Acrania on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Acrania is a rare
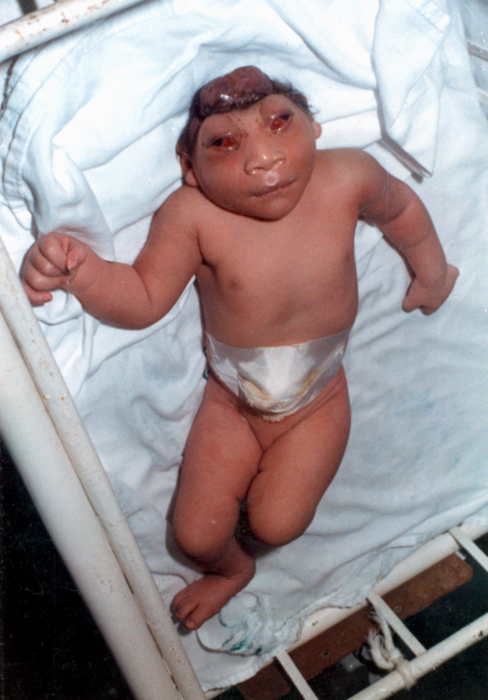
congenital disorder
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can ...
that occurs in the human fetus in which the flat bones in the cranial vault
The cranial vault is the space in the skull within the neurocranium, occupied by the brain.
Development
In humans, the cranial vault is imperfectly composed in newborns, to allow the large human head to pass through the birth canal. During bir ...
are either completely or partially absent. The cerebral hemisphere
The vertebrate cerebrum (brain) is formed by two cerebral hemispheres that are separated by a groove, the longitudinal fissure. The brain can thus be described as being divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres. Each of these hemispheres ...
s develop completely but abnormally. The condition is frequently, though not always, associated with anencephaly
Anencephaly is the absence of a major portion of the brain, skull, and scalp that occurs during embryonic development. It is a cephalic disorder that results from a neural tube defect that occurs when the rostral (head) end of the neural tube fai ...
. The fetus is said to have acrania if it meets the following criteria: the fetus should have a perfectly normal facial bone, a normal cervical column but without the fetal skull and a volume of brain tissue equivalent to at least one-third of the normal brain size.
Causes

Genetics
There are no known family ties in acrania and recurrence rates are extremely low. Not much is known about the exact mechanism involved in acrania. It is hypothesized that, like other developmental malformations, there are multiple origins for acrania. Recent work has identified mutations in the hedgehog acyltransferase (HHAT) gene that have caused acrania along withholoprosencephaly
Holoprosencephaly (HPE) is a cephalic disorder in which the prosencephalon (the forebrain of the embryo) fails to develop into two hemispheres, typically occurring between the 18th and 28th day of gestation. Normally, the forebrain is formed and t ...
and agnathia. The mutation in which causes this disease is a loss-of-function mutation. Before this discovery in 2010, HHAT was known to play a role in the sonic hedgehog pathway. When HHAT contains a loss-of-function mutation, less HHAT protein is produced. is necessary for the production of Hedgehog
A hedgehog is a spiny mammal of the subfamily Erinaceinae, in the eulipotyphlan family Erinaceidae. There are seventeen species of hedgehog in five genera found throughout parts of Europe, Asia, and Africa, and in New Zealand by introducti ...
() proteins post-transcriptionally. As HHAT production decreases, production of long-range Hh proteins decreases proportionally. Decreases in Hh, production disturb the production of extracellular signal-regulated kinases
In molecular biology, extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) or classical MAP kinases are widely expressed protein kinase intracellular signalling molecules that are involved in functions including the regulation of meiosis, mitosis, and p ...
, bone morphogenetic protein
Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) are a group of growth factors also known as cytokines and as metabologens. Originally discovered by their ability to induce the formation of bone and cartilage, BMPs are now considered to constitute a group of piv ...
s, and fibroblast growth factor
Fibroblast growth factors (FGF) are a family of cell signalling proteins produced by macrophages; they are involved in a wide variety of processes, most notably as crucial elements for normal development in animal cells. Any irregularities in the ...
s, all of which play important roles in craniofacial patterning. Disruption of these pathways leads to abnormal bone and cartilage formation causing acrania and multiple other craniofacial patterning problems.
