1812 In The United States on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The following is a partial list of events from the year 1812 in the United States. After years of increasing tensions, the United States declares war on the 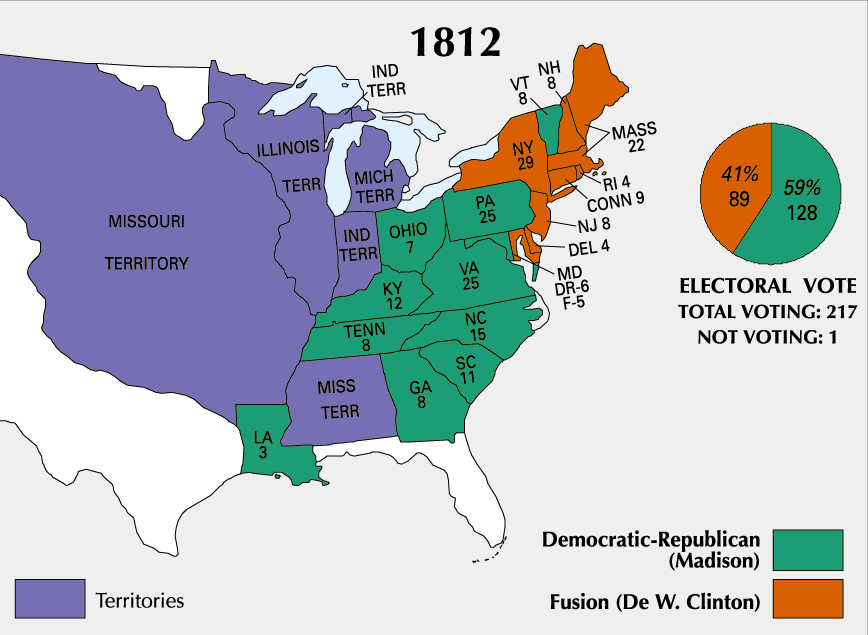
 * April 4 –
* April 4 –
 * July 12 – Americans invade
* July 12 – Americans invade
Maps of the United States in 1812
at Wikimedia Commons * {{Year in North America, 1812 1810s in the United States
British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
, starting the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
.

Incumbents
Federal Government
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-governin ...
* President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ful ...
: James Madison
James Madison Jr. (March 16, 1751June 28, 1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Father. He served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison is hailed as the "Father of the Constitution" for hi ...
( DR-Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
)
* Vice President
A vice president, also director in British English, is an officer in government or business who is below the president (chief executive officer) in rank. It can also refer to executive vice presidents, signifying that the vice president is on t ...
: George Clinton ( DR-New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
) (until April 20), ''vacant'' (starting April 20)
* Chief Justice: John Marshall
John Marshall (September 24, 1755July 6, 1835) was an American politician and lawyer who served as the fourth Chief Justice of the United States from 1801 until his death in 1835. He remains the longest-serving chief justice and fourth-longes ...
(Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
)
* Speaker of the House of Representatives: Henry Clay
Henry Clay Sr. (April 12, 1777June 29, 1852) was an American attorney and statesman who represented Kentucky in both the U.S. Senate and House of Representatives. He was the seventh House speaker as well as the ninth secretary of state, al ...
( DR-Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia to ...
)
* Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of a ...
: 12th
12 (twelve) is the natural number following 11 and preceding 13. Twelve is a superior highly composite number, divisible by 2, 3, 4, and 6.
It is the number of years required for an orbital period of Jupiter. It is central to many systems ...
Events
January–March
* January – ''The New England Journal of Medicine
''The New England Journal of Medicine'' (''NEJM'') is a weekly medical journal published by the Massachusetts Medical Society. It is among the most prestigious peer-reviewed medical journals as well as the oldest continuously published one.
His ...
'' is first published in Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
by Dr John Collins Warren
John Collins Warren (August 1, 1778 – May 4, 1856) was an American surgeon. In 1846 he gave permission to William T.G. Morton to provide ether anesthesia while Warren performed a minor surgical procedure. News of this first public demonstrati ...
as the ''New England Journal of Medicine and Surgery and the Collateral Branches of Medical Science''.
* January 10 – , the first steamship
A steamship, often referred to as a steamer, is a type of steam-powered vessel, typically ocean-faring and seaworthy, that is propelled by one or more steam engines that typically move (turn) propellers or paddlewheels. The first steamships ...
on the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
, arrives in its namesake city, completing its maiden voyage.
* February 2 – Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
establishes a fur trading colony at Fort Ross, California
Fort Ross (Russian: Форт-Росс, Kashaya ''mé·ṭiʔni''), originally Fortress Ross ( pre-reformed Russian: Крѣпость Россъ, tr. ''Krepostʹ Ross''), is a former Russian establishment on the west coast of North America in ...
.
* February 7 – The last of four major New Madrid earthquake
New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created.
