1928 San Felipe Hurricane on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Okeechobee hurricane of 1928, also known as the San Felipe Segundo hurricane, was one of the deadliest hurricanes in the recorded history of the North Atlantic basin, and the fourth deadliest hurricane in the
 While the storm was passing near Dominica, the U.S. Weather Bureau located at San Juan, Puerto Rico, warned about the threat of the hurricane which would strike the island within a day or two. The advisory was sent via
While the storm was passing near Dominica, the U.S. Weather Bureau located at San Juan, Puerto Rico, warned about the threat of the hurricane which would strike the island within a day or two. The advisory was sent via
 While the hurricane was moving through the Bahamas, the Weather Bureau issued storm warnings from Miami to Titusville, later upgrading to a hurricane warning from Miami to Daytona Beach. The agency advised residents to take precautions for the hurricane, citing the potential for strong winds and waves. Hurricane warnings were also posted for the west coast from Punta Rassa to Apalachicola, and after the storm recurved, hurricane warnings were extended along the east coast to Jacksonville. Because of well-issued hurricane warnings, residents were prepared for the storm, and only 26 deaths were recorded in the coastal Palm Beach area.
Strong winds struck southern Florida as the hurricane moved ashore, with three unofficial reports of . In Miami to the south of the center, winds reached , and farther south, Key West reported winds of . The eye at landfall was wide, and after moving inland crossed Lake Okeechobee, where a calm was reported for 30 minutes. Winds at Canal Point, adjacent to the lake, were estimated as high as ; the anemometer blew away after reporting sustained winds of . The pressure at Canal Point dropped to 942 mbar (27.82 inHg). The lowest pressure north of Lake Okeechobee was 966 mbar (28.54 inHg) in Bartow, and along the west coast, winds reached in Tampa.
The hurricane left thousands of people homeless in Florida; property damage was estimated at $25 million ($). It is estimated if a similar storm were to strike as of the year 2003, it would cause $18.7 billion in damages. The cyclone remains one of three Atlantic hurricanes to strike the southern mainland of Florida with a central pressure below 940 mbar (27.76 inHg), the others being the
While the hurricane was moving through the Bahamas, the Weather Bureau issued storm warnings from Miami to Titusville, later upgrading to a hurricane warning from Miami to Daytona Beach. The agency advised residents to take precautions for the hurricane, citing the potential for strong winds and waves. Hurricane warnings were also posted for the west coast from Punta Rassa to Apalachicola, and after the storm recurved, hurricane warnings were extended along the east coast to Jacksonville. Because of well-issued hurricane warnings, residents were prepared for the storm, and only 26 deaths were recorded in the coastal Palm Beach area.
Strong winds struck southern Florida as the hurricane moved ashore, with three unofficial reports of . In Miami to the south of the center, winds reached , and farther south, Key West reported winds of . The eye at landfall was wide, and after moving inland crossed Lake Okeechobee, where a calm was reported for 30 minutes. Winds at Canal Point, adjacent to the lake, were estimated as high as ; the anemometer blew away after reporting sustained winds of . The pressure at Canal Point dropped to 942 mbar (27.82 inHg). The lowest pressure north of Lake Okeechobee was 966 mbar (28.54 inHg) in Bartow, and along the west coast, winds reached in Tampa.
The hurricane left thousands of people homeless in Florida; property damage was estimated at $25 million ($). It is estimated if a similar storm were to strike as of the year 2003, it would cause $18.7 billion in damages. The cyclone remains one of three Atlantic hurricanes to strike the southern mainland of Florida with a central pressure below 940 mbar (27.76 inHg), the others being the
 In Miami, damage was minimal, limited to broken windows and awnings. In Hollywood and
In Miami, damage was minimal, limited to broken windows and awnings. In Hollywood and  In Lake Worth, approximately 50% of homes were damaged or destroyed, while 75% of buildings in the business district suffered damage. Damage along the coast was most severe in Palm Beach. Total coastal damages were estimated as "several million" dollars. In
In Lake Worth, approximately 50% of homes were damaged or destroyed, while 75% of buildings in the business district suffered damage. Damage along the coast was most severe in Palm Beach. Total coastal damages were estimated as "several million" dollars. In
 As the rear
As the rear  Floodwaters persisted for several weeks, greatly impeding attempts to clean up the devastation. Burial services were quickly overwhelmed, and many of the bodies were placed into mass graves. Around 75% of the fatalities were migrant farm workers, making identification of both the dead and missing very difficult; as a result of this, the count of the dead is not very accurate. The
Floodwaters persisted for several weeks, greatly impeding attempts to clean up the devastation. Burial services were quickly overwhelmed, and many of the bodies were placed into mass graves. Around 75% of the fatalities were migrant farm workers, making identification of both the dead and missing very difficult; as a result of this, the count of the dead is not very accurate. The
 In Florida, although the hurricane's destruction affected everything in its path, the death toll was by far the highest and the aftermath the worst in the economically poor areas in the low-lying ground near Lake Okeechobee, such as the towns of Belle Glade, Chosen, Pahokee, South Bay, and Bean City. Around 75% of the fatalities were among
In Florida, although the hurricane's destruction affected everything in its path, the death toll was by far the highest and the aftermath the worst in the economically poor areas in the low-lying ground near Lake Okeechobee, such as the towns of Belle Glade, Chosen, Pahokee, South Bay, and Bean City. Around 75% of the fatalities were among  Robert Hazard, a resident of West Palm Beach, established the Storm of '28 Memorial Park Coalition Inc. to fight for recognition of the black victims of the storm. In 2000, the West Palm Beach burial site was reacquired by the city of West Palm Beach and plans for construction of a memorial began. The
Robert Hazard, a resident of West Palm Beach, established the Storm of '28 Memorial Park Coalition Inc. to fight for recognition of the black victims of the storm. In 2000, the West Palm Beach burial site was reacquired by the city of West Palm Beach and plans for construction of a memorial began. The
 To prevent a recurrence of disasters like this one and the Great Miami Hurricane of 1926, the Florida State Legislature created the Okeechobee Flood Control District, which was authorized to cooperate with the
To prevent a recurrence of disasters like this one and the Great Miami Hurricane of 1926, the Florida State Legislature created the Okeechobee Flood Control District, which was authorized to cooperate with the
Florida's Forgotten Hurricane
NOAA Okeechobee Hurricane Memorial
Footage of storm damage
National Weather Service Memorial Web page
{{DEFAULTSORT:1928 Okeechobee Hurricane O (1928) Okeechobee Hurricane, 1928 San Felipe II Hurricane, 1928 Okeechobee Hurricane, 1928 Okeechobee Hurricane, 1928 1928 Okeechobee Category 5 Atlantic hurricanes Hurricanes in the Leeward Islands Hurricanes in Guadeloupe Hurricanes in Îles des Saintes Hurricanes in Dominica Hurricanes in Montserrat Hurricanes in the United States Virgin Islands Hurricanes in Puerto Rico Hurricanes in the Turks and Caicos Islands Hurricanes in the Bahamas Hurricanes in Florida O (1928) 1928 in the Caribbean 1928 natural disasters in the United States 1928 in the Bahamas September 1928 events
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
, only behind the 1900 Galveston hurricane
The 1900 Galveston hurricane, also known as the Great Galveston hurricane and the Galveston Flood, and known regionally as the Great Storm of 1900 or the 1900 Storm, is the deadliest natural disaster in United States history and the third-de ...
, 1899 San Ciriaco hurricane
The 1899 San Ciríaco hurricane, also known as the 1899 Puerto Rico Hurricane or The Great Bahamas Hurricane of 1899, was the longest-lived Atlantic hurricane on record, and the second-longest-lived tropical cyclone globally on record (in terms ...
, and Hurricane Maria
Hurricane Maria was a deadly Category 5 hurricane that devastated the northeastern Caribbean in September 2017, particularly Dominica, Saint Croix, and Puerto Rico. It is regarded as the worst natural disaster in recorded history to affect ...
