64-gun on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The 64-gun ship of the line was a type of two-decker warship defined during the 18th century, named after the number of their guns. 64-guns had a lower battery of 24-pounders, and an upper battery of 12-pounders. Heavier variants with 18-pounder on the upper deck also existed.
The 64-gun ship of the line was a type of two-decker warship defined during the 18th century, named after the number of their guns. 64-guns had a lower battery of 24-pounders, and an upper battery of 12-pounders. Heavier variants with 18-pounder on the upper deck also existed.
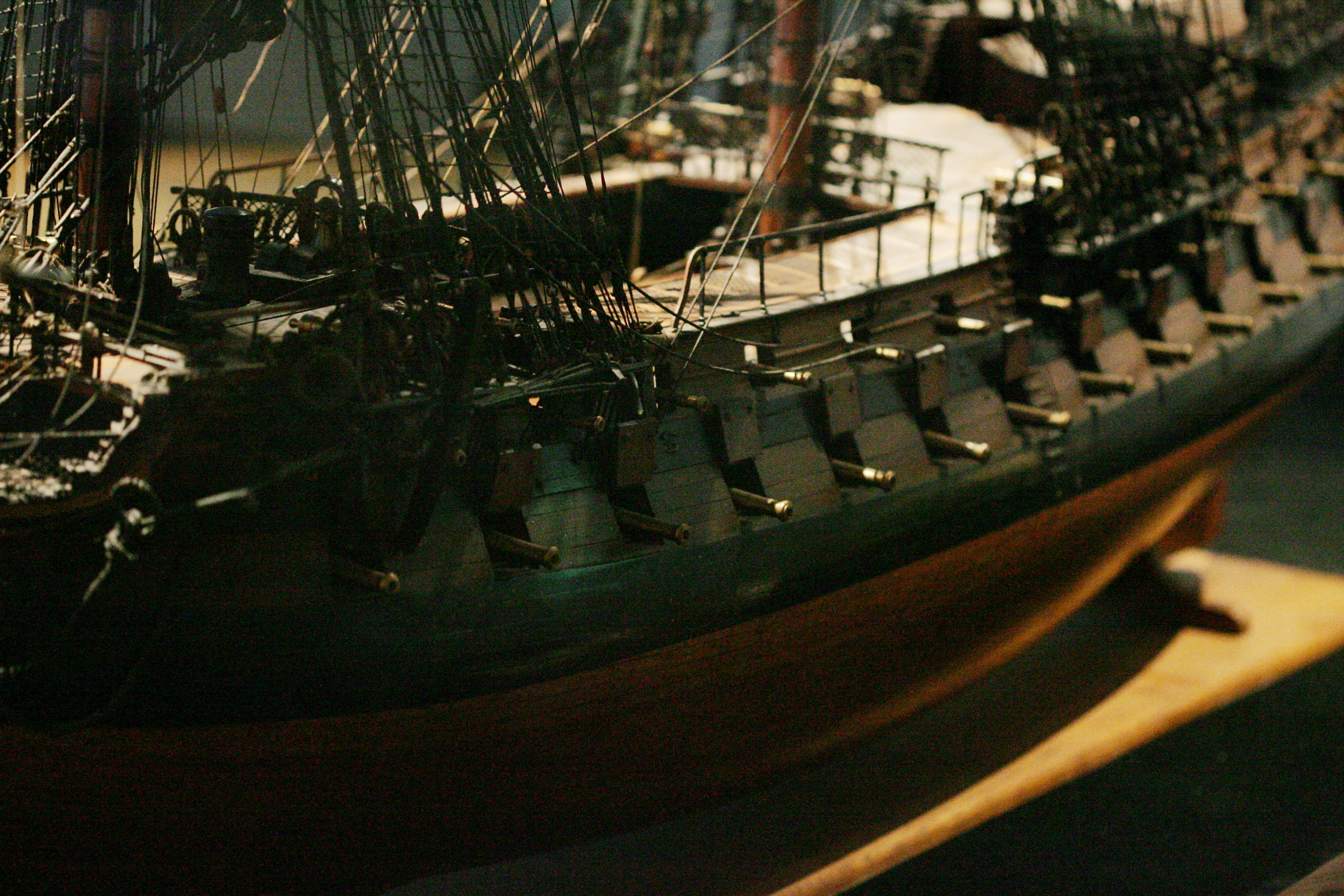 French 64-guns carried the standardised armament of:
* 26 24-pounders on the lower gundeck;
* 28 12-pounders on the upper gundeck;
* 10 6-pounders on the
French 64-guns carried the standardised armament of:
* 26 24-pounders on the lower gundeck;
* 28 12-pounders on the upper gundeck;
* 10 6-pounders on the
 The 64-gun ship of the line was a type of two-decker warship defined during the 18th century, named after the number of their guns. 64-guns had a lower battery of 24-pounders, and an upper battery of 12-pounders. Heavier variants with 18-pounder on the upper deck also existed.
