11 September 2001 attacks on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The September 11 attacks, commonly known as 9/11, were four coordinated
 Bin Laden orchestrated the attacks. He initially denied involvement, but later recanted his false statements.
Bin Laden orchestrated the attacks. He initially denied involvement, but later recanted his false statements.
 Journalist
Journalist
 The attacks were conceived by Khalid Sheikh Mohammed, who first presented it to
The attacks were conceived by Khalid Sheikh Mohammed, who first presented it to  Bin Laden provided leadership and financial support and was involved in selecting participants. He initially selected Nawaf al-Hazmi and Khalid al-Mihdhar, both experienced jihadists who had fought in
Bin Laden provided leadership and financial support and was involved in selecting participants. He initially selected Nawaf al-Hazmi and Khalid al-Mihdhar, both experienced jihadists who had fought in
 Early on the morning of September 11, 2001,
Early on the morning of September 11, 2001,
† Excluding hijackers
§ Including emergency workers
‡ Including hijackers
 At 7:59 a.m., American Airlines Flight 11 took off from Logan International Airport in Boston. Fifteen minutes into the flight, five hijackers armed with boxcutters took over the plane, injuring at least three people (and possibly killing one) before forcing their way into the cockpit. The terrorists also displayed an apparent explosive device in order to frighten the hostages into submission, while additionally spraying
At 7:59 a.m., American Airlines Flight 11 took off from Logan International Airport in Boston. Fifteen minutes into the flight, five hijackers armed with boxcutters took over the plane, injuring at least three people (and possibly killing one) before forcing their way into the cockpit. The terrorists also displayed an apparent explosive device in order to frighten the hostages into submission, while additionally spraying
 In Arlington County, Virginia, 125 Pentagon workers died when Flight 77 crashed into the building's western side. Seventy were civilians and 55 were military personnel, many of whom worked for the United States Army or the United States Navy. The Army lost 47 civilian employees; six civilian contractors; and 22 soldiers, while the Navy lost six civilian employees; three civilian contractors; and 33 sailors. Seven Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA) civilian employees died, and one
In Arlington County, Virginia, 125 Pentagon workers died when Flight 77 crashed into the building's western side. Seventy were civilians and 55 were military personnel, many of whom worked for the United States Army or the United States Navy. The Army lost 47 civilian employees; six civilian contractors; and 22 soldiers, while the Navy lost six civilian employees; three civilian contractors; and 33 sailors. Seven Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA) civilian employees died, and one
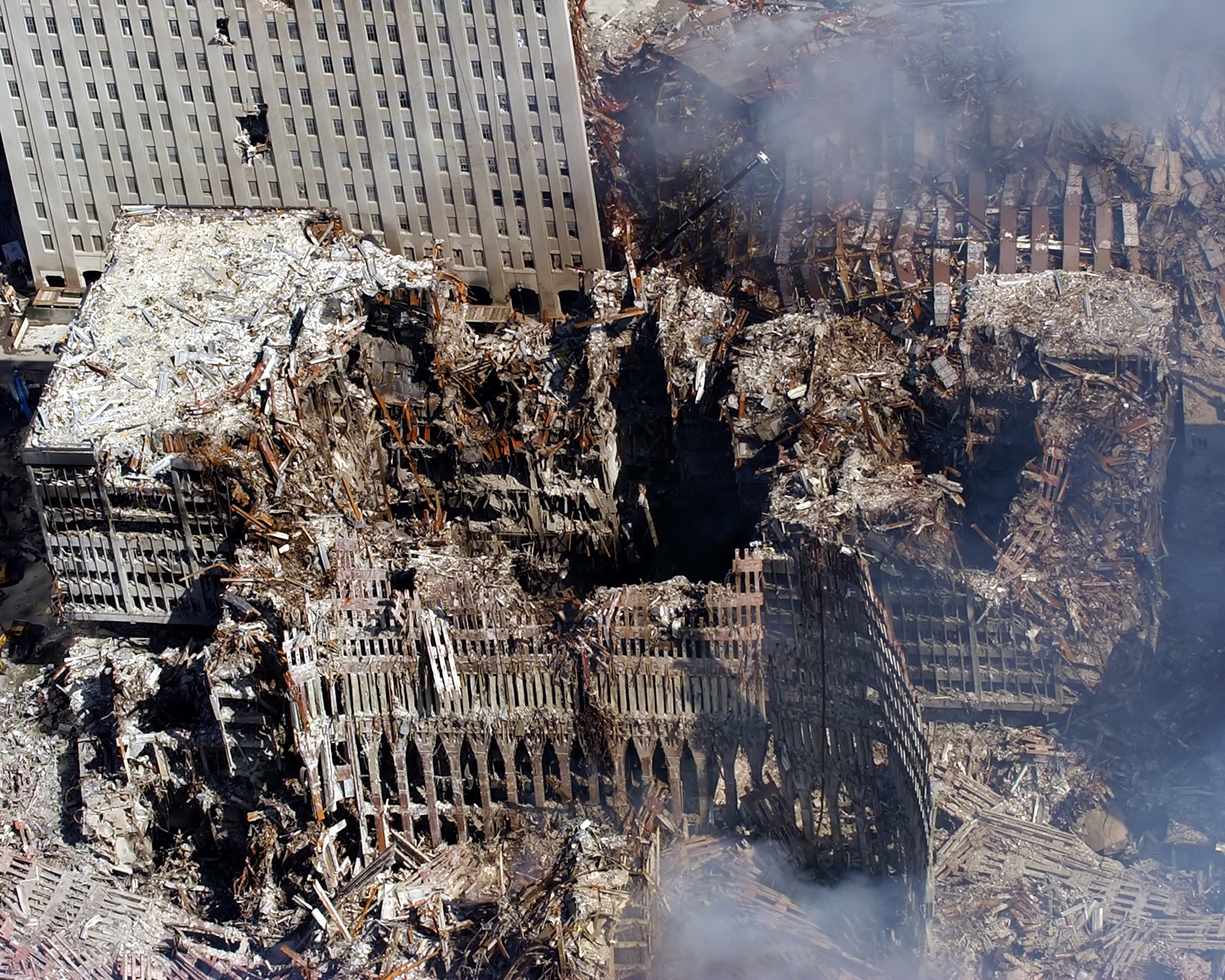
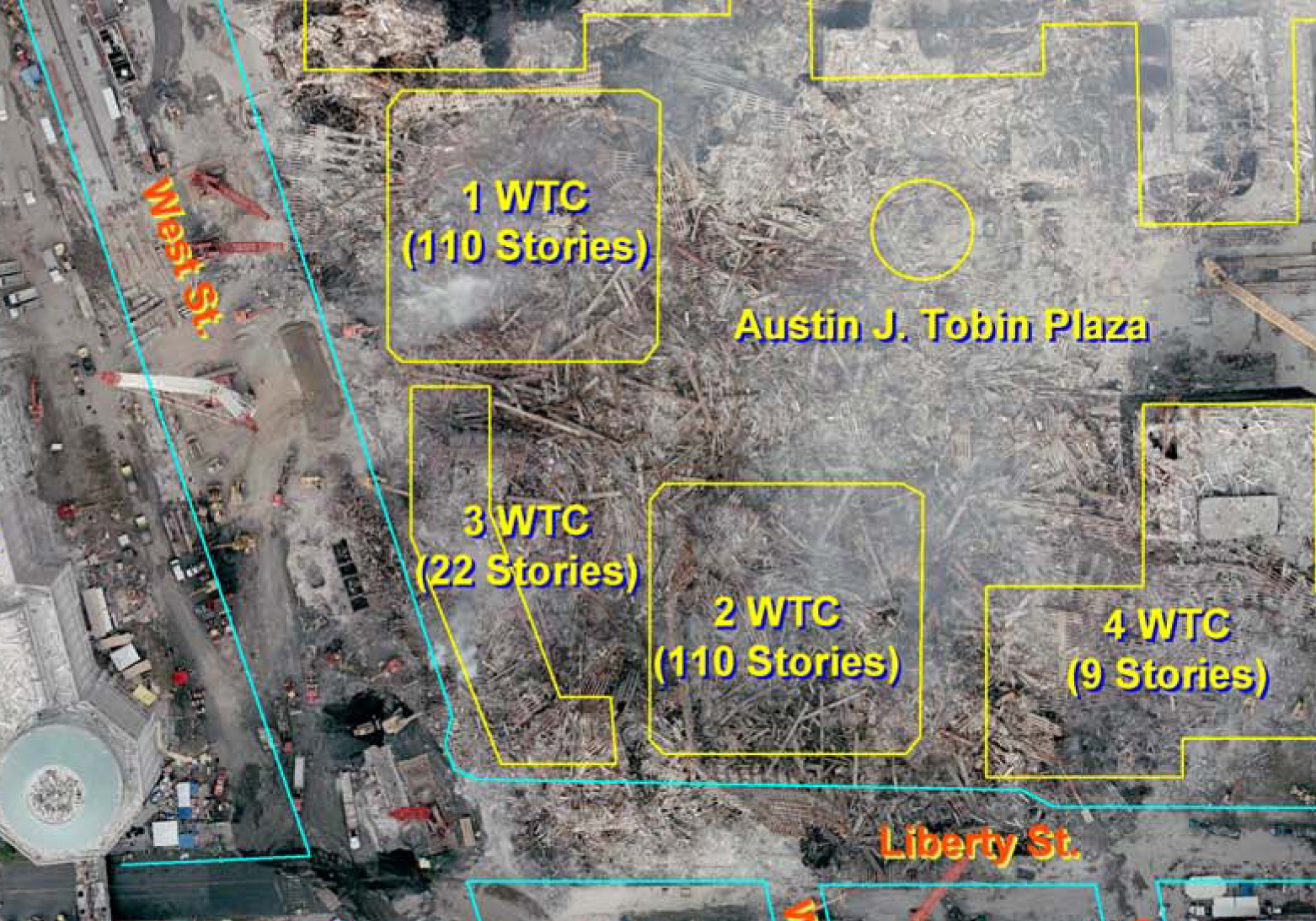

 Along with the 110-floor Twin Towers, numerous other buildings at the World Trade Center site were destroyed or badly damaged, including WTC buildings 3through7 and St. Nicholas Greek Orthodox Church. The North Tower, South Tower, the Marriott Hotel (3WTC), and 7WTC were destroyed. The U.S. Customs House ( 6 World Trade Center), 4World Trade Center, 5 World Trade Center, and both pedestrian bridges connecting buildings were severely damaged. The Deutsche Bank Building (still popularly referred to as the Bankers Trust Building) on 130 Liberty Street was partially damaged and demolished some years later, starting in 2007.Summers and Swan (2011), p. 75. The two buildings of the
Along with the 110-floor Twin Towers, numerous other buildings at the World Trade Center site were destroyed or badly damaged, including WTC buildings 3through7 and St. Nicholas Greek Orthodox Church. The North Tower, South Tower, the Marriott Hotel (3WTC), and 7WTC were destroyed. The U.S. Customs House ( 6 World Trade Center), 4World Trade Center, 5 World Trade Center, and both pedestrian bridges connecting buildings were severely damaged. The Deutsche Bank Building (still popularly referred to as the Bankers Trust Building) on 130 Liberty Street was partially damaged and demolished some years later, starting in 2007.Summers and Swan (2011), p. 75. The two buildings of the
suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Mental disorders (including depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, personality disorders, anxiety disorders), physical disorders (such as chronic fatigue syndrome), and s ...
terrorist attacks carried out by al-Qaeda
Al-Qaeda (; , ) is an Islamic extremism, Islamic extremist organization composed of Salafist jihadists. Its members are mostly composed of Arab, Arabs, but also include other peoples. Al-Qaeda has mounted attacks on civilian and military ta ...
against the United States on Tuesday, September 11, 2001. That morning, nineteen terrorists hijacked
Hijacking may refer to:
Common usage
Computing and technology
* Bluejacking, the unsolicited transmission of data via Bluetooth
* Brandjacking, the unauthorized use of a company's brand
* Browser hijacking
* Clickjacking (including ''like ...
four commercial airliners scheduled to travel from the Northeastern United States
The Northeastern United States, also referred to as the Northeast, the East Coast, or the American Northeast, is a geographic region of the United States. It is located on the Atlantic coast of North America, with Canada to its north, the Southe ...
to California. The hijackers crashed the first two planes into the Twin Towers of the World Trade Center in New York City, and the third plane into the Pentagon (the headquarters of the United States military) in Arlington County, Virginia. The fourth plane was intended to hit a federal government
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-governin ...
building in Washington, D.C., but crashed in a field following a passenger revolt. The attacks killed nearly 3,000 people and instigated the war on terror.
The first impact was that of American Airlines Flight 11. It was crashed into the North Tower of the World Trade Center complex in Lower Manhattan
Lower Manhattan (also known as Downtown Manhattan or Downtown New York) is the southernmost part of Manhattan, the central borough for business, culture, and government in New York City, which is the most populated city in the United States with ...
at 8:46 a.m. Seventeen minutes later, at 9:03, the World Trade Center’s South Tower was hit by United Airlines Flight 175. Both 110-story skyscrapers collapsed within an hour and forty-two minutes, precipitating the collapse of other World Trade Center structures including 7 World Trade Center
7 World Trade Center (7 WTC, WTC-7, or Tower 7) refers to two buildings that have existed at the same location within the World Trade Center site in Lower Manhattan, New York City. The original structure, part of the original World Trade Cent ...
, and damaging nearby buildings. A third flight, American Airlines Flight 77
American Airlines Flight 77 was a scheduled American Airlines domestic transcontinental passenger flight from Washington Dulles International Airport in Dulles, Virginia, to Los Angeles International Airport in Los Angeles, California. The Boe ...
, crashed into the west side of the Pentagon in Arlington County, Virginia, at 9:37 a.m., causing a partial collapse. The fourth and final flight, United Airlines Flight 93, flew in the direction of Washington, D.C. Alerted of the previous attacks, the plane's passengers fought back in an attempt to gain control of the aircraft, but the hijackers ultimately crashed the plane in a field in Stonycreek Township, Pennsylvania, near Shanksville at 10:03 a.m. Investigators determined that Flight 93 was targeting either the United States Capitol or the White House.
