1992 United States Presidential Election on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The 1992 United States presidential election was the 52nd quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 3, 1992.
File:Jerry Brown in 1978 crop.jpg,
File:Senator Paul Tsongas.jpg,
File:Senator Bob Kerrey.jpg,
File:Tom Harkin portrait.jpg,
File:Douglas Wilder 2003 NIH.jpg,
File:EugeneMcCarthy.jpg,
File:patschroeder.jpg,
File:Official City Portrait of Larry Agran.jpg,
File:Pat Buchanan 1985.jpg,
File:George H. W. Bush presidential portrait (cropped).jpg,
File:Rsz davidduke (cropped).jpg,
File:Harold Stassen 1980.jpg,
Paleoconservative journalist
 The public's concern about the federal budget deficit and fears of professional politicians allowed the independent candidacy of billionaire Texan
The public's concern about the federal budget deficit and fears of professional politicians allowed the independent candidacy of billionaire Texan
 Libertarian candidates:
* Andre Marrou, former Alaska
Libertarian candidates:
* Andre Marrou, former Alaska
 New Alliance candidate:
*
New Alliance candidate:
*
 The newly formed
The newly formed
 U.S. Taxpayers' candidates:
* Howard Phillips, conservative political activist from Virginia
*
U.S. Taxpayers' candidates:
* Howard Phillips, conservative political activist from Virginia
*
 Populist candidate:
* Bo Gritz, Former United States Army
Populist candidate:
* Bo Gritz, Former United States Army
 While officially running for the Democratic Presidential nomination, Lyndon LaRouche also decided to run as an Independent in the general election, standing as the National Economic Recovery candidate. LaRouche was in jail at the time, having been convicted of conspiracy to commit mail fraud in December 1988; it was only the second time in history that the presidency was sought from a prison cell (after Socialist Party candidate Eugene V. Debs, while imprisoned for his opposition to U.S. involvement in World War I, ran in 1920). His running-mate was James Bevel, a civil rights activist who had represented the LaRouche movement in its pursuit of the Franklin child prostitution ring allegations.
In addition to the displayed states, LaRouche had nearly made the ballot in the states of New York and Mississippi. In the case of New York, while his petition was valid and had enough signatures, none of his electors filed declarations of candidacy; in the cases of Mississippi a sore-loser law was in place, and because he ran in that state's Democratic presidential primary he was ineligible to run as an Independent in the general. Ohio also had a sore-loser law, but it was ruled in Brown vs. Taft that it did not apply to presidential candidates.
LaRouche and Beval drew 22,863 votes. (<0.1% of the popular vote).
While officially running for the Democratic Presidential nomination, Lyndon LaRouche also decided to run as an Independent in the general election, standing as the National Economic Recovery candidate. LaRouche was in jail at the time, having been convicted of conspiracy to commit mail fraud in December 1988; it was only the second time in history that the presidency was sought from a prison cell (after Socialist Party candidate Eugene V. Debs, while imprisoned for his opposition to U.S. involvement in World War I, ran in 1920). His running-mate was James Bevel, a civil rights activist who had represented the LaRouche movement in its pursuit of the Franklin child prostitution ring allegations.
In addition to the displayed states, LaRouche had nearly made the ballot in the states of New York and Mississippi. In the case of New York, while his petition was valid and had enough signatures, none of his electors filed declarations of candidacy; in the cases of Mississippi a sore-loser law was in place, and because he ran in that state's Democratic presidential primary he was ineligible to run as an Independent in the general. Ohio also had a sore-loser law, but it was ruled in Brown vs. Taft that it did not apply to presidential candidates.
LaRouche and Beval drew 22,863 votes. (<0.1% of the popular vote).
 Socialist Workers candidate:
* James Warren, journalist and steel worker from Illinois, and the 1988 Presidential nominee
James Warren, who was the 1988 presidential nominee of the Socialist Workers Party, received a second consecutive nomination from the Party on the first of November 1991. Warren had two running mates that varied from state to state; Estelle DeBates and Willie Mae Reid, the latter also a resident of Illinois.
Warren received 22,882 votes (<0.1% of the popular vote).
Socialist Workers candidate:
* James Warren, journalist and steel worker from Illinois, and the 1988 Presidential nominee
James Warren, who was the 1988 presidential nominee of the Socialist Workers Party, received a second consecutive nomination from the Party on the first of November 1991. Warren had two running mates that varied from state to state; Estelle DeBates and Willie Mae Reid, the latter also a resident of Illinois.
Warren received 22,882 votes (<0.1% of the popular vote).
 * Ronald Daniels, former director of the
* Ronald Daniels, former director of the
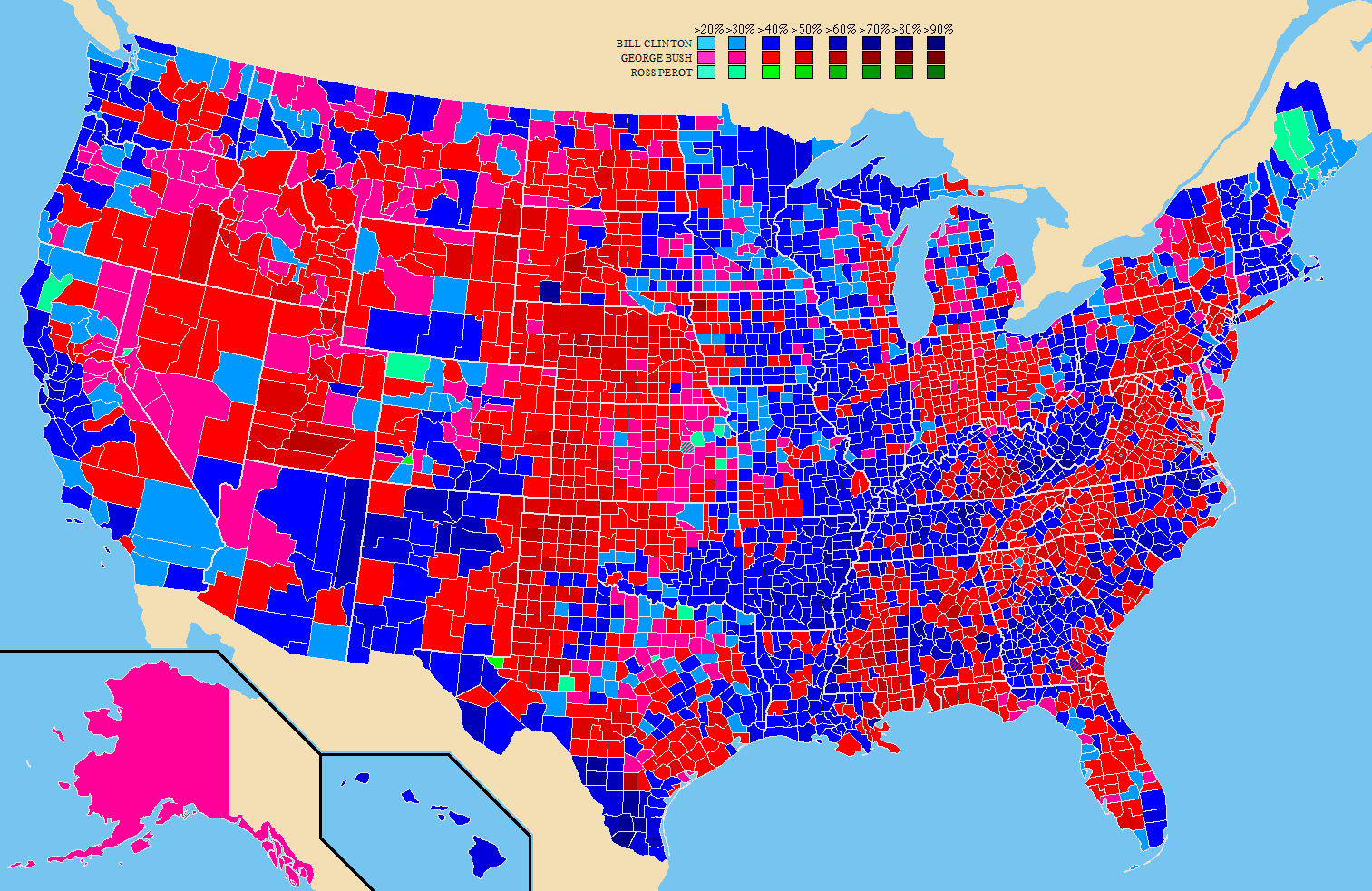

File:1992 United States presidential election results map by county.svg, Results by county, shaded according to winning candidate's percentage of the vote
Source: New York Times President Map
http://usinfo.state.gov/usa/infousa/facts/history/ch13.htm#1992 and titled "An Outline of American History: Chapter 13: Toward the 21st century".
