mecha ...
of CO into one of the carbon-rhodium bonds gives a rhodacyclopentanone intermediate. Beta-carbon elimination to form an alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond.
Alkene is often used as synonym of olefin, that is, any hydrocarbon containing one or more double bonds.H. Stephen Stoker (2015): General, Organic, an ...
from the other carbon-rhodium bond leads to a rhodacyclohexanone intermediate with an exocyclic
In organic chemistry, an alicyclic compound contains one or more all-carbon rings which may be either saturated or unsaturated, but do not have aromatic character. Alicyclic compounds may have one or more aliphatic side chains attached.
The ...
double bond. Reductive elimination
Reductive elimination is an elementary step in organometallic chemistry in which the oxidation state of the metal center decreases while forming a new covalent bond between two ligands. It is the microscopic reverse of oxidative addition, and ...
of the two carbon-rhodium bonds followed by isomerization
In chemistry, isomerization or isomerisation is the process in which a molecule, polyatomic ion or molecular fragment is transformed into an isomer with a different chemical structure. Enolization is an example of isomerization, as is tautome ...
of the exocyclic double bond leads to the desired beta-substituted cyclopentenone
2-Cyclopentenone is a ketone with chemical formula and CAS number 930-30-3. It is structurally similar to cyclopentanone, with the additional feature of α-β unsaturation in the ring system. 2-Cyclopentenone contains two functional groups, a ...
product. This reaction was applied to the total synthesis of (±)-β-cuparenone.
 Using the same rhodium(I) catalyst and C-C bond activation strategy one can access compounds with fused rings. Once again the reaction involves oxidative addition to give a rhodacyclobutane eventually affording a rhodacycloheptene intermediate. Insertion of carbon monoxide into one of the carbon-rhodium bonds form a rhodacyclooctenone intermediate that can reductively eliminate to yield a 6,7-fused ring system. The authors propose that the regioselectivity of the initial oxidative addition is controlled by coordination of the endocyclic double bond to the rhodium catalyst.
Using the same rhodium(I) catalyst and C-C bond activation strategy one can access compounds with fused rings. Once again the reaction involves oxidative addition to give a rhodacyclobutane eventually affording a rhodacycloheptene intermediate. Insertion of carbon monoxide into one of the carbon-rhodium bonds form a rhodacyclooctenone intermediate that can reductively eliminate to yield a 6,7-fused ring system. The authors propose that the regioselectivity of the initial oxidative addition is controlled by coordination of the endocyclic double bond to the rhodium catalyst.

Cyclopropyl halides
Nickel(0) complexes oxidatively cleave halocyclopropanes to give allyl)Ni(II) halides.Cyclopropylketones
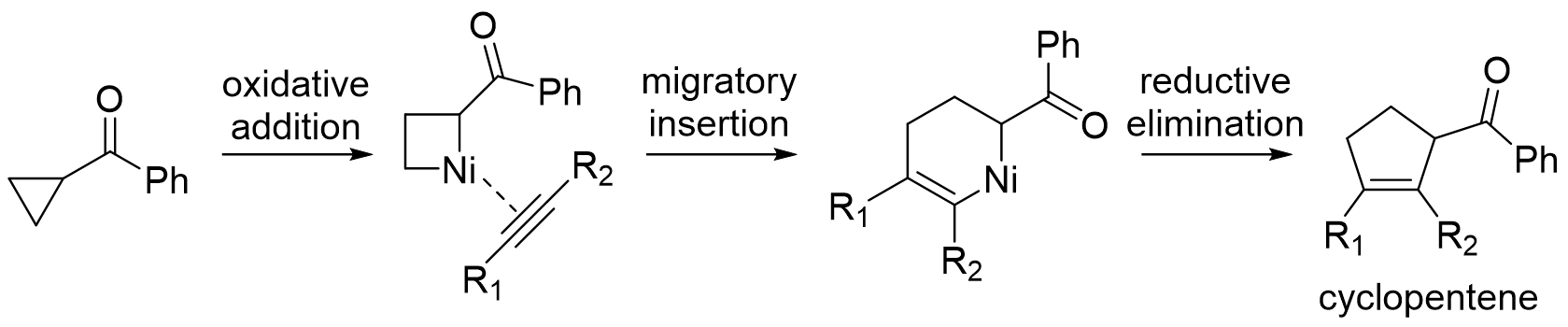
With cyclopropylketones, transition metal can coordinate to the ketone to direct oxidative addition into the proximal C-C bond. The resulting metallacyclobutane intermediate can be in equilibrium with the six-membered alkyl metalenolate
In organic chemistry, enolates are organic anions derived from the deprotonation of carbonyl () compounds. Rarely isolated, they are widely used as reagents in the synthesis of organic compounds.
Bonding and structure
Enolate anions are electr ...
depending on presence of a Lewis acid
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any sp ...
(e.g. dimethylaluminum chloride).
 With the metallacyclobutane intermediate, 1,2-migratory insertion into an
With the metallacyclobutane intermediate, 1,2-migratory insertion into an alkyne
\ce
\ce
Acetylene
\ce
\ce
\ce
Propyne
\ce
\ce
\ce
\ce
1-Butyne
In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and no ...
followed by reductive elimination yields a substituted cyclopentene
Cyclopentene is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless liquid with a petrol-like odor. It has few applications, and thus is mainly used as a minor component of gasoline, present in concentrations of less than 1%. It is one of t ...
product. Examples of intramolecular reactions with a tethered alkyne and intermolecular reactions with a nontethered alkyne both exist with use of a nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow ...
or rhodium catalyst. With the six-membered alkyl metal enolate intermediate, dimerization or reaction with an added alpha-beta unsaturated ketone yields a 1,3-substituted cyclopentane
Cyclopentane (also called C pentane) is a highly flammable alicyclic hydrocarbon with chemical formula C5H10 and CAS number 287-92-3, consisting of a ring of five carbon atoms each bonded with two hydrogen atoms above and below the plane. It oc ...
product.