Within hours of the attacks, the Central Intelligence Agency determined that al-Qaeda was responsible. The United States formally responded by launching the war on terror and invading Afghanistan to depose the Taliban, which had not complied with U.S. demands to expel al-Qaeda from Afghanistan and extradite its leader, Osama bin Laden
Osama bin Mohammed bin Awad bin Laden (10 March 1957 – 2 May 2011) was a Saudi-born extremist militant who founded al-Qaeda and served as its leader from 1988 until Killing of Osama bin Laden, his death in 2011. Ideologically a Pan-Islamism ...
. The U.S.'s invocation of Article 5 of NATO—its only usage to date—called upon allies to fight al-Qaeda. As U.S. and NATO ground forces swept through Afghanistan, bin Laden went into hiding. Although bin Laden denied any involvement, in 2004 he formally claimed responsibility for the attacks. Al-Qaeda's cited motivations included U.S. support of Israel, the presence of U.S. troops in Saudi Arabia, and sanctions against Iraq. After evading capture for almost a decade, bin Laden was killed by the U.S. military on May 2, 2011.
The attacks resulted in 2,977 non-hijacker fatalities, an indeterminate number of injuries, and substantial long-term health consequences, in addition to at least $10billion in infrastructure and property damage. It remains the deadliest terrorist attack in human history and the single deadliest incident for firefighters and law enforcement officers in U.S. history, with 343 and 72 killed, respectively. The destruction of the World Trade Center and its environs seriously harmed the New York City economy and induced global market shocks. Many other countries strengthened anti-terrorism legislation and expanded their powers of law enforcement and intelligence agencies. Cleanup of the World Trade Center site (colloquially "Ground Zero") took eight months and was completed in May 2002, while the Pentagon was repaired within a year. After delays in the design of a replacement complex, the One World Trade Center began construction in November 2006 and opened in November 2014. Memorials to the attacks include the National September 11 Memorial & Museum in New York City, the Pentagon Memorial in Arlington County, and the Flight 93 National Memorial at the Pennsylvania crash site.
Background
Al-Qaeda
The origins of al-Qaeda can be traced to 1979 when the Soviet Union invaded Afghanistan. Osama bin Laden traveled to the central Asian country to volunteer, viewing the war as a holy cause to help fellow Muslims (in Afghanistan) defeatCommunist
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, a s ...
invaders (the Soviets). Bin Laden organized fellow Arab mujahideen
''Mujahideen'', or ''Mujahidin'' ( ar, مُجَاهِدِين, mujāhidīn), is the plural form of ''mujahid'' ( ar, مجاهد, mujāhid, strugglers or strivers or justice, right conduct, Godly rule, etc. doers of jihād), an Arabic term th ...
(the " Afghan Arabs") to resist the Soviets until that country's exit from Afghanistan in 1989. The U.S. Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) funneled several billion dollars worth of weapons to the indigenous Afghan mujahideen resistance, a portion of which bled to the Arab volunteers. However, no direct U.S. aid to bin Laden or any of his affiliates has ever been established.
In 1996, bin Laden issued his first '' fatwā'', calling for American soldiers to leave Saudi Arabia. In a second ''fatwā'' in 1998, bin Laden outlined his objections to American foreign policy with respect to Israel, as well as the continued presence of American troops in Saudi Arabia after the Gulf War. Bin Laden used Islamic texts to exhort Muslims to attack Americans until the stated grievances were reversed. Muslim legal scholars "have throughout Islamic history unanimously agreed that the jihad
Jihad (; ar, جهاد, jihād ) is an Arabic word which literally means "striving" or "struggling", especially with a praiseworthy aim. In an Islamic context, it can refer to almost any effort to make personal and social life conform with Go ...
is an individual duty if the enemy destroys the Muslim countries", according to bin Laden.
Osama bin Laden
 Bin Laden orchestrated the attacks. He initially denied involvement, but later recanted his false statements.
Bin Laden orchestrated the attacks. He initially denied involvement, but later recanted his false statements. Al Jazeera
Al Jazeera ( ar, الجزيرة, translit-std=DIN, translit=al-jazīrah, , "The Island") is a state-owned Arabic-language international radio and TV broadcaster of Qatar. It is based in Doha and operated by the media conglomerate Al Jazeera ...
broadcast a statement by him on September 16, 2001: "I stress that I have not carried out this act, which appears to have been carried out by individuals with their own motivation." In November 2001, U.S. forces recovered a videotape from a destroyed house in Jalalabad, Afghanistan. In the video, bin Laden is seen talking to Khaled al-Harbi
Khaled bin Ouda bin Mohammed al-Harbi, ( ar, خالد بن عودة بن محمد الحربي, ''Khālid bin ‘Ūdah bin Muḥammad al-Ḥarbī'') (c.1963 - present) is a Saudi national who was associated with Osama bin Laden's mujahadeen grou ...
and admits foreknowledge of the attacks. On December 27, 2001, a second bin Laden video was released. In the video, he said:
but he stopped short of admitting responsibility for the attacks.
Shortly before the U.S. presidential election in 2004, bin Laden used a taped statement to publicly acknowledge al-Qaeda's involvement in the attacks on the United States. He admitted his direct link to the attacks and said they were carried out because...
Bin Laden said he had personally directed his followers to attack the World Trade Center and the Pentagon. Another video obtained by Al Jazeera in September 2006 shows bin Laden with one of the attacks' chief planners, Ramzi bin al-Shibh, as well as two hijackers, Hamza al-Ghamdi and Wail al-Shehri, as they made preparations for the attacks. The U.S. never formally indicted bin Laden for the 9/11 attacks, but he was on the FBI's Most Wanted List for the bombings of the U.S. Embassies in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania
Dar es Salaam (; from ar, دَار السَّلَام, Dâr es-Selâm, lit=Abode of Peace) or commonly known as Dar, is the largest city and financial hub of Tanzania. It is also the capital of Dar es Salaam Region. With a population of over s ...
, and Nairobi, Kenya. After a 10-year manhunt, U.S. President Barack Obama announced that bin Laden was killed by American special forces in his compound in Abbottabad
Abbottabad (; Urdu, Punjabi language(HINDKO dialect) آباد, translit=aibṭabād, ) is the capital city of Abbottabad District in the Hazara region of eastern Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. It is the 40th largest city in Pakistan and fourth ...
, Pakistan, on May 1, 2011.
Khalid Sheikh Mohammed
 Journalist
Journalist Yosri Fouda
Yosri Fouda ( ar, يسري فودة ', ), is an Egyptian investigative reporter, author, and television host. He established Al Jazeera's office in London and was one of the star figures in the channel until he resigned in 2009. Fouda also worked ...
of the Arabic television channel Al Jazeera
Al Jazeera ( ar, الجزيرة, translit-std=DIN, translit=al-jazīrah, , "The Island") is a state-owned Arabic-language international radio and TV broadcaster of Qatar. It is based in Doha and operated by the media conglomerate Al Jazeera ...
reported that in April 2002 al-Qaeda member Khalid Sheikh Mohammed admitted his involvement in the attacks, along with Ramzi bin al-Shibh. The 2004 9/11 Commission Report determined that the animosity towards the United States felt by Mohammed, the principal architect of the 9/11 attacks, stemmed from his "violent disagreement with U.S. foreign policy favoring Israel".9/11 Commission Report (2004), p. 147. Mohammed was also an adviser and financier of the 1993 World Trade Center bombing
The 1993 World Trade Center bombing was a terrorist attack on the World Trade Center in New York City, U.S., carried out on February 26, 1993, when a van bomb detonated below the North Tower of the complex. The urea nitrate–hydrogen gas en ...
and the uncle of Ramzi Yousef, the lead bomber in that attack.
Mohammed was arrested on March 1, 2003, in Rawalpindi
Rawalpindi ( or ; Urdu, ) is a city in the Punjab province of Pakistan. It is the fourth largest city in Pakistan after Karachi, Lahore and Faisalabad, and third largest in Punjab after Lahore and Faisalabad. Rawalpindi is next to Pakistan's ...
, Pakistan, by Pakistani security officials working with the CIA. He was then held at multiple CIA secret prisons
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian intelligence agency, foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gat ...
and Guantanamo Bay where he was interrogated and tortured with methods including waterboarding. During U.S. hearings at Guantanamo Bay in March 2007, Mohammed again confessed his responsibility for the attacks, stating he "was responsible for the 9/11 operation from A to Z" and that his statement was not made under duress.
A letter presented by Mohammed's lawyers in the U.S. District Court, Manhattan, on July 26, 2019, indicated that he was interested in testifying about Saudi Arabia's role in the 9/11 attacks and helping the victims and families of the victims of 9/11 in exchange for the United States not seeking the death penalty against him. James Kreindler, one of the lawyers for the victims, raised question over the usefulness of his testimony.
Other al-Qaeda members
In "Substitution for Testimony of Khalid Sheikh Mohammed" from the trial of Zacarias Moussaoui, five people are identified as having been completely aware of the operation's details. They are bin Laden; Khalid Sheikh Mohammed; Ramzi bin al-Shibh;Abu Turab al-Urduni Abu Turab al-Urduni () was a Jordanian jihadist. He was the son-in-law of Ayman al-Zawahiri,9/11 Commission9/11 Report: Notes to Chapter 7. August 2004 who has been described by the United States government as one of five individuals who were aware ...
; and Mohammed Atef
Mohammed Atef ( ar, محمد عاطف, ; born Sobhi Mohammed Abu Sitta Al-Gohary, also known as Abu Hafs al-Masri) was the military chief of al-Qaeda, and was considered one of Osama bin Laden's two deputies, the other being Ayman Al Zawahiri, ...
. To date, only peripheral figures have been tried or convicted for the attacks.
On September 26, 2005, the Spanish high court sentenced Abu Dahdah
Imad Eddin Barakat Yarkas alias Abu Dahdah ( ar, أبو الدحداح 'Abū ad-Daḥdāh) is a Syrian-born Spaniard sentenced to a 27-year prison term in Spain for his part in the September 11, 2001, attacks and for his membership in the banned ...
to 27 years in prison for conspiracy on the 9/11 attacks and being a member of the terrorist organization al-Qaeda. At the same time, another 17 al-Qaeda members were sentenced to penalties of between six and eleven years. On February 16, 2006, the Spanish Supreme Court reduced Abu Dahdah's penalty to 12 years because it considered that his participation in the conspiracy was not proven.
Also in 2006 Moussaoui, who some originally suspected might have been the assigned twentieth hijacker, was convicted for the lesser role of conspiracy to commit acts of terrorism and air piracy. He was sentenced to life in prison without parole in the United States. Mounir el-Motassadeq
Mounir el-Motassadeq (Arabic: منير المتصدق; born April 3, 1974) was convicted by a German court of being a member of al-Qaeda and of assisting some of the hijackers in the September 11 attacks. He was initially convicted of involvemen ...
, an associate of the Hamburg-based hijackers, served 15 years in Germany for his role in helping the hijackers prepare for the attacks. He was released in October 2018 and deported to Morocco.
The Hamburg cell in Germany included radical Islamists who eventually came to be key operatives in the 9/11 attacks. Mohamed Atta; Marwan al-Shehhi; Ziad Jarrah; Ramzi bin al-Shibh; and Said Bahaji were all members of al-Qaeda's Hamburg cell.
Motives
Osama bin Laden's declaration of a holy war against the United States, and a 1998 ''fatwā'' signed by bin Laden and others, calling for the killing of Americans, are seen by investigators as evidence of his motivation. In bin Laden's November 2002 "Letter to America", he explicitly stated that al-Qaeda's motives for their attacks include: * U.S. support of Israel*Mearsheimer (2007), p. 67. *Kushner (2003), p. 389. *Murdico (2003), p. 64. *Kelley (2006), p. 207. *Ibrahim (2007), p. 276. * * Support for the "attacks against Muslims" in Somalia * Support of Philippines against Muslims in the Moro conflict * Support for Israeli "aggression" against Muslims in Lebanon * Support of Russian "atrocities against Muslims" inChechnya
Chechnya ( rus, Чечня́, Chechnyá, p=tɕɪtɕˈnʲa; ce, Нохчийчоь, Noxçiyçö), officially the Chechen Republic,; ce, Нохчийн Республика, Noxçiyn Respublika is a republic of Russia. It is situated in the ...
* Pro-American governments in the Middle East (who "act as your agents") being against Muslim interests
* Support of Indian "oppression against Muslims" in Kashmir
Kashmir () is the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term "Kashmir" denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal Range. Today, the term encompas ...
* The presence of U.S. troops in Saudi Arabia
* The sanctions against Iraq*
*
After the attacks, bin Laden and Ayman al-Zawahiri
Ayman Mohammed Rabie al-Zawahiri (June 19, 1951 – July 31, 2022) was an Egyptian-born terrorist and physician who served as the second emir of al-Qaeda from June 16, 2011, until his death.
Al-Zawahiri graduated from Cairo University with ...
released additional videotapes and audio recordings, some of which repeated those reasons for the attacks. Two particularly important publications were bin Laden's 2002 "Letter to America" and a 2004 videotape by bin Laden.
Bin Laden interpreted Muhammad as having banned the "permanent presence of infidels in Arabia". In 1996, bin Laden issued a '' fatwā'' calling for American troops to leave Saudi Arabia. In 1998, al-Qaeda wrote "for over seven years the United States has been occupying the lands of Islam in the holiest of places, the Arabian Peninsula, plundering its riches, dictating to its rulers, humiliating its people, terrorizing its neighbors, and turning its bases in the Peninsula into a spearhead through which to fight the neighboring Muslim peoples."
In a December 1999 interview, bin Laden said he felt that Americans were "too near to Mecca", and considered this a provocation to the entire Muslim world. One analysis of suicide terrorism suggested that without U.S. troops in Saudi Arabia, al-Qaeda likely would not have been able to get people to commit to suicide missions.
In the 1998 ''fatwā'', al-Qaeda identified the Iraq sanctions as a reason to kill Americans, condemning the "protracted blockade" among other actions that constitute a declaration of war against "Allah, his messenger, and Muslims." The ''fatwā'' declared that "the ruling to kill the Americans and their alliescivilians and militaryis an individual duty for every Muslim who can do it in any country in which it is possible to do it, in order to liberate the al-Aqsa Mosque
Al-Aqsa Mosque (, ), also known as Jami' Al-Aqsa () or as the Qibli Mosque ( ar, المصلى القبلي, translit=al-Muṣallā al-Qiblī, label=none), and also is a congregational mosque located in the Old City of Jerusalem. It is situa ...
and the holy mosque of Mecca from their grip, and in order for their he Americans'
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (pronoun), an English pronoun
* He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana へ
* He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets
* He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' in ...
armies to move out of all the lands of Islam, defeated and unable to threaten any Muslim."
