217 BC on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 __NOTOC__
Year 217 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Geminus and Flaminius/Regulus (or, less frequently, year 537 ''
__NOTOC__
Year 217 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Geminus and Flaminius/Regulus (or, less frequently, year 537 ''
 __NOTOC__
Year 217 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Geminus and Flaminius/Regulus (or, less frequently, year 537 ''
__NOTOC__
Year 217 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Geminus and Flaminius/Regulus (or, less frequently, year 537 ''Ab urbe condita
''Ab urbe condita'' ( 'from the founding of the City'), or ''anno urbis conditae'' (; 'in the year since the city's founding'), abbreviated as AUC or AVC, expresses a date in years since 753 BC, the traditional founding of Rome. It is an exp ...
''). The denomination 217 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini
The terms (AD) and before Christ (BC) are used to label or number years in the Julian and Gregorian calendars. The term is Medieval Latin and means 'in the year of the Lord', but is often presented using "our Lord" instead of "the Lord", ...
calendar era
A calendar era is the period of time elapsed since one ''epoch'' of a calendar and, if it exists, before the next one. For example, it is the year as per the Gregorian calendar, which numbers its years in the Western Christian era (the Coptic ...
became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Events
By place
Roman Republic
*Gaius Flaminius can refer to:
* Gaius Flaminius (consul 223 BC)
* Gaius Flaminius (consul 187 BC)
__NoToC__
Gaius Flaminius was Roman consul in 187 BC, together with Marcus Aemilius Lepidus. During his consulship, he fought to pacify Ligurian tribesmen who had ...
is re-elected consul
Consul (abbrev. ''cos.''; Latin plural ''consules'') was the title of one of the two chief magistrates of the Roman Republic, and subsequently also an important title under the Roman Empire. The title was used in other European city-states throug ...
with Gnaeus Servilius Geminus
Gnaeus Servilius Geminus (died August 2, 216 BC) was a Roman consul, serving as both general and admiral of Roman forces, during the Second Punic War.
The son of Publius Servilius Geminus, Gnaeus Geminus was elected as consul in early 217 BC. By M ...
, in what is considered to be a rebuke
In English law and the canon law of the Church of England, a rebuke is a censure on a member of the clergy. (Google Books) It is the least severe censure available against clergy of the Church of England, less severe than a monition. A rebuke can ...
of the Senate's prosecution of the war
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular o ...
. Flaminius raises new legion
Legion may refer to:
Military
* Roman legion, the basic military unit of the ancient Roman army
* Spanish Legion, an elite military unit within the Spanish Army
* Legion of the United States, a reorganization of the United States Army from 179 ...
s and marches north to meet the Carthaginian The term Carthaginian ( la, Carthaginiensis ) usually refers to a citizen of Ancient Carthage.
It can also refer to:
* Carthaginian (ship), a three-masted schooner built in 1921
* Insurgent privateers; nineteenth-century South American privateers, ...
general Hannibal
Hannibal (; xpu, 𐤇𐤍𐤁𐤏𐤋, ''Ḥannibaʿl''; 247 – between 183 and 181 BC) was a Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Puni ...
.
* Hannibal advances to the Arno River
The Arno is a river in the Tuscany region of Italy. It is the most important river of central Italy after the Tiber.
Source and route
The river originates on Monte Falterona in the Casentino area of the Apennines, and initially takes a s ...
and then outmanoeuvres the army
An army (from Old French ''armee'', itself derived from the Latin verb ''armāre'', meaning "to arm", and related to the Latin noun ''arma'', meaning "arms" or "weapons"), ground force or land force is a fighting force that fights primarily on ...
of Gaius Flaminius at Arretium
Arezzo ( , , ) , also ; ett, 𐌀𐌓𐌉𐌕𐌉𐌌, Aritim. is a city and ''comune'' in Italy and the capital of the province of the same name located in Tuscany. Arezzo is about southeast of Florence at an elevation of above sea level. ...
and reaches Faesulae
Fiesole () is a town and ''comune'' of the Metropolitan City of Florence in the Italian region of Tuscany, on a scenic height above Florence, 5 km (3 miles) northeast of that city. It has structures dating to Etruscan and Roman times.
Sin ...
(modern Fiesole
Fiesole () is a town and ''comune'' of the Metropolitan City of Florence in the Italian region of Tuscany, on a scenic height above Florence, 5 km (3 miles) northeast of that city. It has structures dating to Etruscan and Roman times.
