The 1918–1920 flu pandemic, also known as the Great Influenza epidemic or by the common
misnomer
A misnomer is a name that is incorrectly or unsuitably applied. Misnomers often arise because something was named long before its correct nature was known, or because an earlier form of something has been replaced by a later form to which the nam ...
Spanish flu, was an exceptionally deadly global
influenza pandemic
An influenza pandemic is an epidemic of an influenza virus that spreads across a large region (either multiple continents or worldwide) and infects a large proportion of the population. There have been five major influenza pandemics in the l ...
caused by the
H1N1
Influenza A virus subtype H1N1 (A/H1N1) is a subtype of influenza A virus (IAV). Some human-adapted strains of H1N1 are endemic in humans and are one cause of seasonal influenza (flu). Other strains of H1N1 are endemic in pigs ( swine influen ...
subtype of the
influenza A virus
''Influenza A virus'' (''Alphainfluenzavirus influenzae'') or IAV is the only species of the genus ''Alphainfluenzavirus'' of the virus family '' Orthomyxoviridae''. It is a pathogen with strains that infect birds and some mammals, as well as c ...
. The earliest documented case was March 1918 in
Kansas
Kansas ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to the west. Kansas is named a ...
, United States, with further cases recorded in
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
,
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
and the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
in April. Two years later, nearly a third of the global population, or an estimated 500 million people, had been infected. Estimates of deaths range from 17 million to 50 million, and possibly as high as 100 million,
making it
the deadliest pandemic in history.
The pandemic broke out near the end of
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, when wartime
censors
Censorship is the suppression of speech, public communication, or other information. This may be done on the basis that such material is considered objectionable, harmful, sensitive, or "inconvenient". Censorship can be conducted by governmen ...
in the
belligerent
A belligerent is an individual, group, country, or other entity that acts in a hostile manner, such as engaging in combat. The term comes from the Latin ''bellum gerere'' ("to wage war"). Unlike the use of ''belligerent'' as an adjective meanin ...
countries suppressed bad news to maintain
morale
Morale ( , ) is the capacity of a group's members to maintain belief in an institution or goal, particularly in the face of opposition or hardship. Morale is often referenced by authority figures as a generic value judgment of the willpower, ...
, but newspapers
freely reported the outbreak in
neutral Spain, creating a false impression of Spain as the epicenter and leading to the "Spanish flu" misnomer.
[ Limited historical ]epidemiological
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and Risk factor (epidemiology), determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population, and application of this knowledge to prevent dise ...
data make the pandemic's geographic origin indeterminate, with competing hypotheses on the initial spread.
Most influenza outbreaks disproportionately kill the young and old, but this pandemic had unusually high mortality for young adults. Scientists offer several explanations for the high mortality, including a six-year climate anomaly affecting migration of disease vectors
In epidemiology, a disease vector is any living agent that carries and transmits an infectious pathogen such as a parasite or microbe, to another living organism. Agents regarded as vectors are mostly blood-sucking ( hematophagous) arthropods such ...
with increased likelihood of spread through bodies of water.hygiene
Hygiene is a set of practices performed to preserve health.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), "Hygiene refers to conditions and practices that help to maintain health and prevent the spread of diseases." Personal hygiene refer ...
, exacerbated by the war, promoted bacterial superinfection
A superinfection is a second infection superimposed on an earlier one, especially by a different microbial agent of exogenous or endogenous origin, that is resistant to the treatment being used against the first infection. Examples of this in bact ...
, killing most of the victims after a typically prolonged death bed.
Etymologies
 This pandemic was known by many different names depending on place, time, and context. The
This pandemic was known by many different names depending on place, time, and context. The etymology
Etymology ( ) is the study of the origin and evolution of words—including their constituent units of sound and meaning—across time. In the 21st century a subfield within linguistics, etymology has become a more rigorously scientific study. ...
of alternative names historicises the scourge and its effects on people who would only learn years later
Later may refer to:
* Future
The future is the time after the past and present. Its arrival is considered inevitable due to the existence of time and the laws of physics. Due to the apparent nature of reality and the unavoidability of the futur ...
that virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are ...
es caused influenza
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These sympto ...
. The lack of scientific answers led the ''Sierra Leone Weekly News'' (Freetown
Freetown () is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Sierra Leone. It is a major port city on the Atlantic Ocean and is located in the Western Area of the country. Freetown is Sierra Leone's major urban, economic, financial, cultural, e ...
) to suggest a biblical
The Bible is a collection of religious texts that are central to Christianity and Judaism, and esteemed in other Abrahamic religions such as Islam. The Bible is an anthology (a compilation of texts of a variety of forms) biblical languages ...
framing in July 1918, using an interrogative
An interrogative clause is a clause whose form is typically associated with question-like meanings. For instance, the English sentence (linguistics), sentence "Is Hannah sick?" has interrogative syntax which distinguishes it from its Declarative ...
from Exodus 16
Beshalach, Beshallach, or Beshalah (—Hebrew language, Hebrew for "when elet go" (literally: "in (having) sent"), the second word and first distinctive word in the parashah) is the sixteenth weekly Torah portion (, ''parashah'') in the annua ...
in ancient Hebrew
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and ...
: "One thing is for certain—the doctors are at present flabbergasted; and we suggest that rather than calling the disease influenza they should for the present until they have it in hand, say —'What is it?'"
Descriptive names
Outbreaks of influenza-like illness
Influenza-like illness (ILI), also known as flu-like syndrome or flu-like symptoms, is a medical diagnosis of possible influenza or other illness causing a set of common symptoms. These include fever, shivering, chills, malaise, dry cough, loss ...
were documented in 1916–17 at British military hospitals in Étaples
Étaples or Étaples-sur-Mer (; or ; formerly ; ) is a communes of France, commune in the departments of France, department of Pas-de-Calais, Hauts-de-France, northern France. It is a fishing and leisure port on the Canche river.
History
Étapl ...
, France, and just across the English Channel
The English Channel, also known as the Channel, is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that separates Southern England from northern France. It links to the southern part of the North Sea by the Strait of Dover at its northeastern end. It is the busi ...
at Aldershot
Aldershot ( ) is a town in the Rushmoor district, Hampshire, England. It lies on heathland in the extreme north-east corner of the county, south-west of London. The town has a population of 37,131, while the Farnborough/Aldershot built-up are ...
, England. Clinical indications in common with the 1918 pandemic included rapid symptom progression to a "dusky" heliotrope face. This characteristic blue-violet cyanosis
Cyanosis is the change of Tissue (biology), tissue color to a bluish-purple hue, as a result of decrease in the amount of oxygen bound to the hemoglobin in the red blood cells of the capillary bed. Cyanosis is apparent usually in the Tissue (bi ...
in expiring patients led to the name 'purple death'.
The Aldershot physicians later wrote in ''The Lancet
''The Lancet'' is a weekly peer-reviewed general medical journal, founded in England in 1823. It is one of the world's highest-impact academic journals and also one of the oldest medical journals still in publication.
The journal publishes ...
'', "the influenza pneumococcal purulent bronchitis we and others described in 1916 and 1917 is fundamentally the same condition as the influenza of this present pandemic."purulent
Pus is an exudate, typically white-yellow, yellow, or yellow-brown, formed at the site of inflammation during infections, regardless of cause. An accumulation of pus in an enclosed tissue space is known as an abscess, whereas a visible collecti ...
bronchitis
Bronchitis is inflammation of the bronchi (large and medium-sized airways) in the lungs that causes coughing. Bronchitis usually begins as an infection in the nose, ears, throat, or sinuses. The infection then makes its way down to the bronchi. ...
" is not yet linked to the same A/H1N1
Influenza A virus subtype H1N1 (A/H1N1) is a subtype of influenza A virus (IAV). Some human-adapted strains of H1N1 are endemic in humans and are one cause of seasonal influenza (flu). Other strains of H1N1 are endemic in pigs (swine influenza ...
virus,[ but it may be a precursor.][
In 1918, 'epidemic ]influenza
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These sympto ...
',Kansas
Kansas ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to the west. Kansas is named a ...
, U.S., during late spring, and early reports from Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
began appearing on 21 May. Reports from both places called it 'three-day fever'.
Associative names
Many alternative names are exonyms
An endonym (also known as autonym ) is a common, name for a group of people, individual person, geographical place, language, or dialect, meaning that it is used inside a particular group or linguistic community to identify or designate them ...
in the practice of making new infectious diseases
infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
seem foreign.1889–1890 pandemic
The 1889–1890 pandemic, often referred to as the "Asiatic flu" or "Russian flu", was a worldwide respiratory viral pandemic. It was the last great pandemic of the 19th century, and is among the deadliest pandemics in history. The pandemic k ...
, also known as the 'Russian flu', when the Russians already called epidemic influenza the 'Chinese catarrh', the Germans called it the 'Russian pest', and the Italians called it the 'German disease'. These epithet
An epithet (, ), also a byname, is a descriptive term (word or phrase) commonly accompanying or occurring in place of the name of a real or fictitious person, place, or thing. It is usually literally descriptive, as in Alfred the Great, Suleima ...
s were re-used in the 1918 pandemic, along with new ones.[
]
'Spanish' influenza
 Outside Spain, the disease was soon misnamed 'Spanish influenza'. In a 2 June 1918 ''
Outside Spain, the disease was soon misnamed 'Spanish influenza'. In a 2 June 1918 ''The Times
''The Times'' is a British Newspaper#Daily, daily Newspaper#National, national newspaper based in London. It began in 1785 under the title ''The Daily Universal Register'', adopting its modern name on 1 January 1788. ''The Times'' and its si ...
'' of London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
dispatch titled, "The Spanish Epidemic," a correspondent in Madrid
Madrid ( ; ) is the capital and List of largest cities in Spain, most populous municipality of Spain. It has almost 3.5 million inhabitants and a Madrid metropolitan area, metropolitan area population of approximately 7 million. It i ...
reported over 100,000 victims of, "The unknown disease...clearly of a gripal character," without referring to "Spanish influenza" directly. Three weeks later ''The Times'' reported that, "Everybody thinks of it as the 'Spanish' influenza to-day." Three days after that an advertisement appeared in ''The Times'' for Formamint tablets to prevent "Spanish influenza". When it reached Moscow, ''Pravda
''Pravda'' ( rus, Правда, p=ˈpravdə, a=Ru-правда.ogg, 'Truth') is a Russian broadsheet newspaper, and was the official newspaper of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, when it was one of the most in ...
'' announced, " (the Spanish lady) is in town," making 'the Spanish lady' another common name.
The outbreak did not originate in Spain,censorship
Censorship is the suppression of speech, public communication, or other information. This may be done on the basis that such material is considered objectionable, harmful, sensitive, or "inconvenient". Censorship can be conducted by governmen ...
in belligerent
A belligerent is an individual, group, country, or other entity that acts in a hostile manner, such as engaging in combat. The term comes from the Latin ''bellum gerere'' ("to wage war"). Unlike the use of ''belligerent'' as an adjective meanin ...
nations. Spain was a neutral country
A neutral country is a sovereign state, state that is neutral towards belligerents in a specific war or holds itself as permanently neutral in all future conflicts (including avoiding entering into military alliances such as NATO, Collective Sec ...
unconcerned with appearances of combat readiness
Combat readiness is a condition of the armed forces and their constituent units and formations, warships, aircraft, weapon systems or other military technology and equipment to perform during combat military operations, or functions consistent ...
, and without a wartime propaganda
Propaganda is communication that is primarily used to influence or persuade an audience to further an agenda, which may not be objective and may be selectively presenting facts to encourage a particular synthesis or perception, or using loaded l ...
machine to prop up morale
Morale ( , ) is the capacity of a group's members to maintain belief in an institution or goal, particularly in the face of opposition or hardship. Morale is often referenced by authority figures as a generic value judgment of the willpower, ...
, so its newspapers freely
Freely is a British free-to-air IPTV service launched in 2024 by Everyone TV, a joint venture between the country's public broadcasters BBC, ITV, Channel 4 and 5. The service offers the ability to watch live television and on demand media from t ...
reported epidemic effects, making Spain the apparent locus of the epidemic. The censorship was so effective that Spain's health officials were unaware its neighboring countries were similarly affected.Journal of the American Medical Association
''JAMA'' (''The Journal of the American Medical Association'') is a peer-reviewed medical journal published 48 times a year by the American Medical Association. It publishes original research, reviews, and editorials covering all aspects of ...
'', a Spanish official protested, "we were surprised to learn that the disease was making ravages in other countries, and that people there were calling it the 'Spanish grip'. And wherefore Spanish? ...this epidemic was not born in Spain, and this should be recorded as a historic vindication."

