13th century in the Republic of Venice on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 In
In 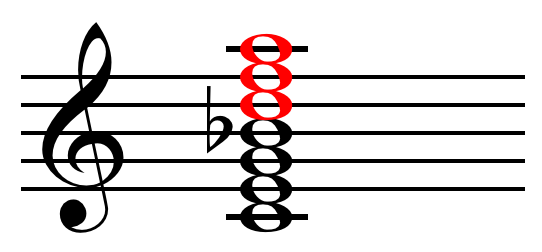 A thirteenth chord is the stacking of six (
A thirteenth chord is the stacking of six (
Most_commonly,_13th_chords_serve_a_Benward_&_Saker_(2009),_p.180._whether_they_have_the_exact_intervals_of_a_dominant_thirteenth_or_not._Typically,_a_dominant_chord_anticipating_a_major_resolution_will_feature_a_natural_13,_while_a_dominant_chord_anticipating_a_minor_resolution_will_feature_a_flat_13.Benward_&_Saker_(2009),_p.180._whether_they_have_the_exact_intervals_of_a_dominant_thirteenth_or_not._Typically,_a_dominant_chord_anticipating_a_major_resolution_will_feature_a_natural_13,_while_a_dominant_chord_anticipating_a_minor_resolution_will_feature_a_flat_13.
In_modern_pop/jazz_harmony,_after_the_dominant_thirteenth,_a_thirteenth_chord_(usually_notated_as_X13,_e.g._C13)_contains_an_implied_flatted_seventh_interval._Thus,_a_C13_consists_of_C,_E,_G,_B,_and_A._The_underlying_harmony_during_a_thirteenth_chord_is_usually_Benward_&_Saker_(2009),_p.180._whether_they_have_the_exact_intervals_of_a_dominant_thirteenth_or_not._Typically,_a_dominant_chord_anticipating_a_major_resolution_will_feature_a_natural_13,_while_a_dominant_chord_anticipating_a_minor_resolution_will_feature_a_flat_13.
In_modern_pop/jazz_harmony,_after_the_dominant_thirteenth,_a_thirteenth_chord_(usually_notated_as_X13,_e.g._C13)_contains_an_implied_flatted_seventh_interval._Thus,_a_C13_consists_of_C,_E,_G,_B,_and_A._The_underlying_harmony_during_a_thirteenth_chord_is_usually_Mixolydian_mode">Mixolydian_
Mixolydian_mode_may_refer_to_one_of_three_things:_the_name_applied_to_one_of_the_ancient_Greek_''harmoniai''_or_''tonoi'',_based_on_a_particular_octave_species_or__scale;_one_of_the_medieval_church_modes;_or_a_modern_musical_mode_or_diatonic_scal_...
_or_Lydian_dominant_scale.html" "title="Mixolydian_mode.html" "title="Four-part_harmony.html" ;"title="dominant_(music)">dominant_diatonic_function.html" "title="dominant_(music).html" ;"title="guitar">n_guitar.html" ;"title="guitar.html" ;"title="n guitar">n guitar">guitar.html" ;"title="n guitar">n guitar thirteenth chords often omit the fifth and the ninth."
 Most commonly, 13th chords serve a dominant (music)">dominant diatonic function">function
Function or functionality may refer to:
Computing
* Function key, a type of key on computer keyboards
* Function model, a structured representation of processes in a system
* Function object or functor or functionoid, a concept of object-oriente ...
Most commonly, 13th chords serve a dominant (music)">dominant diatonic function">function
Function or functionality may refer to:
Computing
* Function key, a type of key on computer keyboards
* Function model, a structured representation of processes in a system
* Function object or functor or functionoid, a concept of object-oriente ...
(V13),Benward & Saker (2009), p.180. whether they have the exact intervals of a dominant thirteenth or not. Typically, a dominant chord anticipating a major resolution will feature a natural 13, while a dominant chord anticipating a minor resolution will feature a flat 13. Since thirteenth chords contain more than four notes, in Four-part harmony">four-voice writing the root, third, seventh, and thirteenth are most often included, excluding the fifth, ninth, and eleventh . The third indicates the quality of the chord as major or minor, the seventh is important for the quality as a dominant chord, while the thirteenth is necessary in a thirteenth chord.