In 2004, Bin Laden claimed that the idea of destroying the towers had first occurred to him in 1982, when he witnessed Israel's bombardment of high-rise apartment buildings during the 1982 Lebanon War
The 1982 Lebanon War, dubbed Operation Peace for Galilee ( he, מבצע שלום הגליל, or מבצע של"ג ''Mivtsa Shlom HaGalil'' or ''Mivtsa Sheleg'') by the Israeli government, later known in Israel as the Lebanon War or the First L ...
. Some analysts, including political scientists John Mearsheimer and Stephen Walt
Stephen Martin Walt (born July 2, 1955) is the Robert and Renee Belfer Professor of International relations at the Harvard Kennedy School at Harvard University and a political scientist.
A member of the realist school of international relations ...
, also claimed that U.S. support of Israel was one motive for the attacks. In 2004 and 2010, bin Laden again connected the September 11 attacks with U.S. support of Israel, although most of the letter expressed bin Laden's disdain for President Bush and bin Laden's hope to "destroy and bankrupt" the U.S.
Other motives have been suggested in addition to those stated by bin Laden and al-Qaeda. Some authors suggested the "humiliation" that resulted from the Islamic world falling behind the Western worldthis discrepancy was rendered especially visible by globalization and a desire to provoke the U.S. into a broader war against the Islamic world in the hope of motivating more allies to support al-Qaeda. Similarly, others have argued that 9/11 was a strategic move with the objective of provoking America into a war that would incite a pan-Islamic revolution.
Documents seized during the 2011 operation that killed bin Laden included a few notes handwritten by bin Laden in September 2002 with the heading "The Birth of the Idea of September 11". In these notes he describes how he was inspired by the crash of EgyptAir Flight 990 on October 31, 1999, which was deliberately crashed by co-pilot Gameel Al-Batouti. "This is how the idea of 9/11 was conceived and developed in my head, and that is when we began the planning" bin Laden continued, adding that no one but Abu Hafs Abu Hafs may refer to:
*Abu Hafs Umar al-Nasafi, a Muslim scholar of 11th/12th century
*Mohammed Atef (Abu Hafs al-Masri), past military chief of al-Qaeda
*Abu Hafs Umar al-Iqritishi, early ninth-century Andalusian pirate and founder of the Emirate ...
and Abu al-Khair knew about it at the time. The 9/11 Commission Report identified Khalid Sheikh Mohammed as the architect of 9/11, but he is not mentioned in bin Laden's notes.
Planning
Osama bin Laden
Osama bin Mohammed bin Awad bin Laden (10 March 1957 – 2 May 2011) was a Saudi-born extremist militant who founded al-Qaeda and served as its leader from 1988 until Killing of Osama bin Laden, his death in 2011. Ideologically a Pan-Islamism ...
in 1996. At that time, bin Laden and al-Qaeda were in a period of transition, having just relocated back to Afghanistan from Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic t ...
.9/11 Commission Report (2004), Chapter 5, pp. ?? The 1998 African embassy bombings and bin Laden's February 1998 fatwā marked a turning point of al-Qaeda's terrorist operation, as bin Laden became intent on attacking the United States.
In late 1998 or early 1999, bin Laden gave approval for Mohammed to go forward with organizing the plot. Mohammed, bin Laden, and Mohammed Atef
Mohammed Atef ( ar, محمد عاطف, ; born Sobhi Mohammed Abu Sitta Al-Gohary, also known as Abu Hafs al-Masri) was the military chief of al-Qaeda, and was considered one of Osama bin Laden's two deputies, the other being Ayman Al Zawahiri, ...
, the deputy of bin Laden, held a series of meetings in early 1999. Atef provided operational support, including target selections and helping arrange travel for the hijackers. Bin Laden overruled Mohammed, rejecting potential targets such as the U.S. Bank Tower in Los Angeles for lack of time.
Bosnia
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and He ...
. Hazmi and Mihdhar arrived in the United States in mid-January 2000. In early 2000, Hazmi and Mihdhar took flying lessons in San Diego, California, but both spoke little English; performed poorly in flying lessons; and eventually served as secondary ("muscle") hijackers.
In late 1999, a group of men from Hamburg, Germany, arrived in Afghanistan. The group included Mohamed Atta; Marwan al-Shehhi; Ziad Jarrah; and Ramzi bin al-Shibh. Bin Laden selected these men because they were educated, could speak English, and had experience living in the West. New recruits were routinely screened for special skills and al-Qaeda leaders consequently discovered that Hani Hanjour already had a commercial pilot's license. Mohammed later said that he helped the hijackers blend in by teaching them how to order food in restaurants and dress in Western clothing.
Hanjour arrived in San Diego on December 8, 2000, joining Hazmi. They soon left for Arizona, where Hanjour took refresher training. Marwan al-Shehhi arrived at the end of May 2000, while Atta arrived on June 3, 2000, and Jarrah arrived on June 27, 2000. Bin al-Shibh applied several times for a visa to the United States, but as a Yemeni, he was rejected out of concerns he would overstay his visa. Bin al-Shibh stayed in Hamburg, providing coordination between Atta and Mohammed. The three Hamburg cell members all took pilot training in South Florida at Huffman Aviation.
In the spring of 2001, the secondary hijackers began arriving in the United States. In July 2001, Atta met with bin al-Shibh in Spain, where they coordinated details of the plot, including final target selection. Bin al-Shibh also passed along bin Laden's wish for the attacks to be carried out as soon as possible. Some of the hijackers received passports from corrupt Saudi officials who were family members or used fraudulent passports to gain entry.
There have been a few theories that 9/11 was selected by the hijackers as the date of the attack because of its resemblance to 9-1-1
, usually written 911, is an emergency telephone number for the United States, Canada, Mexico, Panama, Palau, Argentina, Philippines, Jordan, as well as the North American Numbering Plan (NANP), one of eight N11 codes. Like other emergency nu ...
, the phone number used to report emergencies in the United States. However, Lawrence Wright wrote that the hijackers chose the date when John III Sobieski
John III Sobieski ( pl, Jan III Sobieski; lt, Jonas III Sobieskis; la, Ioannes III Sobiscius; 17 August 1629 – 17 June 1696) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1674 until his death in 1696.
Born into Polish nobility, Sobie ...
, the King of Poland
Poland was ruled at various times either by dukes and princes (10th to 14th centuries) or by kings (11th to 18th centuries). During the latter period, a tradition of free election of monarchs made it a uniquely electable position in Europe (16t ...
and Grand Duke of Lithuania, began the battle which turned back the Ottoman Empire's Muslim armies that were attempting to capture Vienna on 11 September 1683. During 1683, Vienna was the seat of the Holy Roman Empire and Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy (german: Habsburgermonarchie, ), also known as the Danubian monarchy (german: Donaumonarchie, ), or Habsburg Empire (german: Habsburgerreich, ), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities ...
, both major powers in Europe at the time. For Osama bin Laden, this was a date when the West gained some dominance over Islam, and by attacking on this date, he hoped to make a step in Islam "winning" the war for worldwide power and influence.
Prior intelligence
In late 1999, al-Qaeda associate Walid bin Attash ("Khallad") contacted Mihdhar, telling him to meet him in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia; Hazmi and Abu Bara al Yemeni would also be in attendance. The NSA intercepted a telephone call mentioning the meeting, Mihdhar, and the name "Nawaf" (Hazmi). While the agency feared "Something nefarious might be afoot", it took no further action. The CIA had already been alerted by Saudi intelligence about the status of Mihdhar and Hazmi as al-Qaeda members, and a CIA team broke into Mihdhar's Dubai hotel room and discovered that Mihdhar had a U.S. visa. WhileAlec Station
The Bin Laden Issue Station, also known as Alec Station, was a standalone unit of the Central Intelligence Agency in operation from 1996 to 2005 dedicated to tracking Osama bin Laden and his associates, both before and after the 9/11 attacks. It ...
alerted intelligence agencies worldwide about this fact, it did not share this information with the FBI. The Malaysian Special Branch observed the January 5, 2000, meeting of the two al-Qaeda members and informed the CIA that Mihdhar, Hazmi, and Khallad were flying to Bangkok, but the CIA never notified other agencies of this, nor did it ask the State Department
The United States Department of State (DOS), or State Department, is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the Federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government responsible for the country's fore ...
to put Mihdhar on its watchlist. An FBI liaison to Alec Station asked permission to inform the FBI of the meeting but was told: "This is not a matter for the FBI."
By late June, senior counter-terrorism official Richard Clarke and CIA director George Tenet
George John Tenet (born January 5, 1953) is an American intelligence official and academic who served as the Director of Central Intelligence (DCI) for the United States Central Intelligence Agency, as well as a Distinguished Professor in the P ...
were "convinced that a major series of attacks was about to come", although the CIA believed the attacks would likely occur in Saudi Arabia or Israel. In early July, Clarke put domestic agencies on "full alert", telling them "Something really spectacular is going to happen here. soon." He asked the FBI and the State Department to alert the embassies and police departments, and the Defense Department to go to "Threat Condition Delta". Clarke later wrote: "Somewhere in CIA there was information that two known al Qaeda terrorists had come into the United States. Somewhere in FBI, there was information that strange things had been going on at flight schools in the United States... They had specific information about individual terrorists from which one could have deduced what was about to happen. None of that information got to me or the White House."
On July 13, Tom Wilshire, a CIA agent assigned to the FBI's international terrorism division, emailed his superiors at the CIA's Counterterrorism Center (CTC) requesting permission to inform the FBI that Hazmi was in the country and that Mihdhar had a U.S. visa. The CIA never responded.
The same day in July, Margarette Gillespie, an FBI analyst working in the CTC, was told to review material about the Malaysia meeting. She was not told of the participant's presence in the U.S. The CIA gave Gillespie surveillance photos of Mihdhar and Hazmi from the meeting to show to FBI counterterrorism but did not tell her their significance. The Intelink database informed her not to share intelligence material on the meeting with criminal investigators. When shown the photos, the FBI were refused more details on their significance, and they were not given Mihdhar's date of birth nor passport number. In late August 2001, Gillespie told the INS INS or Ins or ''variant'', may refer to:
Places
* Ins, Switzerland, a municipality
* Creech Air Force Base (IATA airport code INS)
* Indonesia, ITF and UNDP code INS
Biology
*'' Ins'', a New World genus of bee flies
* INS, the gene for the insul ...
, the State Department, the Customs Service, and the FBI to put Hazmi and Mihdhar on their watchlists, but the FBI was prohibited from using criminal agents in searching for the duo, hindering their efforts.
Also in July, a Phoenix-based FBI agent sent a message to FBI headquarters, Alec Station, and FBI agents in New York alerting them to "the possibility of a coordinated effort by Osama bin Laden to send students to the United States to attend civil aviation universities and colleges". The agent, Kenneth Williams, suggested the need to interview all flight school managers and identify all Arab students seeking flight training. In July, Jordan alerted the U.S. that al-Qaeda was planning an attack on the U.S.; "months later", Jordan notified the U.S. that the attack's codename was "The Big Wedding" and that it involved aeroplanes.
On August 6, 2001, the CIA's Presidential Daily Brief ("PDB"), designated "For the President Only", was entitled "Bin Ladin Determined to Strike in U.S." The memo noted that FBI information "indicates patterns of suspicious activity in this country consistent with preparations for hijackings or other types of attacks".
In mid-August, one Minnesota flight school alerted the FBI about Zacarias Moussaoui, who had asked "suspicious questions". The FBI found that Moussaoui was a radical who had traveled to Pakistan, and the INS arrested him for overstaying his French visa. Their request to search his laptop was denied by FBI headquarters due to the lack of probable cause.
The failures in intelligence-sharing were attributed to 1995 Justice Department
A justice ministry, ministry of justice, or department of justice is a ministry or other government agency in charge of the administration of justice. The ministry or department is often headed by a minister of justice (minister for justice in a ...
policies limiting intelligence sharing, combined with CIA and NSA reluctance to reveal "sensitive sources and methods" such as tapped phones. Testifying before the 9/11 Commission
The National Commission on Terrorist Attacks Upon the United States, also known as the 9/11 Commission, was set up on November 27, 2002, "to prepare a full and complete account of the circumstances surrounding the September 11 attacks", includin ...
in April 2004, then-Attorney General
In most common law jurisdictions, the attorney general or attorney-general (sometimes abbreviated AG or Atty.-Gen) is the main legal advisor to the government. The plural is attorneys general.
In some jurisdictions, attorneys general also have exec ...
John Ashcroft recalled that the "single greatest structural cause for the September 11th problem was the wall that segregated or separated criminal investigators and intelligence agents". Clarke also wrote: " ere were... failures to get information to the right place at the right time."
Attacks
 Early on the morning of September 11, 2001,
Early on the morning of September 11, 2001, 19 hijackers
The hijackers in the September 11 attacks, who were often referred to as the 9/11 hijackers, were 19 men affiliated with the militant Islamist group al-Qaeda. They hailed from four countries; 15 of them were citizens of Saudi Arabia, two were from ...
took control of four commercial airliners (two Boeing 757s and two Boeing 767
The Boeing 767 is an American wide-body aircraft developed and manufactured by Boeing Commercial Airplanes.
The aircraft was launched as the 7X7 program on July 14, 1978, the prototype first flew on September 26, 1981, and it was certified on ...
s) en route to California (three of them headed to LAX in Los Angeles and one to SFO
San Francisco International Airport is an international airport in an unincorporated area of San Mateo County, south of Downtown San Francisco. It has flights to points throughout North America and is a major gateway to Europe, the Middle ...
in San Francisco) after takeoffs from Logan International Airport in Boston, Massachusetts; Newark Liberty International Airport
Newark Liberty International Airport , originally Newark Metropolitan Airport and later Newark International Airport, is an international airport straddling the boundary between the cities of Newark in Essex County and Elizabeth in Union Count ...
in Newark, New Jersey; and Washington Dulles International Airport in Loudoun and Fairfax
Fairfax may refer to:
Places United States
* Fairfax, California
* Fairfax Avenue, a major thoroughfare in Los Angeles, California
* Fairfax District, Los Angeles, California, centered on Fairfax Avenue
* Fairfax, Georgia
* Fairfax, Indiana
* Fa ...
counties in Virginia. Large planes with long coast-to-coast flights were selected for hijacking because they would have more fuel.