Other exonyms
French press initially used 'American flu', but adopted 'Spanish flu' in lieu of antagonizing an ally.battlefield
A battlefield, battleground, or field of battle is the location of a present or historic battle involving ground warfare. It is commonly understood to be limited to the point of contact between opposing forces, though battles may involve troop ...
in Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeas ...
where many soldiers on both sides fell ill.Senegal
Senegal, officially the Republic of Senegal, is the westernmost country in West Africa, situated on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. It borders Mauritania to Mauritania–Senegal border, the north, Mali to Mali–Senegal border, the east, Guinea t ...
it was named 'Brazilian flu', and in Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
, 'German flu'. In Spain it was also known as the 'French flu' (),zarzuela
() is a Spanish lyric-dramatic genre that alternates between spoken and sung scenes, the latter incorporating operatic and popular songs, as well as dance. The etymology of the name is uncertain, but some propose it may derive from the name o ...
.[ Spanish flu () is now a common name in Spain, but remains controversial there.]Othering
In philosophy, the Other is a fundamental concept referring to anyone or anything perceived as distinct or different from oneself. This distinction is crucial for understanding how individuals construct their own identities, as the encounter wit ...
derived from geopolitical borders and social boundaries.Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin, were a radical Faction (political), faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) which split with the Mensheviks at the 2nd Congress of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party, ...
disease',[ Some Africans called it a 'white man's sickness', but in ]South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
, white men also used the ethnophaulism ().[ ]Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
blamed sumo
is a form of competitive full-contact wrestling where a ''rikishi'' (wrestler) attempts to force his opponent out of a circular ring (''dohyō'') or into touching the ground with any body part other than the soles of his feet (usually by th ...
wrestlers for bringing the disease home from Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
, calling it 'sumo flu' ().
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
'best practices' first published in 2015 now aim to prevent social stigma
Stigma, originally referring to the visible marking of people considered inferior, has evolved to mean a negative perception or sense of disapproval that a society places on a group or individual based on certain characteristics such as their ...
by not associating culturally significant names with new diseases, listing "Spanish flu" under "examples to be avoided".[ Many authors now eschew calling this the Spanish flu,][ instead using variations of '1918–19/20 flu/influenza pandemic'.
]
Local names
Some language endonyms
An endonym (also known as autonym ) is a common, name for a group of people, individual person, geographical place, language, or dialect, meaning that it is used inside a particular group or linguistic community to identify or designate them ...
did not name specific regions or groups of people. Examples specific to this pandemic include: (let enquiries be made concerning it), (the disease of head and coughing and spine),
Other names
This outbreak was also commonly known as the 'great influenza epidemic', after the 'great war', a common name for World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
before World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. French military doctors originally called it 'disease 11' ().children's song
A children's song may be a nursery rhyme set to music, a song that children invent and share among themselves or a modern creation intended for entertainment, use in the home or education. Although children's songs have been recorded and studie ...
from the 1889–90 flu pandemic was shortened and adapted into a skipping-rope rhyme
A skipping rhyme (occasionally skipping-rope rhyme or jump-rope rhyme), is a rhyme chanted by children while skipping. Such rhymes have been recorded in all cultures where skipping is played. Examples of English-language rhymes have been found g ...
popular in 1918. It is a metaphor
A metaphor is a figure of speech that, for rhetorical effect, directly refers to one thing by mentioning another. It may provide, or obscure, clarity or identify hidden similarities between two different ideas. Metaphors are usually meant to cr ...
for the transmissibility of 'Influenza', where that name was clipped to 'Enza':
History
Timeline
First wave of early 1918
The pandemic is conventionally marked as having begun on 4 March 1918 with the recording of the case of Albert Gitchell, an army cook at Camp Funston
Camp Funston is a U.S. Army training camp located on the grounds of Fort Riley, southwest of Manhattan, Kansas. The camp was named for Brigadier General Frederick Funston (1865–1917). It is one of sixteen such camps that were established at ...
in Kansas
Kansas ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to the west. Kansas is named a ...
, United States, despite there having been cases before him. The disease had already been observed away in Haskell County as early as January 1918, prompting local doctor Loring Miner
Loring Vinton Miner (1860–1935) was an American physician who is most notable for being the first in the world to identify and describe the Spanish flu.
Early life and education
Loring Miner was born in 1860 in Kansas.
He graduated from Oh ...
to warn the editors of the U.S. Public Health Service
The United States Public Health Service (USPHS or PHS) is a collection of agencies of the Department of Health and Human Services which manages public health, containing nine out of the department's twelve operating divisions. The assistant se ...
's journal ''Public Health Reports''. Within days of the 4 March case at Camp Funston, 522 men at the camp had reported sick. By 11 March 1918, the virus had reached Queens
Queens is the largest by area of the Boroughs of New York City, five boroughs of New York City, coextensive with Queens County, in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. Located near the western end of Long Island, it is bordered by the ...
, New York. Failure to take preventive measures in March/April was later criticized.
As the U.S. had entered World War I, the disease quickly spread from Camp Funston, a major training ground for troops of the American Expeditionary Forces
The American Expeditionary Forces (AEF) was a formation of the United States Armed Forces on the Western Front (World War I), Western Front during World War I, composed mostly of units from the United States Army, U.S. Army. The AEF was establis ...
, to other U.S. Army
The United States Army (USA) is the primary land service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is designated as the Army of the United States in the United States Constitution.Article II, section 2, clause 1 of the United Stat ...
camps and Europe, becoming an epidemic in the Midwest
The Midwestern United States (also referred to as the Midwest, the Heartland or the American Midwest) is one of the four census regions defined by the United States Census Bureau. It occupies the northern central part of the United States. It ...
, East Coast, and French ports by April 1918, and reaching the Western Front by mid-April. It then quickly spread to the rest of France, Great Britain, Italy, and Spain and in May reached Wrocław
Wrocław is a city in southwestern Poland, and the capital of the Lower Silesian Voivodeship. It is the largest city and historical capital of the region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the Oder River in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Eu ...
and Odessa
ODESSA is an American codename (from the German language, German: ''Organisation der ehemaligen SS-Angehörigen'', meaning: Organization of Former SS Members) coined in 1946 to cover Ratlines (World War II aftermath), Nazi underground escape-pl ...
. After the signing of the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Soviet Russia and the Central Powers (Germany, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and Bulgaria), by which Russia withdrew from World War I. The treaty, whi ...
(March 1918), Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
started releasing Russian prisoners of war, who brought the disease to their country. It reached North Africa, India, and Japan in May, and soon after had likely gone around the world as there had been recorded cases in Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
in April. In June an outbreak was reported in China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
. After reaching Australia in July, the wave started to recede.
The first wave lasted from the first quarter of 1918 and was relatively mild. Mortality rates were not appreciably above normal; in the United States ~75,000 flu-related deaths were reported in the first six months of 1918, compared to ~63,000 deaths during the same time period in 1915.World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, with three-quarters of French troops, half the British forces, and over 900,000 German soldiers sick.
Deadly second wave of late 1918
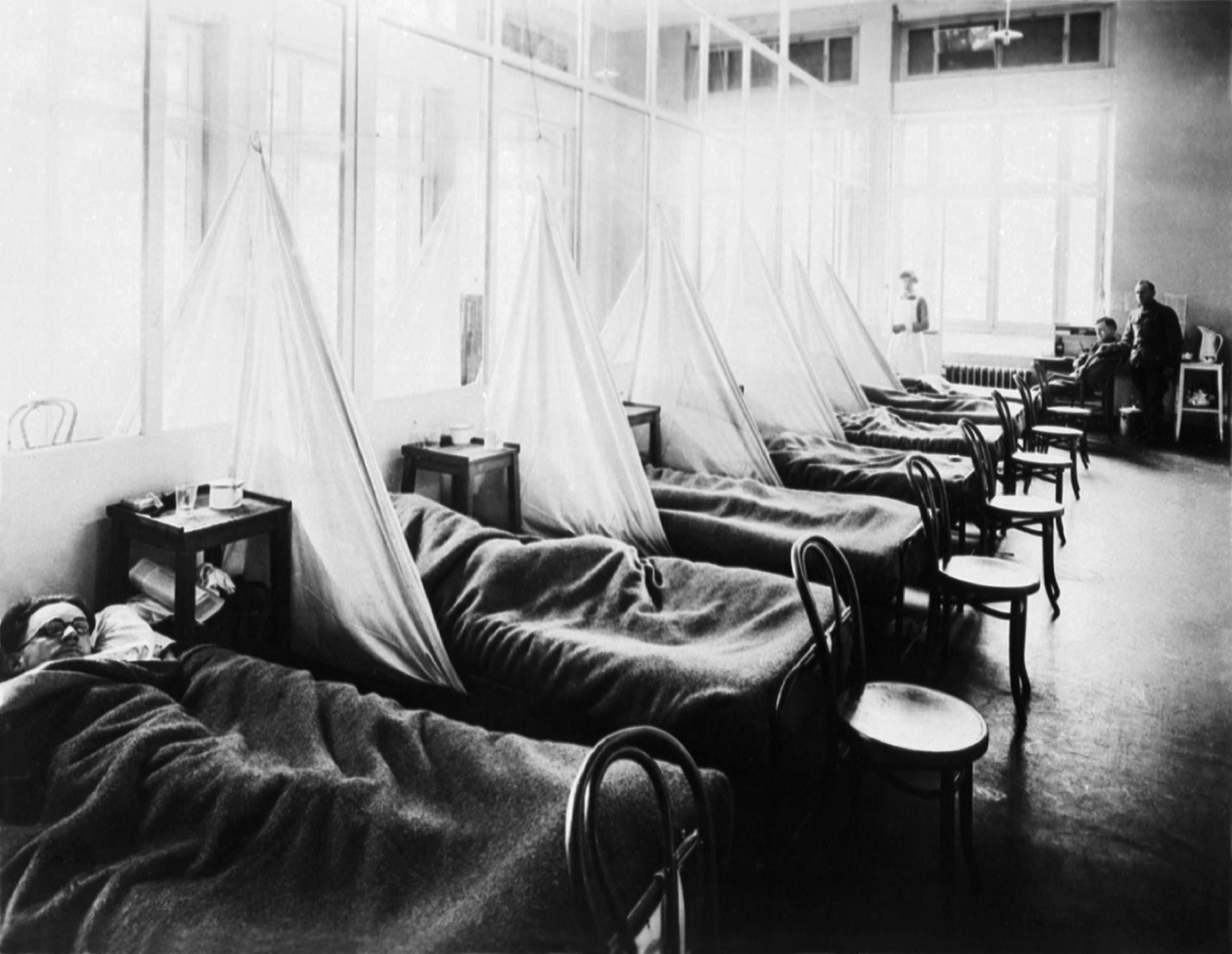
 The second wave began in the second half of August 1918, probably spreading to
The second wave began in the second half of August 1918, probably spreading to Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
, Massachusetts and Freetown
Freetown () is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Sierra Leone. It is a major port city on the Atlantic Ocean and is located in the Western Area of the country. Freetown is Sierra Leone's major urban, economic, financial, cultural, e ...
, Sierra Leone, by ships from Brest, where it had likely arrived with American troops or French recruits for naval training. From the Boston Navy Yard
The Boston Navy Yard, originally called the Charlestown Navy Yard and later Boston Naval Shipyard, was one of the oldest shipbuilding facilities in the United States Navy. It was established in 1801 as part of the recent establishment of t ...
and Camp Devens
Fort Devens is a United States Army Reserve military installation in the towns of Ayer and Shirley, in Middlesex County and Harvard in Worcester County in the U.S. state of Massachusetts. Due to extensive environmental contamination it was l ...
, about west of Boston, other U.S. military sites were soon afflicted, as were troops being transported to Europe. Helped by troop movements, it spread over the next two months to all of North America, and then to Central and South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
, also reaching Brazil and the Caribbean on ships. In July 1918, the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
saw its first cases, in soldiers.South African Native Labour Corps
The South African Native Labour Corps (SANLC) was a force of workers formed in 1916 in response to a British request for workers at French ports. About 25,000 South Africans joined the Corps. The SANLC was utilized in various menial noncombat tas ...
from France. From there it spread around southern Africa and beyond the Zambezi
The Zambezi (also spelled Zambeze and Zambesi) is the fourth-longest river in Africa, the longest east-flowing river in Africa and the largest flowing into the Indian Ocean from Africa. Its drainage basin covers , slightly less than half of t ...