 In
In music
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspect ...
or music theory
Music theory is the study of the practices and possibilities of music. ''The Oxford Companion to Music'' describes three interrelated uses of the term "music theory". The first is the "rudiments", that are needed to understand music notation (ke ...
, a thirteenth is the note
Note, notes, or NOTE may refer to:
Music and entertainment
* Musical note, a pitched sound (or a symbol for a sound) in music
* ''Notes'' (album), a 1987 album by Paul Bley and Paul Motian
* ''Notes'', a common (yet unofficial) shortened version ...
thirteen scale degrees from the root
In vascular plants, the roots are the organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often below the sur ...
of a chord and also the interval between the root and the thirteenth. The interval can be also described as a compound
Compound may refer to:
Architecture and built environments
* Compound (enclosure), a cluster of buildings having a shared purpose, usually inside a fence or wall
** Compound (fortification), a version of the above fortified with defensive struc ...
sixth, spanning an octave
In music, an octave ( la, octavus: eighth) or perfect octave (sometimes called the diapason) is the interval between one musical pitch and another with double its frequency. The octave relationship is a natural phenomenon that has been refer ...
plus a sixth. The thirteenth is most commonly major or minor .
 A thirteenth chord is the stacking of six (
A thirteenth chord is the stacking of six (major
Major (commandant in certain jurisdictions) is a military rank of commissioned officer status, with corresponding ranks existing in many military forces throughout the world. When used unhyphenated and in conjunction with no other indicators ...
or minor) thirds, the last being above the 11th of an eleventh chord
In music theory, an eleventh chord is a chord that contains the tertian extension of the eleventh. Typically found in jazz, an eleventh chord also usually includes the seventh and ninth, and elements of the basic triad structure. Variants inc ...
. Thus a thirteenth chord is a tertian
In music theory, ''tertian'' ( la, tertianus, "of or concerning thirds") describes any piece, chord, counterpoint etc. constructed from the intervals of (major and minor) thirds. An interval such as that between the notes A and C encompasses ...
(built from thirds) chord containing the interval of a thirteenth, and is an extended chord
In music, extended chords are certain chords (built from thirds) or triads with notes ''extended'', or added, beyond the seventh. Ninth, eleventh, and thirteenth chords are extended chords. The thirteenth is the farthest extension diatonical ...
if it includes the ninth and/or the eleventh
In music or music theory, an eleventh is the note eleven scale degrees from the root of a chord and also the interval between the root and the eleventh. The interval can be also described as a compound fourth, spanning an octave plus a f ...
. "The jazzy thirteenth is a very versatile chord and is used in many genres." Since 13th chords tend to become unclear or confused with other chords when inverted, they are generally found in root position
The root position of a chord is the voicing of a triad, seventh chord, or ninth chord in which the root of the chord is the bass note and the other chord factors are above it. In the root position, uninverted, of a C-major triad, the bass is ...
.Benward & Saker (2009). ''Music in Theory and Practice: Volume II'', p.179. Eighth Edition. . For example, depending on voicing, a major triad with an added major sixth is usually called a sixth chord
The term ''sixth chord'' refers to two different kinds of chord, the first in classical music and the second in modern popular music.
The original meaning of the term is a ''chord in first inversion'', in other words with its third in the bass a ...
, because the sixth serves as a substitution for the major seventh, thus considered a chord tone in such context.
However, Walter Piston, writing in 1952, considered that, "a true thirteenth chord, arrived at by superposition of thirds, is a rare phenomenon even in 20th-century music." This may be due to four-part writing, instrument limitations, and voice leading and stylistic considerations. For example, "to make the chord more playable n_guitar.html"_;"title="guitar.html"_;"title="n_guitar">n_guitar">guitar.html"_;"title="n_guitar">n_guitar_thirteenth_chords_often_omit_the_fifth_and_the_ninth."
_Dominant_thirteenth
n_guitar.html"_;"title="guitar.html"_;"title="n_guitar">n_guitar">guitar.html"_;"title="n_guitar">n_guitar_thirteenth_chords_often_omit_the_fifth_and_the_ninth."
Most_commonly,_13th_chords_serve_a_ dominant_diatonic_function.html"__"title="dominant_(music).html"_;"title="guitar">n_guitar.html"_;"title="guitar.html"_;"title="n_guitar">n_guitar">guitar.html"_;"title="n_guitar">n_guitar_thirteenth_chords_often_omit_the_fifth_and_the_ninth."
