The 2008 United States presidential election was the 56th quadrennial
presidential election
A presidential election is the election of any head of state whose official title is President.
Elections by country
Albania
The president of Albania is elected by the Assembly of Albania who are elected by the Albanian public.
Chile
The pre ...
, held on Tuesday, November 4, 2008. The
Democratic ticket of
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...
, the junior
senator
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
from
Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolita ...
, and
Joe Biden, the senior
senator
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
from
Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacent Del ...
, defeated the
Republican
Republican can refer to:
Political ideology
* An advocate of a republic, a type of government that is not a monarchy or dictatorship, and is usually associated with the rule of law.
** Republicanism, the ideology in support of republics or agains ...
ticket of
John McCain
John Sidney McCain III (August 29, 1936 ŌĆō August 25, 2018) was an American politician and United States Navy officer who served as a United States senator from Arizona from 1987 until his death in 2018. He previously served two terms ...
, the senior
senator
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
from
Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Al─Ł ß╣Żonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
, and
Sarah Palin
Sarah Louise Palin (; Heath; born February 11, 1964) is an American politician, commentator, author, and reality television personality who served as the ninth governor of Alaska from 2006 until her resignation in 2009. She was the 2008 R ...
, the
governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
of
Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: ąÉą╗čÅčüą║ą░, Alyaska; ale, Alax╠ésxax╠é; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, An├Īaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S., ...
. Obama became the first
African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
to be elected to the presidency, as well as being only the third sitting United States senator elected president, joining
Warren G. Harding
Warren Gamaliel Harding (November 2, 1865 ŌĆō August 2, 1923) was the 29th president of the United States, serving from 1921 until his death in 1923. A member of the Republican Party, he was one of the most popular sitting U.S. presidents. A ...
and
John F. Kennedy
John Fitzgerald Kennedy (May 29, 1917 ŌĆō November 22, 1963), often referred to by his initials JFK and the nickname Jack, was an American politician who served as the 35th president of the United States from 1961 until his assassination ...
. Meanwhile, Biden became the first senator running mate of a senator elected president since
Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), often referred to by his initials LBJ, was an American politician who served as the 36th president of the United States from 1963 to 1969. He had previously served as the 37th vice ...
(who was Kennedy's running mate) in the
1960 election.
Incumbent Republican
President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966ŌĆō2010 Japanese ful ...
George W. Bush
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Republican Party, Bush family, and son of the 41st president George H. W. Bush, he ...
was ineligible to pursue a third term due to the
term limit
A term limit is a legal restriction that limits the number of terms an officeholder may serve in a particular elected office. When term limits are found in presidential and semi-presidential systems they act as a method of curbing the potenti ...
s established by the
22nd Amendment
The Twenty-second Amendment (Amendment XXII) to the United States Constitution limits the number of times a person is eligible for election to the office of President of the United States to two, and sets additional eligibility conditions for ...
. McCain secured the
Republican nomination by March 2008, defeating former governors
Mitt Romney
Willard Mitt Romney (born March 12, 1947) is an American politician, businessman, and lawyer serving as the junior United States senator from Utah since January 2019, succeeding Orrin Hatch. He served as the 70th governor of Massachusetts f ...
,
Mike Huckabee
Michael Dale Huckabee (born August 24, 1955) is an American politician, Baptist minister, and political commentator who served as the 44th governor of Arkansas from 1996 to 2007. He was a candidate for the Republican Party presidential nomina ...
, and other challengers. The
Democratic primaries
This is a list of Democratic Party presidential primaries.
1912
This was the first time that candidates were chosen through primaries. New Jersey Governor Woodrow Wilson ran to become the nominee, and faced the opposition of Speaker of the Uni ...
were marked by a sharp contest between Obama and the initial front-runner, former First Lady and Senator
Hillary Clinton
Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton ( Rodham; born October 26, 1947) is an American politician, diplomat, and former lawyer who served as the 67th United States Secretary of State for President Barack Obama from 2009 to 2013, as a United States sen ...
. Clinton's victory in the
New Hampshire primary
The New Hampshire presidential primary is the first in a series of nationwide party primary elections and the second party contest (the first being the Iowa caucuses) held in the United States every four years as part of the process of choosi ...
made her the first woman to win a major party's presidential primary. After a long primary season, Obama secured the Democratic nomination in June 2008.
Early campaigning focused heavily on the
Iraq War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Iraq War {{Nobold, {{lang, ar, žŁž▒ž© ž¦┘äž╣ž▒ž¦┘é (Arabic) {{Nobold, {{lang, ku, ž┤█Ģ┌Ģ█ī ž╣█Äž▒ž¦┘é (Kurdish languages, Kurdish)
, partof = the Iraq conflict (2003ŌĆōpresent), I ...
and
Bush's unpopularity. McCain supported the war, as well as a
troop surge that had begun in 2007, while Obama strongly opposed the war. Bush endorsed McCain, but the two did not campaign together, and Bush did not appear in person at the
2008 Republican National Convention
The 2008 Republican National Convention took place at the Xcel Energy Center in Saint Paul, Minnesota, from September 1, through September 4, 2008. The first day of the Republican Party's convention fell on Labor Day, the last day of the popul ...
. Obama campaigned on the theme that "
Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
must change," while McCain emphasized his experience. The campaign was strongly affected by the onset of a
major financial crisis, which peaked in September 2008. McCain's decision to suspend his campaign during the height of the financial crisis backfired as voters viewed his response as erratic.
Obama won a decisive victory over McCain, winning the
Electoral College and the
popular vote
Popularity or social status is the quality of being well liked, admired or well known to a particular group.
Popular may also refer to:
In sociology
* Popular culture
* Popular fiction
* Popular music
* Popular science
* Populace, the total ...
by a sizable margin, including states that had not voted for the Democratic presidential candidate since 1976 (North Carolina) and 1964 (Indiana, Virginia, and Nebraska's 2nd congressional district). Obama received the
largest share of the popular vote won by a Democrat since
Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), often referred to by his initials LBJ, was an American politician who served as the 36th president of the United States from 1963 to 1969. He had previously served as the 37th vice ...
in
1964
Events January
* January 1 ŌĆō The Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland is dissolved.
* January 5 - In the first meeting between leaders of the Roman Catholic and Orthodox churches since the fifteenth century, Pope Paul VI and Patriarch ...
and was the first Democrat to win an outright majority of the popular vote since
Jimmy Carter
James Earl Carter Jr. (born October 1, 1924) is an American politician who served as the 39th president of the United States from 1977 to 1981. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, he previously served as th ...
in
1976
Events January
* January 3 ŌĆō The International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights enters into force.
* January 5 ŌĆō The Pol Pot regime proclaims a new constitution for Democratic Kampuchea.
* January 11 ŌĆō The 1976 Phila ...
. Obama's total count of 69.5 million votes stood as the largest tally ever won by a presidential candidate until
2020
2020 was heavily defined by the COVID-19 pandemic, which led to global Social impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, social and Economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, economic disruption, mass cancellations and postponements of events, COVID- ...
, when this was surpassed by both major party candidates in a high-turnout election. He was the first Democrat to win without
Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the Osage ...
and
Missouri
Missouri is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee ...
since those states joined the Union in 1836 and 1821 and the first Democrat to win the presidency without winning
West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geographers classify West Virginia as part of the Southern United States while the Bur ...
since
1916
Events
Below, the events of the First World War have the "WWI" prefix.
January
* January 1 – The British Royal Army Medical Corps carries out the first successful blood transfusion, using blood that had been stored and cooled.
* ...
.
Obama flipped nine states that had voted Republican in
2004
2004 was designated as an International Year of Rice by the United Nations, and the International Year to Commemorate the Struggle Against Slavery and its Abolition (by UNESCO).
Events January
* January 3 – Flash Airlines Flight 6 ...
:
Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of t ...
,
Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
,
Indiana
Indiana () is a U.S. state in the Midwestern United States. It is the 38th-largest by area and the 17th-most populous of the 50 States. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the United States as the 19th s ...
,
Iowa
Iowa () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wisconsin to the northeast, Illinois to the ...
,
Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. N ...
,
New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ker ...
,
North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and So ...
,
Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
, and
Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
, as well as
Nebraska's 2nd congressional district
Nebraska's 2nd congressional district is a congressional district in the U.S. state of Nebraska that encompasses the core of the OmahaŌĆōCouncil Bluffs metropolitan area. It includes all of Douglas County, which includes Omaha, as well as the ...
. , this is the last time Indiana and North Carolina have voted Democratic, the last time that either a Democratic or Republican candidate received fewer than 200 electoral votes, and the last time an incumbent U.S. senator was a major party nominee. This is the only election in American history where both major party nominees were sitting US Senators.
Background

Article Two of the United States Constitution
Article Two of the United States Constitution establishes the executive branch of the federal government, which carries out and enforces federal laws. Article Two vests the power of the executive branch in the office of the president of the Unite ...
provides that the
President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966ŌĆō2010 Japanese ful ...
and
Vice President
A vice president, also director in British English, is an officer in government or business who is below the president (chief executive officer) in rank. It can also refer to executive vice presidents, signifying that the vice president is on t ...
of the United States must be
natural-born citizens of the United States, at least 35 years old, and residents of the United States for a period of at least 14 years. Candidates for the presidency typically seek the nomination of one of the political parties, in which case each party devises a method (such as a
primary election
Primary elections, or direct primary are a voting process by which voters can indicate their preference for their party's candidate, or a candidate in general, in an upcoming general election, local election, or by-election. Depending on the ...
) to choose the candidate the party deems best suited to run for the position. Traditionally, the primary elections are
indirect election
An indirect election or ''hierarchical voting'' is an election in which voters do not choose directly among candidates or parties for an office (direct voting system), but elect people who in turn choose candidates or parties. It is one of the old ...
s where voters cast ballots for a slate of party delegates pledged to a particular candidate. The party's delegates then officially nominate a candidate to run on the party's behalf. The general election in November is also an indirect election, where voters cast ballots for a slate of members of the
Electoral College; these electors in turn directly elect the president and vice president.
President
George W. Bush
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Republican Party, Bush family, and son of the 41st president George H. W. Bush, he ...
, a
Republican
Republican can refer to:
Political ideology
* An advocate of a republic, a type of government that is not a monarchy or dictatorship, and is usually associated with the rule of law.
** Republicanism, the ideology in support of republics or agains ...
and former
Governor of Texas
The governor of Texas heads the state government of Texas. The governor is the leader of the executive and legislative branch of the state government and is the commander in chief of the Texas Military. The current governor is Greg Abbott, who ...
, was ineligible to seek reelection to a third term due to the
Twenty-second Amendment; in accordance with Section1 of the
Twentieth Amendment, his term expired at noon
eastern standard time
The Eastern Time Zone (ET) is a time zone encompassing part or all of 23 states in the eastern part of the United States, parts of eastern Canada, the state of Quintana Roo in Mexico, Panama, Colombia, mainland Ecuador, Peru, and a small port ...
on January 20, 2009.
Also ineligible to run for an additional term as president was past two-term president
Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton ( n├® Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 and agai ...
. While neither of them ran, former presidents
Jimmy Carter
James Earl Carter Jr. (born October 1, 1924) is an American politician who served as the 39th president of the United States from 1977 to 1981. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, he previously served as th ...
and
George H. W. Bush
George Herbert Walker BushSince around 2000, he has been usually called George H. W. Bush, Bush Senior, Bush 41 or Bush the Elder to distinguish him from his eldest son, George W. Bush, who served as the 43rd president from 2001 to 2009; pr ...
, each having served only one term, were both eligible to run for a second term as president.
Nominations
Democratic Party nomination
Candidate
Withdrawn candidates
Before the primaries
Media speculation had begun almost immediately after the results of the
2004 presidential election were released. In the
2006 midterm elections
The 2006 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 7, 2006, in the middle of Republican President George W. Bush's second term. Democrats won control of both houses of Congress, which was the first and only time either party did so ...
, the Democrats regained majorities in both houses of the
U.S. Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is Bicameralism, bicameral, composed of a lower body, the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives, and an upper body, ...
. Early polls taken before anyone had announced a candidacy had shown Senators
Hillary Clinton
Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton ( Rodham; born October 26, 1947) is an American politician, diplomat, and former lawyer who served as the 67th United States Secretary of State for President Barack Obama from 2009 to 2013, as a United States sen ...
and
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...
as the most popular potential Democratic candidates.
Nevertheless, the media speculated on several other candidates, including
Al Gore
Albert Arnold Gore Jr. (born March 31, 1948) is an American politician, businessman, and environmentalist who served as the 45th vice president of the United States from 1993 to 2001 under President Bill Clinton. Gore was the Democratic Part ...
, the runner-up in the
2000 election;
John Kerry
John Forbes Kerry (born December 11, 1943) is an American attorney, politician and diplomat who currently serves as the first United States special presidential envoy for climate. A member of the Forbes family and the Democratic Party (Unite ...
, the runner-up in the
2004 election;
John Edwards
Johnny Reid Edwards (born June 10, 1953) is an American lawyer and former politician who served as a U.S. senator from North Carolina. He was the Democratic nominee for vice president in 2004 alongside John Kerry, losing to incumbents George ...
