1939 White Paper on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The White Paper of 1939Occasionally also known as the MacDonald White Paper (e.g. Caplan, 2015, p.117) after
The Origins and Evolution of the Palestine Problem Part I: 1917-1947 - Study (30 June 1978)
, accessdate: November 10, 2018 From December 1945 to the 1948 end of the Mandate, 1,500 additional certificates for Jewish immigrants were allocated each month. Key provisions were ultimately never to be implemented, initially because of cabinet opposition after the change in government and later because of preoccupation with World War II.

 During
During
''Chances for Peace: Missed Opportunities in the Arab-Israeli Conflict''
University of Texas Press 2015 pp.28ff. In January 1938, the
Palestine: Historical Background In the wake of World War II, the British believed that Jewish support was either guaranteed or unimportant. However, the government feared hostility from the Arab world. That geopolitical consideration was, in
 These were the main points of the White Paper:
*Section I. The Constitution: It stated that with over 450,000 Jews having now settled in the mandate, the Balfour Declaration about "a national home for the Jewish people" had been met, and it also called for an independent Palestine to be established within 10 years and to be governed jointly by Arabs and Jews:
These were the main points of the White Paper:
*Section I. The Constitution: It stated that with over 450,000 Jews having now settled in the mandate, the Balfour Declaration about "a national home for the Jewish people" had been met, and it also called for an independent Palestine to be established within 10 years and to be governed jointly by Arabs and Jews:
 On 13 July, the authorities announced the suspension of all Jewish immigration into Palestine until March 1940. The reason given was the increase in the number of illegal immigrants.
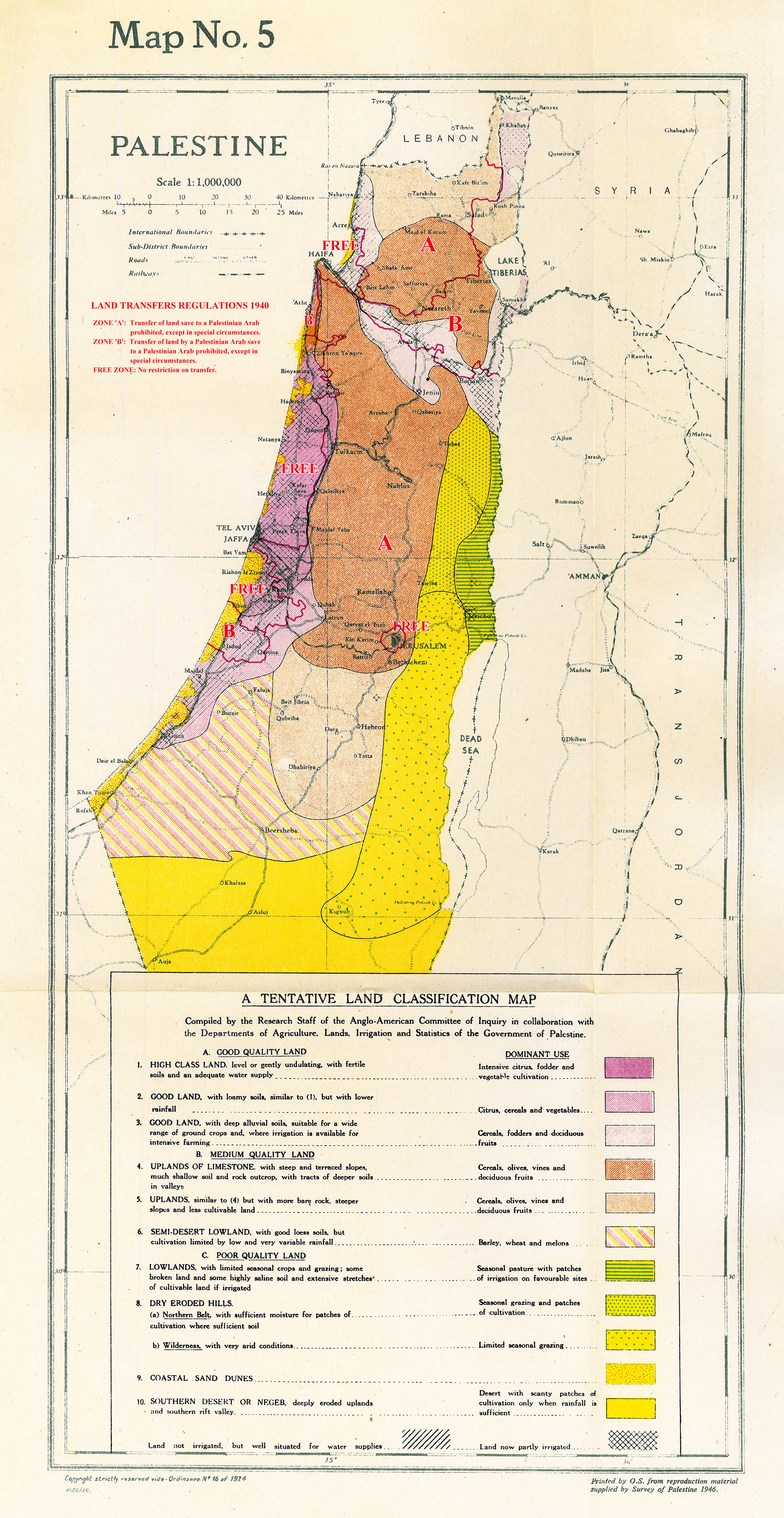
In March 1940, the British High Commissioner for Palestine issued an edict dividing Palestine into three zones:
On 13 July, the authorities announced the suspension of all Jewish immigration into Palestine until March 1940. The reason given was the increase in the number of illegal immigrants.