The four flights were:
* American Airlines Flight 11: a Boeing 767 aircraft, departed Logan Airport at 7:59a.m. en route to Los Angeles with a crew of 11 and 76 passengers, not including five hijackers. The hijackers flew the plane into the northern façade of the North Tower of the World Trade Center in New York City at 8:46a.m.
* United Airlines Flight 175: a Boeing 767 aircraft, departed Logan Airport at 8:14a.m. en route to Los Angeles with a crew of nine and 51 passengers, not including five hijackers. The hijackers flew the plane into the southern façade of the South Tower of the World Trade Center in New York City at 9:03a.m.
* American Airlines Flight 77
American Airlines Flight 77 was a scheduled American Airlines domestic transcontinental passenger flight from Washington Dulles International Airport in Dulles, Virginia, to Los Angeles International Airport in Los Angeles, California. The Boe ...
: a Boeing 757 aircraft, departed Washington Dulles International Airport at 8:20a.m. en route to Los Angeles with a crew of six and 53 passengers, not including five hijackers. The hijackers flew the plane into the western façade of the Pentagon in Arlington County, Virginia, at 9:37a.m.
* United Airlines Flight 93: a Boeing 757 aircraft, departed Newark International Airport at 8:42a.m. en route to San Francisco, with a crew of seven and 33 passengers, not including four hijackers. As passengers attempted to subdue the hijackers, the aircraft crashed into a field in Stonycreek Township, Pennsylvania, near Shanksville, at 10:03a.m.
Media coverage was extensive during the attacks and aftermath, beginning moments after the first crash into the World Trade Center.
* Eastern Daylight Time (UTC-04:00)† Excluding hijackers
§ Including emergency workers
‡ Including hijackers
The four crashes
 At 7:59 a.m., American Airlines Flight 11 took off from Logan International Airport in Boston. Fifteen minutes into the flight, five hijackers armed with boxcutters took over the plane, injuring at least three people (and possibly killing one) before forcing their way into the cockpit. The terrorists also displayed an apparent explosive device in order to frighten the hostages into submission, while additionally spraying
At 7:59 a.m., American Airlines Flight 11 took off from Logan International Airport in Boston. Fifteen minutes into the flight, five hijackers armed with boxcutters took over the plane, injuring at least three people (and possibly killing one) before forcing their way into the cockpit. The terrorists also displayed an apparent explosive device in order to frighten the hostages into submission, while additionally spraying mace
Mace may refer to:
Spices
* Mace (spice), a spice derived from the aril of nutmeg
* '' Achillea ageratum'', known as English mace, a flowering plant once used as a herb
Weapons
* Mace (bludgeon), a weapon with a heavy head on a solid shaft used ...
into the cabin to further hinder any efforts to resist. Back at Logan, United Airlines Flight 175 took off at 8:14 a.m., more or less the same time as Flight 11’s hijacking.Dulles International Airport in Fairfax
Fairfax may refer to:
Places United States
* Fairfax, California
* Fairfax Avenue, a major thoroughfare in Los Angeles, California
* Fairfax District, Los Angeles, California, centered on Fairfax Avenue
* Fairfax, Georgia
* Fairfax, Indiana
* Fa ...
and Loudoun Counties, Virginia, American Airlines Flight 77
American Airlines Flight 77 was a scheduled American Airlines domestic transcontinental passenger flight from Washington Dulles International Airport in Dulles, Virginia, to Los Angeles International Airport in Los Angeles, California. The Boe ...
left the runway at 8:20 a.m. Flight 175’s journey proceeded normally for 28 minutes until 8:42 a.m., when another group of five hijacked the plane, murdering both pilots and stabbing several crew members before assuming control of the aircraft. As was the case with Flight 11, the hijackers used bomb threats to instill fear into the passengers and crew and sprayed chemical weapons to disable any opposition. Concurrently, United Airlines Flight 93 departed from Newark International Airport in New Jersey; originally scheduled to pull away from the gate at 8:00 a.m., the plane was running 42 minutes late. At 8:46 a.m., Flight 11 was deliberately crashed into the north face of the World Trade Center's North Tower (1 WTC). At 8:51 a.m., shortly after the North Tower was struck and only minutes following the hijacking of Flight 175, American Airlines Flight 77
American Airlines Flight 77 was a scheduled American Airlines domestic transcontinental passenger flight from Washington Dulles International Airport in Dulles, Virginia, to Los Angeles International Airport in Los Angeles, California. The Boe ...
was also taken over by another group of five who forcibly entered the cockpit 31 minutes after takeoff. Although the hijackers were equipped with knives that they threatened their victims with, there were no reports of anyone on board actually being stabbed unlike the first two planes, nor did the two people who made phone calls mention the use of mace or a bomb threat of any kind. At 9:03 a.m., seventeen minutes after the first plane crashed into the North Tower, Flight 175 was flown into the South Tower's southern facade (2WTC). After waiting 46 minutes to make their move—a holdup which proved disastrous for the terrorists when combined with the delayed takeoff from the runway—four men aboard Flight 93 struck suddenly, killing at least one passenger before storming the cockpit and seizing control of the plane at 9:28 a.m., turning the plane east and setting course for Washington D.C. Much like their counterparts on the first two flights, the fourth team also used bomb threats to get their way and again filled the cabin with mace. Nine minutes after Flight 93's hijacking, Flight 77 was crashed into the Pentagon. Because of the two delays, the passengers and crew of Flight 93 had time to be made aware of the previous attacks through phone calls to the ground. Knowing their lives were forfeited rendered the bomb threat moot, and an uprising was hastily organized in the hopes of gaining control of the aircraft, with an assault on the hijackers being launched at 9:57 a.m. Within minutes, they had fought their way to the front of the cabin and began breaking down the cockpit door. Fearing their captives would gain the upper hand, the hijackers rolled the plane and pitched it into a nosedive, crashing it into a field near Shanksville, Pennsylvania, southeast of Pittsburgh, at 10:03 a.m. The plane was around 20 minutes away from reaching D.C. at the time of the crash, and its target is believed to have been either the Capitol Building or the White House.
Some passengers and crew members who called from the aircraft using the cabin air phone service and mobile phones provided details: several hijackers were aboard each plane; they used mace
Mace may refer to:
Spices
* Mace (spice), a spice derived from the aril of nutmeg
* '' Achillea ageratum'', known as English mace, a flowering plant once used as a herb
Weapons
* Mace (bludgeon), a weapon with a heavy head on a solid shaft used ...
, tear gas, or pepper spray to overcome attendants; and some people aboard had been stabbed.*
*
* Summers and Swan (2011), pp. 58, 463n, 476n.
*
*
*
* Reports indicated hijackers stabbed and killed pilots, flight attendants, and one or more passengers.9/11 Commission Report, pp. 4–14. According to the 9/11 Commission's final report, the hijackers had recently purchased multi-function hand tools and assorted Leatherman
Leatherman is an American brand of multitools and knives made by Leatherman Tool Group of Portland, Oregon. The company was founded in July 1983 by Timothy S. Leatherman and Steve Berliner in order to market his idea of a capable, eas ...
-type utility knives with locking blades (which were not forbidden to passengers at the time), but were not found among the possessions left behind by the hijackers. A flight attendant on Flight 11, a passenger on Flight 175, and passengers on Flight 93 said the hijackers had bombs, but one of the passengers said he thought the bombs were fake. The FBI found no traces of explosives at the crash sites, and the 9/11 Commission concluded that the bombs were probably fake. On at least two of the hijacked flights―American 11 and United 93―the terrorists tried to ensure nobody would resist by claiming over the PA system that they were taking hostages and were returning to the airport to have a ransom demand met, an obvious attempt to deceive those on-board into staying put by way of a false hope. Both of these attempts fell on deaf ears, however, as the hijacker pilots in both instances (Mohamed Atta and Ziad Jarrah, respectively) keyed the wrong switch and mistakenly transmitted their messages to ATC instead of the people on the plane as intended, in the process tipping off the flight controllers that the planes had been hijacked.
Three buildings in the World Trade Center collapsed due to fire-induced structural failure. The South Tower collapsed at 9:58a.m., having burned for 55minutes in a fire caused by the impact of United Airlines Flight 175 and the explosion of its fuel. The North Tower collapsed at 10:28 a.m. after burning for 102 minutes. When the North Tower collapsed, debris fell on the nearby 7 World Trade Center building (7WTC), damaging the building and starting fires. These fires burned for nearly seven hours, compromising the building's structural integrity, and 7WTC collapsed at 5:21p.m. The west side of the Pentagon sustained significant damage.
At 9:42 a.m., the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) grounded all civilian aircraft within the continental U.S., and civilian aircraft already in flight were told to land immediately. All international civilian aircraft were either turned back or redirected to airports in Canada or Mexico, and were banned from landing on United States territory for three days. The attacks created widespread confusion among news organizations and air traffic controllers. Among the unconfirmed and often contradictory news reports aired throughout the day, one of the most prevalent said a car bomb had been detonated at the U.S. State Department's headquarters in Washington, D.C. Another jet (Delta Air Lines Flight 1989
Delta Air Lines Flight 1989 was a regularly scheduled flight offering nonstop morning service on September 11, 2001, from Logan International Airport to Los Angeles International Airport on a Boeing 767-300ER aircraft. This flight was one ...
) was suspected of having been hijacked, but the aircraft responded to controllers and landed safely in Cleveland, Ohio.
In an April 2002 interview, Khalid Sheikh Mohammed and Ramzi bin al-Shibh, who are believed to have organized the attacks, said Flight 93's intended target was the United States Capitol, not the White House. During the planning stage of the attacks, Mohamed Atta (Flight 11's hijacker and pilot) thought the White House might be too tough a target and sought an assessment from Hani Hanjour (who hijacked and piloted Flight 77).Summers and Swan (2011), p. 323. Mohammed said al-Qaeda initially planned to target nuclear installations rather than the World Trade Center and the Pentagon, but decided against it, fearing things could "get out of control". Final decisions on targets, according to Mohammed, were left in the hands of the pilots. If any pilot could not reach his intended target, he was to crash the plane.
Casualties
The attacks are the deadliest terrorist attacks in world history, causing the deaths of 2,996 people (including the hijackers) and injuring thousands of others. The death toll included 265 on the four planes (from which there were no survivors); 2,606 in the World Trade Center and in the surrounding area; and 125 at the Pentagon. Most who died were civilians; the rest included 343 firefighters, 72 law enforcement officers, 55 military personnel, and the 19 terrorists. After New York, New Jersey lost the most state citizens. More than 90 countries lost citizens in the attacks; for example, the 67 Britons who died were more than in any other terrorist attack anywhere. In Arlington County, Virginia, 125 Pentagon workers died when Flight 77 crashed into the building's western side. Seventy were civilians and 55 were military personnel, many of whom worked for the United States Army or the United States Navy. The Army lost 47 civilian employees; six civilian contractors; and 22 soldiers, while the Navy lost six civilian employees; three civilian contractors; and 33 sailors. Seven Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA) civilian employees died, and one
In Arlington County, Virginia, 125 Pentagon workers died when Flight 77 crashed into the building's western side. Seventy were civilians and 55 were military personnel, many of whom worked for the United States Army or the United States Navy. The Army lost 47 civilian employees; six civilian contractors; and 22 soldiers, while the Navy lost six civilian employees; three civilian contractors; and 33 sailors. Seven Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA) civilian employees died, and one Office of the Secretary of Defense
The Office of the Secretary of Defense (OSD) is a headquarters-level staff of the United States Department of Defense. It is the principal civilian staff element of the U.S. Secretary of Defense, and it assists the Secretary in carrying out aut ...
(OSD) contractor. Lieutenant General Timothy Maude, an Army Deputy Chief of Staff, was the highest-ranking military official killed at the Pentagon.
In New York City, more than 90% of the workers and visitors who died in the towers had been at or above the points of impact. In the North Tower, between 1,344 and 1,402 people were at, above or one floor below the point of impact and all died. Hundreds were killed instantly the moment the plane struck. The estimated 800 people who survived the impact were trapped and died in the fires or from smoke inhalation; fell or jumped from the tower to escape the smoke and flames; or were killed in the building's collapse. The destruction of all three staircases in the tower when Flight 11 hit made it impossible for anyone from the impact zone upwards to escape. 107 people below the point of impact died, including every single occupant of Floor 92, which was right underneath the plane's impact zone.
In the South Tower, around 600 people were on or above the 77th floor with Flight 175 crashed into the building. As with the North Tower, hundreds were killed at the moment of impact. The estimated 300 people above the impact zone who survived the crash were unware that, unlike in the North Tower, escape was still possible. One stairway, Stairwell A
The collapse of the World Trade Center occurred during the terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001, after the Twin Towers were struck by two hijacked commercial airliners. One World Trade Center (WTC 1, or the North Tower) was hit at 8:46 ...
, was left intact after Flight 175 hit, allowing 14 people located on the floors of impact (including Stanley Praimnath
Stanley Praimnath (born October 27, 1956) is a survivor of the attacks on the World Trade Center on September 11, 2001. He worked as an executive for Fuji Bank on the 81st floor of the South Tower (WTC 2), the second tower struck that day. He wa ...
, a man who saw the plane coming at him) and four more from the floors above to escape. New York City 9-1-1
, usually written 911, is an emergency telephone number for the United States, Canada, Mexico, Panama, Palau, Argentina, Philippines, Jordan, as well as the North American Numbering Plan (NANP), one of eight N11 codes. Like other emergency nu ...
operators who received calls from people inside the tower were not well informed of the situation as it rapidly unfolded and as a result, told callers not to descend the tower on their own. In total 630 people died in the South Tower, fewer than half the number killed in the North Tower. In stark contrast to the North Tower, where nearly 200 people fell to their deaths from above the impact zone, only three people were spotted jumping or falling from the upper floors of the South Tower. Casualties in the South Tower were significantly reduced because some occupants decided to leave the building as soon as the North Tower was struck, and because Rick Rescorla, head of security at Morgan Stanley, defied an order to remain in place and evacuated almost all of the company's 2,700 employees in the South Tower to safety after Flight 11 had struck the North Tower. Eric Eisenberg, an executive at AON Insurance, similarly made the decision to evacuate the floors occupied by AON in the moments following the impact of Flight 11, although the company still lost 175 employees in the South Tower. Other pre-impact evacuations were carried out companies such as Fiduciary Trust, CSC, and Euro Brokers―all of whom had offices on floors above the point of impact. The failure to order a full evacuation of the South Tower after the first jet crash into the North Tower was described by '' USA Today'' as "one of the day's great tragedies".