, Kerry's
running mate
A running mate is a person running together with another person on a joint Ticket (election), ticket during an election. The term is most often used in reference to the person in the subordinate position (such as the vice presidential candidate ...
in 2004; senator from Delaware
Joe Biden; New Mexico Governor
Bill Richardson
William Blaine Richardson III (born November 15, 1947) is an American politician, author, and diplomat who served as the 30th governor of New Mexico from 2003 to 2011. He was also the U.S. Ambassador to the United Nations and Energy Secretary ...
; Iowa Governor
Tom Vilsack
Thomas James Vilsack (; born December 13, 1950) is an American politician serving as the 32nd United States Secretary of Agriculture in the Biden administration. He previously served in the role from 2009 to 2017 during the Obama administration. ...
; and Indiana Senator
Evan Bayh
Birch Evans Bayh III ( ; born December 26, 1955) is an American lawyer, lobbyist, and Democratic Party politician who served as a United States senator from Indiana from 1999 to 2011 and the 46th governor of Indiana from 1989 to 1997.
Bayh w ...
.
Edwards was one of the first to formally announce his candidacy for the presidency, on December 28, 2006. This run would be his second attempt at the presidency. Clinton announced intentions to run in the Democratic primaries on January 20, 2007.
Obama announced his candidacy on February 10 in his home state of Illinois.
Early primaries and caucuses
Early in the year, the support for Barack Obama started to increase in the polls and he passed Clinton for the top spot in Iowa; he ended up winning the caucus in that state, with John Edwards coming in second and Clinton in third.
Obama's win was fueled mostly by first time caucus-goers and
Independents and showed voters viewed him as the "candidate of change."
[ Iowa has since been viewed as the state that jump-started Obama's campaign and set him on track to win both the nomination and the presidency. After the Iowa caucus, Joe Biden and ]Christopher Dodd
Christopher John Dodd (born May 27, 1944) is an American lobbyist, lawyer, and Democratic Party politician who served as a United States senator from Connecticut from 1981 to 2011. Dodd is the longest-serving senator in Connecticut's history. ...
withdrew from the nomination contest.[
Obama became the new front runner in New Hampshire, when his poll numbers skyrocketed after his Iowa victory]The Vancouver Sun
The ''Vancouver Sun'', also known as the ''Sun'', is a daily broadsheet newspaper based in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. The newspaper is currently published by the Pacific Newspaper Group, a division of Postmedia Network. Published si ...
'', campaign strategists had "mapped a victory scenario that envisioned the former first lady wrapping up the Democratic presidential nomination by Super Tuesday on Feb. 5." In what is considered a turning point for her campaign, Clinton had a strong performance at the Saint Anselm College
Saint Anselm College is a private Benedictine liberal arts college in Goffstown, New Hampshire. Founded in 1889, it is the third-oldest Catholic college in New England. Named for Saint Anselm of Canterbury (Archbishop of Canterbury from 1093 to ...
, ABC
ABC are the first three letters of the Latin script known as the alphabet.
ABC or abc may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Broadcasting
* American Broadcasting Company, a commercial U.S. TV broadcaster
** DisneyŌĆōABC Television ...
, and Facebook
Facebook is an online social media and social networking service owned by American company Meta Platforms. Founded in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg with fellow Harvard College students and roommates Eduardo Saverin, Andrew McCollum, Dustin M ...
debates several days before the New Hampshire primary
The New Hampshire presidential primary is the first in a series of nationwide party primary elections and the second party contest (the first being the Iowa caucuses) held in the United States every four years as part of the process of choosi ...
as well as an emotional interview in a public broadcast live on TV. Clinton won that primary by 2% of the vote, contrary to the predictions of pollsters who consistently had her trailing Obama for a few days up to the primary date.
Super Tuesday

Super Tuesday
Super Tuesday is the United States presidential primary election day in February or March when the greatest number of U.S. states hold primary elections and caucuses. Approximately one-third of all delegates to the presidential nominating co ...
was February 5, 2008, when the largest-ever number of simultaneous state primary
Primary or primaries may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Music Groups and labels
* Primary (band), from Australia
* Primary (musician), hip hop musician and record producer from South Korea
* Primary Music, Israeli record label
Works
* ...
elections was held.[
] Super Tuesday ended up leaving the Democrats in a virtual tie, with Obama amassing 847 delegates to Clinton's 834 from the 23 states that held Democratic primaries.
California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
was one of the Super Tuesday states that could provide a large number of delegates to the candidates. Obama trailed in the California polling by an average of 6.0% before the primary; he ended up losing that state by 8.3% of the vote.Latino
Latino or Latinos most often refers to:
* Latino (demonym), a term used in the United States for people with cultural ties to Latin America
* Hispanic and Latino Americans in the United States
* The people or cultures of Latin America;
** Latin A ...
turnout that voted for Clinton as the deciding factor.
The Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
, Nebraska
Nebraska () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. It is bordered by South Dakota to the north; Iowa to the east and Missouri to the southeast, both across the Missouri River; Kansas to the south; Colorado to the southwe ...
, Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only stat ...
, Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake M ...
, U.S. Virgin Islands, the District of Columbia, Maryland, and Virginia primaries and the Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
and Maine caucuses all took place after Super Tuesday in February. Obama won all of them, giving him 10 consecutive victories after Super Tuesday.
Ohio, Texas, and Pennsylvania
On March 4, Hillary Clinton carried Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
and Rhode Island
Rhode Island (, like ''road'') is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is the List of U.S. states by area, smallest U.S. state by area and the List of states and territories of the United States ...
in the Democratic primaries; some considered these wins, especially Ohio, a "surprise upset" by 10%, although she did lead in the polling averages in both states.Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
, on April 22. Although Obama made a strong effort to win Pennsylvania, Hillary Clinton won that primary by nearly 10%, with approximately 55% of the vote.NPR
National Public Radio (NPR, stylized in all lowercase) is an American privately and state funded nonprofit media organization headquartered in Washington, D.C., with its NPR West headquarters in Culver City, California. It differs from other ...
, the established Democratic electorate "was older, whiter, more Catholic and more working-class than in most of the primaries to date." After Pennsylvania, Obama had a higher number of delegates and popular votes than Clinton did and was still in a stronger position to win the nomination. Clinton, however, had received the endorsement of more superdelegates than Obama.
Indiana and North Carolina
On May 6, North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and So ...
and Indiana
Indiana () is a U.S. state in the Midwestern United States. It is the 38th-largest by area and the 17th-most populous of the 50 States. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the United States as the 19th s ...
held their Democratic presidential primaries. Clinton and Obama campaigned aggressively there before the voting took place. Polling had shown Obama a few points ahead in North Carolina and Clinton similarly leading in Indiana. In the actual results, Obama outperformed the polls by several points in both states, winning by a significant margin in North Carolina and losing by only 1.1% in Indiana (50.56% to 49.44%). After these primaries, most pundits declared that it had become "increasingly improbable," if not impossible, for Clinton to win the nomination. The small win in Indiana barely kept her campaign alive for the next month. Although she did manage to win the majority of the remaining primaries and delegates, it was not enough to overcome Obama's substantial delegate lead.
Florida and Michigan
During late 2007, the two parties adopted rules against states' moving their primaries to an earlier date in the year. For the Republicans, the penalty for this violation was supposed to be the loss of half the state party's delegates to the convention. The Democratic penalty was the complete exclusion from the national convention of delegates from states that broke these rules. The Democratic Party allowed only four states to hold elections before February 5, 2008. Clinton won a majority of delegates and popular votes from both states (though 40% voted uncommitted in Michigan) and subsequently led a fight to seat all the Florida and Michigan delegates.
There was some speculation that the fight over the delegates could last until the convention in August. On May 31, 2008, the Rules and Bylaws Committee of the Democratic Party reached a compromise on the Florida and Michigan delegate situation. The committee decided to seat delegates from Michigan and Florida at the convention in August, but to only award each a half-vote.
Clinching the nomination
 The major political party nomination process (technically) continues through June of an election year. In previous cycles, the candidates were effectively chosen by the end of the primaries held in March, but, in this cycle, Barack Obama did not win enough delegates to secure the nomination until June 3, after a 17-month campaign against Hillary Clinton. He had a wide lead in states won, while Clinton had won majorities in several of the larger states. Now, because a form of
The major political party nomination process (technically) continues through June of an election year. In previous cycles, the candidates were effectively chosen by the end of the primaries held in March, but, in this cycle, Barack Obama did not win enough delegates to secure the nomination until June 3, after a 17-month campaign against Hillary Clinton. He had a wide lead in states won, while Clinton had won majorities in several of the larger states. Now, because a form of proportional representation
Proportional representation (PR) refers to a type of electoral system under which subgroups of an electorate are reflected proportionately in the elected body. The concept applies mainly to geographical (e.g. states, regions) and political divis ...
and popular vote decided Democratic state delegate contests, numbers were close between Clinton and Obama. By May, Clinton claimed to hold a lead in the popular vote, but the Associated Press
The Associated Press (AP) is an American non-profit news agency headquartered in New York City. Founded in 1846, it operates as a cooperative, unincorporated association. It produces news reports that are distributed to its members, U.S. newspa ...
found that her numbers were "accurate only" in one close scenario.
In June, after the last of the primaries had taken place, Obama secured the Democratic nomination for president, with the help of multiple super delegate endorsements (most of the super delegates had refused to declare their support for either candidate until the primaries were completed). He was the first African American to win the nomination of a major political party in the United States. For several days, Clinton refused to concede the race, although she signaled her presidential campaign was ending in a post-primary speech on June 3 in her home state of New York. She finally conceded the nomination to Obama on June 7. She pledged her full support to the presumptive nominee and vowed to do everything she could to help him get elected.
Republican Party nomination
Not only was the 2008 election the first time since 1952
Events JanuaryŌĆōFebruary
* January 26 ŌĆō Black Saturday in Egypt: Rioters burn Cairo's central business district, targeting British and upper-class Egyptian businesses.
* February 6
** Princess Elizabeth, Duchess of Edinburgh, becomes m ...
that neither the incumbent
The incumbent is the current holder of an official, office or position, usually in relation to an election. In an election for president, the incumbent is the person holding or acting in the office of president before the election, whether seek ...
president nor the incumbent vice president was a candidate in the general election, but it was also the first time since the 1928 election that neither sought his party's nomination for president; as Bush was term-limited from seeking another nomination, the unique aspect was Vice President Cheney's decision not to seek the Republican nomination.[Charles G. Dawes, 30th Vice President (1925ŌĆō1929)](_blank)
, U.S. Senate. The 2008 election was also the third presidential election since 1896
Events
January–March
* January 2 – The Jameson Raid comes to an end, as Jameson surrenders to the Boers.
* January 4 – Utah is admitted as the 45th U.S. state.
* January 5 – An Austrian newspaper reports that Wil ...
in which neither the incumbent president, the incumbent vice president, nor a current or former member of the incumbent president's Cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filing ...
won the nomination of either major party the others being 1920
Events January
* January 1
** PolishŌĆōSoviet War in 1920: The Russian Red Army increases its troops along the Polish border from 4 divisions to 20.
** Kauniainen, completely surrounded by the city of Espoo, secedes from Espoo as its own ma ...
and 1952
Events JanuaryŌĆōFebruary
* January 26 ŌĆō Black Saturday in Egypt: Rioters burn Cairo's central business district, targeting British and upper-class Egyptian businesses.
* February 6
** Princess Elizabeth, Duchess of Edinburgh, becomes m ...
.
Candidate
Withdrawn candidates
Before the primaries
Immediately after the 2006 midterm elections, media pundits began speculating, as they did about the Democrats, about potential Republican candidates for president in 2008.Rudolph Giuliani
Rudolph William Louis Giuliani (, ; born May 28, 1944) is an American politician and lawyer who served as the 107th Mayor of New York City from 1994 to 2001. He previously served as the United States Associate Attorney General from 1981 to 198 ...
led in the polls, followed closely by Arizona Senator John McCain
John Sidney McCain III (August 29, 1936 ŌĆō August 25, 2018) was an American politician and United States Navy officer who served as a United States senator from Arizona from 1987 until his death in 2018. He previously served two terms ...
. The media speculated that Giuliani's pro-choice
Abortion-rights movements, also referred to as pro-choice movements, advocate for the right to have legal access to induced abortion services including elective abortion. They seek to represent and support women who wish to terminate their pre ...
stance on abortion
Abortion is the termination of a pregnancy by removal or expulsion of an embryo or fetus. An abortion that occurs without intervention is known as a miscarriage or "spontaneous abortion"; these occur in approximately 30% to 40% of pregn ...
and McCain's age and support of the unpopular Iraq War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Iraq War {{Nobold, {{lang, ar, žŁž▒ž© ž¦┘äž╣ž▒ž¦┘é (Arabic) {{Nobold, {{lang, ku, ž┤█Ģ┌Ģ█ī ž╣█Äž▒ž¦┘é (Kurdish languages, Kurdish)
, partof = the Iraq conflict (2003ŌĆōpresent), I ...
would be detriments to their candidacies.Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
Senator Fred Thompson
Freddie Dalton Thompson (August 19, 1942 ŌĆō November 1, 2015) was an American politician, attorney, lobbyist, columnist, actor, and radio personality. A member of the Republican Party, he served as a United States Senator from Tennessee f ...
fighting for second place. Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the Osage ...