. The hurricane killed an estimated 2,500 people in the United States; most of the fatalities occurred in the state of Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
, particularly in Lake Okeechobee
Lake Okeechobee (), also known as Florida's Inland Sea, is the largest freshwater lake in the U.S. state of Florida. It is the tenth largest natural freshwater lake among the 50 states of the United States and the second-largest natural freshwa ...
. It was the fourth tropical cyclone, third hurricane, and only major hurricane of the 1928 Atlantic hurricane season. It developed off the west coast of Africa on September 6 as a tropical depression, but it strengthened into a tropical storm later that day, shortly before passing south of the Cape Verde islands. Further intensification was slow and halted late on September 7. About 48 hours later, the storm strengthened and became a Category 1 hurricane on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale. Still moving westward, the system reached Category 4 intensity before striking Guadeloupe on September 12, where it brought great destruction and resulted in 1,200 deaths. The islands of Martinique
Martinique ( , ; gcf, label=Martinican Creole, Matinik or ; Kalinago: or ) is an island and an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France. An integral part of the French Republic, Martinique is located in ...
, Montserrat, and Nevis
Nevis is a small island in the Caribbean Sea that forms part of the inner arc of the Leeward Islands chain of the West Indies. Nevis and the neighbouring island of Saint Kitts constitute one country: the Federation of Saint Kitts and ...
also reported damage and fatalities, but not nearly as severe as in Guadeloupe.
Around midday on September 13, the storm strengthened into a Category 5 hurricane and peaked with sustained winds of . About six hours later, the system made landfall in Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and unincorporated ...
; it remains the only tropical cyclone on record to strike the island at Category 5 intensity. Very strong winds resulted in severe damage in Puerto Rico; 24,728 homes were destroyed and 192,444 were damaged throughout the island, leaving over 500,000 people homeless. Heavy rainfall also led to extreme damage to vegetation and agriculture. On Puerto Rico alone, there were 312 deaths and about US$50 million ($ million today) in damage. While crossing the island and emerging into the Atlantic, the storm weakened slightly, falling to Category 4 intensity. It began crossing through the Bahamas on September 16, where it resulted in 18 fatalities.
The storm made landfall near West Palm Beach, Florida
West Palm Beach is a city in and the county seat of Palm Beach County, Florida, United States. It is located immediately to the west of the adjacent Palm Beach, which is situated on a barrier island across the Lake Worth Lagoon. The populati ...
, early on September 17, with winds of . In the city, more than 1,711 homes were destroyed; the effects were most severe around Lake Okeechobee. The storm surge caused water to pour out of the southern edge of the lake, flooding hundreds of square miles to depths as great as . Numerous houses and buildings were swept away in the cities of Belle Glade, Canal Point, Chosen, Pahokee, and South Bay, Florida
South Bay is a city in Palm Beach County, Florida, United States. It is the westernmost municipality in the South Florida metropolitan area. The population was 4,876 at the 2010 census. As of 2018, the population recorded by the U.S. Census Bureau ...
. At least 2,500 people drowned, while damage was estimated at $25 million. The system weakened significantly while crossing Florida, falling to Category 1 intensity late on September 17. It curved north-northeast and briefly emerged into the Atlantic on September 18, but soon made another landfall near Edisto Island, South Carolina
Edisto Island is one of South Carolina's Sea Islands, the larger part of which lies in Charleston County, with its southern tip in Colleton County. The town of Edisto Beach is in Colleton County, while the Charleston County part of the island is ...
, with winds of . Early on the following day, the system weakened to a tropical storm and became an extratropical cyclone over North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and ...
hours later. Overall, the hurricane caused $100 million in damage and killed at least 4,112 people.
Meteorological history
On September 6, ships reported a tropical depression developing just off the west coast of Africa nearDakar
Dakar ( ; ; wo, Ndakaaru) (from :wo:daqaar, daqaar ''tamarind''), is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Senegal, largest city of Senegal. The city of Dakar proper has a population of 1,030,594, whereas the population of the Dakar ...
, Senegal
Senegal,; Wolof: ''Senegaal''; Pulaar: 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Senegaali); Arabic: السنغال ''As-Sinighal'') officially the Republic of Senegal,; Wolof: ''Réewum Senegaal''; Pulaar : 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 ...
. On the next day, a ship reported winds of , or tropical storm status; on this basis, the Atlantic hurricane reanalysis project
The Atlantic hurricane reanalysis project of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration seeks to correct and add new information about past North Atlantic hurricanes. It was started around 2000 to update HURDAT, the official hurricane ...
estimated that the system attained tropical storm status late on September 6. However, lack of observations for several days prevented the system from being classified in real time as it moved generally westward across the Atlantic Ocean. On September 10, the ''S.S. Commack'' first observed the storm about to the east of Guadeloupe, which at the time was the most easterly report of a tropical cyclone ever received through ship's radio. Later that day, two other ships confirmed the intensity of the storm, and the Hurricane Research Division The Hurricane Research Division (HRD) is a section of the Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory (AOML) in Miami, Florida, and is the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's (NOAA) focus for tropical cyclone research. T ...
estimated it strengthened into a hurricane at 18:00 UTC on September 10.
As the storm neared the Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles ( es, link=no, Antillas Menores; french: link=no, Petites Antilles; pap, Antias Menor; nl, Kleine Antillen) are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc bet ...
, it continued to intensify. Between 17:30 and 18:30 UTC on September 12, the hurricane's eye moved over Guadeloupe with a barometric pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1013.25 millibars, 7 ...
of , suggesting maximum sustained wind
The maximum sustained wind associated with a tropical cyclone is a common
indicator of the intensity of the storm. Within a mature tropical cyclone, it is found within the eyewall at a distance defined as the radius of maximum wind, or RMW. Unl ...
s of , or Category 4 intensity on the Saffir–Simpson scale
The Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale (SSHWS) classifies hurricanes—which in the Western Hemisphere are tropical cyclones that exceed the intensities of tropical depressions and tropical storms—into five categories distinguished b ...
. Continuing to the west-northwest, the hurricane passed about south of Saint Croix
Saint Croix; nl, Sint-Kruis; french: link=no, Sainte-Croix; Danish and no, Sankt Croix, Taino: ''Ay Ay'' ( ) is an island in the Caribbean Sea, and a county and constituent district of the United States Virgin Islands (USVI), an unincor ...
before approaching Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and unincorporated ...
. On September 13, the eye crossed Puerto Rico in eight hours from the southeast to the northwest, moving ashore near Guayama and exiting between Aguadilla
Aguadilla (, ), founded in 1775 by Luis de Córdova, is a city and municipality located in the northwestern tip of Puerto Rico, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, north of Aguada, and Moca and west of Isabela. Aguadilla i ...
and Isabela. A ship near the southern coast reported a pressure of , and the cup anemometer
In meteorology, an anemometer () is a device that measures wind speed and direction. It is a common instrument used in weather stations. The earliest known description of an anemometer was by Italian architect and author Leon Battista Alberti ...
at San Juan reported sustained winds of before failing. As the wind station was north of the storm's center, winds near the landfall point were unofficially estimated as high as . On this basis, the hurricane is believed to have made landfall in Puerto Rico as a Category 5 hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson scale, although there was uncertainty in the peak intensity, due to the large size and slow movement of the storm.
After emerging from Puerto Rico, the hurricane had weakened to winds of about , based on a pressure reading of at Isabela. The storm brushed the northern coast of Hispaniola while moving west-northwestward, gradually restrengthening. On September 15, it passed within of Grand Turk, by which time the winds increased to . The storm continued through the Bahamas as a strong Category 4 hurricane, passing near Nassau at 10:00 UTC on September 16. Initially, Richard Gray of the U.S. Weather Bureau was optimistic that the storm would spare South Florida. However, at 00:00 UTC on September 17, the large hurricane made landfall in southeastern Florida near West Palm Beach
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some R ...
