Acanthodes (beetle) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Acanthodes'' (from el, ἄκανθώδης , 'provided with spines') is an
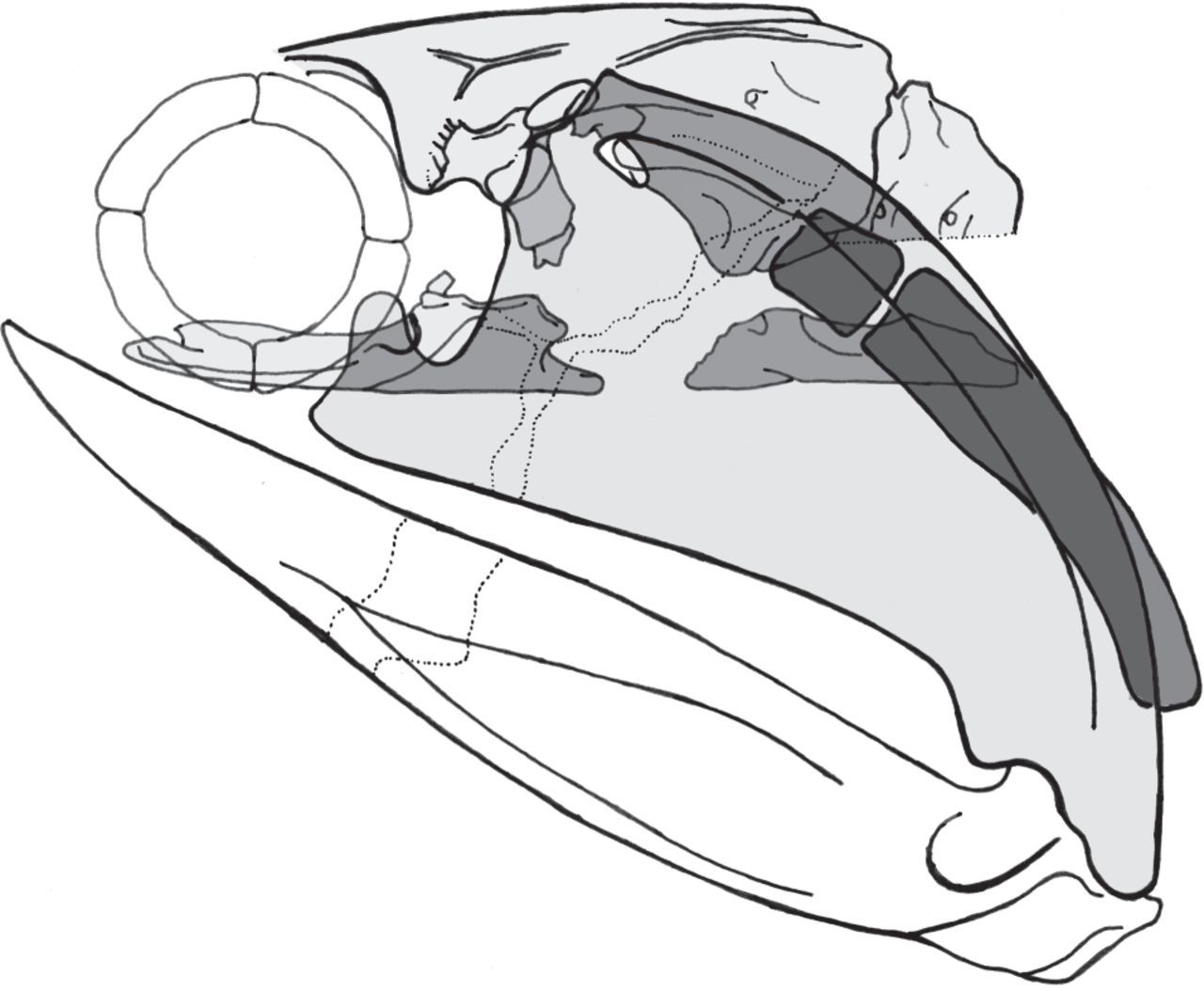 ''Acanthodes'' grew to lengths of at least . The body was elongate and had a pair of pectoral fins, an unpaired dorsal fin far back on the body, with an unpaired long ventral/pelvic fin and an anal fin on the underside of the body, which like other acanthodians were supported by stiff spines at their front edges. The whole body was covered in scales, which varied in shape depending on their position. The vertebral column was typically unossified. ''Acanthodes'' had no teeth and had long gill rakers. Because of this, ''Acanthodes'' is presumed to have been a
''Acanthodes'' grew to lengths of at least . The body was elongate and had a pair of pectoral fins, an unpaired dorsal fin far back on the body, with an unpaired long ventral/pelvic fin and an anal fin on the underside of the body, which like other acanthodians were supported by stiff spines at their front edges. The whole body was covered in scales, which varied in shape depending on their position. The vertebral column was typically unossified. ''Acanthodes'' had no teeth and had long gill rakers. Because of this, ''Acanthodes'' is presumed to have been a
entry at the Fossil Museumentry at Saint Joseph's University
{{Taxonbar, from=Q2335100 Acanthodii genera Carboniferous acanthodians Permian acanthodians Paleozoic fish of North America Paleozoic fish of Europe Prehistoric fish of Australia Taxa named by Louis Agassiz
extinct
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and ...
genus of acanthodian fish. Species have been found in Europe, North America, and Asia, spanning the Early Carboniferous to the Early Permian 01 or '01 may refer to:
* The year 2001, or any year ending with 01
* The month of January
* 1 (number)
Music
* '01 (Richard Müller album), 01'' (Richard Müller album), 2001
* 01 (Son of Dave album), ''01'' (Son of Dave album), 2000
* 01 (Urban ...