In March 1940, the British High Commissioner for Palestine issued an edict dividing Palestine into three zones:
23 May 1939 House of Lords debate
in ''
British White Paper of 1939
at
Peel Commission Report (July 1937)
at
Malcolm MacDonald
Malcolm Ian Macdonald (born 7 January 1950) is an English former professional footballer, manager and media figure. Nicknamed 'Supermac', Macdonald was a quick, powerfully built prolific goalscorer. He played for Fulham, Luton Town, Newcastle ...
, the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
Colonial Secretary, who presided over its creation. was a policy paper issued by the British government
ga, Rialtas a Shoilse gd, Riaghaltas a Mhòrachd
, image = HM Government logo.svg
, image_size = 220px
, image2 = Royal Coat of Arms of the United Kingdom (HM Government).svg
, image_size2 = 180px
, caption = Royal Arms
, date_es ...
, led by Neville Chamberlain
Arthur Neville Chamberlain (; 18 March 18699 November 1940) was a British politician of the Conservative Party who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from May 1937 to May 1940. He is best known for his foreign policy of appeasemen ...
, in response to the 1936–1939 Arab revolt in Palestine
The 1936–1939 Arab revolt in Palestine, later known as The Great Revolt (''al-Thawra al- Kubra'') or The Great Palestinian Revolt (''Thawrat Filastin al-Kubra''), was a popular nationalist uprising by Palestinian Arabs in Mandatory Palestine a ...
. After its formal approval in the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. ...
on 23 May 1939,by 268 votes to 179. it acted as the governing policy for Mandatory Palestine
Mandatory Palestine ( ar, فلسطين الانتدابية '; he, פָּלֶשְׂתִּינָה (א״י) ', where "E.Y." indicates ''’Eretz Yiśrā’ēl'', the Land of Israel) was a geopolitical entity established between 1920 and 1948 ...
from 1939 to the 1948 British departure. After the war, the Mandate was referred to the United Nations.
The policy, first drafted in March 1939, was prepared by the British government unilaterally as a result of the failure of the Arab-Zionist London Conference. The paper called for the establishment of a Jewish national home in an independent Palestinian state within 10 years, rejecting the Peel Commission
The Peel Commission, formally known as the Palestine Royal Commission, was a British Royal Commission of Inquiry, headed by Lord Peel, appointed in 1936 to investigate the causes of unrest in Mandatory Palestine, which was administered by Gre ...
's idea of partitioning Palestine
__NOTOC__
Palestine may refer to:
* State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia
* Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia
* Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East ...
. It also limited Jewish immigration to 75,000 for five years and ruled that further immigration would then be determined by the Arab majority (section II). Jews were restricted from buying Arab land in all but 5% of the Mandate (section III).
The proposal did not meet the political demands proposed by Arab representatives during the London Conference and was officially rejected by the representatives of Palestine Arab parties, who were acting under the influence of Haj Amin Effendi al-Husseini, but the more moderate Arab opinion that was represented by the National Defence Party was prepared to accept the White Paper.
Zionist groups in Palestine immediately rejected the White Paper and led a campaign of attacks on government property that lasted for several months. On 18 May, a Jewish general strike was called.''A Survey of Palestine - prepared in December 1945 and January 1946 for the information of the Anglo-American Committee of Inquiry''. Reprinted 1991 by The Institute of Palestine Studies, Washington. Volumes One: . p.54.