, with estimated winds of . This was based on a pressure reading of in the city, which at the time was the lowest pressure reading in the mainland United States; this broke the previous record of set during the 1926 Miami hurricane
The Great Miami Hurricane of 1926 was a large and intense tropical cyclone that devastated the Greater Miami area and caused catastrophic damage in the Bahamas and the U.S. Gulf Coast in September of the year 1926, accruing a US$100 mi ...
. Peak gusts were estimated near at Canal Point.
The hurricane quickly weakened as it progressed inland and moved over Lake Okeechobee
Lake Okeechobee (), also known as Florida's Inland Sea, is the largest freshwater lake in the U.S. state of Florida. It is the tenth largest natural freshwater lake among the 50 states of the United States and the second-largest natural freshwa ...
, although its large size enabled it to maintain hurricane status for several more days. Late on September 17, the hurricane recurved to the northeast and passed near Jacksonville
Jacksonville is a city located on the Atlantic coast of northeast Florida, the most populous city proper in the state and is the List of United States cities by area, largest city by area in the contiguous United States as of 2020. It is the co ...
early the next day with winds of . At 08:00 UTC on September 18, the storm again reached open waters. Later that day, the hurricane restrengthened slightly over open waters, making a second United States landfall near Edisto Island, South Carolina
Edisto Island is one of South Carolina's Sea Islands, the larger part of which lies in Charleston County, with its southern tip in Colleton County. The town of Edisto Beach is in Colleton County, while the Charleston County part of the island is ...
, at 19:00 UTC with winds of . Accelerating northeastward, the system quickly weakened into a tropical storm over North Carolina. On September 19, the storm transitioned into an extratropical cyclone, although it restrengthened slightly to hurricane strength, due to baroclinic forcing caused by a frontal system. The cyclone turned to the north-northwest, moving quickly through the eastern United States. On September 21, the former hurricane dissipated over Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central C ...
, having merged with another disturbance.
Effects
Leeward Islands
The hurricane moved directly over the Leeward Islands in the Caribbean Sea, strengthening as it did so. On the island of Dominica, winds were clocked at ; there were no reports of damage, though one fatality occurred. InMartinique
Martinique ( , ; gcf, label=Martinican Creole, Matinik or ; Kalinago: or ) is an island and an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France. An integral part of the French Republic, Martinique is located in ...
, further south of the storm's path, there were three fatalities. Guadeloupe received a direct hit from the storm, apparently with little warning; the death toll there was 1,200, and damage reports relayed through Paris indicated "great destruction" on the island. About three-fourths of the island's residents were left homeless. In the community of Saint-François, the only structure to remain standing was the police station, which was built with reinforced concrete. To the east of the town, the merchant ship ''Albatros'' sank; it had been carrying 80 casks of rum. The crew and the five men attempting to save the ship drowned. Approximately 85%–95% of banana crops were destroyed, 70%–80% of tree crops suffered severe damage, and 40% of the sugar cane crop was ruined. The people struggled to survive both in the short and longer term after the storm.
Montserrat, just north of the storm's center, was warned in advance of the storm but still suffered £150,000 (1928 UKP) in damages and 42 deaths; Plymouth and Salem were devastated, and crop losses caused near-starvation conditions before relief could arrive. All commercial and government buildings on the island were destroyed, as were more than 600 homes. Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis (), officially the Federation of Saint Christopher and Nevis, is an island country and microstate consisting of the two islands of Saint Kitts and Nevis, both located in the West Indies, in the Leeward Islands chain ...
also suffered heavily. On the island of St. Kitts, a number of homes built on wooden foundations were demolished. Nine deaths were reported, six of which occurred in a schoolhouse collapse. Thirteen people were killed on the island of Nevis
Nevis is a small island in the Caribbean Sea that forms part of the inner arc of the Leeward Islands chain of the West Indies. Nevis and the neighbouring island of Saint Kitts constitute one country: the Federation of Saint Kitts and ...
.
The storm destroyed hundreds of homes on Antigua, including a doctor's home and a "poor house". Government offices, hospitals, and school were also damaged. On Saint Croix
Saint Croix; nl, Sint-Kruis; french: link=no, Sainte-Croix; Danish and no, Sankt Croix, Taino: ''Ay Ay'' ( ) is an island in the Caribbean Sea, and a county and constituent district of the United States Virgin Islands (USVI), an unincor ...
, nearly all of the island's 11,000 residents suffered some degree of loss. A total of 143 buildings were destroyed, including a sugar mill. The storm resulted in nine deaths on the island. Throughout the Virgin Islands
The Virgin Islands ( es, Islas Vírgenes) are an archipelago in the Caribbean Sea. They are geologically and biogeographically the easternmost part of the Greater Antilles, the northern islands belonging to the Puerto Rico Trench and St. Cro ...
, as many as 700,000 people were rendered homeless.
Puerto Rico
 While the storm was passing near Dominica, the U.S. Weather Bureau located at San Juan, Puerto Rico, warned about the threat of the hurricane which would strike the island within a day or two. The advisory was sent via
While the storm was passing near Dominica, the U.S. Weather Bureau located at San Juan, Puerto Rico, warned about the threat of the hurricane which would strike the island within a day or two. The advisory was sent via telegraph
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas p ...
to 75 police districts and was broadcast from the naval radio station every two hours; this was the first hurricane warning broadcast by radio. Warnings were also posted for 12 ports along the southern coast, causing ships to avoid the island or remain at port. Effective preparation is credited for the relatively low death toll of 312, and not a single ship was lost at sea in the vicinity of Puerto Rico. By comparison, the weaker 1899 San Ciriaco hurricane
The 1899 San Ciríaco hurricane, also known as the 1899 Puerto Rico Hurricane or The Great Bahamas Hurricane of 1899, was the longest-lived Atlantic hurricane on record, and the second-longest-lived tropical cyclone globally on record (in terms ...
killed approximately 3,000 people.
According to the San Juan National Weather Service office, the storm was "up to this time the greatest and more intense and destructive hurricane of record in Puerto Rico." Along the storm path, the eye passed over Guayama, Cayey, and Aibonito, resulting in a period of calm lasting 20 minutes. The island of Puerto Rico received the worst of the storm's winds when the hurricane moved directly across the island at Category 5 strength. The hurricane was extremely large as it crossed Puerto Rico. Hurricane-force winds were measured in Guayama for 18 hours, where a low pressure of 931 mbar (27.5 inHg) was reported. Since the storm is estimated to have been moving at , the diameter of the storm's hurricane winds was estimated very roughly to be .
The rainfall recorded on September 13–14, 1928, remains the record for the maximum rainfall associated with a hurricane in Puerto Rico within a period of forty-eight hours. In those regions where precipitation is more common place, as in Adjuntas in the Cordillera Central and in the Sierra de Luquillo, the rain was over , with recorded in Adjuntas. The anemometer
In meteorology, an anemometer () is a device that measures wind speed and direction. It is a common instrument used in weather stations. The earliest known description of an anemometer was by Italian architect and author Leon Battista Alberti ...
located in Puerta de Tierra
Puerta de Tierra is a ''subbarrio'' (subdistrict) occupying the eastern portion of the Islet of San Juan and the ''barrio'' of San Juan Antiguo in the municipality of San Juan, Puerto Rico. The name Puerta de Tierra (Spanish for ''land gate'') ...
lost one of its cups at 11:44 am on September 13, just when it had registered a maximum speed of —a speed that was sustained for five consecutive minutes. Previously the same instrument had measured for one minute. Because these measurements were taken from San Felipe's eye, at the time, it seemed possible that some estimates of near the center of the storm were not overdrawn.
There was general destruction through the island, with the towns where the eye passed being swept away. Property damage on the island from winds and rain was catastrophic. The northeast portion of the island received winds in excess of Category 3 strength, with hurricane-force winds lasting as long as 18 hours. Official reports stated "several hundred thousand" people were left homeless, and property damages were estimated at $50 million.
