AD 14 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
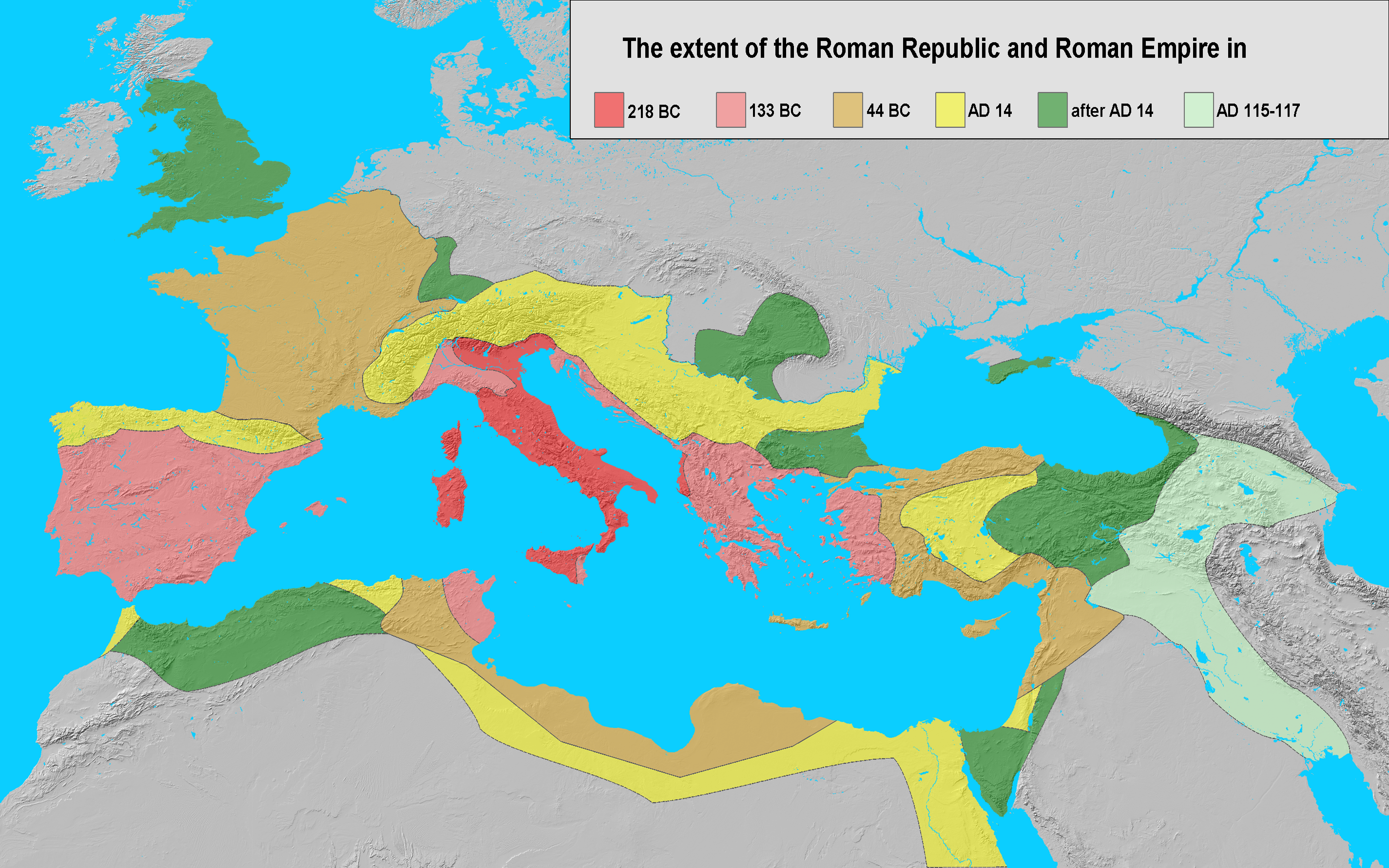 __NOTOC__
AD 14 ( XIV) was a
__NOTOC__
AD 14 ( XIV) was a
 __NOTOC__
AD 14 ( XIV) was a
__NOTOC__
AD 14 ( XIV) was a common year starting on Monday
A common year starting on Monday is any non-leap year (i.e., a year with 365 days) that begins on Monday, 1 January, and ends on Monday, 31 December. Its dominical letter hence is G. The most recent year of such kind was 2018 and the next one wi ...
