40×46mm on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
40 mm grenade (also styled 40mm grenade) is a generic class-name for
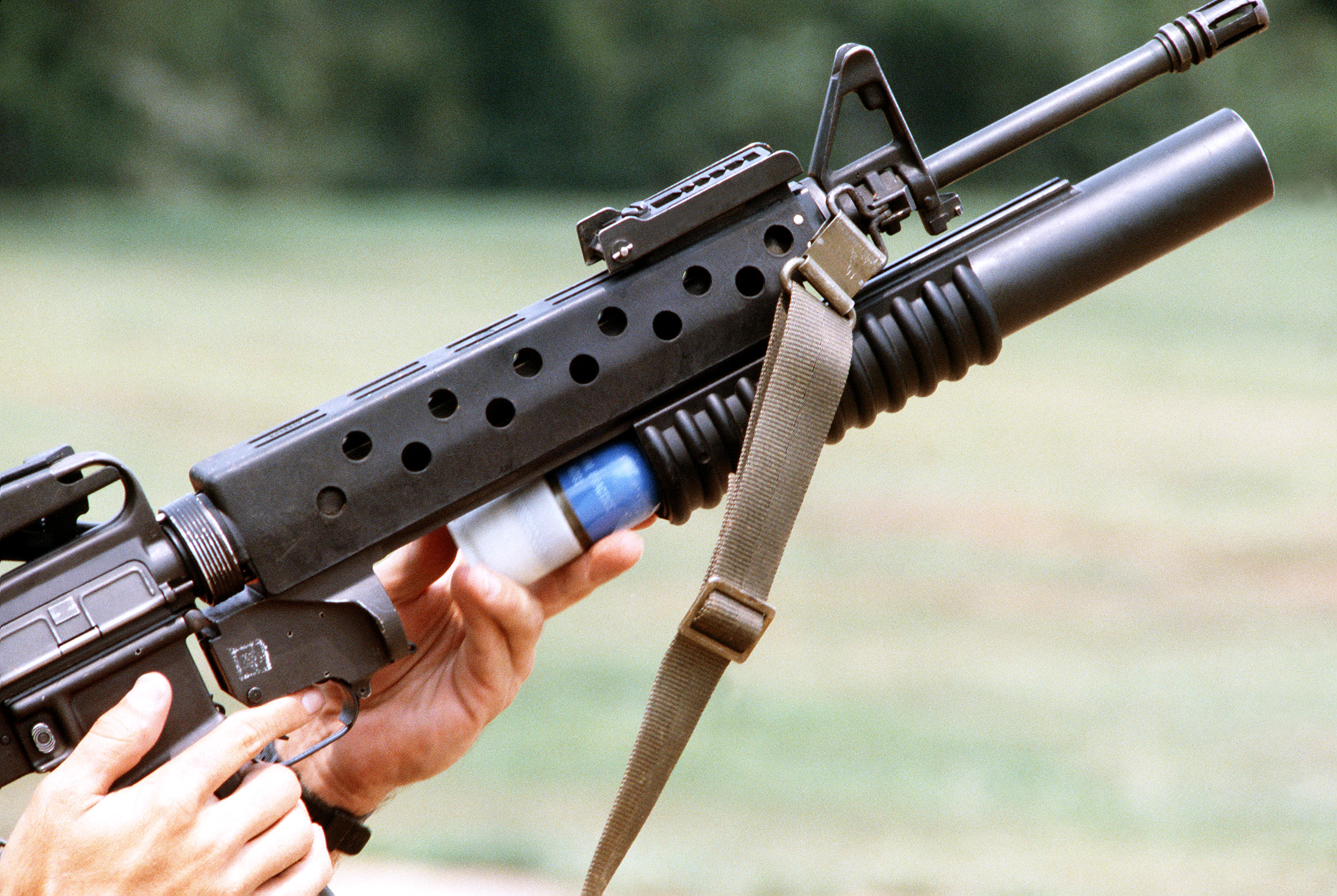

 ''40×46 mm LV'' (''low velocity'') is a NATO-standard high–low
''40×46 mm LV'' (''low velocity'') is a NATO-standard high–low
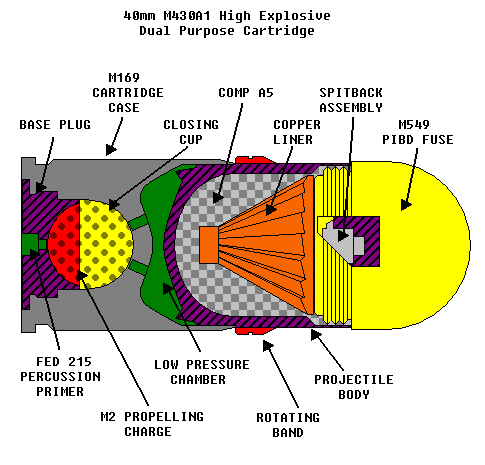
 ''40×53 mm HV'' (''high velocity'') is a NATO-standard high–low grenade launcher cartridge meant for mounted or crew-served automatic grenade launchers, such as the Mk.19 AGL,
''40×53 mm HV'' (''high velocity'') is a NATO-standard high–low grenade launcher cartridge meant for mounted or crew-served automatic grenade launchers, such as the Mk.19 AGL,
 40×47 mm is a cartridge caliber produced in Poland for their Pallad wz. 74 rifle-mounted grenade launchers (used with the AK family of rifles in the Polish Army, like the AKM/AKMS, Tantal and Beryl) and Pallad-D wz. 83 grenade launcher (standalone variant fitted with standard pistol grip and folding stock from the AKMS assault rifle). The construction is similar to the one used in 40×46 mm grenades, but they are not interchangeable.
