47,XXY on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Klinefelter syndrome (KS), also known as 47,XXY, is a chromosome anomaly where a male has an extra

 Klinefelter syndrome is not an inherited condition. The extra X chromosome comes from the mother in approximately 50% of the cases. Maternal age is the only known risk factor. Women at 40 years have a four-times-higher risk of a child with Klinefelter syndrome than women aged 24 years.
The extra chromosome is retained because of a
Klinefelter syndrome is not an inherited condition. The extra X chromosome comes from the mother in approximately 50% of the cases. Maternal age is the only known risk factor. Women at 40 years have a four-times-higher risk of a child with Klinefelter syndrome than women aged 24 years.
The extra chromosome is retained because of a
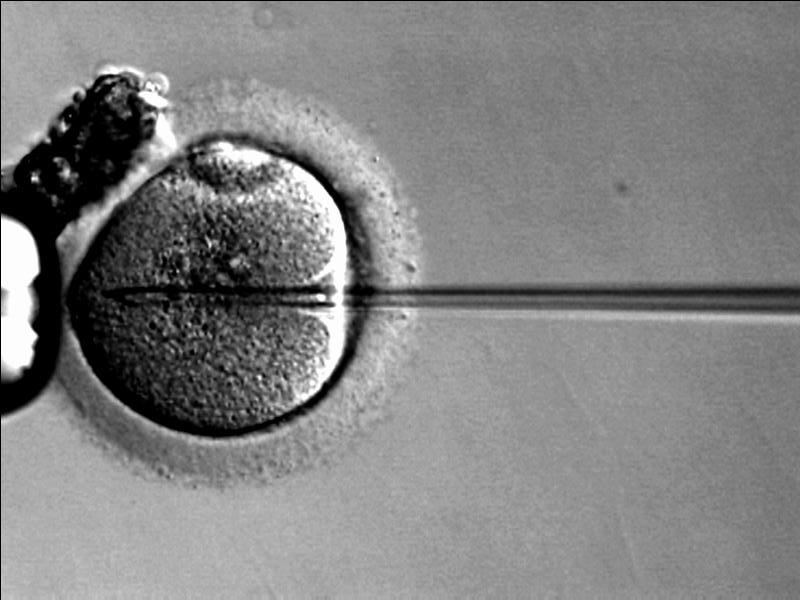 Methods of reproductive medicine, such as
Methods of reproductive medicine, such as
X chromosome
The X chromosome is one of the two sex chromosomes in many organisms, including mammals, and is found in both males and females. It is a part of the XY sex-determination system and XO sex-determination system. The X chromosome was named for its u ...
. These complications commonly include infertility and small, poorly functioning testicle
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is Homology (biology), homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of Androgen, androgens, p ...
s (if present). These symptoms are often noticed only at puberty, although this is one of the most common chromosomal disorders. The birth prevalence of KS in the State of Victoria, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
was estimated to be 223 per 100,000 males. It is named after American endocrinologist
Endocrinology (from ''endocrine'' + '' -ology'') is a branch of biology and medicine dealing with the endocrine system, its diseases, and its specific secretions known as hormones. It is also concerned with the integration of developmental events ...
Harry Klinefelter
Harry Fitch Klinefelter Jr. (; March 20, 1912 – February 20, 1990) was an American rheumatologist and endocrinologist. Klinefelter syndrome is named after him.
Biography
Born March 20, 1912, in Baltimore, Klinefelter studied first at the Univer ...
, who identified the condition in the 1940s, along with his colleagues at Massachusetts General Hospital
Massachusetts General Hospital (Mass General or MGH) is a teaching hospital located in the West End neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts. It is the original and largest clinical education and research facility of Harvard Medical School/Harvar ...
.
The syndrome is defined by the presence of at least one extra X chromosome in addition to a Y chromosome
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes in therian mammals and other organisms. Along with the X chromosome, it is part of the XY sex-determination system, in which the Y is the sex-determining chromosome because the presence of the ...
, yielding a total of 47 or more chromosome
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most import ...
s rather than the usual 46. Klinefelter syndrome occurs randomly. The extra X chromosome comes from the father and mother nearly equally. An older mother may have a slightly increased risk of a child with KS. The syndrome is diagnosed by the genetic test
Genetic testing, also known as DNA testing, is used to identify changes in DNA sequence or chromosome structure. Genetic testing can also include measuring the results of genetic changes, such as RNA analysis as an output of gene expression, or ...
known as karyotyping
A karyotype is the general appearance of the complete set of chromosomes in the cells of a species or in an individual organism, mainly including their sizes, numbers, and shapes. Karyotyping is the process by which a karyotype is discerned by de ...