Governor Mike Huckabee
Michael Dale Huckabee (born August 24, 1955) is an American politician, Baptist minister, and political commentator who served as the 44th governor of Arkansas from 1996 to 2007. He was a candidate for the Republican Party presidential nomina ...
, Giuliani, former governor Mitt Romney
Willard Mitt Romney (born March 12, 1947) is an American politician, businessman, and lawyer serving as the junior United States senator from Utah since January 2019, succeeding Orrin Hatch. He served as the 70th governor of Massachusetts f ...
, and Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
Representative Ron Paul
Ronald Ernest Paul (born August 20, 1935) is an American author, activist, physician and retired politician who served as the U.S. representative for Texas's 22nd congressional district from 1976 to 1977 and again from 1979 to 1985, as well ...
announced their candidacies on January 28, February 5, February 13, and March 12, respectively. McCain officially announced his candidacy on March 1, 2007, after several informal announcements. In the third quarter of 2007, the top four GOP (Republican) fundraisers were Romney, Giuliani, Thompson, and Ron Paul
Ronald Ernest Paul (born August 20, 1935) is an American author, activist, physician and retired politician who served as the U.S. representative for Texas's 22nd congressional district from 1976 to 1977 and again from 1979 to 1985, as well ...
. MSNBC's Chuck Todd christened Giuliani and John McCain
John Sidney McCain III (August 29, 1936 ŌĆō August 25, 2018) was an American politician and United States Navy officer who served as a United States senator from Arizona from 1987 until his death in 2018. He previously served two terms ...
the front runners after the second Republican presidential debate in early 2007.
Early primaries/caucuses
Huckabee, winner of Iowa, had little to no money and hoped for at least a third-place finish in New Hampshire. McCain eventually displaced Rudy Giuliani and Romney as the front runner in New Hampshire
New Hampshire is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
. McCain staged a turnaround victory,South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
, setting him up for a larger and more important victory over Romney in Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
, which held a closed primary on January 29. By this time, after several scandals, no success in the early primaries, and a third-place finish in Florida, Giuliani conceded the nomination and endorsed John McCain the next day.
Super Tuesday
McCain was also endorsed in February by California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
Governor Arnold Schwarzenegger
Arnold Alois Schwarzenegger (born July 30, 1947) is an Austrian and American actor, film producer, businessman, retired professional bodybuilder and politician who served as the 38th governor of California between 2003 and 2011. ''Time'' ...
before the California primary took place on Super Tuesday. This gave him a significant boost in the polls for the state's primary, which awarded the greatest number of delegates of all the states. On Super Tuesday, McCain won his home state of Arizona, taking all 53 delegates. He also won nearly all of California's 173 delegates, the largest of the Super Tuesday prizes. McCain also scored wins in seven other states, picking up 574 delegates.District of Columbia
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
, Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to the ...
, Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake M ...
, and Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
held primaries in February after Super Tuesday. Despite McCain picking up big victories, Huckabee won Louisiana and Kansas. McCain narrowly carried the Washington caucuses over Huckabee and Paul, who amassed a large showing.Virgin Islands
The Virgin Islands ( es, Islas V├Łrgenes) are an archipelago in the Caribbean Sea. They are geologically and biogeographically the easternmost part of the Greater Antilles, the northern islands belonging to the Puerto Rico Trench and St. Croix ...
and Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and Unincorporated ...
closed February for the Republicans. After Super Tuesday, John McCain had become the clear front runner, but by the end of February, he still had not acquired enough delegates to secure the nomination. In March, John McCain clinched the Republican nomination after sweeping all four primaries, Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
, Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
, Vermont
Vermont () is a state in the northeast New England region of the United States. Vermont is bordered by the states of Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, and New York to the west, and the Canadian province of Quebec to ...
, and Rhode Island
Rhode Island (, like ''road'') is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is the List of U.S. states by area, smallest U.S. state by area and the List of states and territories of the United States ...
, putting him over the top of the 1,191 delegates required to win the GOP nomination.[ Mike Huckabee then conceded the race to McCain, leaving Ron Paul, who had just 16 delegates, as his only remaining opponent. Romney would eventually become the Republican presidential nominee 4 years later, which he then lost to ]Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...
.
Third party and other nominations
Along with the Democratic and Republican parties, three other parties nominated candidates with ballot access in enough states to win the minimum 270 electoral votes needed to win the election. These were the Constitution Party, the Green Party
A green party is a formally organized political party based on the principles of green politics, such as social justice, environmentalism and nonviolence.
Greens believe that these issues are inherently related to one another as a foundation ...
, and the Libertarian Party
Active parties by country
Defunct parties by country
Organizations associated with Libertarian parties
See also
* Liberal parties by country
* List of libertarian organizations
* Lists of political parties
Lists of political part ...
. In addition, independent candidate Ralph Nader
Ralph Nader (; born February 27, 1934) is an American political activist, author, lecturer, and attorney noted for his involvement in consumer protection, environmentalism, and government reform causes.
The son of Lebanese immigrants to the Un ...
ran his own campaign.
The Constitution Party nominated writer, pastor, and conservative talk show host Chuck Baldwin
Charles Obadiah Baldwin (born May 3, 1952) is an American right-wing politician, radio host, and founder-former pastor of Crossroad Baptist Church in Pensacola, Florida. As of January 2011 he was pastor of Liberty Fellowship in Kalispell, Montan ...
for president, and attorney Darrell Castle from Tennessee for vice president.Iraq War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Iraq War {{Nobold, {{lang, ar, žŁž▒ž© ž¦┘äž╣ž▒ž¦┘é (Arabic) {{Nobold, {{lang, ku, ž┤█Ģ┌Ģ█ī ž╣█Äž▒ž¦┘é (Kurdish languages, Kurdish)
, partof = the Iraq conflict (2003ŌĆōpresent), I ...
, the Sixteenth Amendment, ''Roe v. Wade
''Roe v. Wade'', 410 U.S. 113 (1973),. was a landmark decision of the U.S. Supreme Court in which the Court ruled that the Constitution of the United States conferred the right to have an abortion. The decision struck down many federal and st ...
'', the IRS
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) is the revenue service for the United States federal government, which is responsible for collecting U.S. federal taxes and administering the Internal Revenue Code, the main body of the federal statutory tax ...
, and the Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve System (often shortened to the Federal Reserve, or simply the Fed) is the central banking system of the United States of America. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, after a ...
.
The Green Party nominated former Democratic representative Cynthia McKinney
Cynthia Ann McKinney (born March 17, 1955) is an American politician, academic, and conspiracy theorist. As a member of the Democratic Party, she served six terms in the United States House of Representatives. She was the first African American ...
from Georgia for president, and political activist Rosa Clemente
Rosa Alicia Clemente (born April 18, 1972) is an American community organizer, independent journalist, and hip-hop activist. She was the vice presidential running mate of Green Party Presidential candidate Cynthia McKinney in the 2008 U.S. Pres ...
from New York for vice president. McKinney campaigned on a platform that supported single-payer universal health care
Single-payer healthcare is a type of universal healthcare in which the costs of essential healthcare for all residents are covered by a single public system (hence "single-payer").
Single-payer systems may contract for healthcare services from p ...
, the withdrawal of American troops from Iraq and Afghanistan, reparations for African Americans, and the creation of a Department of Peace.
The Libertarian Party nominated former Republican representative Bob Barr
Robert Laurence Barr Jr. (born November 5, 1948) is an American attorney and politician. He served as a federal prosecutor and as a United States House of Representatives, Congressman. He represented Georgia's 7th congressional district as a Re ...
from Georgia for president, and his former rival for the Libertarian nomination Wayne Allyn Root
Wayne Allyn Root (born July 20, 1961) is an American conservative television and radio host, author, activist, conservative political commentator and conspiracy theorist. He is the host of two new television shows, daily at 7 PM ET on Lindell TV ...
from Nevada, for vice president. During the 2008 presidential campaign, Barr advocated a reworking or abolition of the income tax
An income tax is a tax imposed on individuals or entities (taxpayers) in respect of the income or profits earned by them (commonly called taxable income). Income tax generally is computed as the product of a tax rate times the taxable income. Tax ...
and opposed the war in Iraq and the Patriot Act
The USA PATRIOT Act (commonly known as the Patriot Act) was a landmark Act of the United States Congress, signed into law by President George W. Bush. The formal name of the statute is the Uniting and Strengthening America by Providing Appropr ...
.
Candidates gallery
File:Naderspeak.JPG,
File:Bob Barr-2008 cropped.jpg,
File:CBaldwin08.jpg,
File:Cynthia McKinney.jpg,
Party conventions
* April 23ŌĆō26, 2008: 2008 Constitution Party National Convention held in Kansas City, Missouri
Kansas City (abbreviated KC or KCMO) is the largest city in Missouri by population and area. As of the 2020 census, the city had a population of 508,090 in 2020, making it the 36th most-populous city in the United States. It is the central ...
.
* May 23ŌĆō26, 2008: 2008 Libertarian National Convention, held in Denver, Colorado
Denver () is a consolidated city and county, the capital, and most populous city of the U.S. state of Colorado. Its population was 715,522 at the 2020 census, a 19.22% increase since 2010. It is the 19th-most populous city in the Unit ...
.
* July 10ŌĆō13, 2008: 2008 Green Party National Convention, held in Chicago, Illinois
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
.
* August 25ŌĆō28, 2008: 2008 Democratic National Convention
The 2008 Democratic National Convention was a quadrennial presidential nominating convention of the Democratic Party where it adopted its national platform and officially nominated its candidates for president and vice president. The conventi ...
, held in Denver, Colorado
Denver () is a consolidated city and county, the capital, and most populous city of the U.S. state of Colorado. Its population was 715,522 at the 2020 census, a 19.22% increase since 2010. It is the 19th-most populous city in the Unit ...
.
* September 1ŌĆō4, 2008: 2008 Republican National Convention
The 2008 Republican National Convention took place at the Xcel Energy Center in Saint Paul, Minnesota, from September 1, through September 4, 2008. The first day of the Republican Party's convention fell on Labor Day, the last day of the popul ...
, held in Saint Paul, Minnesota
Saint Paul (abbreviated St. Paul) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital of the U.S. state of Minnesota and the county seat of Ramsey County, Minnesota, Ramsey County. Situated on high bluffs overlooking a bend in the Mississip ...
.
General election campaign
Issues
Iraq
The unpopular war in Iraq
This is a list of wars involving the Republic of Iraq and its predecessor states.
Other armed conflicts involving Iraq
* Wars during Mandatory Iraq
** Ikhwan raid on South Iraq 1921
* Smaller conflicts, revolutions, coups and periphery confli ...
was a key issue during the campaign before the economic crisis
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the p ...
. John McCain supported the war while Barack Obama opposed it (Obama's early and strong opposition to the war helped him stand out against the other Democratic candidates during the primaries, as well as stand out to a war-weary electorate during the general campaign). Though McCain meant it as a peacetime presence like the United States maintained in Germany and Japan after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countriesŌĆöincluding all of the great powersŌĆöforming two opposin ...
,[; video at ] his statement that the United States could be in Iraq for as much as the next 50 to 100 years would prove costly. Obama used it against him as part of his strategy to tie him to the unpopular President Bush.
John McCain's support for the troop 'surge' employed by General David Petraeus
David Howell Petraeus (; born November 7, 1952) is a retired United States Army general and public official. He served as Director of the Central Intelligence Agency from September 6, 2011, until his resignation on November 9, 2012. Prior to h ...
, which was one of several factors credited with improving the security situation in Iraq, may have boosted McCain's stance on the issue in voters' minds. McCain (who supported the invasion) argued that his support for the successful surge showed his superior judgment. However, Obama was quick to remind voters that there would have been no need for a "surge" had there been no war at all, thus questioning McCain's judgment.
Bush's unpopularity
George W. Bush had become increasingly unpopular among Americans by late 2005 due in part by the growing unpopularity of the Iraq War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Iraq War {{Nobold, {{lang, ar, žŁž▒ž© ž¦┘äž╣ž▒ž¦┘é (Arabic) {{Nobold, {{lang, ku, ž┤█Ģ┌Ģ█ī ž╣█Äž▒ž¦┘é (Kurdish languages, Kurdish)
, partof = the Iraq conflict (2003ŌĆōpresent), I ...
domestically and internationally, as well as Bush's handling of the financial crisis of 2007ŌĆō08 and Hurricane Katrina
Hurricane Katrina was a destructive Category 5 Atlantic hurricane that caused over 1,800 fatalities and $125 billion in damage in late August 2005, especially in the city of New Orleans and the surrounding areas. It was at the time the cost ...
in 2005. By the time Obama was elected as President of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United Stat ...
on November 4, 2008, Bush's approval rating was in the low to mid 20s and his disapproval grew increasingly significant, being in the high 60s, and even low 70s in some polls. Polls consistently showed that his approval ratings among American voters had averaged around 30 percent.[Presidential Job Approval Center](_blank)
Gallup.com In March 2008, Bush endorsed McCain at the White House, but did not make a single appearance for McCain during the campaign. Bush appeared at the 2008 GOP convention only through a live video broadcast. He chose not to appear in person due to disaster events in the Gulf of Mexico in the aftermath of Hurricane Gustav
Hurricane Gustav () was the second most destructive hurricane of the 2008 Atlantic hurricane season. The seventh tropical cyclone, third hurricane, and second major hurricane of the season, Gustav caused serious damage and casualties in Haiti, ...