On the island there was no building that was not affected. Some sugar mills ("Centrales") that had cost millions of dollars to build were reduced to rubble. Reports say that 24,728 homes were destroyed and 192,444 were partially destroyed. Most of the sugarcane fields were flooded, ruining the year's crops. Half of the coffee plants and half of the shade tree
A shade tree is a large tree whose primary role is to provide shade in the surrounding environment due to its spreading canopy and crown, where it may give shelter from sunlight in the heat of the summer for people who seek recreational needs i ...
s that covered these were destroyed; almost all of the coffee harvest was lost. The coffee industry would take years to recover since coffee needs shade trees to grow. The tobacco farms also had great losses. After this hurricane, Puerto Rico never regained its position as a major coffee exporter.
Communications were disrupted by fallen trees, landslides, and damaged bridges. Some 770 school buildings were destroyed or damaged. According to some estimates of the day, excluding personal losses, the damages reached $85.312 million and more than 500,000 people were left homeless. Until Hurricane Maria
Hurricane Maria was a deadly Category 5 hurricane that devastated the northeastern Caribbean in September 2017, particularly Dominica, Saint Croix, and Puerto Rico. It is regarded as the worst natural disaster in recorded history to affect ...
89 years later, San Felipe II was officially classified as Puerto Rico's biggest, worst, and most devastating hurricane to ever have hit the island.
Greater Antilles and Bahamas
After affecting Puerto Rico, the hurricane passed just north of theDominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with ...
, causing very little damage. This was due to the small core and weaker winds to the south of the center. Advance warning reduced the number of ships traversing the region.
While the hurricane was passing nearby, Grand Turk reported winds of . According to a ship report in the region, "The force of the wind ... could only be judged by the noise made by the storm, which reminded me of the New York subway going full speed passing switches." Winds approached at Nassau before the anemometer failed. In addition to the winds, the storm dropped heavy rainfall in the region, totaling in Nassau. As in Puerto Rico, authorities in the Bahamas had ample warning of the hurricane's approach, and preparations minimized the loss of life in the islands. Two boats were wrecked as they washed ashore in Grand Turk, although the crews were saved. A sloop traversing from Ambergris Cay to Grand Turk was lost, killing all 18 people on board. The storm caused heavy damage throughout the Bahamas, mostly to property and crops.
In Nassau, some buildings which had been recently repaired after the 1926 Nassau hurricane
The 1926 Nassau hurricane also known as the San Liborio hurricane or The Great Bahamas Hurricane of 1926, in Puerto Rico, was a destructive Category 4 hurricane that affected the Bahamas at peak intensity. Although it weakened considerably before ...
were destroyed during this storm. A 10-year-old girl drowned after falling into an open trench filled with water. At the Fort Montague Hotel, the windows, doors, and furniture were badly damaged. Similar damage was reported at the Royal Victoria Hotel, while the British Colonial Hotel was largely spared. However, the gardens of the three hotels were "damaged almost beyond recognition".
On Bimini
Bimini is the westernmost district of the Bahamas and comprises a chain of islands located about due east of Miami. Bimini is the closest point in the Bahamas to the mainland United States and approximately west-northwest of Nassau. The popula ...
, sustained winds of were observed, causing major damage to buildings. Ninety-five houses and some other buildings, including a few churches and government buildings, were damaged or destroyed on Eleuthera
Eleuthera () refers both to a single island in the archipelagic state of The Commonwealth of the Bahamas and to its associated group of smaller islands. Eleuthera forms a part of the Great Bahama Bank. The island of Eleuthera incorporates the ...
. Minor damage was reported on Rum Cay
Rum Cay (formerly known as Mamana and Santa Maria de la Concepción) is an island and district of the Bahamas. It measures in area, it is located at Lat.: N23 42' 30" - Long.: W 74 50' 00". It has many rolling hills that rise to about 120 feet (3 ...
. Most of the food crops were destroyed. On San Salvador Island
San Salvador Island (known as Watling's Island from the 1680s until 1925) is an island and district of The Bahamas. It is widely believed that during Christopher Columbus's first expedition to the New World, this island was the first land h ...
, four buildings were demolished, including two churches, while several other structures suffered minor damage. Food crops were nearly wiped out.
Florida
 While the hurricane was moving through the Bahamas, the Weather Bureau issued storm warnings from Miami to Titusville, later upgrading to a hurricane warning from Miami to Daytona Beach. The agency advised residents to take precautions for the hurricane, citing the potential for strong winds and waves. Hurricane warnings were also posted for the west coast from Punta Rassa to Apalachicola, and after the storm recurved, hurricane warnings were extended along the east coast to Jacksonville. Because of well-issued hurricane warnings, residents were prepared for the storm, and only 26 deaths were recorded in the coastal Palm Beach area.
Strong winds struck southern Florida as the hurricane moved ashore, with three unofficial reports of . In Miami to the south of the center, winds reached , and farther south, Key West reported winds of . The eye at landfall was wide, and after moving inland crossed Lake Okeechobee, where a calm was reported for 30 minutes. Winds at Canal Point, adjacent to the lake, were estimated as high as ; the anemometer blew away after reporting sustained winds of . The pressure at Canal Point dropped to 942 mbar (27.82 inHg). The lowest pressure north of Lake Okeechobee was 966 mbar (28.54 inHg) in Bartow, and along the west coast, winds reached in Tampa.
The hurricane left thousands of people homeless in Florida; property damage was estimated at $25 million ($). It is estimated if a similar storm were to strike as of the year 2003, it would cause $18.7 billion in damages. The cyclone remains one of three Atlantic hurricanes to strike the southern mainland of Florida with a central pressure below 940 mbar (27.76 inHg), the others being the
While the hurricane was moving through the Bahamas, the Weather Bureau issued storm warnings from Miami to Titusville, later upgrading to a hurricane warning from Miami to Daytona Beach. The agency advised residents to take precautions for the hurricane, citing the potential for strong winds and waves. Hurricane warnings were also posted for the west coast from Punta Rassa to Apalachicola, and after the storm recurved, hurricane warnings were extended along the east coast to Jacksonville. Because of well-issued hurricane warnings, residents were prepared for the storm, and only 26 deaths were recorded in the coastal Palm Beach area.
Strong winds struck southern Florida as the hurricane moved ashore, with three unofficial reports of . In Miami to the south of the center, winds reached , and farther south, Key West reported winds of . The eye at landfall was wide, and after moving inland crossed Lake Okeechobee, where a calm was reported for 30 minutes. Winds at Canal Point, adjacent to the lake, were estimated as high as ; the anemometer blew away after reporting sustained winds of . The pressure at Canal Point dropped to 942 mbar (27.82 inHg). The lowest pressure north of Lake Okeechobee was 966 mbar (28.54 inHg) in Bartow, and along the west coast, winds reached in Tampa.
The hurricane left thousands of people homeless in Florida; property damage was estimated at $25 million ($). It is estimated if a similar storm were to strike as of the year 2003, it would cause $18.7 billion in damages. The cyclone remains one of three Atlantic hurricanes to strike the southern mainland of Florida with a central pressure below 940 mbar (27.76 inHg), the others being the 1926 Miami hurricane
The Great Miami Hurricane of 1926 was a large and intense tropical cyclone that devastated the Greater Miami area and caused catastrophic damage in the Bahamas and the U.S. Gulf Coast in September of the year 1926, accruing a US$100 mi ...
and Hurricane Andrew of 1992.
In addition to the human fatalities, 1,278 livestock and 47,389 poultry were killed, respectively. Agriculture was significantly affected, with the storm destroying what may have been the largest "citrus crop in the history of the industry". Approximately 6% of oranges and 18% of grapefruit were ruined, respectively. Harvesting the remaining crops was delayed until mid-October due to inundated groves. Communications also suffered severely. Throughout the state, 32,000 households were left without telephone service and 400 poles were broken and about 2,500 others leaning. Governor of Florida
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
John W. Martin
John Wellborn Martin (June 21, 1884 – February 22, 1958) was an American politician who served as the List of Governors of Florida, 24th Governor of Florida, from 1925 to 1929. He also served as Mayor of Jacksonville, Mayor of Jacksonville, Flo ...
estimated that 15,000 families were left homeless in Palm Beach County alone. Additionally, about 11,500 families would need to be "re-established".