.
Signs and symptoms
Klinefelter syndrome has different manifestations and these will vary from one patient to another. Among the primary features are infertility and small, poorly functioning testicles. Often, symptoms may be subtle and many people do not realize they are affected. In other cases, symptoms are more prominent and may include weaker muscles, greater height, poor motor coordination, less body hair,gynecomastia
Gynecomastia (also spelled gynaecomastia) is the non-cancerous enlargement of one or both breasts in men due to the growth of breast tissue as a result of a hormone imbalance between estrogens and androgens. Updated by Brent Wisse (10 Novemb ...
(breast growth), and low libido. In the majority of the cases, these symptoms are noticed only at puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a female, the testicles i ...
.
Prenatal
Chromosomal abnormalities, including Klinefelter syndrome, are the most common cause of spontaneous abortion. Generally, the severity of the malformations is proportional to the number of extra X chromosomes present in the karyotype. For example, patients with 49 chromosomes (XXXXY) have a lower IQ and more severe physical manifestations than those with 48 chromosomes (XXXY).Physical manifestations
As babies and children, those with XXY chromosomes may have lower muscle tone and reduced strength. They may sit up, crawl, and walk later than other infants. An average KS child will start walking at 19 months of age. They may also have less muscle control and coordination than other children of their age. During puberty, KS subjects show less muscular body, less facial and body hair, and broader hips as a consequence of low levels of testosterone. Delays in motor development may occur, which can be addressed through occupational and physical therapies. As teens, males with XXY may develop breast tissue, have weaker bones, and a lower energy level than others. Testicles are affected and are usually less than 2 cm in length (and always shorter than 3.5 cm), 1 cm in width, and 4ml in volume. By adulthood, individuals with KS tend to become taller than average, with proportionally longer arms and legs, less-muscular bodies, more belly fat, wider hips, and narrower shoulders. Some will show little to no symptomology, a lanky, youthful build and facial appearance, or a rounded body type. Gynecomastia (increased breast tissue) in males is common, affecting up to 80% of cases. Approximately 10% of males with XXY chromosomes have gynecomastia noticeable enough that they may choose to have surgery. Individuals with KS are often infertile or have reduced fertility. Advanced reproductive assistance is sometimes possible in order to produce an offspring since approximately 50% of males with Klinefelter syndrome can producesperm
Sperm (: sperm or sperms) is the male reproductive Cell (biology), cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm ...
.
Psychological characteristics
Cognitive development
Some degree of language learning or reading impairment may be present, and neuropsychological testing often reveals deficits inexecutive functions
In cognitive science and neuropsychology, executive functions (collectively referred to as executive function and cognitive control) are a set of cognitive processes that support goal-directed behavior, by regulating thoughts and actions thro ...
, although these deficits can often be overcome through early intervention. It is estimated that 10% of those with Klinefelter syndrome are autistic
Autism, also known as autism spectrum disorder (ASD), is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by differences or difficulties in social communication and interaction, a preference for predictability and routine, sensory processing di ...
. Additional abnormalities may include impaired attention, reduced organizational and planning abilities, deficiencies in judgment (often presented as a tendency to interpret non-threatening stimuli as threatening), and dysfunctional decision processing.
The overall IQ tends to be lower than average. Language milestones may also be delayed, particularly when compared to other people their age. Between 25% and 85% of males with XXY have some kind of language problem, such as delay in learning to speak, trouble using language to express thoughts and needs, problems reading, and trouble processing what they hear. They may also have a harder time doing work that involves reading and writing, but most hold jobs and have successful careers.