** An
** This page is in the public domain as a government publication.
online
* Germond, Jack, and Jules Witcover. ''Mad As Hell: Revolt at the Ballot Box, 1992'' (1993)
online
* Goldman, Peter. et al. ''Quest for the Presidency 1992'' (1994) 805pp. * Herron, Michael C., et al. "Measurement of political effects in the United States economy: A study of the 1992 presidential election." ''Economics & Politics'' 11.1 (1999): 51-81. * * * Kellstedt, Lyman A., et al. "Religious voting blocs in the 1992 election: The year of the evangelical?." ''Sociology of Religion'' 55.3 (1994): 307-326. ellstedt, Lyman A., et al. "Religious voting blocs in the 1992 election: The year of the evangelical?." Sociology of Religion 55.3 (1994): 307-326. online* Klein, Jill Gabrielle. "Negativity in impressions of presidential candidates revisited: The 1992 election." ''Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin'' 22.3 (1996): 288-295. * Ladd, Everett Carll. "The 1992 vote for President Clinton: Another brittle mandate?." ''Political Science Quarterly'' 108.1 (1993): 1-28
online
* Lipset, Seymour Martin. "The significance of the 1992 election." ''PS: Political Science and Politics'' 26.1 (1993): 7-16
online
* Nelson, Michael ed. ''The Elections of 1992'' (1993) * Nelson, Michael. ''Clinton's Elections: 1992, 1996, and the Birth of a New Era of Governance'' (2020
excerpt
* O'Mara, Margaret. ''Pivotal Tuesdays: Four Elections That Shaped the Twentieth Century'' (2015), compares 1912, 1932, 1968, 1992 in terms of social, economic, and political history * Ornstein, Norman J. "Foreign policy and the 1992 election." ''Foreign Affairs'' 71.3 (1992): 1-16
online
* Pomper, Gerald M. ed. ''The Election of 1992'' (1993). * Post, Jerrold M. "The Political psychology of the Ross Perot phenomenon." in ''The Clinton Presidency'' (Routledge, 2019. 37-56). * * * Troy, Gil. "Stumping in the bookstores: A literary history of the 1992 presidential campaign." ''Presidential Studies Quarterly'' (1995): 697-710
online
* Weaver, David, and Dan Drew. "Voter learning in the 1992 presidential election: Did the “nontraditional” media and debates matter?." ''Journalism & Mass Communication Quarterly'' 72.1 (1995): 7-17.
online
* Clinton, Bill, and Al Gore. ''Putting People First: How We Can All Change America'' (1992) * Cramer, Richard Ben. ''What It Takes: The Way to the White House'' (1992)
online
* Dionne, E. J. ''Why Americans Hate Politics'' (1992)
online
* Duffy, Michael, and Dan Goodgame. ''Marching in Place: The Status Quo Presidency of George Bush'' (1992
online
* Edsall Thomas Byrne, and Mary D. Edsall. ''Chain Reaction: The Impact of Race, Rights, and Taxes on American Politics'' (1992
online
* Ehrenhalt, Alan. ''The United States of Ambition: Politicians, Power, and the Pursuit of Office'' (1992
online
* Gore, Al. ''Earth in the Balance: Ecology and the Human Spirit'' (1992)
online
* Greider, William. ''Who Will Tell the People: The Betrayal of American Democracy'' (1992
online
* Jamieson, Kathleen Hall. ''Dirty Politics: Deception, Distraction, and Democracy'' (1992
online
* Perot, Ross. ''United We Stand: How We Can Take Back Our Country'' (1992
online
* Phillips, Kevin. ''The Politics of Rich and Poor: Wealth and the American Electorate in the Reagan Aftermath'' (1992
online
* Sabato, Larry J. ''Feeding Frenzy: How Attack Journalism Has Transformed American Politics'' (1991
online
* Will, George F. ''Restoration: Congress, Term Limits and the Recovery of Deliberative Democracy'' (1992
online
1992 popular vote by state
Presidential Campaign Commercials
Campaign commercials from the 1992 election
*
''Booknotes'' interview with Tom Rosenstiel on ''Strange Bedfellows: How Television and the Presidential Candidates Changed American Politics, 1992'', August 8, 1993.
Election of 1992 in Counting the Votes
{{Authority control Al Gore Dan Quayle Presidency of George H. W. Bush George H. W. Bush Bill Clinton Ross Perot November 1992 events in the United States
Democratic
Democrat, Democrats, or Democratic may refer to:
Politics
*A proponent of democracy, or democratic government; a form of government involving rule by the people.
*A member of a Democratic Party:
**Democratic Party (United States) (D)
**Democratic ...
Governor Bill Clinton of Arkansas defeated incumbent Republican President George H. W. Bush
George Herbert Walker BushSince around 2000, he has been usually called George H. W. Bush, Bush Senior, Bush 41 or Bush the Elder to distinguish him from his eldest son, George W. Bush, who served as the 43rd president from 2001 to 2009; pr ...
, independent businessman Ross Perot
Henry Ross Perot (; June 27, 1930 – July 9, 2019) was an American business magnate, billionaire, politician and philanthropist. He was the founder and chief executive officer of Electronic Data Systems and Perot Systems. He ran an inde ...
of Texas, and a number of minor candidates. The election marked the end of a period of Republican dominance in American presidential politics that began in 1968
The year was highlighted by protests and other unrests that occurred worldwide.
Events January–February
* January 5 – "Prague Spring": Alexander Dubček is chosen as leader of the Communist Party of Czechoslovakia.
* Januar ...
, and also marked the end of 12 years of Republican rule of the White House, as well as the end of the Greatest Generation's 32-year American rule and the beginning of the Baby boomers 28-year dominance until 2020. It was the last time the incumbent president failed to win a second term until 2020
2020 was heavily defined by the COVID-19 pandemic, which led to global Social impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, social and Economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, economic disruption, mass cancellations and postponements of events, COVID- ...
, when Donald Trump lost the election to Joe Biden; it was the first such occurrence since 1980
Events January
* January 4 – U.S. President Jimmy Carter proclaims a grain embargo against the USSR with the support of the European Commission.
* January 6 – Global Positioning System time epoch begins at 00:00 UTC.
* January 9 – ...
.
Bush had alienated many of the conservatives in his party by breaking his 1988 campaign pledge against raising taxes, but he fended off a primary challenge
In U.S. politics, a primary challenge is when an incumbent holding elective office is challenged by a member of their own political party in a primary election. Such events, known informally as "being primaried," are noteworthy and not frequent i ...
from paleoconservative commentator Pat Buchanan
Patrick Joseph Buchanan (; born November 2, 1938) is an American paleoconservative political commentator, columnist, politician, and broadcaster. Buchanan was an assistant and special consultant to U.S. Presidents Richard Nixon, Gerald Ford, an ...
. Bush's popularity following his success in the Gulf War dissuaded high-profile Democratic candidates like Mario Cuomo from entering the 1992 Democratic primaries. Clinton, a leader of the centrist Democratic Leadership Council, established himself as the front-runner for the Democratic nomination by sweeping the Super Tuesday primaries. He defeated former Governor of California Jerry Brown, former Massachusetts Senator Paul Tsongas
Paul Efthemios Tsongas (; February 14, 1941 – January 18, 1997) was an American politician who represented Massachusetts in the United States Senate from 1979 until 1985 and in the United States House of Representatives from 1975 until 197 ...
, and other candidates to win his party's nomination, and chose Tennessee Senator Al Gore
Albert Arnold Gore Jr. (born March 31, 1948) is an American politician, businessman, and environmentalist who served as the 45th vice president of the United States from 1993 to 2001 under President Bill Clinton. Gore was the Democratic Part ...
as his running mate. Billionaire Ross Perot launched an independent campaign, emphasizing his opposition to the North American Free Trade Agreement
The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA ; es, Tratado de Libre Comercio de América del Norte, TLCAN; french: Accord de libre-échange nord-américain, ALÉNA) was an agreement signed by Canada, Mexico, and the United States that crea ...
and his plan to reduce the national debt
A country's gross government debt (also called public debt, or sovereign debt) is the financial liabilities of the government sector. Changes in government debt over time reflect primarily borrowing due to past government deficits. A deficit oc ...
.
The economy had recovered from a recession in the spring of 1991, followed by 19 consecutive months of economic growth, but perceptions of the economy's slow growth harmed Bush, for he had inherited a substantial economic boom from his predecessor Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
. Bush's greatest strength, foreign policy
A State (polity), state's foreign policy or external policy (as opposed to internal or domestic policy) is its objectives and activities in relation to its interactions with other states, unions, and other political entities, whether bilaterall ...
, was regarded as much less important following the dissolution of the Soviet Union
The dissolution of the Soviet Union, also negatively connoted as rus, Разва́л Сове́тского Сою́за, r=Razvál Sovétskogo Soyúza, ''Ruining of the Soviet Union''. was the process of internal disintegration within the Sov ...
and the end of the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
, as well as the relatively peaceful climate in the Middle East after the Gulf War. Perot led in several polls taken in June 1992, but severely damaged his candidacy by temporarily dropping out of the race in July. The Bush campaign criticized Clinton's character and emphasized Bush's foreign policy successes, while Clinton focused on the economy.
Clinton won a plurality in the popular vote and a majority of the electoral vote, breaking a streak of three consecutive Republican victories. He won states in every region of the country; he swept the Northeast
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each sepa ...
and the West Coast West Coast or west coast may refer to:
Geography Australia
* Western Australia
*Regions of South Australia#Weather forecasting, West Coast of South Australia
* West Coast, Tasmania
**West Coast Range, mountain range in the region
Canada
* Britis ...
, marking the start of Democratic dominance in both regions in both presidential and statewide elections. Clinton also performed well in the eastern Midwest
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four Census Bureau Region, census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of ...
, the Mountain West, Appalachia
Appalachia () is a cultural region in the Eastern United States that stretches from the Southern Tier of New York State to northern Alabama and Georgia. While the Appalachian Mountains stretch from Belle Isle in Newfoundland and Labrador, Ca ...
