907 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 __NOTOC__
Year 907 ( CMVII) was a
__NOTOC__
Year 907 ( CMVII) was a
His power is centered in

 __NOTOC__
Year 907 ( CMVII) was a
__NOTOC__
Year 907 ( CMVII) was a common year starting on Thursday
A common year starting on Thursday is any non-leap year (i.e. a year with 365 days) that begins on Thursday, 1 January, and ends on Thursday, 31 December. Its dominical letter hence is D. The most recent year of such kind was 2015 and the next one ...
(link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar
The Julian calendar, proposed by Roman consul Julius Caesar in 46 BC, was a reform of the Roman calendar. It took effect on , by edict. It was designed with the aid of Greek mathematicians and astronomers such as Sosigenes of Alexandr ...
.
Events
By place
Byzantine Empire
* Rus'ŌĆōByzantine War:Varangian
The Varangians (; non, V├”ringjar; gkm, ╬Æ╬¼Žü╬▒╬│╬│╬┐╬╣, ''V├Īrangoi'';Varangian
" Online Etymo ...
prince " Online Etymo ...
Oleg of Novgorod
Oleg ( orv, čĀą╗ąĄą│čŖ, ą×ą╗čīą│čŖ; non, Helgi; died 912), also known as Oleg the Wise (russian: ą×ą╗ąĄą│ ąÆąĄčēąĖą╣, lit=Oleg the Prophet; uk, ą×ą╗ąĄą│ ąÆč¢čēąĖą╣), was a Varangian prince of the Rus' who was ruler of Novgorod. He later con ...
leads the Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rus╩╣, also known as Kyivan Rus╩╣ ( orv, , Rus─Ł, or , , ; Old Norse: ''Gar├░ar├Łki''), was a state in Eastern and Northern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of ...
in a campaign against Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, ┘éž│žĘ┘åžĘ┘Ŗ┘å┘Ŗ┘ć
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
, concluded by the Rus'ŌĆōByzantine Treaty (in which the city of Chernihiv
Chernihiv ( uk, ą¦ąĄčĆąĮč¢╠üą│č¢ą▓, , russian: ą¦ąĄčĆąĮąĖ╠üą│ąŠą▓, ; pl, Czernih├│w, ; la, Czernihovia), is a city and municipality in northern Ukraine, which serves as the administrative center of Chernihiv Oblast and Chernihiv Raion within ...
in the Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, ąŻą║čĆą░茹Įą░, Ukra├»na, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
is first mentioned). He lays siege
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition warfare, attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity con ...
to the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
capital with some 2,000 ships ( dugout boats), and secures trading
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market.
An early form of trade, barter, saw the direct exchan ...
rights from the world's leading center of commerce.
Europe
*July 4
Events Pre-1600
* 362 BC – Battle of Mantinea: The Thebans, led by Epaminondas, defeated the Spartans.
* 414 – Emperor Theodosius II, age 13, yields power to his older sister Aelia Pulcheria, who reigned as regent and proclaim ...
– 6 – Battle of Pressburg
The Battle of Pressburg (german: Schlacht von Pressburg) or Battle of Pozsony ( hu, Pozsonyi csata), or Battle of Bratislava ( sk, Bitka pri Bratislave) was a three-day-long battle, fought between 4ŌĆō6 July 907, during which the East Francian arm ...
: At "Brezalauspurc" (probably modern-day Bratislava
Bratislava (, also ; ; german: Pre├¤burg/Pressburg ; hu, Pozsony) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Slovakia. Officially, the population of the city is about 475,000; however, it is estimated to be more than 660,000 ŌĆö approxim ...
in Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovensk├Ī republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the s ...
), the advancing East Frankish army (60,000 men) is annihilated by the Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and┬Ā ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Urali ...
led by Grand Prince ├ürp├Īd
├ürp├Īd (; 845 ŌĆō 907) was the head of the confederation of the Magyar tribes at the turn of the 9th and 10th centuries. He might have been either the sacred ruler or ''kende'' of the Hungarians, or their military leader or '' gy ...