Behavior and personality traits
Compared to individuals with a normal number of chromosomes, males affected by Klinefelter syndrome may display behavioral differences. These are phenotypically displayed as higher levels of anxiety and depression, mood dysregulation, impaired social skills, emotional immaturity during childhood, and low frustration tolerance. These neurocognitive disabilities are most likely due to the presence of the extra X chromosome, as indicated by studies carried out on animal models carrying an extra X chromosome. In 1995, a scientific study evaluated the psychosocial adaptation of 39 adolescents with sex chromosome abnormalities. It demonstrated that males with XXY tend to be quiet, shy and undemanding; they are less self-confident, less active, and more helpful and obedient than other children their age. They may struggle in school and sports, meaning they may have more trouble "fitting in" with other kids. As adults, they live lives similar to others without the condition; they have friends, families, and normal social relationships. Nonetheless, some individuals may experience social and emotional problems due to problems in childhood. They show a lower sex drive and low self-esteem, in most cases due to their feminine physical characteristics.Concomitant illness
Those with XXY are more likely than others to have certain health problems, such asautoimmune disorders
An autoimmune disease is a condition that results from an anomalous response of the adaptive immune system, wherein it mistakenly targets and attacks healthy, functioning parts of the body as if they were foreign organisms. It is estimated tha ...
, breast cancer
Breast cancer is a cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a Breast lump, lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, Milk-rejection sign, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipp ...
, venous thromboembolic disease, and osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to more porous bone, and consequent increase in Bone fracture, fracture risk.
It is the most common reason f ...
. Nonetheless, the risk of breast cancer is still below the normal risk for women. These patients are also more prone to develop cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina, heart attack), heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumati ...
due to the predominance of metabolic abnormalities such as dyslipidemia
Dyslipidemia is a metabolic disorder characterized by abnormally high or low amounts of any or all lipids (e.g. fats, triglycerides, cholesterol, phospholipids) or lipoproteins in the blood. Dyslipidemia is a risk factor for the development of ...
and type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes (T2D), formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent ...
. It has not been demonstrated that hypertension is related with KS.
In contrast to these potentially increased risks, rare X-linked recessive ''Main Article'': Sex linkage
X-linked recessive inheritance is a mode of Mendelian inheritance, inheritance in which a mutation in a gene on the X chromosome causes the phenotype to be always expressed in males (who are necessarily hemizygous for ...
conditions are thought to occur less frequently in those with XXY than in those without, since these conditions are transmitted by genes on the X chromosome, and people with two X chromosomes are typically only carriers rather than affected by these X-linked recessive conditions.
Cause
nondisjunction
Nondisjunction is the failure of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate properly during cell division (mitosis/meiosis). There are three forms of nondisjunction: failure of a pair of homologous chromosomes to separate in meiosis I ...
event during paternal meiosis I
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one co ...
, maternal meiosis I, or maternal meiosis II, also known as gametogenesis
Gametogenesis is a biological process by which diploid or haploid precursor cells undergo cell division and differentiation to form mature haploid gametes. Depending on the biological life cycle of the organism, gametogenesis occurs by meiotic d ...
. The relevant nondisjunction in meiosis I occurs when homologous chromosomes, in this case the X and Y or two X sex chromosomes, fail to separate, producing a sperm with an X and a Y chromosome or an egg with two X chromosomes. Fertilizing a normal (X) egg with this sperm produces an XXY or Klinefelter offspring. Fertilizing a double X egg with a normal sperm also produces an XXY or Klinefelter offspring.
Another mechanism for retaining the extra chromosome is through a nondisjunction event during meiosis II in the egg. Nondisjunction occurs when sister chromatids on the sex chromosome, in this case an X and an X, fail to separate. An XX egg is produced, which when fertilized with a Y sperm, yields an XXY offspring. This XXY chromosome arrangement is one of the most common genetic variations from the XY karyotype, occurring in approximately one in 500 live male births.
In mammals with more than one X chromosome, the genes on all but one X chromosome are not expressed; this is known as X inactivation
X-inactivation (also called Lyonization, after English geneticist Mary F. Lyon, Mary Lyon) is a process by which one of the copies of the X chromosome is inactivated in therian female mammals. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by being ...
. This happens in XXY males, as well as normal XX females. However, in XXY males, a few genes located in the pseudoautosomal region
The pseudoautosomal regions or PARs are Homology (biology), homologous sequences of Nucleotide, nucleotides found within the Sex chromosome, sex chromosomes of species with an XY sex-determination system, XY or ZW sex-determination system, ZW mech ...
s of their X chromosomes have corresponding genes on their Y chromosome and are capable of being expressed.
Variations
The condition 48, XXYY or 48, XXXY occurs in one in 18,000–50,000 male births. The incidence of 49, XXXXY is one in 85,000 to 100,000 male births. These variations are extremely rare. Additional chromosomal material can contribute to cardiac, neurological, orthopedic, urinogenital and other anomalies. Thirteen cases of individuals with a 47,XXY karyotype and a female phenotype have been described. Approximately 15–20% of males with KS may have amosaic
A mosaic () is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/Mortar (masonry), mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and ...