Most_commonly,_13th_chords_serve_a_dominant_(music)">dominant_diatonic_function">function_
Function_or_functionality_may_refer_to:
__Computing_
*_Function_key,_a_type_of_key_on_computer_keyboards
*_Function_model,_a_structured_representation_of_processes_in_a_system
*_Function_object_or_functor_or_functionoid,_a_concept_of_object-oriente_...
_(V13),_Dominant_thirteenth
_Dominant_thirteenth
dominant_diatonic_function.html"__"title="dominant_(music).html"_;"title="guitar">n_guitar.html"_;"title="guitar.html"_;"title="n_guitar">n_guitar">guitar.html"_;"title="n_guitar">n_guitar_thirteenth_chords_often_omit_the_fifth_and_the_ninth."
Most_commonly,_13th_chords_serve_a_dominant_(music)">dominant_diatonic_function">function_
Function_or_functionality_may_refer_to:
__Computing_
*_Function_key,_a_type_of_key_on_computer_keyboards
*_Function_model,_a_structured_representation_of_processes_in_a_system
*_Function_object_or_functor_or_functionoid,_a_concept_of_object-oriente_...
_(V13),_Dominant_thirteenth
dominant_diatonic_function.html"__"title="dominant_(music).html"_;"title="guitar">n_guitar.html"_;"title="guitar.html"_;"title="n_guitar">n_guitar">guitar.html"_;"title="n_guitar">n_guitar_thirteenth_chords_often_omit_the_fifth_and_the_ninth."
Most_commonly,_13th_chords_serve_a_dominant_(music)">dominant_diatonic_function">function_
Function_or_functionality_may_refer_to:
__Computing_
*_Function_key,_a_type_of_key_on_computer_keyboards
*_Function_model,_a_structured_representation_of_processes_in_a_system
*_Function_object_or_functor_or_functionoid,_a_concept_of_object-oriente_...
_(V13),_Dominant_thirteenth
Dominant thirteenth
 Most commonly, 13th chords serve a dominant (music)">dominant diatonic function">function
Function or functionality may refer to:
Computing
* Function key, a type of key on computer keyboards
* Function model, a structured representation of processes in a system
* Function object or functor or functionoid, a concept of object-oriente ...
Most commonly, 13th chords serve a dominant (music)">dominant diatonic function">function
Function or functionality may refer to:
Computing
* Function key, a type of key on computer keyboards
* Function model, a structured representation of processes in a system
* Function object or functor or functionoid, a concept of object-oriente ... In modern pop/jazz harmony, after the dominant thirteenth, a thirteenth chord (usually notated as X13, e.g. C13) contains an implied flatted seventh interval. Thus, a C13 consists of C, E, G, B, and A. The underlying harmony during a thirteenth chord is usually Mixolydian mode">Mixolydian
Mixolydian mode may refer to one of three things: the name applied to one of the ancient Greek ''harmoniai'' or ''tonoi'', based on a particular octave species or scale; one of the medieval church modes; or a modern musical mode or diatonic scal ...
In modern pop/jazz harmony, after the dominant thirteenth, a thirteenth chord (usually notated as X13, e.g. C13) contains an implied flatted seventh interval. Thus, a C13 consists of C, E, G, B, and A. The underlying harmony during a thirteenth chord is usually Mixolydian mode">Mixolydian
Mixolydian mode may refer to one of three things: the name applied to one of the ancient Greek ''harmoniai'' or ''tonoi'', based on a particular octave species or scale; one of the medieval church modes; or a modern musical mode or diatonic scal ...or Lydian dominant scale">Lydian dominant In music, the acoustic scale, overtone scale, Lydian dominant scale, Lydian 7 scale, or the Pontikonisian Scale is a Heptatonic scale, seven-note synthetic scale, synthetic Scale (music), scale. : This differs from the major scale in having an ...
(see chord-scale system). A thirteenth chord does not imply the quality of the ninth or eleventh scale degrees. In general, what gives a thirteenth chord its characteristic sound is the dissonance between the flat seventh and the thirteenth, an interval of a
major seventh
In music from Western culture, a seventh is a musical interval encompassing seven staff positions (see Interval number for more details), and the major seventh is one of two commonly occurring sevenths. It is qualified as ''major'' because it i ...