Sin ...
) and Perugia
Perugia (, , ; lat, Perusia) is the capital city of Umbria in central Italy, crossed by the River Tiber, and of the province of Perugia.
The city is located about north of Rome and southeast of Florence. It covers a high hilltop and part o ...
.
* June 21
Events Pre-1600
* 533 – A Byzantine expeditionary fleet under Belisarius sails from Constantinople to attack the Vandals in Africa, via Greece and Sicily (approximate date).
* 1307 – Külüg Khan is enthroned as Khagan of the Mo ...
– On the northern shore
A shore or a shoreline is the fringe of land at the edge of a large body of water, such as an ocean, sea, or lake. In physical oceanography, a shore is the wider fringe that is geologically modified by the action of the body of water past a ...
of Lake Trasimene
Lake Trasimeno ( , also ; it, Lago Trasimeno ; la, Trasumennus; ett, Tarśmina), also referred to as Trasimene ( ) or Thrasimene in English, is a lake in the province of Perugia, in the Umbria region of Italy on the border with Tuscany. Th ...
, in Umbria
it, Umbro (man) it, Umbra (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, ...
, Hannibal's troop
A troop is a military sub-subunit, originally a small formation of cavalry, subordinate to a squadron. In many armies a troop is the equivalent element to the infantry section or platoon. Exceptions are the US Cavalry and the King's Troop Ro ...
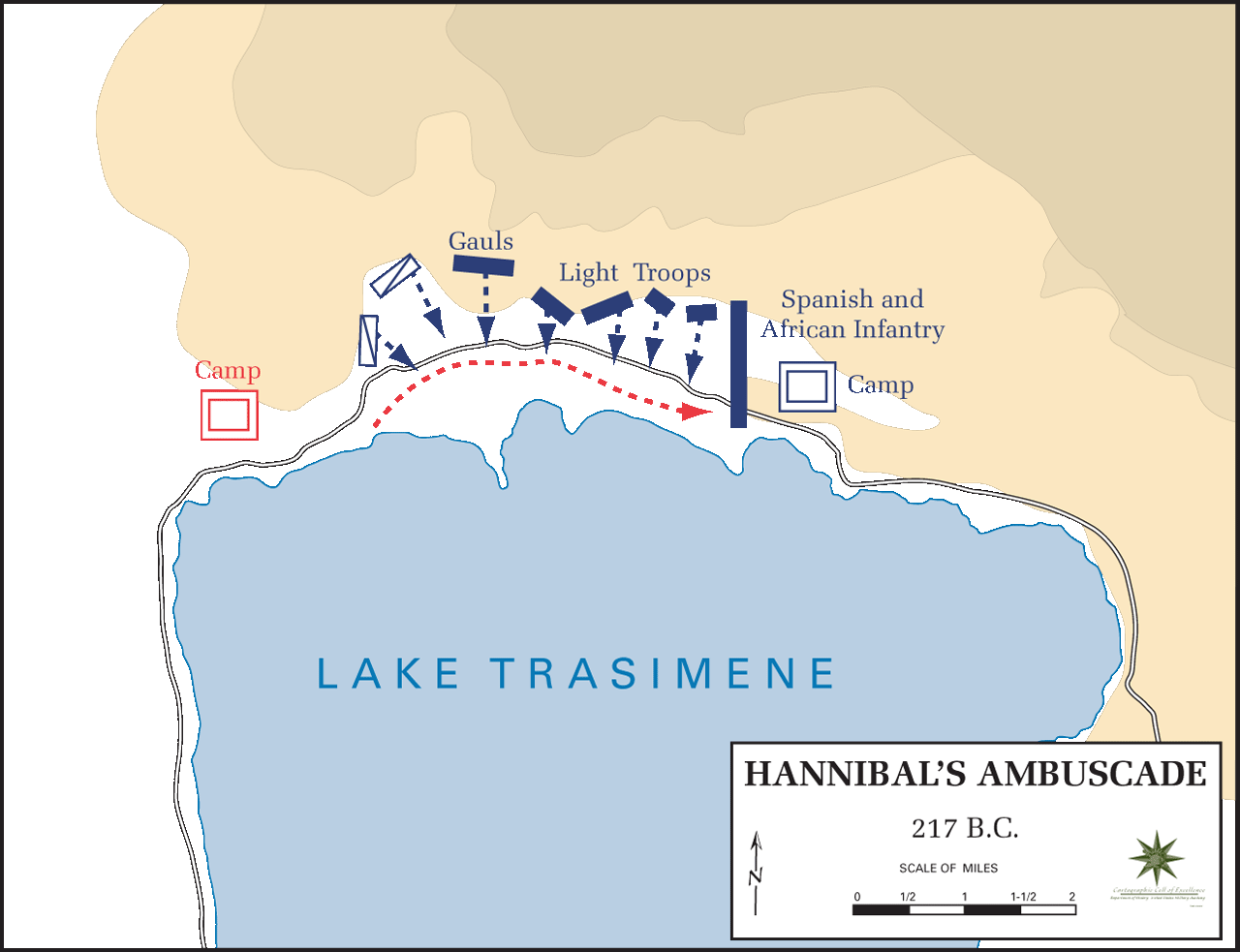
s all but annihilate Gaius Flaminius' army in the Battle of Lake Trasimene
The Battle of Lake Trasimene was fought when a Carthaginian force under Hannibal ambushed a Roman army commanded by Gaius Flaminius on 21 June 217 BC, during the Second Punic War. It took place on the north shore of Lake Trasimene, to the ea ...