40×47 mm is a cartridge caliber produced in Poland for their Pallad wz. 74 rifle-mounted grenade launchers (used with the AK family of rifles in the Polish Army, like the AKM/AKMS, Tantal and Beryl) and Pallad-D wz. 83 grenade launcher (standalone variant fitted with standard pistol grip and folding stock from the AKMS assault rifle). The construction is similar to the one used in 40×46 mm grenades, but they are not interchangeable.
 40×47 mm is a cartridge caliber produced in Romania for their AG-40 model 77 and model 80 (today AG-40P) rifle-mounted grenade launchers. It features a casing with a high–low system. The propellant has low pressure and gives the projectile an average velocity of depending on the ammunition type.
Production was originally handled by the arms factory ''Uzina Mecanica Filiasi'', however production was later moved to the arms factory ''Uzina Mecanica Tohan Zărnești'', today more commonly known as ''S. Tohan S.A.'', a subsidiary of ROMARM.
Several types of the Romanian 40×47 mm exist:
* High explosive
* High-explosive fragmentation
* Smoke
* Incendiary
* Tear gas
* Practice, featuring a small flash charge and smoke signal.
* Inert
Tohan currently (2021) offers a 40×47 mm high explosive type called GETZ (Grenadă Explozivă Tohan Zărnești) and an inert version called GITZ (Grenadă Inertă Tohan Zărnești). Both cartridges are long, with GETZ weighing and GITZ .
40×47 mm is a cartridge caliber produced in Romania for their AG-40 model 77 and model 80 (today AG-40P) rifle-mounted grenade launchers. It features a casing with a high–low system. The propellant has low pressure and gives the projectile an average velocity of depending on the ammunition type.
Production was originally handled by the arms factory ''Uzina Mecanica Filiasi'', however production was later moved to the arms factory ''Uzina Mecanica Tohan Zărnești'', today more commonly known as ''S. Tohan S.A.'', a subsidiary of ROMARM.
Several types of the Romanian 40×47 mm exist:
* High explosive
* High-explosive fragmentation
* Smoke
* Incendiary
* Tear gas
* Practice, featuring a small flash charge and smoke signal.
* Inert
Tohan currently (2021) offers a 40×47 mm high explosive type called GETZ (Grenadă Explozivă Tohan Zărnești) and an inert version called GITZ (Grenadă Inertă Tohan Zărnești). Both cartridges are long, with GETZ weighing and GITZ .
 ''40 mm VOG-25'' (
''40 mm VOG-25'' (
Milkor Worldwide
Defense Review overview of Mk 47 Mod 0 'Striker' 40mm Grenade Machine Gun
Defense Review overview of Corner Shot 40 personal grenade launcher
Defense Review overview of Penn Arms PGL65-40 'Fourkiller Tactical Model' 40 mm Multiple Grenade Launcher
Defense Review overview of Metal Storm 40mm Weapon System
{{Modern US Infantry Weapons Grenades Ammunition Projectiles Military cartridges Paramilitary cartridges Large-caliber cartridges
grenade launcher
A grenade launcher is a weapon that fires a specially-designed large-caliber projectile, often with an explosive, smoke or gas warhead. Today, the term generally refers to a class of dedicated firearms firing unitary grenade cartridges. The mos ...
ammunition
Ammunition (informally ammo) is the material fired, scattered, dropped, or detonated from any weapon or weapon system. Ammunition is both expendable weapons (e.g., bombs, missiles, grenades, land mines) and the component parts of other weap ...