Regulations on land transfers and clauses restricting immigration were implemented, but at the end of the five years in 1944, only 51,000 of the 75,000 immigration certificates provided for had been used. In light of this, the British offered to allow immigration to continue beyond the cutoff date of 1944, at a rate of 1,500 per month, until the remaining quota was filled.Study (30 June 1978)The Origins and Evolution of the Palestine Problem Part I: 1917-1947 - Study (30 June 1978)
, accessdate: November 10, 2018 From December 1945 to the 1948 end of the Mandate, 1,500 additional certificates for Jewish immigrants were allocated each month. Key provisions were ultimately never to be implemented, initially because of cabinet opposition after the change in government and later because of preoccupation with World War II.
Background

 During
During World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, the British had made two promises regarding territory in the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
. Britain had promised the Hashemite
The Hashemites ( ar, الهاشميون, al-Hāshimīyūn), also House of Hashim, are the royal family of Jordan, which they have ruled since 1921, and were the royal family of the kingdoms of Hejaz (1916–1925), Syria (1920), and Iraq (1921� ...
governors of Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate. ...
, through Lawrence of Arabia
Thomas Edward Lawrence (16 August 1888 – 19 May 1935) was a British archaeologist, army officer, diplomat, and writer who became renowned for his role in the Arab Revolt (1916–1918) and the Sinai and Palestine Campaign (1915–191 ...
and the McMahon–Hussein Correspondence
The McMahon–Hussein Correspondence is a series of letters that were exchanged during World War I in which the Government of the United Kingdom agreed to recognize Arab independence in a large region after the war in exchange for the Sharif ...
, independence for a united Arab country in Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
in exchange for supporting the British against the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
. The Ottoman Caliphate had declared a military jihad
Jihad (; ar, جهاد, jihād ) is an Arabic word which literally means "striving" or "struggling", especially with a praiseworthy aim. In an Islamic context, it can refer to almost any effort to make personal and social life conform with Go ...
for the Germans, and the British hoped that an alliance with the Arabs would quell the chances of a general Muslim uprising in British-held territories in Africa, India and the Far East. Britain had also negotiated the Sykes–Picot Agreement
The Sykes–Picot Agreement () was a 1916 secret treaty between the United Kingdom and France, with assent from the Russian Empire and the Kingdom of Italy, to define their mutually agreed Sphere of influence, spheres of influence and control in a ...
to partition the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
between Britain and France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
.
A variety of strategic factors, such as securing Jewish support in Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russ ...
while the Russian front collapsed, culminated in the 1917 Balfour Declaration
The Balfour Declaration was a public statement issued by the British government in 1917 during the First World War announcing its support for the establishment of a "national home for the Jewish people" in Palestine, then an Ottoman regio ...
in which Britain promised to create and foster a Jewish national home in Palestine
__NOTOC__
Palestine may refer to:
* State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia
* Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia
* Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East ...
. The broad delineations of territory and goals for both the creation of a Jewish homeland in Palestine and Arab self-determination
The right of a people to self-determination is a cardinal principle in modern international law (commonly regarded as a ''jus cogens'' rule), binding, as such, on the United Nations as authoritative interpretation of the Charter's norms. It stat ...
were approved in the San Remo Conference
The San Remo conference was an international meeting of the post-World War I Allied Supreme Council as an outgrowth of the Paris Peace Conference, held at Villa Devachan in Sanremo, Italy, from 19 to 26 April 1920. The San Remo Resolution pas ...
.
In June 1922, the League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference that ...
approved the Palestine Mandate, effective September 1923, an explicit document on Britain's responsibilities and powers of administration in Palestine, including 'secur ngthe establishment of the Jewish national home', and 'safeguarding the civil and religious rights of all the inhabitants of Palestine'. In September 1922, the British government presented the Trans-Jordan memorandum
The Transjordan memorandum was a British memorandum passed by the Council of the League of Nations on 16 September 1922, as an addendum to the British Mandate for Palestine.
The memorandum described how the British government planned to implem ...
to the League of Nations that stated that the Emirate of Transjordan
The Emirate of Transjordan ( ar, إمارة شرق الأردن, Imārat Sharq al-Urdun, Emirate of East Jordan), officially known as the Amirate of Trans-Jordan, was a British protectorate established on 11 April 1921,
would be excluded from all the provisions dealing with Jewish settlement, in accordance with Article 25 of the Mandate. The memorandum was approved on 23 September. Stiff Arab opposition and pressure against Jewish immigration made Britain redefine Jewish immigration by restricting its flow according to the country's economic capacity to absorb the immigrants. In effect, annual quotas were put in place as to how many Jews could immigrate, but Jews possessing a large sum of money (£500) were allowed to enter the country freely.
Following Adolf Hitler's rise to power
Adolf Hitler's rise to power began in the newly established Weimar Republic in September 1919 when Hitler joined the '' Deutsche Arbeiterpartei'' (DAP; German Workers' Party). He rose to a place of prominence in the early years of the party. Be ...
