568th Strategic Missile Squadron on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The 568th Strategic Missile Squadron is an inactive
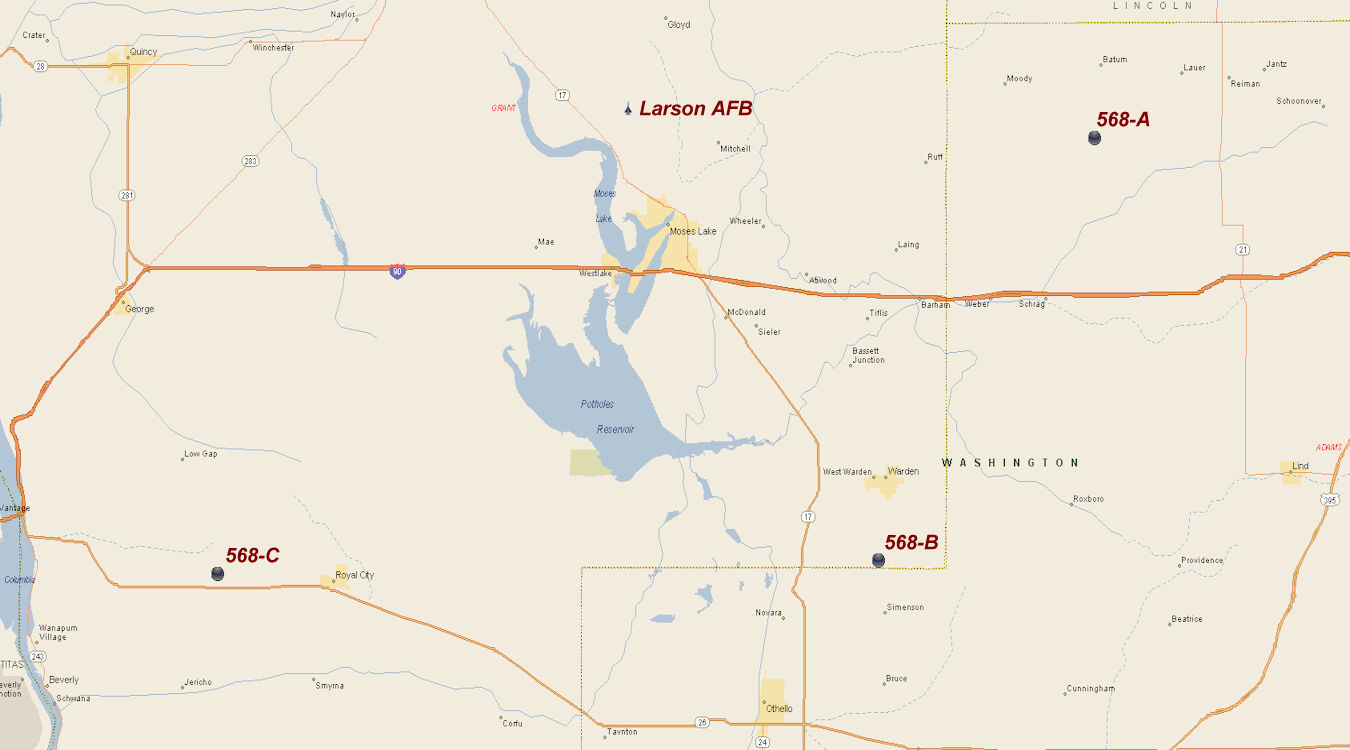 The squadron was deployed in a 3x3 configuration, which meant a total of nine missiles were divided into three sites. Each site had three ICBMs ready to launch at any given time. Its three missile sites were:
: 568-A, 8 miles N of Schrag, Washington
: 568-B, 4 miles SSW of Warden, Washington
: 568-C, 6 miles SE of Frenchman Hills, Washington
In May 1963, Headquarters USAF decided that Titan I missiles were to be phased out between 1965 and 1968. One year later,
The squadron was deployed in a 3x3 configuration, which meant a total of nine missiles were divided into three sites. Each site had three ICBMs ready to launch at any given time. Its three missile sites were:
: 568-A, 8 miles N of Schrag, Washington
: 568-B, 4 miles SSW of Warden, Washington
: 568-C, 6 miles SE of Frenchman Hills, Washington
In May 1963, Headquarters USAF decided that Titan I missiles were to be phased out between 1965 and 1968. One year later,
United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Signal ...
unit. It was last assigned to the 462d Strategic Aerospace Wing 46 may refer to:
* 46 (number)
* 46 (album), ''46'' (album), a 1983 album by Kino (band), Kino
* "Forty Six", a song by Karma to Burn from the album ''Appalachian Incantation'', 2010
* One of the years 46 BC, AD 46, 1946, 2046
{{Number disambiguat ...
at Larson Air Force Base
Larson Air Force Base is a former United States Air Force base located five miles (8 km) northwest of the central business district (CBD) of Moses Lake, in Grant County, Washington. After its closure in 1966, the airport facility became G ...