. Duke Luitpold and Archbishop Dietmar I are killed, together with 19 dukes, 2 bishops and 3 abbots. The East Frankish Kingdom
East Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the East Franks () was a successor state of Charlemagne's empire ruled by the Carolingian dynasty until 911. It was created through the Treaty of Verdun (843) which divided the former empire int ...
loses control of the March of Pannonia
The March of Pannonia or Eastern March ( la, marcha orientalis) was a frontier march of the Carolingian Empire, named after the former Roman province of ''Pannonia'' and carved out of the preceding and larger Avar march.
It was referred to in so ...
.
* Summer – The Hungarians invade Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total lan ...
, causing great destruction, occupying many towns and, on their way home, defeating a Bavarian army at Lengenfeld
Lengenfeld is a town in the Vogtlandkreis district, in the Free State of Saxony in eastern Germany. The town is situated 19 km southwest of Zwickau, and 18 km northeast of Plauen.
History
During World War II, in the town, Germany op ...
. The Hungarian-Bavarian border is fixed on the Enns River
The Enns (, ) is a southern tributary of the river Danube, joining northward at Enns, Austria. The Enns spans , in a flat-J-shape. It flows from its source near the village Flachau, generally eastward through Radstadt, Schladming, and Liezen, then ...
.
Britain
* Lady├åthelfl├”d
├åthelfl├”d, Lady of the Mercians ( 870 ŌĆō 12 June 918) ruled Mercia in the English Midlands from 911 until her death. She was the eldest daughter of Alfred the Great, king of the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of Wessex, and his wife Ealhswith.
Æth ...
of Mercia
la, Merciorum regnum
, conventional_long_name=Kingdom of Mercia
, common_name=Mercia
, status=Kingdom
, status_text=Independent kingdom (527ŌĆō879)Client state of Wessex ()
, life_span=527ŌĆō918
, era=Heptarchy
, event_start=
, date_start=
, ye ...
refortifies Chester
Chester is a cathedral city and the county town of Cheshire, England. It is located on the River Dee, close to the EnglishŌĆōWelsh border. With a population of 79,645 in 2011,"2011 Census results: People and Population Profile: Chester Loca ...
against Viking
Vikings ; non, v├Łkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
attacks. King Edward the Elder
Edward the Elder (17 July 924) was King of the Anglo-Saxons from 899 until his death in 924. He was the elder son of Alfred the Great and his wife Ealhswith. When Edward succeeded to the throne, he had to defeat a challenge from his cousin Æt ...
founds Romsey Abbey
Romsey Abbey is the name currently given to a parish church of the Church of England in Romsey, a market town in Hampshire, England. Until the Dissolution of the Monasteries it was the church of a Benedictine Order, Benedictine nunnery. The surv ...
(Hampshire
Hampshire (, ; abbreviated to Hants) is a ceremonial county, ceremonial and non-metropolitan county, non-metropolitan counties of England, county in western South East England on the coast of the English Channel. Home to two major English citi ...
).
Arabian Empire
* EmirIsma'il ibn Ahmad
Ab┼½ Ibr─üh─½m Ism─ü'─½l ibn-i AßĖźmad-i S─üm─üni ( fa, ž¦ž©┘ł ž¦ž©ž▒ž¦┘ć█ī┘ģ ž¦ž│┘ģž¦ž╣█ī┘ä ž©┘å ž¦žŁ┘ģž» ž│ž¦┘ģž¦┘å█ī; May 849 ŌĆō 24 November 907), better known simply as Ismail-i Samani (), and also known as Isma'il ibn-i Ahmad (), was the S ...
dies after a 15-year reign in which he has extended his borders to Tabaristan
Tabaristan or Tabarestan ( fa, žĘž©ž▒ž│ž¬ž¦┘å, ß╣¼abarest─ün, or mzn, ž¬ž©ž▒ž│ž¬┘ł┘å, Tabarestun, ultimately from Middle Persian: , ''Tapur(i)st─ün''), was the name applied to a mountainous region located on the Caspian coast of northern Iran. ...
and Khorasan
Khorasan may refer to:
* Greater Khorasan, a historical region which lies mostly in modern-day northern/northwestern Afghanistan, northeastern Iran, southern Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan
* Khorasan Province, a pre-2004 province of Ira ...