Coastal South Florida
 In Miami, damage was minimal, limited to broken windows and awnings. In Hollywood and
In Miami, damage was minimal, limited to broken windows and awnings. In Hollywood and Fort Lauderdale
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
, windows and roofs were damaged, although to a fairly minor extent. Numerous power lines and telephone wires were downed in the latter city. Northward, from Pompano Beach
Pompano Beach ( ) is a city in Broward County, Florida, United States. It is located along the coast of the Atlantic Ocean, just north of Fort Lauderdale. The nearby Hillsboro Inlet forms part of the Atlantic Intracoastal Waterway. As of the 2020 ...
to Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousandth t ...
, buildings suffered serious damage from the heavy winds and 10 ft (3 m) storm surge. Nearly all small frame houses were destroyed in Deerfield Beach
Deerfield Beach is a city in Broward County, Florida, United States, just south of the Palm Beach County line. The city is named for the numerous deer that once roamed the area. As of the 2020 census, the population was 86,859. It is a principal ...
, while several citizens estimated that at least 50% of homes were demolished. The town's post office, depot, and an entire business block were also destroyed. An eight-year-old boy drowned in a ditch near where his family sought refuge. In Boca Raton, two garages and several houses were destroyed. At the Cloister Inn, windows were shattered and the roof was damaged; across the street, 32 freight cars belonging to a train along the Florida East Coast Railway were tossed by the wind into a nearby ditch. A short distance to the north, a warehouse was flattened. A building occupied by a restaurant and a store was flattened. In Delray Beach
Delray Beach is a city in Palm Beach County, Florida, United States. The population of Delray Beach as of April 1, 2020 was 66,846 according to the 2020 United States Census. Located 52 miles (83 kilometers) north of Miami, Delray Beach is in the ...
, four churches suffered severe damage and the Alta Repp and Seacrest hotels both lost a portion of their roof. The police reported three deaths within the city. In Delray Beach and Lantana
''Lantana'' () is a genus of about 150 species of perennial flowering plants in the verbena family, Verbenaceae. They are native to tropical regions of the Americas and Africa but exist as an introduced species in numerous areas, especially in ...
, all houses and the railroad station were badly damaged. In Boynton Beach, about 75% of businesses suffered complete destruction. Fifteen people were injured by a roof collapse while taking refuge in the auditorium of a high school.
 In Lake Worth, approximately 50% of homes were damaged or destroyed, while 75% of buildings in the business district suffered damage. Damage along the coast was most severe in Palm Beach. Total coastal damages were estimated as "several million" dollars. In
In Lake Worth, approximately 50% of homes were damaged or destroyed, while 75% of buildings in the business district suffered damage. Damage along the coast was most severe in Palm Beach. Total coastal damages were estimated as "several million" dollars. In West Palm Beach
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some R ...
, the storm destroyed 1,711 homes and damaged 6,369 others, and demolished 268 businesses and impacted 490 other businesses; the city suffered the worst damage, totaling just under $13.8 million. Likewise, there was also severe wind damage in Palm Beach. A few buildings constructed by Henry Flagler, such as The Breakers
The Breakers is a Gilded Age mansion located at 44 Ochre Point Avenue, Newport, Rhode Island, US. It was built between 1893 and 1895 as a summer residence for Cornelius Vanderbilt II, a member of the wealthy Vanderbilt family.
The 70-room man ...
, the Royal Poinciana Hotel
The Royal Poinciana Hotel was a Gilded Age hotel in Palm Beach, Florida, United States. Developed by Standard Oil founder Henry Flagler and approximately 1,000 workers, the hotel opened on February 11, 1894. As Flagler's first structure ...
, and Whitehall
Whitehall is a road and area in the City of Westminster, Central London. The road forms the first part of the A3212 road from Trafalgar Square to Chelsea. It is the main thoroughfare running south from Trafalgar Square towards Parliament Sq ...
, were damaged. Mar-a-Lago
Mar-a-Lago ( from the Spanish for ''sea to lake'') is a resort and national historic landmark in Palm Beach, Florida, owned by former U.S. president Donald Trump. Trump acquired Mar-a-Lago in 1985 and referred to it as his "Winter White House ...
suffered few effects other than uprooted trees and the destruction of a large Roman-style window, according to Marjorie Merriweather Post
Marjorie Merriweather Post (March 15, 1887 – September 12, 1973) was an American businesswoman, socialite, and philanthropist. She was also the owner of General Foods Corporation.
Post used much of her fortune to collect art, particularly I ...
. Rodman Wanamaker's house, known as " La Guerida" and later the "Winter White House
Listed below are the private residences of the various presidents of the United States. For a list of official residences, see President of the United States § Residence.
Private homes of the presidents
This is a list of homes where ...
" when used by President John F. Kennedy
John Fitzgerald Kennedy (May 29, 1917 – November 22, 1963), often referred to by his initials JFK and the nickname Jack, was an American politician who served as the 35th president of the United States from 1961 until his assassination ...
, suffered heavy damage during the storm. The Alba, Billows, New Palm Beach, and Royal Daneli hotels all suffered water damage, while the Alba Hotel was also deroofed. Nearby, the Rainbow Pier had only structural damage to its railings, though the pier office was blown away. Approximately 600 structures, including 10 hotels, were damaged in Palm Beach. Damage totaled over $2 million.
The strongest winds in the eyewall affected northern Palm Beach County, particularly the vicinity of Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousandth t ...
as the eye made landfall farther south. At the Jupiter Inlet Lighthouse, the mortar was reportedly "squeezed ... like toothpaste" from between the bricks during the storm, swaying the tower off the base. The lighthouse keeper, Captain Seabrook, and his son, Franklin, worked to keep the light on during the storm after the electricity went out. After the generator failed to work, they hand-cranked the light's mantle. The building formerly used as a Weather Bureau Office was destroyed. Nearby, six people died after a house was demolished. Six other fatalities occurred west of Jupiter after a school where people sought shelter collapsed.
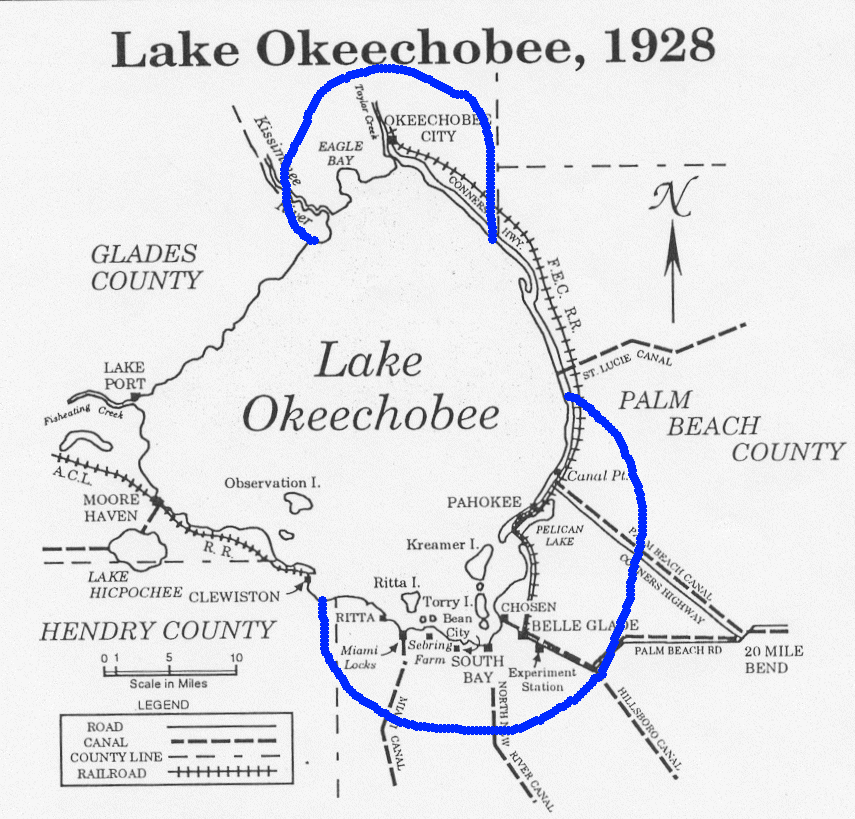
Lake Okeechobee and Everglades
Inland, the hurricane wreaked much more widespread destruction along the more heavily populated coast of Lake Okeechobee. Residents had been warned to evacuate the low ground earlier in the day, but after the hurricane did not arrive on schedule, many thought it had missed and returned to their homes. In the weeks prior to the storm, heavy rainfall had caused the lake to rise between August 10 and September 10 and filled nearby canals and ditches. Precipitation from the hurricane itself caused Lake Okeechobee to rise further. When the worst of the storm crossed the lake, the south-blowing wind caused a storm surge to overflow the small dike that had been built at the south end of the lake. The resulting flood covered an area of hundreds of square miles with water that in some places was more than 20 ft (6 m) deep. Houses were floated off their foundations and dashed to pieces against any obstacles encountered. Most survivors and bodies were washed out into theEverglades
The Everglades is a natural region of tropical wetlands in the southern portion of the U.S. state of Florida, comprising the southern half of a large drainage basin within the Neotropical realm. The system begins near Orlando with the Kissim ...