(subsonic
Subsonic may refer to:
Motion through a medium
* Any speed lower than the speed of sound within a sound-propagating medium
* Subsonic aircraft, a flying machine that flies at air speeds lower than the speed of sound
* Subsonic ammunition, a type o ...
shells) in caliber
In guns, particularly firearms, caliber (or calibre; sometimes abbreviated as "cal") is the specified nominal internal diameter of the gun barrel Gauge (firearms) , bore – regardless of how or where the bore is measured and whether the f ...
. The generic name stems from the fact that several countries have developed or adopted grenade launchers in 40 mm caliber.
This is a general collection of the world's many different "40 mm grenades".
NATO
NATO currently uses three standardized 40 mm grenade families: 40 mm low velocity (LV), 40 mm medium velocity (MV), and 40 mm high velocity (HV). Low- and medium-velocity cartridges are used for different hand-heldgrenade launcher
A grenade launcher is a weapon that fires a specially-designed large-caliber projectile, often with an explosive, smoke or gas warhead. Today, the term generally refers to a class of dedicated firearms firing unitary grenade cartridges. The mos ...
s, while the high-velocity cartridge is used for automatic grenade launchers.
40×46 mm LV (40 mm low velocity)

 ''40×46 mm LV'' (''low velocity'') is a NATO-standard high–low
''40×46 mm LV'' (''low velocity'') is a NATO-standard high–low grenade launcher
A grenade launcher is a weapon that fires a specially-designed large-caliber projectile, often with an explosive, smoke or gas warhead. Today, the term generally refers to a class of dedicated firearms firing unitary grenade cartridges. The mos ...
cartridge meant for hand-held grenade launchers, such as the M79, M203, Milkor MGL, and Heckler & Koch AG36.
The propellant has low pressure and gives the projectile an average velocity of depending on the ammunition type.
40 mm low-velocity ammunition types (NATO)
Besides combat ammo there also exists crowd control ammunition like sponge grenades.40 mm low-velocity ammunition types (Sweden)
Sweden currently operates theM203 grenade launcher
The M203 is a single-shot 40 mm under-barrel grenade launcher designed to attach to a rifle. It uses the same rounds as the older stand-alone M79 break-action grenade launcher, which utilizes the high-low propulsion system to keep recoil force ...
(designated in Sweden) and thus uses the 40 mm low-velocity cartridge. Going against Swedish military tradition, the 40 mm low-velocity cartridge currently lacks a specified indigenous designation in Swedish service. Instead only the projectile types have designations.
Currently these projectile types can be found in Swedish service manuals.
Mockups and inert types also exist for loading exercises and educational purposes.
40 mm low-velocity ammunition types (Romania)
Romanian arms producer ROMARM has made a version of their 40 mm rifle-mounted grenade launcher AG-40 chambered in 40×46 mm NATO (then designated AG-40PN). Production of Romanian 40 mm low-velocity ammunition is handled by the arms factory , a subsidiary of ROMARM. The projectiles seem to be of Romanian origin based on available information.SAGM fuze
The United States Army Armament Research, Development and Engineering Center (ARDEC) began development of a 40 mm smart airburstfuze
In military munitions, a fuze (sometimes fuse) is the part of the device that initiates function. In some applications, such as torpedoes, a fuze may be identified by function as the exploder. The relative complexity of even the earliest fuze d ...
(proximity fuze
A proximity fuze (or fuse) is a Fuze (munitions), fuze that detonates an Explosive material, explosive device automatically when the distance to the target becomes smaller than a predetermined value. Proximity fuzes are designed for targets such ...
