5-ton 6×6 Truck on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 The 5‑ton 6x6 truck, officially "Truck, 5-ton, 4x4", was a class of heavy-duty
The 5‑ton 6x6 truck, officially "Truck, 5-ton, 4x4", was a class of heavy-duty
 Cargo trucks had a long low sided box with a bottom hinged tailgate, bodies with drop sides were also standardized. Both had removable side racks with fold down troop seats and bows for a tarpaulin. Long cargo trucks, with an extra long wheelbase, had a long box with side racks and bows for a tarpaulin. There were no drop side versions, and none had troop seats.
Cargo trucks had a long low sided box with a bottom hinged tailgate, bodies with drop sides were also standardized. Both had removable side racks with fold down troop seats and bows for a tarpaulin. Long cargo trucks, with an extra long wheelbase, had a long box with side racks and bows for a tarpaulin. There were no drop side versions, and none had troop seats.

 Medium wrecker trucks were used to recover disabled or stuck trucks and lift large components. A rotating, telescoping, and elevating hydraulic boom could lift a maximum of . Although the truck was not meant to carry a load, the boom could support when towing.
Medium wrecker trucks were used to recover disabled or stuck trucks and lift large components. A rotating, telescoping, and elevating hydraulic boom could lift a maximum of . Although the truck was not meant to carry a load, the boom could support when towing.
 Tractor trucks were used to tow
Tractor trucks were used to tow
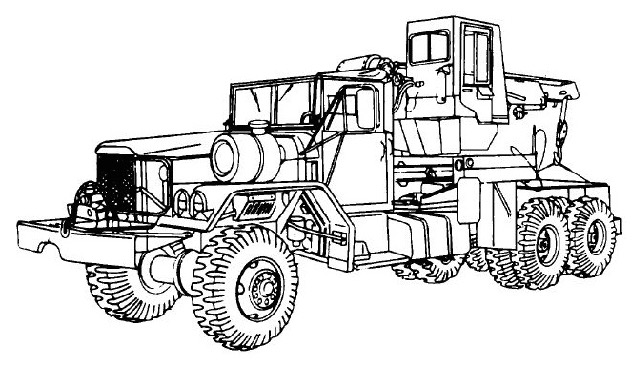 Medium wrecker tractor trucks, with an extra long wheelbase, were a wrecker with a fifth wheel mounted behind the boom. Meant for aircraft recovery, the truck could perform wrecker duties and load and tow semi trailers.
Medium wrecker tractor trucks, with an extra long wheelbase, were a wrecker with a fifth wheel mounted behind the boom. Meant for aircraft recovery, the truck could perform wrecker duties and load and tow semi trailers.
 Expansible van trucks had a long van body with a slide out section on each side. When the sections are extended the working floor was over wide. Some had hydraulic lift-gates.
Expansible van trucks had a long van body with a slide out section on each side. When the sections are extended the working floor was over wide. Some had hydraulic lift-gates.
 Bridge transporting trucks had a stake body long for carrying bridging equipment and components. In the M939 series there were no standardized bridge models, instead specialized bodies were mounted on chassis-cabs.
Bridge transporting trucks had a stake body long for carrying bridging equipment and components. In the M939 series there were no standardized bridge models, instead specialized bodies were mounted on chassis-cabs.
 Logging bolster trucks, with a bolster trailer, were used to carry long loads like logs, poles, and bridge sections. When unloaded the trailer could be loaded onto the truck. There were no bolster trucks in the M939 series.
Logging bolster trucks, with a bolster trailer, were used to carry long loads like logs, poles, and bridge sections. When unloaded the trailer could be loaded onto the truck. There were no bolster trucks in the M939 series.
File:M51 Truck, Dump, 5-Ton, 6x6 (pic2).jpg, M51 Dump truck
File:US Army articulated truck - Flickr - Terry Wha.jpg, M52 Tractor
File:Puckapunyal-crane-2-1.jpg, M816 Wrecker
File:Halo_3_ODST-firefight_truck.jpg, M820 Expansible Van
File:M923.jpg, M923 Cargo truck
File:RQ-2 Pioneer launched from its twin rail catapult 1.JPEG, M927 w/drone launcher
M39 series at Olive-Drab.com
M809 series at Olive-Drab
M809 series Technical Manuals at NSN Lookup
M939 series at Olive-Drab
M939 series Technical Manuals at NSN Lookup
Military trucks of the United States


 The 5‑ton 6x6 truck, officially "Truck, 5-ton, 4x4", was a class of heavy-duty
The 5‑ton 6x6 truck, officially "Truck, 5-ton, 4x4", was a class of heavy-duty six-wheel drive
Six-wheel drive (6WD or 6×6) is an all-wheel drive drivetrain configuration of three axles with at least two wheels on each axle capable of being driven simultaneously by the vehicle's engine. Unlike four-wheel drive drivetrains, the configurat ...
trucks used by the US Armed Forces
The United States Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States. The armed forces consists of six service branches: the Army, Marine Corps, Navy, Air Force, Space Force, and Coast Guard. The president of the United States is the ...