, and parts of the South
South is one of the cardinal directions or Points of the compass, compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Pro ...
. This election was the first time a Democrat had won the presidency without Texas since its statehood and North Carolina since 1844
In the Philippines, it was the only leap year with 365 days, as December 31 was skipped when 1845 began after December 30.
Events
January–March
* January 15 – The University of Notre Dame, based in the city of the same name, receives ...
. This was also the last time to date that the state of Montana voted Democratic in a presidential election, and the last time until 2020 that Georgia did so. Clinton flipped a total of 22 states that had voted Republican in the election of 1988. Clinton would win with the smallest vote share of the national vote since Woodrow Wilson in 1912, when the Republican Party experienced a drastic split.
Perot won 18.9% of the popular vote, the highest share of the vote won by a candidate outside of the two major parties since 1912
Events January
* January 1 – The Republic of China (1912–49), Republic of China is established.
* January 5 – The Prague Conference (6th All-Russian Conference of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party) opens.
* January 6 ...
. Although he failed to win any electoral votes, he beat either main candidate in some states and found significant support in every state, resulting in no state giving an absolute majority to any candidate except Clinton's home state of Arkansas. As such, this is the final election to date in which the Democratic nominee won less than 50% of the vote in California, Connecticut, Delaware, Hawaii, Illinois, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Jersey, New York, Rhode Island, and Vermont; and in which the Republican nominee won less than 50% in Alabama, Alaska, Idaho, Kansas, and Nebraska. It is also the third and final election since the Civil War in which a Republican or Democratic nominee failed to break 50% in a single state, the first two being 1912
Events January
* January 1 – The Republic of China (1912–49), Republic of China is established.
* January 5 – The Prague Conference (6th All-Russian Conference of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party) opens.
* January 6 ...
for William Howard Taft and 1984
Events
January
* January 1 – The Bornean Sultanate of Brunei gains full independence from the United Kingdom, having become a British protectorate in 1888.
* January 7 – Brunei becomes the sixth member of the Association of Southeast A ...
for Walter Mondale. As of 2022, this is the last time that either a Democratic or Republican candidate received less than 40% of the popular vote.
Nominations
Democratic Party nomination
Overview
Following the successful performance by U.S. and coalition forces in the Persian Gulf War, PresidentGeorge H. W. Bush
George Herbert Walker BushSince around 2000, he has been usually called George H. W. Bush, Bush Senior, Bush 41 or Bush the Elder to distinguish him from his eldest son, George W. Bush, who served as the 43rd president from 2001 to 2009; pr ...
's approval ratings were 89%. His re-election was considered very likely; several high-profile candidates, such as Mario Cuomo and Jesse Jackson
Jesse Louis Jackson (né Burns; born October 8, 1941) is an American political activist, Baptist minister, and politician. He was a candidate for the Democratic presidential nomination in 1984 and 1988 and served as a shadow U.S. senator ...
refused to seek the Democratic nomination. Senator Al Gore
Albert Arnold Gore Jr. (born March 31, 1948) is an American politician, businessman, and environmentalist who served as the 45th vice president of the United States from 1993 to 2001 under President Bill Clinton. Gore was the Democratic Part ...
refused to seek the nomination due to the fact his son had been struck by a car and was undergoing surgery and physical therapy. However, Tom Harkin, Paul Tsongas
Paul Efthemios Tsongas (; February 14, 1941 – January 18, 1997) was an American politician who represented Massachusetts in the United States Senate from 1979 until 1985 and in the United States House of Representatives from 1975 until 197 ...
, Jerry Brown, Larry Agran, Bob Kerrey, Douglas Wilder
Lawrence Douglas Wilder (born January 17, 1931) is an American lawyer and politician who served as the 66th Governor of Virginia from 1990 to 1994. He was the first African American to serve as governor of a U.S. state since the Reconstruction ...
and Bill Clinton chose to run as candidates.
U.S. Senator Tom Harkin (Iowa) ran as a populist liberal with labor union support. Former U.S. Senator Paul Tsongas (Mass.) highlighted his political independence and fiscal conservatism. Former California Governor Jerry Brown, who had run for the Democratic nomination in 1976 and 1980, declared a significant reform agenda, including Congressional term limits, campaign finance reform Campaign finance reform may refer to:
* Reform of campaign finance
Campaign finance, also known as election finance or political donations, refers to the funds raised to promote candidates, political parties, or policy initiatives and referen ...
, and the adoption of a flat income tax. Nebraska Senator Bob Kerrey was an attractive candidate based on his business and military background, but made several gaffes on the campaign trail. Arkansas Governor Bill Clinton positioned himself as a centrist, or New Democrat. He was relatively unknown nationally before the primary season. That quickly changed however, when Gennifer Flowers alleged an extramarital affair. Clinton denied the story, appearing on ''60 Minutes
''60 Minutes'' is an American television news magazine broadcast on the CBS television network. Debuting in 1968, the program was created by Don Hewitt and Bill Leonard, who chose to set it apart from other news programs by using a unique styl ...
'' with his wife, Hillary Clinton; in 1998, he admitted the affair.
The primary began with Harkin winning his native Iowa as expected. Tsongas won the New Hampshire primary
The New Hampshire presidential primary is the first in a series of nationwide party primary elections and the second party contest (the first being the Iowa caucuses) held in the United States every four years as part of the process of choosi ...
on February 18, but Clinton's second-place finish, helped by his speech labeling himself "The Comeback Kid," energized his campaign. Brown won the Maine caucus and Kerrey won South Dakota. Clinton won his first primary in Georgia. Tsongas won the Utah and Maryland primaries and a caucus in Washington. Harkin won caucuses in Idaho and Minnesota while Jerry Brown won Colorado. Kerrey dropped out two days later. Clinton won the South Carolina and Wyoming primaries and Tsongas won Arizona. Harkin dropped out. Brown won the Nevada caucus. Clinton swept nearly all of the Super Tuesday primaries on March 10 making him the solid front runner. Clinton won the Michigan and Illinois primaries. Tsongas dropped out after finishing 3rd in Michigan. Brown, however, began to pick up steam, aided by using a phone number to receive funding from small donors. Brown scored surprising wins in Connecticut, Vermont and Alaska. As the race moved to the primaries in New York and Wisconsin, Brown had taken the lead in polls in both states. Then he made a serious gaffe by announcing to an audience of New York City's Jewish community that he would consider Reverend Jesse Jackson
Jesse Louis Jackson (né Burns; born October 8, 1941) is an American political activist, Baptist minister, and politician. He was a candidate for the Democratic presidential nomination in 1984 and 1988 and served as a shadow U.S. senator ...
as a vice presidential candidate; Jackson had offended many Jewish people with remarks he had made during his own presidential campaigns. Clinton won dramatically in New York (41%–26%) and closely in Wisconsin (37%–34%). Clinton then proceeded to win a long streak of primaries leading up to Brown's home state of California. Clinton won this state 48% to 41% and secured the delegates needed to lock the nomination.
The convention met in New York City, and the official tally was:
* Bill Clinton 3,372
* Jerry Brown 596
* Paul Tsongas
Paul Efthemios Tsongas (; February 14, 1941 – January 18, 1997) was an American politician who represented Massachusetts in the United States Senate from 1979 until 1985 and in the United States House of Representatives from 1975 until 197 ...
289
* Robert P. Casey
Robert Patrick Casey Sr. (January 9, 1932 – May 30, 2000) was an American lawyer and politician from Pennsylvania who served as the 42nd Governor of Pennsylvania from 1987 to 1995. He served as a member of the Pennsylvania Senate for the ...
10
* Pat Schroeder 5
* Larry Agran 3
* Al Gore
Albert Arnold Gore Jr. (born March 31, 1948) is an American politician, businessman, and environmentalist who served as the 45th vice president of the United States from 1993 to 2001 under President Bill Clinton. Gore was the Democratic Part ...
1
Clinton chose U.S. Senator Al Gore
Albert Arnold Gore Jr. (born March 31, 1948) is an American politician, businessman, and environmentalist who served as the 45th vice president of the United States from 1993 to 2001 under President Bill Clinton. Gore was the Democratic Part ...
( D- Tennessee) to be his running mate on July 9, 1992. Choosing fellow Southerner Gore went against the popular strategy of balancing a Southern candidate with a Northern partner. Gore served to balance the ticket in other ways, as he was perceived as strong on family values and environmental issues, while Clinton was not. Also, Gore's similarities to Clinton allowed him to push some of his key campaign themes, such as centrism and generational change.
Republican Party nomination
Pat Buchanan
Patrick Joseph Buchanan (; born November 2, 1938) is an American paleoconservative political commentator, columnist, politician, and broadcaster. Buchanan was an assistant and special consultant to U.S. Presidents Richard Nixon, Gerald Ford, an ...
was the primary opponent of President Bush; Ron Paul
Ronald Ernest Paul (born August 20, 1935) is an American author, activist, physician and retired politician who served as the U.S. representative for Texas's 22nd congressional district from 1976 to 1977 and again from 1979 to 1985, as well ...