, Washington. It was equipped with the first-generation SM-68 Titan I The SM-68 Titan (individual variants later designated HGM-25 Titan I and LGM-25 Titan II) was the designation of two intercontinental ballistic missiles developed for the United States Air Force. The Titan I and Titan II missiles were operational be ...
intercontinental ballistic missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more thermonuclear warheads). Conventional, chemical, and biological weapons c ...
, with a mission of nuclear deterrence. The squadron
Squadron may refer to:
* Squadron (army), a military unit of cavalry, tanks, or equivalent subdivided into troops or tank companies
* Squadron (aviation), a military unit that consists of three or four flights with a total of 12 to 24 aircraft, de ...
was inactivated as part of the phaseout of the Titan I ICBM on 25 March 1965.
The squadron was first activated during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
as the 568th Bombardment Squadron. After training in the United States, it deployed to the European Theater of Operations
The European Theater of Operations, United States Army (ETOUSA) was a Theater of Operations responsible for directing United States Army operations throughout the European theatre of World War II, from 1942 to 1945. It commanded Army Ground For ...
, where it participated in the strategic bombing campaign against Germany. It was twice awarded the Distinguished Unit Citation
The Presidential Unit Citation (PUC), originally called the Distinguished Unit Citation, is awarded to units of the uniformed services of the United States, and those of allied countries, for extraordinary heroism in action against an armed enem ...
for its actions in combat. After V-E Day
Victory in Europe Day is the day celebrating the formal acceptance by the Allies of World War II of Germany's unconditional surrender of its armed forces on Tuesday, 8 May 1945, marking the official end of World War II in Europe in the Easter ...
, the squadron returned to the United States, where it was inactivated in August 1945. The squadron was active in the reserve
Reserve or reserves may refer to:
Places
* Reserve, Kansas, a US city
* Reserve, Louisiana, a census-designated place in St. John the Baptist Parish
* Reserve, Montana, a census-designated place in Sheridan County
* Reserve, New Mexico, a US vi ...
from 1947 until 1949, but does not appear to have been fully manned or equipped at this time.
History
World War II
Activation and training in the United States
Thesquadron
Squadron may refer to:
* Squadron (army), a military unit of cavalry, tanks, or equivalent subdivided into troops or tank companies
* Squadron (aviation), a military unit that consists of three or four flights with a total of 12 to 24 aircraft, de ...
was first activated at Geiger Field
Spokane International Airport is a commercial airport located approximately west-southwest of downtown Spokane, Washington, United States. It is the primary airport serving the Inland Northwest, which consists of 30 counties and includes areas ...
, Washington in January 1943 as the 568th Bombardment Squadron, one of the four original squadrons of the 390th Bombardment Group
39 may refer to:
* 39 (number), the natural number following 38 and preceding 40
* one of the years:
** 39 BC
** AD 39
** 1939
** 2039
* ''39'' (album), a 2000 studio album by Mikuni Shimokawa
* "'39", a 1975 song by Queen
* "Thirty Nine", a ...
. A cadre
Cadre may refer to:
*Cadre (military), a group of officers or NCOs around whom a unit is formed, or a training staff
*Cadre (politics), a politically controlled appointment to an institution in order to circumvent the state and bring control to th ...
from the squadron and group
A group is a number of persons or things that are located, gathered, or classed together.
Groups of people
* Cultural group, a group whose members share the same cultural identity
* Ethnic group, a group whose members share the same ethnic iden ...
went to the Army Air Force School of Applied Tactics
The Army Air Forces Tactical Center was a major command and military training organization of the United States Army Air Forces during World War II. It trained cadres from newly formed units in combat operations under simulated field condition ...
at Orlando Army Air Base
Orlando Executive Airport is a public airport three miles (6 km) east of downtown Orlando, in Orange County, Florida. It is owned and operated by the Greater Orlando Aviation Authority (GOAA) and serves general aviation.