, European Jews
The history of the Jews in Europe spans a period of over two thousand years. Some Jews, a Judaean tribe from the Levant, Natural History 102:11 (November 1993): 12–19. migrated to Europe just before the rise of the Roman Empire. A notable e ...
were increasingly prepared to spend the money necessary to enter Palestine. The 1935 Nuremberg Laws
The Nuremberg Laws (german: link=no, Nürnberger Gesetze, ) were antisemitic and racist laws that were enacted in Nazi Germany on 15 September 1935, at a special meeting of the Reichstag convened during the annual Nuremberg Rally of th ...
stripped the 500,000 German Jews of their citizenship. Jewish migration was impeded by Nazi restrictions on the transfer of finances abroad (departing Jews had to abandon their property), but the Jewish Agency
The Jewish Agency for Israel ( he, הסוכנות היהודית לארץ ישראל, translit=HaSochnut HaYehudit L'Eretz Yisra'el) formerly known as The Jewish Agency for Palestine, is the largest Jewish non-profit organization in the world. ...
was able to negotiate an agreement that allowed Jews resident in Germany to buy German goods for export to Palestine, thus circumventing the restrictions.
The large numbers of Jews entering Palestine was a cause of the 1936–1939 Arab revolt in Palestine
The 1936–1939 Arab revolt in Palestine, later known as The Great Revolt (''al-Thawra al- Kubra'') or The Great Palestinian Revolt (''Thawrat Filastin al-Kubra''), was a popular nationalist uprising by Palestinian Arabs in Mandatory Palestine a ...
. Britain responded to the revolt by appointing a royal commission, the Peel Commission
The Peel Commission, formally known as the Palestine Royal Commission, was a British Royal Commission of Inquiry, headed by Lord Peel, appointed in 1936 to investigate the causes of unrest in Mandatory Palestine, which was administered by Gre ...
, which went to Palestine and undertook a thorough study of the issues. The Peel Commission recommended in 1937 for Palestine to be partitioned into two states: one Arab the other Jewish. The proposal was rejected by the Arabs while the Zionist response was "neither positive nor negative" and the Peel Commission failed to stem the violence.Elie Podeh''Chances for Peace: Missed Opportunities in the Arab-Israeli Conflict''
University of Texas Press 2015 pp.28ff. In January 1938, the
Woodhead Commission
The Woodhead Commission (officially the Palestine Partition Commission''Palestine Partition Commission Report'', Command Paper 5854, Printed and published by His Majesty's Stationery Office, London, 1938 (310 pages and 13 maps)) was a British techn ...
explored the practicalities of partition and considered three different plans, one of which was based on the Peel Plan. Reporting in 1938, the Woodhead Commission rejected the plan, primarily on the grounds that it could not be implemented without a massive forced transfer of Arabs, an option that the British government had already ruled out. With dissent from some of its members, the Commission instead recommended a plan that would leave the Galilee under British mandate, but it emphasised serious problems with it such as a lack of financial self-sufficiency of the proposed Arab state. The British government accompanied the publication of the Woodhead Report by a statement of policy rejecting partition as impracticable for "political, administrative and financial difficulties". It proposed a substantially-smaller Jewish state, including the coastal plain only. The Évian Conference
The Évian Conference was convened 6–15 July 1938 at Évian-les-Bains, France, to address the problem of German and Austrian Jewish refugees wishing to flee persecution by Nazi Germany. It was the initiative of United States President Franklin ...
, convened by the United States in July 1938, failed to find any agreement to deal with the rapidly growing number of Jewish refugees, increasing pressure on the British to find a solution to the problem of Jewish immigration to Palestine.
London Conference
In February 1939, the British called the London Conference to negotiate an agreement between Arabs and Jews in Palestine. The Arab delegates attended on the condition that they would not meet directly with the Jewish representatives, which would constitute recognition of Jewish claims over Palestine. The British government, therefore, held separate meetings with the two sides. The conference ended in failure on March 17.Anglo-American Committee of Inquiry - Appendix IVPalestine: Historical Background In the wake of World War II, the British believed that Jewish support was either guaranteed or unimportant. However, the government feared hostility from the Arab world. That geopolitical consideration was, in
Raul Hilberg
Raul Hilberg (June 2, 1926 – August 4, 2007) was a Jewish Austrian-born American political scientist and historian. He was widely considered to be the preeminent scholar on the Holocaust. Christopher R. Browning has called him the founding fath ...
's word, "decisive" to British policies since Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
, Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
and Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the A ...
were independent and allied with Britain.