, making it one of the youngest known acanthodian genera.
Description
 ''Acanthodes'' grew to lengths of at least . The body was elongate and had a pair of pectoral fins, an unpaired dorsal fin far back on the body, with an unpaired long ventral/pelvic fin and an anal fin on the underside of the body, which like other acanthodians were supported by stiff spines at their front edges. The whole body was covered in scales, which varied in shape depending on their position. The vertebral column was typically unossified. ''Acanthodes'' had no teeth and had long gill rakers. Because of this, ''Acanthodes'' is presumed to have been a
''Acanthodes'' grew to lengths of at least . The body was elongate and had a pair of pectoral fins, an unpaired dorsal fin far back on the body, with an unpaired long ventral/pelvic fin and an anal fin on the underside of the body, which like other acanthodians were supported by stiff spines at their front edges. The whole body was covered in scales, which varied in shape depending on their position. The vertebral column was typically unossified. ''Acanthodes'' had no teeth and had long gill rakers. Because of this, ''Acanthodes'' is presumed to have been a suspension feeder
Filter feeders are a sub-group of suspension feeding animals that feed by straining suspended matter and food particles from water, typically by passing the water over a specialized filtering structure. Some animals that use this method of feedin ...
, filtering plankton from the water. A specimen of ''Acanthodes bridgei ''was so well-preserved that traces of its eye tissue were sufficient to establish that ''Acanthodes'' had both rod and cone photoreceptor cell
A photoreceptor cell is a specialized type of neuroepithelial cell found in the retina that is capable of visual phototransduction. The great biological importance of photoreceptors is that they convert light (visible electromagnetic radiatio ...
s, suggesting that it was capable of color vision
Color vision, a feature of visual perception, is an ability to perceive differences between light composed of different wavelengths (i.e., different spectral power distributions) independently of light intensity. Color perception is a part of ...
.
Ecology
The various species of ''Acanthodes'' are known to have inhabited freshwater lakes, as well as saline lagoons. ''Acanthodes bronni,'' which lived in freshwater lakes in southern Germany during the Early Permian, is known to have been fed upon by thetemnospondyl
Temnospondyli (from Greek language, Greek τέμνειν, ''temnein'' 'to cut' and σπόνδυλος, ''spondylos'' 'vertebra') is a diverse order (biology), order of small to giant tetrapods—often considered Labyrinthodontia, primitive amphi ...
amphibians '' Archegosaurus'' and ''Cheliderpeton
''Cheliderpeton'' (often misspelled ''Chelyderpeton'') is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian. It lived during the Early Permian in what is now Europe. Fossils have been found from the Ruprechtice horizon of the Intrasudetic Basin of Bohem ...
''. ''Acanthodes'' was likely capable of opening its jaws wide as an adaptation to suspension feeding.
Taxonomy
The classification of acanthodians was historically contentious, however, in the 2010s based in part based on detailed studies of the skull of ''Acanthodes'', it became widely accepted that acanthodians represented aparaphyletic
In taxonomy (general), taxonomy, a group is paraphyletic if it consists of the group's most recent common ancestor, last common ancestor and most of its descendants, excluding a few Monophyly, monophyletic subgroups. The group is said to be pa ...
assemblage of stem-group Chondrichthyes. Within the "Acanthodii", ''Acanthodes'' is traditionally placed within the Acanthodiformes, which is now also considered to be paraphyletic.
Species
After Beznosov, 2009 * ''Acanthodes bronni'' Agassiz, 1833 (type), Germany, Lower Permian * ''Acanthodes bourbonensis'' Heidtke, 1996, Early Permian, France * ''Acanthodes boyi'' Heidtke, 1993, Early Permian, Germany * ''Acanthodes bridgei'' Zidek, 1976, Late Carboniferous (Stephanian), Kansas, USA * ''Acanthodes fritschi'' Zajic, 1998, Late Carboniferous (Stephanian), Czech Republic * ''Acanthodes gracilis'' (Beyrich, 1848), Early Permian, Czech Republic, Poland and Germany * ''Acanthodes kinneyi'' Zidek, 1992, Late Carboniferous (Stephanian), New Mexico, USA * ''Acanthodes lopatini'' Rohon, 1889, Early Carboniferous (Tournaisian), southern Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia * ''Acanthodes luedersensis'' (Dalquest ''et'' ''al''., 1988), Early Permian of Texas, USA * ''Acanthodes lundi'' Zidek, 1980, Late Carboniferous (Namurian), Montana, USA * ''Acanthodes nitidus'' Woodward, 1891, Early Carboniferous (Visean), Scotland * ''Acanthodes ovensi'' White, 1927, Early Carboniferous (Tournaisian), Scotland * ''Acanthodes sippeli'' Heidtke, 1996, Late Carboniferous (Namurian), Germany * ''Acanthodes stambergi'' Zajic, 2005, Early Permian, Czech Republic * ''Acantodes sulcatus'' Agassiz, 1835, Early Carboniferous (Visean), Scotland * ''Acanthodes tholeyi'' Heidtke, 1990, Early Permian, Germany * ''Acanthodes wardi'' Egerton, 1866, Late Carboniferous (Westphalian), England and Scotland.References
* Parker, Steve. Dinosaurus: the complete guide to dinosaurs. Firefly Books Inc, 2003. Pg. 60External links
entry at the Fossil Museum
{{Taxonbar, from=Q2335100 Acanthodii genera Carboniferous acanthodians Permian acanthodians Paleozoic fish of North America Paleozoic fish of Europe Prehistoric fish of Australia Taxa named by Louis Agassiz