The 64-gun ship of the line was a type of two-decker warship defined during the 18th century, named after the number of their guns. 64-guns had a lower battery of 24-pounders, and an upper battery of 12-pounders. Heavier variants with 18-pounder on the upper deck also existed.
History
The French Navy used "64-gun" as a typology for its ships. In the BritishRoyal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
, such lighter two-deckers were considered to be Third-rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy, a third rate was a ship of the line which from the 1720s mounted between 64 and 80 guns, typically built with two gun decks (thus the related term two-decker). Years of experience proved that the third r ...
s, like 74-gun
The "seventy-four" was a type of two- decked sailing ship of the line, which nominally carried 74 guns. It was developed by the French navy in the 1740s, replacing earlier classes of 60- and 62-gun ships, as a larger complement to the recently-de ...
s and 80-gun
8 (eight) is the natural number following 7 and preceding 9.
In mathematics
8 is:
* a composite number, its proper divisors being , , and . It is twice 4 or four times 2.
* a power of two, being 2 (two cubed), and is the first number of t ...
s.
During the reign of Louis XIV
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of Vers ...
, numerous ships carried 60 or 62 guns, with a lower battery pierced for 12 guns on each side. During the reign of Louis XV
Louis XV (15 February 1710 – 10 May 1774), known as Louis the Beloved (french: le Bien-Aimé), was King of France from 1 September 1715 until his death in 1774. He succeeded his great-grandfather Louis XIV at the age of five. Until he reache ...
, standardisation efforts were undertaken to rationalise the design and construction of these ships, with a common armament of 24-pounder, 12-pounder and 8-pounder long gun
The 8-pounder long gun was a light calibre piece of artillery mounted on French warships of the Age of sail. It fired a projectile of eight ''livres'' in weight, equivalent to 8.633 English pounds, or 8 lb 10 oz (the French ''livre'' was 7.916% he ...
s. The first 64-gun in this sense was ''Borée'', launched in 1734
Events
January– March
* January 8 – Salzburgers, Lutherans who were expelled by the Roman Catholic Bishop of Salzburg, Austria, in October 1731, set sail for the British Colony of Province of Georgia, Georgia in North America ...
and pierced with 13 gun port
A gunport is an opening in the side of the hull of a ship, above the waterline, which allows the muzzle of artillery pieces mounted on the gun deck to fire outside. The origin of this technology is not precisely known, but can be traced back to ...
s on each side of her lower battery. The British started copying these ships from 1764
1764 ( MDCCLXIV) was a leap year starting on Sunday and is the fifth year of the 1760s decade, the 64th year of the 18th century, and the 764th year of the 2nd millennium.
Events
January–June
* January 7 – The Siculicidium is ...
with HMS ''Asia'', and also stopped building 60-gun ships. British ships had a slightly heavier broadside, as they typically carried 18-pounders on their upper gundeck, while the French would usually have 12-pounders.
64-guns were no match for 74-guns, which had a 36-pounders (in France) or 32-pounders (in England) lower battery and 18-pounders on the upper gundeck (some later units even experimented with 24-pounders in the upper deck), and were usually slower than frigates. Their main advantage were their cheaper cost, and lower draft. This would be especially important for operations in India.
The French built 61 of these 64-gun ships, the last one being ''Jason'' in 1779. Three were razeed, turning them into frigates capable of carrying a 24-pounder main armament, although these ships typically fell back to 18-pounders like most heavy frigates of their time.
The British built 43, and maintained production a while longer, as 64-guns were useful for escorting merchant convoys. The last British 64-gun to be launched was HMS ''Veteran'', in 1787.
Dimensions
Most 64-gun were one-offs, and the others were part of short series put in production in the mid-18th century. In France, the main classes of 64-guns were * The ''Lion'' class: ''Lion'', ''Sage'' and ''Fantasque'' (1751-1758) ; * The ''Artésien'' class, by Joseph-Louis Ollivier: '' Artésien'', ''Roland
Roland (; frk, *Hrōþiland; lat-med, Hruodlandus or ''Rotholandus''; it, Orlando or ''Rolando''; died 15 August 778) was a Frankish military leader under Charlemagne who became one of the principal figures in the literary cycle known as the ...