, the Libertarian Party's presidential nominee in 1988, had planned to run against the President, but dropped out shortly after Buchanan's entry in December. Buchanan's best showing was in the New Hampshire primary on February 18, 1992—where Bush won by a 53–38% margin. President Bush won 73% of all primary votes, with 9,199,463 votes. Buchanan won 2,899,488 votes; unpledged delegates won 287,383 votes, and David Duke, Grand Wizard of the Ku Klux Klan
The Ku Klux Klan (), commonly shortened to the KKK or the Klan, is an American white supremacist, right-wing terrorist, and hate group whose primary targets are African Americans, Jews, Latinos, Asian Americans, Native Americans, and ...
, won 119,115 votes. Just over 100,000 votes were cast for all other candidates, half of which were write-in votes for H. Ross Perot. Former Minnesota Governor Harold Stassen, who had run for President 9 times since 1944, also mounted his final campaign.
President George H. W. Bush
George Herbert Walker BushSince around 2000, he has been usually called George H. W. Bush, Bush Senior, Bush 41 or Bush the Elder to distinguish him from his eldest son, George W. Bush, who served as the 43rd president from 2001 to 2009; pr ...
and Vice President Dan Quayle easily won renomination by the Republican Party
Republican Party is a name used by many political parties around the world, though the term most commonly refers to the United States' Republican Party.
Republican Party may also refer to:
Africa
*Republican Party (Liberia)
* Republican Part ...
. However, the success of the opposition forced the moderate Bush to move further to the right than in the previous election, and to incorporate many socially conservative planks in the party platform. Bush allowed Buchanan to give a prime time address at the Republican National Convention
The Republican National Convention (RNC) is a series of presidential nominating conventions held every four years since 1856 by the United States Republican Party. They are administered by the Republican National Committee. The goal of the Repu ...
in Houston, Texas, and his culture war speech alienated many moderates.
With intense pressure on the Buchanan delegates to relent, the tally for president went as follows:
* George H. W. Bush
George Herbert Walker BushSince around 2000, he has been usually called George H. W. Bush, Bush Senior, Bush 41 or Bush the Elder to distinguish him from his eldest son, George W. Bush, who served as the 43rd president from 2001 to 2009; pr ...
2166
* Pat Buchanan
Patrick Joseph Buchanan (; born November 2, 1938) is an American paleoconservative political commentator, columnist, politician, and broadcaster. Buchanan was an assistant and special consultant to U.S. Presidents Richard Nixon, Gerald Ford, an ...
18
* former ambassador Alan Keyes 1
Vice President Dan Quayle was renominated by voice vote.
Independent Nomination
Ross Perot
Henry Ross Perot (; June 27, 1930 – July 9, 2019) was an American business magnate, billionaire, politician and philanthropist. He was the founder and chief executive officer of Electronic Data Systems and Perot Systems. He ran an inde ...
to explode on the scene in dramatic fashion—at one point Perot was leading the major party candidates in the polls. Perot crusaded against the North American Free Trade Agreement
The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA ; es, Tratado de Libre Comercio de América del Norte, TLCAN; french: Accord de libre-échange nord-américain, ALÉNA) was an agreement signed by Canada, Mexico, and the United States that crea ...
(NAFTA), and internal and external national debt, tapping into voters' potential fear of the deficit. His volunteers succeeded in collecting enough signatures to get his name on the ballot in all 50 states. In June, Perot led the national public opinion polls with support from 39% of the voters (versus 31% for Bush and 25% for Clinton). Perot severely damaged his credibility by dropping out of the presidential contest in July and remaining out of the race for several weeks before re-entering. He compounded this damage by eventually claiming, without evidence, that his withdrawal was due to Republican operatives attempting to disrupt his daughter's wedding.
Perot and retired Vice Admiral James Stockdale drew 19,743,821 votes (19% of the popular vote).
Minor parties and independents
Libertarian Party nomination
State Representative
A state legislature is a legislative branch or body of a political subdivision in a federal system.
Two federations literally use the term "state legislature":
* The legislative branches of each of the fifty state governments of the United Sta ...
and 1988 vice presidential nominee
* Richard B. Boddie
Richard is a male given name. It originates, via Old French, from Old Frankish and is a compound of the words descending from Proto-Germanic ''*rīk-'' 'ruler, leader, king' and ''*hardu-'' 'strong, brave, hardy', and it therefore means 'str ...
, political science professor from California
The 6th Libertarian Party National Convention was held in Chicago, Illinois. There, the Libertarian Party nominated Andre Marrou, former Alaska State Representative
A state legislature is a legislative branch or body of a political subdivision in a federal system.
Two federations literally use the term "state legislature":
* The legislative branches of each of the fifty state governments of the United Sta ...
and the Party's 1988 vice-presidential candidate, for President. Nancy Lord was his running mate.
Marrou and Lord drew 291,627 votes (0.28% of the popular vote).
New Alliance Party nomination
Lenora Fulani
Lenora Branch Fulani (born April 25, 1950) is an American psychologist, psychotherapist, and political activist. She is best known for her presidential campaigns and development of youth programs serving minority communities in the New York City ...
, Psychotherapist and political activist from New Jersey, and the 1988 Presidential nominee
Lenora Fulani
Lenora Branch Fulani (born April 25, 1950) is an American psychologist, psychotherapist, and political activist. She is best known for her presidential campaigns and development of youth programs serving minority communities in the New York City ...
, who was the 1988 presidential nominee of the New Alliance Party, received a second consecutive nomination from the Party in 1992. Unlike in 1988, Fulani failed to gain ballot access in every state, deciding to concentrate some of that campaign funding towards exposure of her candidacy and the Party to the national public.
Fulani also sought the endorsement of the Peace and Freedom Party
The Peace and Freedom Party (PFP) is a left-wing political party with affiliates and former members in more than a dozen American states, including California, Colorado, Florida, Hawaii, Indiana and Utah, but none now have ballot status besides C ...
of California, but despite winning a majority in that party's primary, she would lose the nomination to Ronald Daniels, the former Director the National Rainbow Coalition
The National Rainbow Coalition (NARC) is a political party in Kenya. As an alliance, it was in power from 2002 and 2005 when it collapsed due to disagreements between members over a constitutional referendum.
Formation
In preparation of the 2002 ...
. Rather than pursuing a ballot space of her own, Fulani would endorse Daniels's candidacy in California.
Fulani and her running mate Maria Elizabeth Muñoz received 73,622 votes (0.1% of the popular vote).
Natural Law Party nomination
Natural Law Party
The Natural Law Party (NLP) is a transnational party founded in 1992 on "the principles of Transcendental Meditation", the laws of nature, and their application to all levels of government. At its peak, it was active in up to 74 countries; it co ...
nominated scientist and researcher John Hagelin for President and Mike Tompkins for Vice President. The Natural Law Party had been founded in 1992 by Hagelin and 12 others who felt that governmental problems could be solved more effectively by following "Natural Laws". The party platform included preventive health care, sustainable agriculture and renewable energy technologies. During this and future campaigns, Hagelin favored abortion rights without public financing, campaign finance law reform, improved gun control, a flat tax, the eradication of PACs, a ban on soft money contributions, and school vouchers.
The party's first presidential ticket appeared on the ballot in 28 states and drew 37,137 votes (<0.1% of the popular vote).
U.S. Taxpayers' Party nomination
Pat Buchanan
Patrick Joseph Buchanan (; born November 2, 1938) is an American paleoconservative political commentator, columnist, politician, and broadcaster. Buchanan was an assistant and special consultant to U.S. Presidents Richard Nixon, Gerald Ford, an ...
, conservative columnist from Virginia (declined interest)
* Gordon J. Humphrey, former Senator from New Hampshire (declined interest)
The U.S. Taxpayers Party ran its first presidential ticket in 1992, having only been formed the prior year. Initially Howard Phillips had hoped to successfully entice a prominent conservative politician, such as the former Senator Gordon J. Humphrey from New Hampshire, or even Patrick Buchanan who at the time had only been mulling over running against President Bush (he would officially declare in December 1991).
No one, however, announced any intention to seek the Taxpayers Party nomination; Buchanan himself in the end endorsed President Bush at the Republican National Convention in Houston. Phillips had been unofficially nominated earlier in the year so as to allow the Party to be able to seek ballot access properly. While initially a temporary post, it was made permanent at the party's national convention, which was held in New Orleans on September 4 and 5. At the convention, which was attended by delegates from thirty-two states and Washington, D.C., Phillips received 264 votes on the first ballot, while Albion Knight was approved as his running mate by acclamation.
Earlier that year, in the June 2 California primary, Phillips had received 15,456 votes in the American Independent Party primary. On August 30, the American Independent Party voted to affiliate with the U.S. Taxpayers Party, an affiliation which continued until 2008.
Phillips and Knight drew 43,369 votes (<0.1% of the popular vote).
Populist Party nomination
Special Forces
Special forces and special operations forces (SOF) are military units trained to conduct special operations. NATO has defined special operations as "military activities conducted by specially designated, organized, selected, trained and equip ...
officer and Vietnam veteran
Former United States Army Special Forces
Special forces and special operations forces (SOF) are military units trained to conduct special operations. NATO has defined special operations as "military activities conducted by specially designated, organized, selected, trained and equip ...
officer and Vietnam veteran Bo Gritz was the nominee of the Populist Party, facing virtually no opposition. Under the campaign slogan "God, Guns and Gritz" and publishing his political manifesto "The Bill of Gritz" (playing on his last name rhyming with "rights"), he called for staunch opposition to what he called "global government" and "The New World Order", ending all foreign aid, abolishing federal income tax, and abolishing the Federal Reserve System. During the campaign, Gritz openly proclaimed the United States to be a "Christian Nation", stating that the country's legal statutes "should reflect unashamed acceptance of Almighty God and His Laws". His run on the America First/Populist Party ticket was prompted by his association with another far-right political Christian talk radio host, Tom Valentine. During his campaign, part of Gritz's standard stump speech was an idea to pay off the National debt by minting a coin at the Treasury and sending it to the Federal Reserve. This predates the 2012 trillion dollar coin concept.