, where many of the bodies were never found. Agricultural losses in the area surrounding Lake Okeechobee were also significant, with virtually all crops destroyed and over 150 tractors suffering damage.
 As the rear
As the rear eyewall
The eye is a region of mostly calm weather at the center of tropical cyclones. The eye of a storm is a roughly circular area, typically in diameter. It is surrounded by the ''eyewall'', a ring of towering thunderstorms where the most severe weat ...
passed over the area, the flood reversed itself, breaking the dikes along the northern coast of the lake and causing similar but smaller flooding. Route 98, then known as Conner's Highway, was closed until January, when the bridge across the Onosohatchee River at Taylor Creek was replaced after the original bridge was carried about upstream during the storm. In Okeechobee County
Okeechobee County () is a county located in the Florida Heartland region of the state of Florida. As of the 2020 census, the population was 39,644. The county seat is Okeechobee.
Okeechobee County comprises the Okeechobee, FL Micropolitan St ...
, homes along the lake were destroyed by the storm surge, while dwellings within the city of Okeechobee were severely damaged or demolished by winds of at least . However, brick and concrete dwellings suffered little damage. A number of three-story business buildings collapsed during the storm. Almost all roads were left impassable, while communications were nearly wiped out. Overall, 27 deaths occurred in Okeechobee County
Okeechobee County () is a county located in the Florida Heartland region of the state of Florida. As of the 2020 census, the population was 39,644. The county seat is Okeechobee.
Okeechobee County comprises the Okeechobee, FL Micropolitan St ...
. Along the southwestern shore of Lake Okeechobee, the towns of Clewiston
Clewiston is a city in Hendry County, Florida, United States. Its location is northwest of Fort Lauderdale on the Atlantic coastal plain. The population was 7,327 at the 2020 census, up from 7,155 at the 2010 census. The estimated population in 2 ...
and Moore Haven were both flooded, but most houses suffered more damage due to strong winds.
On Kreamer Island, many residents received information about the storm when it was too late to evacuate. In some houses, 20–30 people sought shelter inside and later stood on tables and chairs to remain above the water. Most of the houses were swept away into rows of pine trees and others more than half a mile (0.8 km) away. Despite this, only one person drowned on the island. Residents of Torry Island did not have enough time to prepare for the storm. They tried to evacuate, but with the causeway already inundated, twenty-three people sought refuge in a packinghouse. Floodwaters entered the building, forcing the occupants into the rafters. The building was eventually pushed into a nearby canal. Ten people drowned, but thirteen others survived by clinging to a barge or tree tops, while one woman tied herself to a telegraph pole. Others who survived were swept far away from the original sites of the building and the barge. A teenage boy was carried from the packinghouse to the Everglades Experiment Station in Belle Glade – a distance of about . On Ritta Island, a number of persons who had successfully climbed to the roof of their houses to escape floodwaters were struck by trees or received fatal bites from water moccasins.
In South Bay, nearly all houses were destroyed and several buildings were unroofed. At least 160 fatalities occurred in the city. The future first mayor of South Bay, Aubrey (a.k.a. "Orb" or "A.O.") Walker, along with his brother, Haughty D. Walker (a.k.a. "Haught"), survived the great hurricane of 1928 by gathering family members and joining a number of other South Bay citizens on a barge in the canal; this action allowed them to survive the flood waters that swept over South Bay and ultimately engulfed Okeelanta. Throughout the 1920s, Okeelanta had suffered several floods and muck fires. After being flooded severely during the 1928 hurricane, it was abandoned. Bean City was also destroyed during the hurricane, but it was eventually rebuilt by Arthur Wells. Sebring Farms was reduced to piles of rubber, with only four tall royal palm trees left standing. The hotel at Miami Locks was the only building to survive the storm. Ninety-nine people died in that town. In Chosen, only two people escaped a house that had sheltered nineteen people. Twenty other residents took refuge in a building which lost its roof during the storm, forcing the occupants to move into the restroom. A house that was full of people floated about half a mile (0.8 km) from its original location. The refugees were unaware that the house was moving until it collided with a railroad embankment.
 Floodwaters persisted for several weeks, greatly impeding attempts to clean up the devastation. Burial services were quickly overwhelmed, and many of the bodies were placed into mass graves. Around 75% of the fatalities were migrant farm workers, making identification of both the dead and missing very difficult; as a result of this, the count of the dead is not very accurate. The
Floodwaters persisted for several weeks, greatly impeding attempts to clean up the devastation. Burial services were quickly overwhelmed, and many of the bodies were placed into mass graves. Around 75% of the fatalities were migrant farm workers, making identification of both the dead and missing very difficult; as a result of this, the count of the dead is not very accurate. The Red Cross
The International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is a humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million volunteers, members and staff worldwide. It was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure respect for all human beings, and ...
estimated the number of fatalities as 1,836, which was taken as the official count by the National Weather Service
The National Weather Service (NWS) is an agency of the United States federal government that is tasked with providing weather forecasts, warnings of hazardous weather, and other weather-related products to organizations and the public for the ...
for many years. Older sources usually list 3,411 as the hurricane's total count of fatalities, including the Caribbean. However, in 2003, the U.S. death count was revised to "at least" 2,500, making the Okeechobee hurricane one of the deadliest natural disasters in United States history. A mass grave at the Port Mayaca Cemetery east of Port Mayaca contains the bodies of 1,600 victims of the hurricane.
Central and North Florida
InFort Myers
Fort Myers (or Ft. Myers) is a city in southwestern Florida and the county seat and commercial center of Lee County, Florida, United States. The Census Bureau's Population Estimates Program calculated that the city's population was 92,245 in 20 ...
, property damage was slight, limited mostly to scores of small boats and fishing shacks along the waterfront. Nearly all cigar factories in Tampa were closed after wind and rain drove too much moisture into the buildings. Offshore, the fishing smack ''Wallace A. McDonnell'' was beached near Piney Point, though all of the crew survived. The Cuban schooner ''Isabel Alvado'' sank offshore Boca Grande. The crew, who were immigrants, were rescued by the Coast Guard
A coast guard or coastguard is a maritime security organization of a particular country. The term embraces wide range of responsibilities in different countries, from being a heavily armed military force with customs and security duties to ...
and later deported. In Martin County, a bridge connecting Stuart and Palm City was severely damaged and closed to traffic as a result. A temporary ferry service across the St. Lucie River
The St. Lucie River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed April 18, 2011 estuary linked to a coastal river system in St. Lucie and Martin counties in the Florida, United ...
was established and operated until repairs to the bridge were complete in the summer of 1929. In Fort Pierce
Fort Pierce is a city in and the county seat of St. Lucie County, Florida, United States. The city is part of the Treasure Coast region of Atlantic Coast Florida. It is also known as the Sunrise City, sister to San Francisco, California, the Suns ...