. He establishes independence throughout the eastern part of his empire from his capital at Bukhara
Bukhara (Uzbek language, Uzbek: /, ; tg, ąæčāčģąŠčĆąŠ, ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan, with a population of 280,187 , and the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara ...
. Isma'il is succeeded by his son Ahmad Samani
Ahmad ibn Ismail (died 24 January 914) was amir of the Samanids (907ŌĆō914). He was the son of Ismail Samani. He was known as the "''Martyred Amir''".
Biography
Ahmad is first mentioned in the early 900s, when he was appointed as the governor o ...
as ruler of the Samanid Empire
The Samanid Empire ( fa, ž│ž¦┘ģž¦┘å█īž¦┘å, S─üm─üniy─ün) also known as the Samanian Empire, Samanid dynasty, Samanid amirate, or simply as the Samanids) was a Persianate society, Persianate Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslim empire, of Iranian peoples, Ira ...
.
China
* TheFive Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period
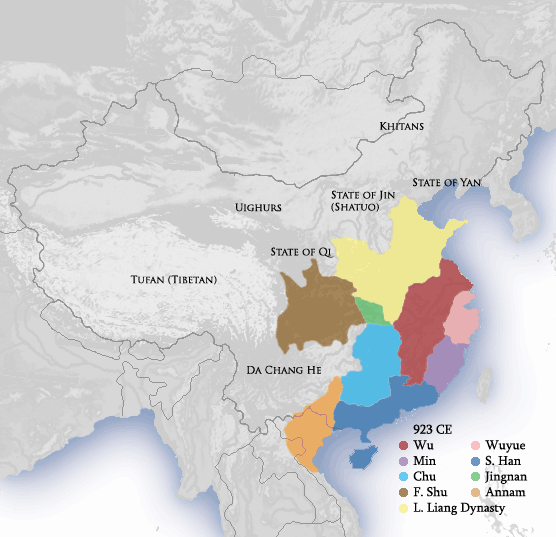
The Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period (), from 907 to 979, was an era of political upheaval and division in 10th-century Imperial China. Five dynastic states quickly succeeded one another in the Central Plain, and more than a dozen conc ...
begins in China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
.
** February 27
Events Pre-1600
* 380 – Edict of Thessalonica: Emperor Theodosius I and his co-emperors Gratian and Valentinian II declare their wish that all Roman citizens convert to Nicene Christianity.
* 425 – The University of Constantinople ...
– Abaoji
Abaoji (872ŌĆō6 September 926), posthumously known by his temple name as the Emperor Taizu of Liao, was a Khitan leader and the founding emperor of the Liao dynasty of China, ruling from 916 to 926. He had a sinicised name, Yel├╝ Yi; some sourc ...
, ruler (''khagan
Khagan or Qaghan (Mongolian:; or ''Khagan''; otk, É░┤É░ŹÉ░Ż ), or , tr, Ka─¤an or ; ug, ┘鞦ž║ž¦┘å, Qaghan, Mongolian Script: ; or ; fa, ž«ž¦┘鞦┘å ''Kh─üq─ün'', alternatively spelled Ka─¤an, Kagan, Khaghan, Kaghan, Khakan, Khakhan ...
'') of the confederation of Khitans
The Khitan people (Khitan small script: ; ) were a historical nomadic people from Northeast Asia who, from the 4th century, inhabited an area corresponding to parts of modern Mongolia, Northeast China and the Russian Far East.
As a people desce ...
, proclaims himself emperor and establishes the Liao dynasty
The Liao dynasty (; Khitan: ''Mos J├”lud''; ), also known as the Khitan Empire (Khitan: ''Mos diau-d kitai huld╩Æi gur''), officially the Great Liao (), was an imperial dynasty of China that existed between 916 and 1125, ruled by the Yel├╝ ...
, killing most of the other Khitan chieftains. He occupies territories along China's northern border including parts of Hebei
Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% Hui, an ...
and Shanxi
Shanxi (; ; formerly romanised as Shansi) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the North China region. The capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-lev ...
provinces.