During August 1992, Gritz attracted national attention as mediator during the government standoff with Randy Weaver at Ruby Ridge, Idaho.
He received 106,152 votes nationwide (0.1% of the popular vote). In two states he had a respectable showing for a minor third party candidate: Utah, where he received 3.8% of the vote and Idaho, where he received 2.1% of the vote. In some counties, his support topped 10%, and in Franklin County, Idaho, was only a few votes away from pushing Bill Clinton into fourth place in the county.
Lyndon LaRouche's candidacy
Socialist Workers' Party nomination
Ron Daniels candidacy
National Rainbow Coalition
The National Rainbow Coalition (NARC) is a political party in Kenya. As an alliance, it was in power from 2002 and 2005 when it collapsed due to disagreements between members over a constitutional referendum.
Formation
In preparation of the 2002 ...
Ronald Daniels was the former executive director for the Center for Constitutional Rights, the former director of the National Rainbow Coalition
The National Rainbow Coalition (NARC) is a political party in Kenya. As an alliance, it was in power from 2002 and 2005 when it collapsed due to disagreements between members over a constitutional referendum.
Formation
In preparation of the 2002 ...
, and the worked on both of Jesse Jackson
Jesse Louis Jackson (né Burns; born October 8, 1941) is an American political activist, Baptist minister, and politician. He was a candidate for the Democratic presidential nomination in 1984 and 1988 and served as a shadow U.S. senator ...
's campaigns for the Democratic presidential nomination. Asiba Tupahache, a Native American activist from New York was his running-mate.
Though running an Independent campaign under the label "Campaign for a Better Tomorrow", Daniels was endorsed by a number of third parties across the states, most notably the Peace and Freedom Party of California; though he had lost that party's presidential primary to Lenora Fulani
Lenora Branch Fulani (born April 25, 1950) is an American psychologist, psychotherapist, and political activist. She is best known for her presidential campaigns and development of youth programs serving minority communities in the New York City ...
, the nominee of the New Alliance Party, the delegates at its convention voted in favor of his candidacy 110–91, the only time it has ever nominated someone other than the winner of the primary.
Daniels and Tupachache drew 27,396 votes (<0.1% of the popular vote).
Other nominations
The 1992 campaign also marked the entry of Ralph Nader into presidential politics as a candidate. Despite the advice of several liberal and environmental groups, Nader did not formally run. Rather, he tried to make an impact in theNew Hampshire primaries
The New Hampshire presidential primary is the first in a series of nationwide party primary elections and the second party contest (the first being the Iowa caucuses) held in the United States every four years as part of the process of choos ...
, urging members of both parties to write-in his name. As a result, several thousand Democrats and Republicans wrote-in Nader's name. Despite supporting mostly liberal legislation during his career as a consumer advocate, Nader received more votes from Republicans than Democrats.
The Worker's League nominated Helen Halyard
The Socialist Equality Party (SEP) is a Trotskyist political party in the United States, one of several Socialist Equality parties around the world affiliated with the International Committee of the Fourth International (ICFI). The ICFI publishes ...
for President; she was the party's nominee for Vice President in 1984 and 1988. Fred Mazelis was nominated for Vice President. Halyard and Mazelis drew 3,050 votes.
Ballot Access: Michigan, New Jersey ''(33 Electoral)''
John Yiamouyiannis, a major opponent of water fluoridation, ran as an Independent under the label "Take Back America". Allen C. McCone was his running-mate. Yiamouyiannis and McCone drew 2,199 votes.
Ballot Access: Arkansas, Iowa, Louisiana, Tennessee ''(33 Electoral)''
The Socialist Party nominated J. Quinn Brisben for President and Barbara Garson for Vice President. Brisben and Garson drew 2,909 votes.
Ballot Access: DC, Tennessee, Utah, Wisconsin ''(30 Electoral)''
The Grassroots Party nominated Jack Herer, a noted cannabis activist for President and Derrick Grimmer for Vice President. Herer and Grimmer drew 3,875 votes.
Ballot Access: Iowa, Minnesota, Wisconsin ''(28 Electoral)''
The Prohibition Party
The Prohibition Party (PRO) is a political party in the United States known for its historic opposition to the sale or consumption of alcoholic beverages and as an integral part of the temperance movement. It is the oldest existing third party ...
nominated Earl Dodge
Earl Farwell Dodge Jr. (December 24, 1932 – November 7, 2007) was an American politician who served as the Prohibition Party's chairman and presidential candidate from the 1984 to 2000 presidential elections and later ran with the nomination ...
, the party's chairman for President and George Ormsby for Vice President. Dodge and Ormsby drew 935 votes.
Ballot Access: Arkansas, New Mexico, Tennessee ''(22 Electoral)''
Drew Bradford was an Independent candidate for the Presidency; he did not have a running-mate. Bradford drew 4,749 votes.
Ballot Access: New Jersey ''(15 Electoral)''
Eugene R. Hem was an Independent candidate for the Presidency, running under the label "The Third Party". His running-mate was Joanne Roland. Hem and Roland drew 405 votes.
Ballot Access: Wisconsin ''(11 Electoral)''
Delbert Ehlers was an Independent candidate for the Presidency. His running-mate was Rick Wendt. Ehlers and Wendt drew 1,149 votes.
Ballot Access: Iowa ''(7 Electoral)''
James Boren was an Independent candidate for the Presidency, running under the label "Apathy". His running-mate was Bill Weidman. Boren and Weidman drew 956 votes.
Ballot Access: Arkansas ''(6 Electoral)''
Professor Isabell Masters
Isabell Masters (January 9, 1913 – September 11, 2011) of Topeka, Kansas, was a five-time Perennial candidate, perennial Third party (United States), third-party candidate (Looking Back Party) for President of the United States.
Masters' five ...
was an Independent candidate for the Presidency, running under the label "Looking Back". Her running-mate was her son, Walter Ray Masters. Masters drew 327 votes.
Ballot Access: Arkansas ''(6 Electoral)''
The American Party nominated Robert J. Smith for President and Doris Feimer for Vice President. However, for a time neither the Utah or South Carolina state parties would endorse the ticket. The American Party of South Carolina would ultimately endorse the candidacy of Howard Phillips, the nominee of the U.S. Taxpayers Party, while the American Party of Utah would decide to endorse Smith. Smith and Feimer drew 291 votes.
Ballot Access: Utah ''(5 Electoral)''
The Workers World Party nominated Gloria La Riva for President and Larry Holmes for Vice President. Initially the party had voted not to field a presidential candidate in 1992, but it was later found that the party would need to get at least half a percent of the vote in New Mexico in order to maintain its ballot access in that state. La Riva and Holmes drew 181 votes.
Ballot Access: New Mexico ''(5 Electoral)''
General election
Campaign
After Bill Clinton secured the Democratic Party's nomination in the spring of 1992, polls showed Ross Perot leading the race, followed by President Bush and Clinton in third place after a grueling nomination process. Two-way trial heats between Bush and Clinton in early 1992 showed Bush in the lead. As the economy continued to sour and the President's approval rating continued to slide, the Democrats began to rally around their nominee. On July 9, 1992, Clinton chose Tennessee senator and former 1988 presidential candidate Al Gore to be his running mate. As Governor Clinton's nomination acceptance speech approached, Ross Perot dropped out of the race, convinced that staying in the race with a "revitalized Democratic Party" would cause the race to be decided by the United States House of Representatives. Clinton gave his acceptance speech on July 16, 1992, promising to bring a "new covenant" to America, and to work to heal the gap that had developed between the rich and the poor during the Reagan/Bush years. The Clinton campaign received the biggest convention "bounce" in history which brought him from 25 percent in the spring, behind Bush and Perot, to 55 percent versus Bush's 31 percent. After the convention, Clinton and Gore began a bus tour around the United States, while the Bush/Quayle campaign began to criticize Clinton's character, highlighting accusations of infidelity and draft dodging. The Bush campaign emphasized its foreign policy successes such as Desert Storm, and the end of the Cold War. Bush also contrasted his military service to Clinton's lack thereof, and criticized Clinton's lack of foreign policy expertise. However, as the economy was the main issue, Bush's campaign floundered across the nation, even in strongly Republican areas, and Clinton maintained leads with over 50 percent of the vote nationwide consistently, while Bush typically saw numbers in the upper 30s. As Bush's economic edge had evaporated, his campaign looked to energize its socially conservative base at the1992 Republican National Convention
The 1992 Republican National Convention was held in the Astrodome in Houston, Texas, from August 17 to August 20, 1992. The convention nominated President George H. W. Bush and Vice President Dan Quayle for reelection. It was Bush's fourth co ...
in Houston, Texas. At the convention, Bush's primary campaign opponent Pat Buchanan gave his famous "culture war" speech, criticizing Clinton's and Gore's social progressiveness, and voicing skepticism on his "New Democrat" brand. After President Bush accepted his renomination, his campaign saw a small bounce in the polls, but this was short-lived, as Clinton maintained his lead. The campaign continued with a lopsided lead for Clinton through September, until Ross Perot decided to re-enter the race. Ross Perot's re-entry in the race was welcomed by the Bush campaign, as Fred Steeper, a poll taker for Bush, said, "He'll be important if we accomplish our goal, which is to draw even with Clinton." Initially, Perot's return saw the Texas billionaire's numbers stay low, until he was given the opportunity to participate in a trio of unprecedented three-man debates. The race narrowed, as Perot's numbers significantly improved as Clinton's numbers declined, while Bush's numbers remained more or less the same from earlier in the race as Perot and Bush began to hammer at Clinton on character issues once again.