Overview
Orlando ...
, Florida for advanced training. The 390th Group was the first to go through this training process, which was followed by later combat groups. The squadron was filled out with Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress
The Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress is a four-engined heavy bomber developed in the 1930s for the United States Army Air Corps (USAAC). Relatively fast and high-flying for a bomber of its era, the B-17 was used primarily in the European Theater ...
heavy bomber
Heavy bombers are bomber aircraft capable of delivering the largest payload of air-to-ground weaponry (usually bombs) and longest range (takeoff to landing) of their era. Archetypal heavy bombers have therefore usually been among the larges ...
s beginning the following month and trained at Geiger and at Great Falls Army Air Base
Great may refer to: Descriptions or measurements
* Great, a relative measurement in physical space, see Size
* Greatness, being divine, majestic, superior, majestic, or transcendent
People
* List of people known as "the Great"
*Artel Great (born ...
, Montana until early July 1943. The squadron's air echelon ferried their B-17s to England via the north Atlantic ferry route, with the first bombers arriving on 13 July. The ground echelon departed for Camp Shanks
Camp Shanks was a United States Army installation in the Orangetown, New York area. Named after Major General David C. Shanks, it was situated near the juncture of the Erie Railroad and the Hudson River. The camp was the largest U.S. Army embarka ...
and the New York Port of Embarkation, sailing on the on 17 July, reaching England ten days later.Maurer, ''Combat Groups'', pp. 277-278Freeman, pp. 255-256
Combat in the European Theater
The squadron arrived at its combat station,RAF Framlingham
Royal Air Force Framlingham or more simply RAF Framlingham is a former Royal Air Force station located southeast of Framlingham, Suffolk, England.
History United States Army Air Forces use
Framlingham airfield was built in 1942 and was u ...
in July 1943 and flew its first combat mission on 12 August against targets in the Ruhr
The Ruhr ( ; german: Ruhrgebiet , also ''Ruhrpott'' ), also referred to as the Ruhr area, sometimes Ruhr district, Ruhr region, or Ruhr valley, is a polycentric urban area in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population density of 2,800/km ...
. Five days later, the squadron attacked the Messerschmitt
Messerschmitt AG () was a German share-ownership limited, aircraft manufacturing corporation named after its chief designer Willy Messerschmitt from mid-July 1938 onwards, and known primarily for its World War II fighter aircraft, in partic ...
factory at Regensburg
Regensburg or is a city in eastern Bavaria, at the confluence of the Danube, Naab and Regen rivers. It is capital of the Upper Palatinate subregion of the state in the south of Germany. With more than 150,000 inhabitants, Regensburg is the f ...
, for which it earned its first Distinguished Unit Citation
The Presidential Unit Citation (PUC), originally called the Distinguished Unit Citation, is awarded to units of the uniformed services of the United States, and those of allied countries, for extraordinary heroism in action against an armed enem ...
(DUC). The Regensburg mission was a "shuttle" mission, and the squadron continued after striking the target to recover at Twelfth Air Force
The Twelfth Air Force (12 AF; Air Forces Southern, (AFSOUTH)) is a Numbered Air Force of the United States Air Force Air Combat Command (ACC). It is headquartered at Davis–Monthan Air Force Base, Arizona.
The command is the air component to U ...
bases in North Africa. Poor weather at the departure bases extended the time required to assemble the strike force, making fuel reserves critical. Half of the fighter cover missed the rendezvous, lessening the bombers' protection. For an hour and a half after its entry into German airspace, the strike force bore attacks from German interceptors
An interceptor aircraft, or simply interceptor, is a type of fighter aircraft designed specifically for the defensive interception role against an attacking enemy aircraft, particularly bombers and reconnaissance aircraft. Aircraft that are c ...
. The 390th Group suffered the heaviest losses of the leading wing
A wing is a type of fin that produces lift while moving through air or some other fluid. Accordingly, wings have streamlined cross-sections that are subject to aerodynamic forces and act as airfoils. A wing's aerodynamic efficiency is expres ...