Content
 These were the main points of the White Paper:
*Section I. The Constitution: It stated that with over 450,000 Jews having now settled in the mandate, the Balfour Declaration about "a national home for the Jewish people" had been met, and it also called for an independent Palestine to be established within 10 years and to be governed jointly by Arabs and Jews:
These were the main points of the White Paper:
*Section I. The Constitution: It stated that with over 450,000 Jews having now settled in the mandate, the Balfour Declaration about "a national home for the Jewish people" had been met, and it also called for an independent Palestine to be established within 10 years and to be governed jointly by Arabs and Jews:
His Majesty's Government believe that the framers of the Mandate in which the Balfour Declaration was embodied could not have intended that Palestine should be converted into a Jewish State against the will of the Arab population of the country. ... His Majesty's Government therefore now declare unequivocally that it is not part of their policy that Palestine should become a Jewish State. They would indeed regard it as contrary to their obligations to the Arabs under the Mandate, as well as to the assurances which have been given to the Arab people in the past, that the Arab population of Palestine should be made the subjects of a Jewish State against their will.
The objective of His Majesty's Government is the establishment within 10 years of an independent Palestine State in such treaty relations with the United Kingdom as will provide satisfactorily for the commercial and strategic requirements of both countries in the future. .The independent State should be one in which Arabs and Jews share government in such a way as to ensure that the essential interests of each community are safeguarded.*Section II. Immigration: Jewish immigration to Palestine under the British Mandate was to be limited to 75,000 over the next five years and then would depend on Arab consent:
His Majesty's Government do not .find anything in the Mandate or in subsequent Statements of Policy to support the view that the establishment of a Jewish National Home in Palestine cannot be effected unless immigration is allowed to continue indefinitely. If immigration has an adverse effect on the economic position in the country, it should clearly be restricted; and equally, if it has a seriously damaging effect on the political position in the country, that is a factor that should not be ignored. Although it is not difficult to contend that the large number of Jewish immigrants who have been admitted so far have been absorbed economically, the fear of the Arabs that this influx will continue indefinitely until the Jewish population is in a position to dominate them has produced consequences which are extremely grave for Jews and Arabs alike and for the peace and prosperity of Palestine. The lamentable disturbances of the past three years are only the latest and most sustained manifestation of this intense Arab apprehension ... it cannot be denied that fear of indefinite Jewish immigration is widespread amongst the Arab population and that this fear has made possible disturbances which have given a serious setback to economic progress, depleted the Palestine exchequer, rendered life and property insecure, and produced a bitterness between the Arab and Jewish populations which is deplorable between citizens of the same country. If in these circumstances immigration is continued up to the economic absorptive capacity of the country, regardless of all other considerations, a fatal enmity between the two peoples will be perpetuated, and the situation in Palestine may become a permanent source of friction amongst all peoples in the Near and Middle East.
Jewish immigration during the next five years will be at a rate which, if economic absorptive capacity permits, will bring the Jewish population up to approximately one third of the total population of the country. Taking into account the expected natural increase of the Arab and Jewish populations, and the number of illegal Jewish immigrants now in the country, this would allow of the admission, as from the beginning of April this year, of some 75,000 immigrants over the next four years. These immigrants would, subject to the criterion of economic absorptive capacity, be admitted as follows: For each of the next five years a quota of 10,000 Jewish immigrants will be allowed on the understanding that a shortage one year may be added to the quotas for subsequent years, within the five-year period, if economic absorptive capacity permits. In addition, as a contribution towards the solution of the Jewish refugee problem, 25,000 refugees will be admitted as soon as the High Commissioner is satisfied that adequate provision for their maintenance is ensured, special consideration being given to refugee children and dependents. The existing machinery for ascertaining economic absorptive capacity will be retained, and the High Commissioner will have the ultimate responsibility for deciding the limits of economic capacity. Before each periodic decision is taken, Jewish and Arab representatives will be consulted. After the period of five years, no further Jewish immigration will be permitted unless the Arabs of Palestine are prepared to acquiesce in it.*Section III. Land: No restriction had been imposed on the transfer of land from Arabs to Jews, but the ''White Paper'' now stated:
The Reports of several expert Commissions have indicated that, owing to the natural growth of the Arab population and the steady sale in recent years of Arab land to Jews, there is now in certain areas no room for further transfers of Arab land, whilst in some other areas such transfers of land must be restricted if Arab cultivators are to maintain their existing standard of life and a considerable landless Arab population is not soon to be created. In these circumstances, the High Commissioner will be given general powers to prohibit and regulate transfers of land.
Reactions
Parliamentary approval
On 22 May 1939, theHouse of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. ...
debated a motion that the White Paper was inconsistent with the terms of the Mandate, but it was defeated by 268 votes to 179. The following day, the House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the Bicameralism, upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by Life peer, appointment, Hereditary peer, heredity or Lords Spiritual, official function. Like the ...
accepted the new policy without a vote.