, most of the effects were confined to the waterfront areas. A warehouse, fish houses, docks, and a bridge across the Indian River were destroyed, while several other buildings were unroofed. Damage in the city totaled about $150,000.
In the interior areas of Central and North Florida, effects were mainly confined to agricultural losses, particularly citrus, though wind damage occurred to structures. Between Sebring and Lake Wales, 200 telephone poles were toppled. In Bartow, business building windows were shattered and signs were knocked down, while several roofs and chimneys also suffered damage. Winds gusting up to lashed Lakeland. Many trees were uprooted and several buildings were impacted, including the hospital and a number of businesses. At Florida Southern College
Florida Southern College (Florida Southern, Southern or FSC) is a private college in Lakeland, Florida. In 2019, the student population at FSC consisted of 3,073 students along with 130 full-time faculty members. The college offers 50 undergradu ...
(FSC), the north side of the gymnasium collapsed while other buildings on campus were damaged to a lesser degree. The trees in the citrus grove surrounding FSC lost much of their fruit. Overall, Lakeland suffered about $50,000 in damage. In Orlando
Orlando () is a city in the U.S. state of Florida and is the county seat of Orange County. In Central Florida, it is the center of the Orlando metropolitan area, which had a population of 2,509,831, according to U.S. Census Bureau figures re ...
, damage to properties was described as slight. Strong winds up to affected the Jacksonville area, resulting in minor damage at Jacksonville Beach
Jacksonville Beach is a coastal resort city in Duval County, Florida, United States. It was incorporated on May 22, 1907, as Pablo Beach, and would later change its name to Jacksonville Beach in 1925. The city is part of group of communities col ...
.
Elsewhere
Outside Florida, damage from the hurricane elsewhere in the United States was minor. In Georgia, low-lying streets were flooded or washed out in the Savannah area. Additionally, winds downed trees and power lines. Heavy rainfall occurred from eastern Florida through coastal Georgia, the Carolinas, and southeast Virginia. The highest rainfall total was atDarlington, South Carolina
Darlington is a city located in Darlington County, South Carolina, United States. In 2010, its population was 6,289. It is the county seat of Darlington County. It is part of the Florence, South Carolina Metropolitan Statistical Area.
Darlington ...
. The storm caused flooding in North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and ...
and brought near-hurricane-force winds and a 7 foot (2.1 m) storm surge to the Norfolk
Norfolk () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in East Anglia in England. It borders Lincolnshire to the north-west, Cambridgeshire to the west and south-west, and Suffolk to the south. Its northern and eastern boundaries are the No ...
area. After the hurricane became extratropical, its wind field became very large. Atlantic City, New Jersey, recorded winds of despite being far from the center.
Aftermath
In the immediate aftermath of the storm, relief arrived from nearby areas such asMiami
Miami ( ), officially the City of Miami, known as "the 305", "The Magic City", and "Gateway to the Americas", is a coastal metropolis and the county seat of Miami-Dade County in South Florida, United States. With a population of 442,241 at ...
. Early on September 18, a train leaving Miami carried 20 doctors and 20 nurses to West Palm Beach. The Miami Red Cross
The International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is a humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million volunteers, members and staff worldwide. It was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure respect for all human beings, and ...
Citizens Relief Committee, which was established to provide aid for victims of the storm, transported "hundreds of loaves of bread, gallons of milk, pounds of coffee and sugar, blankets, cots, and medical supplies." The first relief train was ridden by U.S. Senator Joseph T. Robinson, the Democratic vice presidential nominee during the election that year. At least 100 people were brought to Miami for medical treatment. In Lake Worth, 25 people were treated for various injuries at the Gulf Stream Hotel and the local fire station. Dr. W. A. Claxton, chief of the Miami Department of Public Welfare, requested antitoxin
An antitoxin is an antibody with the ability to neutralize a specific toxin. Antitoxins are produced by certain animals, plants, and bacteria in response to toxin exposure. Although they are most effective in neutralizing toxins, they can also ...
, typhoid serum, and at least 200 tetanus serums. There was also a request for 1,000 more cots in West Palm Beach and Kelsey City.
Racial issues
migrant farm workers
A migrant worker is a person who migrates within a home country or outside it to pursue work. Migrant workers usually do not have the intention to stay permanently in the country or region in which they work.
Migrant workers who work outsi ...
, most of whom were black.
The black workers did most of the post-hurricane cleanup work. Reflecting racial and class discrimination, authorities reserved the few caskets available for burials for the bodies of whites. White victims received a formal burial service, although in a mass grave, at Woodlawn Cemetery in downtown West Palm Beach. This was the only mass gravesite to receive a timely memorial.
In contrast, the bodies of black victims were burned in funeral pyres or thrown into mass burial sites such as the ones in West Palm Beach
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some R ...
and Port Mayaca.
 Robert Hazard, a resident of West Palm Beach, established the Storm of '28 Memorial Park Coalition Inc. to fight for recognition of the black victims of the storm. In 2000, the West Palm Beach burial site was reacquired by the city of West Palm Beach and plans for construction of a memorial began. The
Robert Hazard, a resident of West Palm Beach, established the Storm of '28 Memorial Park Coalition Inc. to fight for recognition of the black victims of the storm. In 2000, the West Palm Beach burial site was reacquired by the city of West Palm Beach and plans for construction of a memorial began. The site
Site most often refers to:
* Archaeological site
* Campsite, a place used for overnight stay in an outdoor area
* Construction site
* Location, a point or an area on the Earth's surface or elsewhere
* Website, a set of related web pages, typical ...
was listed on the U.S.
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
National Register of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic ...
in 2002 and a state historical marker was added in 2003 during events to commemorate the 75th anniversary of the hurricane.
African-American writer Zora Neale Hurston explored the effects of the hurricane on black migrant workers in her seminal 1937 novel, ''Their Eyes Were Watching God
''Their Eyes Were Watching God'' is a 1937 novel by American writer Zora Neale Hurston. It is considered a classic of the Harlem Renaissance, and Hurston's best known work. The novel explores main character Janie Crawford's "ripening from a v ...
''. This is her best-known work and it was included on ''TIME
Time is the continued sequence of existence and events that occurs in an apparently irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequence events, ...
'' magazine's 2005 list of the '100 best English-language novels published since 1923'.
Improved building codes
In the aftermath of the hurricane in coastal Florida, observers noted that well-constructed buildings with shutters had suffered practically no damage from winds that caused serious structural problems to lesser buildings. Buildings with well-constructed frames, and those made of steel, concrete, brick, or stone, were largely immune to winds. The use of shutters prevented damage to windows and the interior of the buildings. With the 1928 hurricane coming so soon after the 1926 Miami hurricane, where a similar pattern had been noticed, one lasting result of the 1928 storm was improved state and local building codes.Flood control
 To prevent a recurrence of disasters like this one and the Great Miami Hurricane of 1926, the Florida State Legislature created the Okeechobee Flood Control District, which was authorized to cooperate with the
To prevent a recurrence of disasters like this one and the Great Miami Hurricane of 1926, the Florida State Legislature created the Okeechobee Flood Control District, which was authorized to cooperate with the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers
, colors =
, anniversaries = 16 June (Organization Day)
, battles =
, battles_label = Wars
, website =
, commander1 = ...
in flood control undertakings. After a personal inspection of the area by President Herbert Hoover
Herbert Clark Hoover (August 10, 1874 – October 20, 1964) was an American politician who served as the 31st president of the United States from 1929 to 1933 and a member of the Republican Party, holding office during the onset of the Gr ...
, the Corps of Engineers drafted a plan to provide for the construction of floodway channels, control gates, and major levees along the shores of Lake Okeechobee. A long-term system was designed for the purpose of flood control, water conservation, prevention of saltwater intrusion
Saltwater intrusion is the movement of saline water into freshwater aquifers, which can lead to groundwater quality degradation, including drinking water sources, and other consequences. Saltwater intrusion can naturally occur in coastal aquifers, ...