'', ''Alexandre Alexandre may refer to:
* Alexandre (given name)
* Alexandre (surname)
* Alexandre (film)
See also
* Alexander
* Xano (disambiguation) Xano is the name of:
* Xano, a Portuguese hypocoristic of the name "Alexandre (disambiguation) Alexandre may re ...
'', '' Protée'' and '' Éveillé'' 64 (launched 10 December 1772 at Brest)
* The ''Brillant'' class: '' Brillant'' and ''Solitaire
Solitaire is any tabletop game which one can play by oneself, usually with cards, but also with dominoes. The term "solitaire" is also used for single-player games of concentration and skill using a set layout tiles, pegs or stones. These game ...
''
* The ''Réfléchi'' class: '' Réfléchi'' and '' Caton''
The late 18th century 64-guns were between 43 and 48 metres long, about 13.5 metres wide, and had a hull depth of 5.5 to 6 metres.
Armament
 French 64-guns carried the standardised armament of:
* 26 24-pounders on the lower gundeck;
* 28 12-pounders on the upper gundeck;
* 10 6-pounders on the
French 64-guns carried the standardised armament of:
* 26 24-pounders on the lower gundeck;
* 28 12-pounders on the upper gundeck;
* 10 6-pounders on the forecastle
The forecastle ( ; contracted as fo'c'sle or fo'c's'le) is the upper deck of a sailing ship forward of the foremast, or, historically, the forward part of a ship with the sailors' living quarters. Related to the latter meaning is the phrase " be ...
and quarterdeck
The quarterdeck is a raised deck behind the main mast of a sailing ship. Traditionally it was where the captain commanded his vessel and where the ship's colours were kept. This led to its use as the main ceremonial and reception area on bo ...
.
Amounting to a 510-pound broadside.
British ships would typically carry:
* 26 24-pounders on the lower gundeck;
* 26 18-pounders on the upper;
* 10 4-pounders and 2 9-pounders on forecastle
The forecastle ( ; contracted as fo'c'sle or fo'c's'le) is the upper deck of a sailing ship forward of the foremast, or, historically, the forward part of a ship with the sailors' living quarters. Related to the latter meaning is the phrase " be ...
and quarterdeck
The quarterdeck is a raised deck behind the main mast of a sailing ship. Traditionally it was where the captain commanded his vessel and where the ship's colours were kept. This led to its use as the main ceremonial and reception area on bo ...
..
Amounting to a 575-pound broadside.
Crew
French regulations of 1 January 1786 defined the wartime crew as 538 men, while the peacetime crew was 377. This comprised 12 officers, 7 student or volunteer officiers, 47 non-commissioned officers, 36 gunners of thetroupes de marine
The (TDM, ) is a corps of the French Army that includes several specialities: infantry, artillery, armoured, airborne, engineering, and transmissions (Signals).
Despite its name, it forms part of the Army, not the Navy. Intended for amphibio ...
, 6 helmsmen, 288 seamen, 70 soldiers of the troupes de marine
The (TDM, ) is a corps of the French Army that includes several specialities: infantry, artillery, armoured, airborne, engineering, and transmissions (Signals).
Despite its name, it forms part of the Army, not the Navy. Intended for amphibio ...
or Line infantry
Line infantry was the type of infantry that composed the basis of European land armies from the late 17th century to the mid-19th century. Maurice of Nassau and Gustavus Adolphus are generally regarded as its pioneers, while Turenne and Monte ...
, 44 boys
A boy is a young male human. The term is commonly used for a child or an adolescent. When a male human reaches adulthood, he is described as a man.
Definition, etymology, and use
According to the ''Merriam-Webster Dictionary'', a boy is "a ...
, 13 valets and 12 others.
Sources and references
Citations
Bibliography
*External links
* * * * {{Cite web, title=La monographie de lArtésien'' (1764), url=http://www.ancre.fr/Product.aspx?ID=3879293&L=FR, website=ancre.fr/, archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100304184536/http://www.ancre.fr/Product.aspx?ID=3879293&L=FR, archive-date=4 March 2010 Ships of the line Ship of the line classes Naval sailing ship types Nautical terminology *