. Although he supported the war in Iraq, McCain made an effort to show that he had disagreed with Bush on many other key issues such as climate change. During the entire general election campaign, Obama countered by pointing out in ads and at numerous campaign rallies that McCain had claimed in an interview that he voted with Bush 90% of the time, and congressional voting records supported this for the years Bush was in office.
Age issue
Similar to Senator Bob Dole
Robert Joseph Dole (July 22, 1923 ŌĆō December 5, 2021) was an American politician and attorney who represented Kansas in the United States Senate from 1969 to 1996. He was the Republican Leader of the Senate during the final 11 years of his te ...
's 1996 presidential campaign, one of the more widely leveled charges against McCain was the issue of his ageŌĆöhe turned 72 in August and there was widespread concern about the idea of electing a man who would be 80 years old if he completed two full terms in office (the oldest president, Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
, had been a month shy of 78 when he left office in January 1989). In addition, McCain suffered from the ill effects of his captivity in North Vietnam and reportedly had difficulty lifting his arms above his head. His age in particular was considered a liability against the youthful Senator Obama, who was the first Generation X
Generation X (or Gen X for short) is the Western world, Western demographic Cohort (statistics), cohort following the baby boomers and preceding the millennials. Researchers and popular media use the mid-to-late 1960s as starting birth years a ...
er to run for president on a major party ticket. McCain for comparison was born before World War II and belonged to the Silent Generation
The Silent Generation, also known as the Traditionalist Generation, is the Western demographic cohort following the Greatest Generation and preceding the Baby Boomers. The Silent Generation is generally defined as people born from 1928 to 1945. ...
. Much like Bob Dole, McCain attempted to counter these charges by releasing all of his medical records, something Obama did not do. McCain's wife Cindy dismissed concerns about his health by arguing that "We went hiking the Grand Canyon
The Grand Canyon (, yuf-x-yav, Wi:ka╩╝i:la, , Southern Paiute language: PaxaŌĆÖuipi, ) is a steep-sided canyon carved by the Colorado River in Arizona, United States. The Grand Canyon is long, up to wide and attains a depth of over a m ...
last summer and ohn Ohn is a Burmese name, used by people from Myanmar. Notable people with the name include:
* Daw Ohn (1913ŌĆō2003), Burmese professor in Pali
* Ohn Gyaw (born 1932), Burmese Minister of Foreign Affairs from 1991 to 1998
* Ohn Kyaing (born 1944), Bur ...
did great and had no trouble keeping up with us." McCain also appeared at several campaign stops with his still-active 95-year-old mother. In a speech on the House floor, Pennsylvania Congressman John Murtha
John Patrick Murtha Jr. (; June 17, 1932 ŌĆō February 8, 2010) was an American politician from the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. Murtha, a Democrat, represented Pennsylvania's 12th congressional district in the United States House of Represent ...
criticized McCain's age by saying "Seven presidents have come and gone since I've been in Congress, and I saw the toll the job took on each one of them." If elected, McCain would have been the first president born in the 1930s. McCain ultimately died in 2018, just one year after the completion of Obama's second term.
Like the Clinton campaign in 1996, Obama avoided discussing McCain's age directly, instead preferring to simply call his ideas and message "old" and "old hat". He also made a strong appeal to youth voters and back during his primary contest with Hillary Clinton, had stated "When I watched the feud between the Clintons and ewt Gingrichunfold during the 1990s, I was reminded of old quarrels started on college campuses long ago. It's time for a new generation to take over." Obama's active use of a Blackberry and other modern technology also stood in contrast to the Arizona Senator's admission that he did not use a computer or a cell phone. McCain's service in Vietnam, while marketable to baby boomers, was referred to as "unimportant" to younger voters.
 Obama promised "universal health care, full employment, a green America, and an America respected instead of feared by its enemies".
Polls regularly found the general electorate as a whole divided more evenly between 'change' and 'experience' as candidate qualities than the Democratic primary electorate, which split in favor of 'change' by a nearly 2ŌĆō1 margin. Advantages for McCain and Obama on experience and the ability to bring change, respectively, remained steady through the November 4 election. However, final pre-election polling found that voters considered Obama's inexperience less of an impediment than McCain's association with sitting president George W. Bush, an association which was rhetorically framed by the Obama campaign throughout the election season as "more of the same".
McCain appeared to undercut his line of attack by picking first-term Alaska governor
Obama promised "universal health care, full employment, a green America, and an America respected instead of feared by its enemies".
Polls regularly found the general electorate as a whole divided more evenly between 'change' and 'experience' as candidate qualities than the Democratic primary electorate, which split in favor of 'change' by a nearly 2ŌĆō1 margin. Advantages for McCain and Obama on experience and the ability to bring change, respectively, remained steady through the November 4 election. However, final pre-election polling found that voters considered Obama's inexperience less of an impediment than McCain's association with sitting president George W. Bush, an association which was rhetorically framed by the Obama campaign throughout the election season as "more of the same".
McCain appeared to undercut his line of attack by picking first-term Alaska governor Sarah Palin
Sarah Louise Palin (; Heath; born February 11, 1964) is an American politician, commentator, author, and reality television personality who served as the ninth governor of Alaska from 2006 until her resignation in 2009. She was the 2008 R ...
to be his running mate. Palin had been governor only since 2006, and before that had been a council member and mayor of Wasilla
Wasilla ( Dena'ina:┬Ā''Benteh'') is a city in Matanuska-Susitna Borough, United States and the fourth-largest city in Alaska. It is located on the northern point of Cook Inlet in the Matanuska-Susitna Valley of the southcentral part of the st ...
. The choice of Palin was controversial; however, it appeared to solve two pressing concernsŌĆöMcCain's age and health (since a youthful vice president would succeed him to office if he died or became incapacitated) and appealing to right-wing conservatives, a group that had been comparatively unmoved by McCain. Palin also came off as more down-to-earth and relatable to average Americans than McCain, widely criticized as a "Beltway insider". However, media interviews suggested that Palin lacked knowledge on certain key issues, and they cast doubt among many voters about her qualifications to be vice president or president. In this regard, her inexperience was also a liability when McCain's age and health were factored inŌĆöthere was a higher-than-normal probability of Palin succeeding to the presidency and many moderates and independents chafed at this idea. "One 72 year old heartbeat away from the presidency" became a popular anti-GOP slogan. Late night TV host David Letterman
David Michael Letterman (born April 12, 1947) is an American television host, comedian, writer and producer. He hosted late night television talk shows for 33 years, beginning with the February 1, 1982 debut of ''Late Night with David Letterman' ...
jokingly referred to Palin as resembling "a slutty flight attendant" and even Obama himself on a September 9 speech referred to the Alaska governor's policies as "the equivalent of putting lipstick on a pig". She also came under attack on everything from her 17-year-old daughter giving birth to a child out of wedlock to actively participating in hunting moose and other animals. Because of Palin's conservative views, there was also concern that she would alienate independents and moderates, two groups that pundits observed McCain would need to win the election.
Economy
Polls taken in the last few months of the presidential campaign and exit polls conducted on Election Day showed the economy as the top concern for voters. In the fall of 2008, many news sources were reporting that the economy was suffering its most serious downturn since the Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
. During this period, John McCain's election prospects fell with several politically costly comments about the economy.
On August 20, John McCain said in an interview with ''Politico
''Politico'' (stylized in all caps), known originally as ''The Politico'', is an American, German-owned political journalism newspaper company based in Arlington County, Virginia, that covers politics and policy in the United States and intern ...
'' that he was uncertain how many houses he and his wife, Cindy, owned; "I thinkŌĆöI'll have my staff get to you," he told the media outlet. Both on the stump and in Obama's political ad, "Seven", the gaffe was used to portray McCain as somebody unable to relate to the concerns of ordinary Americans. This out-of-touch image was further cultivated when, on September 15, the day of the Lehman Brothers bankruptcy
The bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers on September 15, 2008, was the climax of the subprime mortgage crisis. After the financial services firm was notified of a pending credit downgrade due to its heavy position in subprime mortgages, the Federal ...
, at a morning rally in Jacksonville, Florida
Jacksonville is a city located on the Atlantic coast of northeast Florida, the most populous city proper in the state and is the largest city by area in the contiguous United States as of 2020. It is the seat of Duval County, with which the ...
, McCain declared that "the fundamentals of our economy are strong," despite what he described as "tremendous turmoil in our financial markets and Wall Street." With the perception among voters to the contrary, the comment appeared to cost McCain politically.
On September 24, 2008, after the onset of the 2008 global financial crisis
8 (eight) is the natural number following 7 and preceding 9.
In mathematics
8 is:
* a composite number, its proper divisors being , , and . It is twice 4 or four times 2.
* a power of two, being 2 (two cubed), and is the first number of t ...
, McCain announced that he was suspending his campaign to return to Washington so he could help craft a $700 billion bailout package for the troubled financial industry, and he stated that he would not debate Obama until Congress passed the bailout bill. Despite this decision, McCain was portrayed as somebody not playing a significant role in the negotiations for the first version of the bill, which fell short of passage in the House. He eventually decided to attend the first presidential debate on September 26, despite Congress' lack of immediate action on the bill. His ineffectiveness in the negotiations and his reversal in decision to attend the debates were seized upon to portray McCain as erratic in his response to the economy. Days later, a second version of the original bailout bill was passed by both the House and Senate, with Obama, his vice presidential running mate Joe Biden, and McCain all voting for the measure (Hillary Clinton would as well).
All the aforementioned remarks and campaign issues hurt McCain's standing with voters. All these also occurred after the onset of the economic crisis and after McCain's poll numbers had started to fall. Although sound bites of all of these "missteps" were played repeatedly on national television, many pundits and analysts say that the actual financial crisis and economic conditions caused McCain's large drop in support in mid-September and severely damaged his campaign.
Health care
John McCain
John Sidney McCain III (August 29, 1936 ŌĆō August 25, 2018) was an American politician and United States Navy officer who served as a United States senator from Arizona from 1987 until his death in 2018. He previously served two terms ...
's proposals focused on open-market competition rather than government funding or control. At the heart of his plan were tax credits ŌĆō $2,500 for individuals and $5,000 for families who do not subscribe to or do not have access to health care through their employer. To help people who are denied coverage by insurance companies due to pre-existing conditions, McCain proposed working with states to create what he calls a "Guaranteed Access Plan".
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...
called for universal health care
Universal health care (also called universal health coverage, universal coverage, or universal care) is a health care system in which all residents of a particular country or region are assured access to health care. It is generally organized ar ...
. His health care plan proposed creating a National Health Insurance Exchange that would include both private insurance plans and a Medicare-like government run option. Coverage would be guaranteed regardless of health status, and premiums would not vary based on health status either. It would have required parents to cover their children, but did not require adults to buy insurance.
Critics of McCain's plan argued that it would not significantly reduce the number of uninsured Americans, would increase costs, reduce consumer protections and lead to less generous benefit packages.[Thomas Buchmueller, Sherry A. Glied, Anne Royalty, and Katherine Swartz]
"Cost And Coverage Implications Of The McCain Plan To Restructure Health Insurance,"
''Health Affairs
''Health Affairs'' is a monthly peer-reviewed public health journal, healthcare journal established in 1981 by John K. Iglehart; since 2014, the editor-in-chief is Alan Weil. It was described by ''The Washington Post'' as "the bible of health poli ...
'', September 16, 2008 Critics of Obama's plan argued that it would increase federal regulation of private health insurance without addressing the underlying incentives behind rising health care spending.[Joseph Antos, Gail Wilensky, and Hanns Kuttner]
"The Obama Plan: More Regulation, Unsustainable Spending,"
''Health Affairs
''Health Affairs'' is a monthly peer-reviewed public health journal, healthcare journal established in 1981 by John K. Iglehart; since 2014, the editor-in-chief is Alan Weil. It was described by ''The Washington Post'' as "the bible of health poli ...
'', September 16, 2008 Mark Pauly suggested that a combination of the two approaches would work better than either one alone.
A poll released in early November 2008 found that voters supporting Obama listed health care as their second priority; voters supporting McCain listed it as fourth, tied with the war in Iraq. Affordability was the primary health care priority among both sets of voters. Obama voters were more likely than McCain voters to believe government can do much about health care costs.
Presidential debates
The United States presidential election of 2008 was sponsored by the Commission on Presidential Debates
The Commission on Presidential Debates (CPD) is a nonprofit corporation established in 1987 under the joint sponsorship of the Democratic and Republican political parties in the United States. The CPD sponsors and produces debates for U.S. pres ...
(CPD), a bipartisan
Bipartisanship, sometimes referred to as nonpartisanship, is a political situation, usually in the context of a two-party system (especially those of the United States and some other western countries), in which opposing political parties find co ...
organization that sponsored four debates that occurred at various locations around the United States (U.S.) in September and October 2008. Three of the debates involved the presidential nominees, and one involved the vice-presidential nominees.