, and preservation of fish and wildlife populations. One of the solutions was the construction of the Herbert Hoover Dike.
In the early 21st century, there are concerns related to the dike's stability because studies have indicated long-term problems with "piping" and erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is dis ...
. Leaks have been reported after several heavy rain events. Proposed solutions to the dike's problems have included the construction of a seepage
Soil mechanics is a branch of soil physics and applied mechanics that describes the behavior of soils. It differs from fluid mechanics and solid mechanics in the sense that soils consist of a heterogeneous mixture of fluids (usually air and wat ...
berm
A berm is a level space, shelf, or raised barrier (usually made of compacted soil) separating areas in a vertical way, especially partway up a long slope. It can serve as a terrace road, track, path, a fortification line, a border/ separation ...
on the landward side of the dike, with the first stage costing approximately $67 million (US$).
Name
The storm was named the ''San Felipe II'' hurricane inPuerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and unincorporated ...
because the eye of the cyclone made landfall there on September 13, the Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
feast day of Saint Philip Saint Philip, São Filipe, or San Felipe may refer to:
People
* Saint Philip the Apostle
* Saint Philip the Evangelist also known as Philip the Deacon
* Saint Philip Neri
* Saint Philip Benizi de Damiani also known as Saint Philip Benitius or Fili ...
, father of Saint Eugenia of Rome
Eugenia of Rome (died c AD 258) was an early Christian Roman martyr whose feast day is celebrated on December 25 in the Roman Catholic Church, on December 24 (January 6, New Style) in the Eastern Orthodox Church, and on January 23 in the Armenia ...
. (King Philip II of Spain happened to die on this day.) It was named "Segundo", Spanish for "the Second", because of the weaker but destructive " San Felipe hurricane" that had struck Puerto Rico on that same day in 1876.
In Puerto Rico, since European colonization
The historical phenomenon of colonization is one that stretches around the globe and across time. Ancient and medieval colonialism was practiced by the Phoenicians, the Greeks, the Turks, and the Arabs.
Colonialism in the modern sense began ...
, storms and hurricanes were named after the name of the saint's day that the storm hit the island. For example, they named the Great Hurricane of 1780
The Great Hurricane of 1780 was the deadliest Atlantic hurricane on record. An estimated 22,000 people died throughout the Lesser Antilles when the storm passed through the islands from October 10 to October 16. Specifics on the hurricane's tra ...
as ''San Calixto'', after Saint Callixtus, whose feast day is October 14; the 1867 San Narciso hurricane
The San Narciso Hurricane was the ninth and last known hurricane of the 1867 Atlantic hurricane season. Forming in late October, the hurricane, the costliest and deadliest storm of the 1867 Atlantic hurricane season, caused at least 811 deaths in ...
, the 1899 San Ciriaco hurricane
The 1899 San Ciríaco hurricane, also known as the 1899 Puerto Rico Hurricane or The Great Bahamas Hurricane of 1899, was the longest-lived Atlantic hurricane on record, and the second-longest-lived tropical cyclone globally on record (in terms ...
, and the 1932 San Ciprian hurricane were also named after the saints' feast days on which they occurred (respectively, Saint Narcissus of Jerusalem
Saint Narcissus of Jerusalem (c. 99 (reputedly) – c. 216) was an early patriarch of Jerusalem. He is venerated as a saint by both the Western and Eastern Churches. In the Roman Catholic Church, his feast day is celebrated on October 29, while ...
on October 29, Saint Cyriacus
Cyriacus ( el, Ἅγιος Κυριακός, fl. 303 AD), sometimes Anglicized as Cyriac, according to Christian tradition, is a Christian martyr who was killed in the Diocletianic Persecution. He is one of twenty-seven saints, most of them mart ...
on August 8, and Saint Cyprian on September 26).
In 1953, the United States Weather Bureau
The National Weather Service (NWS) is an agency of the United States federal government that is tasked with providing weather forecasts, warnings of hazardous weather, and other weather-related products to organizations and the public for the ...
(now the National Weather Service) started naming hurricanes by human female names until 1978. That year both gender names began to be used after control over naming was relinquished to the World Meteorological Organization
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for promoting international cooperation on atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology and geophysics.
The WMO originated from the Intern ...
. It was not until 1960 that Puerto Rico stopped naming hurricanes after saints. Two cyclones have been given both women's and saint's names: Hurricane Betsy ( Santa Clara, August 12, 1956) and Hurricane Donna
Hurricane Donna, known in Puerto Rico as Hurricane San Lorenzo, was the strongest hurricane of the 1960 Atlantic hurricane season, and caused severe damage to the Lesser Antilles, the Greater Antilles, and the East Coast of the United States, e ...
( San Lorenzo, September 5, 1960).
See also
*List of disasters in the United States by death toll
This list of United States disasters by death toll includes disasters that occurred either in the United States, at diplomatic missions of the United States, or incidents outside of the United States in which a number of U.S. citizens were killed ...
* Lists of Atlantic hurricanes
* List of Category 5 Atlantic hurricanes
A Category 5 Atlantic hurricane is a tropical cyclone that reaches Category 5 intensity on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale, within the Atlantic Ocean to the north of the equator. They are among the strongest tropical cyclones that can ...
* List of Florida hurricanes
The List of Florida hurricanes encompasses approximately 500 tropical or subtropical cyclones that affected the state of Florida. More storms hit Florida than any other U.S. state, and since 1851 only eighteen hurricane seasons passed without ...
* 1899 San Ciriaco hurricane
The 1899 San Ciríaco hurricane, also known as the 1899 Puerto Rico Hurricane or The Great Bahamas Hurricane of 1899, was the longest-lived Atlantic hurricane on record, and the second-longest-lived tropical cyclone globally on record (in terms ...
– A destructive, long-lived Category 4 hurricane that took a similar path, devastating Puerto Rico and the Bahamas and later affecting Florida
* 1926 Miami hurricane
The Great Miami Hurricane of 1926 was a large and intense tropical cyclone that devastated the Greater Miami area and caused catastrophic damage in the Bahamas and the U.S. Gulf Coast in September of the year 1926, accruing a US$100 mi ...
– A catastrophic Category 4 hurricane that caused numerous fatalities and widespread destruction
* Hurricane Irma
Hurricane Irma was an extremely powerful Cape Verde hurricane that caused widespread destruction across its path in September 2017. Irma was the first Category 5 hurricane to strike the Leeward Islands on record, followed by Maria two ...
(2017) – An extremely intense Category 5 hurricane that followed a similar path, causing widespread devastation
* Hurricane Maria
Hurricane Maria was a deadly Category 5 hurricane that devastated the northeastern Caribbean in September 2017, particularly Dominica, Saint Croix, and Puerto Rico. It is regarded as the worst natural disaster in recorded history to affect ...
(2017) – A Category 5 hurricane that was tenth most intense Atlantic hurricane on record and the second most intense hurricane to hit Puerto Rico
References
External links
Florida's Forgotten Hurricane
NOAA Okeechobee Hurricane Memorial
Footage of storm damage
National Weather Service Memorial Web page
{{DEFAULTSORT:1928 Okeechobee Hurricane O (1928) Okeechobee Hurricane, 1928 San Felipe II Hurricane, 1928 Okeechobee Hurricane, 1928 Okeechobee Hurricane, 1928 1928 Okeechobee Category 5 Atlantic hurricanes Hurricanes in the Leeward Islands Hurricanes in Guadeloupe Hurricanes in Îles des Saintes Hurricanes in Dominica Hurricanes in Montserrat Hurricanes in the United States Virgin Islands Hurricanes in Puerto Rico Hurricanes in the Turks and Caicos Islands Hurricanes in the Bahamas Hurricanes in Florida O (1928) 1928 in the Caribbean 1928 natural disasters in the United States 1928 in the Bahamas September 1928 events