Genetic counseling
Little genetic counseling can be offered for acrania because the genetic origins are not fully understood. In order to make genetic counseling for families easier this disease is often differentially diagnosed with other diseases that can occur at the same time such asanencephaly
Anencephaly is the absence of a major portion of the brain, skull, and scalp that occurs during embryonic development. It is a cephalic disorder that results from a neural tube defect that occurs when the rostral (head) end of the neural tube fai ...
and acalvaria
Acalvaria is a rare malformation consisting of absence of the calvarial bones, dura mater and associated muscles in the presence of a normal skull base and normal facial bones. The central nervous system is usually unaffected. The presumed pathog ...
, though these diseases may not always occur simultaneously. Recurrence rates are extremely low, so genetic counseling is not always necessary.
Amniotic band syndrome
Duringamniotic band syndrome
Constriction ring syndrome (CRS) is a congenital disorder with unknown cause. Because of the unknown cause there are many different, and sometimes incorrect names. It is a malformation due to intrauterine bands or rings that give deep grooves in, ...
(ABS), fibrous bands may entrap various parts of the developing fetus causing malformations. When these fibrous bands form around the developing skull, the bones will not form properly. ABS occurring in the developing brain neural tissue is one cause of acrania. When is the cause of acrania the fibrous bands cannot be detected through ultrasound.
Mechanism
During the fourth week of human development theneuropore
Neurulation refers to the folding process in vertebrate embryos, which includes the transformation of the neural plate into the neural tube. The embryo at this stage is termed the neurula.
The process begins when the notochord induces the forma ...
in a normally developing fetus closes. When this process is either interrupted or never initiated, acrania occurs. The desmocranium becomes a membranous coverage instead of forming the epidermis of the scalp. Whether from being blocked by amniotic bands or by just not initiating, the migration of mesenchyme
Mesenchyme () is a type of loosely organized animal embryonic connective tissue of undifferentiated cells that give rise to most tissues, such as skin, blood or bone. The interactions between mesenchyme and epithelium help to form nearly every o ...
under the ectoderm
The ectoderm is one of the three primary germ layers formed in early embryonic development. It is the outermost layer, and is superficial to the mesoderm (the middle layer) and endoderm (the innermost layer). It emerges and originates from t ...
does not occur. Because this migration does not occur, the skull, and all involved muscles, are never formed. Without the presence of the neurocranium
In human anatomy, the neurocranium, also known as the braincase, brainpan, or brain-pan is the upper and back part of the skull, which forms a protective case around the brain. In the human skull, the neurocranium includes the calvaria (skull), ...
, the brain fails to separate into two separate lobes. The hindbrain proceeds to develop normally, allowing for the child to be carried to term, but the diencephalon
The diencephalon (or interbrain) is a division of the forebrain (embryonic ''prosencephalon''). It is situated between the telencephalon and the midbrain (embryonic ''mesencephalon''). The diencephalon has also been known as the 'tweenbrain in ol ...
and ocular lobe remain small and underdeveloped.
Ectodermal mesenchyme
Mesenchyme
Mesenchyme () is a type of loosely organized animal embryonic connective tissue of undifferentiated cells that give rise to most tissues, such as skin, blood or bone. The interactions between mesenchyme and epithelium help to form nearly every o ...
is formed in the developing embryo and will eventually become cartilage and bone. When ectodermal mesenchyme fails to migrate into the head region of the embryo, the skull will not be able to form. What exactly causes the failure of mesenchymal migration is unknown.
Diagnosis
Acrania can be diagnosed early in pregnancy through anultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequency, frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing range, hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hea ...
. This abnormality appears during the beginning or end of the fourth week of the fetus's development. An absence of the skull is needed in order to make a diagnosis. A presence of brain tissue will confirm the diagnosis of acrania and differentiate it from other developmental problems such as anencephaly
Anencephaly is the absence of a major portion of the brain, skull, and scalp that occurs during embryonic development. It is a cephalic disorder that results from a neural tube defect that occurs when the rostral (head) end of the neural tube fai ...
.
Prognosis
Anencephaly is a fatal condition. Infants with anencephaly are stillborn in about 75 percent of cases. Newborns who survive die within several hours, days, or weeks. This disease is rare, occurring in 1 in 20,000 live births. In order to better manage an acrania diagnosis, early detection is of extreme importance. Families may choose either to terminate the pregnancy, or to carry the fetus to term, depending on the laws where they live. Acrania may cause a fetus to spontaneously abort before reaching term.References
External links
* {{Congenital malformations and deformations of nervous system Congenital disorders of nervous system