Presidential debates
The Commission on Presidential Debates organized four presidential debatesCharacter issues
Many character issues were raised during the campaign, including allegations that Clinton had dodged the draft during the Vietnam War, and had usedmarijuana
Cannabis, also known as marijuana among other names, is a psychoactive drug from the cannabis plant. Native to Central or South Asia, the cannabis plant has been used as a drug for both recreational and entheogenic purposes and in various tra ...
, which Clinton claimed he had pretended to smoke, but "didn't inhale." Bush also accused Clinton of meeting with communists on a trip to Russia he took as a student. Clinton was often accused of being a philanderer by political opponents.
Allegations were also made that Bill Clinton had engaged in a long-term extramarital affair with Gennifer Flowers. Clinton denied ever having an affair with Flowers.

Results
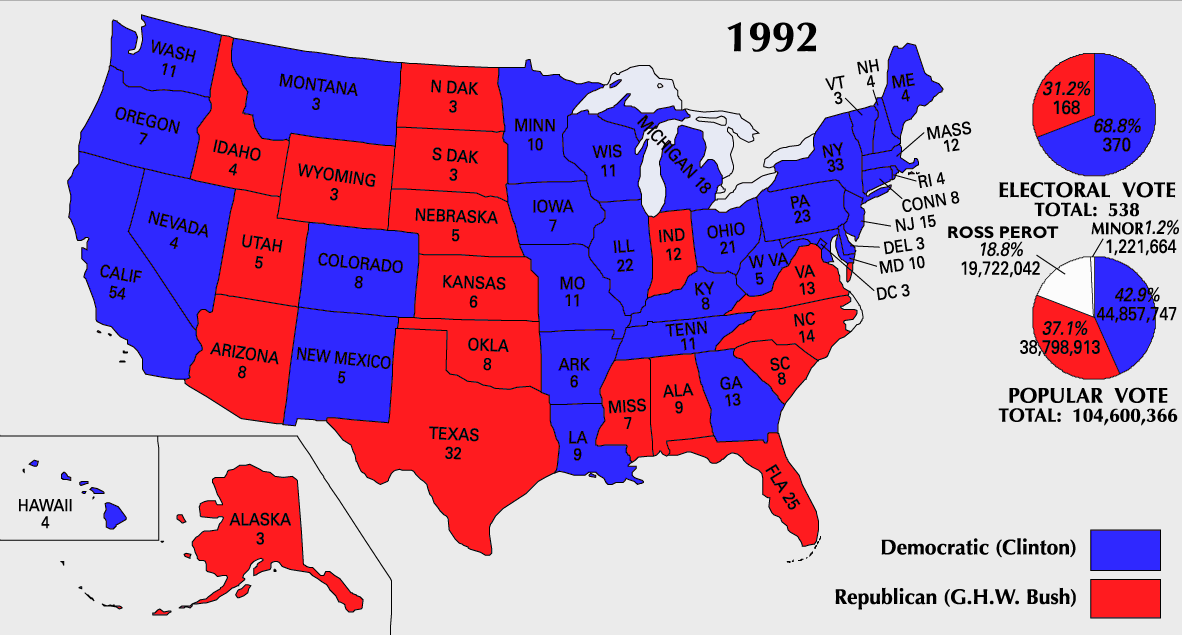
On November 3, Bill Clinton won the election to serve as the 42nd president of the United States by a wide margin in the Electoral College, receiving 43% of the popular vote against Bush's 37.4% and Perot's 18.9%. It was the first time since1968
The year was highlighted by protests and other unrests that occurred worldwide.
Events January–February
* January 5 – "Prague Spring": Alexander Dubček is chosen as leader of the Communist Party of Czechoslovakia.
* Januar ...
that a candidate won the White House with under 50% of the popular vote. Only Washington, D.C., and Clinton's home state of Arkansas gave the majority of their votes to a single candidate in the entire country; the rest were won by pluralities of the vote. Clinton was the first Democrat since 1964 to win a majority of states.
Even though Clinton roughly received 3.1 million more votes than Democratic nominee Michael Dukakis had four years earlier, the Democrats recorded a 2.6 percentage point ''decrease'' in their share of the popular vote compared to 1988 due to the higher turnout. His 43% share of the popular vote was the second-lowest for any winning candidate in the 20th century after Woodrow Wilson in 1912
Events January
* January 1 – The Republic of China (1912–49), Republic of China is established.
* January 5 – The Prague Conference (6th All-Russian Conference of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party) opens.
* January 6 ...
(41.8%). President Bush's 37.4% was the lowest percentage total for a sitting president seeking re-election since William Howard Taft, also in 1912 (23.2%). 1992 was, as the 1912 election was, a three-way race (that time between Taft, Wilson, and Theodore Roosevelt). It was also the lowest percentage for a major-party candidate since Alf Landon received 36.5% of the vote in 1936
Events
January–February
* January 20 – George V of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions and Emperor of India, dies at his Sandringham Estate. The Prince of Wales succeeds to the throne of the United Kingdom as King E ...
. Bush had a lower percentage of the popular vote than even Herbert Hoover, who was defeated in 1932
Events January
* January 4 – The British authorities in India arrest and intern Mahatma Gandhi and Vallabhbhai Patel.
* January 9 – Sakuradamon Incident (1932), Sakuradamon Incident: Korean nationalist Lee Bong-chang fails in his effort ...
(39.7%). However, none of these races included a major third candidate. Bush was the last president voted out of office after one term until Donald Trump in 2020
2020 was heavily defined by the COVID-19 pandemic, which led to global Social impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, social and Economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, economic disruption, mass cancellations and postponements of events, COVID- ...
, as Clinton, Bush’s son George W. Bush and Barack Obama were all re-elected to second terms in office.
Independent candidate Ross Perot
Henry Ross Perot (; June 27, 1930 – July 9, 2019) was an American business magnate, billionaire, politician and philanthropist. He was the founder and chief executive officer of Electronic Data Systems and Perot Systems. He ran an inde ...
received 19,743,821 with 18.9% of the popular vote. The billionaire used his own money to advertise extensively, and is the only third-party candidate ever allowed into the nationally televised presidential debates with both major party candidates (Independent John Anderson John Anderson may refer to:
Business
*John Anderson (Scottish businessman) (1747–1820), Scottish merchant and founder of Fermoy, Ireland
* John Byers Anderson (1817–1897), American educator, military officer and railroad executive, mentor of ...
debated Republican Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
in 1980
Events January
* January 4 – U.S. President Jimmy Carter proclaims a grain embargo against the USSR with the support of the European Commission.
* January 6 – Global Positioning System time epoch begins at 00:00 UTC.
* January 9 – ...
, but without Democrat Jimmy Carter, who had refused to appear in a three-man debate). Speaking about the North American Free Trade Agreement
The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA ; es, Tratado de Libre Comercio de América del Norte, TLCAN; french: Accord de libre-échange nord-américain, ALÉNA) was an agreement signed by Canada, Mexico, and the United States that crea ...
, Perot described its effect on American jobs as causing a " giant sucking sound". For a period of time, Perot was leading in the polls, but he lost much of his support when he temporarily withdrew from the election, only to declare himself a candidate again soon after. This was also the most recent time that a third-party candidate won at least one county.
Perot's almost 19% of the popular vote made him the most successful third-party presidential candidate in terms of popular vote since Theodore Roosevelt in the 1912 election. Also, his 19% of the popular vote was the highest ever for a candidate who did not win any electoral votes. Although he did not win any states, Perot managed to finish ahead of one of the two major party candidates in two states: In Maine, he received 30.44% of the vote to Bush's 30.39% (Clinton won Maine with 38.77%); in Utah, he collected 27.34% of the vote to Clinton's 24.65%. Bush won that state with 43.36%. He also came in 2nd in Maine's 2nd Congressional District where he had his best overall showing. He won 33.2% of the vote there and missed out on the district's 1 elector by only 4.5% of the vote.
The election was the most recent in which Montana voted for the Democratic candidate, the last time Florida backed the losing candidate until 2020 and Georgia voted for the Democratic candidate until 2020
2020 was heavily defined by the COVID-19 pandemic, which led to global Social impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, social and Economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, economic disruption, mass cancellations and postponements of events, COVID- ...
, and the last time that Colorado voted Democratic until 2008. This was also the first time since Texas' admission to the Union in 1845 that a Democrat won the White House without winning the state, and the second time a Democrat won the White House without North Carolina (the first was 1844), and the second time since Florida's admission (also in 1845) that a Democrat won without winning the state ( John F. Kennedy in 1960
It is also known as the "Year of Africa" because of major events—particularly the independence of seventeen African nations—that focused global attention on the continent and intensified feelings of Pan-Africanism.