) in 2011 to improve the ability of grenade launchers like the M203 and M320 to engage targets in defilade. Called ''small arms grenade munition
Small may refer to:
Science and technology
* SMALL, an ALGOL-like programming language
* Small (anatomy), the lumbar region of the back
* ''Small'' (journal), a nano-science publication
* <small>, an HTML element that defines smaller text
...
s'' (SAGMs), they double the lethality of the standard M433 grenade round by adding a small "smart" fuze sensor that detonates in the air to hit targets in cover or behind obstacles. The airburst function is similar to the XM25 CDTE, which has an onboard laser system to determine the distance to the target, but SAGMs are considered complementary to the XM25 rather than competing against it, as the XM25 provides low-angle fire while 40 mm launchers fire a lobbing trajectory. Integrated sensors and logic devices scan and filter the environment and then autonomously airburst the fuze without needing to be told to by the firer, thereby not requiring the soldier to carry extra weapon accessories. SAGMs enable soldiers to accurately incapacitate personnel targets in defilade at ranges between 50 and 500 meters. The round is engineered with three firing modes: airburst; point detonation; and self-destruct. A successful demonstration occurred in November 2013. Although the SAGM sensor does not need a laser rangefinder or any pre-fire programming sequence, it does require some skill by the user to aim and fire the round correctly so that it can detect the wall or obstruction to detonate in the air. The SAGM was to undergo evaluation in July 2015 and, if successful, transition into an official Army Program of Record by the end of the year. Not only does the fuze burst over walls, but it can detonate when passing cover like trees, bursting just as it senses and passes the trunk. The sort of sensor
A sensor is a device that produces an output signal for the purpose of sensing a physical phenomenon.
In the broadest definition, a sensor is a device, module, machine, or subsystem that detects events or changes in its environment and sends ...
SAGMs use to differentiate clutter from triggering obstacles is highly classified, but shows airburst reliability of 76 percent.
40×51 mm MV (40 mm medium velocity)
''40×51 mm MV'' (medium velocity), also known as ''40×51 mm extended range low pressure'' (ERLP), is a NATO-standard high–low grenade launcher cartridge meant for hand-held grenade launchers. Its purpose is to be an intermediate cartridge between the 40×46 mm low-velocity and 40×53 mm high-velocity cartridges and is thus referred to as 40 mm medium velocity. The propellant has medium pressure and gives the projectile an average velocity of depending on the ammunition type. It has a maximum range of 800 meters, exceeding conventional extended range low-velocity variants by up to 375 meters. The 40×51 mm MV cartridge was designed by Rheinmetall Denel Munitions for the US Special Operations Command (USSOCOM) after a 2008 requirement for enhanced range and lethality from hand-held 40 mm grenades. Rheinmetall answered by developing a new family of 40 mm grenades named 40 mm medium velocity and by 2019 the cartridge was undergoing NATO qualification. Besides NATO the cartridge has been ordered by the South African National Defence Force (SANDF) as the cartridge for their next generation multiple grenade launcher, the Milkor Y4. SANDF approved acquisition in February 2018 but deliveries could not be finished until the end of 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic.40×53 mm HV (40 mm high velocity)

 ''40×53 mm HV'' (''high velocity'') is a NATO-standard high–low grenade launcher cartridge meant for mounted or crew-served automatic grenade launchers, such as the Mk.19 AGL,
''40×53 mm HV'' (''high velocity'') is a NATO-standard high–low grenade launcher cartridge meant for mounted or crew-served automatic grenade launchers, such as the Mk.19 AGL, Mk 47 Striker
The Mk 47 or Striker 40 is a 40mm automatic grenade launcher with an integrated fire control system, capable of launching smart programmable 40mm air burst grenades in addition to various unguided rounds.
Design
The Mk 47 has the latest sensin ...
, HK GMG
The GMG (''Granatmaschinengewehr'' or "grenade machine gun") is an automatic grenade launcher developed by Heckler & Koch for the German Army. It is also often referred to as GMW or GraMaWa (''Granatmaschinenwaffe'').
Design details
The GMG f ...
, STK 40 AGL
The STK 40 AGL, formerly the CIS 40 AGL is a 40 mm automatic grenade launcher, developed in the late 1980s and produced by the Singaporean defence firm Chartered Industries of Singapore (CIS, now ST Kinetics). The launcher is employed primaril ...
, and Daewoo K4.
The propellant has high pressure and gives the projectile an average velocity of depending on the ammunition type.
40 mm high-velocity ammunition types (NATO)
40 mm high-velocity ammunition types (Sweden)
Sweden currently operates theMk 19 grenade launcher
The Mk 19 grenade launcher (pronounced Mark 19) is an American 40 mm belt-fed automatic grenade launcher that was first developed during the Vietnam War.
Overview
The Mk 19 is a belt-fed, blowback-operated, air-cooled, crew-serve ...
