1783 Calabrian Earthquakes on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The 1783 Calabrian earthquakes were a sequence of five strong earthquakes that hit the region of
 This event occurred at about midday 40 km NE of the first mainshock on the 5th. Severe damage extended 15 km along the front of the Serre Mountains, levelling all the villages between
This event occurred at about midday 40 km NE of the first mainshock on the 5th. Severe damage extended 15 km along the front of the Serre Mountains, levelling all the villages between
Calabria
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
in southern Italy (then part of the Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples ( la, Regnum Neapolitanum; it, Regno di Napoli; nap, Regno 'e Napule), also known as the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was ...
), the first two of which produced significant tsunamis. The epicenters form a clear alignment extending nearly 100 km from the Straits of Messina to about 18 km SSW of Catanzaro. The epicenter of the first earthquake occurred in the plain of Palmi
Palmi may refer to:
People Given name
Palmi is an Icelandic male given name. Notable people with this surname include:
* Pálmi Gestsson (born 1957), Icelandic actor and voice actor
* Pálmi Gunnarsson (born 1950), Icelandic musician
* Pálmi Ha ...
. The earthquakes occurred over a period of nearly two months, all with estimated magnitudes of 5.9 or greater. Estimates of the total number of deaths lie in the range 32,000 to 50,000.
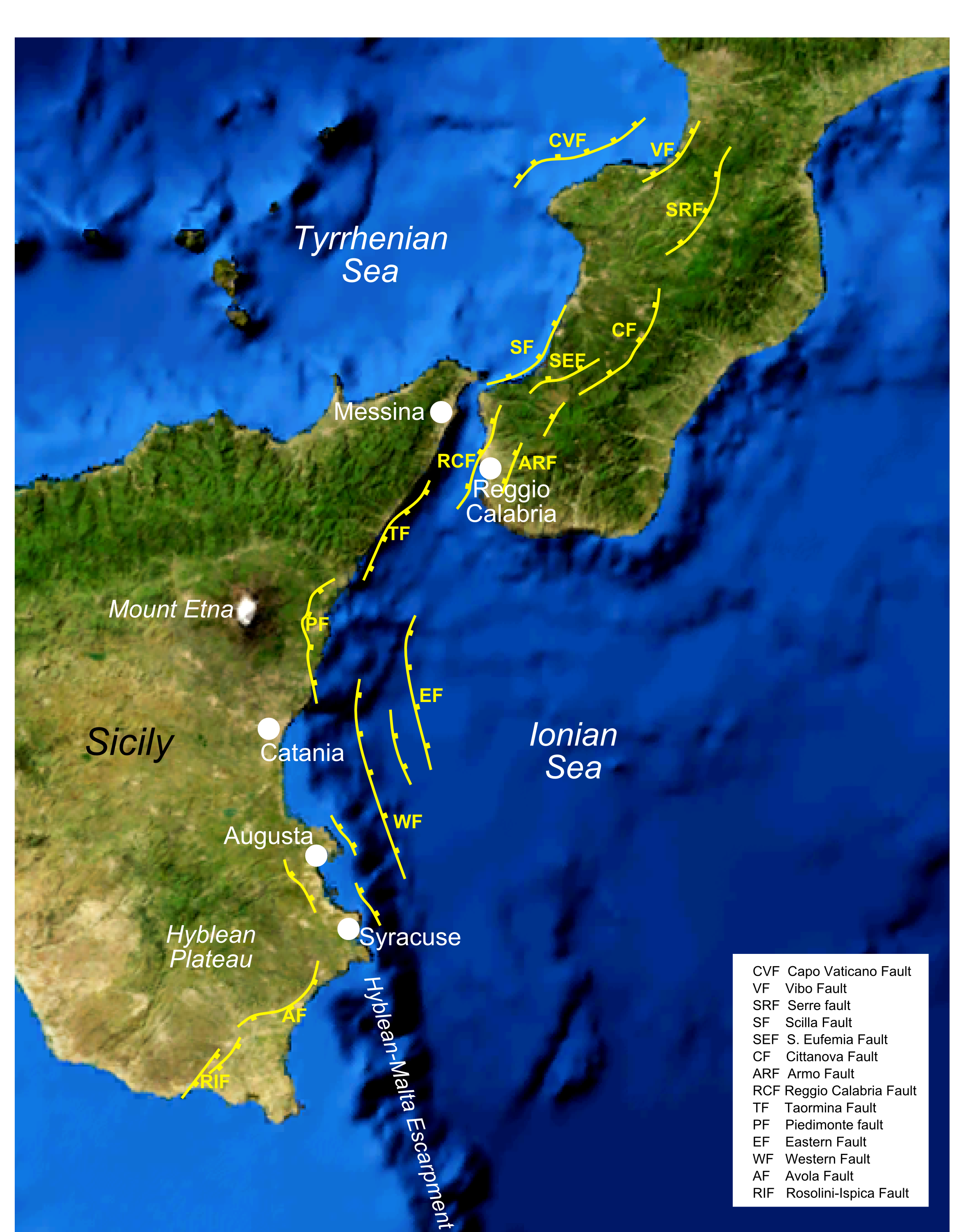
Tectonic setting
The southwestern part of Calabria and the eastern part of Sicily are areas of active crustalextension
Extension, extend or extended may refer to:
Mathematics
Logic or set theory
* Axiom of extensionality
* Extensible cardinal
* Extension (model theory)
* Extension (predicate logic), the set of tuples of values that satisfy the predicate
* E ...
within the Siculo-Calabrian rift Zone. This 350 km long zone developed within the Apennine chain during the Pleistocene and takes up WNW–ESE directed extension.