** May 12
Events Pre-1600
* 254 – Pope Stephen I succeeds Pope Lucius I, becoming the 23rd pope of the Catholic Church, and immediately takes a stand against Novatianism.
* 907 – Zhu Wen forces Emperor Ai into abdicating, ending the Tang d ...
*** The short-lived Qi Kingdom is founded by the warlord Li Maozhen
Li Maozhen (; 856 ŌĆō May 17, 924), born Song Wentong (), courtesy name Zhengchen (), formally Prince Zhongjing of Qin (), was the only ruler of the Chinese Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period state Qi (901ŌĆō924). He had become a powerful wa ...
(Prince of Qi).Academia Sinica
Academia Sinica (AS, la, 1=Academia Sinica, 3=Chinese Academy; ), headquartered in Nangang, Taipei, is the national academy of Taiwan. Founded in Nanking, the academy supports research activities in a wide variety of disciplines, ranging from ...
br>Chinese-Western Calendar ConverterHis power is centered in
Shaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see #Name, ┬¦ Name) is a landlocked Provinces of China, province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichu ...
province, in Northwest China
Northwest China () is a statistical region of China which includes the autonomous regions of Xinjiang and Ningxia and the provinces of Shaanxi, Gansu and Qinghai. It has an area of 3,107,900 km2.
The region is characterized by a (semi-)arid con ...
. The Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690ŌĆō705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dyn ...
comes to an end after 289 years as Emperor Ai is forced to abdicate by chancellor Zhu Quanzhong
Emperor Taizu of Later Liang (), personal name Zhu Quanzhong () (December 5, 852 ŌĆō July 18, 912), n├® Zhu Wen (), name later changed to Zhu Huang (), nickname Zhu San (µ£▒õĖē, literally, "the third Zhu"), was a Chinese military general, mona ...
.
*** The short-lived Wu Kingdom is founded by Yang Wo
Yang Wo () (886 ŌĆō June 9, 908), courtesy name Chengtian (), formally Prince Wei of Hongnong (), later further posthumously honored King Jing of Wu () and then as Emperor Jing of Wu () with the temple name Liezu (), was the first independent ruler ...
(Prince of Hongnong) in Jiangdu
Jiangdu (), historically known as Kiangtu is one of three districts of Yangzhou, Jiangsu province, China. The district spans an area of , and as of November 1, 2020, has 926,577 inhabitants. Formerly a county, Jiangdu became a district in July 199 ...
(South Central China
South Central China, South-Central China or Central-South China ( zh, c = õĖŁÕŹŚ, p = Zh┼Źngn├Īn, l = Central-South), is a region of the People's Republic of China defined by State Council that includes the provinces of Guangdong, Hainan, Hen ...
). He refuses to acknowledge the rule of Zhu Quanzhong.
** June 1
Events Pre-1600
*1215 – Zhongdu (now Beijing), then under the control of the Jurchen people, Jurchen ruler Emperor Xuanzong of Jin, is captured by the Mongols under Genghis Khan, ending the Battle of Zhongdu.
*1252 – Alfonso X is pr ...
– Zhu Quanzhong (Zhu Wen) usurps the throne
A throne is the seat of state of a potentate or dignitary, especially the seat occupied by a sovereign on state occasions; or the seat occupied by a pope or bishop on ceremonial occasions. "Throne" in an abstract sense can also refer to the monar ...
and proclaims himself the first emperor of Later Liang. China is controlled by successive short-lived kingdoms (until 960
Year 960 ( CMLX) was a leap year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
By place
Byzantine Empire
* Summer – Siege of Chandax: A Byzantine fleet with an expeditionary force (co ...
).
** June 8
Events Pre-1600
* 218 – Battle of Antioch: With the support of the Syrian legions, Elagabalus defeats the forces of emperor Macrinus.
* 452 – Attila leads a Hun army in the invasion of Italy, devastating the northern provinces ...
– The Chu
Chu or CHU may refer to:
Chinese history
* Chu (state) (c. 1030 BCŌĆō223 BC), a state during the Zhou dynasty
* Western Chu (206 BCŌĆō202 BC), a state founded and ruled by Xiang Yu
* Chu Kingdom (Han dynasty) (201 BCŌĆō70 AD), a kingdom of the Ha ...