At least 200 people fell or jumped to their deaths from the burning towers (as exemplified in the photograph '' The Falling Man''), landing on the streets and rooftops of adjacent buildings hundreds of feet below. Some occupants of each tower above the point of impact made their way toward the roof in the hope of helicopter rescue, but the roof access doors were locked. No plan existed for helicopter rescues, and the combination of roof equipment, thick smoke, and intense heat prevented helicopters from approaching.
A total of 411 emergency workers died as they tried to rescue people and fight fires. The New York City Fire Department (FDNY) lost 343 firefighters, including a chaplain and two paramedics. The New York City Police Department (NYPD) lost 23 officers. The Port Authority Police Department (PAPD) lost 37 officers. Eight emergency medical technicians (EMTs) and paramedics from private emergency medical services (EMS) units were killed.
Cantor Fitzgerald L.P. (an investment bank on the North Tower's 101st–105th floors) lost 658 employees, considerably more than any other employer. Marsh Inc., located immediately below Cantor Fitzgerald on floors 93–100, lost 358 employees, and 175 employees of Aon Corporation were also killed. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) estimated that about 17,400 civilians were in the World Trade Center complex at the time of the attacks. Turnstile counts from the Port Authority suggest 14,154 people were typically in the Twin Towers by 8:45a.m. Most people below the impact zone safely evacuated the buildings.
Weeks after the attack, the death toll was estimated to be over 6,000, more than twice the number of deaths eventually confirmed. The city was only able to identify remains for about 1,600 of the World Trade Center victims. The medical examiner's office collected "about 10,000 unidentified bone and tissue fragments that cannot be matched to the list of the dead". Bone fragments were still being found in 2006 by workers who were preparing to demolish the damaged Deutsche Bank Building.
In 2010, a team of anthropologists and archaeologists searched for human remains and personal items at the Fresh Kills Landfill, where 72 more human remains were recovered, bringing the total found to 1,845. DNA profiling continues in an attempt to identify additional victims. The remains are being held in storage in Memorial Park, outside the New York City Medical Examiner's facilities. It was expected that the remains would be moved in 2013 to a repository behind a wall at the 9/11 museum.
In July 2011, a team of scientists at the Office of Chief Medical Examiner was still trying to identify remains, in the hope that improved technology will allow them to identify other victims. On August 7, 2017, the 1,641st victim was identified as a result of newly available DNA technology, and a 1,642nd on July 26, 2018. Three more victims were identified in 2019 and further two in 2021. As of September 2021, 1,106 victims are yet to be identified.
Damage


World Financial Center World Financial Center may refer to:
China
* Chongqing World Financial Center
* Shanghai World Financial Center
* Tianjin World Financial Center
United States
* Brookfield Place (New York City), formerly the World Financial Center complex
** 2 ...
also suffered damage. The last fires at the World Trade Center site were extinguished on December 20, exactly 100 days after the attacks.
The Deutsche Bank Building across Liberty Street from the World Trade Center complex was later condemned as uninhabitable because of toxic conditions inside the office tower, and was deconstructed. The Borough of Manhattan Community College's Fiterman Hall at 30 West Broadway was condemned due to extensive damage from the attacks, and was reopened in 2012.
Other neighboring buildings (including 90 West Street
90 West Street (previously known as the West Street Building and the Brady Building) is a 23-story residential building in the Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. Located on West Street just south of the World Trade Cen ...
and the Verizon Building) suffered major damage but have been restored. World Financial Center World Financial Center may refer to:
China
* Chongqing World Financial Center
* Shanghai World Financial Center
* Tianjin World Financial Center
United States
* Brookfield Place (New York City), formerly the World Financial Center complex
** 2 ...
buildings, One Liberty Plaza, the Millenium Hilton
The Millennium Downtown New York is a hotel in Lower Manhattan, New York City, located at the southeast corner of Fulton Street (Manhattan), Fulton Street and Church Street (Manhattan), Church Street. The hotel is adjacent to 195 Broadway, with ...
, and 90 Church Street had moderate damage and have since been restored. Communications equipment on top of the North Tower was also destroyed, with only WCBS-TV maintaining a backup transmitter on the Empire State Building
The Empire State Building is a 102-story Art Deco skyscraper in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. The building was designed by Shreve, Lamb & Harmon and built from 1930 to 1931. Its name is derived from "Empire State", the nickname of the st ...
, but media stations were quickly able to reroute the signals and resume their broadcasts.
The PATH train system's World Trade Center station was located under the complex. As a result, the entire station was demolished completely when the towers collapsed, and the tunnels leading to Exchange Place station in Jersey City, New Jersey
Jersey City is the second-most populous city in the U.S. state of New Jersey, after Newark.World Trade Center Transportation Hub, which reopened in March 2015. The
 The New York City Fire Department deployed 200 units (half of the department) to the World Trade Center. Their efforts were supplemented by numerous off-duty firefighters and emergency medical technicians.''McKinsey Report'', "Emergency Medical Service response", pp. ??''McKinsey Report'', "Executive Summary", pp. ?? The New York City Police Department sent Emergency Service Units and other police personnel and deployed its aviation unit. Once on the scene, the FDNY, the NYPD, and the PAPD did not coordinate efforts and performed redundant searches for civilians.
As conditions deteriorated, the NYPD aviation unit relayed information to police commanders, who issued orders for its personnel to evacuate the towers; most NYPD officers were able to safely evacuate before the buildings collapsed.''McKinsey Report'', "NYPD", pp. ?? With separate command posts set up and incompatible radio communications between the agencies, warnings were not passed along to FDNY commanders.
After the first tower collapsed, FDNY commanders issued evacuation warnings. Due to technical difficulties with malfunctioning radio repeater systems, many firefighters never heard the evacuation orders. 9-1-1 dispatchers also received information from callers that was not passed along to commanders on the scene. Within hours of the attack, a substantial search and rescue operation was launched. After months of around-the-clock operations, the World Trade Center site was cleared by the end of May 2002.
The New York City Fire Department deployed 200 units (half of the department) to the World Trade Center. Their efforts were supplemented by numerous off-duty firefighters and emergency medical technicians.''McKinsey Report'', "Emergency Medical Service response", pp. ??''McKinsey Report'', "Executive Summary", pp. ?? The New York City Police Department sent Emergency Service Units and other police personnel and deployed its aviation unit. Once on the scene, the FDNY, the NYPD, and the PAPD did not coordinate efforts and performed redundant searches for civilians.
As conditions deteriorated, the NYPD aviation unit relayed information to police commanders, who issued orders for its personnel to evacuate the towers; most NYPD officers were able to safely evacuate before the buildings collapsed.''McKinsey Report'', "NYPD", pp. ?? With separate command posts set up and incompatible radio communications between the agencies, warnings were not passed along to FDNY commanders.
After the first tower collapsed, FDNY commanders issued evacuation warnings. Due to technical difficulties with malfunctioning radio repeater systems, many firefighters never heard the evacuation orders. 9-1-1 dispatchers also received information from callers that was not passed along to commanders on the scene. Within hours of the attack, a substantial search and rescue operation was launched. After months of around-the-clock operations, the World Trade Center site was cleared by the end of May 2002.
 At 8:32 a.m., FAA officials were notified Flight11 had been hijacked and they, in turn, notified the North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD). NORAD scrambled two
At 8:32 a.m., FAA officials were notified Flight11 had been hijacked and they, in turn, notified the North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD). NORAD scrambled two
 The U.S. set up the
The U.S. set up the
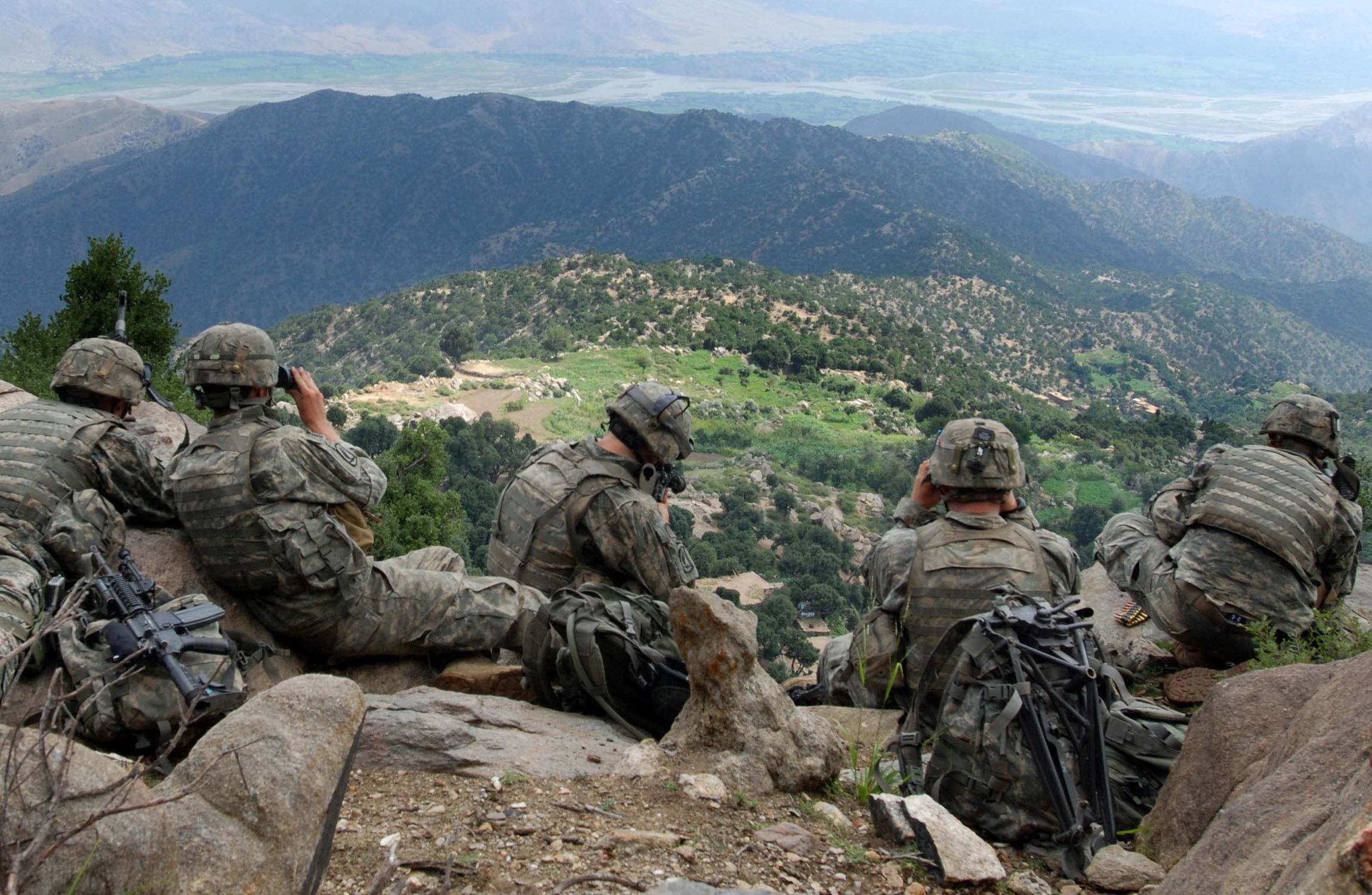 The NATO council declared that the terrorist attacks on the United States were an attack on all NATO nations that satisfied Article 5 of the NATO charter. This marked the first invocation of Article 5, which had been written during the
The NATO council declared that the terrorist attacks on the United States were an attack on all NATO nations that satisfied Article 5 of the NATO charter. This marked the first invocation of Article 5, which had been written during the
'' Ali Soufan''. ''CTC Sentinel''. November 2018, Vol. 11, Issue 10. Combating Terrorism CenterCTC at West Point
Permanent link and archived version at Wayback MachinePermanent link and archived version at archive.is
Retrieved and archived on November 19, 2018
Permanent link
at WebCite (November 30, 2018. 14:42:35 UTC).'
Permanent link and Archived Version at Perma.cc
(August 5, 2021). "In the months after 9/11, Soleimani saw an opportunity to defeat the Taliban once and for all by unconventional meansnamely, cooperation with the United States. Early in the war, he directed Iranian diplomats to share intelligence on Taliban military positions with their U.S. counterparts. The Americans, in return, told the Iranians what they knew about an al-Qa`ida fixer hiding out in eastern Iran."''
 Hundreds of thousands of tons of toxic debris containing more than 2,500 contaminants, including known carcinogens, were spread across Lower Manhattan due to the Twin Towers' collapse. Exposure to the toxins in the debris is alleged to have contributed to fatal or debilitating illnesses among people who were at Ground Zero. The Bush administration ordered the
Hundreds of thousands of tons of toxic debris containing more than 2,500 contaminants, including known carcinogens, were spread across Lower Manhattan due to the Twin Towers' collapse. Exposure to the toxins in the debris is alleged to have contributed to fatal or debilitating illnesses among people who were at Ground Zero. The Bush administration ordered the
 Also hurt were small businesses in
Also hurt were small businesses in
 As a result of the attacks, many governments across the world passed legislation to combat terrorism. In Germany, where several of the 9/11 terrorists had resided and taken advantage of that country's liberal asylum policies, two major anti-terrorism packages were enacted. The first removed legal loopholes that permitted terrorists to live and raise money in Germany. The second addressed the effectiveness and communication of intelligence and law enforcement. Canada passed the
As a result of the attacks, many governments across the world passed legislation to combat terrorism. In Germany, where several of the 9/11 terrorists had resided and taken advantage of that country's liberal asylum policies, two major anti-terrorism packages were enacted. The first removed legal loopholes that permitted terrorists to live and raise money in Germany. The second addressed the effectiveness and communication of intelligence and law enforcement. Canada passed the
 The FBI was quickly able to identify the hijackers, including leader Mohamed Atta, when his luggage was discovered at Boston's Logan Airport. Atta had been forced to check two of his three bags due to space limitations on the 19-seat commuter flight he took to Boston. Due to a new policy instituted to prevent flight delays, the luggage failed to make it aboard American Airlines Flight 11 as planned. The luggage contained the hijackers' names, assignments, and al-Qaeda connections. "It had all these Arab-language papers that amounted to the Rosetta stone of the investigation", said one FBI agent. Within hours of the attacks, the FBI released the names and in many cases the personal details of the suspected pilots and hijackers. Abu Jandal, who served as bin Laden's chief bodyguard for years, confirmed the identity of seven hijackers as al-Qaeda members during interrogations with the FBI on September 17. He had been jailed in a Yemeni prison since 2000. On September 27, 2001, photos of all 19 hijackers were released, along with information about possible nationalities and aliases. Fifteen of the men were from Saudi Arabia, two were from the United Arab Emirates, one was from Egypt, and one was from Lebanon.