47,XXY/46,XY constitutional karyotype and varying degrees of spermatogenic failure. Often symptoms are milder in mosaic cases, with regular male secondary sex characteristics and testicular volume even falling within typical adult ranges. Another possible mosaicism is 47,XXY/46,XX with clinical features suggestive of KS and male phenotype, but this is very rare. Thus far, only about 10 cases of 47,XXY/46,XX have been described in literature.
Analogous XXY syndromes are known to occur in cat
The cat (''Felis catus''), also referred to as the domestic cat or house cat, is a small domesticated carnivorous mammal. It is the only domesticated species of the family Felidae. Advances in archaeology and genetics have shown that the ...
s—specifically, the presence of calico or tortoiseshell markings in male cats is an indicator of the relevant abnormal karyotype. As such, male cats with calico or tortoiseshell markings are a model organism
A model organism is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workings of other organisms. Mo ...
for KS, because a color gene involved in cat tabby
A tabby cat, or simply tabby, is any domestic cat (''Felis catus'') with a coat pattern distinguished by an M-shaped marking on its forehead, stripes by its eyes and across its cheeks, along its back, around its legs and tail, and characteris ...
coloration is on the X chromosome.
Mosaicism
Approximately 15–20% of males with KS may have amosaic
A mosaic () is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/Mortar (masonry), mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and ...
47,XXY/46,XY constitutional karyotype and varying degrees of spermatogenic failure. Often, symptoms are milder in mosaic cases, with regular male secondary sex characteristics and testicular volume even falling within typical adult ranges. Another possible mosaicism is 47,XXY/46,XX with clinical features suggestive of KS and male phenotype, but this is very rare. Thus far, only approximately 10 cases of 47,XXY/46,XX have been described in literature.
Random versus skewed X-inactivation
Women typically have two X chromosomes, with half of their X chromosomes switching off early in embryonic development. The same happens with people with Klinefelter's, including in both cases a small proportion of individuals with a skewed ratio between the two Xs.Pathogenesis
The term "hypogonadism
Hypogonadism means diminished functional activity of the human gonad, gonads—the testicles or the ovary, ovaries—that may result in diminished biosynthesis, production of sex hormones. Low androgen (e.g., testosterone) levels are referred t ...
" in XXY symptoms is often misinterpreted to mean "small testicles", when it instead means decreased testicular hormone/endocrine function. Because of (primary) hypogonadism, individuals often have a low serum testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting se ...
level, but high serum follicle-stimulating hormone
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) is a gonadotropin, a glycoprotein polypeptide hormone. FSH is synthesized and secreted by the gonadotropic cells of the anterior pituitary gland and regulates the development, growth, puberty, pubertal maturat ...
and luteinizing hormone
Luteinizing hormone (LH, also known as luteinising hormone, lutropin and sometimes lutrophin) is a hormone produced by gonadotropic cells in the anterior pituitary gland. The production of LH is regulated by gonadotropin-releasing hormone (G ...
levels, hypergonadotropic hypogonadism. Despite this misunderstanding of the term, testicular growth also is arrested.
Destruction and hyalinization of the seminiferous tubules
Seminiferous tubules are located within the testicles, and are the specific location of meiosis, and the subsequent creation of male gametes, namely spermatozoa.
Structure
The epithelium of the tubule consists of a type of sustentacular cells ...
cause a reduction in the function of Sertoli cells
Sertoli cells are a type of sustentacular "nurse" cell found in human testes which contribute to the process of spermatogenesis (the production of sperm) as a structural component of the seminiferous tubules. They are activated by follicle-sti ...
and Leydig cells, leading to decreased production of FSH and testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting se ...
. This results in impaired spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis is the process by which haploid spermatozoa develop from germ cells in the seminiferous tubules of the testicle. This process starts with the Mitosis, mitotic division of the stem cells located close to the basement membrane of ...
and further endocrine dysfunction.