Columbia University
Columbia University (also known as Columbia, and officially as Columbia University in the City of New York) is a private research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Church in Manhatt ...
political union and took place there on October 19. All candidates who could theoretically win the 270 electoral votes needed to win the election were invited, and Ralph Nader
Ralph Nader (; born February 27, 1934) is an American political activist, author, lecturer, and attorney noted for his involvement in consumer protection, environmentalism, and government reform causes.
The son of Lebanese immigrants to the Un ...
, Cynthia McKinney
Cynthia Ann McKinney (born March 17, 1955) is an American politician, academic, and conspiracy theorist. As a member of the Democratic Party, she served six terms in the United States House of Representatives. She was the first African American ...
, and Chuck Baldwin
Charles Obadiah Baldwin (born May 3, 1952) is an American right-wing politician, radio host, and founder-former pastor of Crossroad Baptist Church in Pensacola, Florida. As of January 2011 he was pastor of Liberty Fellowship in Kalispell, Montan ...
agreed to attend. Amy Goodman
Amy Goodman (born April 13, 1957) is an American broadcast journalist, syndicated columnist, investigative reporter, and author. Her investigative journalism career includes coverage of the East Timor independence movement, Morocco's occupation ...
, principal host of ''Democracy Now!
''Democracy Now!'' is an hour-long American TV, radio, and Internet news program hosted by journalists Amy Goodman (who also acts as the show's executive producer), Juan Gonz├Īlez, and Nermeen Shaikh. The show, which airs live each weekday at ...
'', moderated. It was broadcast on cable by C-SPAN
Cable-Satellite Public Affairs Network (C-SPAN ) is an American cable and satellite television network that was created in 1979 by the cable television industry as a nonprofit public service. It televises many proceedings of the United States ...
and on the Internet by Break-the-Matrix.
Campaign costs
The reported cost of campaigning for president has increased significantly in recent years. One source reported that if the costs for both Democratic and Republican campaigns were added together (for the presidential primary election, general election, and the political conventions), the costs have more than doubled in only eight years ($448.9 million in 1996, $649.5 million in 2000, and $1.01 billion in 2004).
Expense summary
According to required campaign filings as reported by the Federal Election Commission
The Federal Election Commission (FEC) is an independent regulatory agency of the United States whose purpose is to enforce campaign finance law in United States federal elections. Created in 1974 through amendments to the Federal Election Cam ...
(FEC), 148 candidates for all parties collectively raised $1,644,712,232 and spent $1,601,104,696 for the primary and general campaigns combined through November 24, 2008. The amounts raised and spent by the major candidates, according to the same source, were as follows:
Notable expressions and phrases
* Drill, baby, drill
"Drill, baby, drill!" was a 2008 Republican campaign slogan first used at the 2008 Republican National Convention by former Maryland Lieutenant Governor Michael Steele, who was later elected Chairman of the Republican National Committee. The sloga ...
: Republican self-described energy policy
* Yes We Can: Obama's campaign slogan
* That one: McCain's reference to Obama during the 2nd debate.
* Lipstick on a pig
The phrase to put "lipstick on a pig" means making superficial or cosmetic changes to a product in a futile effort to disguise its fundamental failings.
There are many phrases using pigs, or swine, dating back to biblical times. This phrase seem ...
: Obama used this phrase to insinuate that any changes that McCain was advocating from the policies of George W. Bush
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Republican Party, Bush family, and son of the 41st president George H. W. Bush, he ...
would only be slight modifications of Bush's policies but the underlying policies would be the same, and in Obama's opinion, bad. Some called it sexist, claiming it was a reference to Sarah Palin, who cracked a joke during the Republican convention
The Republican National Convention (RNC) is a series of U.S. presidential nominating convention, presidential nominating conventions held every four years since 1856 by the United States Republican Party. They are administered by the Republican N ...
that the only difference between a hockey mom and a pit bull is lipstick.
Internet campaigns
Fundraising
Howard Dean
Howard Brush Dean III (born November 17, 1948) is an American physician, author, lobbyist, and retired politician who served as the 79th governor of Vermont from 1991 to 2003 and chair of the Democratic National Committee (DNC) from 2005 to 200 ...
collected large contributions through the Internet in his 2004 primary run. In 2008, candidates went even further to reach out to Internet users through their own sites and such sites as YouTube
YouTube is a global online video platform, online video sharing and social media, social media platform headquartered in San Bruno, California. It was launched on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim. It is owned by ...
, MySpace, and Facebook
Facebook is an online social media and social networking service owned by American company Meta Platforms. Founded in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg with fellow Harvard College students and roommates Eduardo Saverin, Andrew McCollum, Dustin M ...
.
Promotion
Not only did the Internet allow candidates to raise money, but also it gave them a tool to appeal to newer and younger demographics. Political pundits were now evaluating candidates based on their social media following.
Senator Barack Obama's victory is credited to his competitive edge in social media and Internet following. Obama had over 2 million American supporters on Facebook
Facebook is an online social media and social networking service owned by American company Meta Platforms. Founded in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg with fellow Harvard College students and roommates Eduardo Saverin, Andrew McCollum, Dustin M ...
and 100,000 followers on Twitter
Twitter is an online social media and social networking service owned and operated by American company Twitter, Inc., on which users post and interact with 280-character-long messages known as "tweets". Registered users can post, like, and ...
, while McCain attracted only 600,000 Facebook supporters (likes) and 4,600 followers on Twitter. Obama's YouTube channel held 115,000 subscribers and more than 97 million video views. Obama had maintained a similar advantage over Senator Hillary Clinton in the Democratic primary.
Obama's edge in social media was crucial to the election outcome. According to a study by the Pew Internet and American Life project, 35 percent of Americans relied on online video for election news. Ten percent of Americans used social networking sites to learn about the election. The 2008 election showed huge increases in Internet use.
Another study done after the election gave a lot of insight on young voters. Thirty-seven percent of Americans ages 18ŌĆō24 got election news from social networking sites. Almost a quarter of Americans saw something about the election in an online video.smear campaign
A smear campaign, also referred to as a smear tactic or simply a smear, is an effort to damage or call into question someone's reputation, by propounding negative propaganda. It makes use of discrediting tactics.
It can be applied to individual ...
s, traditionally done with fliers and push calling, also spread to the Internet. Organizations specializing in the production and distribution of viral material, such as Brave New Films
Brave New Films (BNF) is a nonprofit film company based in Culver City, California. Founded by filmmaker Robert Greenwald, BNF produces feature-length documentaries and investigative videos that seek "to educate, influence and empower viewers to ...
, emerged; such organizations have been said to be having a growing influence on American politics.
Controversies
Voter suppression allegations
Allegations of voter list purges using unlawful criteria caused controversy in at least six swing states
In American politics, the term swing state (also known as battleground state or purple state) refers to any state that could reasonably be won by either the Democratic or Republican candidate in a statewide election, most often referring to pres ...
: Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of t ...
, Indiana
Indiana () is a U.S. state in the Midwestern United States. It is the 38th-largest by area and the 17th-most populous of the 50 States. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the United States as the 19th s ...
, Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
, Michigan
Michigan () is a state in the Great Lakes region of the upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the 10th-largest state by population, the 11th-largest by area, and the ...
, Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. N ...
and North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and So ...
. On October 5, 2008, the Republican
Republican can refer to:
Political ideology
* An advocate of a republic, a type of government that is not a monarchy or dictatorship, and is usually associated with the rule of law.
** Republicanism, the ideology in support of republics or agains ...
Lt. Governor of Montana, John Bohlinger
John Bohlinger, Jr. (born April 21, 1936) is an American businessman and politician who served as the 33rd Lieutenant Governor of Montana from 2005 to 2013. He ran for the office as a Republican on a bipartisan ticket headed by Democratic guber ...
, accused the Montana Republican Party of vote caging to purge 6,000 voters from three counties which trend Democratic. Allegations arose in Michigan that the Republican Party planned to challenge the eligibility of voters based on lists of foreclosed homes. The campaign of Democratic presidential nominee Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...
filed a lawsuit challenging this. The House Judiciary Committee
The U.S. House Committee on the Judiciary, also called the House Judiciary Committee, is a standing committee of the United States House of Representatives. It is charged with overseeing the administration of justice within the federal courts, a ...
wrote to the Department of Justice
A justice ministry, ministry of justice, or department of justice is a ministry or other government agency in charge of the administration of justice. The ministry or department is often headed by a minister of justice (minister for justice in a v ...
requesting an investigation.
Libertarian
Libertarianism (from french: libertaire, "libertarian"; from la, libertas, "freedom") is a political philosophy that upholds liberty as a core value. Libertarians seek to maximize autonomy and political freedom, and minimize the state's e ...
candidate Bob Barr
Robert Laurence Barr Jr. (born November 5, 1948) is an American attorney and politician. He served as a federal prosecutor and as a United States House of Representatives, Congressman. He represented Georgia's 7th congressional district as a Re ...
filed a lawsuit in Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
to have Obama and McCain removed from the ballot in that state. His campaign alleged that both of the candidates had missed the August 26 deadline to file and had been included on the ballot in violation of Texas election law. Neither Obama nor McCain had been confirmed as the candidate of their respective parties at the time of the deadline. The Texas Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of Texas (SCOTX) is the supreme court, court of last resort for civil matters (including juvenile delinquency cases, which are categorized as civil under the Texas Family Code) in the U.S. state of Texas. A different court, the ...
dismissed the lawsuit without explanation.
In Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
, identified by both parties as a key state, allegations surfaced from both Republicans and Democrats that individuals from out of state were moving to the state temporarily and attempting to vote despite not meeting the state's requirement of permanent residency for more than 29 days. The Franklin County Board of Elections referred 55 cases of possible voting irregularities to the local prosecutor.Marshall
Marshall may refer to:
Places
Australia
* Marshall, Victoria, a suburb of Geelong, Victoria
Canada
* Marshall, Saskatchewan
* The Marshall, a mountain in British Columbia
Liberia
* Marshall, Liberia
Marshall Islands
* Marshall Islands, an i ...
and Rhodes
Rhodes (; el, ╬ĪŽī╬┤╬┐Žé , translit=R├│dos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the So ...
scholars studying at Oxford University
Oxford () is a city in England. It is the county town and only city of Oxfordshire. In 2020, its population was estimated at 151,584. It is north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and north-east of Bristol. The city is home to the ...
, settled with Franklin County Prosecutor Ron O'Brien to have their challenged ballots withdrawn. The Obama campaign and others alleged that members of the McCain campaign had also voted without properly establishing residency.
Media bias
Republicans and independents leveled significant criticism at media outlets' coverage of the presidential election season. An October 22, 2008 Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan American think tank (referring to itself as a "fact tank") based in Washington, D.C.
It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the w ...
poll estimated 70% of registered voters believed journalists wanted Barack Obama to win the election, as opposed to 9% for John McCain. Another Pew survey, conducted after the election, found that 67% of voters thought that the press fairly covered Obama, versus 30% who viewed the coverage as unfair. Regarding McCain, 53% of voters viewed his press coverage as fair versus 44% who characterized it as unfair. Among affiliated Democrats, 83% believed the press fairly covered Obama; just 22% of Republicans thought the press was fair to McCain.
At the February debate, Tim Russert
Timothy John Russert (May 7, 1950 ŌĆō June 13, 2008) was an American television journalist and lawyer who appeared for more than 16 years as the longest-serving moderator of NBC's ''Meet the Press''. He was a senior vice president at NBC News, Wa ...
of NBC News
NBC News is the news division of the American broadcast television network NBC. The division operates under NBCUniversal Television and Streaming, a division of NBCUniversal, which is, in turn, a subsidiary of Comcast. The news division's var ...
was criticized for what some perceived as disproportionately tough questioning of Democratic presidential contender Hillary Clinton
Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton ( Rodham; born October 26, 1947) is an American politician, diplomat, and former lawyer who served as the 67th United States Secretary of State for President Barack Obama from 2009 to 2013, as a United States sen ...
.Russian President
The president of the Russian Federation ( rus, ą¤čĆąĄąĘąĖą┤ąĄąĮčé ąĀąŠčüčüąĖą╣čüą║ąŠą╣ ążąĄą┤ąĄčĆą░čåąĖąĖ, Prezident Rossiyskoy Federatsii) is the head of state of the Russian Federation. The president leads the executive branch of the federal ...
(Dmitry Medvedev
Dmitry Anatolyevich Medvedev ( rus, links=no, ąöą╝ąĖčéčĆąĖą╣ ąÉąĮą░č鹊ą╗čīąĄą▓ąĖčć ą£ąĄą┤ą▓ąĄą┤ąĄą▓, p=╦łdm╩▓itr╩▓╔¬j ╔Én╔É╦łtol╩▓j╔¬v╩▓╔¬t╔Ģ m╩▓╔¬d╦łv╩▓ed╩▓╔¬f; born 14 September 1965) is a Russian politician who has been serving as the dep ...
).Saturday Night Live
''Saturday Night Live'' (often abbreviated to ''SNL'') is an American late-night live television sketch comedy and variety show created by Lorne Michaels and developed by Dick Ebersol that airs on NBC and Peacock. Michaels currently serves a ...