By midday, the U.S. National Security Agency and German intelligence agencies had intercepted communications pointing to Osama bin Laden. Two of the hijackers were known to have traveled with a bin Laden associate to Malaysia in 2000 and hijacker
The FBI was quickly able to identify the hijackers, including leader Mohamed Atta, when his luggage was discovered at Boston's Logan Airport. Atta had been forced to check two of his three bags due to space limitations on the 19-seat commuter flight he took to Boston. Due to a new policy instituted to prevent flight delays, the luggage failed to make it aboard American Airlines Flight 11 as planned. The luggage contained the hijackers' names, assignments, and al-Qaeda connections. "It had all these Arab-language papers that amounted to the Rosetta stone of the investigation", said one FBI agent. Within hours of the attacks, the FBI released the names and in many cases the personal details of the suspected pilots and hijackers. Abu Jandal, who served as bin Laden's chief bodyguard for years, confirmed the identity of seven hijackers as al-Qaeda members during interrogations with the FBI on September 17. He had been jailed in a Yemeni prison since 2000. On September 27, 2001, photos of all 19 hijackers were released, along with information about possible nationalities and aliases. Fifteen of the men were from Saudi Arabia, two were from the United Arab Emirates, one was from Egypt, and one was from Lebanon.
By midday, the U.S. National Security Agency and German intelligence agencies had intercepted communications pointing to Osama bin Laden. Two of the hijackers were known to have traveled with a bin Laden associate to Malaysia in 2000 and hijacker
 The U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
The U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
Cortlandt Street station Cortlandt Street may refer to:
Streets
* Cortlandt Street (Manhattan), street in Lower Manhattan, most of which became part of the World Trade Center in the 1970s
Subway stations
* Cortlandt Street (BMT Broadway Line), a New York City Subway stati ...
on the New York City Subway
The New York City Subway is a rapid transit system owned by the government of New York City and leased to the New York City Transit Authority, an affiliate agency of the state-run Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA). Opened on October 2 ...
's IRT Broadway–Seventh Avenue Line was also in close proximity to the World Trade Center complex, and the entire station, along with the surrounding track, was reduced to rubble. The latter station was rebuilt and reopened to the public on September 8, 2018.
The Pentagon was severely damaged by the impact of American Airlines Flight 77 and the ensuing fires, causing one section of the building to collapse. As the airplane approached the Pentagon, its wings knocked down light poles and its right engine hit a power generator before crashing into the western side of the building.''American Airlines Flight 77 FDR Report'', pp. ?? The plane hit the Pentagon at the first-floor level. The front part of the fuselage disintegrated on impact, while the mid and tail sections kept moving for another fraction of a second. Debris from the tail section penetrated the furthest into the building, breaking through of the three outermost of the building's five rings.
Rescue efforts
 The New York City Fire Department deployed 200 units (half of the department) to the World Trade Center. Their efforts were supplemented by numerous off-duty firefighters and emergency medical technicians.''McKinsey Report'', "Emergency Medical Service response", pp. ??''McKinsey Report'', "Executive Summary", pp. ?? The New York City Police Department sent Emergency Service Units and other police personnel and deployed its aviation unit. Once on the scene, the FDNY, the NYPD, and the PAPD did not coordinate efforts and performed redundant searches for civilians.
As conditions deteriorated, the NYPD aviation unit relayed information to police commanders, who issued orders for its personnel to evacuate the towers; most NYPD officers were able to safely evacuate before the buildings collapsed.''McKinsey Report'', "NYPD", pp. ?? With separate command posts set up and incompatible radio communications between the agencies, warnings were not passed along to FDNY commanders.
After the first tower collapsed, FDNY commanders issued evacuation warnings. Due to technical difficulties with malfunctioning radio repeater systems, many firefighters never heard the evacuation orders. 9-1-1 dispatchers also received information from callers that was not passed along to commanders on the scene. Within hours of the attack, a substantial search and rescue operation was launched. After months of around-the-clock operations, the World Trade Center site was cleared by the end of May 2002.
The New York City Fire Department deployed 200 units (half of the department) to the World Trade Center. Their efforts were supplemented by numerous off-duty firefighters and emergency medical technicians.''McKinsey Report'', "Emergency Medical Service response", pp. ??''McKinsey Report'', "Executive Summary", pp. ?? The New York City Police Department sent Emergency Service Units and other police personnel and deployed its aviation unit. Once on the scene, the FDNY, the NYPD, and the PAPD did not coordinate efforts and performed redundant searches for civilians.
As conditions deteriorated, the NYPD aviation unit relayed information to police commanders, who issued orders for its personnel to evacuate the towers; most NYPD officers were able to safely evacuate before the buildings collapsed.''McKinsey Report'', "NYPD", pp. ?? With separate command posts set up and incompatible radio communications between the agencies, warnings were not passed along to FDNY commanders.
After the first tower collapsed, FDNY commanders issued evacuation warnings. Due to technical difficulties with malfunctioning radio repeater systems, many firefighters never heard the evacuation orders. 9-1-1 dispatchers also received information from callers that was not passed along to commanders on the scene. Within hours of the attack, a substantial search and rescue operation was launched. After months of around-the-clock operations, the World Trade Center site was cleared by the end of May 2002.
Aftermath
The 9/11 attacks resulted in immediate responses to the event, including domestic reactions; closings and cancellations;hate crime
A hate crime (also known as a bias-motivated crime or bias crime) is a prejudice-motivated crime which occurs when a perpetrator targets a victim because of their membership (or perceived membership) of a certain social group or racial demograph ...
s; Muslim-American responses to the event; international responses to the attack; and military responses to the events. An extensive compensation program was quickly established by Congress in the aftermath to compensate the victims and families of victims of the 9/11 attacks as well.
Immediate response
 At 8:32 a.m., FAA officials were notified Flight11 had been hijacked and they, in turn, notified the North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD). NORAD scrambled two
At 8:32 a.m., FAA officials were notified Flight11 had been hijacked and they, in turn, notified the North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD). NORAD scrambled two F-15s
The McDonnell Douglas (now Boeing) F-15E Strike Eagle is an American all-weather multirole strike fighter derived from the McDonnell Douglas F-15 Eagle. The F-15E was designed in the 1980s for long-range, high-speed interdiction without relyin ...
from Otis Air National Guard Base in Massachusetts and they were airborne by 8:53 a.m. Because of slow and confused communication from FAA officials, NORAD had nine minutes' notice, and no notice about any of the other flights before they crashed.
After both of the Twin Towers had already been hit, more fighters were scrambled from Langley Air Force Base
Langley Air Force Base is a United States Air Force base located in Hampton, Virginia, adjacent to Newport News, Virginia, Newport News. It was one of List of airfields of the Training Section of the United States Army Air Service, thirty-two ...
in Virginia at 9:30 a.m. At 10:20 a.m., Vice President Dick Cheney
Richard Bruce Cheney ( ; born January 30, 1941) is an American politician and businessman who served as the 46th vice president of the United States from 2001 to 2009 under President George W. Bush. He is currently the oldest living former U ...
issued orders to shoot down any commercial aircraft that could be positively identified as being hijacked. These instructions were not relayed in time for the fighters to take action. Some fighters took to the air without live ammunition, knowing that to prevent the hijackers from striking their intended targets, the pilots might have to intercept and crash their fighters into the hijacked planes, possibly ejecting at the last moment.
For the first time in U.S. history, the emergency preparedness plan called Security Control of Air Traffic and Air Navigation Aids
The Plan for the Security Control of Air Traffic and Air Navigation Aids (SCATANA) is an emergency preparedness plan of the United States which prescribes the joint action to be taken by appropriate elements of the Department of Defense, Federal A ...
(SCATANA) was invoked, thus stranding tens of thousands of passengers across the world. Ben Sliney, in his first day as the National Operations Manager of the FAA, ordered that American airspace would be closed to all international flights, causing about 500 flights to be turned back or redirected to other countries. Canada received 226 of the diverted flights and launched Operation Yellow Ribbon to deal with the large numbers of grounded planes and stranded passengers.
The 9/11 attacks had immediate effects on the American people. Police and rescue workers from around the country took a leave of absence from their jobs and traveled to New York City to help recover bodies from the twisted remnants of the Twin Towers. Blood donations across the U.S. surged in the weeks after 9/11.
The deaths of adults in the attacks resulted in over 3,000 children losing a parent. Subsequent studies documented children's reactions to these actual losses and to feared losses of life, the protective environment in the attacks' aftermath, and the effects on surviving caregivers.
Domestic reactions
Following the attacks, President George W. Bush's approval rating soared to 90%. On September 20, 2001, he addressed the nation and a joint session of Congress regarding the events of September 11 and the subsequent nine days of rescue and recovery efforts, and described his intended response to the attacks.New York City mayor
The mayor of New York City, officially Mayor of the City of New York, is head of the executive branch of the government of New York City and the chief executive of New York City. The mayor's office administers all city services, public property ...
Rudy Giuliani
Rudolph William Louis Giuliani (, ; born May 28, 1944) is an American politician and lawyer who served as the 107th Mayor of New York City from 1994 to 2001. He previously served as the United States Associate Attorney General from 1981 to 198 ...
's highly visible role won him high praise in New York and nationally.
Many relief funds were immediately set up to assist the attacks' victims, with the task of providing financial assistance to the survivors of the attacks and to the victims' families. By the deadline for victims' compensation on September 11, 2003, 2,833 applications had been received from the families of those who were killed.
Contingency plans for the continuity of government and the evacuation of leaders were implemented soon after the attacks. Congress was not told that the United States had been under a continuity of government status until February 2002.
In the largest restructuring of the U.S. government in contemporary history, the United States enacted the Homeland Security Act
The Homeland Security Act (HSA) of 2002, () was introduced in the aftermath of the September 11 attacks and subsequent mailings of anthrax spores. The HSA was cosponsored by 118 members of Congress. The act passed the U.S. Senate by a vote of ...
of 2002, creating the Department of Homeland Security. Congress also passed the USA PATRIOT Act, saying it would help detect and prosecute terrorism and other crimes. Civil liberties groups have criticized the PATRIOT Act, saying it allows law enforcement to invade citizens' privacy and that it eliminates judicial oversight of law enforcement and domestic intelligence.
In an effort to effectively combat future acts of terrorism, the National Security Agency (NSA) was given broad powers. NSA commenced warrantless surveillance of telecommunications, which was sometimes criticized since it permitted the agency "to eavesdrop on telephone and e-mail communications between the United States and people overseas without a warrant". In response to requests by various intelligence agencies, the United States Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Court permitted an expansion of powers by the U.S. government in seeking, obtaining, and sharing information on U.S. citizens as well as non-U.S. people from around the world.
Hate crimes
Six days after the attacks, President Bush made a public appearance at Washington, D.C.'s largest Islamic Center and acknowledged the "incredibly valuable contribution" that millions of American Muslims made to their country and called for them "to be treated with respect". Numerous incidents ofharassment
Harassment covers a wide range of behaviors of offensive nature. It is commonly understood as behavior that demeans, humiliates or embarrasses a person, and it is characteristically identified by its unlikelihood in terms of social and moral ...
and hate crime
A hate crime (also known as a bias-motivated crime or bias crime) is a prejudice-motivated crime which occurs when a perpetrator targets a victim because of their membership (or perceived membership) of a certain social group or racial demograph ...
s against Muslims and South Asians were reported in the days following the attacks.
Sikh
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism, Sikhism (Sikhi), a Monotheism, monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Gu ...
s were also subject to targeting due to the use of turbans in the Sikh faith, which are stereotypically associated with Muslims. There were reports of attacks on mosques and other religious buildings (including the firebombing of a Hindu temple), and assaults on individuals, including one murder: Balbir Singh Sodhi, a Sikh mistaken for a Muslim, who was fatally shot on September 15, 2001, in Mesa, Arizona
Mesa ( ) is a city in Maricopa County, Arizona, Maricopa County, in the U.S. state of Arizona. It is the most populous city in the East Valley (Phoenix metropolitan area), East Valley section of the Phoenix Metropolitan Area. It is bordered by ...
. Two dozen members of Osama bin Laden's family were urgently evacuated out of the country on a private charter plane under FBI supervision three days after the attacks.
According to an academic study, people perceived to be Middle Eastern
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (European ...
were as likely to be victims of hate crimes as followers of Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
during this time. The study also found a similar increase in hate crimes against people who may have been perceived as Muslims, Arabs, and others thought to be of Middle Eastern origin. A report by the South Asian American advocacy group known as South Asian Americans Leading Together documented media coverage of 645 bias incidents against Americans of South Asian or Middle Eastern descent between September 11 and 17 2001. Various crimes such as vandalism, arson, assault, shootings, harassment, and threats in numerous places were documented. Women wearing hijab
In modern usage, hijab ( ar, حجاب, translit=ḥijāb, ) generally refers to headcoverings worn by Muslim women. Many Muslims believe it is obligatory for every female Muslim who has reached the age of puberty to wear a head covering. While ...
were also targeted.
Discrimination and racial profiling
A poll of Arab-Americans, conducted in May 2002, found that 20% had personally experienced discrimination since September 11. A July 2002 poll of Muslim Americans found that 48% believed their lives had changed for the worse since September 11, and 57% had experienced an act of bias or discrimination. Following the September 11 attacks, many Pakistani Americans identified themselves as Indians to avoid potential discrimination and obtain jobs (Pakistan was created as a result of thepartition of India
The Partition of British India in 1947 was the Partition (politics), change of political borders and the division of other assets that accompanied the dissolution of the British Raj in South Asia and the creation of two independent dominions: ...
in 1947).