(link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar
The Julian calendar, proposed by Roman consul Julius Caesar in 46 BC, was a reform of the Roman calendar. It took effect on , by edict. It was designed with the aid of Greek mathematicians and astronomers such as Sosigenes of Alexandr ...
. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship
A consul held the highest elected political office of the Roman Republic ( to 27 BC), and ancient Romans considered the consulship the second-highest level of the ''cursus honorum'' (an ascending sequence of public offices to which politic ...
of Pompeius and Appuleius Appuleius is the '' nomen'' of the Roman '' gens Appuleia''. It may refer to various members of that family, including:
* Lucius Appuleius Saturninus, tribune of the plebs in 100 B.C.
* Lucius Caecilicus Minutianus Appuleius, ancient Roman writer ...
(or, less frequently, year 767 ''Ab urbe condita
''Ab urbe condita'' ( 'from the founding of the City'), or ''anno urbis conditae'' (; 'in the year since the city's founding'), abbreviated as AUC or AVC, expresses a date in years since 753 BC, the traditional founding of Rome. It is an exp ...
''). The denomination AD 14 for this year has been used since the early medieval period
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
, when the Anno Domini
The terms (AD) and before Christ (BC) are used to label or number years in the Julian and Gregorian calendars. The term is Medieval Latin and means 'in the year of the Lord', but is often presented using "our Lord" instead of "the Lord", ...
calendar era
A calendar era is the period of time elapsed since one ''epoch'' of a calendar and, if it exists, before the next one. For example, it is the year as per the Gregorian calendar, which numbers its years in the Western Christian era (the Coptic ...
became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Events
By place
Roman Empire
*Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pri ...
' third (and final) 20-year census of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
reports a total of 4,973,000 citizens.
* August 19
Events Pre-1600
*295 BC – The first temple to Venus, the Roman goddess of love, beauty and fertility, is dedicated by Quintus Fabius Maximus Gurges during the Third Samnite War.
*43 BC – Gaius Julius Caesar Octavianus, later know ...
– Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pri ...
, the first Roman emperor, dies and is declared to be a god.
* September 18
Events Pre-1600
* 96 – Domitian, who has been conducting a reign of terror for the past three years, is assassinated as a result of a plot by his wife Domitia and two Praetorian prefects.
* 96 – Nerva is proclaimed Roman emperor a ...
– Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus (; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was the second Roman emperor. He reigned from AD 14 until 37, succeeding his stepfather, the first Roman emperor Augustus. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC. His father ...
succeeds his stepfather Augustus as Roman emperor.
* Legions on the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
mutiny after the death of Augustus; Germanicus
Germanicus Julius Caesar (24 May 15 BC – 10 October AD 19) was an ancient Roman general, known for his campaigns in Germania. The son of Nero Claudius Drusus and Antonia the Younger, Germanicus was born into an influential branch of the Patric ...
restores discipline amongst the legions.
* Germanicus is appointed commander of the forces in Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, beginning a campaign that will end in 16.
* Germanicus leads a brutal raid against the Marsi
The Marsi were an Italic people of ancient Italy, whose chief centre was Marruvium, on the eastern shore of Lake Fucinus (which was drained for agricultural land in the late 19th century). The area in which they lived is now called Marsica. ...
, a German tribe on the upper Ruhr
The Ruhr ( ; german: Ruhrgebiet , also ''Ruhrpott'' ), also referred to as the Ruhr area, sometimes Ruhr district, Ruhr region, or Ruhr valley, is a polycentric urban area in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population density of 2,800/km ...
river, who are massacred.
* The town and port of Nauportus
Nauportus ''(Navport, Navportus)'' ( grc, Ναύπορτον), was an ancient Roman town in Pannonia Superior (later 10th Italian region) on the road from Aquileia to Emona with a port at the Nauportus river, now the Ljubljanica River.
Strabo ...
are plundered by a mutinous Roman legion
The Roman legion ( la, legiō, ) was the largest military unit of the Roman army, composed of 5,200 infantry and 300 equites (cavalry) in the period of the Roman Republic (509 BC–27 BC) and of 5,600 infantry and 200 auxilia in the period of ...
that was sent there to build roads and bridges.