.
 In the
In the common practice period
In European art music, the common-practice period is the era of the tonal system. Most of its features persisted from the mid-Baroque period through the Classical and Romantic periods, roughly from 1650 to 1900. There was much stylistic evoluti ...
the "most common" pitches present in V13 chord are the root, 3rd, 7th, and 13th; with the 5th, 9th, and 11th "typically omitted".Benward & Saker (2009), p.183-84. The 13th is most often in the soprano, or highest voice, and usually resolves down by a 3rd to the tonic I or i. If the V13 is followed by a I9 the 13th may resolve to the 9th.
Other thirteenth chords
 These voice leading guidelines may not be followed after the common practice period in techniques such as
These voice leading guidelines may not be followed after the common practice period in techniques such as parallel harmony
In music, parallel harmony, also known as harmonic parallelism, harmonic planing or parallel voice leading, is the parallel movement of two or more melodies (see voice leading).
Illustrative example
Lines with parallel harmony can be viewed as ...
and in the following example:
13th chords may less often be built on degrees other than the dominant, such as the tonic or subdominant.
While the dominant thirteenth is the most common thirteenth chord, the major thirteenth is also fairly common.Hal Leonard Corp. (2003). ''Picture Chord Encyclopedia: Photos, Diagrams and Music Notation for Over 1,600 Keyboard Chords'', p.10. . A major thirteenth chord (containing a major seventh) will nearly always feature a chromatically raised eleventh (C E G B D F A) (see Lydian mode), except for cases when the eleventh is omitted altogether. "It is customary to omit the eleventh on dominant or major thirteenth chords because the eleventh conflicts with the third," in these chords by a semitone.
Inversions
Generally found in root position, theinversion
Inversion or inversions may refer to:
Arts
* , a French gay magazine (1924/1925)
* ''Inversion'' (artwork), a 2005 temporary sculpture in Houston, Texas
* Inversion (music), a term with various meanings in music theory and musical set theory
* ...
of a complete thirteenth chord including ''all'' seven notes, itself, "a rare phenomenon", is a theoretical impossibility since a new thirteenth chord with a different root is produced, for example Cmaj13 (C-E-G-B-D-F-A) becomes Em139 (E-G-B-D-F-A-C) then G13 (G-B-D-F-A-C-E), and so on, when inverted.
Gallery
Given the number of notes that may be included, there are a great variety of thirteenth chords. The following chords are notated belowlead sheet
A lead sheet or fake sheet is a form of musical notation that specifies the essential elements of a popular song: the melody, lyrics and harmony. The melody is written in modern Western music notation, the lyric is written as text below the st ...
symbols:
dissonant
In music, consonance and dissonance are categorizations of simultaneous or successive Sound, sounds. Within the Western tradition, some listeners associate consonance with sweetness, pleasantness, and acceptability, and dissonance with harshness ...
, seemingly secundal
In music or music theory, secundal is the quality of a chord made from seconds, and anything related to things constructed from seconds such as counterpoint. Secundal chords are often called tone clusters more generally, especially when non-di ...
tone cluster.
Image:Dominant thirteenth chord on C m13.png, A dominant thirteenth in F minor.

See also
*Jazz chord
Jazz chords are chords, chord voicings and chord symbols that jazz musicians commonly use in composition, improvisation, and harmony. In jazz chords and theory, most triads that appear in lead sheets or fake books can have sevenths added to the ...
*Harmonic planing
In music, parallel harmony, also known as harmonic parallelism, harmonic planing or parallel voice leading, is the parallel movement of two or more melodies (see voice leading).
Illustrative example
Lines with parallel harmony can be viewed as ...
*Ladder of thirds
A modal frame in music is "a number of types permeating and unifying African, European, and American song" and melody., quoted in Richard Middleton (1990/2002). ''Studying Popular Music'', p. 203. Philadelphia: Open University Press. . It may al ...
*Mystic chord
In music, the mystic chord or Prometheus chord is a six-note synthetic chord and its associated scale, or pitch collection; which loosely serves as the harmonic and melodic basis for some of the later pieces by Russian composer Alexander Scriabi ...
References
{{Intervals Chord factors Extended chords Sixths (music) Compound intervals