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz
Albums and EPs
* ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
* ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator, ...
s strike New Madrid, Missouri
New Madrid ( es, Nueva Madrid) is a city in New Madrid County, Missouri, United States. The population was 2,787 at the 2020 census. New Madrid is the county seat of New Madrid County. The city is located 42 miles (68 km) southwest of Cairo ...
, with an estimated moment magnitude
The moment magnitude scale (MMS; denoted explicitly with or Mw, and generally implied with use of a single M for magnitude) is a measure of an earthquake's magnitude ("size" or strength) based on its seismic moment. It was defined in a 1979 pape ...
of over 8.
* March 26 – The ''Boston Gazette
The ''Boston Gazette'' (1719–1798) was a newspaper published in Boston, in the British North American colonies. It was a weekly newspaper established by William Brooker, who was just appointed Postmaster of Boston, with its first issue release ...
'' prints a political cartoon coining the term "Gerrymander
In representative democracies, gerrymandering (, originally ) is the political manipulation of electoral district boundaries with the intent to create undue advantage for a party, group, or socioeconomic class within the constituency. The m ...
" after former Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut assachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England ...
Governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
Elbridge Gerry
Elbridge Gerry (; July 17, 1744 – November 23, 1814) was an American Founding Father, merchant, politician, and diplomat who served as the fifth vice president of the United States under President James Madison from 1813 until his death in 18 ...
's approval (on February 11) of legislation creating oddly shaped electoral districts designed to help incumbents win re-election.
April–June
 * April 4 –
* April 4 – U.S. President
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States ...
James Madison
James Madison Jr. (March 16, 1751June 28, 1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Father. He served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison is hailed as the "Father of the Constitution" for hi ...
enacts a 90-day embargo
Economic sanctions are commercial and financial penalties applied by one or more countries against a targeted self-governing state, group, or individual. Economic sanctions are not necessarily imposed because of economic circumstances—they m ...
on trade with the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
.
* April 20 – George Clinton, Vice President of the United States
The vice president of the United States (VPOTUS) is the second-highest officer in the executive branch of the U.S. federal government, after the president of the United States, and ranks first in the presidential line of succession. The vice ...
, dies in office.
* April 30 – Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
is admitted as the 18th U.S. state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sover ...
(''see History of Louisiana
The history of the area that is now the U.S. state of Louisiana, can be traced back thousands of years to when it was occupied by indigenous peoples. The first indications of permanent settlement, ushering in the Archaic period, appear about 5, ...
'').
* May 8 - Hail to the Chief
"Hail to the Chief" is the personal anthem of the president of the United States, adapted by James Sanderson from an original Scottish Gaelic melody.
The song's playing accompanies the appearance of the president of the United States at many ...
is published as the presidential anthem of the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
.
* June 1 – War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
: U.S. President
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States ...
James Madison
James Madison Jr. (March 16, 1751June 28, 1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Father. He served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison is hailed as the "Father of the Constitution" for hi ...
asks the U.S. Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is Bicameralism, bicameral, composed of a lower body, the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives, and an upper body, ...
to declare war on Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
.
* June 4 – Following Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
's admittance as a U.S. state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sover ...
, the territory created by that name is renamed the Missouri Territory
The Territory of Missouri was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from June 4, 1812, until August 10, 1821. In 1819, the Territory of Arkansas was created from a portion of its southern area. In 1821, a southeas ...
.
* June 18 – The War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
begins between the United States and the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
.
July–September
 * July 12 – Americans invade
* July 12 – Americans invade Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
at Windsor, Upper Canada.
* August 5 – War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
: Tecumseh
Tecumseh ( ; October 5, 1813) was a Shawnee chief and warrior who promoted resistance to the expansion of the United States onto Native American lands. A persuasive orator, Tecumseh traveled widely, forming a Native American confederacy and ...
's Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
force ambushes Thomas Van Horne
Thomas B. Van Horne, (June 1, 1782 – September 21, 1841) served as a federal land register and Ohio State Senator. He is noted for his leadership during the War of 1812.
Early life
Born in New Jersey June 1, 1782, his ancestors were emigr ...
's 200 Americans at Brownstone Creek, causing them to flee and retreat.
* August 7 – 130 Filibusters of the Gutiérrez–Magee Expedition cross from Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
into Spanish Texas
Spanish Texas was one of the interior provinces of the colonial Viceroyalty of New Spain from 1690 until 1821. The term "interior provinces" first appeared in 1712, as an expression meaning "far away" provinces. It was only in 1776 that a lega ...
, soon after they capture the town of Nacogdoches
Nacogdoches ( ) is a small city in East Texas and the county seat of Nacogdoches County, Texas, United States. The 2020 U.S. census recorded the city's population at 32,147. Nacogdoches is a sister city of the smaller, similarly named Natchitoch ...
.
* August 15 – War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
: Battle of Fort Dearborn
The Battle of Fort Dearborn (sometimes called the Fort Dearborn Massacre) was an engagement between United States troops and Potawatomi Native Americans that occurred on August 15, 1812, near Fort Dearborn in what is now Chicago, Illinois (at that ...