. The basic cargo version was designed to transport a 5-ton (4,500 kg) load over all roads and cross-country terrain in all weather. Through three evolutionary series ( M39, M809
M8 or M-8 or M.08 or ''variant, may refer to:
Computing and electronics
* M8 (cipher), an encryption algorithm
* Leica M8, a digital rangefinder camera
* HTC One (M8), a smartphone
* Meizu M8, a smartphone
Places
* Messier 8, also known as M8 o ...
, and M939) there have been component improvements, but all trucks were mechanically very similar. They were the standard heavy-duty truck of the US military for 40 years, until replaced by the Medium Tactical Vehicle (MTV) beginning in 1991.
History
A 20 June 1945 report by the Army Ground Forces Equipment Review Board recommended that all 4‑ton to 6‑ton tactical trucks should be replaced by a single standard 5‑ton (4,536 kg) 6x6 truck series. In 1949 specifications were set and truck manufactures began working on prototypes. Chrysler, GMC, and Mack's designs were advanced,International Harvester
The International Harvester Company (often abbreviated by IHC, IH, or simply International ( colloq.)) was an American manufacturer of agricultural and construction equipment, automobiles, commercial trucks, lawn and garden products, household e ...
's was a conservative conventional, similar in size and layout to the earlier 6-ton (G512) series.
The International Harvester design was chosen and rushed into production in January 1951, it would be standardized as the M39 series. Kaiser (renamed Kaiser-Jeep
Kaiser Jeep was the result of the 1953 merger of Kaiser Motors, an independent passenger car maker based in Willow Run, Michigan, with the Toledo, Ohio-based Willys-Overland Company.
Willys-Overland had been at one point before World War II ...
in 1963) also became a major manufacturer, with Diamond T and Mack building smaller numbers. In 1963 Kaiser-Jeep began building the final order, production was completed in 1965.
In the 1960s more trucks were required, and the Army wanted to replace the multifuel
Multifuel, sometimes spelled multi-fuel, is any type of engine, boiler, or heater or other fuel-burning device which is designed to burn multiple types of fuels in its operation. One common application of multifuel technology is in military s ...
engines with a standard diesel. AM General
AM General is an American heavy vehicle and contract automotive manufacturer based in South Bend, Indiana. It is best known for the civilian Hummer and the military Humvee that are assembled in Mishawaka, Indiana. For a relatively brief period, ...
(successor of Kaiser-Jeep) developed an updated and redesigned version of the M39 series. Standardized as the M809 series, the primary difference was the engine. The hood, frame, and fenders were lengthened to make room for the larger engine, and it had a redesigned grille. All had an air cleaner on the left front fender, a quick visual way to tell them from the earlier M39 series. Jeep/AM General built all M809s between 1969 and 1982.
The M939 series was a Product Improvement Package of the M809, with updated engine, transmission, and brakes. A new, larger cab and tilt-forward hood were a major visual change from earlier trucks. Early M939s were rebuilds of M809 vehicles, suffix –A2 are new production by Bowen-McLaughlin-York/BMY with later model Cummins engine.
Engines
The 5-ton family had five different engines in its life, one gasoline, one multifuel, and three different diesels. The M39 series had three different engines, all with different operating characteristics. The 1951 design was originally powered by a Continental R6602, a inline 6 cylindergasoline engine
A petrol engine (gasoline engine in American English) is an internal combustion engine designed to run on petrol (gasoline). Petrol engines can often be adapted to also run on fuels such as liquefied petroleum gas and ethanol blends (such as ''E ...
. These models had no external air filter and had the exhaust outlet under the right side of the truck's body. The engine was a successful design but by 1960 its and the use of gasoline as a fuel in heavy trucks were becoming a problem.
In 1962-1963 Diamond T and Mack began retrofitting M52 semi-tractors and M54 cargo trucks to the -A1 standard. They had a Mack ENDT-673, a turbocharged inline 6 cylinder diesel engine. These were the only diesel M39 series models.