During the debate, Lloyd George called the White Paper an "act of perfidy", and Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 Winston Churchill in the Second World War, dur ...
voted against his party although it was in the government. The Liberal
Liberal or liberalism may refer to:
Politics
* a supporter of liberalism
** Liberalism by country
* an adherent of a Liberal Party
* Liberalism (international relations)
* Sexually liberal feminism
* Social liberalism
Arts, entertainment and m ...
MP James Rothschild
James Mayer de Rothschild, Baron de Rothschild (born Jakob Mayer Rothschild; 15 May 1792 – 15 November 1868) was a German- French banker and the founder of the French branch of the Rothschild family.
Early life
James de Rothschild was bor ...
stated during the parliamentary debate that "for the majority of the Jews who go to Palestine it is a question of migration or of physical extinction".
Some supporters of the government were opposed to the policy on the grounds that it appeared in their view to contradict the Balfour Declaration
The Balfour Declaration was a public statement issued by the British government in 1917 during the First World War announcing its support for the establishment of a "national home for the Jewish people" in Palestine, then an Ottoman regio ...
. Several government MPs voted against the proposals or abstained, including Cabinet Ministers such as the illustrious Jewish Secretary of State for War
The Secretary of State for War, commonly called War Secretary, was a secretary of state in the Government of the United Kingdom, which existed from 1794 to 1801 and from 1854 to 1964. The Secretary of State for War headed the War Office and ...
Leslie Hore-Belisha
Leslie Hore-Belisha, 1st Baron Hore-Belisha, PC (; 7 September 1893 – 16 February 1957) was a British Liberal, then National Liberal Member of Parliament (MP) and Cabinet Minister. He later joined the Conservative Party. He proved highly su ...
.
League of Nations
The Permanent Mandates Commission unanimously held that the White Paper was in conflict with the interpretation that the Mandatory Government, with the concurrence of the organs of the League, had put upon the mandate in the past. Four of the members felt that the policy was not in harmony with the terms of the Mandate, and the other three held that existing circumstances would justify the policy if the Council of the League of Nations did not oppose it. The outbreak of the Second World War suspended any further deliberations.Arab reactions
TheArab Higher Committee
The Arab Higher Committee ( ar, اللجنة العربية العليا) or the Higher National Committee was the central political organ of the Arab Palestinians in Mandatory Palestine. It was established on 25 April 1936, on the initiative o ...
initially argued that the independence of a future Palestine government would prove to be illusory since the Jews could prevent its functioning by withholding participation, and in any case, real authority would still be in the hands of British officials. The limitations on Jewish immigration were also held to be insufficient since there was no guarantee immigration would not resume after five years. In place of the policy enunciated in the White Paper, the Arab Higher Committee called for "a complete and final prohibition" of Jewish immigration and a repudiation of the Jewish national home policy altogether.
In June 1939, Hajj Amin al-Husayni
Mohammed Amin al-Husseini ( ar, محمد أمين الحسيني 1897
– 4 July 1974) was a Palestinian Arab nationalist and Muslim leader in Mandatory Palestine.
Al-Husseini was the scion of the al-Husayni family of Jerusalemite Arab notab ...
initially "astonished" the other members of the Arab Higher Committee by turning down the White Paper. According to Benny Morris
Benny Morris ( he, בני מוריס; born 8 December 1948) is an Israeli historian. He was a professor of history in the Middle East Studies department of Ben-Gurion University of the Negev in the city of Beersheba, Israel. He is a member of t ...
, the reason that the advantageous proposal was turned down was entirely selfish: "it did not place him at the helm of the future Palestinian state."
In July 1940, after two weeks of meetings with the British representative, S. F. Newcombe
Lt Col. Stewart Francis Newcombe (1878–1956) was a British army officer and associate of T. E. Lawrence.
He was commissioned in the Royal Engineers in 1898 and fought in the Second Boer War. He served with the Egyptian army from May 1901 un ...
, the leader of the Palestinian Arab delegates to the London Conference, Jamal al-Husseini
Jamal al-Husayni (1894-1982) ( ar, جمال الحُسيني), was born in Jerusalem and was a member of the highly influential and respected Husayni family.
Husayni served as Secretary to the Executive Committee of the Palestine Arab Congress ...
and fellow delegate Musa al-Alami, agreed to the terms of the White Paper, and both signed a copy of it in the presence of the prime minister of Iraq, Nuri as-Said
Nuri Pasha al-Said CH (December 1888 – 15 July 1958) ( ar, نوري السعيد) was an Iraqi politician during the British mandate in Iraq and the Hashemite Kingdom of Iraq. He held various key cabinet positions and served eight terms as ...
.