Kingdom is founded by the warlord Ma Yin
Ma Yin (; c. 853 ŌĆō December 2, 930), courtesy name Batu (ķ£ĖÕ£¢), formally King Wumu of Chu (µźÜµŁ”ń®åńÄŗ), was Chinese military general and politician who became the first ruler of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period state Chu and the o ...
(Prince of Chu) in Changsha
Changsha (; ; ; Changshanese pronunciation: (), Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is the capital and the largest city of Hunan Province of China. Changsha is the 17th most populous city in China with a population of over 10 million, an ...
. Present-day Hunan
Hunan (, ; ) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the South Central China region. Located in the middle reaches of the Yangtze watershed, it borders the province-level divisions of Hubei to the north, Jiangxi to ...
and Guangxi
Guangxi (; ; Chinese postal romanization, alternately romanized as Kwanghsi; ; za, Gvangjsih, italics=yes), officially the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (GZAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the People's Republic ...
provinces (Southern China
South China () is a geographical and cultural region that covers the southernmost part of China. Its precise meaning varies with context. A notable feature of South China in comparison to the rest of China is that most of its citizens are not n ...
) are under his control.''New History of the Five Dynasties
The ''Historical Records of the Five Dynasties'' (''Wudai Shiji'') is a Chinese history book on the Five Dynasties period (907ŌĆō960), written by the Song dynasty official Ouyang Xiu in private. It was drafted during Ouyang's exile from 1036 to ...
'', vol. 66 .
** November 3
Events Pre-1600
* 361 – Emperor Constantius II dies of a fever at Mopsuestia in Cilicia; on his deathbed he is baptised and declares his cousin Julian rightful successor.
*1333 – The River Arno floods causing massive damage in F ...
– The Former Shu
Great Shu (Chinese: Õż¦Ķ£Ć, Pinyin: D├ĀshŪö) called in retrospect Former Shu (Chinese: ÕēŹĶ£Ć, Pinyin: Qi├ĪnshŪö) or occasionally Wang Shu (ńÄŗĶ£Ć), was one of the Ten Kingdoms formed during the chaotic period between the rules of the Tang dynas ...
Kingdom is founded by the warlord Wang Jian (Prince of Shu) in Chengdu
Chengdu (, ; Simplified Chinese characters, simplified Chinese: µłÉķāĮ; pinyin: ''Ch├®ngd┼½''; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ), Chinese postal romanization, alternatively Romanization of Chi ...
. His power is centered in Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the ...
province, in Southwest China
Southwest China () is a region in the south of the People's Republic of China.
Geography
Southwest China is a rugged and mountainous region, transitioning between the Tibetan Plateau to the west and the Chinese coastal hills (õĖ£ÕŹŚõĖśķÖĄ) and ...
.
** December 1
Events Pre-1600
* 800 – A council is convened in the Vatican, at which Charlemagne is to judge the accusations against Pope Leo III.
*1420 – Henry V of England enters Paris alongside his father-in-law King Charles VI of France.
* ...
– The Wuyue
Wuyue (; ), 907ŌĆō978, was an independent coastal kingdom founded during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period (907ŌĆō960) of Chinese history. It was ruled by the Haiyan Qian clan (µĄĘńøÉķÆ▒µ░Å), whose family name remains widespread in t ...
Kingdom is founded by the warlord in Hangzhou
Hangzhou ( or , ; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), also romanized as Hangchow, is the capital and most populous city of Zhejiang, China. It is located in the northwestern part of the province, sitting at the head of Hangzhou Bay, whi ...
. His proclaims himself king, his power is centered in Jiangsu
Jiangsu (; ; pinyin: Jiāngsū, Postal romanization, alternatively romanized as Kiangsu or Chiangsu) is an Eastern China, eastern coastal Provinces of the People's Republic of China, province of the China, People's Republic of China. It is o ...
province (Eastern China
East China () is a geographical and a loosely defined cultural region that covers the eastern coastal area of China.
A concept abolished in 1978, for economical purposes the region was defined from 1949 to 1961 by the Chinese Central Governme ...