, reaching Ethiopia in November. On 15 September, New York City saw its first fatality from influenza. The Philadelphia Liberty Loans Parade, held in Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
, Pennsylvania, on 28 September 1918 to promote government bonds
A government bond or sovereign bond is a form of bond issued by a government to support public spending. It generally includes a commitment to pay periodic interest, called coupon payments'','' and to repay the face value on the maturity da ...
for World War I, resulted in an outbreak causing 12,000 deaths.Arkhangelsk
Arkhangelsk (, ) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center of Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia. It lies on both banks of the Northern Dvina near its mouth into the White Sea. The city spreads for over along the ...
by the North Russia intervention
The North Russia intervention, also known as the Northern Russian expedition, the Archangel campaign, and the Murman deployment, was part of the Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War after the October Revolution. The intervention brought a ...
, and then spread throughout Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
following the Russian Civil War
The Russian Civil War () was a multi-party civil war in the former Russian Empire sparked by the 1917 overthrowing of the Russian Provisional Government in the October Revolution, as many factions vied to determine Russia's political future. I ...
and the Trans-Siberian railway
The Trans-Siberian Railway, historically known as the Great Siberian Route and often shortened to Transsib, is a large railway system that connects European Russia to the Russian Far East. Spanning a length of over , it is the longest railway ...
, reaching Iran (where it spread through Mashhad
Mashhad ( ; ), historically also known as Mashad, Meshhed, or Meshed in English, is the List of Iranian cities by population, second-most-populous city in Iran, located in the relatively remote north-east of the country about from Tehran. ...
), and then India in September and China and Japan in October. The celebrations of the Armistice of 11 November 1918
The Armistice of 11 November 1918 was the armistice signed in a railroad car, in the Compiègne Forest near the town of Compiègne, that ended fighting on land, at sea, and in the air in World War I between the Entente and their las ...
also caused outbreaks in Lima
Lima ( ; ), founded in 1535 as the Ciudad de los Reyes (, Spanish for "City of Biblical Magi, Kings"), is the capital and largest city of Peru. It is located in the valleys of the Chillón River, Chillón, Rímac River, Rímac and Lurín Rive ...
and Nairobi
Nairobi is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Kenya. The city lies in the south-central part of Kenya, at an elevation of . The name is derived from the Maasai language, Maasai phrase , which translates to 'place of cool waters', a ...
, but by December the wave was mostly over.
The second wave of the 1918 pandemic was much more deadly than the first. The first wave had resembled typical flu epidemics; those most at risk were the sick and elderly, while younger, healthier people recovered easily. October 1918 was the month with the highest fatality rate of the whole pandemic. In the United States, ~292,000 deaths were reported between September–December 1918, compared to ~26,000 during the same time period in 1915.Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
reported over 40,000 deaths from influenza and acute respiratory disease. Bombay
Mumbai ( ; ), also known as Bombay ( ; its official name until 1995), is the capital city of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Maharashtra. Mumbai is the financial centre, financial capital and the list of cities i ...
reported ~15,000 deaths in a population of 1.1 million.David Arnold
David Arnold (born 23 January 1962) is an English film composer whose credits include scoring five James Bond films (1997-2008), as well as ''Stargate'' (1994), ''Independence Day'' (1996), ''Godzilla'' (1998), '' Shaft'' (2000), '' 2 Fast 2 F ...
estimates at least 12 million dead, about 5% of the population.
Third wave of 1919
Pandemic activity persisted into 1919 in many places, possibly attributable to climate, specifically in the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined by humans as being in the same celestial sphere, celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the Solar ...
, where it was winter and thus the usual time for influenza activity.Michigan
Michigan ( ) is a peninsular U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, Upper Midwestern United States. It shares water and land boundaries with Minnesota to the northwest, Wisconsin to the west, ...
, for example, experienced a swift resurgence of influenza that reached its peak in December, possibly as a result of the lifting of the ban on public gatherings. Pandemic interventions, such as bans on public gatherings and the closing of schools, were reimposed in many places in an attempt to suppress the spread.Los Angeles
Los Angeles, often referred to by its initials L.A., is the List of municipalities in California, most populous city in the U.S. state of California, and the commercial, Financial District, Los Angeles, financial, and Culture of Los Angeles, ...
,Memphis
Memphis most commonly refers to:
* Memphis, Egypt, a former capital of ancient Egypt
* Memphis, Tennessee, a major American city
Memphis may also refer to:
Places United States
* Memphis, Alabama
* Memphis, Florida
* Memphis, Indiana
* Mem ...
, Nashville
Nashville, often known as Music City, is the capital and List of municipalities in Tennessee, most populous city in the U.S. state of Tennessee. It is the county seat, seat of Davidson County, Tennessee, Davidson County in Middle Tennessee, locat ...
, San Francisco
San Francisco, officially the City and County of San Francisco, is a commercial, Financial District, San Francisco, financial, and Culture of San Francisco, cultural center of Northern California. With a population of 827,526 residents as of ...
, and St. Louis
St. Louis ( , sometimes referred to as St. Louis City, Saint Louis or STL) is an independent city in the U.S. state of Missouri. It lies near the confluence of the Mississippi and the Missouri rivers. In 2020, the city proper had a populatio ...
.England and Wales
England and Wales () is one of the Law of the United Kingdom#Legal jurisdictions, three legal jurisdictions of the United Kingdom. It covers the constituent countries England and Wales and was formed by the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542. Th ...
by mid-February, peaking in early March, though it did not fully subside until May. France also experienced a significant wave that peaked in February, alongside the Netherlands. Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ...
, Finland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, ...
, and Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
saw recrudescences of pandemic activity in March, and Sweden in April.Melbourne
Melbourne ( , ; Boonwurrung language, Boonwurrung/ or ) is the List of Australian capital cities, capital and List of cities in Australia by population, most populous city of the States and territories of Australia, Australian state of Victori ...
, peaking in mid-February.New South Wales
New South Wales (commonly abbreviated as NSW) is a States and territories of Australia, state on the Eastern states of Australia, east coast of :Australia. It borders Queensland to the north, Victoria (state), Victoria to the south, and South ...
and South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a States and territories of Australia, state in the southern central part of Australia. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories by area, which in ...
.Victoria
Victoria most commonly refers to:
* Queen Victoria (1819–1901), Queen of the United Kingdom and Empress of India
* Victoria (state), a state of Australia
* Victoria, British Columbia, Canada, a provincial capital
* Victoria, Seychelles, the capi ...
between April and June.Queensland
Queensland ( , commonly abbreviated as Qld) is a States and territories of Australia, state in northeastern Australia, and is the second-largest and third-most populous state in Australia. It is bordered by the Northern Territory, South Austr ...
was not infected until late April; Western Australia
Western Australia (WA) is the westernmost state of Australia. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east, and South Australia to the south-east. Western Aust ...
avoided the disease until early June, and Tasmania
Tasmania (; palawa kani: ''Lutruwita'') is an island States and territories of Australia, state of Australia. It is located to the south of the Mainland Australia, Australian mainland, and is separated from it by the Bass Strait. The sta ...
remained free from it until mid-August.Madagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
, which saw its first cases in April; the outbreak had spread to practically all sections of the island by June. In other parts, influenza recurred in the form of a true "third wave". Hong Kong
Hong Kong)., Legally Hong Kong, China in international treaties and organizations. is a special administrative region of China. With 7.5 million residents in a territory, Hong Kong is the fourth most densely populated region in the wor ...
experienced another outbreak in June, as did South Africa during its fall and winter months in the Southern Hemisphere. New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
experienced some cases in May.
Parts of South America experienced a resurgence of pandemic activity throughout 1919. A third wave hit Brazil between January and June.Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes, Andes Mountains and the Paci ...
, which had been affected for the first time in October 1918, experienced a severe second wave, with mortality peaking in August 1919.Montevideo
Montevideo (, ; ) is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Uruguay, largest city of Uruguay. According to the 2023 census, the city proper has a population of 1,302,954 (about 37.2% of the country's total population) in an area of . M ...
similarly experienced a second outbreak between July and September.
The third wave particularly affected Spain, Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
, Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
and Great Britain, resulting in hundreds of thousands of deaths.
Fourth wave of 1920
In the Northern Hemisphere, fears of a "recurrence" of the flu grew as fall approached. Experts cited past flu epidemics, such as that of 1889–1890, to predict that such a recurrence a year later was not unlikely, though not all agreed. In September 1919, U.S. Surgeon General
The surgeon general of the United States is the operational head of the United States Public Health Service Commissioned Corps (PHSCC) and thus the leading spokesperson on matters of public health in the federal government of the United States. T ...
Rupert Blue
Rupert Lee Blue (May 30, 1868 – April 12, 1948) was an American physician and soldier. He was the fourth Surgeon General of the United States from 1912 to 1920. He served as president of the American Medical Association in 1916–17.
Biog ...
said a return of the flu later in the year would "probably, but by no means certainly," occur. France had readied a public information campaign before the end of the summer, and Britain began preparations in the autumn with the manufacture of vaccine.
In Japan, the flu broke out again in December and spread rapidly throughout the country, a fact attributed at the time to cold weather. The fourth wave in the United States subsided as swiftly as it had appeared, reaching a peak in early February. "An epidemic of considerable proportions marked the early months of 1920", the U.S. Mortality Statistics would later note; according to data at this time, the epidemic resulted in one third as many deaths as the 1918–1919 experience. New York City alone reported 6,374 deaths between December 1919 and April 1920, almost twice the number of the first wave in spring 1918.
The fourth wave in the United States subsided as swiftly as it had appeared, reaching a peak in early February. "An epidemic of considerable proportions marked the early months of 1920", the U.S. Mortality Statistics would later note; according to data at this time, the epidemic resulted in one third as many deaths as the 1918–1919 experience. New York City alone reported 6,374 deaths between December 1919 and April 1920, almost twice the number of the first wave in spring 1918.Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
experienced its peak of the pandemic in early 1920, recording 1,489 deaths from flu-related causes, compared with 615 in 1918 and 796 in 1919.
Poland experienced a devastating outbreak during the winter months, with its capital Warsaw
Warsaw, officially the Capital City of Warsaw, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the Vistula, River Vistula in east-central Poland. Its population is officially estimated at ...
reaching a peak of 158 deaths in a single week, compared to the peak of 92 in December 1918; however, the 1920 epidemic passed in a matter of weeks, while the 1918–1919 wave had developed over the entire second half of 1918. By contrast, the outbreak in western Europe was considered "benign", with the age distribution of deaths beginning to take on that of seasonal flu
Flu season is an annually recurring time period characterized by the prevalence of an outbreak of influenza (flu). The season occurs during the cold half of the year in each hemisphere. It takes approximately two days to show symptoms. Influen ...
.Peru
Peru, officially the Republic of Peru, is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the south and west by the Pac ...
experienced "asynchronous recrudescent waves" throughout the year. A severe third wave hit Lima
Lima ( ; ), founded in 1535 as the Ciudad de los Reyes (, Spanish for "City of Biblical Magi, Kings"), is the capital and largest city of Peru. It is located in the valleys of the Chillón River, Chillón, Rímac River, Rímac and Lurín Rive ...
, the capital city, between January and March, resulting in an all-cause excess mortality rate approximately four times greater than that of the 1918–1919 wave. Ica similarly experienced another severe pandemic wave in 1920, between July and October. A fourth wave also occurred in Brazil, in February.Korea
Korea is a peninsular region in East Asia consisting of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and smaller islands. Since the end of World War II in 1945, it has been politically Division of Korea, divided at or near the 38th parallel north, 3 ...
and Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
experienced pronounced outbreaks in late 1919 and early 1920.
Post-pandemic
By mid-1920, the pandemic was largely considered to be "over" by the public as well as governments. Though parts of Chile experienced a third, milder wave between November 1920 and March 1921,Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
approximately doubled in January 1922 alone. In Helsinki
Helsinki () is the Capital city, capital and most populous List of cities and towns in Finland, city in Finland. It is on the shore of the Gulf of Finland and is the seat of southern Finland's Uusimaa region. About people live in the municipali ...
, a major epidemic (the fifth since 1918) prevailed between November and December 1921. The flu was also widespread in the United States, its prevalence in California reportedly greater in early March 1922 than at any point since the pandemic ended in 1920.
In the years after 1920, the disease came to represent the "seasonal flu". The virus, H1N1, remained endemic, occasionally causing more severe or otherwise notable outbreaks.H2N2
Influenza A virus subtype H2N2 (A/H2N2) is a subtype of '' Influenza A virus''. H2N2 has mutated into various strains including the " Asian flu" strain (now extinct in the wild), H3N2, and various strains found in birds. It is also suspected o ...