– Potawatomi
The Potawatomi , also spelled Pottawatomi and Pottawatomie (among many variations), are a Native American people of the western Great Lakes region, upper Mississippi River and Great Plains. They traditionally speak the Potawatomi language, a m ...
warriors overrun the U.S. fort in Illinois Territory
The Territory of Illinois was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 1, 1809, until December 3, 1818, when the southern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Illinois. Its ca ...
.
* August 16 – War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
: American General
A general officer is an Officer (armed forces), officer of highest military ranks, high rank in the army, armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry.
In some usages the term "general officer" refers t ...
William Hull
William Hull (June 24, 1753 – November 29, 1825) was an American soldier and politician. He fought in the American Revolutionary War and was appointed as Governor of Michigan Territory (1805–13), gaining large land cessions from several Ame ...
surrenders Fort Detroit
Fort Pontchartrain du Détroit or Fort Detroit (1701–1796) was a fort established on the north bank of the Detroit River by the French officer Antoine de la Mothe Cadillac and the Italian Alphonse de Tonty in 1701. In the 18th century, Fre ...
without a fight to the British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurk ...
.
* August 19 – War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
, USS ''Constitution'' vs HMS ''Guerriere'': defeats the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
frigate off the coast of Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
. The British shot is said to have bounced off ''Constitution''s sides, earning her the nickname "Old Ironsides".
* September 13; Gutiérrez–Magee Expedition: The Expedition, having since grown to 300 men, captures the town of Santísima Trinidad de Salcedo.
October–December
* October – Thecapital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
of Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
is permanently moved from Lancaster to Harrisburg
Harrisburg is the capital city of the Pennsylvania, Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Dauphin County, Pennsylvania, Dauphin County. With a population of 50,135 as of the 2021 census, Harrisburg is the List of c ...
.
* October 9 – War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
: American naval forces under Lieutenant Jesse Duncan Elliott capture two British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
warships, and .
* October 13 – War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
– Battle of Queenston Heights
The Battle of Queenston Heights was the first major battle in the War of 1812. Resulting in a British victory, it took place on 13 October 1812 near Queenston, Upper Canada (now Ontario).
The battle was fought between United States regulars wit ...
: As part of the Niagara campaign
The Niagara campaign occurred in 1814 and was the final campaign launched by the United States to invade Canada during the War of 1812. The campaign was launched to counter the British offensive in the Niagara region which had been initiated with t ...
in Upper Canada
The Province of Upper Canada (french: link=no, province du Haut-Canada) was a part of British Canada established in 1791 by the Kingdom of Great Britain, to govern the central third of the lands in British North America, formerly part of the ...
, United States forces under General Stephen Van Rensselaer
Stephen Van Rensselaer III (; November 1, 1764January 26, 1839) was an American landowner, businessman, militia officer, and politician. A graduate of Harvard College, at age 21, Van Rensselaer took control of Rensselaerswyck, his family's mano ...
are repulsed from invading Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
by British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
and native troops led by Sir Isaac Brock
Major-General Sir Isaac Brock KB (6 October 1769 – 13 October 1812) was a British Army officer and colonial administrator from Guernsey. Brock was assigned to Lower Canada in 1802. Despite facing desertions and near-mutinies, he c ...
(although he dies during the battle).
* November 5 – James Madison
James Madison Jr. (March 16, 1751June 28, 1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Father. He served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison is hailed as the "Father of the Constitution" for hi ...
defeats DeWitt Clinton
DeWitt Clinton (March 2, 1769February 11, 1828) was an American politician and naturalist. He served as a United States senator, as the mayor of New York City, and as the seventh governor of New York. In this last capacity, he was largely res ...
in the U.S. presidential election.
* November 13 – Gutiérrez-Magee Expedition: Manuel María de Salcedo
Manuel María de Salcedo y Quiroga, (1776 in Málaga, Spain – executed, April 3, 1813), was a governor of Spanish Texas from 1808 until his execution in 1813. Salcedo gained leadership experience helping his father Juan Manuel de Salcedo, ...
, the governor of Spanish Texas
Spanish Texas was one of the interior provinces of the colonial Viceroyalty of New Spain from 1690 until 1821. The term "interior provinces" first appeared in 1712, as an expression meaning "far away" provinces. It was only in 1776 that a lega ...
, begins a four month long siege of Presidio La Bahia
A presidio ( en, jail, fortification) was a fortified base established by the Spanish Empire around between 16th and 18th centuries in areas in condition of their control or influence. The presidios of Spanish Philippines in particular, were cent ...
near Goliad
Goliad ( ) is a city in Goliad County, Texas, United States. It is known for the 1836 Goliad massacre during the Texas Revolution. It had a population of 1,620 at the 2020 census. Founded on the San Antonio River, it is the county seat of Gol ...