Diagnosis
The standard diagnostic method is the analysis of the chromosomes' karyotype onlymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include T cells (for cell-mediated and cytotoxic adaptive immunity), B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity), an ...
s. A small blood sample is sufficient as test material. In the past, the observation of the Barr body was common practice, as well. To investigate the presence of a possible mosaicism, analysis of the karyotype using cells from the oral mucosa is performed. Physical characteristics of a Klinefelter syndrome can be tall stature, low body hair, and occasionally an enlargement of the breast. Usually, a small testicle volume of 1–5 ml per testicle (standard values: 12–30 ml) occurs. During puberty and adulthood, low testosterone levels with increased levels of the pituitary hormones FSH and LH in the blood can indicate the presence of Klinefelter syndrome. A spermiogram can also be part of the further investigation. Often, an azoospermia is present, or rarely an oligospermia. Furthermore, Klinefelter syndrome can be diagnosed as a coincidental prenatal finding in the context of invasive prenatal diagnosis (amniocentesis, chorionic villus sampling). Approximately 10% of KS cases are found by prenatal diagnosis
Prenatal testing is a tool that can be used to detect some birth defects at various stages prior to birth. Prenatal testing consists of prenatal screening and prenatal diagnosis, which are aspects of prenatal care that focus on detecting problem ...
.
The symptoms of KS are often variable, so a karyotype analysis should be ordered when small testes, infertility, gynecomastia, long arms/legs, developmental delay, speech/language deficits, learning disabilities/academic issues, and/or behavioral issues are present in an individual.
Prognosis
The lifespan of individuals with Klinefelter syndrome appears to be reduced by around 2.1 years compared to the general male population. These results are still questioned data, are not absolute, and need further testing.Treatment
As the genetic variation is irreversible, no causal therapy is available. From the onset of puberty, the existing testosterone deficiency can be compensated by appropriate hormone-replacement therapy. Testosterone preparations are available in the form of syringes, patches, or gel. If gynecomastia is present, the surgical removal of the breast may be considered for psychological benefits and to reduce the risk of breast cancer. The use ofbehavioral therapy
Behaviour therapy or behavioural psychotherapy is a broad term referring to clinical psychotherapy that uses techniques derived from behaviourism and/or cognitive psychology. It looks at specific, learned behaviours and how the environment, or oth ...
can mitigate any language disorders, difficulties at school, and socialization. An approach by occupational therapy
Occupational therapy (OT), also known as ergotherapy, is a healthcare profession. Ergotherapy is derived from the Greek wiktionary:ergon, ergon which is allied to work, to act and to be active. Occupational therapy is based on the assumption t ...
is useful in children, especially those who have dyspraxia.
Infertility treatment
intracytoplasmic sperm injection
Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI ) is an in vitro fertilization (IVF) procedure in which a single sperm cell is injected directly into the cytoplasm of an egg. This technique is used in order to prepare the gametes for the obtention of embr ...
(ICSI) with previously conducted testicular sperm extraction (TESE), have led to men with Klinefelter syndrome producing biological offspring. By 2010, over 100 successful pregnancies have been reported using in vitro fertilization
In vitro fertilisation (IVF) is a process of fertilisation in which an egg is combined with sperm in vitro ("in glass"). The process involves monitoring and stimulating the ovulatory process, then removing an ovum or ova (egg or eggs) from ...
technology with surgically removed sperm material from men with KS.
History
The syndrome was named after American endocrinologistHarry Klinefelter
Harry Fitch Klinefelter Jr. (; March 20, 1912 – February 20, 1990) was an American rheumatologist and endocrinologist. Klinefelter syndrome is named after him.
Biography
Born March 20, 1912, in Baltimore, Klinefelter studied first at the Univer ...
, who in 1942 worked with Fuller Albright and E. C. Reifenstein at Massachusetts General Hospital
Massachusetts General Hospital (Mass General or MGH) is a teaching hospital located in the West End neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts. It is the original and largest clinical education and research facility of Harvard Medical School/Harvar ...
in Boston, Massachusetts
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
, and first described it in the same year. The account given by Klinefelter came to be known as Klinefelter syndrome as his name appeared first on the published paper, and seminiferous tubule dysgenesis was no longer used. Considering the names of all three researchers, it is sometimes also called Klinefelter–Reifenstein–Albright syndrome. In 1956, Klinefelter syndrome was found to result from an extra chromosome. Plunkett and Barr found the sex chromatin body in cell nuclei of the body. This was further clarified as XXY in 1959 by Patricia Jacobs
Patricia Ann Jacobs (born 8 October 1934) is a Scottish Human genetics, geneticist and is Honorary Professor of Human Genetics, Co-director of Research, Wessex Regional Genetics Laboratory, within the University of Southampton.