, the reassortant product of the human H1N1 and an avian influenza
Avian influenza, also known as avian flu or bird flu, is a disease caused by the influenza A virus, which primarily affects birds but can sometimes affect mammals including humans. Wild aquatic birds are the primary host of the influenza A viru ...
virus, which thereafter became the active influenza A virus in humans.pandemic
A pandemic ( ) is an epidemic of an infectious disease that has a sudden increase in cases and spreads across a large region, for instance multiple continents or worldwide, affecting a substantial number of individuals. Widespread endemic (epi ...
that principally affected those 26 and under.H3N2
Influenza A virus subtype H3N2 (A/H3N2) is a subtype of influenza A virus (IAV). Some human-adapted strains of A/H3N2 are endemic in humans and are one cause of seasonal influenza (flu). Other strains of H1N1 are endemic in pigs ( swine influen ...
(which itself had displaced H2N2 through a pandemic in 1968).pandemic
A pandemic ( ) is an epidemic of an infectious disease that has a sudden increase in cases and spreads across a large region, for instance multiple continents or worldwide, affecting a substantial number of individuals. Widespread endemic (epi ...
, and thereafter took the place of the seasonal H1N1 to circulate alongside H3N2.
Potential origins
Despite its name, historical and epidemiological
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and Risk factor (epidemiology), determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population, and application of this knowledge to prevent dise ...
data cannot identify the geographic origin of the Spanish flu. However, several theories have been proposed.
United States
The first confirmed cases originated in the United States. Historian Alfred W. Crosby
Alfred Worcester Crosby Jr. (January 15, 1931 – March 14, 2018) was a professor of History, Geography, and American Studies at the University of Texas at Austin, and University of Helsinki. He was the author of books including '' The Columbian ...
stated in 2003 that the flu originated in Kansas
Kansas ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to the west. Kansas is named a ...
, and author John M. Barry described a January 1918 outbreak in Haskell County, Kansas
Haskell County is a county located in the U.S. state of Kansas. Its county seat and most populous city is Sublette. As of the 2020 census, the county population was 3,780. The county was named after Dudley Haskell, a congressman during the ...
, as the origin in his 2004 article.
A 2018 study of tissue slides and medical reports led by professor Michael Worobey found evidence against the disease originating from Kansas, as those cases were milder and had fewer deaths compared to the infections in New York City in the same period. The study did find evidence through phylogenetic analyses
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as Computational phylogenetics, phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organ ...
that the virus likely had a North American origin, though it was not conclusive. In addition, the haemagglutinin glycoproteins of the virus suggest that it originated long before 1918, and other studies suggest that the reassortment of the H1N1 virus likely occurred in or around 1915.
Europe
The major UK troop staging and hospital camp in Étaples
Étaples or Étaples-sur-Mer (; or ; formerly ; ) is a communes of France, commune in the departments of France, department of Pas-de-Calais, Hauts-de-France, northern France. It is a fishing and leisure port on the Canche river.
History
Étapl ...
in France has been theorized by virologist John Oxford
John Sydney Oxford (born 6 March 1942) is an English virologist and a professor at Queen Mary, University of London. He is a leading expert on influenza, including bird flu and the 1918 Spanish Influenza, and HIV/AIDS.
Education
Oxford was e ...
as being at the center of the Spanish flu.Aldershot
Aldershot ( ) is a town in the Rushmoor district, Hampshire, England. It lies on heathland in the extreme north-east corner of the county, south-west of London. The town has a population of 37,131, while the Farnborough/Aldershot built-up are ...
,poison gas
Many gases have toxic properties, which are often assessed using the LC50 (median lethal concentration) measure. In the United States, many of these gases have been assigned an NFPA 704 health rating of 4 (may be fatal) or 3 (may cause serious ...
attacks, and other casualties of war. It also was home to a piggery
Intensive pig farming, also known as pig factory farming, is the primary method of pig production, in which grower pigs are housed indoors in group-housing or straw-lined sheds in establishments also known as piggeries, whilst pregnant sows a ...
and poultry
Poultry () are domesticated birds kept by humans for the purpose of harvesting animal products such as meat, Eggs as food, eggs or feathers. The practice of animal husbandry, raising poultry is known as poultry farming. These birds are most typ ...
was regularly brought in to feed the camp. Oxford and his team postulated that a precursor virus, harbored in birds, mutated
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA replication, DNA or viral rep ...
and then migrated to pigs kept near the front.Chinese Medical Association
In China, the practice of medicine is a mixture of government, charitable, and private institutions, while many people rely on traditional medicine. Until reforms in the late twentieth and early twenty-first century, physicians were quasi-governm ...
'' found evidence that the 1918 virus had been circulating in the European armies for months and possibly years before the 1918 pandemic.Andrew Price-Smith
Dr. Andrew Price-Smith (1968–2019) was a political scientist and academic writer best known for his work on 'health security' and 'environmental security.' An expert on the effects of Influenza pandemics and government efforts to contain them, ...
published data from the Austrian archives suggesting the influenza began in Austria in early 1917.
A 2009 study in ''Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses
''Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering virology, published by John Wiley & Sons for the International Society for Influenza and other Respiratory Virus Diseases. As of 2018, the editor is Benjam ...
'' found that Spanish flu mortality simultaneously peaked within the two-month period of October and November 1918 in all fourteen European countries analyzed, which is inconsistent with the pattern that researchers would expect if the virus had originated somewhere in Europe and then spread outwards.
China
In 1993, Claude Hannoun, the leading expert on the Spanish flu at the Pasteur Institute
The Pasteur Institute (, ) is a French non-profit private foundation dedicated to the study of biology, micro-organisms, diseases, and vaccines. It is named after Louis Pasteur, who invented pasteurization and vaccines for anthrax and rabies. Th ...
, asserted the precursor virus was likely to have come from China and then mutated in the United States near Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
and from there spread to Brest, France, Europe's battlefields, and the rest of the world, with Allied forces as the main disseminators.Memorial University of Newfoundland
Memorial University of Newfoundland, or MUN (), is a Public university, public research university in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador, based in St. John's, Newfoundland and Labrador, St. John's, with satellite campuses in Corner Brook ...
argued that the mobilization of 96,000 Chinese laborers to work behind the British and French lines might have been the source of the pandemic. Humphries found archival evidence that a respiratory illness that struck northern China (where the laborers came from) in November 1917 was identified a year later by Chinese health officials as identical to the Spanish flu.acquired immunity
The adaptive immune system (AIS), also known as the acquired immune system, or specific immune system is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized cells, organs, and processes that eliminate pathogens specifically. The ac ...
to the flu virus.Guangdong Province
) means "wide" or "vast", and has been associated with the region since the creation of Guang Prefecture in AD 226. The name "''Guang''" ultimately came from Guangxin ( zh, labels=no, first=t, t= , s=广信), an outpost established in Han dynasty ...
it was reported that early outbreaks of influenza in 1918 disproportionately impacted young men. The June outbreak infected children and adolescents between 11 and 20 years of age, while the October outbreak was most common in those aged 11 to 15.
Epidemiology and pathology
Transmission and mutation
The basic reproduction number
In epidemiology, the basic reproduction number, or basic reproductive number (sometimes called basic reproduction ratio or basic reproductive rate), denoted R_0 (pronounced ''R nought'' or ''R zero''), of an infection is the expected number ...
of the virus was between 2 and 3. The close quarters and massive troop movements of World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
hastened the pandemic, and probably both increased transmission and augmented mutation. The war may also have reduced people's resistance to the virus. Some speculate the soldiers' immune systems were weakened by malnourishment and the stresses of combat and chemical attacks, increasing their susceptibility. Modern transportation systems and increased travel was a significant factor in the worldwide occurrence. Another was lies and denial by governments, leaving the population ill-prepared to handle the outbreaks.natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the Heredity, heritable traits characteristic of a population over generation ...
favors a mild strain. Those who get very ill stay home, and those mildly ill continue with their lives, preferentially spreading the mild strain. In the trenches, natural selection was reversed. Soldiers with a mild strain stayed where they were, while the severely ill were sent on crowded trains to crowded field hospitals, spreading the deadlier virus. The second wave began, and the flu quickly spread around the world again. (During modern pandemics, health officials look for deadlier strains of a virus when it reaches places with social upheaval.) The fact that most of those who recovered from first-wave infections had become immune
In biology, immunity is the state of being insusceptible or resistant to a noxious agent or process, especially a pathogen or infectious disease. Immunity may occur naturally or be produced by prior exposure or immunization.
Innate and adaptive ...
showed that it must have been the same strain of flu. This was most dramatically illustrated in Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a population of 1.4 million in the Urban area of Copenhagen, urban area. The city is situated on the islands of Zealand and Amager, separated from Malmö, Sweden, by the ...
, which escaped with a combined mortality rate of 0.29% (0.02% in the first wave and 0.27% in the second wave) because of exposure to the less-lethal first wave.
After the lethal second wave, new cases dropped abruptly. In Philadelphia, for example, 4,597 people died in the week ending 16 October, but by 11 November, influenza had almost disappeared from the city. One explanation for the rapid decline in lethality is that doctors became more effective in the prevention and treatment of pneumonia that developed after the victims had contracted the virus. However, John Barry stated in his 2004 book '' The Great Influenza: The Epic Story of the Deadliest Plague In History'' that researchers have found no evidence to support this position. Another theory holds that the 1918 virus mutated extremely rapidly to a less lethal strain. Such evolution of influenza is a common occurrence: there is a tendency for pathogenic viruses to become less lethal with time, as the hosts of more dangerous strains tend to die out. Fatal cases did continue into 1919, however. One notable example was that of ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey in North America) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an Ice rink, ice skating rink with Ice hockey rink, lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. Tw ...
player Joe Hall Joseph Hall may refer to:
Sports
* Joe Hall (American football) (born 1979), American football player
* Joe Hall (baseball) (born 1966), American baseball player
* Joe Hall (ice hockey) (1881–1919), Canadian ice hockey player
* Joe B. Hall (1928� ...
, who died of the flu in April after an outbreak that resulted in the cancellation of the 1919 Stanley Cup Finals
The 1919 Stanley Cup Finals was the ice hockey playoff series to determine the 1919 Stanley Cup champions. The series was cancelled due to an outbreak of Spanish flu after five games had been played, and no champion was declared. It was the only ...
.
Signs and symptoms
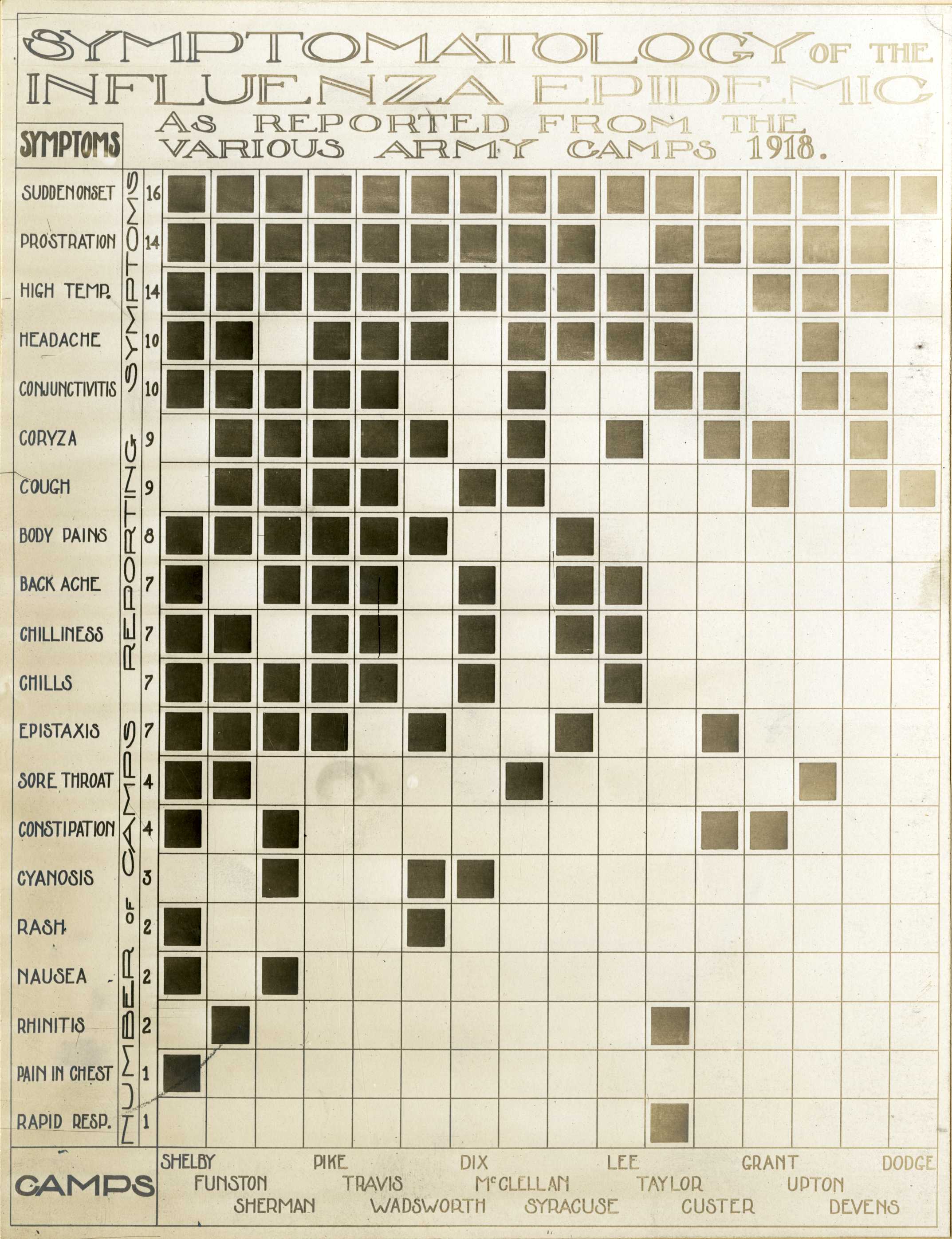 The majority of the infected experienced only the typical flu symptoms of sore throat, headache, and fever, especially during the first wave. However, during the second wave, the disease was much more serious, often complicated by
The majority of the infected experienced only the typical flu symptoms of sore throat, headache, and fever, especially during the first wave. However, during the second wave, the disease was much more serious, often complicated by bacterial pneumonia
Bacterial pneumonia is a type of pneumonia caused by bacterial infection.