, killing thousands (including Flaminius) and driving others to drown in the lake. Reinforcements of about 4,000 cavalry from Ariminum
Rimini ( , ; rgn, Rémin; la, Ariminum) is a city in the Emilia-Romagna region of northern Italy and capital city of the Province of Rimini. It sprawls along the Adriatic Sea, on the coast between the rivers Marecchia (the ancient ''Ariminus ...
under the praetor
Praetor ( , ), also pretor, was the title granted by the government of Ancient Rome to a man acting in one of two official capacities: (i) the commander of an army, and (ii) as an elected '' magistratus'' (magistrate), assigned to discharge vario ...
, Gaius Centenius Gaius Centenius ( fl. 3rd century BC) was a propraetor of the Roman army. He fought at the Second Punic War, and was defeated at the Battle of Lake Trasimene.
According to Polybius, the Roman consul Gnaeus Servilius Geminus, who was en route to mee ...
, are intercepted before they arrive and are also destroyed. The Carthaginian troops then march on Rome.
* Gaius Flaminius' supporters in the Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
begin to lose power to the more aristocratic factions as the Romans fear Hannibal is about to besiege their city. The Senate appoint Quintus Fabius Maximus Verrucosus
Quintus Fabius Maximus Verrucosus, surnamed Cunctator ( 280 – 203 BC), was a Roman statesman and general of the third century BC. He was consul five times (233, 228, 215, 214, and 209 BC) and was appointed dictator in 221 and 217 BC. He was ...
as dictator
A dictator is a political leader who possesses absolute power. A dictatorship is a state ruled by one dictator or by a small clique. The word originated as the title of a Roman dictator elected by the Roman Senate to rule the republic in times ...
.
* Quintus Fabius Maximus begins his strategy of "delay". This involves avoiding a set battle with the Carthaginians and creating a "scorched earth" area around Hannibal's army. Manoeuvring among the hills, where Hannibal's cavalry is ineffective, Fabius cuts off his enemy's supplies and harasses Hannibal's forces incessantly. Fabius gains the name ''Cunctator'' (''The Delayer'') for this strategy.
* Hannibal ravages Apulia
it, Pugliese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographic ...
and Campania
Campania (, also , , , ) is an administrative Regions of Italy, region of Italy; most of it is in the south-western portion of the Italian peninsula (with the Tyrrhenian Sea to its west), but it also includes the small Phlegraean Islands and the i ...
; meanwhile the delaying tactics of Quintus Fabius Maximus' army allows only skirmishes to occur between the two armies.
* Fabius' delaying policy becomes increasingly unpopular in Rome, and Fabius is compelled to return to Rome to defend his actions under the guise of observing some religious obligations. Marcus Minucius Rufus, the master of horse, is left in command and manages to catch the Carthaginians off guard near their camp in Geronium and inflicts severe losses on them in a large skirmish. This "victory" causes the Romans, disgruntled with Fabius, to elevate Minucius to the equal rank of dictator with Fabius.
* Minucius takes command of half the army and camps separately from Fabius near Geronium. Hannibal, informed of this development, lays an elaborate trap, which draws out Minucius and his army and then Hannibal attacks it from all sides. The timely arrival of Fabius with the other half of the army enables Minucius to escape after a severe mauling. After the battle, Minucius turns over his army to Fabius and resumes the duties of Master of Horse.