. The siege continues until February 19
Events Pre-1600
* 197 – Emperor Septimius Severus defeats usurper Clodius Albinus in the Battle of Lugdunum, the bloodiest battle between Roman armies.
* 356 – The anti-paganism policy of Constantius II forbids the worship of pagan ...
, 1813
Events
January–March
* January 18–January 23 – War of 1812: The Battle of Frenchtown is fought in modern-day Monroe, Michigan between the United States and a British and Native American alliance.
* January 24 – T ...
.
* December 7 – Missouri Territory
The Territory of Missouri was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from June 4, 1812, until August 10, 1821. In 1819, the Territory of Arkansas was created from a portion of its southern area. In 1821, a southeas ...
is effective.
* December 29 – War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
: USS ''Constitution'' defeats the British frigate off the coast of Brazil.
Undated
* TheBishop James Madison Society The Bishop James Madison Society is a secret society of the College of William and Mary in Virginia. Students founded the society in the year 1812 as a tribute to the life of the late Bishop James Madison, eighth president of William and Mary and c ...
is founded at the College of William & Mary
The College of William & Mary (officially The College of William and Mary in Virginia, abbreviated as William & Mary, W&M) is a public research university in Williamsburg, Virginia. Founded in 1693 by letters patent issued by King William III ...
, Williamsburg, Virginia
Williamsburg is an Independent city (United States), independent city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it had a population of 15,425. Located on the Virginia Peninsula ...
.
* The City Bank of New York
Citibank, N. A. (N. A. stands for " National Association") is the primary U.S. banking subsidiary of financial services multinational Citigroup. Citibank was founded in 1812 as the City Bank of New York, and later became First National City Ba ...
is founded.
* The General Land Office
The General Land Office (GLO) was an independent agency of the United States government responsible for public domain lands in the United States. It was created in 1812 to take over functions previously conducted by the United States Department o ...
becomes an independent agency of the U.S. government, responsible for land in the public domain.
* The Williamsport Academy for the Education of Youth is founded in Pennsylvania.
* The Old Oscar Pepper Distillery (now the Woodford Reserve Distillery
Woodford Reserve is a brand of premium small batch Kentucky straight bourbon whiskey produced in Woodford County, Kentucky, by the Brown-Forman Corporation. It is made from a mixture of copper pot still spirits produced at the company's Woodford ...
), the oldest Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia to ...
Bourbon Bourbon may refer to:
Food and drink
* Bourbon whiskey, an American whiskey made using a corn-based mash
* Bourbon barrel aged beer, a type of beer aged in bourbon barrels
* Bourbon biscuit, a chocolate sandwich biscuit
* A beer produced by Bras ...
distillery
Distillation, or classical distillation, is the process of separating the components or substances from a liquid mixture by using selective boiling and condensation, usually inside an apparatus known as a still. Dry distillation is the heati ...
, is established along Glenn's Creek in Woodford County, Kentucky
Woodford County is a county located in the U.S. state of Kentucky. As of the 2020 census, the population was 26,871. Its county seat is Versailles. The area was home to Pisgah Academy. Woodford County is part of the Lexington-Fayette, KY Metrop ...
.
*Baptist Training Union
Baptists form a major branch of Protestantism distinguished by baptizing professing Christian believers only ( believer's baptism), and doing so by complete immersion. Baptist churches also generally subscribe to the doctrines of soul compe ...
now Wayland Baptist Theological Seminary is founded by Escaped and Free Slaves in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
* Princeton Theological Seminary
Princeton Theological Seminary (PTSem), officially The Theological Seminary of the Presbyterian Church, is a private school of theology in Princeton, New Jersey. Founded in 1812 under the auspices of Archibald Alexander, the General Assembly of ...
is founded in New Jersey.
Ongoing
*War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
(1812–1814)
* Gutiérrez–Magee Expedition
The Gutiérrez–Magee Expedition was an 1812–1813 joint filibustering expedition by Mexico and the United States against Spanish Texas during the early years of the Mexican War of Independence.
Background
In 1810, Father Miguel Hidalgo y Cost ...
(1812-1813)
Births
* January 2 –Augustus C. Dodge
Augustus Caesar Dodge (January 2, 1812November 20, 1883) was a Democratic Party (United States), Democratic delegate to the United States House of Representatives, U.S. House of Representatives from Iowa Territory, a U.S. minister to Spain, and o ...
, United States Senator from Iowa from 1848 to 1855 (died 1883
Events
January–March
* January 4 – ''Life'' magazine is founded in Los Angeles, California, United States.
* January 10 – A fire at the Newhall Hotel in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, United States, kills 73 people.
* Ja ...
)
* January 11 – Alexander H. Stephens
Alexander Hamilton Stephens (February 11, 1812 – March 4, 1883) was an American politician who served as the vice president of the Confederate States from 1861 to 1865, and later as the 50th governor of Georgia from 1882 until his death in 1 ...