Types
Gram-positive
'' Streptococcus pneumoniae'' () is the most common bacterial cause of pneumonia in all age groups except newborn infants. ''Streptococcus pneumoniae ...
, which was often the cause of death. This more serious type would cause ''heliotrope cyanosis'' to develop, whereby the skin would first develop two mahogany spots over the cheekbones which would then over a few hours color the entire face blue, followed by black coloration first in the extremities and then the limbs and the torso. Death would follow within hours or days due to the lungs being filled with fluids. Other signs and symptoms reported included spontaneous mouth and nosebleeds, miscarriages for pregnant women, a peculiar smell, teeth and hair falling out, delirium
Delirium (formerly acute confusional state, an ambiguous term that is now discouraged) is a specific state of acute confusion attributable to the direct physiological consequence of a medical condition, effects of a psychoactive substance, or ...
, dizziness, insomnia, loss of hearing or smell, and impaired vision. One observer wrote, "One of the most striking of the complications was hemorrhage
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, ...
from mucous membrane
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It ...
s, especially from the nose, stomach, and intestine. Bleeding from the ears and petechial hemorrhages in the skin also occurred".
The majority of deaths were from bacterial pneumonia
Bacterial pneumonia is a type of pneumonia caused by bacterial infection.
Types
Gram-positive
'' Streptococcus pneumoniae'' () is the most common bacterial cause of pneumonia in all age groups except newborn infants. ''Streptococcus pneumoniae ...
,secondary infection
infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
associated with influenza. This pneumonia was itself caused by common upper respiratory-tract bacteria, which were able to get into the lungs via the damaged bronchial tubes
A bronchus ( ; : bronchi, ) is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus. Thes ...
. The virus also killed people directly by causing massive hemorrhages and edema
Edema (American English), also spelled oedema (British English), and also known as fluid retention, swelling, dropsy and hydropsy, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue (biology), tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. S ...
in the lungs. Modern analysis has shown the virus to be particularly deadly because in animal trials it triggers an overreaction of the body's immune system (cytokine storm
A cytokine storm, also called hypercytokinemia, is a pathological reaction in humans and other animals in which the innate immune system causes an uncontrolled and excessive release of pro-inflammatory signaling molecules called cytokines. Cytok ...
). The strong immune reactions of young adults were postulated to have ravaged the body, whereas the weaker immune reactions of children and middle-aged adults resulted in fewer deaths.
Misdiagnosis
Because the virus that caused the disease was too small to be seen under a microscope at the time, there were problems with correctly diagnosing it. The bacterium ''Haemophilus influenzae
''Haemophilus influenzae'' (formerly called Pfeiffer's bacillus or ''Bacillus influenzae'') is a Gram-negative, Motility, non-motile, Coccobacillus, coccobacillary, facultative anaerobic organism, facultatively anaerobic, Capnophile, capnophili ...
'' was instead mistakenly thought to be the cause, as it was big enough to be seen and was present in many, though not all, patients. For this reason, a vaccine that was used against that bacillus did not make infection rarer but did decrease the death rate.
During the deadly second wave there were also fears that it was in fact plague, dengue fever
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne disease caused by dengue virus, prevalent in tropical and subtropical areas. Asymptomatic infections are uncommon, mild cases happen frequently; if symptoms appear, they typically begin 3 to 14 days after i ...
, or cholera
Cholera () is an infection of the small intestine by some Strain (biology), strains of the Bacteria, bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea last ...
. Another misdiagnosis was typhus
Typhus, also known as typhus fever, is a group of infectious diseases that include epidemic typhus, scrub typhus, and murine typhus. Common symptoms include fever, headache, and a rash. Typically these begin one to two weeks after exposu ...
, which was common in circumstances of social upheaval, and was therefore also affecting Russia in the aftermath of the October Revolution
The October Revolution, also known as the Great October Socialist Revolution (in Historiography in the Soviet Union, Soviet historiography), October coup, Bolshevik coup, or Bolshevik revolution, was the second of Russian Revolution, two r ...
. In Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes, Andes Mountains and the Paci ...
, the view of the country's elite was that the nation was in severe decline, and therefore doctors assumed that the disease was typhus caused by poor hygiene, causing a mismanaged response which did not ban mass gatherings.
Role of climate conditions
 Studies have shown that the immune system of Spanish flu victims could have been weakened by unseasonably cold and wet weather for extended periods during the pandemic. This affected especially troops exposed to incessant rains and lower-than-average temperatures during World War I, and especially during the second wave of the pandemic. Climate data and mortality records analyzed at
Studies have shown that the immune system of Spanish flu victims could have been weakened by unseasonably cold and wet weather for extended periods during the pandemic. This affected especially troops exposed to incessant rains and lower-than-average temperatures during World War I, and especially during the second wave of the pandemic. Climate data and mortality records analyzed at Harvard University
Harvard University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the History of the Puritans in North America, Puritan clergyma ...
and the Climate Change Institute at the University of Maine
The University of Maine (UMaine) is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Orono, Maine, United States. It was established in 1865 as the land-grant college of Maine and is the Flagship universitie ...
identified a severe climate anomaly that impacted Europe from 1914 to 1919, with several environmental indicators directly influencing the severity and spread of the pandemic.cloud condensation nuclei
Cloud condensation nuclei (CCNs), also known as cloud seeds, are small particles typically 0.2 μm, or one hundredth the size of a cloud droplet. CCNs are a unique subset of aerosols in the atmosphere on which water vapour condenses. This c ...
) contributed to increased precipitation.
Responses
Public health management
While systems for alerting public health authorities of infectious spread did exist in 1918, they did not generally include influenza, leading to a delayed response. Nevertheless, actions were taken. Maritime quarantines were declared on islands such as Iceland, Australia, and American Samoa, saving many lives. Social distancing
In public health, social distancing, also called physical distancing, (NB. Regula Venske is president of the PEN Centre Germany.) is a set of non-pharmaceutical interventions or measures intended to prevent the spread of a contagious dise ...
measures were introduced, for example closing schools, theatres, and places of worship, limiting public transportation, and banning mass gatherings. Wearing face masks became common in some places, such as Japan, though there were debates over their efficacy. There was also some resistance to their use, as exemplified by the Anti-Mask League of San Francisco. Vaccines were developed, but as these were based on bacteria and not the actual virus, they could only help with secondary infections. The enforcement of restrictions varied. To a large extent, the New York City health commissioner ordered businesses to open and close on staggered shifts to avoid overcrowding on the subways.
A later study found that measures such as banning mass gatherings and requiring the wearing of face masks could cut the death rate up to 50 percent, but this was dependent on their being imposed early in the outbreak and not being lifted prematurely.
Medical treatment
As there were no antiviral drug
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Antiviral drugs are a class of antimicrobials ...
s to treat the virus, and no antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
s to treat the secondary bacterial infections, doctors would rely on an assortment of medicines with varying degrees of effectiveness, such as aspirin
Aspirin () is the genericized trademark for acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions that aspirin is ...
, quinine
Quinine is a medication used to treat malaria and babesiosis. This includes the treatment of malaria due to ''Plasmodium falciparum'' that is resistant to chloroquine when artesunate is not available. While sometimes used for nocturnal leg ...
, arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a metalloid and one of the pnictogens, and therefore shares many properties with its group 15 neighbors phosphorus and antimony. Arsenic is not ...
s, digitalis
''Digitalis'' ( or ) is a genus of about 20 species of herbaceous perennial plants, shrubs, and Biennial plant, biennials, commonly called foxgloves.
''Digitalis'' is native to Europe, Western Asia, and northwestern Africa. The flowers are ...
, strychnine
Strychnine (, , American English, US chiefly ) is a highly toxicity, toxic, colorless, bitter, crystalline alkaloid used as a pesticide, particularly for killing small vertebrates such as birds and rodents. Strychnine, when inhaled, swallowed, ...
, epsom salts
Epsomite, Epsom salt, or magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, is a hydrous magnesium sulfate mineral with formula .
Physical properties
Epsomite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system. The normal form is as massive encrustations, while acicula ...
, castor oil
Castor oil is a vegetable oil pressed from castor beans, the seeds of the plant ''Ricinus communis''. The seeds are 40 to 60 percent oil. It is a colourless or pale yellow liquid with a distinct taste and odor. Its boiling point is and its den ...
, and iodine
Iodine is a chemical element; it has symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists at standard conditions as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a vi ...
. Traditional treatments, such as bloodletting
Bloodletting (or blood-letting) was the deliberate withdrawal of blood from a patient to prevent or cure illness and disease. Bloodletting, whether by a physician or by leeches, was based on an ancient system of medicine in which blood and othe ...
, ayurveda
Ayurveda (; ) is an alternative medicine system with historical roots in the Indian subcontinent. It is heavily practised throughout India and Nepal, where as much as 80% of the population report using ayurveda. The theory and practice of ayur ...
, and kampo
Kampo or , often known simply as , is the study of traditional medicine in Japan following its introduction, beginning in the 7th century. It was adapted and modified to suit Japanese culture and traditions. Traditional Japanese medicine us ...
, were also applied.
Information dissemination
Due to World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, many countries engaged in wartime censorship, and suppressed reporting of the pandemic. For example, the Italian newspaper ''Corriere della Sera
(; ) is an Italian daily newspaper published in Milan with an average circulation of 246,278 copies in May 2023. First published on 5 March 1876, is one of Italy's oldest newspapers and is Italy's most read newspaper. Its masthead has remain ...
'' was prohibited from reporting daily death tolls. The newspapers of the time were also generally paternalistic
Paternalism is action that limits a person's or group's liberty or autonomy against their will and is intended to promote their own good. It has been defended in a variety of contexts as a means of protecting individuals from significant harm, s ...
and worried about mass panic. Misinformation
Misinformation is incorrect or misleading information. Misinformation and disinformation are not interchangeable terms: misinformation can exist with or without specific malicious intent, whereas disinformation is distinct in that the information ...
also spread along with the disease. In Ireland there was a belief that noxious gases were rising from the mass graves of Flanders Fields
Flanders Fields is a common English name of the World War I battlefields in an area straddling the Belgian provinces of West Flanders and East Flanders as well as the French department of Nord, part of which makes up the area known as French Flan ...
and being "blown all over the world by winds". There were also rumors that the Germans were behind it, for example by poisoning the aspirin
Aspirin () is the genericized trademark for acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions that aspirin is ...
manufactured by Bayer
Bayer AG (English: , commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies and biomedical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer' ...
, or by releasing poison gas from U-boat
U-boats are Submarine#Military, naval submarines operated by Germany, including during the World War I, First and Second World Wars. The term is an Anglicization#Loanwords, anglicized form of the German word , a shortening of (), though the G ...
s.
Mortality
 The Spanish flu infected around 500 million people, about one-third of the world's population. Estimates on deaths vary greatly, but it is considered to be one of the deadliest pandemics in history. An early estimate from 1927 put global mortality at 21.6 million.