(designated ''40 mm granatspruta 92'' in Sweden) and thus uses the 40 mm high-velocity cartridge. Going against Swedish military tradition, the 40 mm high-velocity cartridge currently lacks a specified indigenous designation in Swedish service. Instead only the projectile types have designations.
Currently these projectile types can be found in Swedish service manuals.
Mockups and inert types also exist for loading exercises and educational purposes.
Green ammunition
The MK281 is a new type of 40 mm target practice grenade ammunition that has been accepted for use into the United States Marine Corps and the United States Army. It is "green" because it is non-toxic and non-dud producing (since it is a training round), meaning that there is no unexploded ordnance left to clean up on the range andheavy metals
upright=1.2, Crystals of osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead">lead.html" ;"title="osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead">osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead
Heavy metals are generally defined as ...
in the fuze do not leak into the ground. The MK281 was introduced into parts of the U.S. Armed Forces because of an executive order mandating that they buy green ammunition. The MK281 is manufactured by an American subsidiary of the Rheinmetall Group.
The United States Army has a requirement for a non-dud producing 40 mm training ammunition in both high- and low-velocity variants. The Army awarded four contracts to three United States companies to test designs. The resulting ammunition will not contain explosive energetics and have day and night visible, infrared, and thermal signatures.
Other
40×47 mm (Poland)
 40×47 mm is a cartridge caliber produced in Poland for their Pallad wz. 74 rifle-mounted grenade launchers (used with the AK family of rifles in the Polish Army, like the AKM/AKMS, Tantal and Beryl) and Pallad-D wz. 83 grenade launcher (standalone variant fitted with standard pistol grip and folding stock from the AKMS assault rifle). The construction is similar to the one used in 40×46 mm grenades, but they are not interchangeable.
40×47 mm is a cartridge caliber produced in Poland for their Pallad wz. 74 rifle-mounted grenade launchers (used with the AK family of rifles in the Polish Army, like the AKM/AKMS, Tantal and Beryl) and Pallad-D wz. 83 grenade launcher (standalone variant fitted with standard pistol grip and folding stock from the AKMS assault rifle). The construction is similar to the one used in 40×46 mm grenades, but they are not interchangeable.
40×47 mm (Romania)
 40×47 mm is a cartridge caliber produced in Romania for their AG-40 model 77 and model 80 (today AG-40P) rifle-mounted grenade launchers. It features a casing with a high–low system. The propellant has low pressure and gives the projectile an average velocity of depending on the ammunition type.
Production was originally handled by the arms factory ''Uzina Mecanica Filiasi'', however production was later moved to the arms factory ''Uzina Mecanica Tohan Zărnești'', today more commonly known as ''S. Tohan S.A.'', a subsidiary of ROMARM.
Several types of the Romanian 40×47 mm exist:
* High explosive
* High-explosive fragmentation
* Smoke
* Incendiary
* Tear gas
* Practice, featuring a small flash charge and smoke signal.
* Inert
Tohan currently (2021) offers a 40×47 mm high explosive type called GETZ (Grenadă Explozivă Tohan Zărnești) and an inert version called GITZ (Grenadă Inertă Tohan Zărnești). Both cartridges are long, with GETZ weighing and GITZ .
40×47 mm is a cartridge caliber produced in Romania for their AG-40 model 77 and model 80 (today AG-40P) rifle-mounted grenade launchers. It features a casing with a high–low system. The propellant has low pressure and gives the projectile an average velocity of depending on the ammunition type.
Production was originally handled by the arms factory ''Uzina Mecanica Filiasi'', however production was later moved to the arms factory ''Uzina Mecanica Tohan Zărnești'', today more commonly known as ''S. Tohan S.A.'', a subsidiary of ROMARM.
Several types of the Romanian 40×47 mm exist:
* High explosive
* High-explosive fragmentation
* Smoke
* Incendiary
* Tear gas
* Practice, featuring a small flash charge and smoke signal.
* Inert
Tohan currently (2021) offers a 40×47 mm high explosive type called GETZ (Grenadă Explozivă Tohan Zărnești) and an inert version called GITZ (Grenadă Inertă Tohan Zărnești). Both cartridges are long, with GETZ weighing and GITZ .