Egypt
*June 22
Events Pre-1600
* 217 BC – Battle of Raphia: Ptolemy IV Philopator of Egypt defeats Antiochus III the Great of the Seleucid kingdom.
* 168 BC – Battle of Pydna: Romans under Lucius Aemilius Paullus defeat Macedonian King Perseus ...
– Egyptian
Egyptian describes something of, from, or related to Egypt.
Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to:
Nations and ethnic groups
* Egyptians, a national group in North Africa
** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of years of ...
native hoplite
Hoplites ( ) ( grc, ὁπλίτης : hoplítēs) were citizen-soldiers of Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek Polis, city-states who were primarily armed with spears and shields. Hoplite soldiers used the phalanx formation to be effective in war with ...
s under Ptolemy IV
egy, Iwaennetjerwymenkhwy Setepptah Userkare Sekhemankhamun Clayton (2006) p. 208.
, predecessor = Ptolemy III
, successor = Ptolemy V
, horus = ''ḥnw-ḳni sḫꜤi.n-sw-it.f'Khunuqeni sekhaensuitef'' The strong youth whose f ...
crush the Seleucid
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
army under Antiochus III
Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας ; c. 2413 July 187 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 222 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the res ...
in the Battle of Raphia
The Battle of Raphia, also known as the Battle of Gaza, was fought on 22 June 217 BC near modern Rafah between the forces of Ptolemy IV Philopator, king and pharaoh of Ptolemaic Egypt and Antiochus III the Great of the Seleucid Empire during t ...
near Gaza. The realization of their military importance leads to demands by native Egyptians for greater privileges and so to the development of racial difficulties which will weaken the Ptolemy dynasty in the future.
* Although holding the initiative after the Battle of Raphia
The Battle of Raphia, also known as the Battle of Gaza, was fought on 22 June 217 BC near modern Rafah between the forces of Ptolemy IV Philopator, king and pharaoh of Ptolemaic Egypt and Antiochus III the Great of the Seleucid Empire during t ...
, Ptolemy IV, on his chief minister Sosibius
Sosibius ( el, Σωσίβιoς; lived 3rd century BC) was the chief minister of Ptolemy Philopator (221–204 BC), king of Egypt. Nothing is known of his origin or parentage, though he may have been a son of Sosibius of Tarentum; nor have we any ac ...
' advice, negotiates a peace, and the Seleucid army withdraws from Coele Syria
Coele-Syria (, also spelt Coele Syria, Coelesyria, Celesyria) alternatively Coelo-Syria or Coelosyria (; grc-gre, Κοίλη Συρία, ''Koílē Syría'', 'Hollow Syria'; lat, Cœlē Syria or ), was a region of Syria in classical antiquit ...
. Antiochus III gives up all his conquests except the city of Seleucia-in-Pieria.
Greece
*Philip V of Macedon
Philip V ( grc-gre, Φίλιππος ; 238–179 BC) was king ( Basileus) of Macedonia from 221 to 179 BC. Philip's reign was principally marked by an unsuccessful struggle with the emerging power of the Roman Republic. He would lead Macedon ag ...
, continuing his war with the Aetolian League
The Aetolian (or Aitolian) League ( grc-gre, Κοινὸν τῶν Αἰτωλῶν) was a confederation of tribal communities and cities in ancient Greece centered in Aetolia in central Greece. It was probably established during the early Hellen ...
lays siege to Phthiotic Thebes
Phthiotic Thebes ( grc, Θῆβαι Φθιώτιδες, Thebai Phthiotides or Φθιώτιδες Θήβες or Φθιώτιδος Θήβες; la, Thebae Phthiae) or Thessalian Thebes (Θῆβαι Θεσσαλικαἰ, ''Thebai Thessalikai'') was ...
, captures it and sells the inhabitants into slavery.