The Spanish flu infected around 500 million people, about one-third of the world's population. Estimates on deaths vary greatly, but it is considered to be one of the deadliest pandemics in history. An early estimate from 1927 put global mortality at 21.6 million.American Journal of Epidemiology
The American Journal of Epidemiology (''AJE'') is a peer-reviewed journal for empirical research findings, opinion pieces, and methodological developments in the field of epidemiological research. The current editor-in-chief is Enrique Schisterma ...
'' estimated the total to be about 17 million,Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses
''Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering virology, published by John Wiley & Sons for the International Society for Influenza and other Respiratory Virus Diseases. As of 2018, the editor is Benjam ...
'' based on data from fourteen European countries estimated a total of 2.64 million excess deaths in Europe attributable to the Spanish flu during the 1918–1919 phase of the pandemic. This represents a mortality rate of about 1.1% of the European population ( 250 million in 1918), considerably higher than the mortality rate in the U.S., which the authors hypothesize is likely due to the severe effects of the war in Europe.India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, about 5% of the population. The death toll in India's British-ruled districts was 13.88 million. Another estimate gives at least 12 million dead. The decade between 1911 and 1921 was the only census period in which India's population fell, mostly due to devastation of the pandemic. While India is generally described as the country most severely affected by the Spanish flu, at least one study argues that other factors may partially account for the very high excess mortality rates observed in 1918, citing unusually high 1917 mortality and wide regional variation (ranging from 0.47% to 6.66%).The Lancet
''The Lancet'' is a weekly peer-reviewed general medical journal, founded in England in 1823. It is one of the world's highest-impact academic journals and also one of the oldest medical journals still in publication.
The journal publishes ...
'' also noted that Indian provinces had excess mortality rates ranging from 2.1% to 7.8%, stating: "Commentators at the time attributed this huge variation to differences in nutritional status and diurnal fluctuations in temperature."Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies (; ), was a Dutch Empire, Dutch colony with territory mostly comprising the modern state of Indonesia, which Proclamation of Indonesian Independence, declared independence on 17 Au ...
(now Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
), 1.5 million were assumed to have died among 30 million inhabitants. In Tahiti
Tahiti (; Tahitian language, Tahitian , ; ) is the largest island of the Windward Islands (Society Islands), Windward group of the Society Islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France. It is located in the central part of t ...
, 13% of the population died in one month. Similarly, in Western Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa and known until 1997 as Western Samoa, is an island country in Polynesia, part of Oceania, in the South Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main islands ( Savai'i and Upolu), two smaller, inhabit ...
22% of the population of 38,000 died within two months.
In Istanbul
Istanbul is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, constituting the country's economic, cultural, and historical heart. With Demographics of Istanbul, a population over , it is home to 18% of the Demographics ...
, capital of the Ottoman Empire, 6,403Māori
Māori or Maori can refer to:
Relating to the Māori people
* Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group
* Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand
* Māori culture
* Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the Co ...
in six weeks, with Māori dying at eight times the rate of .
In Australia, the flu killed around 12,000Four Corners
Four Corners is a region of the Southwestern United States consisting of the southwestern corner of Colorado, southeastern corner of Utah, northeastern corner of Arizona, and northwestern corner of New Mexico. Most of the Four Corners regio ...
area, there were 3,293 registered deaths among Native Americans. Entire Inuit
Inuit (singular: Inuk) are a group of culturally and historically similar Indigenous peoples traditionally inhabiting the Arctic and Subarctic regions of North America and Russia, including Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwe ...
and Alaskan Native
Alaska Natives (also known as Native Alaskans, Alaskan Indians, or Indigenous Alaskans) are the Indigenous peoples of Alaska that encompass a diverse arena of cultural and linguistic groups, including the Iñupiat, Yupik, Aleut, Eyak, Tlin ...
village communities died in Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
. In Canada, 50,000 died.
In Brazil, 300,000 died, including president Rodrigues Alves
Francisco de Paula Rodrigues Alves, PC (; 7 July 1848 – 16 January 1919) was a Brazilian politician who first served as president of the Province of São Paulo in 1887, then as Treasury minister in the 1890s. Rodrigues Alves was elected the ...
.
In the UK, as many as 250,000 died; in France, more than 400,000.
In Ghana
Ghana, officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It is situated along the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, and shares borders with Côte d’Ivoire to the west, Burkina Faso to the north, and Togo to t ...
, the influenza epidemic killed at least 100,000 people. Tafari Makonnen
Haile Selassie I (born Tafari Makonnen or '' Lij'' Tafari; 23 July 189227 August 1975) was Emperor of Ethiopia from 1930 to 1974. He rose to power as the Regent Plenipotentiary of Ethiopia (') under Empress Zewditu between 1916 and 1930. Wide ...
(the future Emperor of Ethiopia
The emperor of Ethiopia (, "King of Kings"), also known as the Atse (, "emperor"), was the hereditary monarchy, hereditary ruler of the Ethiopian Empire, from at least the 13th century until the abolition of the monarchy in 1975. The emperor w ...
) was one of the first Ethiopians who contracted influenza but survived.Addis Ababa
Addis Ababa (; ,) is the capital city of Ethiopia, as well as the regional state of Oromia. With an estimated population of 2,739,551 inhabitants as of the 2007 census, it is the largest city in the country and the List of cities in Africa b ...
, range from 5,000 to 10,000, or higher.
The death toll in Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
has been estimated at 450,000, though the epidemiologists who suggested this number called it a "shot in the dark". If it is correct, Russia lost roughly 0.4% of its population, meaning it suffered the lowest influenza-related mortality in Europe. Another study considers this number unlikely, given that the country was in the grip of a civil war
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
, and the infrastructure of daily life had broken down; the study suggests that Russia's death toll was closer to 2%, or 2.7 million people.
Devastated communities
 Even in areas where mortality was low, so many adults were incapacitated that daily life was hampered. Some communities closed all stores or required customers to leave orders outside. There were reports that healthcare workers could not tend the sick nor the gravediggers bury the dead because they too were ill. Mass graves were dug by
Even in areas where mortality was low, so many adults were incapacitated that daily life was hampered. Some communities closed all stores or required customers to leave orders outside. There were reports that healthcare workers could not tend the sick nor the gravediggers bury the dead because they too were ill. Mass graves were dug by steam shovel
A steam shovel is a large steam engine, steam-powered excavating machine designed for lifting and moving material such as Rock (geology), rock and soil. It is the earliest type of power shovel or excavator. Steam shovels played a major role in ...
and bodies buried without coffins in many places.
Bristol Bay
Bristol Bay (, ) is the easternmost arm of the Bering Sea, at 57° to 59° North 157° to 162° West in Southwest Alaska. Bristol Bay is 400 km (250 mi) long and 290 km (180 mi) wide at its mouth. A number of rivers flow in ...
, a region of Alaska populated by Indigenous people
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territ ...
, suffered a death rate of 40 percent, with some villages entirely disappearing. Nenana, Alaska
Nenana () is a home rule city in the Yukon-Koyukuk Census Area of the Unorganized Borough in Interior Alaska. Nenana developed as a Lower Tanana community at the confluence where the tributary Nenana River enters the Tanana. The populatio ...
, avoided the extent of the pandemic between 1918 and 1919, but the flu at last reached the town in spring 1920. Reports suggested that during the first two weeks of May, the majority of the town's population became infected; 10% of the population were estimated to have died, most of whom were Alaska Natives.
Several Pacific island
The Pacific islands are a group of islands in the Pacific Ocean. They are further categorized into three major island groups: Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Depending on the context, the term ''Pacific Islands'' may refer to one of several ...
territories were hit particularly hard. The pandemic reached them from New Zealand, which was too slow to implement measures to prevent ships carrying the flu from leaving its ports. From New Zealand, the flu reached Tonga
Tonga, officially the Kingdom of Tonga, is an island country in Polynesia, part of Oceania. The country has 171 islands, of which 45 are inhabited. Its total surface area is about , scattered over in the southern Pacific Ocean. accordin ...
(killing 8% of the population), Nauru
Nauru, officially the Republic of Nauru, formerly known as Pleasant Island, is an island country and microstate in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies within the Micronesia subregion of Oceania, with its nearest neighbour being Banaba (part of ...
(16%), and Fiji
Fiji, officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists of an archipelago of more than 330 islands—of which about ...
(5%, 9,000 people). Worst affected was Western Samoa, which had been occupied by New Zealand in 1914. 90% of the population was infected; 30% of adult men, 22% of adult women, and 10% of children died. The disease spread fastest through the higher social classes among the Indigenous peoples, because of the custom of gathering oral tradition
Oral tradition, or oral lore, is a form of human communication in which knowledge, art, ideas and culture are received, preserved, and transmitted orally from one generation to another.Jan Vansina, Vansina, Jan: ''Oral Tradition as History'' (19 ...
from chiefs on their deathbeds; many community elders were infected through this process.
In Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
, the mortality was estimated at between 902,400 and 2,431,000, or 8% to 22% of the total population. The country was going through the Persian famine of 1917–1919
The Persian famine of 1917–1919 (Persian: قحطی ۱۲۹۶-۱۲۹۸ ایران) was a period of widespread mass starvation and disease in Qajar Iran, Iran under the rule of the Qajar dynasty during World War I. The famine took place in the ter ...
concurrently.
In Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelan ...
, during the worst 12 months, the Spanish flu accounted for one-third of all deaths.
In South Africa it is estimated that about 300,000 people amounting to 6% of the population died within six weeks. Government actions in the early stages of the virus' arrival in the country in September 1918 are believed to have unintentionally accelerated its spread. Almost a quarter of the working population of Kimberley
Kimberly or Kimberley may refer to:
Places and historical events
Australia
Queensland
* Kimberley, Queensland, a coastal locality in the Shire of Douglas
South Australia
* County of Kimberley, a cadastral unit in South Australia
Ta ...
, consisting of workers in the diamond mines, died. In British Somaliland
British Somaliland, officially the Somaliland Protectorate (), was a protectorate of the United Kingdom in modern Somaliland. It was bordered by Italian Somalia, French Somali Coast and Ethiopian Empire, Abyssinia (Italian Ethiopia from 1936 ...
, one official estimated that 7% of the native population died. This huge death toll resulted from an extremely high infection rate of up to 50% and the extreme severity of the symptoms.
Other areas
In the Pacific, American SamoaNew Caledonia
New Caledonia ( ; ) is a group of islands in the southwest Pacific Ocean, southwest of Vanuatu and east of Australia. Located from Metropolitan France, it forms a Overseas France#Sui generis collectivity, ''sui generis'' collectivity of t ...
quarantine
A quarantine is a restriction on the movement of people, animals, and goods which is intended to prevent the spread of disease or pests. It is often used in connection to disease and illness, preventing the movement of those who may have bee ...
s. However, the outbreak was delayed into 1926 for American Samoa and 1921 for New Caledonia as the quarantine period ended.Marajó
Marajó () is a large coastal island in the state of Pará, Brazil. It is the main and largest of the islands in the Marajó Archipelago. Marajó Island is separated from the mainland by Marajó Bay, Pará River, smaller rivers (especially M ...
, in Brazil's Amazon River Delta had not reported an outbreak. Saint Helena
Saint Helena (, ) is one of the three constituent parts of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha, a remote British overseas territory.
Saint Helena is a volcanic and tropical island, located in the South Atlantic Ocean, some 1,874 km ...
also reported no deaths.
 Estimates for the death toll in China have varied widely,
Estimates for the death toll in China have varied widely,British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
-controlled Hong Kong, Canton
Canton may refer to:
Administrative divisions
* Canton (administrative division), territorial/administrative division in some countries
* Township (Canada), known as ''canton'' in Canadian French
Arts and entertainment
* Canton (band), an It ...
, Peking
Beijing, previously romanized as Peking, is the capital city of China. With more than 22 million residents, it is the world's most populous national capital city as well as China's second largest city by urban area after Shanghai. It is l ...
, Harbin
Harbin, ; zh, , s=哈尔滨, t=哈爾濱, p=Hā'ěrbīn; IPA: . is the capital of Heilongjiang, China. It is the largest city of Heilongjiang, as well as being the city with the second-largest urban area, urban population (after Shenyang, Lia ...
and Shanghai
Shanghai, Shanghainese: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: is a direct-administered municipality and the most populous urban area in China. The city is located on the Chinese shoreline on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the ...
. These data were collected by the Chinese Maritime Customs Service
The Chinese Maritime Customs Service was a Chinese governmental tax collection agency and information service from its founding in 1854 until it split in 1949 into services operating in the Republic of China on Taiwan, and in the People's Republ ...
, which was largely staffed by non-Chinese foreigners.Calcutta
Kolkata, also known as Calcutta (List of renamed places in India#West Bengal, its official name until 2001), is the capital and largest city of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of West Bengal. It lies on the eastern ba ...
or Bombay, where influenza was much more devastating.Shanghai
Shanghai, Shanghainese: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: is a direct-administered municipality and the most populous urban area in China. The city is located on the Chinese shoreline on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the ...