Events
January
* Ja ...
was the first).
Clinton was also the only Democrat at that point to win every electoral vote in the Northeast except for Lyndon Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), often referred to by his initials LBJ, was an American politician who served as the 36th president of the United States from 1963 to 1969. He had previously served as the 37th vice ...
in 1964
Events January
* January 1 – The Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland is dissolved.
* January 5 - In the first meeting between leaders of the Roman Catholic and Orthodox churches since the fifteenth century, Pope Paul VI and Patriarch ...
. John Kerry and Barack Obama have been the only Democrats to repeat this since. Also, this was the first time since 1964 that the following nine states had voted Democratic: California, Colorado, Illinois, Montana, Nevada, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New Mexico, and Vermont.
The 168 electoral votes received by Bush, added to the 426 electoral votes he received in 1988
File:1988 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The oil platform Piper Alpha explodes and collapses in the North Sea, killing 165 workers; The USS Vincennes (CG-49) mistakenly shoots down Iran Air Flight 655; Australia celebrates its Australian ...
, gave him the most total electoral votes received by any candidate who was elected to the office of president only once (594), and the ninth largest number of electoral votes received by any candidate who was elected to the office of president behind Grover Cleveland's 664, Barack Obama's 697, Woodrow Wilson's 712, Bill Clinton's 749, Richard Nixon's 821, Dwight Eisenhower
Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower (born David Dwight Eisenhower; ; October 14, 1890 – March 28, 1969) was an American military officer and statesman who served as the 34th president of the United States from 1953 to 1961. During World War II, ...
's 899, Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
's 1,014 and Franklin D. Roosevelt's 1,876 total electoral votes.
Clinton was the first President to not have any prior military experience since Franklin Roosevelt in 1944.
Analysis
Several factors made the results possible. First, the campaign came on the heels of an economic slowdown. Exit polling showed that 75% thought the economy was in fairly or very bad shape while 63% thought their personal finances were better or the same as four years ago. The decision by Bush to accept a tax increase adversely affected his re-election bid. Pressured by rising budget deficits, Bush agreed to a budget compromise with Congress which raised taxes and reduced the federal budget deficit. Clinton was able to condemn the tax increase effectively on both its own merits and as a reflection of Bush's dishonesty. Effective Democratic TV ads were aired showing a clip of Bush's 1988 acceptance speech in which he promised " Read my lips … No new taxes." Most importantly, Bush's coalition was in disarray, for both the aforementioned reasons and for unrelated reasons. The end of theCold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
allowed old rivalries among conservatives to re-emerge and meant that other voters focused more on domestic policy, to the detriment of Bush, a social and fiscal moderate. The consequence of such a perception depressed conservative turnout.
Unlike Bush, Clinton was able to unite his fractious and ideologically diverse party behind his candidacy, even when its different wings were in conflict. To garner the support of moderates and conservative Democrats, he attacked Sister Souljah, an obscure rap music
Rapping (also rhyming, spitting, emceeing or MCing) is a musical form of vocal delivery that incorporates "rhyme, rhythmic speech, and street vernacular". It is performed or chanted, usually over a backing beat or musical accompaniment. The ...
ian whose lyrics Clinton condemned. Furthermore, Clinton made clear his support of the death penalty and would later champion making school uniform
A school uniform is a uniform worn by students primarily for a school or otherwise an educational institution.They are common in primary and secondary schools in various countries.
An example of a uniform would be requiring button-down shir ...
s in public schools a requirement. Clinton could also point to his centrist record as governor of Arkansas. More liberal Democrats were impressed by Clinton's record on abortion and affirmative action. His strong connections to African Americans also played a key role. In addition, he organized significant numbers of young voters and became a symbol of the rise of the Baby Boomer generation to political power. Supporters remained energized and confident, even in times of scandal or missteps.
The effect of Ross Perot
Henry Ross Perot (; June 27, 1930 – July 9, 2019) was an American business magnate, billionaire, politician and philanthropist. He was the founder and chief executive officer of Electronic Data Systems and Perot Systems. He ran an inde ...
's candidacy has been a contentious point of debate for many years. In the ensuing months after the election, various Republicans asserted that Perot had acted as a spoiler, enough to the detriment of Bush to lose him the election. While many disaffected conservatives may have voted for Ross Perot to protest Bush's tax increase, further examination of the Perot vote in the Election Night exit polls not only showed that Perot siphoned votes nearly equally among Bush and Clinton, but roughly two-thirds of those voters who cited Bush's broken "No New Taxes" pledge as "very important" (25%) voted for Bill Clinton. The voting numbers reveal that to win the electoral vote Bush would have had to win 10 of the 11 states Clinton won by less than five percentage points. For Bush to earn a majority of the popular vote, he would have needed 12.2% of Perot's 18.9% of the vote, 65% of Perot's support base. State exit polls suggested that Perot did not alter the electoral college count, except potentially in one state (Ohio), which nonetheless showed a result in the margin of error. Furthermore, Perot was most popular in states that strongly favored either Clinton or Bush, limiting his real electoral impact for either candidate.
Perot gained relatively little support in the Southern states and happened to have the best showing in states with few electoral votes. Perot appealed to disaffected voters all across the political spectrum who had grown weary of the two-party system. NAFTA played a role in Perot's support, and Perot voters were relatively moderate on hot-button social issues. A 1999 study in the ''American Journal of Political Science'' estimated that Perot's candidacy hurt the Clinton campaign, reducing "Clinton's margin of victory over Bush by seven percentage point." In 2016, '' FiveThirtyEight'' noted that it was "unlikely" that Perot was a spoiler.
Clinton, Bush, and Perot did not focus on abortion during the campaign. Exit polls, however, showed that attitudes toward abortion "significantly influenced" the vote, as pro-choice Republicans defected from Bush.
Implications
According to Seymour Martin Lipset, this election had several unique characteristics. Voters felt that economic conditions were worse than they actually were, which harmed Bush. A rare event was a strong third-party candidate. Liberals launched a backlash against 12 years of a conservative White House. The chief factor was Clinton's uniting his party, and winning over a number of heterogeneous groups. Clinton's election ended an era in which the Republican Party had controlled the White House for 12 consecutive years, and for 20 of the previous 24 years. The election also brought the Democrats full control of the legislative and executive branches of the federal government, including both houses of U.S. Congress and the presidency, for the first time since the administration of the last Democratic president, Jimmy Carter. This would not last for very long, however, as the Republicans won control of both the House and Senate in 1994. Reelected in 1996, Clinton would become the first Democratic President since Franklin D. Roosevelt to serve two full terms in the White House. 1992 was arguably a political realignment election. It made the Democratic Party dominant in presidential elections in the Northeast, the Great Lakes region (until2016
File:2016 Events Collage.png, From top left, clockwise: Bombed-out buildings in Ankara following the 2016 Turkish coup d'état attempt; the impeachment trial of Brazilian President Dilma Rousseff; Damaged houses during the 2016 Nagorno-Karabakh ...
) and the West Coast, where many states had previously either been swing states or Republican-leaning. Clinton picked up several states that went Republican in 1988, and which have remained in the Democratic column ever since: California, Connecticut, Delaware, Illinois, most of Maine (besides the state's second congressional district, which broke the state's total straight Democratic voting record since, when it voted for Republican presidential candidate Donald Trump in 2016), Maryland, New Jersey, and Vermont. Vermont, carried by Clinton, had been heavily Republican for generations prior to the election, voting for a Democrat only once (in 1964). The state has been won by the Democratic nominee in every presidential election since. Bill Clinton narrowly defeated Bush in New Jersey (by two points), which had voted for the Republican nominee all but twice since 1948
Events January
* January 1
** The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) is inaugurated.
** The Constitution of New Jersey (later subject to amendment) goes into effect.
** The railways of Britain are nationalized, to form British ...
. Clinton would later win the state in 1996 by eighteen points; like Vermont, Republicans have not won the state since. California, which had been a Republican stronghold since 1952, was now trending Democratic. Clinton, a native Southerner, was able to carry several states in the South that the GOP had won for much of the past two decades, but ultimately won only four of eleven former Confederate states. This reflected the final shift of the South to the Republican Party. In subsequent presidential elections from 1996 to 2020, 28 out of the 50 states were carried by the same party as in 1992 (15 for the Democrats and 13 for the Republicans).