By May 2002, there were 488 complaints of employment discrimination
Employment discrimination is a form of illegal discrimination in the workplace based on legally protected characteristics. In the U.S., federal anti-discrimination law prohibits discrimination by employers against employees based on age, race, g ...
reported to the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC). 301 of those were complaints from people fired from their jobs. Similarly, by June 2002, the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) had investigated 111 September 11th-related complaints from airline passengers purporting that their religious or ethnic appearance caused them to be singled out at security screenings. DOT investigated an additional 31 complaints from people who alleged they were completely blocked from boarding airplanes on the same grounds.
Muslim American response
Muslim organizations in the United States were swift to condemn the attacks and called "upon Muslim Americans to come forward with their skills and resources to help alleviate the sufferings of the affected people and their families". These organizations included the Islamic Society of North America, American Muslim Alliance, American Muslim Council, Council on American-Islamic Relations,Islamic Circle of North America
Islamic Circle of North America (ICNA) is an Islamic North American grassroots umbrella organization.
History
ICNA is an offshoot of the Muslim Students' Association (MSA), and was founded by immigrants from South Asia. In 1971, a number of South ...
, and the Shari'a Scholars Association of North America. Along with monetary donations, many Islamic organizations launched blood drives and provided medical assistance, food, and shelter for victims.
Interfaith efforts
Curiosity about Islam increased after the attacks. As a result, many mosques and Islamic centers began holding open houses and participating in outreach efforts to educate non-Muslims about the faith. In the first 10 years after the attacks, interfaith community service increased from 8 to 20 percent. and the percentage of U.S. congregations involved in interfaith worship doubled from 7 to 14 percent.International reactions
The attacks were denounced by mass media and governments worldwide. Across the globe, nations offered pro-American support and solidarity. Leaders in most Middle Eastern countries, as well as Libya and Afghanistan, condemned the attacks. Iraq was a notable exception, with an immediate official statement that, "the American cowboys are reaping the fruit of their crimes against humanity". The government of Saudi Arabia officially condemned the attacks, but privately many Saudis favored bin Laden's cause. AlthoughPalestinian Authority
The Palestinian National Authority (PA or PNA; ar, السلطة الوطنية الفلسطينية '), commonly known as the Palestinian Authority and officially the State of Palestine,
(PA) president Yasser Arafat also condemned the attacks, there were reports of celebrations of disputed size in the West Bank, Gaza Strip
The Gaza Strip (;The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p.761 "Gaza Strip /'gɑːzə/ a strip of territory under the control of the Palestinian National Authority and Hamas, on the SE Mediterranean coast including the town of Gaza.. ...
, and East Jerusalem
East Jerusalem (, ; , ) is the sector of Jerusalem that was held by Jordan during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, as opposed to the western sector of the city, West Jerusalem, which was held by Israel.
Jerusalem was envisaged as a separat ...
. Palestinian leaders discredited news broadcasters that justified the attacks or showed celebrations, and the Authority claimed such celebration do not represent the Palestinians' sentiment, adding that it would not allow "a few kids" to "smear the real face of the Palestinians". Footage by CNN and other news outlets were suggested by a report originating at a Brazilian university to be from 1991; this was later proven to be a false accusation, resulting in a statement being issued by CNN. As in the United States, the aftermath of the attacks saw tensions increase in other countries between Muslims and non-Muslims.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1368 condemned the attacks and expressed readiness to take all necessary steps to respond and combat all forms of terrorism in accordance with their Charter
A charter is the grant of authority or rights, stating that the granter formally recognizes the prerogative of the recipient to exercise the rights specified. It is implicit that the granter retains superiority (or sovereignty), and that the rec ...
. Numerous countries introduced anti-terrorism legislation and froze bank accounts they suspected of al-Qaeda ties. Law enforcement and intelligence agencies in a number of countries arrested alleged terrorists.
British Prime Minister Tony Blair said Britain stood "shoulder to shoulder" with the United States. A few days later, Blair flew to Washington, D.C., to affirm British solidarity with the United States. In a speech to Congress nine days after the attacks, which Blair attended as a guest, President Bush declared "America has no truer friend than Great Britain." Subsequently, Prime Minister Blair embarked on two months of diplomacy to rally international support for military action; he held 54 meetings with world leaders and traveled more than 40,000 miles (60,000km).
 The U.S. set up the
The U.S. set up the Guantanamo Bay detention camp
The Guantanamo Bay detention camp ( es, Centro de detención de la bahía de Guantánamo) is a United States military prison located within Guantanamo Bay Naval Base, also referred to as Guantánamo, GTMO, and Gitmo (), on the coast of Guant ...
to hold inmates they defined as "illegal enemy combatants
An unlawful combatant, illegal combatant or unprivileged combatant/belligerent is a person who directly engages in armed conflict in violation of the laws of war and therefore is claimed not to be protected by the Geneva Conventions.
The Internati ...
". The legitimacy of these detentions has been questioned by the European Union and human rights organizations.
On September 25, 2001, Iran's fifth president, Mohammad Khatami
Sayyid Mohammad Khatami ( fa, سید محمد خاتمی, ; born 14 October 1943) is an Iranian politician who served as the fifth president of Iran from 3 August 1997 to 3 August 2005. He also served as Iran's Minister of Culture from 1982 to ...
, meeting British Foreign Secretary Jack Straw, said: "Iran fully understands the feelings of the Americans about the terrorist attacks in New York and Washington on September 11." He said although the American administrations had been at best indifferent about terrorist operations in Iran (since 1979), the Iranians felt differently and had expressed their sympathetic feelings with bereaved Americans in the tragic incidents in the two cities. He also stated that "Nations should not be punished in place of terrorists."
According to Radio Farda's website, when the news of the attacks was released, some Iranian citizens gathered in front of the Embassy of Switzerland in Tehran, which serves as the protecting power of the United States in Iran (U.S. interests-protecting office in Iran), to express their sympathy, and some of them lit candles as a symbol of mourning. This piece of news at Radio Farda's website also states that in 2011, on the anniversary of the attacks, the United States Department of State published a post at its blog, in which the Department thanked the Iranian people for their sympathy and stated that it would never forget Iranian people's kindness on those harsh days. After the attacks, both the President and the Supreme Leader of Iran, condemned the attacks. The BBC and '' Time'' magazine published reports on holding candlelit vigils for the victims by Iranian citizens on their websites. According to '' Politico Magazine'', following the attacks, Sayyed Ali Khamenei, the Supreme Leader of Iran, "suspended the usual ' Death to America' chants at Friday prayers" temporarily.
In September 2001, shortly after the attacks, some fans of AEK Athens burned an Israeli flag and unsuccessfully tried to burn an American flag. Though the American flag did not catch fire, the fans booed during a moment of silence for victims of the attacks.
Effects in Afghanistan
Most of the Afghan population was already going hungry at the time of the September 11 attacks. In the aftermath of the attacks, tens of thousands of people attempted to flee Afghanistan due to the possibility of military retaliation by the United States. Pakistan, already home to many Afghan refugees from previous conflicts, closed its border with Afghanistan on September 17, 2001. Thousands of Afghans also fled to the frontier with Tajikistan, although were denied entry. The Taliban leaders in Afghanistan themselves pleaded against military action, saying "We appeal to the United States not to put Afghanistan into more misery because our people have suffered so much.", referring to two decades of conflict and the humanitarian crisis attached to it. All United Nations expatriates had left Afghanistan after the attacks and no national or international aid workers were at their post. Workers were instead preparing in bordering countries like Pakistan, China and Uzbekistan to prevent a potential "humanitarian catastrophe", amid a critically low food stock for the Afghan population. The World Food Programme stopped importing wheat to Afghanistan on September 12 due to security risks. '' The Wall Street Journal'' suggested the creation of abuffer zone
A buffer zone is a neutral zonal area that lies between two or more bodies of land, usually pertaining to countries. Depending on the type of buffer zone, it may serve to separate regions or conjoin them.
Common types of buffer zones are demil ...
in an inevitable war, similarly as in the Bosnian War
The Bosnian War ( sh, Rat u Bosni i Hercegovini / Рат у Босни и Херцеговини) was an international armed conflict that took place in Bosnia and Herzegovina between 1992 and 1995. The war is commonly seen as having started ...
.
Approximately one month after the attacks, the United States led a broad coalition of international forces to overthrow the Taliban regime from Afghanistan for their harboring of al-Qaeda. Though Pakistani authorities were initially reluctant to align themselves with the United States against the Taliban, they permitted the coalition access to their military bases, and arrested and handed over to the U.S. over 600 suspected al-Qaeda members.
In a speech by the Nizari Ismaili Imam at the Nobel Institute in 2005, Aga Khan IV stated that the "9/11 attack on the United States was a direct consequence of the international community ignoring the human tragedy that was Afghanistan at that time".
Military operations
At 2:40 p.m. on September 11,Secretary of Defense
A defence minister or minister of defence is a cabinet official position in charge of a ministry of defense, which regulates the armed forces in sovereign states. The role of a defence minister varies considerably from country to country; in som ...
Donald Rumsfeld
Donald Henry Rumsfeld (July 9, 1932 – June 29, 2021) was an American politician, government official and businessman who served as Secretary of Defense from 1975 to 1977 under president Gerald Ford, and again from 2001 to 2006 under Presi ...
was issuing rapid orders to his aides to look for evidence of Iraqi involvement. According to notes taken by senior policy official Stephen Cambone
Stephen Anthony Cambone (born June 22, 1952) was the first United States Under Secretary of Defense for Intelligence, a post created in March 2003. Cambone first came to the attention of the public at large during the testimony of Major General An ...
, Rumsfeld asked for, "Best info fast. Judge whether good enough hit S.H. addam Husseinat same time. Not only UBL" sama bin Laden
Sama or SAMA may refer to:
Places
* Sama, Burkina Faso, a town in the Kouka Department, Banwa Province, Burkina Faso
* Sama, China (Sanya), a city in Hainan, China
* Sama, Chalus, a village in Mazandaran Province, Iran
* Sama, Nowshahr, a vill ...
Cambone's notes quoted Rumsfeld as saying, "Need to move swiftlyNear term target needsgo massivesweep it all up. Things related and not."
In a meeting at Camp David
Camp David is the country retreat for the president of the United States of America. It is located in the wooded hills of Catoctin Mountain Park, in Frederick County, Maryland, near the towns of Thurmont and Emmitsburg, about north-northwe ...
on September 15 the Bush administration rejected the idea of attacking Iraq in response to 9/11. Nonetheless, they later invaded the country with allies, citing "Saddam Hussein's support for terrorism". At the time, as many as seven in ten Americans believed the Iraqi president played a role in the 9/11 attacks. Three years later, Bush conceded that he had not.
 The NATO council declared that the terrorist attacks on the United States were an attack on all NATO nations that satisfied Article 5 of the NATO charter. This marked the first invocation of Article 5, which had been written during the
The NATO council declared that the terrorist attacks on the United States were an attack on all NATO nations that satisfied Article 5 of the NATO charter. This marked the first invocation of Article 5, which had been written during the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
with an attack by the Soviet Union in mind. Australian Prime Minister John Howard, who was in Washington, D.C. during the attacks, invoked Article IV of the ANZUS treaty. The Bush administration announced a War on Terror, with the stated goals of bringing bin Laden and al-Qaeda to justice and preventing the emergence of other terrorist networks. These goals would be accomplished by imposing economic and military sanctions against states harboring terrorists, and increasing global surveillance and intelligence sharing.
On September 14, 2001, the U.S. Congress passed the Authorization for Use of Military Force Against Terrorists. It is still in effect, and grants the President the authority to use all "necessary and appropriate force" against those whom he determined "planned, authorized, committed or aided" the September 11 attacks or who harbored said persons or groups.
On October 7, 2001, the War in Afghanistan began when U.S. and British forces initiated aerial bombing campaigns targeting Taliban and al-Qaeda camps, then later invaded Afghanistan with ground troops of the Special Forces
Special forces and special operations forces (SOF) are military units trained to conduct special operations. NATO has defined special operations as "military activities conducted by specially designated, organized, selected, trained and equip ...
. This eventually led to the overthrow of the Taliban's rule of Afghanistan with the Fall of Kandahar on December 7, 2001, by U.S.-led coalition forces. Osama bin Laden, who went into hiding in the White Mountains, was targeted by U.S. coalition forces in the Battle of Tora Bora, but he escaped across the Pakistani border and would remain out of sight for almost ten years.
The Philippines and Indonesia, among other nations with their own internal conflicts with Islamic terrorism
Islamic terrorism (also known as Islamist terrorism or radical Islamic terrorism) refers to terrorist acts with religious motivations carried out by fundamentalist militant Islamists and Islamic extremists.
Incidents and fatalities f ...
, also increased their military readiness. The military forces of the United States of America and the Islamic Republic of Iran cooperated with each other to overthrow the Taliban regime
The government of Afghanistan, officially called the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is the central government of Afghanistan, a unitary state. Under the leadership of the Taliban, the government is a theocracy and an emirate with political powe ...
which had had conflicts with the government of Iran. Iran's Quds Force helped U.S. forces and Afghan rebels in the 2001 uprising in Herat
The 2001 uprising in Herat was a coordinated insurrection and uprising in the Afghan city of Herat as part of the United States war in Afghanistan. The city was captured on November 12 by Northern Alliance forces as well as Special Forces of t ...
.Qassem Soleimani and Iran's Unique Regional StrategyCombating Terrorism Center at West Point'' Ali Soufan''. ''CTC Sentinel''. November 2018, Vol. 11, Issue 10. Combating Terrorism CenterCTC at West Point
Permanent link and archived version at Wayback Machine
Retrieved and archived on November 19, 2018
Permanent link
at WebCite (November 30, 2018. 14:42:35 UTC).'
Permanent link and Archived Version at Perma.cc
(August 5, 2021). "In the months after 9/11, Soleimani saw an opportunity to defeat the Taliban once and for all by unconventional meansnamely, cooperation with the United States. Early in the war, he directed Iranian diplomats to share intelligence on Taliban military positions with their U.S. counterparts. The Americans, in return, told the Iranians what they knew about an al-Qa`ida fixer hiding out in eastern Iran."''
Effects
Health issues
 Hundreds of thousands of tons of toxic debris containing more than 2,500 contaminants, including known carcinogens, were spread across Lower Manhattan due to the Twin Towers' collapse. Exposure to the toxins in the debris is alleged to have contributed to fatal or debilitating illnesses among people who were at Ground Zero. The Bush administration ordered the
Hundreds of thousands of tons of toxic debris containing more than 2,500 contaminants, including known carcinogens, were spread across Lower Manhattan due to the Twin Towers' collapse. Exposure to the toxins in the debris is alleged to have contributed to fatal or debilitating illnesses among people who were at Ground Zero. The Bush administration ordered the Environmental Protection Agency
A biophysical environment is a biotic and abiotic surrounding of an organism or population, and consequently includes the factors that have an influence in their survival, development, and evolution. A biophysical environment can vary in scale f ...