, the only Vice President of the Confederate States of America
The Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States or the Confederacy was an unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 9, 1865. The Confeder ...
(died 1883)
* February 22 – John B. Weller
John B. Weller (February 22, 1812August 17, 1875) was the fifth governor of California from January 8, 1858 to January 9, 1860 who earlier had served as a congressman from Ohio and a U.S. senator from California, and minister to Mexico.
Lif ...
, United States Senator from California from 1852 to 1857 (died 1875
Events
January–March
* January 1 – The Midland Railway of England abolishes the Second Class passenger category, leaving First Class and Third Class. Other British railway companies follow Midland's lead during the rest of the ...
)
* February 15 – Charles Lewis Tiffany
Charles Lewis Tiffany (February 15, 1812 – February 18, 1902) was an American businessman and jeweler who founded New York City's Tiffany & Co. in 1837. Known for his jewelry expertise, Tiffany created the country's first retail catalog and ...
, founder of Tiffany & Co. (died 1902
Events
January
* January 1
** The Nurses Registration Act 1901 comes into effect in New Zealand, making it the first country in the world to require state registration of nurses. On January 10, Ellen Dougherty becomes the world's f ...
)
* February 16 – Henry Wilson
Henry Wilson (born Jeremiah Jones Colbath; February 16, 1812 – November 22, 1875) was an American politician who was the 18th vice president of the United States from 1873 until his death in 1875 and a senator from Massachusetts from 1855 to ...
, 18th Vice President of the United States
The vice president of the United States (VPOTUS) is the second-highest officer in the executive branch of the U.S. federal government, after the president of the United States, and ranks first in the presidential line of succession. The vice ...
from 1873 to 1875 (died 1875
Events
January–March
* January 1 – The Midland Railway of England abolishes the Second Class passenger category, leaving First Class and Third Class. Other British railway companies follow Midland's lead during the rest of the ...
)
* March 11 – James Speed, U.S. Attorney General from 1864 to 1866 under Presidents Abraham Lincoln and Andrew Johnson (died 1887
Events
January–March
* January 11 – Louis Pasteur's anti-rabies treatment is defended in the Académie Nationale de Médecine, by Dr. Joseph Grancher.
* January 20
** The United States Senate allows the Navy to lease Pearl Har ...
)
* March 12 – Isaac P. Christiancy, Chief Justice of Michigan Supreme Court and U.S. Senator from Michigan from 1875 to 1879 (died 1890
Events
January–March
* January 1
** The Kingdom of Italy establishes Eritrea as its colony, in the Horn of Africa.
** In Michigan, the wooden steamer ''Mackinaw'' burns in a fire on the Black River.
* January 2
** The steamship ...
)
* March 13 – James E. English
James Edward English (March 13, 1812 – March 2, 1890) was a United States Representative and later U.S. Senator from Connecticut, and Governor of Connecticut.
Early life and education
English was born in New Haven, Connecticut and atten ...
, United States Senator from Connecticut from 1875 to 1876 (died 1890)
* March 22 – Stephen Pearl Andrews
Stephen Pearl Andrews (March 22, 1812 – May 21, 1886) was an American libertarian socialist, individualist anarchist, linguist, political philosopher, outspoken Abolitionism in the United States, abolitionist and author of several books on the ...
, anarchist and proponent of pantarchy
Pantarchy is a social theory proposed by Stephen Pearl Andrews in the 19th century. Andrews was considered the "American rival of Comte," because of his work on an all-encompassing philosophy of universology, and his political proposals had similar ...
(died 1886
Events
January–March
* January 1 – Upper Burma is formally annexed to British Burma, following its conquest in the Third Anglo-Burmese War of November 1885.
* January 5– 9 – Robert Louis Stevenson's novella ''Strange ...
)
* April 2 – Susan May Williams, railroad heiress who married a nephew of Emperor Napoleon I (died 1881)
* April 16 – Sarah Harris Fayerweather
Sarah Harris Fayerweather (April 16 1812 – November 16 1878) was an African-American activist, abolitionist, and school integrationist. Beginning in January 1833 at the age of twenty, she attended Prudence Crandall's Canterbury Female Boarding Sc ...
, African-American whose 1832 admission to a Connecticut school resulted in the first integrated schoolhouse (died 1878
Events January–March
* January 5 – Russo-Turkish War – Battle of Shipka Pass IV: Russian and Bulgarian forces defeat the Ottoman Empire.
* January 9 – Umberto I becomes King of Italy.
* January 17 – Battle o ...
)
* May 4 – John W. Stevenson
John White Stevenson (May 4, 1812August 10, 1886) was the List of Governors of Kentucky, 25th governor of Kentucky and represented the state in both houses of the United States Congress, U.S. Congress. The son of former Speaker of the United St ...
, United States Senator from Kentucky from 1871 to 1877 (died 1886
Events
January–March
* January 1 – Upper Burma is formally annexed to British Burma, following its conquest in the Third Anglo-Burmese War of November 1885.