The -A2 had the army standard design LDS-465-1 multifuel engine built by Continental. It was a turbocharged inline 6 cylinder multifuel engine. Using M.A.N.
MAN SE (abbreviation of ''Maschinenfabrik Augsburg- Nürnberg'', ) was a manufacturing and engineering company based in Munich, Germany. Its primary output was commercial vehicles and diesel engines through its MAN Truck & Bus and MAN Latin Am ...
technology it was a diesel type that could also use other fuel oils or a gasoline/oil mix in an emergency. Also used by the M35 M35, M.35 or M-35 may refer to:
Military
* M35 series 2½-ton 6×6 cargo truck, a US Army truck
* , a Royal Navy mine countermeasures vessel launched in 1982
* ADGZ or ''M35 Mittlere Panzerwagen'', a 1930s Austrian Army heavy armored car
* Cannone ...
-ton series this engine was successful in the smaller trucks but was underpowered compared to all other-5-ton models.
The M809 series used a Cummins
Cummins Inc. is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and distributes engines, filtration, and power generation products. Cummins also services engines and related equipment, including fuel systems, controls, air ...
NHC250 engine, a naturally aspirated inline 6 cylinder diesel engine
The diesel engine, named after Rudolf Diesel, is an internal combustion engine in which ignition of the fuel is caused by the elevated temperature of the air in the cylinder due to mechanical compression; thus, the diesel engine is a so-call ...
developing at 2100rpm
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or with the notation min−1) is a unit of rotational speed or rotational frequency for rotating machines.
Standards
ISO 80000-3:2019 defines a unit of rotation as the dimensionl ...
and of torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational equivalent of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). It represents the capability of a force to produce change in the rotational motion of th ...
at 1500rpm. All models of the M809 series used this engine throughout their service life. The N series was a very successful commercial design, with a conservative rating the engine was more powerful and less stressed than the multifuel engine.
The M939 and M939A1 models were rebuilds of the M809 series and used their NHC 250 engine. Although the design is dated it is still powerful and reliable in service and was not significantly up-graded. The M939A2 new production models use a modern Cummins 6CTA8.3 turbocharged and aftercooled inline 6 cylinder diesel engine. This is also a successful commercial design.
Driveline
The M39 and M809 series had a Spicer 5 speed manual synchromesh transmission. The M939 used an Allison automatic, for better engine speed control and driving ease. A two speedtransfer case
A transfer case is a part of the drivetrain of four-wheel-drive, all-wheel-drive, and other multiple powered axle vehicles. The transfer case transfers power from the transmission to the front and rear axles by means of drive shafts. It also syn ...
also engaged the front axle. M39s and M809s used one which engaged the front axle automatically if the rear wheels turned faster than the front, as when the rear wheels spun. The M939s had an improved type, which always engaged the front axle in the low range, in the high range the driver could engage and disengage it with an air control.
Chassis
A ladder frame with three live beam axles, the front onleaf spring
A leaf spring is a simple form of spring commonly used for the suspension in wheeled vehicles. Originally called a ''laminated'' or ''carriage spring'', and sometimes referred to as a semi-elliptical spring, elliptical spring, or cart spring, i ...
s, the rear tandem on leaf springs with locating arms. Brakes on the M39 and M809 were air over hydraulic with drum brakes on all wheels, M939s were full air. Many trucks were available with a front-mounted capacity winch.
There were three wheelbase
In both road and rail vehicles, the wheelbase is the horizontal distance between the centers of the front and rear wheels. For road vehicles with more than two axles (e.g. some trucks), the wheelbase is the distance between the steering (front ...
s (Measurements are from the centerline of the front axle to the centerline of rear tandem). The short, used for tractors and dumps, was , the long, used for cargo, wreckers, and bolsters, was , and the extra long, used for long cargo, tractor wreckers, and expansible vans, was .
Most models had 11.00x20 size tires with dual rear tires, bridge trucks and some chassis-cabs had 14.00x20 with dual rear tires. Early M939s used 11.00x20s with dual tires, but M939A1s had 14.00x20s with single rear tires and M939A2s introduced a central tire inflation system.
Models
Cargo trucks
 Cargo trucks had a long low sided box with a bottom hinged tailgate, bodies with drop sides were also standardized. Both had removable side racks with fold down troop seats and bows for a tarpaulin. Long cargo trucks, with an extra long wheelbase, had a long box with side racks and bows for a tarpaulin. There were no drop side versions, and none had troop seats.