''. In October 2007, liberal
Liberal or liberalism may refer to:
Politics
* a supporter of liberalism
** Liberalism by country
* an adherent of a Liberal Party
* Liberalism (international relations)
* Sexually liberal feminism
* Social liberalism
Arts, entertainment and m ...
commentators accused Russert of harassing Clinton over the issue of supporting drivers' licenses for illegal immigrants
Illegal immigration is the migration of people into a country in violation of the immigration laws of that country or the continued residence without the legal right to live in that country. Illegal immigration tends to be financially upwa ...
.ABC News
ABC News is the news division of the American broadcast network ABC. Its flagship program is the daily evening newscast ''ABC World News Tonight, ABC World News Tonight with David Muir''; other programs include Breakfast television, morning ...
hosted a debate in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
. Moderators Charles Gibson
Charles deWolf Gibson (born March 9, 1943) is an American broadcast television anchor, journalist and podcaster. Gibson was a host of ''Good Morning America'' from 1987 to 1998 and again from 1999 to 2006, and the anchor of ''World News with Char ...
and George Stephanopoulos
George Robert Stephanopoulos ( el, ╬ō╬ĄŽÄŽü╬│╬╣╬┐Žé ╬ŻŽä╬ĄŽå╬▒╬ĮŽīŽĆ╬┐Žģ╬╗╬┐Žé ; born February 10, 1961) is an American television host, political commentator, and former Democratic advisor. Stephanopoulos currently is a coanchor with Robin Robe ...
were criticized by viewers, blog
A blog (a truncation of "weblog") is a discussion or informational website published on the World Wide Web consisting of discrete, often informal diary-style text entries (posts). Posts are typically displayed in reverse chronological order ...
gers and media critics for the poor quality of their questions.Iraq War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Iraq War {{Nobold, {{lang, ar, žŁž▒ž© ž¦┘äž╣ž▒ž¦┘é (Arabic) {{Nobold, {{lang, ku, ž┤█Ģ┌Ģ█ī ž╣█Äž▒ž¦┘é (Kurdish languages, Kurdish)
, partof = the Iraq conflict (2003ŌĆōpresent), I ...
. Included in that category were continued questions about Obama's former pastor, Senator Hillary Clinton's assertion that she had to duck sniper fire in Bosnia
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called BosniaŌĆōHerzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and He ...
more than a decade ago, and Senator Obama's not wearing an American flag pin.op-ed
An op-ed, short for "opposite the editorial page", is a written prose piece, typically published by a North-American newspaper or magazine, which expresses the opinion of an author usually not affiliated with the publication's editorial board. O ...
published on April 27, 2008, in ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'', Elizabeth Edwards
Mary Elizabeth Anania Edwards (July 3, 1949 ŌĆō December 7, 2010) was an American attorney, author, and health care activist. She was married to John Edwards, the former U.S. Senator from North Carolina who was the 2004 United States Democrati ...
wrote that the media covered much more of "the rancor of the campaign" and "amount of money spent" than "the candidates' priorities, policies and principles." Author Erica Jong
Erica Jong (n├®e Mann; born March 26, 1942) is an American novelist, satirist, and poet, known particularly for her 1973 novel ''Fear of Flying''. The book became famously controversial for its attitudes towards female sexuality and figured pro ...
commented that "our press has become a sea of triviality, meanness and irrelevant chatter." A Gallup poll released on May 29, 2008, also estimated that more Americans felt the media was being harder on Hillary Clinton than they were towards Barack Obama. ''Time'' magazine columnist Mark Halperin
Mark Evan Halperin (born January 11, 1965)Mark Halperin. ''Contemporary Authors Online''. Detroit: Gale, 2010. Gale Biography In Context. is an American journalist, currently a host and commentator for Newsmax TV. Halperin previously worked as ...
stated that the media during the 2008 election had a "blind, almost slavish" worship of Obama.
The Project for Excellence in Journalism
The Project for Excellence in Journalism was a tax-exempt research organization in the United States that used empirical methods to evaluate and study the performance of the press.
The organization's director was Tom Rosenstiel, a professor of j ...
and Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
's conducted a study of 5,374 media narratives and assertions about the presidential candidates from January 1 through March 9, 2008. The study found that Obama received 69% favorable coverage and Clinton received 67%, compared to only 43% favorable media coverage of McCain. Another study by the Center for Media and Public Affairs The Center for Media and Public Affairs (CMPA) is a self-described nonpartisan and nonprofit research and educational organization that is affiliated with George Mason University in Fairfax, Virginia. It was founded in 1985 by political scientists ...
at George Mason University
George Mason University (George Mason, Mason, or GMU) is a public research university in Fairfax County, Virginia with an independent City of Fairfax, Virginia postal address in the Washington, D.C. Metropolitan Area. The university was origin ...
found the media coverage of Obama to be 72% negative from June 8 to July 21 compared to 57% negative for McCain. An October 29 study found 29% of stories about Obama to be negative, compared to 57% of stories about McCain being negative.
Conduct

Election Day
Election day or polling day is the day on which general elections are held. In many countries, general elections are always held on a Saturday or Sunday, to enable as many voters as possible to participate; while in other countries elections ar ...
was on November 4, 2008. The majority of states allowed early voting, with all states allowing some form of absentee voting. Voters cast votes for listed presidential candidates but were actually selecting representatives for their state's Electoral College slate.
A McCain victory quickly became improbable as Obama amassed early wins in his home state of Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolita ...
, the Northeast
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directionsŌĆönorth, east, south, and westŌĆöeach se ...
, and the critical battleground states of Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
(which no Republican has ever been elected president without winning) and Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
by 9:30 PM Eastern Standard Time. Obama won the entire Northeast by comfortable margins and the Great Lakes states
The Great Lakes region of North America is a binational CanadianŌĆō American region that includes portions of the eight U.S. states of Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Minnesota, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania and Wisconsin along with the Canadia ...
of Michigan
Michigan () is a state in the Great Lakes region of the upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the 10th-largest state by population, the 11th-largest by area, and the ...
, Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake M ...
, and Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over to ...
by double digits. McCain held on to traditionally Republican states like North Dakota
North Dakota () is a U.S. state in the Upper Midwest, named after the Native Americans in the United States, indigenous Dakota people, Dakota Sioux. North Dakota is bordered by the Canadian provinces of Saskatchewan and Manitoba to the north a ...
, South Dakota
South Dakota (; Sioux language, Sioux: , ) is a U.S. state in the West North Central states, North Central region of the United States. It is also part of the Great Plains. South Dakota is named after the Lakota people, Lakota and Dakota peo ...
, Nebraska
Nebraska () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. It is bordered by South Dakota to the north; Iowa to the east and Missouri to the southeast, both across the Missouri River; Kansas to the south; Colorado to the southwe ...
(though notably, Obama did win an electoral vote from Nebraska's 2nd congressional district), Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to the ...
, Oklahoma
Oklahoma (; Choctaw language, Choctaw: ; chr, ßÄŻßĦßÄ│ßÄ░ßÄ╣, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the nor ...
, Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columbi ...
, Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
, Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. To the north, it shares a small portion of the CanadaŌĆōUnited States border with the province of British Columbia. It borders the states of Montana and Wyom ...
, Wyoming
Wyoming () is a U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is bordered by Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho to the west, Utah to the south ...
, and his home state of Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Al─Ł ß╣Żonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
. Out of the southern states, Obama won Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
, North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and So ...
, Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacent Del ...
, Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean to ...
, and Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
. Obama also won the hotly contested states of Iowa
Iowa () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wisconsin to the northeast, Illinois to the ...
and New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ker ...
, which Al Gore
Albert Arnold Gore Jr. (born March 31, 1948) is an American politician, businessman, and environmentalist who served as the 45th vice president of the United States from 1993 to 2001 under President Bill Clinton. Gore was the Democratic Part ...
had won in 2000 and George W. Bush in 2004. Also, for only the second time since 1936
Events
January–February
* January 20 – George V of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions and Emperor of India, dies at his Sandringham Estate. The Prince of Wales succeeds to the throne of the United Kingdom as King E ...
(1964
Events January
* January 1 ŌĆō The Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland is dissolved.
* January 5 - In the first meeting between leaders of the Roman Catholic and Orthodox churches since the fifteenth century, Pope Paul VI and Patriarch ...
being the other), Indiana
Indiana () is a U.S. state in the Midwestern United States. It is the 38th-largest by area and the 17th-most populous of the 50 States. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the United States as the 19th s ...
went Democratic, giving Obama all eight Great Lakes states, the first time a presidential candidate had won all of them since Richard Nixon in 1972.
CNN
CNN (Cable News Network) is a multinational cable news channel headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia, U.S. Founded in 1980 by American media proprietor Ted Turner and Reese Schonfeld as a 24-hour cable news channel, and presently owned by the M ...
and Fox News
The Fox News Channel, abbreviated FNC, commonly known as Fox News, and stylized in all caps, is an American multinational conservative cable news television channel based in New York City. It is owned by Fox News Media, which itself is owne ...
called Virginia for Obama shortly before 11:00 PM, leaving him only 50 electoral votes shy of victory with only six West Coast West Coast or west coast may refer to:
Geography Australia
* Western Australia
*Regions of South Australia#Weather forecasting, West Coast of South Australia
* West Coast, Tasmania
**West Coast Range, mountain range in the region
Canada
* Britis ...
states (California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
, Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
, Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
, Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. To the north, it shares a small portion of the CanadaŌĆōUnited States border with the province of British Columbia. It borders the states of Montana and Wyom ...
, Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: ąÉą╗čÅčüą║ą░, Alyaska; ale, Alax╠ésxax╠é; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, An├Īaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S., ...
, and Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only stat ...
) still voting. All American networks called the election in favor of Obama at 11:00 PM as the polls closed on the West Coast. Obama was immediately declared the winner in California, Oregon, Washington, and Hawaii, McCain won Idaho, and the Electoral College totals were updated to 297 for Obama and 146 for McCain (270 are needed to win). McCain gave a concession speech half an hour later in his hometown of Phoenix, Arizona
Phoenix ( ; nv, Hoozdo; es, F├®nix or , yuf-x-wal, Bany├Ā:nyuw├Ī) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of cities and towns in Arizona#List of cities and towns, most populous city of the U.S. state of Arizona, with 1 ...
. Obama appeared just before midnight Eastern Time in Grant Park, Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
, in front of a crowd of 250,000 people to deliver his victory speech.
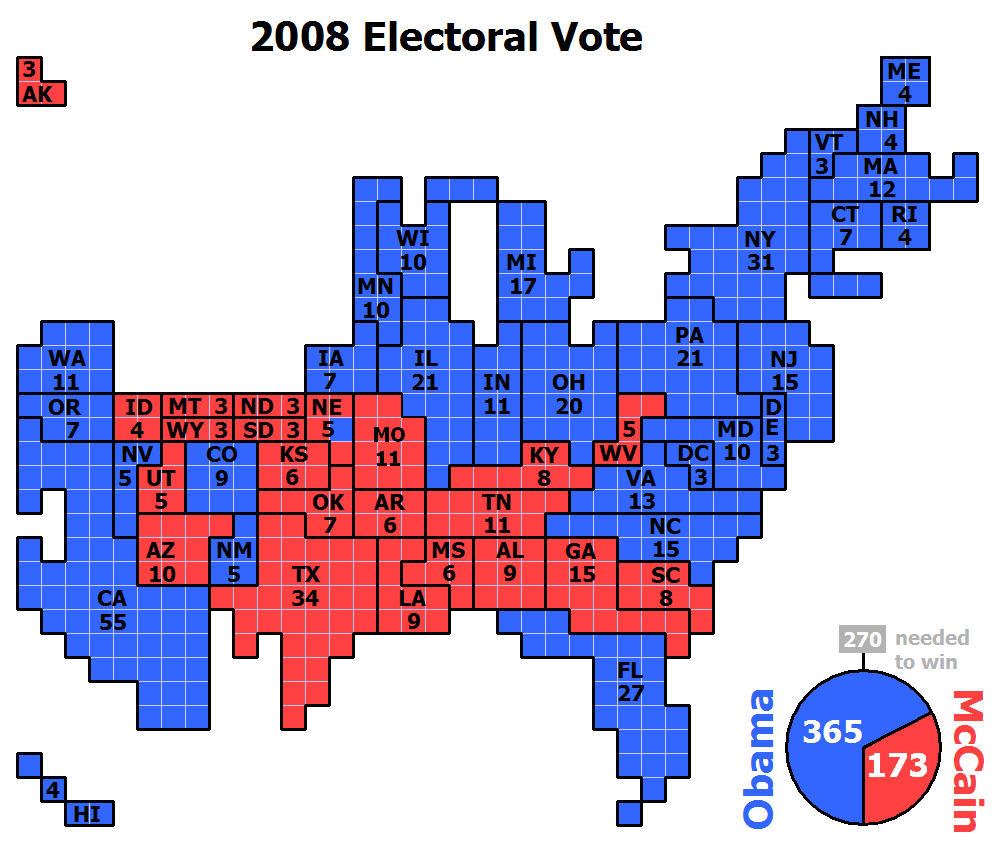 Following Obama's speech, spontaneous street parties broke out in cities across the United States including
Following Obama's speech, spontaneous street parties broke out in cities across the United States including Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
, Houston
Houston (; ) is the most populous city in Texas, the most populous city in the Southern United States, the fourth-most populous city in the United States, and the sixth-most populous city in North America, with a population of 2,304,580 in ...