* January 5– 9 – Robert Louis Stevenson's novella ''Strange ...
)
* May 6 – Martin Delany
Martin Robison Delany (May 6, 1812January 24, 1885) was an abolitionist, journalist, physician, soldier, and writer, and arguably the first proponent of black nationalism. Delany is credited with the Pan-African slogan of "Africa for Africans."
...
, African-American abolitionist, journalist, and physician (died 1885
Events
January–March
* January 3– 4 – Sino-French War – Battle of Núi Bop: French troops under General Oscar de Négrier defeat a numerically superior Qing Chinese force, in northern Vietnam.
* January 4 – ...
)
* May 17 – Elias Nelson Conway
Elias Nelson Conway (May 17, 1812 – February 28, 1892) was an American politician and lawyer who served as the fifth governor of Arkansas from 1852 to 1860.
Early life
Conway was born in Greeneville, Tennessee. Born into a political family, ...
, 5th Governor of Arkansas from 1852 to 1860 (died 1892
Events
January–March
* January 1 – Ellis Island begins accommodating immigrants to the United States.
* February 1 - The historic Enterprise Bar and Grill was established in Rico, Colorado.
* February 27 – Rudolf Diesel applies for ...
)
* May 30 – John Alexander McClernand
John Alexander McClernand (May 30, 1812 – September 20, 1900) was an American lawyer and politician, and a Union Army general in the American Civil War. He was a prominent Democratic politician in Illinois and a member of the United States H ...
, lawyer, politician, and Union General during the American Civil War (died 1900
As of March 1 ( O.S. February 17), when the Julian calendar acknowledged a leap day and the Gregorian calendar did not, the Julian calendar fell one day further behind, bringing the difference to 13 days until February 28 ( O.S. February 15), 2 ...
)
* July 27 – Thomas Lanier Clingman
Thomas Lanier Clingman (July 27, 1812November 3, 1897), known as the "Prince of Politicians," was a Democratic member of the United States House of Representatives from 1843 to 1845 and from 1847 to 1858, and U.S. senator from the state of Nort ...
, North Carolina congressman, senator, and confederate general (died 1897
Events
January–March
* January 2 – The International Alpha Omicron Pi sorority is founded, in New York City.
* January 4 – A British force is ambushed by Chief Ologbosere, son-in-law of the ruler. This leads to a puniti ...
)
* July 30 – Harrison Ludington
Harrison Ludington (July 30, 1812June 17, 1891) was an American businessman, Republican politician, and Wisconsin pioneer. He served as the 13th governor of Wisconsin and was the 20th and 22nd mayor of Milwaukee, Wisconsin.
Early life and ca ...
, 13th Governor of Wisconsin from 1876 to 1878 (died 1891
Events
January–March
* January 1
** Paying of old age pensions begins in Germany.
** A strike of 500 Hungarian steel workers occurs; 3,000 men are out of work as a consequence.
**Germany takes formal possession of its new Africa ...
)
* August 11 – Joseph Projectus Machebeuf
Joseph Projectus Machebeuf (August 11, 1812 – July 10, 1889) was a French Roman Catholic missionary and the first Bishop of Denver.
Biography
The oldest of five children, Machebeuf was born in Riom to Michael and Gilberte (née Plauc) Mac ...
, French-American Catholic missionary and the first Bishop of Denver (died 1889
Events
January–March
* January 1
** The total solar eclipse of January 1, 1889 is seen over parts of California and Nevada.
** Paiute spiritual leader Wovoka experiences a vision, leading to the start of the Ghost Dance movement in the ...
)
* August 18 – John Hugh Means
John Hugh Means (August 18, 1812September 1, 1862) was the 64th Governor of South Carolina from 1850 to 1852 and an infantry colonel in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. He was killed in action at the Second Battle of M ...
, 64th Governor of South Carolina from 1850 to 1852 (died 1862
Events
January–March
* January 1 – The United Kingdom annexes Lagos Island, in modern-day Nigeria.
* January 6 – French intervention in Mexico: French, Spanish and British forces arrive in Veracruz, Mexico.
* January ...
)
* August 22 – Joseph Mozier, American-born sculptor best known for his work in Italy. (died 1870
Events
January–March
* January 1
** The first edition of ''The Northern Echo'' newspaper is published in Priestgate, Darlington, England.
** Plans for the Brooklyn Bridge are completed.
* January 3 – Construction of the Broo ...
)
* September 13 – John McMurtry, builder and architect (died 1890
Events
January–March
* January 1
** The Kingdom of Italy establishes Eritrea as its colony, in the Horn of Africa.
** In Michigan, the wooden steamer ''Mackinaw'' burns in a fire on the Black River.
* January 2
** The steamship ...
)
* September 18 – Herschel Vespasian Johnson
Herschel Vespasian Johnson (September 18, 1812August 16, 1880) was an American politician. He was the 41st Governor of Georgia from 1853 to 1857 and the vice presidential nominee of the Douglas wing of the Democratic Party in the 1860 U.S. pre ...