– which had a population of over 2 million – there were only 266 recorded deaths from influenza
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These sympto ...
among the Chinese population in 1918.
Patterns of fatality
The pandemic mostly killed young adults. In 1918–1919, 99% of pandemic influenza deaths in the U.S. occurred in people under 65, and nearly half of deaths were in young adults 20 to 40 years old. In 1920, the mortality rate among people under 65 had decreased sixfold to half the mortality rate of people over 65, but 92% of deaths still occurred in people under 65. This is unusual since influenza is typically most deadly to weak individuals, such as infant
In common terminology, a baby is the very young offspring of adult human beings, while infant (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'baby' or 'child') is a formal or specialised synonym. The terms may also be used to refer to juveniles of ...
s under age two, adults over age 70, and the immunocompromise
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromise, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that affec ...
d. In 1918, older adults may have had partial protection caused by exposure to the 1889–1890 flu pandemic.Oslo
Oslo ( or ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Norway. It constitutes both a county and a municipality. The municipality of Oslo had a population of in 2022, while the city's greater urban area had a population of 1,064,235 in 2022 ...
, death rates were inversely correlated with apartment size, as the poorer people living in smaller apartments died at a higher rate. Social status was also reflected in the higher mortality among immigrant communities, with Italian Americans
Italian Americans () are Americans who have full or partial Italians, Italian ancestry. The largest concentrations of Italian Americans are in the urban Northeastern United States, Northeast and industrial Midwestern United States, Midwestern ...
, a recently arrived group at the time, nearly twice as likely to die compared to the average Americans. These disparities reflected worse diets, crowded living conditions, and problems accessing healthcare. Paradoxically, however, African Americans
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from any of the Black racial groups of Africa ...
were relatively spared.
More men than women were killed by the flu, as they were more likely to go out and be exposed, while women tended to stay at home. For the same reason men also were more likely to have pre-existing tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
, which severely worsened the chances of recovery. However, in India the opposite was true, potentially because Indian women were neglected with poorer nutrition, and were expected to care for the sick.
A study conducted by He ''et al''. (2011) examined the factors that underlie variability in temporal patterns and their correlation to patterns of mortality and morbidity. Their analysis suggests that temporal variations in transmission rate provide the best explanation, and the variation in transmission required to generate these three waves is within biologically plausible values. Another study by He ''et al''. (2013) used a simple epidemic model
Mathematical models can project how infectious diseases progress to show the likely outcome of an epidemic (including in plants) and help inform public health and plant health interventions. Models use basic assumptions or collected statistics al ...
incorporating three factors to infer the cause of the three waves of the 1918 influenza pandemic. These factors were school opening and closing, temperature changes throughout the outbreak, and human behavioral changes in response to the outbreak. Their modeling results showed that all three factors are important, but human behavioral responses showed the most significant effects.
Effects
World War I
Academic Andrew Price-Smith has argued that the virus helped tip the balance of power in the latter days of the war towards the Allied cause. He provides data that the viral waves hit the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,; ; , ; were one of the two main coalitions that fought in World War I (1914–1918). It consisted of the German Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulga ...
before the Allied powers and that morbidity
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are asso ...
and mortality in Germany and Austria were considerably higher than in Britain and France. A 2006 ''Lancet'' study corroborates higher excess mortality rates in Germany (0.76%) and Austria (1.61%) compared to Britain (0.34%) and France (0.75%).Oxford University Computing Services
Oxford University Computing Services (OUCS) until 2012 provided the central Information Technology services for the University of Oxford. The service was based at 7-19 Banbury Road in central north Oxford, England, near the junction with Keble Ro ...
writes that "Many researchers have suggested that the conditions of the war significantly aided the spread of the disease. And others have argued that the course of the war (and subsequent peace treaty) was influenced by the pandemic." Kahn has developed a model that can be used to test these theories.
Economic
 Many businesses in the entertainment and service industries suffered losses in revenue, while the healthcare industry reported profit gains. Historian Nancy Bristow has argued that the pandemic, when combined with the increasing number of women attending college, contributed to the success of women in nursing. This was due in part to the failure of medical doctors, who were predominantly men, to contain the illness. Nursing staff, who were mainly women, celebrated the success of their patient care and did not associate the spread of the disease with their work.
A 2020 study found that U.S. cities that implemented early and extensive non-medical measures (quarantine, etc.) suffered no additional adverse economic effects due to implementing those measures. However, the validity of this study has been questioned because of the coincidence of WWI and other problems with data reliability.
Many businesses in the entertainment and service industries suffered losses in revenue, while the healthcare industry reported profit gains. Historian Nancy Bristow has argued that the pandemic, when combined with the increasing number of women attending college, contributed to the success of women in nursing. This was due in part to the failure of medical doctors, who were predominantly men, to contain the illness. Nursing staff, who were mainly women, celebrated the success of their patient care and did not associate the spread of the disease with their work.
A 2020 study found that U.S. cities that implemented early and extensive non-medical measures (quarantine, etc.) suffered no additional adverse economic effects due to implementing those measures. However, the validity of this study has been questioned because of the coincidence of WWI and other problems with data reliability.
Long-term effects
A 2006 study in the ''Journal of Political Economy'' found that "cohorts ''in utero'' during the pandemic displayed reduced educational attainment, increased rates of physical disability, lower income, lower socioeconomic status, and higher transfer payments
In macroeconomics and finance, a transfer payment (also called a government transfer or simply fiscal transfer) is a redistribution of income and wealth by means of the government making a payment, without goods or services being received in r ...
received compared with other birth cohorts." A 2018 study found that the pandemic reduced educational attainment in populations. The flu has also been linked to the outbreak of encephalitis lethargica
Encephalitis lethargica (EL) is an atypical form of encephalitis. Also known as "von Economo Encephalitis", "sleeping sickness" or "sleepy sickness" (distinct from tsetse fly–transmitted sleeping sickness), it was first described in 1917 by ne ...
in the 1920s.
Survivors faced an elevated mortality risk. Some survivors did not fully recover from physiological conditions resulting from infection.
Legacy
 The Spanish flu began to fade from public awareness over the decades until the
The Spanish flu began to fade from public awareness over the decades until the bird flu
"Bird Flu" is an urumee melam-dance song by recording artist M.I.A. on her second studio album '' Kala'' (2007). It was released as a digital download in 2006 through XL Recordings under exclusive license to Interscope Records in the US. Cri ...
and other pandemics in the 1990s and 2000s.Guy Beiner
Guy Beiner (Hebrew: גיא ביינר) is an Israeli-born historian of the late-modern period with particular expertise in Irish history and Memory studies. He is the Sullivan Chair of Irish Studies at Boston College.
Academic career
Guy Beiner ...
, who demonstrated how the pandemic was overshadowed by the commemoration of the First World War and mostly neglected in mainstream historiography, yet was remembered in private and local traditions across the globe.diphtheria
Diphtheria is an infection caused by the bacteria, bacterium ''Corynebacterium diphtheriae''. Most infections are asymptomatic or have a mild Course (medicine), clinical course, but in some outbreaks, the mortality rate approaches 10%. Signs a ...
, and cholera all occurred near the same time. These outbreaks probably lessened the significance of the influenza pandemic for the public. In some areas, the flu was not reported on, the only mention being that of advertisements for medicines claiming to cure it.
Additionally, the outbreak coincided with the deaths and media focus on the First World War. The majority of fatalities, from both the war and the epidemic, were among young adults. The high number of war-related deaths of young adults may have overshadowed the deaths caused by flu. Particularly in Europe, where the war's toll was high, the flu may not have had a tremendous psychological impact or may have seemed an extension of the war's tragedies.
In literature and other media
Despite the toll of the pandemic, it was never a large theme in American literature.Katherine Anne Porter
Katherine Anne Porter (May 15, 1890 – September 18, 1980) was an American journalist, essayist, short story writer, novelist, poet, and political activist. Her 1962 novel '' Ship of Fools'' was the best-selling novel in the United States that y ...
's 1939 novella '' Pale Horse, Pale Rider'' is one of the most well-known fictional accounts of the pandemic.The Last Town on Earth
''The Last Town on Earth'' is a 2006 novel by American writer Thomas Mullen. The novel explores events in the fictional town of Commonwealth, Washington in 1918 during World War I and the Spanish flu epidemic. The town agrees to quarantine itse ...
'' focuses on a town which attempts to limit the spread of the flu by preventing people from entering or leaving. '' The Pull of the Stars'' is a 2020 novel by Emma Donoghue
Emma Donoghue (born October 1969) is an Irish Canadians, Irish Canadian novelist, screenwriter, playwright and literary historian. Her 2010 novel ''Room (novel), Room'' was a finalist for the Booker Prize and an international best-seller. Donog ...
set in Dublin during the Spanish flu. Publishers fast-tracked publication because of the then ongoing COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
.
Comparison with other pandemics
Research
 Similarities between a reconstruction of the virus and avian viruses, combined with the human pandemic preceding the first reports of influenza in swine, led researchers to conclude the influenza virus jumped directly from birds to humans, and swine caught the disease from humans.
Similarities between a reconstruction of the virus and avian viruses, combined with the human pandemic preceding the first reports of influenza in swine, led researchers to conclude the influenza virus jumped directly from birds to humans, and swine caught the disease from humans. An effort to recreate the Spanish flu strain (a strain of influenza A subtype H1N1) was a collaboration among the
An effort to recreate the Spanish flu strain (a strain of influenza A subtype H1N1) was a collaboration among the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology
The Armed Forces Institute of Pathology (AFIP) (1862 – September 15, 2011) was a U.S. government institution concerned with diagnostic consultation, education, and research in the medical specialty of pathology.
Overview
It was founded in ...
, the USDA ARS
The Agricultural Research Service (ARS) is the principal in-house research agency of the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). ARS is one of four agencies in USDA's Research, Education and Economics mission area. ARS is charged with ext ...
Southeast Poultry Research Laboratory, and Mount Sinai School of Medicine
The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai (ISMMS or Mount Sinai), formerly the Mount Sinai School of Medicine, is a private medical school in New York City, New York, United States. The school is the academic teaching arm of the Mount Sina ...
in New York City. The effort resulted in the announcement in 2005 that the group had successfully determined the virus' genetic sequence
Genetic may refer to:
*Genetics, in biology, the science of genes, heredity, and the variation of organisms
**Genetic, used as an adjective, refers to genes
*** Genetic disorder, any disorder caused by a genetic mutation, whether inherited or de no ...
, using historic tissue samples recovered by pathologist Johan Hultin
Johan Hultin (October 7, 1924 – January 22, 2022) was a Swedish-born American pathologist known for recovering tissues containing traces of the 1918 influenza virus that killed millions worldwide.
Life and career
Hultin was born into a wealth ...
from an Inuit female flu victim buried in the Alaskan permafrost
Permafrost () is soil or underwater sediment which continuously remains below for two years or more; the oldest permafrost has been continuously frozen for around 700,000 years. Whilst the shallowest permafrost has a vertical extent of below ...
and samples preserved from American soldiers. This enabled researchers at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency under the United S ...
(CDC) and the Mount Sinai School of Medicine
The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai (ISMMS or Mount Sinai), formerly the Mount Sinai School of Medicine, is a private medical school in New York City, New York, United States. The school is the academic teaching arm of the Mount Sina ...
, led by Dr Terrence Tumpey, to synthesize RNA segments from the H1N1 virus and reconstruct infective virus particles.Macaca fascicularis
The crab-eating macaque (''Macaca fascicularis''), also known as the long-tailed macaque or cynomolgus macaque, is a Cercopithecinae, cercopithecine primate native to Southeast Asia. As a Synanthrope, synanthropic species, the crab-eating macaqu ...
'') infected with the recreated flu strain exhibited classic symptoms of the 1918 pandemic, and died from an overreaction of the immune system. This may explain why the Spanish flu had its surprising effect on younger, healthier people, as a person with a stronger immune system would potentially have a stronger overreaction.
In December 2008, research by Yoshihiro Kawaoka
is a virologist specializing in the study of the influenza and Ebola viruses. He holds a professorship in virology in the Department of Pathobiological Sciences at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, USA, and at the University of Tokyo, Japan.
...
of the University of Wisconsin
A university () is an institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Uni ...
linked three specific genes (termed PA, PB1, and PB2) and a nucleoprotein
Nucleoproteins are proteins conjugated with nucleic acids (either DNA or RNA). Typical nucleoproteins include ribosomes, nucleosomes and viral nucleocapsid proteins.