40×74.5 mm (Romania)
40×74.5 mm is a cartridge caliber produced in Romania for their AGA-40 Model 85 automatic grenade launcher. It features a casing with a high–low system. The propellant has high pressure and gives the projectile an average velocity of depending on the ammunition type. Production is handled by the arms factory ''Uzina Mecanica Plopeni'', a subsidiary of ROMARM. Three ammunition types are known: * A high-explosive grenade producing 150 fragments weighing each, creating a deadly radius of upon impact. * Ahigh-explosive dual-purpose
High-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) is the effect of a shaped charge explosive that uses the Munroe effect to penetrate heavy armor. The warhead functions by having an explosive charge collapse a metal liner inside the warhead into a high-velocity ...
grenade capable of penetrating of steel armor.
* An inert cartridge for loading exercise.
Caseless ammunition
40 mm VOG-25 (Russia)
 ''40 mm VOG-25'' (
''40 mm VOG-25'' (Russian Cyrillic
The Russian alphabet (russian: ру́сский алфави́т, russkiy alfavit, , label=none, or russian: ру́сская а́збука, russkaya azbuka, label=none, more traditionally) is the script used to write the Russian language. I ...
: ''ВОГ-25'') (GRAU-Index: 7P17 (Russian Cyrillic
The Russian alphabet (russian: ру́сский алфави́т, russkiy alfavit, , label=none, or russian: ру́сская а́збука, russkaya azbuka, label=none, more traditionally) is the script used to write the Russian language. I ...
: ''7П17'')) is a unique type of 40 mm grenade designed in the Soviet Union for hand-held grenade launchers, such as the Soviet GP-25 Kostyor and GP-30 Obuvka. Instead of a casing, the VOG-25 is caseless ammunition
Caseless ammunition (CL), or rather caseless cartridge, is a configuration of weapon-cartridge that eliminates the cartridge case that typically holds the primer, propellant and projectile together as a unit. Instead, the propellant and primer ar ...
, featuring its propellant in an expansion chamber at the base of the projectile, functioning more like a mortar round than conventional cased ammunition.
Today it is used primarily by the Russian Armed Forces
The Armed Forces of the Russian Federation (, ), commonly referred to as the Russian Armed Forces, are the military forces of Russia. In terms of active-duty personnel, they are the world's fifth-largest military force, with at least two m ...
in weapons such as the GP-34, BG-15 Mukha and RG-6. Several types exist but the most common version is the default VOG-25 high-explosive version.
The VOG-25 is long, weighs , and features a explosive charge. It has a muzzle velocity
Muzzle velocity is the speed of a projectile (bullet, pellet, slug, ball/shots or shell) with respect to the muzzle at the moment it leaves the end of a gun's barrel (i.e. the muzzle). Firearm muzzle velocities range from approximately to i ...
of and will self-destruct after 14 seconds.
40 mm Metal Storm (Australia)
During its time (1994–2012),Metal Storm Limited
Metal Storm Limited was a research and development company based in Brisbane, Australia, that specialized in electronically initiated superposed load weapons technology and owned the proprietary rights to the electronic ballistics technology ...
in Australia designed several automatic caseless 40 mm grenade launcher systems based on their own caseless ammunition weapon design. Unlike common caseless ammunition and their weapon systems the Metal Storm design lacked a feeding magazine and instead stacked the projectiles in front of each other in the barrel with the propellant in between the projectiles. The system lacked moving parts and the propellant was electronically primed, allowing for rates of fire up to one million rounds per minute.
The 40 mm grenades used in the systems were off the shelf existing warheads converted to function in the design.
See also
*35 mm grenade
The 35 mm grenade is a type of grenade launcher ammunition of Chinese origin. The type consists of many high-velocity and low-velocity grenades with a caliber of .
History
Thirty-five millimeter grenades are proprietary designs originating ...
* 40×46mmSR Hellhound
* United States 40 mm grenades
The United States Armed Forces has created a plethora of different types of 40 mm grenades in both the low-velocity 40×46 mm and high-velocity 40×53 mm calibers which uses what it calls a '' high-low propulsion system'' which keeps reco ...
Notes
References
External links
Milkor Worldwide
Defense Review overview of Mk 47 Mod 0 'Striker' 40mm Grenade Machine Gun
Defense Review overview of Corner Shot 40 personal grenade launcher
Defense Review overview of Penn Arms PGL65-40 'Fourkiller Tactical Model' 40 mm Multiple Grenade Launcher
Defense Review overview of Metal Storm 40mm Weapon System
{{Modern US Infantry Weapons Grenades Ammunition Projectiles Military cartridges Paramilitary cartridges Large-caliber cartridges