, Las Vegas
Las Vegas (; Spanish for "The Meadows"), often known simply as Vegas, is the 25th-most populous city in the United States, the most populous city in the state of Nevada, and the county seat of Clark County. The city anchors the Las Vegas ...
, Miami
Miami ( ), officially the City of Miami, known as "the 305", "The Magic City", and "Gateway to the Americas", is a East Coast of the United States, coastal metropolis and the County seat, county seat of Miami-Dade County, Florida, Miami-Dade C ...
, Chicago, Columbus
Columbus is a Latinized version of the Italian surname "''Colombo''". It most commonly refers to:
* Christopher Columbus (1451-1506), the Italian explorer
* Columbus, Ohio, capital of the U.S. state of Ohio
Columbus may also refer to:
Places ...
, Detroit
Detroit ( , ; , ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is also the largest U.S. city on the United StatesŌĆōCanada border, and the seat of government of Wayne County. The City of Detroit had a population of 639,111 at th ...
, Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
, Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the largest city in the state of California and the second most populous city in the United States after New York City, as well as one of the world' ...
, Portland
Portland most commonly refers to:
* Portland, Oregon, the largest city in the state of Oregon, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States
* Portland, Maine, the largest city in the state of Maine, in the New England region of the northeas ...
, Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
, San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish language, Spanish for "Francis of Assisi, Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the List of Ca ...
, Denver
Denver () is a consolidated city and county, the capital, and most populous city of the U.S. state of Colorado. Its population was 715,522 at the 2020 census, a 19.22% increase since 2010. It is the 19th-most populous city in the Unit ...
, Atlanta
Atlanta ( ) is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Georgia. It is the seat of Fulton County, the most populous county in Georgia, but its territory falls in both Fulton and DeKalb counties. With a population of 498,715 ...
, Madison, Wisconsin, Madison, and New York City and around the world in London; Bonn; Berlin; Obama, Japan; Toronto; Rio de Janeiro; Sydney; and Nairobi.
Later on election night, after Obama was named the winner, he picked up several more wins in swing states in which the polls had shown a close race. These included Florida, Indiana
Indiana () is a U.S. state in the Midwestern United States. It is the 38th-largest by area and the 17th-most populous of the 50 States. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the United States as the 19th s ...
, Virginia, and the western states of Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of t ...
and Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. N ...
. All of these states had been carried by Bush in 2004
2004 was designated as an International Year of Rice by the United Nations, and the International Year to Commemorate the Struggle Against Slavery and its Abolition (by UNESCO).
Events January
* January 3 – Flash Airlines Flight 6 ...
. North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and So ...
and the Missouri bellwether, bellwether state of Missouri remained undecided for several days. Eventually Obama was declared the winner in North Carolina and McCain in Missouri, with Obama pulling out a rare win in Nebraska's 2nd congressional district. This put the projected electoral vote count at 365 for Obama and 173 for McCain. Obama's victories in the populous swing states of Florida, Ohio, Pennsylvania, North Carolina, and Virginia contributed to his decisive win. The presidential electors cast their ballots for president and vice president, and Congress tallied these votes on January 8, 2009.
Turnout
The voter turnout for this election was broadly predicted to be high by American standards, and a record number of votes were cast. The final tally of total votes counted was 131.3 million, compared to 122.3 million in 2004 (which also boasted the highest record since 1968 United States presidential election, 1968, the last presidential election before the voting age was lowered to 18). Expressed as a percentage of eligible voters, 131.2 million votes could reflect a turnout as high as 63.0% of eligible voters, which would be the highest since 1960 United States presidential election, 1960.
Ballot access
No other candidate had ballot access in enough states to win 270 electoral votes. All six candidates appeared on the ballot for a majority of the voters, while the 17 other listed candidates were available to no more than 30% of the voters.
The following candidates and parties had ballot listing or write-in status in more than one state:
* Alan Keyes (America's Independent Party) received 47,746 votes; listed in three states: Colorado and Florida, plus California (listed as American Independent), and also had write-in status in Kentucky, Ohio, Texas, and Utah.
* Ron Paul
Ronald Ernest Paul (born August 20, 1935) is an American author, activist, physician and retired politician who served as the U.S. representative for Texas's 22nd congressional district from 1976 to 1977 and again from 1979 to 1985, as well ...
received 42,426 votes; listed in Louisiana (Louisiana Taxpayers) and in Montana (Constitution), with write-in status in California.
* Gloria La Riva (Party for Socialism and Liberation) received 6,808 votes nationally; listed in 12 states: Arkansas, Colorado, Florida, Iowa, Louisiana, New Jersey, New York, Rhode Island, Utah, Vermont, Washington, and Wisconsin.
* Brian Moore (political activist), Brian Moore (Socialist Party USA, Socialist Party, see Brian Moore presidential campaign, 2008) received 6,538 votes; listed in eight states: Colorado, Florida, Iowa, New Jersey, Ohio, and Wisconsin, and Tennessee (independent) and Vermont (Liberty Union). He also filed for write-in status in 17 other states: Alaska, Connecticut, Illinois, Indiana, Kansas, Kentucky, Michigan, Minnesota, Montana, New York, North Carolina, Oregon, Texas, Utah, Virginia, Washington, and Wyoming.
* R├│ger Calero (Socialist Workers Party (United States), Socialist Workers Party) received 5,151 votes; listed in ten states. He was listed by name in Delaware, Minnesota, New Jersey, New York, and Vermont. James Harris was listed as his stand-in in Colorado, Florida, Iowa, Louisiana, and Washington, and also had write-in status in California.
* Charles Jay (Boston Tea Party (political party), Boston Tea Party) received 2,422 votes; listed in Colorado and Florida, and in Tennessee (as independent), with write-in status in Arizona, Montana, and Utah.
* Tom Stevens (Objectivist Party politician), Tom Stevens (Objectivist Party, Objectivist) received 755 votes; listed in Colorado and Florida.
* Gene Amondson (Prohibition Party, Prohibition) received 653 votes; listed in Colorado, Florida, and Louisiana.
* Jonathan Allen (Heartquake) received 483 votes; listed only in Colorado, with write-in status in Arizona, Georgia, Montana, Texas, and other states.
The following candidates (parties) were listed on the ballot in only one state:
* Richard Duncan (Independent) ŌĆō Ohio; 3,905 votes.
* John Joseph Polachek (New Party (United States), New Party) Illinois; 1,149 votes.
* Frank McEnulty (New American Independent Party, New American Independent) ŌĆō Colorado (listed as unaffiliated); 829 votes.
* Jeffrey Wamboldt (We the People Foundation, We the People) ŌĆō Wisconsin; 764 votes.
* Jeff Boss (Vote Here) ŌĆō New Jersey; 639 votes.
* George Phillies ŌĆō New Hampshire (also listed with the label Libertarian); 531 votes.
* Ted Weill (Reform Party of the United States of America, Reform) ŌĆō Mississippi; 481 votes.
* Bradford Lyttle (United States Pacifist Party, U.S. Pacifist) ŌĆō Colorado; 110 votes.
In Nevada, 6,267 votes were cast for "None of These Candidates". In the three states that officially keep track of "blank" votes for president, 103,193 votes were recorded as "blank". More than 100,000 write-in votes were cast and recorded for a scattering of other candidates, including 62 votes for "Santa Claus" (in ten states) and 11 votes for "Mickey Mouse" (in five states).
According to the Federal Election Commission, an unusually high number of "miscellaneous" write-ins were cast for president in 2008, including 112,597 tallied in the 17 states that record votes for non-listed candidates. There were more presidential candidates on the ballot than at any other time in U. S. history, except for the 1992 United States presidential election, 1992 election, which also had 23 candidates listed in at least one state.
Results
Popular vote totals are from th
official Federal Election Commission report
The results of the electoral vote were certified by Congress on January 8, 2009.
Results by state
The following table records the official vote tallies for each state for those presidential candidates who were listed on ballots in enough states to have a theoretical chance for a majority in the Electoral College. State popular vote results are from th
official Federal Election Commission report
The column labeled "Margin" shows Obama's margin of victory over McCain (the margin is negative for states and districts won by McCain).
Note: Maine and Nebraska each allow for their electoral votes to be split between candidates. In both states, two electoral votes are awarded to the winner of the statewide race and one electoral vote is awarded to the winner of each congressional district.
Cartographic gallery
File:2008prescountymap.PNG, Popular vote by county. Red represents counties that went for McCain; blue represents counties that went for Obama. Connecticut, Hawaii, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont had all counties go to Obama. Oklahoma had all counties go to McCain.
File:ElectionMapPurpleCounty.png, Presidential popular votes by county as a scale from red/Republican to blue/Democratic.
File:2008CartogramElection.jpg, Cartogram of popular vote with each county rescaled in proportion to its population. Deeper blue represents a Democratic majority; brighter red represents a Republican majority.
File:US Election04-08shift.png, Voting shifts per county from the 2004 to the 2008 election. Darker blue indicates the county voted more Democratic. Darker red indicates the county voted more Republican.
File:2008 United States presidential election results map by county.svg, Results by county, shaded according to winning candidate's percentage of the vote.
File:Presidential Elections 2004-2008 Swing in County Margins.svg, Change in vote margins at the county level from the 2004 election to the 2008 election. Obama made dramatic gains in every region of the country except for Arizona (McCain's home state), Alaska (Palin's home state), Appalachia, and the inner South, where McCain improved over Bush.
File:2008 presidential election, results by congressional district (popular vote percentage).svg, Results by Congressional Districts, shaded according to winning candidate's percentage of the vote.
Close states
 States where the margin of victory was under 1% (26 electoral votes; 15 won by Obama, 11 by McCain):
# Missouri, 0.13% (3,903 votes) ŌĆō 11 electoral votes
# North Carolina, 0.31% (14,177 votes) ŌĆō 15 electoral votes
States where the margin of victory was between 1% and 5% (62 electoral votes; 59 won by Obama, 3 by McCain):
# Indiana, 1.03% (28,391 votes) ŌĆō 11 electoral votes
# Nebraska's 2nd congressional district, 1.21% (3,370 votes) ŌĆō 1 electoral vote
# Montana, 2.26% (11,096 votes) ŌĆō 3 electoral votes
# Florida, 2.82% (236,450 votes) ŌĆō 27 electoral votes
# Ohio, 4.59% (262,224 votes) ŌĆō 20 electoral votes
States/districts where the margin of victory was between 5% and 10% (73 electoral votes; 33 won by Obama, 40 by McCain):
# Georgia, 5.21% (204,636 votes) ŌĆō 15 electoral votes
# Virginia, 6.30% (234,527 votes) ŌĆō 13 electoral votes
# South Dakota, 8.41% (32,130 votes) ŌĆō 3 electoral votes
# Arizona, 8.52% (195,404 votes) ŌĆō 10 electoral votes
# North Dakota, 8.63% (27,323 votes) ŌĆō 3 electoral votes
# Colorado, 8.95% (215,004 votes) ŌĆō 9 electoral votes (tipping-point state)
# South Carolina, 8.98% (172,447 votes) ŌĆō 8 electoral votes
# Iowa, 9.53% (146,561 votes) ŌĆō 7 electoral votes
# New Hampshire, 9.61% (68,292 votes) ŌĆō 4 electoral votes
# Nebraska's 1st congressional district, 9.77% (26,768 votes) ŌĆō 1 electoral vote
Blue denotes states or congressional districts won by Democrat Barack Obama; red denotes those won by Republican John McCain.
States where the margin of victory was under 1% (26 electoral votes; 15 won by Obama, 11 by McCain):
# Missouri, 0.13% (3,903 votes) ŌĆō 11 electoral votes
# North Carolina, 0.31% (14,177 votes) ŌĆō 15 electoral votes
States where the margin of victory was between 1% and 5% (62 electoral votes; 59 won by Obama, 3 by McCain):
# Indiana, 1.03% (28,391 votes) ŌĆō 11 electoral votes
# Nebraska's 2nd congressional district, 1.21% (3,370 votes) ŌĆō 1 electoral vote
# Montana, 2.26% (11,096 votes) ŌĆō 3 electoral votes
# Florida, 2.82% (236,450 votes) ŌĆō 27 electoral votes
# Ohio, 4.59% (262,224 votes) ŌĆō 20 electoral votes
States/districts where the margin of victory was between 5% and 10% (73 electoral votes; 33 won by Obama, 40 by McCain):
# Georgia, 5.21% (204,636 votes) ŌĆō 15 electoral votes
# Virginia, 6.30% (234,527 votes) ŌĆō 13 electoral votes
# South Dakota, 8.41% (32,130 votes) ŌĆō 3 electoral votes
# Arizona, 8.52% (195,404 votes) ŌĆō 10 electoral votes
# North Dakota, 8.63% (27,323 votes) ŌĆō 3 electoral votes
# Colorado, 8.95% (215,004 votes) ŌĆō 9 electoral votes (tipping-point state)
# South Carolina, 8.98% (172,447 votes) ŌĆō 8 electoral votes
# Iowa, 9.53% (146,561 votes) ŌĆō 7 electoral votes
# New Hampshire, 9.61% (68,292 votes) ŌĆō 4 electoral votes
# Nebraska's 1st congressional district, 9.77% (26,768 votes) ŌĆō 1 electoral vote
Blue denotes states or congressional districts won by Democrat Barack Obama; red denotes those won by Republican John McCain.