Structures
Nucleoproteins tend to be positively charged, facilitating inte ...
derived from Spanish flu samples to the ability of the 1918 flu virus to invade the lungs and cause pneumonia. These genes were inserted into a modern H1N1 strain and triggered similar symptoms in animal testing.
In 2008 an investigation used the virus sequence to obtain the Hemagglutinin (HA) antigen and observe the adaptive immunity in 32 survivors of the 1918 pandemic; all of them presented seroreactivity and 7 of 8 further tested presented memory B cell
In immunology, a memory B cell (MBC) is a type of B lymphocyte that forms part of the adaptive immune system. These cells develop within germinal centers of the secondary lymphoid organs. Memory B cells circulate in the blood stream in a quie ...
s able to produce antibodies that bound to the HA antigen, highlighting the ability of immunological memory
Immunological memory is the ability of the immune system to quickly and specifically recognize an antigen that the body has previously encountered and initiate a corresponding immune response. Generally, they are secondary, tertiary and other subse ...
.
In June 2010, a team at the Mount Sinai School of Medicine reported the 2009 flu pandemic vaccine provided some cross-protection against the Spanish flu pandemic strain.
In 2013, the AIR Worldwide Research and Modeling Group "estimated the effects of a similar pandemic occurring today using the AIR Pandemic Flu Model". In the model, "a modern-day 'Spanish flu' event would result in additional life insurance losses of between US$15.3–27.8 billion in the United States alone", with 188,000–337,000 deaths in the United States.
In 2018, Michael Worobey, a professor at the University of Arizona
The University of Arizona (Arizona, U of A, UArizona, or UA) is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Tucson, Arizona, United States. Founded in 1885 by the 13th Arizona Territorial Legislature, it ...
who is examining the history of the 1918 pandemic, revealed that he obtained tissue slides created by William Rolland, a physician who reported on a respiratory illness likely to be the virus while a pathologist in the British military during World War One.
See also
*
*
*
*
*
* List of epidemics and pandemics
This is a list of the largest known epidemics and pandemics caused by an infectious disease in humans. Widespread non-communicable diseases such as cardiovascular disease and cancer are not included. An epidemic is the rapid spread of disease to ...
* List of Spanish flu cases
Footnotes
References
Citations
Bibliography
*
* – Open access material by the Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences at Health Sciences Research Commons.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Videos
We Heard the Bells: The Influenza of 1918
– NIH
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in 1887 and is part of the United States Department of Health and Human Service ...
interviews with Spanish Flu survivors.
Presentation by Nancy Bristow on the Influenza Pandemic and World War I, November 1, 2019
C-SPAN
Cable-Satellite Public Affairs Network (C-SPAN ) is an American Cable television in the United States, cable and Satellite television in the United States, satellite television network, created in 1979 by the cable television industry as a Non ...
*
''Dr. Wise on Influenza''
(1919)An 18-minute, dramatised public information film
Public information films (PIFs) are a series of government-commissioned short films, shown during television advertising breaks in the United Kingdom. The name is sometimes also applied, ''faute de mieux'', to similar films from other countries, ...
( silent) produced by Britain's Local Government Board
The Local Government Board (LGB) was a British Government supervisory body overseeing local administration in England and Wales from 1871 to 1919.
The LGB was created by the Local Government Board Act 1871 ( 34 & 35 Vict. c. 70) and took over the ...
, the predecessor of the Ministry of Health. Via the British Film Institute National Archive.
External links
The American Influenza Epidemic of 1918–1919: A Digital Encyclopedia
– largest digital collection of newspapers, archival manuscripts, and interpretive essays exploring the impact of the epidemic on 50 U.S. cities (University of Michigan
The University of Michigan (U-M, U of M, or Michigan) is a public university, public research university in Ann Arbor, Michigan, United States. Founded in 1817, it is the oldest institution of higher education in the state. The University of Mi ...
).
{{portal bar, Biology, Medicine, Viruses
Pandemics
1910s epidemics
1920s epidemics
1918 disease outbreaks
1919 disease outbreaks
1920 disease outbreaks
 This pandemic was known by many different names depending on place, time, and context. The
This pandemic was known by many different names depending on place, time, and context. The  Outside Spain, the disease was soon misnamed 'Spanish influenza'. In a 2 June 1918 ''
Outside Spain, the disease was soon misnamed 'Spanish influenza'. In a 2 June 1918 ''

 The second wave began in the second half of August 1918, probably spreading to
The second wave began in the second half of August 1918, probably spreading to  The fourth wave in the United States subsided as swiftly as it had appeared, reaching a peak in early February. "An epidemic of considerable proportions marked the early months of 1920", the U.S. Mortality Statistics would later note; according to data at this time, the epidemic resulted in one third as many deaths as the 1918–1919 experience. New York City alone reported 6,374 deaths between December 1919 and April 1920, almost twice the number of the first wave in spring 1918. Detroit, Milwaukee, Kansas City, Minneapolis, and St. Louis were hit particularly hard, with death rates higher than all of 1918.
The fourth wave in the United States subsided as swiftly as it had appeared, reaching a peak in early February. "An epidemic of considerable proportions marked the early months of 1920", the U.S. Mortality Statistics would later note; according to data at this time, the epidemic resulted in one third as many deaths as the 1918–1919 experience. New York City alone reported 6,374 deaths between December 1919 and April 1920, almost twice the number of the first wave in spring 1918. Detroit, Milwaukee, Kansas City, Minneapolis, and St. Louis were hit particularly hard, with death rates higher than all of 1918.  The majority of the infected experienced only the typical flu symptoms of sore throat, headache, and fever, especially during the first wave. However, during the second wave, the disease was much more serious, often complicated by
The majority of the infected experienced only the typical flu symptoms of sore throat, headache, and fever, especially during the first wave. However, during the second wave, the disease was much more serious, often complicated by  Studies have shown that the immune system of Spanish flu victims could have been weakened by unseasonably cold and wet weather for extended periods during the pandemic. This affected especially troops exposed to incessant rains and lower-than-average temperatures during World War I, and especially during the second wave of the pandemic. Climate data and mortality records analyzed at
Studies have shown that the immune system of Spanish flu victims could have been weakened by unseasonably cold and wet weather for extended periods during the pandemic. This affected especially troops exposed to incessant rains and lower-than-average temperatures during World War I, and especially during the second wave of the pandemic. Climate data and mortality records analyzed at  The Spanish flu infected around 500 million people, about one-third of the world's population. Estimates on deaths vary greatly, but it is considered to be one of the deadliest pandemics in history. An early estimate from 1927 put global mortality at 21.6 million. An estimate from 1991 states that the virus killed between 25 and 39 million people. A 2005 estimate put the death toll at 50 million, and possibly as high as 100 million. However, a 2018 reassessment in the ''
The Spanish flu infected around 500 million people, about one-third of the world's population. Estimates on deaths vary greatly, but it is considered to be one of the deadliest pandemics in history. An early estimate from 1927 put global mortality at 21.6 million. An estimate from 1991 states that the virus killed between 25 and 39 million people. A 2005 estimate put the death toll at 50 million, and possibly as high as 100 million. However, a 2018 reassessment in the '' Even in areas where mortality was low, so many adults were incapacitated that daily life was hampered. Some communities closed all stores or required customers to leave orders outside. There were reports that healthcare workers could not tend the sick nor the gravediggers bury the dead because they too were ill. Mass graves were dug by
Even in areas where mortality was low, so many adults were incapacitated that daily life was hampered. Some communities closed all stores or required customers to leave orders outside. There were reports that healthcare workers could not tend the sick nor the gravediggers bury the dead because they too were ill. Mass graves were dug by  Estimates for the death toll in China have varied widely, reflecting the lack of centralized collection of health data at the time due to the Warlord period. China may have experienced a relatively mild flu season in 1918 compared to other areas of the world. However, some reports from its interior suggest that mortality rates from influenza were perhaps higher in at least a few locations in 1918. At the very least, there is little evidence that China as a whole was seriously affected by the flu compared to other countries.
The first estimate of the Chinese death toll was made in 1991 by Patterson and Pyle, which estimated a toll of between 5 and 9 million. However, this study was criticized by later studies due to flawed methodology, and newer studies have published estimates of a far lower mortality rate in China. For instance, Iijima in 1998 estimates the death toll in China to be between 1 and 1.28 million based on data available from Chinese port cities. The lower estimates of the Chinese death toll are based on the low mortality rates that were found in Chinese port cities and on the assumption that poor communications prevented the flu from penetrating the interior of China. However, some contemporary newspaper and post office reports, as well as reports from missionary doctors, suggest that the flu did penetrate the Chinese interior and that influenza was severe in at least some locations in the countryside of China.
Although medical records from China's interior are lacking, extensive medical data were recorded in Chinese port cities, such as then
Estimates for the death toll in China have varied widely, reflecting the lack of centralized collection of health data at the time due to the Warlord period. China may have experienced a relatively mild flu season in 1918 compared to other areas of the world. However, some reports from its interior suggest that mortality rates from influenza were perhaps higher in at least a few locations in 1918. At the very least, there is little evidence that China as a whole was seriously affected by the flu compared to other countries.
The first estimate of the Chinese death toll was made in 1991 by Patterson and Pyle, which estimated a toll of between 5 and 9 million. However, this study was criticized by later studies due to flawed methodology, and newer studies have published estimates of a far lower mortality rate in China. For instance, Iijima in 1998 estimates the death toll in China to be between 1 and 1.28 million based on data available from Chinese port cities. The lower estimates of the Chinese death toll are based on the low mortality rates that were found in Chinese port cities and on the assumption that poor communications prevented the flu from penetrating the interior of China. However, some contemporary newspaper and post office reports, as well as reports from missionary doctors, suggest that the flu did penetrate the Chinese interior and that influenza was severe in at least some locations in the countryside of China.
Although medical records from China's interior are lacking, extensive medical data were recorded in Chinese port cities, such as then  Many businesses in the entertainment and service industries suffered losses in revenue, while the healthcare industry reported profit gains. Historian Nancy Bristow has argued that the pandemic, when combined with the increasing number of women attending college, contributed to the success of women in nursing. This was due in part to the failure of medical doctors, who were predominantly men, to contain the illness. Nursing staff, who were mainly women, celebrated the success of their patient care and did not associate the spread of the disease with their work.
A 2020 study found that U.S. cities that implemented early and extensive non-medical measures (quarantine, etc.) suffered no additional adverse economic effects due to implementing those measures. However, the validity of this study has been questioned because of the coincidence of WWI and other problems with data reliability.
Many businesses in the entertainment and service industries suffered losses in revenue, while the healthcare industry reported profit gains. Historian Nancy Bristow has argued that the pandemic, when combined with the increasing number of women attending college, contributed to the success of women in nursing. This was due in part to the failure of medical doctors, who were predominantly men, to contain the illness. Nursing staff, who were mainly women, celebrated the success of their patient care and did not associate the spread of the disease with their work.
A 2020 study found that U.S. cities that implemented early and extensive non-medical measures (quarantine, etc.) suffered no additional adverse economic effects due to implementing those measures. However, the validity of this study has been questioned because of the coincidence of WWI and other problems with data reliability.
 The Spanish flu began to fade from public awareness over the decades until the
The Spanish flu began to fade from public awareness over the decades until the  Similarities between a reconstruction of the virus and avian viruses, combined with the human pandemic preceding the first reports of influenza in swine, led researchers to conclude the influenza virus jumped directly from birds to humans, and swine caught the disease from humans. More recent research has suggested the strain may have originated in a nonhuman, mammalian species, in 1882–1913. This ancestor virus diverged about 1913–1915 into the classical swine and human H1N1 influenza lineages. The last common ancestor of human strains dates between February 1917 and April 1918. Because pigs are more readily infected with avian influenza viruses than are humans, they were suggested as the original recipients of the virus, passing the virus to humans sometime between 1913 and 1918.
Similarities between a reconstruction of the virus and avian viruses, combined with the human pandemic preceding the first reports of influenza in swine, led researchers to conclude the influenza virus jumped directly from birds to humans, and swine caught the disease from humans. More recent research has suggested the strain may have originated in a nonhuman, mammalian species, in 1882–1913. This ancestor virus diverged about 1913–1915 into the classical swine and human H1N1 influenza lineages. The last common ancestor of human strains dates between February 1917 and April 1918. Because pigs are more readily infected with avian influenza viruses than are humans, they were suggested as the original recipients of the virus, passing the virus to humans sometime between 1913 and 1918.
 An effort to recreate the Spanish flu strain (a strain of influenza A subtype H1N1) was a collaboration among the
An effort to recreate the Spanish flu strain (a strain of influenza A subtype H1N1) was a collaboration among the