16APSK 2 3 2D DPD Comparison 2 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Amplitude and phase-shift keying (APSK) is a 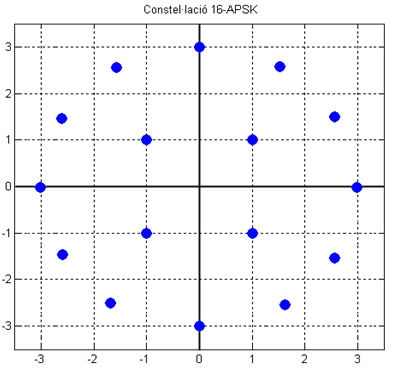
Approaching The Gaussian Channel Capacity With APSK Constellations
''IEEE Communications Letters''. The previous solution, where the constellation has a Gaussian shape, is called
DVB-Flexible Serially Concatenated Convolutional Turbo Codes with Near-Shannon bound performance for telemetry applications
Turbo‐coded APSK modulations design for satellite broadband communications
International journal of satellite communications and networking, 24(4), pp.261-281. Quantized radio modulation modes {{electronics-stub
digital
Digital usually refers to something using discrete digits, often binary digits.
Technology and computing Hardware
*Digital electronics, electronic circuits which operate using digital signals
**Digital camera, which captures and stores digital i ...
modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform, called the ''carrier signal'', with a separate signal called the ''modulation signal'' that typically contains informatio ...
scheme that conveys data
In the pursuit of knowledge, data (; ) is a collection of discrete values that convey information, describing quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted ...
by modulating both the amplitude
The amplitude of a periodic variable is a measure of its change in a single period (such as time or spatial period). The amplitude of a non-periodic signal is its magnitude compared with a reference value. There are various definitions of amplit ...
and the phase
Phase or phases may refer to:
Science
*State of matter, or phase, one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist
*Phase (matter), a region of space throughout which all physical properties are essentially uniform
* Phase space, a mathematic ...
of a carrier wave
In telecommunications, a carrier wave, carrier signal, or just carrier, is a waveform (usually sinusoidal) that is modulated (modified) with an information-bearing signal for the purpose of conveying information. This carrier wave usually has a ...
. In other words, it combines both amplitude-shift keying
Amplitude-shift keying (ASK) is a form of amplitude modulation that represents digital data as variations in the amplitude of a carrier wave.
In an ASK system, a symbol, representing one or more bits, is sent by transmitting a fixed-amplitude car ...
(ASK) and phase-shift keying
Phase-shift keying (PSK) is a digital modulation process which conveys data by changing (modulating) the phase of a constant frequency reference signal (the carrier wave). The modulation is accomplished by varying the sine and cosine inputs at a ...
(PSK). This allows for a lower bit error rate
In digital transmission, the number of bit errors is the number of received bits of a data stream over a communication channel that have been altered due to noise, interference, distortion or bit synchronization errors.
The bit error rate (BER) i ...
for a given modulation order
The modulation order of a digital communication scheme is determined by the number of the different symbols that can be transmitted using it.
Modulation order can only be defined for digital modulations. The simplest forms of digital modulation ar ...
and signal-to-noise ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR or S/N) is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. SNR is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power, often expressed in deci ...
, at the cost of increased complexity, compared to ASK or PSK alone.
Quadrature amplitude modulation
Quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) is the name of a family of digital modulation methods and a related family of analog modulation methods widely used in modern telecommunications to transmit information. It conveys two analog message signal ...
(QAM) can be considered a subset of APSK because all QAM schemes modulate both the amplitude and phase of the carrier. Conventionally, QAM constellations are rectangular and APSK constellations are circular, however this is not always the case. The distinction between the two is in their production; QAM is produced from two orthogonal signals. The advantage of APSK over conventional QAM is a lower number of possible amplitude levels and therefore a lower peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR). The resilience of APSK to amplifier and channel non-linearities afforded by its low PAPR have made it especially attractive for satellite communications, including DVB-S2
Digital Video Broadcasting - Satellite - Second Generation (DVB-S2) is a digital television broadcast standard that has been designed as a successor for the popular DVB-S system. It was developed in 2003 by the Digital Video Broadcasting Proje ...
.

Constellations
There are many APSK constellations. Circular constellations are the most common. There may be multiple circular constellations of the same order, for example 16-APSK could be implemented using a (1, 5, 10) constellation or a (5, 11) constellation. Increasing the number of rings decreases the bit error rate but increases the PAPR. Other APSK constellations include triangular, rectangular and hexagonal constellations. A careful design of the constellation geometry can approach the Gaussian capacity as the constellation size grows to infinity. For the regular QAM constellations, a gap of 1.56 dB is observed.H. MéricApproaching The Gaussian Channel Capacity With APSK Constellations
''IEEE Communications Letters''. The previous solution, where the constellation has a Gaussian shape, is called
constellation shaping
Constellation shaping is an energy efficiency enhancement method for digital signal modulation that improves upon amplitude and phase-shift keying (APSK) and conventional quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) by modifying the uniform distribution ...
.
References
Literature
DVB-Flexible Serially Concatenated Convolutional Turbo Codes with Near-Shannon bound performance for telemetry applications
CCSDS
The Consultative Committee for Space Data Systems (CCSDS) was founded in 1982 for governmental and quasi-governmental space agencies to discuss and develop standards for space data and information systems. Currently composed of "eleven member agenc ...
-131.2-O-1.
*
* De Gaudenzi, R., Guillén i Fàbregas, A. and Martinez, A., 2006Turbo‐coded APSK modulations design for satellite broadband communications
International journal of satellite communications and networking, 24(4), pp.261-281. Quantized radio modulation modes {{electronics-stub