Early life and e ...
and John Anderson Strong. The first published report of a man with a 47,XXY karyotype was by Patricia Jacobs and John Strong at Western General Hospital in Edinburgh, Scotland
Edinburgh is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. The city is located in southeast Scotland and is bounded to the north by the Firth of Forth and to the south by the Pentland Hills. Edinburgh ...
, in 1959. This karyotype was found in a 24-year-old man who had signs of KS. Jacobs described her discovery of this first reported human or mammalian chromosome aneuploidy
Aneuploidy is the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell (biology), cell, for example a human somatic (biology), somatic cell having 45 or 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46. It does not include a difference of one or more plo ...
in her 1981 William Allan Memorial Award address.
Klinefelter syndrome has been identified in ancient burials. In August 2022, a team of scientists published a study of a skeleton found in Bragança, north-eastern Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
, of a man who died around 1000 AD and was discovered by their investigations to have a 47,XXY karyotype. In 2021, bioarchaeological investigation of the individual buried with the Suontaka sword, previously assumed to be a woman, concluded that person "whose gender identity may well have been non-binary", had Klinefelter syndrome.
Cultural and social impacts
In many societies, the symptoms of Klinefelter syndrome have contributed to significantsocial stigma
Stigma, originally referring to the visible marking of people considered inferior, has evolved to mean a negative perception or sense of disapproval that a society places on a group or individual based on certain characteristics such as their ...
, particularly due to infertility and gynecomastia. Historically, these traits were often associated with a perceived lack of masculinity
Masculinity (also called manhood or manliness) is a set of attributes, behaviors, and roles generally associated with men and boys. Masculinity can be theoretically understood as Social construction of gender, socially constructed, and there i ...
, which could result in social ostracism. However, in recent years, increased awareness and advocacy have led to a reduction in stigma, with individuals diagnosed with KS more likely to receive proper medical care and support. Advocacy organizations, such as the American Association for Klinefelter Syndrome Information and Support (AAKSIS), have played a crucial role in promoting understanding and improving the quality of life for affected individuals.
Epidemiology
This syndrome, evenly distributed in allethnic groups
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, traditions, society, rel ...
, has a prevalence
In epidemiology, prevalence is the proportion of a particular population found to be affected by a medical condition (typically a disease or a risk factor such as smoking or seatbelt use) at a specific time. It is derived by comparing the number o ...
of approximately four subjects per every 10,000 (0.04%) males in the general population. However, it is estimated that only 25% of the individuals with Klinefelter syndrome are diagnosed throughout their lives. The rate of Klinefelter syndrome among infertile males is 3.1%. The syndrome is the main cause of male hypogonadism. One survey in the United Kingdom found that the majority of people with KS identify as male, however, a significant number have a different gender identity
Gender identity is the personal sense of one's own gender. Gender identity can correlate with a person's assigned sex or can differ from it. In most individuals, the various biological determinants of sex are congruent and consistent with the in ...
. The prevalence of KS is higher than expected in transgender women.
See also
* Sex chromosome anomalies *Aneuploidy
Aneuploidy is the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell (biology), cell, for example a human somatic (biology), somatic cell having 45 or 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46. It does not include a difference of one or more plo ...
* Intersex
Intersex people are those born with any of several sex characteristics, including chromosome patterns, gonads, or genitals that, according to the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights, "do not fit typical binar ...
* Taurodontism
* Trisomy X
Trisomy X, also known as triple X syndrome and characterized by the karyotype 47,XXX, is a chromosome disorder in which a female has an extra copy of the X chromosome. It is relatively common and occurs in 1 in 1,000 females, but is rarely diagn ...
* Turner syndrome
Turner syndrome (TS), commonly known as 45,X, or 45,X0,Also written as 45,XO. is a chromosomal disorder in which cells of females have only one X chromosome instead of two, or are partially missing an X chromosome (sex chromosome monosomy) lea ...
* XYY syndrome
XYY syndrome, also known as Jacobs syndrome, is an aneuploid genetic condition in which a male has an extra Y chromosome. There are usually few symptoms. These may include being taller than average and an increased risk of learning disabiliti ...
* XXYY syndrome
References
Further reading
*External links
{{Authority control Diseases named after discoverers Genetic anomalies Intersex variations Sex chromosome aneuploidies Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate 1940s neologisms