Zionists
Zionist groups in Palestine immediately rejected the White Paper and began a campaign of attacks on government property and Arab civilians, which lasted for several months. On 18 May, a Jewish general strike was called. On 27 February 1939, in response to enthusiastic Arab demonstrations after reports that the British were proposing to allow independence to Palestine on the same terms as Iraq, a co-ordinatedIrgun
Irgun • Etzel
, image = Irgun.svg , image_size = 200px
, caption = Irgun emblem. The map shows both Mandatory Palestine and the Emirate of Transjordan, which the Irgun claimed in its entirety for a future Jewish state. The acronym "Etzel" i ...
bombing campaign across the country killed 38 Arabs and wounded 44.
In response to the White Paper, the right-wing Zionist militant group Irgun began formulating plans for a rebellion to evict the British and to establish an independent Jewish state. Ze'ev Jabotinsky
Ze'ev Jabotinsky ( he, זְאֵב זַ׳בּוֹטִינְסְקִי, ''Ze'ev Zhabotinski'';, ''Wolf Zhabotinski'' 17 October 1880 – 3 August 1940), born Vladimir Yevgenyevich Zhabotinsky, was a Russian Jewish Revisionist Zionist leade ...
, the founder of Irgun, who had been exiled from Palestine by the British, proposed a plan for a revolt to take place in October 1939, which he sent to the Irgun High Command in six coded letters. Jabotinsky's plan, he and other "illegals" would start by arriving in Palestine by boat. Then, the Irgun would help him and the other passengers escape. Next, the Irgun would raid and occupy Government House and other British centres of power in Palestine, raise the Jewish national flag and hold them for at least 24 hours, even at a heavy cost. Simultaneously, Zionist leaders in Western Europe and the United States would proclaim an independent Jewish state in Palestine and function as a government-in-exile. Irgun seriously considered carrying out the plan but was concerned over the heavy losses that would be inevitable. Irgun leader Avraham Stern, who would later break from Irgun to form Lehi, formed a plan for 40,000 armed Jewish fighters recruited in Europe to sail to Palestine and join the rebellion. The Polish government supported his plan and began training Jews and setting aside weaponry for them. However, the outbreak of World War II in September 1939 quickly put an end to those plans.
After the outbreak of war in September 1939, the head of the Jewish Agency for Palestine
The Jewish Agency for Israel ( he, הסוכנות היהודית לארץ ישראל, translit=HaSochnut HaYehudit L'Eretz Yisra'el) formerly known as The Jewish Agency for Palestine, is the largest Jewish non-profit organization in the world. ...
, David Ben-Gurion
David Ben-Gurion ( ; he, דָּוִד בֶּן-גּוּרִיּוֹן ; born David Grün; 16 October 1886 – 1 December 1973) was the primary national founder of the State of Israel and the first prime minister of Israel. Adopting the name ...
declared, "We will fight the White Paper as if there is no war, and fight the war as if there is no White Paper."
Aftermath
 On 13 July, the authorities announced the suspension of all Jewish immigration into Palestine until March 1940. The reason given was the increase in the number of illegal immigrants.
In March 1940, the British High Commissioner for Palestine issued an edict dividing Palestine into three zones:
On 13 July, the authorities announced the suspension of all Jewish immigration into Palestine until March 1940. The reason given was the increase in the number of illegal immigrants.
In March 1940, the British High Commissioner for Palestine issued an edict dividing Palestine into three zones:
In Zone A, consisting of about 63 percent of the country including the stony hills, land transfers save to a Palestinian Arab were in general forbidden. In Zone B. consisting of about 32 percent of the country, transfers from a Palestinian Arab save to another Palestinian Arab were severely restricted at the discretion of the High Commissioner. In the remainder of Palestine, consisting of about five percent of the country-which, however, includes the most fertile areas—land sales remained unrestricted.In December 1942, when the extermination of the Jews became public knowledge, there were 34,000 immigration certificates remaining. In February 1943, the British government announced that the remaining certificates could be used as soon as practicable to rescue Jewish children from Southeastern Europe, particularly Bulgaria. This plan was partly successful, but many of those who received certificates were not able to emigrate although those in Bulgaria survived.Ofer, Dalia, ''Escaping the Holocaust'' (1990) pages 218ff, 290. In July, it was announced that any Jewish refugee who reached a neutral country in transit would be given clearance for Palestine. During 1943 about half the remaining certificates were distributed, and by the end of the war, there were 3,000 certificates left. At the end of World War II, the British Labour Party conference voted to rescind the White Paper and to establish a Jewish state in Palestine, but the party's Foreign Minister,
Ernest Bevin
Ernest Bevin (9 March 1881 – 14 April 1951) was a British statesman, trade union leader, and Labour Party politician. He co-founded and served as General Secretary of the powerful Transport and General Workers' Union in the years 1922–19 ...