Cyclopropylimines
Oxidative addition into cyclopropylimines gives a metalloenamine intermediate similar to oxidative addition to cyclopropylketones giving alkylmetalloenolates. These intermediates can also reaction with alpha-beta unsaturated ketones to give disubstituted cyclopentane products following reductive elimination. With rhodium, the intermediate metalloenamine reacts with tethered alkynes. and alkenes to give cyclized products such aspyrrole
Pyrrole is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound, a five-membered ring with the formula C4 H4 NH. It is a colorless volatile liquid that darkens readily upon exposure to air. Substituted derivatives are also called pyrroles, e.g., ''N''-met ...
s and cyclohexenone
Cyclohexenone is an organic compound which is a versatile intermediate used in the synthesis of a variety of chemical products such as pharmaceuticals and fragrances. It is colorless liquid, but commercial samples are often yellow.
Industrially, ...
s, respectively.

Alylidenecyclopropanes
Alkylidenecyclopropanes more readily undergo C-C bond oxidative addition than cyclopropanes. Following oxidative addition, 1,2-insertion mechanisms are common and reductive elimination yields the desired product. The 1,2-insertion step usually occurs with an alkyne, alkene, or allene and the final product is often a 5 or 7 membered ring. Six-membered rings may be formed after dimerization of the metallocyclobutane intermediate with another alkylidenecyclopropane substrate and subsequent reductive elimination. Common transition metals utilized with alkylidenecyclopropanes are nickel, rhodium, andpalladium
Palladium is a chemical element with the symbol Pd and atomic number 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1803 by the English chemist William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas, which was itself nam ...
. It has been shown that the metallacyclobutane intermediate following oxidative addition to the distal C-C bond can isomerize.



Vinylcyclopropanes
Oxidative addition of vinylcyclopropanes primarily occurs at the proximal position, giving pi-allyl intermediates. Through subsequent insertion reactions (e.g. withalkyne
\ce
\ce
Acetylene
\ce
\ce
\ce
Propyne
\ce
\ce
\ce
\ce
1-Butyne
In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and no ...
s, alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond.
Alkene is often used as synonym of olefin, that is, any hydrocarbon containing one or more double bonds.H. Stephen Stoker (2015): General, Organic, an ...
s, and carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide ( chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the si ...
), rings of various sizes and fused ring systems can be formed.

Cyclopropenes
Oxidative addition into cyclopropenes normally occurs at the less hindered position to yield the metallacyclobutane. This reaction can result in formation ofcyclopentadienone
Cyclopentadienone is an organic compound with molecular formula
In chemistry, a chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using che ...
s, cyclohexenones, and phenols
In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of one or more hydroxyl groups (— O H) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest is phenol, . Phenolic compounds ...
.

References
{{Reflist, 30em Chemical bond properties Cyclopropanes Organometallic chemistry