* Sextus Appuleius and Sextus Pompeius serve as Roman consuls.
China
* First year of ''tianfeng'' era of the ChineseXin Dynasty
The Xin dynasty (; ), also known as Xin Mang () in Chinese historiography, was a short-lived Chinese imperial dynasty which lasted from 9 to 23 AD, established by the Han dynasty consort kin Wang Mang, who usurped the throne of the Emperor Ping o ...
.
* Famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, Demographic trap, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. Th ...
hits China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
; some citizens turn to cannibalism
Cannibalism is the act of consuming another individual of the same species as food. Cannibalism is a common ecological interaction in the animal kingdom and has been recorded in more than 1,500 species. Human cannibalism is well documented, b ...
.
By topic
Art
* TheHellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
period ends, according to some scholars (usual date 31 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 31 BC was either a common year starting on Tuesday, Wednesday or Thursday or a leap year starting on Tuesday or Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar (the sources differ, see leap year error for ...
).
Births
*Lucius Caecilius Iucundus
Lucius Caecilius Iucundus (born c. 14 A.D., '' fl.'' 62 A.D.) was a banker who lived in the Roman town of Pompeii around 14 A.D.–62 A.D. His house still stands and can be seen in the ruins of the city of Pompeii which remain after being parti ...
, Roman banker (d. AD 62
AD 62 (Roman numerals, LXII) was a common year starting on Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Publius Marius, Marius and Lucius Afinius Gallus, Afinius ...
)
* Marcus Junius Silanus, Roman consul (d. AD 54
AD 54 ( LIV) was a common year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Lentulus and Marcellus (or, less frequently, year 807 ''Ab urbe condita'' ...
)
Deaths
*August 19
Events Pre-1600
*295 BC – The first temple to Venus, the Roman goddess of love, beauty and fertility, is dedicated by Quintus Fabius Maximus Gurges during the Third Samnite War.
*43 BC – Gaius Julius Caesar Octavianus, later know ...
– Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pri ...
, Roman emperor (b. 63 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 63 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Cicero and Hybrida (or, less frequently, year 691 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 63 BC for this year has been use ...
)
* August 20
Events Pre-1600
* AD 14 – Agrippa Postumus, maternal grandson of the late Roman emperor Augustus, is mysteriously executed by his guards while in exile.
* 636 – Battle of Yarmouk: Arab forces led by Khalid ibn al-Walid take con ...
– Agrippa Postumus
Marcus Agrippa Postumus (12 BC – AD 14),: "The elder Agrippa died, in the summer of 12 BC, while Julia was pregnant with their fifth child. The boy was very likely born sometime after June 26 of the following year. When his grandfather adopted ...
, Augustus (b. 12 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 12 BC was either a common year starting on Saturday, Sunday or Monday or a leap year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar (the sources differ, see leap year error for further information ...
)
* Gnaeus Pompeius (Rufus), Roman consul
* Julia the Elder
Julia the Elder (30 October 39 BC – AD 14), known to her contemporaries as Julia Caesaris filia or Julia Augusti filia (Classical Latin: IVLIA•CAESARIS•FILIA or IVLIA•AVGVSTI•FILIA), was the daughter and only biological child of August ...
, daughter of AugustusTacitus, The Annals 1.53 (b. 39 BC)
* Lucius Aemilius Paullus, Roman consul
* Parthenius of Nicaea Parthenius of Nicaea ( el, Παρθένιος ὁ Νικαεύς) or Myrlea ( el, ὁ Μυρλεανός) in Bithynia was a Greeks, Greek Philologist, grammarian and poet. According to the ''Suda'', he was the son of Heraclides and Eudora, or accord ...
, Greek grammarian
* Paullus Fabius Maximus
Paullus Fabius Maximus (died AD 14) was a Roman senator, active toward the end of the first century BC. He was consul in 11 BC as the colleague of Quintus Aelius Tubero, and a confidant of emperor Augustus.
Background
The patrician Fabii were on ...
, Roman consul
* Sempronius Gracchus
Sempronius Gracchus was a Roman nobleman who seduced Julia the Elder when she was wife of Marcus Agrippa; this led to a long-term affair. Gracchus was involved in an intrigue with the imperial family of Augustus by which he sought to undermine th ...
, Roman nobleman
Notes
{{DEFAULTSORT:14 als:10er#14