Accessory Sex Glands on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
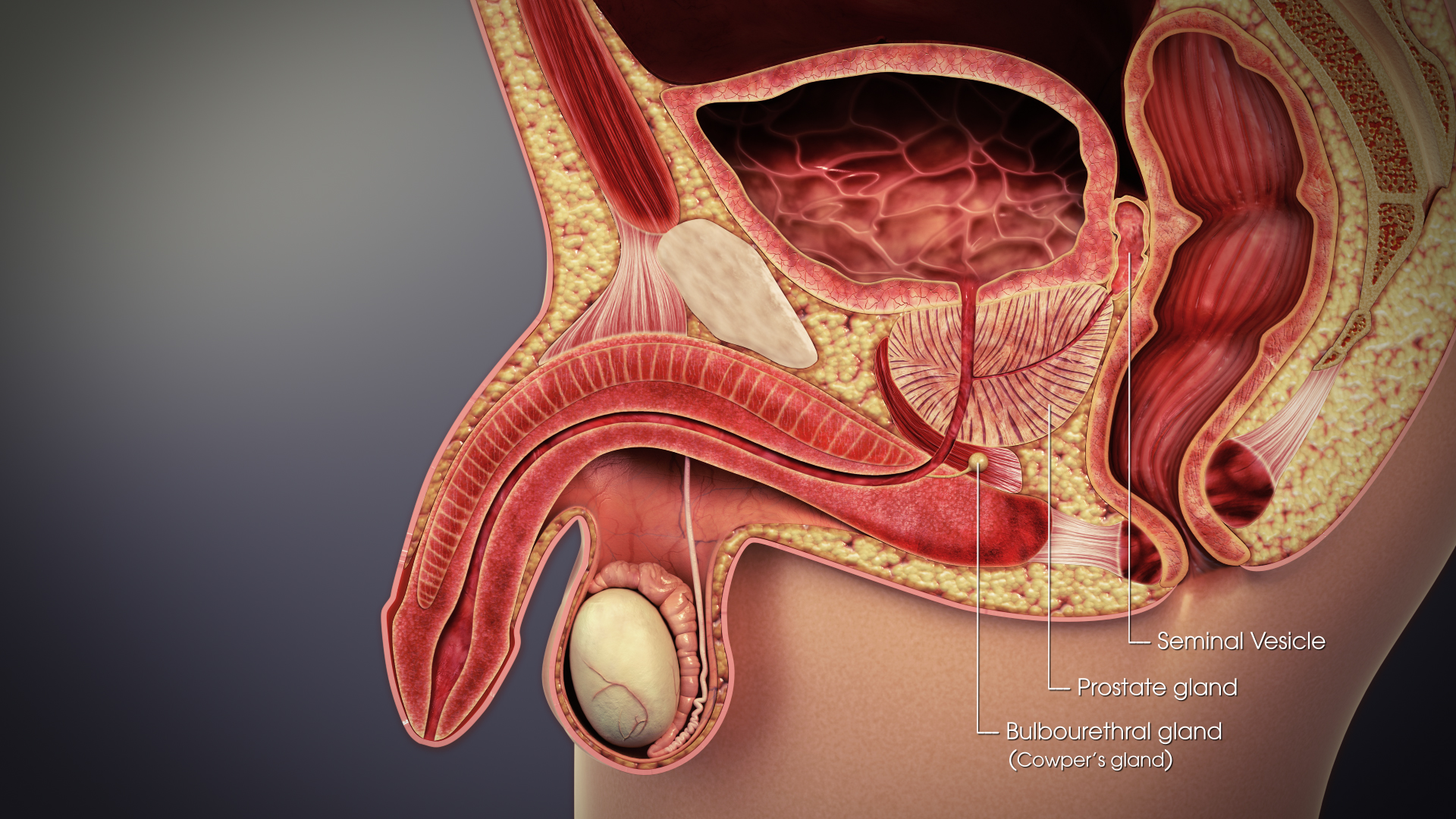 Male accessory glands (MAG) in humans are the seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and the bulbourethral glands (also called Cowper's glands).
In insects, male accessory glands produce products that mix with the sperm to protect and preserve them, including seminal fluid proteins. Some insecticides can induce an increase in the protein content of the male accessory glands of certain types of insects. This has the unintended effect of increasing the number of offspring they produce.
These glands secrete fluid for nourishment of
Male accessory glands (MAG) in humans are the seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and the bulbourethral glands (also called Cowper's glands).
In insects, male accessory glands produce products that mix with the sperm to protect and preserve them, including seminal fluid proteins. Some insecticides can induce an increase in the protein content of the male accessory glands of certain types of insects. This has the unintended effect of increasing the number of offspring they produce.