Statistics
Counties with highest percentage of Democratic vote:
# Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
92.46%
# Prince George's County, Maryland 88.87%
# The Bronx, Bronx County, New York 88.71%
# Oglala Lakota County, South Dakota, Shannon County, South Dakota 88.69%
# Petersburg, Virginia 88.64%
Counties with highest percentage of Republican vote:
# King County, Texas 92.64%
# Roberts County, Texas 92.08%
# Ochiltree County, Texas 91.70%
# Glasscock County, Texas 90.13%
# Beaver County, Oklahoma 89.25%
Voter demographics
Source: Exit polls conducted by Edison Research of Somerville, New Jersey, for the National Election Pool, a consortium of ABC News, Associated Press, CBS News, CNN, Fox News, and NBC News.
Analysis
Obama, having a White American, white mother and Kenyan father of the Luo (Kenya and Tanzania), Luo ethnic group, became the first African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
as well as the first Multiracial people, biracial president. Several black people had previously run for president, including Shirley Chisolm, Jesse Jackson, Lenora Fulani, Carol Moseley Braun, Alan Keyes, and Al Sharpton, though Obama was the first one even to win the nomination of a major party, let alone the general election. The Obama-Biden ticket was also the first winning ticket in American history in which neither candidate was a white Protestant, as Biden is Roman Catholic and the first Roman Catholic to be elected vice president; all previous tickets with Catholic vice presidential candidates had been defeated (William E. Miller, 1964, Sargent Shriver#Vice Presidential candidate, 1972, Geraldine Ferraro#1984 vice-presidential candidacy, 1984). The Obama-Biden ticket was the first winning ticket consisting of two sitting Senators since 1960 United States presidential election, 1960 (John F. Kennedy
John Fitzgerald Kennedy (May 29, 1917 ŌĆō November 22, 1963), often referred to by his initials JFK and the nickname Jack, was an American politician who served as the 35th president of the United States from 1961 until his assassination ...
/Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), often referred to by his initials LBJ, was an American politician who served as the 36th president of the United States from 1963 to 1969. He had previously served as the 37th vice ...
) (in the previous election cycle (2004
2004 was designated as an International Year of Rice by the United Nations, and the International Year to Commemorate the Struggle Against Slavery and its Abolition (by UNESCO).
Events January
* January 3 – Flash Airlines Flight 6 ...
) Democrats also Democratic Party presidential primaries, 2004, nominated two sitting senators, John Kerry
John Forbes Kerry (born December 11, 1943) is an American attorney, politician and diplomat who currently serves as the first United States special presidential envoy for climate. A member of the Forbes family and the Democratic Party (Unite ...
of and John Edwards
Johnny Reid Edwards (born June 10, 1953) is an American lawyer and former politician who served as a U.S. senator from North Carolina. He was the Democratic nominee for vice president in 2004 alongside John Kerry, losing to incumbents George ...
of North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and So ...
, but they lost to incumbents Bush and Cheney), and Obama became the first Northern Democratic president since Kennedy. Also, Obama became the first Democratic candidate to win a majority of the popular vote since Jimmy Carter
James Earl Carter Jr. (born October 1, 1924) is an American politician who served as the 39th president of the United States from 1977 to 1981. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, he previously served as th ...
in 1976
Events January
* January 3 ŌĆō The International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights enters into force.
* January 5 ŌĆō The Pol Pot regime proclaims a new constitution for Democratic Kampuchea.
* January 11 ŌĆō The 1976 Phila ...
, the first to win a majority of both votes and states since Lyndon Johnson in 1964
Events January
* January 1 ŌĆō The Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland is dissolved.
* January 5 - In the first meeting between leaders of the Roman Catholic and Orthodox churches since the fifteenth century, Pope Paul VI and Patriarch ...
, and the first Northern Democrat to win a majority of both votes and states since Franklin Roosevelt in 1944 United States presidential election, 1944. Obama became the first Northern Democrat to win any state in the former Confederacy since Hubert Humphrey won Texas in 1968. This was the first presidential election since 1952 in which neither of the major-party nominees was the incumbent president or vice-president.
 Prior to the election, commentators discussed whether Senator Obama would be able to redraw the electoral map by winning states that had been voting for Republican candidates in recent decades. In many ways, he was successful. He won every region of the country by double digits except the South, which John McCain won by nine percent. Obama won
Prior to the election, commentators discussed whether Senator Obama would be able to redraw the electoral map by winning states that had been voting for Republican candidates in recent decades. In many ways, he was successful. He won every region of the country by double digits except the South, which John McCain won by nine percent. Obama won Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacent Del ...
, the District of Columbia, Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean to ...
, North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and So ...
, Florida, and Virginia in the Southern United States, South (as defined by the US Census Bureau). McCain won most of the Deep South, where white voters had generally supported Republican candidates by increasingly large margins in the previous few decades. Obama won all of the 2004 swing states (states that either Kerry or Bush won by less than 5%) by a margin of 8.5 percent or more except for Ohio, which the Democrat carried by 4.5 percent. Obama also defied political bellwethers, becoming the first person to win the presidency while losing Missouri since 1956 United States presidential election, 1956 (as well as the first Democrat ever to do so) and while losing Kentucky and Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
since 1960 United States presidential election, 1960. He was the first Democrat to win without Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the Osage ...
since that state joined the Union in 1836 and the first Democrat to win the presidency without winning West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geographers classify West Virginia as part of the Southern United States while the Bur ...
since 1916
Events
Below, the events of the First World War have the "WWI" prefix.
January
* January 1 – The British Royal Army Medical Corps carries out the first successful blood transfusion, using blood that had been stored and cooled.
* ...
. Because one West Virginia elector voted for the Democrat in 1916, Obama was the first Democrat to win without any electors from the state since its founding in 1863. Indiana
Indiana () is a U.S. state in the Midwestern United States. It is the 38th-largest by area and the 17th-most populous of the 50 States. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the United States as the 19th s ...
and Virginia voted for the Democratic nominee for the first time since 1964
Events January
* January 1 ŌĆō The Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland is dissolved.
* January 5 - In the first meeting between leaders of the Roman Catholic and Orthodox churches since the fifteenth century, Pope Paul VI and Patriarch ...
. Indiana returned to being a reliably red state in subsequent elections; Virginia, however, has been won by Democrats in every presidential election since and would grow increasingly Democratic at the state level. North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and So ...
, which Obama was the first Democrat to carry since 1976 United States presidential election in North Carolina, 1976, would return to the Republican column in the following elections, though only by narrow margins each time.
Obama was also relatively competitive in some traditionally Republican states he lost, notably Montana, which he lost by under 3%, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia, which he lost by just 5%. He is also the only 21st-century Democrat to lose North Dakota and South Dakota by just single digits.
This was the first presidential election in which Nebraska split its electoral votes between two candidates. Together with Maine, which would not split its votes until 2016 United States presidential election, 2016, Nebraska is one of two states that allow a split in electoral votes without Faithless elector, faithless electors: a candidate receives one electoral vote for each congressional district won (Nebraska has three, Maine two), while the statewide winner receives an additional two electoral votes. Obama won the electoral vote from Nebraska's 2nd congressional district, largely comprising the city of Omaha. Nebraska's other four electoral votes went to John McCain. This would not happen again until 2020 United States presidential election in Nebraska, 2020.
, this election is the last time that Indiana and North Carolina voted Democratic, and is also the most recent election where one of the nominees has since died.
This election exhibited the continuation of some of the polarization trends evident in the 2000 United States presidential election, 2000 and 2004 elections. McCain won whites 55ŌĆō43 percent, while Obama won blacks 95ŌĆō4 percent, Hispanics 67ŌĆō31 percent, and Asians 62ŌĆō35 percent. Voters aged 18ŌĆō29 voted for Obama by 66ŌĆō32 percent while elderly voters backed McCain 53ŌĆō45 percent. The 25-year age gap between McCain and Obama was the widest in U.S. presidential election history among the top two candidates.
See also
* Barack Obama religion conspiracy theories
* Barack Obama citizenship conspiracy theories
* First inauguration of Barack Obama
* Newspaper endorsements in the 2008 United States presidential election
* Presidential transition of Barack Obama
* 2008 United States gubernatorial elections
* 2008 United States House of Representatives elections
* 2008 United States Senate elections
* Third-party and independent candidates for the 2008 United States presidential election
Opinion polling
* Nationwide opinion polling for the 2008 United States presidential election
* Statewide opinion polling for the 2008 United States presidential election
* International opinion polling for the 2008 United States presidential election
* Scientific forecasts: FiveThirtyEight
Notes
References
Further reading
* Plouffe, David. The Audacity to Win. 2009
* Balz, Dan, and Haynes Johnson. ''The Battle for America 2008: The Story of an Extraordinary Election'' (2009), by leading reporters with inside information
* Crotty, William. "Policy and Politics: The Bush Administration and the 2008 Presidential Election," ''Polity,'' July 2009, Vol. 41 Issue 3, pp 282ŌĆō31
online
* Curtis, Mark. ''Age of Obama: A Reporter's Journey With Clinton, McCain and Obama in the Making of the President in 2008'' (2009)
* Gidlow, Liette. Obama, Clinton, Palin: Making History in Election 2000 (2012)
* Nelson, Michael. ''The Elections of 2008'' (2009), factual summar
except and text search
* Sussman, Glen. "Choosing a New Direction: The Presidential Election of 2008," ''White House Studies,'' 2009, Vol. 9 Issue 1, pp 1ŌĆō20
* Wolffe, Richard. ''Renegade: The Making of a President'' (2010
excerpt and text search
narrative
Voters
* Abramson, Paul R., John H. Aldrich, and David W. Rohde. ''Change and Continuity in the 2008 Elections'' (2009
excerpt and text search
* Corwin E. Smidt and others. ''The Disappearing God Gap? Religion in the 2008 Presidential Election'' (Oxford University Press; 2010) 278 pages. Finds that the gap between church-attending traditionalists and other voters is not closing, as has been claimed, but is changing in significant ways; draws on survey data from voters who were interviewed in the spring of 2008 and then again after the election.
* Crespino, Joseph. "The U.S. South and the 2008 Election," ''Southern Spaces'' (2008
online
* Jessee, Stephen A. "Voter Ideology and Candidate Positioning in the 2008 Presidential Election," ''American Politics Research,'' March 2010, Vol. 38 Issue 2, pp 195ŌĆō210
* Kenski, Kate, Bruce W. Hardy, and Kathleen Hall Jamieson. ''The Obama Victory: How Media, Money, and Message Shaped the 2008 Election'' (Oxford University Press; 2010) 378 pages. Draws on interviews with key campaign advisors as well as the National Annenberg Election Survey
excerpt and text search
* Sabato, Larry. ''The Year of Obama: How Barack Obama Won the White House'' (2009)
* Stempel III, Guido H. and Thomas K. Hargrove, eds. ''The 21st-Century Voter: Who Votes, How They Vote, and Why They Vote'' (2 vol. 2015).
* Todd, Chuck, and Sheldon Gawiser. ''How Barack Obama Won: A State-by-State Guide to the Historic 2008 Presidential Election'' (2009
excerpt and text search
External links
*
Beyond Red and Blue: 7 Ways to View the Presidential Election Map
Ćöfrom ''Scientific American''
Campaign commercials from the 2008 election
US Election 2008 Web Monitor
* Joseph Crespino
"The U.S. South and the 2008 Election"
''Southern Spaces'', December 11, 2008.
Election of 2008 in Counting the Votes
{{Authority control
2008 United States presidential election,
Barack Obama 2008 presidential campaign
John McCain 2008 presidential campaign
Barack Obama
John McCain
Joe Biden
Sarah Palin
November 2008 events in the United States


 The major political party nomination process (technically) continues through June of an election year. In previous cycles, the candidates were effectively chosen by the end of the primaries held in March, but, in this cycle, Barack Obama did not win enough delegates to secure the nomination until June 3, after a 17-month campaign against Hillary Clinton. He had a wide lead in states won, while Clinton had won majorities in several of the larger states. Now, because a form of
The major political party nomination process (technically) continues through June of an election year. In previous cycles, the candidates were effectively chosen by the end of the primaries held in March, but, in this cycle, Barack Obama did not win enough delegates to secure the nomination until June 3, after a 17-month campaign against Hillary Clinton. He had a wide lead in states won, while Clinton had won majorities in several of the larger states. Now, because a form of  Following Obama's speech, spontaneous street parties broke out in cities across the United States including
Following Obama's speech, spontaneous street parties broke out in cities across the United States including  Prior to the election, commentators discussed whether Senator Obama would be able to redraw the electoral map by winning states that had been voting for Republican candidates in recent decades. In many ways, he was successful. He won every region of the country by double digits except the South, which John McCain won by nine percent. Obama won
Prior to the election, commentators discussed whether Senator Obama would be able to redraw the electoral map by winning states that had been voting for Republican candidates in recent decades. In many ways, he was successful. He won every region of the country by double digits except the South, which John McCain won by nine percent. Obama won