).
By topic
Religion
*February 1
Events Pre-1600
* 1327 – The teenaged Edward III is crowned King of England, but the country is ruled by his mother Queen Isabella and her lover Roger Mortimer.
* 1411 – The First Peace of Thorn is signed in Thorn (Toru┼ä), Mon ...
– Nicholas I Mystikos
Nicholas I Mystikos or Nicholas I Mysticus ( el, ╬Ø╬╣╬║Žī╬╗╬▒╬┐Žé ╬æ╬ä ╬£ŽģŽāŽä╬╣╬║ŽīŽé, ''Nikolaos I Mystikos''; 852 – 11 May 925) was the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople from March 901 to February 907 and from May 912 to his death ...
is deposed as Patriarch of Constanstinople, (having fallen out with the Byzantine Emperor Leo VI Leo VI (or Leon VI, notably in Greek) may refer to :
* Leo VI the Wise, Byzantine emperor 886 to 912
* Pope Leo VI, 928 to 929
* King Leo VI of Armenia (1342 ŌĆō 1393), of the House of Lusignan, last Latin king of the Armenian crusader Kingdom of C ...
), and is replaced by Euthymius I Syncellus.
Births
*November 26
Events Pre-1600
* 783 – The Asturian queen Adosinda is held at a monastery to prevent her king from retaking the throne from Mauregatus.
*1161 – Battle of Caishi: A Song dynasty fleet fights a naval engagement with Jin dynasty ...
– Rudesind
Saint Rudesind ( gl, San Rosendo, Rudesindo; pt, S├Żo Rosendo lat, Rudesindus) (November 26, 907 ŌĆō March 1, 977) was a Galician bishop and abbot. He was also a regional administrator and military leader under his kinsmen, the Kings of Le├│n. ...
, Galician bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is ca ...
(d. 977
Year 977 ( CMLXXVII) was a common year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
By place Europe
* May – Boris II, dethroned emperor (''tsar'') of Bulgaria, and his brother Roman ma ...
)
* Bertha of Swabia
Bertha of Swabia (french: Berthe; german: Berta; AD ŌĆō after January 2, 966), a member of the Alemannic Hunfriding dynasty, was queen of Burgundy from 922 until 937 and queen of Italy from 922 until 926, by her marriage with King Rudolph II. She ...
, Frankish queen (approximate date)
* Parantaka I
Parantaka Chola I (Tamil : Ó«¬Ó«░Ó«ŠÓ«©Ó»ŹÓ«żÓ«Ģ Ó«ÜÓ»ŗÓ«┤Ó«®Ó»Ź I) (873 CEŌĆō955 CE) was a Chola emperor who ruled for forty-eight years, annexing Pandya by defeating Rajasimhan II. The best part of his reign was marked by increasing success ...
, ruler of the Chola Kingdom
The Chola dynasty was a Tamil thalassocratic empire of southern India and one of the longest-ruling dynasties in the history of the world. The earliest datable references to the Chola are from inscriptions dated to the 3rd century BCE d ...
(India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
)
* Robert of Vermandois
Robert of Vermandois ( – ) was Count of Meaux and Count of Troyes, son of Herbert II, Count of Vermandois and his wife, Adele of France, daughter of Robert I of France.
Robert succeeded his father as Count of Meaux in 943 and became Count ...
, Frankish nobleman
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy. It is normally ranked immediately below royalty. Nobility has often been an estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. The characteristi ...
(approximate date)
* Wenceslaus I, duke of Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, ─īechy ; ; hsb, ─ī─øska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
(approximate date)
Deaths
*May 2
Events Pre-1600
* 1194 – King Richard I of England gives Portsmouth its first Royal Charter.
* 1230 – William de Braose is hanged by Prince Llywelyn the Great.
* 1536 – Anne Boleyn, Queen of England, is arrested and impris ...
– Boris I
Boris I, also known as Boris-Mihail (Michael) and ''Bogoris'' ( cu, ąæąŠčĆąĖčüčŖ ąÉęā / ąæąŠčĆąĖčüčŖ-ą£ąĖčģą░ąĖą╗čŖ bg, ąæąŠčĆąĖčü I / ąæąŠčĆąĖčü-ą£ąĖčģą░ąĖą╗; died 2 May 907), was the ruler of the First Bulgarian Empire in 852–889. At ...