Cargo trucks had a long low sided box with a bottom hinged tailgate, bodies with drop sides were also standardized. Both had removable side racks with fold down troop seats and bows for a tarpaulin. Long cargo trucks, with an extra long wheelbase, had a long box with side racks and bows for a tarpaulin. There were no drop side versions, and none had troop seats.
Dump trucks

Dump truck
A dump truck, known also as a dumping truck, dump trailer, dumper trailer, dump lorry or dumper lorry or a dumper for short, is used for transporting materials (such as dirt, gravel, or demolition waste) for construction as well as coal. A typi ...
s were used to haul sand, gravel, dirt, rubble, scrap, and other bulk materials. They had a dump body with cab protector and a tailgate that could hinge at either the top or bottom. They could be equipped with overhead bows, a tarpaulin, and troop seats, but the relatively small size of the body limited their passenger or cargo load.
Medium wrecker trucks
 Medium wrecker trucks were used to recover disabled or stuck trucks and lift large components. A rotating, telescoping, and elevating hydraulic boom could lift a maximum of . Although the truck was not meant to carry a load, the boom could support when towing.
Medium wrecker trucks were used to recover disabled or stuck trucks and lift large components. A rotating, telescoping, and elevating hydraulic boom could lift a maximum of . Although the truck was not meant to carry a load, the boom could support when towing.
Tractor trucks
 Tractor trucks were used to tow
Tractor trucks were used to tow semi-trailer
A semi-trailer is a trailer without a front axle. In the United States, the term is also used to refer to the combination of a truck and a semi-trailer; a tractor-trailer.
A large proportion of a semi-trailer's weight is supported by a trac ...
s up to with on their fifth wheel.
On improved roads they could tow up to with on their fifth wheel.
Tractor trucks normally tow a 12-ton ( load rated 4-wheel (two axles) trailer. There are stake/platform, van, tank, and low-bed models. There is also a 15-ton () low bed trailer, the heaviest possible off-road. A 25-ton () low-bed trailer can be towed on prepared surfaces.
Unlike commercial trucks the fifth-wheel can also pivot side to side, making a more flexible connection to the trailer. Even so, off-road performance is limited
to relatively flat and solid ground.
Medium wrecker tractor trucks
 Medium wrecker tractor trucks, with an extra long wheelbase, were a wrecker with a fifth wheel mounted behind the boom. Meant for aircraft recovery, the truck could perform wrecker duties and load and tow semi trailers.
Medium wrecker tractor trucks, with an extra long wheelbase, were a wrecker with a fifth wheel mounted behind the boom. Meant for aircraft recovery, the truck could perform wrecker duties and load and tow semi trailers.
Expansible van trucks
 Expansible van trucks had a long van body with a slide out section on each side. When the sections are extended the working floor was over wide. Some had hydraulic lift-gates.
Expansible van trucks had a long van body with a slide out section on each side. When the sections are extended the working floor was over wide. Some had hydraulic lift-gates.
Bridge transporting trucks
 Bridge transporting trucks had a stake body long for carrying bridging equipment and components. In the M939 series there were no standardized bridge models, instead specialized bodies were mounted on chassis-cabs.
Bridge transporting trucks had a stake body long for carrying bridging equipment and components. In the M939 series there were no standardized bridge models, instead specialized bodies were mounted on chassis-cabs.
Logging bolster trucks
 Logging bolster trucks, with a bolster trailer, were used to carry long loads like logs, poles, and bridge sections. When unloaded the trailer could be loaded onto the truck. There were no bolster trucks in the M939 series.
Logging bolster trucks, with a bolster trailer, were used to carry long loads like logs, poles, and bridge sections. When unloaded the trailer could be loaded onto the truck. There were no bolster trucks in the M939 series.
Chassis cabs
Chassis cabs were produced in different wheelbases for specialty bodies. The largest, the M39 series M139C/D, was an Honest John rocket launcher.Model numbers
Gallery
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * and * * * * * * {{cite book, url=https://www.liberatedmanuals.com/TM-55-2320-272-14-1.pdf, title=TM 55-2320-272-14-1 Transport Guidance Technical Manual Truck 5-ton, 6x6, M939-Series, M939A1-Series, and M939A2-Series, publisher=US Dept. of the Army, date=1993, access-date=2 August 2019External links
M39 series at Olive-Drab.com
M809 series at Olive-Drab
M809 series Technical Manuals at NSN Lookup
M939 series at Olive-Drab
M939 series Technical Manuals at NSN Lookup
Military trucks of the United States