, but had the best bombing results, which destroyed equipment used for the assembly of the Me 262
The Messerschmitt Me 262, nicknamed ''Schwalbe'' (German: "Swallow") in fighter versions, or ''Sturmvogel'' (German: "Storm Bird") in fighter-bomber versions, is a fighter aircraft and fighter-bomber that was designed and produced by the German ...
jet fighter, delaying its introduction into service.
On 14 October 1943, the squadron carried out an attack on the ball bearing
A ball bearing is a type of rolling-element bearing that uses balls to maintain the separation between the bearing races.
The purpose of a ball bearing is to reduce rotational friction and support radial and axial loads. It achieves this ...
factories at Schweinfurt
Schweinfurt ( , ; ) is a city in the district of Lower Franconia in Bavaria, Germany. It is the administrative centre of the surrounding district (''Landkreis'') of Schweinfurt and a major industrial, cultural and educational hub. The urban agg ...
, braving unrelenting attacks by enemy fighters, despite which, the 390th Group had the highest accuracy of the attacking force. For this mission it received a second DUC. In late February 1944, the squadron participated in Big Week
Big Week or Operation Argument was a sequence of raids by the United States Army Air Forces and RAF Bomber Command from 20 to 25 February 1944, as part of the Strategic bombing during World War II#US bombing in Europe, European strategic bombin ...
, the concentrated assault on Germany's aircraft manufacturing industry, including plants manufacturing aircraft instruments and depots for aviation supplies. Other strategic targets included attacks on navy bases at Bremen
Bremen (Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Bräm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (german: Stadtgemeinde Bremen, ), is the capital of the German state Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (''Freie Hansestadt Bremen''), a two-city-state consis ...
, bridges at Cologne
Cologne ( ; german: Köln ; ksh, Kölle ) is the largest city of the German western States of Germany, state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW) and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with 1.1 m ...
, marshalling yards
A classification yard (American and Canadian English (Canadian National Railway use)), marshalling yard (British, Hong Kong, Indian, Australian, and Canadian English (Canadian Pacific Railway use)) or shunting yard (Central Europe) is a railway ya ...
at Frankfurt am Main
Frankfurt, officially Frankfurt am Main (; Hessian: , "Frank ford on the Main"), is the most populous city in the German state of Hesse. Its 791,000 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located on its na ...
, factories at Mannheim
Mannheim (; Palatine German: or ), officially the University City of Mannheim (german: Universitätsstadt Mannheim), is the second-largest city in the German state of Baden-Württemberg after the state capital of Stuttgart, and Germany's 2 ...
, synthetic oil plants at Merseburg
Merseburg () is a town in central Germany in southern Saxony-Anhalt, situated on the river Saale, and approximately 14 km south of Halle (Saale) and 30 km west of Leipzig. It is the capital of the Saalekreis district. It had a diocese ...
, oil refineries at Zeitz
Zeitz ( hsb, Žič) is a town in the Burgenlandkreis district, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It is situated on the river White Elster, in the triangle of the federal states Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia and Saxony.
History
Zeitz was first recorded und ...
.
The squadron was occasionally diverted from the strategic bombing campaign to fly air support
In military tactics, close air support (CAS) is defined as air action such as air strikes by fixed or rotary-winged aircraft against hostile targets near friendly forces and require detailed integration of each air mission with fire and movement ...
and interdiction Interdiction is a military term for the act of delaying, disrupting, or destroying enemy forces or supplies en route to the battle area. A distinction is often made between strategic and tactical interdiction. The former refers to operations whose e ...
missions. It bombed near Caen
Caen (, ; nrf, Kaem) is a commune in northwestern France. It is the prefecture of the department of Calvados. The city proper has 105,512 inhabitants (), while its functional urban area has 470,000,D Day
The Normandy landings were the landing operations and associated airborne operations on Tuesday, 6 June 1944 of the Allied invasion of Normandy in Operation Overlord during World War II. Codenamed Operation Neptune and often referred to as D ...
. It provided support during Operation Cobra
Operation Cobra was the codename for an Offensive (military), offensive launched by the United States First United States Army, First Army under Lieutenant General Omar Bradley seven weeks after the D-Day landings, during the Invasion of Norman ...