, United States Senator from Georgia from 1863 to 1865 (died 1880
Events
January–March
* January 22 – Toowong State School is founded in Queensland, Australia.
* January – The international White slave trade affair scandal in Brussels is exposed and attracts international infamy.
* February � ...
)
* September 29 – George N. Stearns, founder of E. C. Stearns & Company (died 1882
Events
January–March
* January 2
** The Standard Oil Trust is secretly created in the United States to control multiple corporations set up by John D. Rockefeller and his associates.
** Irish-born author Oscar Wilde arrives in ...
)
* October 1 – Stephen P. Hempstead
Stephen P. Hempstead (October 1, 1812February 16, 1883) was the second Governor of Iowa. A Democrat, he served from 1850 to 1854.
Biography
Hempstead moved to the Iowa territory, and was active in politics in the years leading up to Iowa's g ...
, 2nd Governor of Iowa from 1850 to 1854. (died 1883
Events
January–March
* January 4 – ''Life'' magazine is founded in Los Angeles, California, United States.
* January 10 – A fire at the Newhall Hotel in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, United States, kills 73 people.
* Ja ...
)
* October 6 – Lazarus W. Powell
Lazarus Whitehead Powell (October 6, 1812 – July 3, 1867) was the 19th Governor of Kentucky, serving from 1851 to 1855. He was later elected to represent Kentucky in the U.S. Senate from 1859 to 1865.
The reforms enacted during Powell's term ...
, United States Senator from Kentucky from 1859 to 1865. (died 1867
Events
January–March
* January 1 – The Covington–Cincinnati Suspension Bridge opens between Cincinnati, Ohio, and Covington, Kentucky, in the United States, becoming the longest single-span bridge in the world. It was renamed a ...
)
* October 9 – Almon W. Babbitt, Mormon pioneer and first secretary/treasurer of Utah Territory (died 1856
Events
January–March
* January 8 – Borax deposits are discovered in large quantities by John Veatch in California.
* January 23 – American paddle steamer SS ''Pacific'' leaves Liverpool (England) for a transatlantic voyag ...
)
* October 20 – Austin Flint
Austin Flint I (October 20, 1812 – March 13, 1886) was an American physician. He was a founder of Buffalo Medical College, precursor to The State University of New York at Buffalo. He served as president of the American Medical Association.
...
, co-founder of Buffalo Medical College and president of the American Medical Association (died 1886
Events
January–March
* January 1 – Upper Burma is formally annexed to British Burma, following its conquest in the Third Anglo-Burmese War of November 1885.
* January 5– 9 – Robert Louis Stevenson's novella ''Strange ...
)
* October 21 – David H. Armstrong, Canadian-born United States Senator from Missouri from 1877 to 1879 (died 1893
Events
January–March
* January 2 – Webb C. Ball introduces railroad chronometers, which become the general railroad timepiece standards in North America.
* Mark Twain started writing Puddn'head Wilson.
* January 6 – Th ...
)
* October 22 – James "Grizzly" Adams, mountain man and bear trainer (died 1860
Events
January–March
* January 2 – The discovery of a hypothetical planet Vulcan is announced at a meeting of the French Academy of Sciences in Paris, France.
* January 10 – The Pemberton Mill in Lawrence, Massachusett ...
)
* November 1 – John Bernard Fitzpatrick
John Bernard Fitzpatrick (November 1, 1812 – February 13, 1866) was an American bishop of the Roman Catholic Church. He served as Bishop of Boston from 1846 until his death in 1866.
Early life and education
Fitzpatrick was born in Boston, Ma ...
, Bishop of Boston (died 1866
Events January–March
* January 1
** Fisk University, a historically black university, is established in Nashville, Tennessee.
** The last issue of the abolitionist magazine '' The Liberator'' is published.
* January 6 – Ottoman tr ...
)
* November 4 – Richard M. Bishop, 34th Governor of Ohio from 1878 to 1880 (died 1893
Events
January–March
* January 2 – Webb C. Ball introduces railroad chronometers, which become the general railroad timepiece standards in North America.
* Mark Twain started writing Puddn'head Wilson.
* January 6 – Th ...
)
* November 28 – George Ticknor Curtis
George Ticknor Curtis (November 28, 1812 – March 28, 1894) was an American historian, lawyer, and writer.
Biography
Curtis was born in Watertown, Massachusetts, and graduated from Harvard University in 1832 and then Harvard Law School. Aft ...
, author, lawyer and historian (died 1894
Events January–March
* January 4 – A military alliance is established between the French Third Republic and the Russian Empire.
* January 7 – William Kennedy Dickson receives a patent for motion picture film in the United S ...