, persisted with the policy, which remained in effect until the May 1948 British departure from Palestine.
After the war, the determination of Holocaust survivors
Holocaust survivors are people who survived the Holocaust, defined as the persecution and attempted annihilation of the Jews by Nazi Germany and Axis powers, its allies before and during World War II in Europe and North Africa. There is no unive ...
to reach Palestine led to large scale illegal Jewish migration to Palestine. British efforts to block the migration led to violent resistance by the Zionist underground.
Illegal immigrants detained by the British Government were interned in camps on Cyprus. The immigrants had no citizenship and could not be returned to any country. Those interned included a large number of children and orphans.
Immigration statistics compiled in December 1945 indicated that the White Paper allowance had been exceeded by 790 persons when illegal immigrants were included.Supplement to Survey of Palestine, June 1947, pages 15ff On January 31, 1946, the High Commissioner announced:
It will be recalled that in the Statement of the Secretary of State for Foreign Affairs of November 13, 1945, it was made clear that His Majesty's Government could not divest themselves of the duties and responsibilities under the Mandate while the Mandate continued. They therefore proposed that they would consult with the Arabs with a view to an arrangement which would ensure that pending the receipt of the interim recommendations of the nglo-AmericanCommittee of Inquiry there would be no interruption of Jewish immigration at the present monthly rate. These consultations with the Arabs have been proceeding over a long period and have reached no conclusive result. In these circumstances His Majesty's Government have now decided for cogent reasons that they must allow immigration to continue provisionally at the proposed rate of 1,500 a month. Preference will be given to those European Jews who have a special claim such as those to whom the Palestine Government have already undertaken obligations, and relatives in Europe of Jews already established in Palestine. Illegal immigrants will of course, continue to be deducted from quotas.The quota of 1,500 certificates for Jewish immigrants per month continued until the end of the mandate. The Provisional Council of Israel's first constitutional act was a Proclamation that "All legislation resulting from the British Government's White Paper of May, 1939, will at midnight tonight become null and void. This includes the immigration provisions as well as the land transfer regulations of February, 1940."
See also
*Yishuv
Yishuv ( he, ישוב, literally "settlement"), Ha-Yishuv ( he, הישוב, ''the Yishuv''), or Ha-Yishuv Ha-Ivri ( he, הישוב העברי, ''the Hebrew Yishuv''), is the body of Jewish residents in the Land of Israel (corresponding to the s ...
* Aliyah Bet
''Aliyah Bet'' ( he, עלייה ב', " Aliyah 'B'" – bet being the second letter of the Hebrew alphabet) was the code name given to illegal immigration by Jews, most of whom were refugees escaping from Nazi Germany, and later Holocau ...
* Arab–Israeli conflict
The Arab–Israeli conflict is an ongoing intercommunal phenomenon involving political tension, military conflicts, and other disputes between Arab countries and Israel, which escalated during the 20th century, but had mostly faded out by the ...
* British Mandate of Palestine British Mandate of Palestine or Palestine Mandate most often refers to:
* Mandate for Palestine: a League of Nations mandate under which the British controlled an area which included Mandatory Palestine and the Emirate of Transjordan.
* Mandatory P ...
* Churchill White Paper, 1922
* Passfield white paper
The Passfield White Paper, issued October 20, 1930, by colonial secretary Lord Passfield (Sidney Webb), was a formal statement of British policy in Palestine, which previously had been set by the Churchill White Paper of 1922. The new statement r ...
, 1930
* Proposals for a Palestinian state
The history of the State of Palestine describes the creation and evolution of the State of Palestine in the West Bank and Gaza Strip.
During the Mandatory period, numerous plans of partition of Palestine were proposed but without the agreem ...
* '' Army of Shadows: Palestinian Collaboration with Zionism, 1917–1948''
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * *External links
23 May 1939 House of Lords debate
in ''
Hansard
''Hansard'' is the traditional name of the transcripts of parliamentary debates in Britain and many Commonwealth countries. It is named after Thomas Curson Hansard (1776–1833), a London printer and publisher, who was the first official print ...
''British White Paper of 1939
at
Yale University
Yale University is a private research university in New Haven, Connecticut. Established in 1701 as the Collegiate School, it is the third-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and among the most prestigious in the wo ...
Peel Commission Report (July 1937)
at
Jewish Virtual Library
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""Th ...
{{DEFAULTSORT:White Paper Of 1939
Mandatory Palestine
History of Palestine (region)
White papers
1939 in the United Kingdom
1939 in international relations
Documents of Mandatory Palestine
Expulsions of Jews
British Empire in World War II
Mandatory Palestine in World War II
1939 documents
Documents of the United Kingdom