, the breakout at Saint Lo
In religious belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of holiness, likeness, or closeness to God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and denomination. In Catholic, Eastern Ortho ...
in late July 1944. During the Battle of the Bulge
The Battle of the Bulge, also known as the Ardennes Offensive, was the last major German offensive (military), offensive military campaign, campaign on the Western Front (World War II), Western Front during World War II. The battle lasted fr ...
from December 1944 through January 1945, it cut German supply lines to the battle area. It attacked Axis air base
An air base (sometimes referred to as a military air base, military airfield, military airport, air station, naval air station, air force station, or air force base) is an aerodrome used as a military base by a military force for the operation ...
s to support Operation Varsity
Operation Varsity (24 March 1945) was a successful airborne forces operation launched by Allied troops that took place toward the end of World War II. Involving more than 16,000 paratroopers and several thousand aircraft, it was the largest air ...
, the airborne assault across the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
, in March 1945. The squadron flew its last combat mission on 20 April 1945.
Return to the United States and inactivation
Just prior to and afterV-E Day
Victory in Europe Day is the day celebrating the formal acceptance by the Allies of World War II of Germany's unconditional surrender of its armed forces on Tuesday, 8 May 1945, marking the official end of World War II in Europe in the Easter ...
, the squadron dropped food supplies to civilians in the Netherlands. The squadron's aircraft began returning to the United States on 25 June 1945, while the ground echelon sailed on the in early August. The squadron reassembled at Sioux Falls Army Air Field
Sioux Falls Regional Airport , also known as Joe Foss Field, is a public and military use airport three miles northwest of Sioux Falls, South Dakota, United States. It is named in honor of aviator and Sioux Falls native Joe Foss, who later served a ...
, South Dakota later that month and was inactivated there on 28 August 1945.
Reserve operations
The squadron was activated in thereserve
Reserve or reserves may refer to:
Places
* Reserve, Kansas, a US city
* Reserve, Louisiana, a census-designated place in St. John the Baptist Parish
* Reserve, Montana, a census-designated place in Sheridan County
* Reserve, New Mexico, a US vi ...
at Lowry Field
Lowry Air Force Base (Lowry Field in 1938–1948) is a former United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) training base during World War II and a United States Air Force (USAF) training base during the Cold War, serving as the initial 1955–1958 si ...
, Colorado, where it trained under the supervision of Air Defense Command
Aerospace Defense Command was a major command (military formation), command of the United States Air Force, responsible for continental air defense. It was activated in 1968 and disbanded in 1980. Its predecessor, Air Defense Command, was est ...
(ADC)'s 138th AAF Base Unit (Reserve Training) (later the 2468th Air Force Reserve Training Center). It is not clear to what degree the squadron was staffed or equipped while a reserve unit. In 1948 Continental Air Command
Continental Air Command (ConAC) (1948–1968) was a Major Command of the United States Air Force (USAF) responsible primarily for administering the Air National Guard and Air Force Reserve.
During the Korean War, ConAC provided the necessary au ...
(ConAC) assumed responsibility for managing reserve and Air National Guard
The Air National Guard (ANG), also known as the Air Guard, is a federal military reserve force of the United States Air Force, as well as the air militia of each U.S. state, the District of Columbia, the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, and the ter ...
units from ADC. President Truman’s reduced 1949 defense budget required reductions in the number of units in the Air Force, The 568th was inactivated in June 1949 as reserve flying operations at Lowry came to an end.
Intercontinental ballistic missiles
The squadron was redesignated the 568th Strategic Missile Squadron, organized atLarson Air Force Base
Larson Air Force Base is a former United States Air Force base located five miles (8 km) northwest of the central business district (CBD) of Moses Lake, in Grant County, Washington. After its closure in 1966, the airport facility became G ...
, Washington on 1 April 1961 and assigned to the 4170th Strategic Wing
The 462d Air Expeditionary Group is a provisional unit of the United States Air Force. It is assigned to Air Mobility Command to activate or inactivate as needed to meet operational requirements. Its last assignment was at Naval Support Facilit ...
. The squadron was equipped with SM-68 Titan I The SM-68 Titan (individual variants later designated HGM-25 Titan I and LGM-25 Titan II) was the designation of two intercontinental ballistic missiles developed for the United States Air Force. The Titan I and Titan II missiles were operational be ...
intercontinental ballistic missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more thermonuclear warheads). Conventional, chemical, and biological weapons c ...
s. When the squadron was declared operational on 28 December 1962, the deployment of the Titan I was complete.