)
* December 18 – Jesse D. Bright
Jesse David Bright (December 18, 1812 – May 20, 1875) was the ninth Lieutenant Governor of Indiana and U.S. Senator from Indiana who served as President pro tempore of the Senate on three occasions. He was the only senator from a Northern sta ...
, United States Senator from Indiana from 1845 to 1862 (died 1875
Events
January–March
* January 1 – The Midland Railway of England abolishes the Second Class passenger category, leaving First Class and Third Class. Other British railway companies follow Midland's lead during the rest of the ...
)
Undated
*Stephen Mallory
Stephen Russell Mallory (1812 – November 9, 1873) was a Democratic senator from Florida from 1851 to the secession of his home state and the outbreak of the American Civil War. For much of that period, he was chairman of the Committee on Na ...
, United States Senator from Florida from 1851 to 1861 (died 1873)
* William K. Sebastian
William King Sebastian (June 12, 1812May 20, 1865) was an American politician and lawyer from Helena, Arkansas. He represented Arkansas as a U.S. Senator, Democrat, from 1848 to 1861. Sebastian withdrew from the Senate at the start of the Civil W ...
, United States Senator from Arkansas from 1848 to 1861 (died in 1865
Events
January–March
* January 4 – The New York Stock Exchange opens its first permanent headquarters at Broad Street (Manhattan), 10-12 Broad near Wall Street, in New York City.
* January 13 – American Civil War : Sec ...
)
Deaths
* April 20 – George Clinton, fourthVice President of the United States
The vice president of the United States (VPOTUS) is the second-highest officer in the executive branch of the U.S. federal government, after the president of the United States, and ranks first in the presidential line of succession. The vice ...
from 1805 to 1812 (born 1739
Events
January–March
* January 1 – Bouvet Island is discovered by French explorer Jean-Baptiste Charles Bouvet de Lozier, in the South Atlantic Ocean.
* January 3: A 7.6 earthquake shakes the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region ...
)
* May 12 – Martha Ballard
Martha Moore Ballard (February 9, 1735 – June 9, 1812) was an American midwife and healer. Unusually for the time, Ballard kept a diary with thousands of entries over nearly three decades, which has provided historians with invaluable insi ...
, diarist and midwife (born 1734
Events
January– March
* January 8 – Salzburgers, Lutherans who were expelled by the Roman Catholic Bishop of Salzburg, Austria, in October 1731, set sail for the British Colony of Province of Georgia, Georgia in North America ...
or 1735
Events
January–March
* January 2 – Alexander Pope's poem ''Epistle to Dr Arbuthnot'' is published in London.
* January 8 – George Frideric Handel's opera ''Ariodante'' is premièred at the Royal Opera House in Covent G ...
)
* June 17 – Jean La Lime
Jean La Lime or Lalime (died June 17, 1812) was a trader from Quebec, Canada who worked in what became the Northwest Territory of the United States. He worked as an agent for William Burnett, also of Canada, to sell to the Native Americans and ta ...
, Victim of "the first murder in Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
"; killed by John Kinzie
John Kinzie (December 23, 1763 – June 6, 1828) was a fur trader from Quebec who first operated in Detroit and what became the Northwest Territory of the United States. A partner of William Burnett from Canada, about 1802-1803 Kinzie moved w ...
* December 20 – Sacagawea
Sacagawea ( or ; also spelled Sakakawea or Sacajawea; May – December 20, 1812 or April 9, 1884)Sacagawea
...
, Shoshone interpreter and guide on the ...
Lewis and Clark Expedition
The Lewis and Clark Expedition, also known as the Corps of Discovery Expedition, was the United States expedition to cross the newly acquired western portion of the country after the Louisiana Purchase. The Corps of Discovery was a select gro ...
(born c. 1788
Events
January–March
* January 1 – The first edition of ''The Times'', previously ''The Daily Universal Register'', is published in London.
* January 2 – Georgia ratifies the United States Constitution, and becomes the fourth U.S ...
)
* December 24 – George Beck, artist and poet (born 1749
Events
January–March
* January 3
** Benning Wentworth issues the first of the New Hampshire Grants, leading to the establishment of Vermont.
** The first issue of ''Berlingske'', Denmark's oldest continually operating newspaper, ...
)
* December 26 – Joel Barlow
Joel Barlow (March 24, 1754 – December 26, 1812) was an American poet, and diplomat, and politician. In politics, he supported the French Revolution and was an ardent Jeffersonian republican.
He worked as an agent for American speculator Wil ...
, poet (born 1754)
See also
*Timeline of United States history (1790–1819)
This section of the Timeline of United States history concerns events from 1790 to 1819.
1790s
Presidency of George Washington
*1790 – Rhode Island ratifies the United States Constitution, Constitution and becomes 13th state
*1791 – The ...
* Worldwide events in 1812
*War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
External links
Maps of the United States in 1812
at Wikimedia Commons * {{Year in North America, 1812 1810s in the United States
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
Years of the 19th century in the United States