, ruler (''knyaz
, or ( Old Church Slavonic: ąÜąĮ覹Ęčī) is a historical Slavic title, used both as a royal and noble title in different times of history and different ancient Slavic lands. It is usually translated into English as prince or duke, dependi ...
'') of the Bulgarian Empire
In the medieval history of Europe, Bulgaria's status as the Bulgarian Empire ( bg, ąæčŖą╗ą│ą░čĆčüą║ąŠ čåą░čĆčüčéą▓ąŠ, ''Balgarsko tsarstvo'' ) occurred in two distinct periods: between the seventh and the eleventh centuries and again between the ...
* July 4
Events Pre-1600
* 362 BC – Battle of Mantinea: The Thebans, led by Epaminondas, defeated the Spartans.
* 414 – Emperor Theodosius II, age 13, yields power to his older sister Aelia Pulcheria, who reigned as regent and proclaim ...
** Dietmar I, archbishop of Salzburg
Salzburg (, ; literally "Salt-Castle"; bar, Soizbuag, label=Bavarian language, Austro-Bavarian) is the List of cities and towns in Austria, fourth-largest city in Austria. In 2020, it had a population of 156,872.
The town is on the site of the ...
** Luitpold, margrave of Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total lan ...
* Alan I Alan I may refer to:
* Alan I, King of Brittany (died 907)
* Alan I, Viscount of Rohan
Alan I of Rohan (1084ŌĆō1147), also known as ''Alain le Noir'', was the 1st Viscount de Rohan and Viscount of Castelnoec. He was the third son of Odo I, Vi ...
, duke ('king') of Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo language, Gallo: ''Berta├©yn'' ) is a peninsula, Historical region, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known ...
* ├ürp├Īd
├ürp├Īd (; 845 ŌĆō 907) was the head of the confederation of the Magyar tribes at the turn of the 9th and 10th centuries. He might have been either the sacred ruler or ''kende'' of the Hungarians, or their military leader or '' gy ...
, Grand Prince of the Hungarians
Grand Prince ( hu, Nagyfejedelem) was the title used by contemporary sources to name the leader of the Magyar tribes, federation of the Hungarian tribes in the tenth century.Constantine VII mentioned ├ürp├Īd in his book De Administrando Imperio as ...
(approximate date)
* Herbert I Herbert I may refer to:
* Herbert I, Count of Vermandois (c. 848/850 ŌĆō 907)
* Herbert I, Count of Maine (died in 1036)
{{hndis, Herbert 01 ...
, Frankish nobleman
* Isma'il ibn Ahmad
Ab┼½ Ibr─üh─½m Ism─ü'─½l ibn-i AßĖźmad-i S─üm─üni ( fa, ž¦ž©┘ł ž¦ž©ž▒ž¦┘ć█ī┘ģ ž¦ž│┘ģž¦ž╣█ī┘ä ž©┘å ž¦žŁ┘ģž» ž│ž¦┘ģž¦┘å█ī; May 849 ŌĆō 24 November 907), better known simply as Ismail-i Samani (), and also known as Isma'il ibn-i Ahmad (), was the S ...
, emir of the Samanid Empire
The Samanid Empire ( fa, ž│ž¦┘ģž¦┘å█īž¦┘å, S─üm─üniy─ün) also known as the Samanian Empire, Samanid dynasty, Samanid amirate, or simply as the Samanids) was a Persianate society, Persianate Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslim empire, of Iranian peoples, Ira ...
* Radelchis II, Lombard prince
* Rudesind I
Rudesindus I (in office 877ŌĆō907) was a medieval Galician clergyman.
References
* ''Episcopologio Mindoniense''. CAL PARDO, Enrique, 2003, .
External links
*Official web site of the Diocese of Mondo├▒edo-Ferrol
9th-century Galicia ...
, bishop of Dumium (Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de Espa├▒a.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de Espa├▒a (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
)
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:907