These glands secrete fluid for nourishment of
 Male accessory glands (MAG) in humans are the seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and the bulbourethral glands (also called Cowper's glands).
In insects, male accessory glands produce products that mix with the sperm to protect and preserve them, including seminal fluid proteins. Some insecticides can induce an increase in the protein content of the male accessory glands of certain types of insects. This has the unintended effect of increasing the number of offspring they produce.
These glands secrete fluid for nourishment of
Male accessory glands (MAG) in humans are the seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and the bulbourethral glands (also called Cowper's glands).
In insects, male accessory glands produce products that mix with the sperm to protect and preserve them, including seminal fluid proteins. Some insecticides can induce an increase in the protein content of the male accessory glands of certain types of insects. This has the unintended effect of increasing the number of offspring they produce.
These glands secrete fluid for nourishment of sperm
Sperm is the male reproductive cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm with a tail known as a flagellum, whi ...
.
Accessory glands
The male accessory glands are the ampullary gland, seminal vesicles, prostate,bulbourethral gland
The bulbourethral glands or Cowper's glands (named for English anatomist William Cowper) are two small exocrine glands in the reproductive system of many male mammals (of all domesticated animals, they are absent only in dogs). They are homolog ...
, and urethral glands.
The products of these glands serve to nourish and activate the spermatozoa, to clear the urethral tract prior to ejaculation, serve as the vehicle of transport of the spermatozoa in the female tract, and to plug the female tract after placement of spermatozoa to help ensure fertilization. Although the glands are usually described as being branched tubular
Tubular may refer to:
*having the form of a hollow cylinder, or tube
*having the form of a cylinder
*''Tubular'', a television-related entertainment blog on the ''Houston Chronicle'' website
*''Tubular'', a level in the video game ''Super Mario Wor ...
or branched tubuloalveolar
Alveolar glands, also called saccular glands are glands with a saclike secretory portion, in conrast with tubular glands. They typically have an enlarged lumen (cavity), hence the name: they have a shape similar to alveoli, the very small air ...
, they vary in their organization and in their distribution in different species.
Ampullary glands
Each of these branched tubular glands lined by simple columnarepithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellul ...
is an enlargement of the vas deferens in its terminal portion. These are typical tubular glands in ruminants, horses and dogs; absent in the cat and poorly developed in boars. The function of the white serous secretion is not known.
Seminal vesicles
The secretory endpieces of these glands are lined with simple columnarepithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellul ...
; the main ducts are lined with stratified columnar epithelium. These glands do not occur in carnivores, but are present in some form in horses, ruminants and swine. Seminal fluid, the product of this gland, serves as a vehicle for the transport of spermatozoa.
Prostate gland
Grossly the prostate gland can be divided into two parts: the body and the disseminate part. Low cuboidal to low columnarepithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellul ...
provides the lining for this compound, tubuloalveolar gland which consists primarily of serous secretory end pieces. The secretion of this gland is more serous in dogs and more mucous in bulls. It serves to promote the movement of spermatozoa and to form a vaginal plug
A mating plug, also known as a copulation plug, sperm plug, vaginal plug, or sphragis (Latin, from Greek σφραγίς ''sphragis'', "a seal"), is gelatinous secretion used in the mating of some species. It is deposited by a male into a female ge ...
. Additionally, in bulls, the secretion contains high amounts of fructose
Fructose, or fruit sugar, is a Ketose, ketonic monosaccharide, simple sugar found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galacto ...
and citric acid. Concretions may be present in the secretory end pieces as well as parts of the duct system. The prostate and Cowper's glands are the only male accessory glands in marsupials.
Bulbourethral glands
The lining of these paired, compound, tubuloalveloar glands is simple columnarepithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellul ...
. A capsule of dense connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tiss ...
contains some smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It is divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit mus ...
as well as skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscl ...
of the bulbospongiosus and urethral muscles. All domestic species have these glands except the dog, and their mucus secretion serves to clear the urethra of urine and to lubricate it and the vagina. The product may also serve as an energy source for the spermatozoa.
Urethral glands
In some species, branched tubular mucous glands are found along the length of the urethra, especially dorsal to the lumen of the urethra. The exact function of their product is not clear.Distribution in insects
The male accessory gland is also prevalent in some species of butterflies and moths. An example is the cotton leafworm, or '' Spodoptera litura'', in which the males transfer MAG to the females during copulation. This results in a wide range of post-mating behavior in the females, the most noteworthy being the decrease in sexual receptivity in the females. This helps to assure that no other males will mate with that female, allowing her eggs to be fertilized by the current male's own sperm.See also
* Male accessory gland infection (MAGI)References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Male Accessory Gland Animal reproductive system