Events

February 5
This earthquake, with an estimated magnitude of 7.0, affected a large area including most of the southern Italian peninsula and shook the whole island of Sicily. Many villages were damaged and as many as 180 almost completely destroyed, with more than 25,000 casualties. A tsunami affected the coastline on both sides of the Straits of Messina, destroying the harbour walls atMessina
Messina (, also , ) is a harbour city and the capital of the Italian Metropolitan City of Messina. It is the third largest city on the island of Sicily, and the 13th largest city in Italy, with a population of more than 219,000 inhabitants in ...
. The earthquake had already caused widespread death and destruction in Messina. Homes were razed to the ground, the medieval Duomo was badly damaged and most of the historic buildings were reduced to rubble.
Near the epicenter the ground shaking was so intense that people were knocked off their feet and heavy stones were found to be dislodged and upturned. Large landslide
Landslides, also known as landslips, are several forms of mass wasting that may include a wide range of ground movements, such as rockfalls, deep-seated grade (slope), slope failures, mudflows, and debris flows. Landslides occur in a variety of ...
s caused major destruction at Terranova and Molochio but even well-constructed buildings not thus affected were almost completely destroyed, such as in Oppido Mamertina and Casalnuovo.
The earthquake is thought to have involved rupturing of the Galatro, Cittanova and Sant'Eufemia faults, which form the southeastern boundary to the Gioia Basin.
February 6
This magnitude 6.2 event occurred during the night following the first event and struck the area just to the southwest. Most of the damage and casualties appear to have been caused by a tsunami that was set off by a major collapse of Monte Pací into the sea near Scilla shortly after the earthquake. Many of Scilla's residents, frightened by the tremors of the previous day had moved onto the open beach for the night, where they were overwhelmed by the waves. The tsunami caused severe flooding in the town, reaching as far as 200 m inland, and there were more than 1500 deaths. The earthquake is thought to have involved rupturing of the Scilla fault, which defines the coast around Scilla.February 7
 This event occurred at about midday 40 km NE of the first mainshock on the 5th. Severe damage extended 15 km along the front of the Serre Mountains, levelling all the villages between
This event occurred at about midday 40 km NE of the first mainshock on the 5th. Severe damage extended 15 km along the front of the Serre Mountains, levelling all the villages between Acquaro
Acquaro ( Calabrian: ) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Vibo Valentia in the Italian region Calabria, located about southwest of Catanzaro and about southeast of Vibo Valentia.
Geography
Acquaro borders the following municipalit ...
and Soriano Calabro
Soriano Calabro (Central-Southern Calabrian, Calabrian: ) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Vibo Valentia in the Italy, Italian region Calabria, located about southwest of Catanzaro and about southeast of Vibo Valentia. As of 31 ...
.
The earthquake is thought to have involved rupturing of the southern segment of the Serre fault that bounds the Mesima Basin.
March 1
This earthquake was the weakest of the sequence and caused relatively little damage. The earthquake is thought to have involved rupturing of the northern segment of the Serre fault.March 28
The final event of the sequence was of similar magnitude to the first and had an epicenter about 20 km east of the fourth, nearGirifalco
Girifalco is a ''comune'' and town in the province of Catanzaro in the Calabria region of southern Italy.
History
The first settlements in the area date back to prehistoric times, as evidenced by the archaeological finds discovered in the area and ...
and Borgia
The House of Borgia ( , ; Spanish and an, Borja ; ca-valencia, Borja ) was an Italian-Aragonese Spanish noble family, which rose to prominence during the Italian Renaissance. They were from Valencia, the surname being a toponymic from the town ...
in the Catanzaro Basin. The earthquake lasted for about ten seconds, and many villages were destroyed with many hundreds dead in Borgia, Girifalco, Maida and Cortale. Landslides were common and sand volcanoes were seen, particularly on the banks of the Amato river.
This earthquake has not been tied to a particular fault, but a recent re-evaluation of the intensity data indicates that the isoseismal areas are elongated NE–SW, suggesting faulting of similar trend to that observed for the other earthquakes in the sequence.
Summary of earthquakes
The earthquake parameters shown below are taken from the CFTI4 online catalogue. The epicentral locations are here related to the nearest large village or town.Relationship between earthquakes
All the earthquakes in this sequence are thought to be linked by a process of triggering caused by stress redistribution following each individual event.See also
* List of earthquakes in Italy * List of historical earthquakesReferences
Further reading
* {{DEFAULTSORT:1783 Calabrian Earthquakes Earthquakes in Italy Calabrian earthquakes 1780s earthquakes 1783 natural disasters History of Calabria Palmi