* Learning of Hannibal's victory over the Romans at Lake Trasimene
Lake Trasimeno ( , also ; it, Lago Trasimeno ; la, Trasumennus; ett, Tarśmina), also referred to as Trasimene ( ) or Thrasimene in English, is a lake in the province of Perugia, in the Umbria region of Italy on the border with Tuscany. Th ...
and seeing a chance to recover his Illyria
In classical antiquity, Illyria (; grc, Ἰλλυρία, ''Illyría'' or , ''Illyrís''; la, Illyria, ''Illyricum'') was a region in the western part of the Balkan Peninsula inhabited by numerous tribes of people collectively known as the Illyr ...
n kingdom from the Romans, Demetrius of Pharos
Demetrius of Pharos (also Pharus) ( grc, Δημήτριος ἐκ Φάρου and Δημήτριος ὁ Φάριος) was a ruler of Pharos involved in the First Illyrian War, after which he ruled a portion of the Illyrian Adriatic coast on beha ...
immediately advises Philip V to make peace with the Aetolians, and turn his attentions toward Illyria and Italy. Philip, at once begins negotiations with the Aetolians. At a conference on the coast near Naupactus
Nafpaktos ( el, Ναύπακτος) is a town and a former municipality in Aetolia-Acarnania, West Greece, situated on a bay on the north coast of the Gulf of Corinth, west of the mouth of the river Mornos.
It is named for Naupaktos (, Latinize ...
, Philip meets the Aetolian leaders and a peace treaty is concluded, ending the three-year-long "Social War".
Spain
* Publius Cornelius Scipio is sent with reinforcements by Rome toSpain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
as proconsul
A proconsul was an official of ancient Rome who acted on behalf of a consul. A proconsul was typically a former consul. The term is also used in recent history for officials with delegated authority.
In the Roman Republic, military command, or ' ...
. In a naval battle on the Ebro River
, name_etymology =
, image = Zaragoza shel.JPG
, image_size =
, image_caption = The Ebro River in Zaragoza
, map = SpainEbroBasin.png
, map_size =
, map_caption = The Ebro ...
at Tarraco
Tarraco is the ancient name of the current city of Tarragona (Catalonia, Spain). It was the oldest Roman settlement on the Iberian Peninsula. It became the capital of the Roman province of Hispania Citerior during the period of the Roman Republic ...
, the Carthaginian general Hasdrubal's fleet is largely destroyed by a daring surprise Roman attack led by Publius Cornelius Scipio and his brother Gnaeus Cornelius Scipio Calvus
Gnaeus Cornelius Scipio Calvus (died 211 BC) was a Roman general and statesman during the third century BC. He played a major part in the Second Punic War establishing Roman Rule in the east of the Iberian Peninsula and tying up several Carthagini ...
. As a result, the Romans are able to strengthen their hold on the Ebro River region.
Births
*Xin Zhui
Xin Zhui (; –168 or 169 BC), also known as Lady Dai, or Marquise of Dai, was a Chinese noblewoman, and wife to Li Cang (), the Marquis of Dai, and Chancellor of the Changsha Kingdom, during the Western Han dynasty of ancient China. Her tomb, ...
, a Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warr ...
noblewoman
Deaths
*Arsaces I Arsaces or Arsakes (, , Graecized form of Old Persian ) is the eponymous Greek form of the dynastic name of the Parthian Empire of Iran adopted by all epigraphically attested rulers of the Arsacid dynasties. The indigenous Parthian and Armenian fo ...
, King of Parthia
Parthia ( peo, 𐎱𐎼𐎰𐎺 ''Parθava''; xpr, 𐭐𐭓𐭕𐭅 ''Parθaw''; pal, 𐭯𐭫𐭮𐭥𐭡𐭥 ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Med ...
* Gaius Flaminius can refer to:
* Gaius Flaminius (consul 223 BC)
* Gaius Flaminius (consul 187 BC)
__NoToC__
Gaius Flaminius was Roman consul in 187 BC, together with Marcus Aemilius Lepidus. During his consulship, he fought to pacify Ligurian tribesmen who had ...
, Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
consul
Consul (abbrev. ''cos.''; Latin plural ''consules'') was the title of one of the two chief magistrates of the Roman Republic, and subsequently also an important title under the Roman Empire. The title was used in other European city-states throug ...
and general
* Pinnes
Pinnes ( grc-gre, Πίννης; also Pinnius; c. 230 – 217 BC) was the son of Agron, king of the Ardiaei in Illyria, and Agron's first wife Triteuta. He officially succeeded his father as king in 230 BC, but the Ardiaean kingdom was ruled by ...
(also Pinneus or Pineus), son of Agron, king of Illyria
In classical antiquity, Illyria (; grc, Ἰλλυρία, ''Illyría'' or , ''Illyrís''; la, Illyria, ''Illyricum'') was a region in the western part of the Balkan Peninsula inhabited by numerous tribes of people collectively known as the Illyr ...
, and Agron's first wife Triteuta
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:217 Bc