Detailed results
Source (Popular Vote): Source (Electoral Vote):
Results by state
Maine and Nebraska district results
†Maine and Nebraska each allowed their electoral votes to be split between candidates using the Congressional District Method for electoral vote assignment. In both states, two electoral votes were awarded to the winner of the statewide race and one electoral vote was awarded to the winner of each congressional district. District results for Maine and Nebraska do not include results for Marrou or other candidates and so totals differ from those for the states' at-large. Because Perot finished in 2nd place in some districts, the margins of the districts do not match the margin at-large.Close states
States with margin of victory less than 1% (27 electoral votes): # Georgia – 0.59% (13,714 votes) # North Carolina – 0.79% (20,619 votes) States/Districts with margin of victory less than 5% (175 electoral votes): # New Hampshire – 1.22% (6,556 votes) # Ohio – 1.83% (90,632 votes) # Florida – 1.89% (100,612 votes) # Arizona – 1.95% (29,036 votes) # New Jersey – 2.37% (79,341 votes) # Montana – 2.51% (10,300 votes) # Nevada – 2.63% (13,320 votes) # Kentucky – 3.21% (47,926 votes) # Texas – 3.48% (214,256 votes) # South Dakota – 3.52% (11,830 votes) # Colorado – 4.26% (66,831 votes) # Wisconsin – 4.35% (110,211 votes) # Virginia – 4.37% (111,867 votes) # Maine's 2nd Congressional District – 4.54% (14,237 votes) (margin over Ross Perot) # Louisiana – 4.61% (82,585 votes) # Tennessee – 4.65% (92,221 votes) (tipping point state) States with margin of victory between 5% and 10% (131 electoral votes): # Kansas – 5.14% (59,517 votes) # Wyoming – 5.60% (11,187 votes) # Iowa – 6.02% (81,462 votes) # Indiana – 6.12% (140,955 votes) # Connecticut – 6.43% (104,005 votes) # Alabama – 6.77% (114,203 votes) # Michigan – 7.39% (316,242 votes) # South Carolina – 8.14% (97,993 votes) # Maine's 1st Congressional District – 8.11% (29,494 votes) # Delaware – 8.19% (23,741 votes) # Maine – 8.33% (56,600 votes) (margin over Ross Perot) # New Mexico – 8.56% (48,793 votes) # Oklahoma – 8.63% (119,863 votes) # Mississippi – 8.91% (87,535 votes) # Pennsylvania – 9.02% (447,323 votes) # Alaska – 9.17% (23,706 votes) # Oregon – 9.95% (145,557 votes)Source: New York Times President Map
Statistics
Counties with Highest Percent of Vote (Democratic) # Washington, D.C. 84.64% # Starr County, Texas 82.80% # Macon County, Alabama 82.78% # Duval County, Texas 79.56% # Jefferson County, Mississippi 79.39% Counties with Highest Percent of Vote (Republican) # Jackson County, Kentucky 74.96% #Sioux County, Iowa
Sioux County is a county located in the U.S. state of Iowa. As of the 2020 census, the population was 35,872. Its county seat is Orange City. Its largest city is Sioux Center.
History
Sioux County was formed on January 15, 1851. It has ...
72.21%
# Hansford County, Texas 69.08%
# Ochiltree County, Texas 68.06%
# Shelby County, Alabama 67.97%
Counties with Highest Percent of Vote (Other)
# Loving County, Texas 46.88%
# San Juan County, Colorado 40.40%
# Billings County, North Dakota 39.82%
# Somerset County, Maine 38.95%
# Esmeralda County, Nevada 37.67%
Voter demographics
Source: Voter News Serviceexit poll
An election exit poll is a poll of voters taken immediately after they have exited the polling stations. A similar poll conducted before actual voters have voted is called an entrance poll. Pollsters – usually private companies working for n ...
, reported in '' The New York Times'', November 10, 1996, 28.
See also
*Newspaper endorsements in the 1992 United States presidential election
The following table is the list of newspaper endorsements in the 1992 United States presidential election. It mostly contains major newspapers of 1992, which made their presidential endorsement from September–November 1992. Many newspaper, who ha ...
* Chicken George
* " Giant sucking sound"
* "It's the economy, stupid
"The economy, stupid" is a phrase that was coined by James Carville in 1992. It is often quoted from a televised quip by Carville as
"It’s the economy, stupid." Carville was a strategist in Bill Clinton's successful 1992 presidential campaign a ...
"
* " Read my lips: no new taxes"
* 1992 United States gubernatorial elections
United States gubernatorial elections were held on November 3, 1992, in 12 states and two territories. Going into the elections, six of the seats were held by Democrats and six by Republicans. After the elections, eight seats were held by Democr ...
* 1992 United States Senate elections
The 1992 United States Senate elections, held November 3, 1992, were elections for the United States Senate that coincided with Bill Clinton's victory in the presidential election. Both parties swapped a pair of seats, resulting in no net change ...
* 1992 United States House of Representatives elections
The 1992 United States House of Representatives elections coincided with the 1992 United States presidential election, 1992 presidential election, in which Democratic Party (United States), Democrat Bill Clinton was elected as President of the Uni ...
* First inauguration of Bill Clinton
References
* ** Bulk of article text as of January 9, 2003 copied from this page, when it was located atFurther reading
* * * Buell Jr, Emmett H. "The 1992 Elections." ''Journal of Politics'' (1994): 1133-1144; reviews leading political science studies of the election * Ceaser, James, and Andrew Busch. ''Upside Down and Inside Out: The 1992 Elections and American Politics'' (1993). * Crotty, William, ed. ''America's Choice: The Election of 1992'' (1993) * * * Doherty, Kathryn M., and James G. Gimpel. "Candidate Character vs. the Economy in the 1992 Election." ''Political Behavior'' 19.3 (1997): 177-196online
* Germond, Jack, and Jules Witcover. ''Mad As Hell: Revolt at the Ballot Box, 1992'' (1993)
online
* Goldman, Peter. et al. ''Quest for the Presidency 1992'' (1994) 805pp. * Herron, Michael C., et al. "Measurement of political effects in the United States economy: A study of the 1992 presidential election." ''Economics & Politics'' 11.1 (1999): 51-81. * * * Kellstedt, Lyman A., et al. "Religious voting blocs in the 1992 election: The year of the evangelical?." ''Sociology of Religion'' 55.3 (1994): 307-326. ellstedt, Lyman A., et al. "Religious voting blocs in the 1992 election: The year of the evangelical?." Sociology of Religion 55.3 (1994): 307-326. online* Klein, Jill Gabrielle. "Negativity in impressions of presidential candidates revisited: The 1992 election." ''Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin'' 22.3 (1996): 288-295. * Ladd, Everett Carll. "The 1992 vote for President Clinton: Another brittle mandate?." ''Political Science Quarterly'' 108.1 (1993): 1-28
online
* Lipset, Seymour Martin. "The significance of the 1992 election." ''PS: Political Science and Politics'' 26.1 (1993): 7-16
online
* Nelson, Michael ed. ''The Elections of 1992'' (1993) * Nelson, Michael. ''Clinton's Elections: 1992, 1996, and the Birth of a New Era of Governance'' (2020
excerpt
* O'Mara, Margaret. ''Pivotal Tuesdays: Four Elections That Shaped the Twentieth Century'' (2015), compares 1912, 1932, 1968, 1992 in terms of social, economic, and political history * Ornstein, Norman J. "Foreign policy and the 1992 election." ''Foreign Affairs'' 71.3 (1992): 1-16
online
* Pomper, Gerald M. ed. ''The Election of 1992'' (1993). * Post, Jerrold M. "The Political psychology of the Ross Perot phenomenon." in ''The Clinton Presidency'' (Routledge, 2019. 37-56). * * * Troy, Gil. "Stumping in the bookstores: A literary history of the 1992 presidential campaign." ''Presidential Studies Quarterly'' (1995): 697-710
online
* Weaver, David, and Dan Drew. "Voter learning in the 1992 presidential election: Did the “nontraditional” media and debates matter?." ''Journalism & Mass Communication Quarterly'' 72.1 (1995): 7-17.
Political commentary and campaign statements
* Barlett, Donald L. and James B. Steele. ''America: What Went Wrong?'' (1992online
* Clinton, Bill, and Al Gore. ''Putting People First: How We Can All Change America'' (1992) * Cramer, Richard Ben. ''What It Takes: The Way to the White House'' (1992)
online
* Dionne, E. J. ''Why Americans Hate Politics'' (1992)
online
* Duffy, Michael, and Dan Goodgame. ''Marching in Place: The Status Quo Presidency of George Bush'' (1992
online
* Edsall Thomas Byrne, and Mary D. Edsall. ''Chain Reaction: The Impact of Race, Rights, and Taxes on American Politics'' (1992
online
* Ehrenhalt, Alan. ''The United States of Ambition: Politicians, Power, and the Pursuit of Office'' (1992
online
* Gore, Al. ''Earth in the Balance: Ecology and the Human Spirit'' (1992)
online
* Greider, William. ''Who Will Tell the People: The Betrayal of American Democracy'' (1992
online
* Jamieson, Kathleen Hall. ''Dirty Politics: Deception, Distraction, and Democracy'' (1992
online
* Perot, Ross. ''United We Stand: How We Can Take Back Our Country'' (1992
online
* Phillips, Kevin. ''The Politics of Rich and Poor: Wealth and the American Electorate in the Reagan Aftermath'' (1992
online
* Sabato, Larry J. ''Feeding Frenzy: How Attack Journalism Has Transformed American Politics'' (1991
online
* Will, George F. ''Restoration: Congress, Term Limits and the Recovery of Deliberative Democracy'' (1992
online
External links
1992 popular vote by state
Presidential Campaign Commercials
C-SPAN
Cable-Satellite Public Affairs Network (C-SPAN ) is an American cable and satellite television network that was created in 1979 by the cable television industry as a nonprofit public service. It televises many proceedings of the United States ...
Campaign commercials from the 1992 election
*
''Booknotes'' interview with Tom Rosenstiel on ''Strange Bedfellows: How Television and the Presidential Candidates Changed American Politics, 1992'', August 8, 1993.
Election of 1992 in Counting the Votes
{{Authority control Al Gore Dan Quayle Presidency of George H. W. Bush George H. W. Bush Bill Clinton Ross Perot November 1992 events in the United States