 The squadron was deployed in a 3x3 configuration, which meant a total of nine missiles were divided into three sites. Each site had three ICBMs ready to launch at any given time. Its three missile sites were:
: 568-A, 8 miles N of Schrag, Washington
: 568-B, 4 miles SSW of Warden, Washington
: 568-C, 6 miles SE of Frenchman Hills, Washington
In May 1963, Headquarters USAF decided that Titan I missiles were to be phased out between 1965 and 1968. One year later,
The squadron was deployed in a 3x3 configuration, which meant a total of nine missiles were divided into three sites. Each site had three ICBMs ready to launch at any given time. Its three missile sites were:
: 568-A, 8 miles N of Schrag, Washington
: 568-B, 4 miles SSW of Warden, Washington
: 568-C, 6 miles SE of Frenchman Hills, Washington
In May 1963, Headquarters USAF decided that Titan I missiles were to be phased out between 1965 and 1968. One year later, Secretary of Defense
A defence minister or minister of defence is a cabinet official position in charge of a ministry of defense, which regulates the armed forces in sovereign states. The role of a defence minister varies considerably from country to country; in som ...
Robert McNamara
Robert Strange McNamara (; June 9, 1916 – July 6, 2009) was an American business executive and the eighth United States Secretary of Defense, serving from 1961 to 1968 under Presidents John F. Kennedy and Lyndon B. Johnson. He remains the Lis ...
directed the acceleration of this program to remove these missiles prior to the end of Fiscal Year 1965 and in November 1964, announced this publicly. The squadron's first Titan Is were taken off alert on 4 January 1965 and the squadron was inactivated on 25 March 1965.
Lineage
* Constituted as the 568th Bombardment Squadron (Heavy) on 15 January 1943 : Activated on 26 January 1943 : Redesignated 568th Bombardment Squadron, Heavy c. 20 August 1943 : Inactivated on 28 August 1945 * Redesignated 568th Bombardment Squadron, Very Heavy on 28 January 1947 : Activated in the reserve on 27 February 1947 : Inactivated on 27 June 1949 * Redesignated 568th Strategic Missile Squadron and activated on 24 October 1960 (not organized) : Organized on 1 April 1961 : Inactivated on 25 March 1965Lineage, including assignments and aircraft, through March 1953 in Maurer, ''Combat Squadrons'', pp. 665-666SAC Missile Chronology, p. 47Assignments
* 390th Bombardment Group, 26 January 1943 – 28 August 1945 * Second Air Force, 27 February 1947 *Tenth Air Force
The Tenth Air Force (10 AF) is a unit of the U.S. Air Force, specifically a numbered air force of the Air Force Reserve Command (AFRC). 10 AF is headquartered at Naval Air Station Fort Worth Joint Reserve Base/Carswell Field (formerly Carswell AF ...
, 1 July 1948 – 27 June 1949
* Strategic Air Command, 24 October 1960 (not organized)
* 4170th Strategic Wing, 1 April 1961
* 462d Strategic Aerospace Wing, 1 February 1963 – 25 March 1965Ravenstein, p. 256
Stations
* Geiger Field, Washington, 26 January 1943 * Great Falls Army Air Base, Montana, 6 June-5 July 1943 * RAF Framlingham (AAF-153), England, 26 July 1943 – 6 August 1945 * Sioux Falls Army Air Field, South Dakota, 14–28 August 1945 * Lowry Field (later Lowry Air Force Base), Colorado, 27 February 1947 – 27 June 1949 * Larson Air Force Base, Washington, 1 April 1961 – 25 March 1965Station information through March 1953 in Maurer, ''Combat Squadrons'', pp. 665-666, except as noted.Aircraft and missiles
* B-17 Flying Fortress, 1943–1945 * SM-68 Titan I (later HGN-25A), 1961–1965Awards and campaigns
See also
*List of United States Air Force missile squadrons
This article lists the missile squadrons of the United States Air Force. There are nine missile squadrons currently active in the United States (listed in bold type); all nine are equipped to operate intercontinental ballistic missiles.
Aerodyna ...
* B-17 Flying Fortress units of the United States Army Air Forces
This is a list of United States Army Air Forces B-17 Flying Fortress units of the United States Army Air Forces, including variants and other historical information. Heavy bomber training organizations primarily under II Bomber Command in t ...
References
Notes
; Explanatory notes ; CitationsBibliography
* * * * * * * * * {{USAAF 2d Air Force World War II Strategic missile squadrons of the United States Air Force Military units and formations disestablished in 1965