(EPA) to issue reassuring statements regarding air quality in the aftermath of the attacks, citing national security, but the EPA did not determine that air quality had returned to pre-September 11 levels until June 2002.
Health effects extended to residents, students, and office workers of Lower Manhattan and nearby Chinatown
A Chinatown () is an ethnic enclave of Chinese people located outside Greater China, most often in an urban setting. Areas known as "Chinatown" exist throughout the world, including Europe, North America, South America, Asia, Africa and Austra ...
. Several deaths have been linked to the toxic dust, and the victims' names were included in the World Trade Center memorial. Approximately 18,000 people have been estimated to have developed illnesses as a result of the toxic dust. There is also scientific speculation that exposure to various toxic products in the air may have negative effects on fetal development. A notable children's environmental health center is currently analyzing the children whose mothers were pregnant during the WTC collapse and were living or working nearby. A study of rescue workers released in April 2010 found that all those studied had impaired lung functions, and that 30%–40% were reporting little or no improvement in persistent symptoms that started within the first year of the attack.
Years after the attacks, legal disputes over the costs of illnesses related to the attacks were still in the court system. On October 17, 2006, a federal judge rejected New York City's refusal to pay for health costs for rescue workers, allowing for the possibility of numerous suits against the city. Government officials have been faulted for urging the public to return to lower Manhattan in the weeks shortly after the attacks. Christine Todd Whitman, administrator of the EPA in the attacks' aftermath, was heavily criticized by a U.S. District Judge for incorrectly saying that the area was environmentally safe. Mayor Giuliani was criticized for urging financial industry personnel to return quickly to the greater Wall Street
Wall Street is an eight-block-long street in the Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It runs between Broadway in the west to South Street and the East River in the east. The term "Wall Street" has become a metonym for t ...
area.
On December 22, 2010, the United States Congress passed the James L. Zadroga 9/11 Health and Compensation Act, which President Barack Obama signed into law on January 2, 2011. It allocated $4.2billion to create the World Trade Center Health Program
The World Trade Center Health Program (WTC Health Program) provides medical benefits to specific groups of individuals who were affected by the September 11 attacks in 2001 against the United States. The WTC Health Program was established by Title ...
, which provides testing and treatment for people suffering from long-term health problems related to the 9/11 attacks. The WTC Health Program replaced preexisting 9/11-related health programs such as the Medical Monitoring and Treatment Program and the WTC Environmental Health Center program.
In 2020, the NYPD confirmed that 247 NYPD police officers had died due to 9/11-related illnesses. In September 2022, the FDNY confirmed that the total number of firefighters that died due to 9/11-related illnesses was 299. Both agencies believe that the death toll will rise dramatically in the coming years. The Port Authority of New York and New Jersey Police Department (PAPD), which is the law enforcement agency which has jurisdiction over the World Trade Center due to the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey owning the site, has confirmed that four of its police officers have died of 9/11-related illnesses. The chief of the PAPD at the time, Joseph Morris, made sure that industrial-grade respirators were provided to all PAPD police officers within 48 hours and decided that the same 30 to 40 police officers would be stationed at the World Trade Center pile, drastically lowering the number of total PAPD personnel who would be exposed to the air. The FDNY and NYPD had rotated hundreds, if not thousands, of different personnel from all over New York City to the pile which exposed so many of them to dust that would give them cancer or other diseases years or decades later. Also, they were not given adequate respirators and breathing equipment that could have prevented future diseases.
Economic
The attacks had a significant economic impact on United States and world markets. The stock exchanges did not open on September 11 and remained closed until September 17. Reopening, the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) fell 684 points, or 7.1%, to 8921, a record-setting one-day point decline. By the end of the week, the DJIA had fallen 1,369.7 points (14.3%), at the time its largest one-week point drop in history. In 2001 dollars, U.S. stocks lost $1.4trillion in valuation for the week. In New York City, about 430,000 job-months and $2.8billion in wages were lost in the first three months after the attacks. The economic effects were mainly on the economy's export sectors. The city's GDP was estimated to have declined by $27.3billion for the last three months of 2001 and all of 2002. The U.S. government provided $11.2billion in immediate assistance to the Government of New York City in September 2001, and $10.5billion in early 2002 for economic development and infrastructure needs. Also hurt were small businesses in
Also hurt were small businesses in Lower Manhattan
Lower Manhattan (also known as Downtown Manhattan or Downtown New York) is the southernmost part of Manhattan, the central borough for business, culture, and government in New York City, which is the most populated city in the United States with ...
near the World Trade Center (18,000 of which were destroyed or displaced), resulting in lost jobs and their consequent wages. Assistance was provided by Small Business Administration loans; federal government Community Development Block Grants; and Economic Injury Disaster Loans. Some of Lower Manhattan office space was damaged or destroyed. Many wondered whether these jobs would return, and if the damaged tax base would recover. Studies of 9/11's economic effects show the Manhattan office real-estate market and office employment were less affected than first feared, because of the financial services industry's need for face-to-face interaction.
North American air space was closed for several days after the attacks and air travel decreased upon its reopening, leading to a nearly 20% cutback in air travel capacity, and exacerbating financial problems in the struggling U.S. airline industry.
The September 11 attacks also led to the U.S. wars in Afghanistan and Iraq, as well as additional homeland security spending, totaling at least $5trillion.
Cultural influence
The impact of 9/11 extends beyond geopolitics and into society and culture in general. Immediate responses to 9/11 included greater focus on home life and time spent with family, higher church attendance, and increased expressions of patriotism such as the flying of American flags. The radio industry responded by removing certain songs from playlists, and the attacks have subsequently been used as background, narrative, or thematic elements infilm
A film also called a movie, motion picture, moving picture, picture, photoplay or (slang) flick is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, feelings, beauty, or atmosphere ...
, music, literature, and humor
Humour (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English) or humor (American English) is the tendency of experiences to provoke laughter and provide amusement. The term derives from the humorism, humoral medicine of the ancient Gre ...
. Already-running television shows as well as programs developed after 9/11 have reflected post-9/11 cultural concerns.
9/11 conspiracy theories have become social phenomena, despite lack of support from expert scientists, engineers, and historians. 9/11 has also had a major impact on the religious faith of many individuals; for some it strengthened, to find consolation to cope with the loss of loved ones and overcome their grief; others started to question their faith or lose it entirely, because they could not reconcile it with their view of religion.
The culture of America succeeding the attacks is noted for heightened security and an increased demand thereof, as well as paranoia and anxiety regarding future terrorist attacks that includes most of the nation. Psychologists have also confirmed that there has been an increased amount of national anxiety in commercial air travel. Anti-Muslim hate crimes rose nearly ten-fold in 2001 and have subsequently remained "roughly five times higher than the pre-9/11 rate."
Government policies toward terrorism
Canadian Anti-Terrorism Act
The Canadian ''Anti-terrorism Act'' (french: Loi antiterroriste) (the ''Act'') was passed by the Parliament of Canada in response to the September 11, 2001, attacks in the United States. It received Royal Assent on December 18, 2001, as Bill C-36. ...
, their first anti-terrorism law. The United Kingdom passed the Anti-terrorism, Crime and Security Act 2001 and the Prevention of Terrorism Act 2005. New Zealand enacted the Terrorism Suppression Act 2002.
In the United States, the Department of Homeland Security was created by the Homeland Security Act of 2002
The Homeland Security Act (HSA) of 2002, () was introduced in the aftermath of the September 11 attacks and subsequent mailings of anthrax spores. The HSA was cosponsored by 118 members of Congress. The act passed the U.S. Senate by a vote of ...
to coordinate domestic anti-terrorism efforts. The USA Patriot Act gave the federal government greater powers, including the authority to detain foreign terror suspects for a week without charge; to monitor terror suspects' telephone communications, e-mail, and Internet use; and to prosecute suspected terrorists without time restrictions. The FAA ordered that airplane cockpits be reinforced to prevent terrorists gaining control of planes, and assigned sky marshals to flights.
Further, the Aviation and Transportation Security Act made the federal government, rather than airports, responsible for airport security. The law created the Transportation Security Administration to inspect passengers and luggage, causing long delays and concern over passenger privacy. After suspected abuses of the USA Patriot Act were brought to light in June 2013 with articles about the collection of American call records by the NSA and the PRISM program (see Global surveillance disclosures (2013–present)), Representative Jim Sensenbrenner
Frank James Sensenbrenner Jr. (; born June 14, 1943) is an American politician who represented in the United States House of Representatives from 1979 to 2021 (numbered as the 9th district until 2003). He is a member of the Republican Party.
...
,(R- Wisconsin) who introduced the Patriot Act in 2001, said that the NSA overstepped its bounds.
Criticism of the war on terror has focused on its morality, efficiency, and cost. According to a 2021 study conducted under the auspices of the Watson Institute for International and Public Affairs, the several post-9/11 wars participated in by the United States in its War on Terror have caused the displacement, conservatively calculated, of 38 million people in Afghanistan, Pakistan, Iraq, Libya, Syria, Yemen, Somalia, and the Philippines. The study estimated these wars caused the deaths of 897,000 to 929,000 people and cost $8 trillion dollars. The U.S. Constitution and U.S. law
The law of the United States comprises many levels of Codification (law), codified and uncodified forms of law, of which the most important is the nation's Constitution of the United States, Constitution, which prescribes the foundation of the ...
prohibits the use of torture, yet such human rights violations occurred during the War on Terror under the euphemism Enhanced interrogation. In 2005, ''The Washington Post'' and Human Rights Watch (HRW) published revelations concerning CIA flights and " black sites", covert prisons operated by the CIA. The term "torture by proxy" is used by some critics to describe situations in which the CIA and other U.S. agencies have transferred suspected terrorists to countries known to employ torture.
Investigations
FBI
Immediately after the attacks, theFederal Bureau of Investigation
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic intelligence and security service of the United States and its principal federal law enforcement agency. Operating under the jurisdiction of the United States Department of Justice, t ...
started PENTTBOM
PENTTBOM is the codename for the Federal Bureau of Investigation's probe into the September 11 attacks of 2001, the largest criminal inquiry in the FBI's history. Its name stands for " Pentagon/ Twin Towers Bombing Investigation". The investigat ...
, the largest criminal inquiry in United States history. At its height, more than half of the FBI's agents worked on the investigation and followed a half-million leads. The FBI concluded that there was "clear and irrefutable" evidence linking al-Qaeda and bin Laden to the attacks.
 The FBI was quickly able to identify the hijackers, including leader Mohamed Atta, when his luggage was discovered at Boston's Logan Airport. Atta had been forced to check two of his three bags due to space limitations on the 19-seat commuter flight he took to Boston. Due to a new policy instituted to prevent flight delays, the luggage failed to make it aboard American Airlines Flight 11 as planned. The luggage contained the hijackers' names, assignments, and al-Qaeda connections. "It had all these Arab-language papers that amounted to the Rosetta stone of the investigation", said one FBI agent. Within hours of the attacks, the FBI released the names and in many cases the personal details of the suspected pilots and hijackers. Abu Jandal, who served as bin Laden's chief bodyguard for years, confirmed the identity of seven hijackers as al-Qaeda members during interrogations with the FBI on September 17. He had been jailed in a Yemeni prison since 2000. On September 27, 2001, photos of all 19 hijackers were released, along with information about possible nationalities and aliases. Fifteen of the men were from Saudi Arabia, two were from the United Arab Emirates, one was from Egypt, and one was from Lebanon.
By midday, the U.S. National Security Agency and German intelligence agencies had intercepted communications pointing to Osama bin Laden. Two of the hijackers were known to have traveled with a bin Laden associate to Malaysia in 2000 and hijacker
The FBI was quickly able to identify the hijackers, including leader Mohamed Atta, when his luggage was discovered at Boston's Logan Airport. Atta had been forced to check two of his three bags due to space limitations on the 19-seat commuter flight he took to Boston. Due to a new policy instituted to prevent flight delays, the luggage failed to make it aboard American Airlines Flight 11 as planned. The luggage contained the hijackers' names, assignments, and al-Qaeda connections. "It had all these Arab-language papers that amounted to the Rosetta stone of the investigation", said one FBI agent. Within hours of the attacks, the FBI released the names and in many cases the personal details of the suspected pilots and hijackers. Abu Jandal, who served as bin Laden's chief bodyguard for years, confirmed the identity of seven hijackers as al-Qaeda members during interrogations with the FBI on September 17. He had been jailed in a Yemeni prison since 2000. On September 27, 2001, photos of all 19 hijackers were released, along with information about possible nationalities and aliases. Fifteen of the men were from Saudi Arabia, two were from the United Arab Emirates, one was from Egypt, and one was from Lebanon.
By midday, the U.S. National Security Agency and German intelligence agencies had intercepted communications pointing to Osama bin Laden. Two of the hijackers were known to have traveled with a bin Laden associate to Malaysia in 2000 and hijacker Mohammed Atta
Mohamed Mohamed el-Amir Awad el-Sayed Atta ( ; ar, محمد محمد الأمير عوض السيد عطا ; September 1, 1968 – September 11, 2001) was an Egyptian hijacker and the ringleader of the September 11 attacks in 2001 in which fo ...
had previously gone to Afghanistan. He and others were part of a terrorist cell in Hamburg. One of the members of the Hamburg cell in Germany was discovered to have been in communication with Khalid Sheik Mohammed who was identified as a member of al-Qaeda
Al-Qaeda (; , ) is an Islamic extremism, Islamic extremist organization composed of Salafist jihadists. Its members are mostly composed of Arab, Arabs, but also include other peoples. Al-Qaeda has mounted attacks on civilian and military ta ...
.
Authorities in the United States and United Kingdom also obtained electronic intercepts, including telephone conversations and electronic bank transfers, which indicated that Mohammed Atef
Mohammed Atef ( ar, محمد عاطف, ; born Sobhi Mohammed Abu Sitta Al-Gohary, also known as Abu Hafs al-Masri) was the military chief of al-Qaeda, and was considered one of Osama bin Laden's two deputies, the other being Ayman Al Zawahiri, ...
, a bin Laden deputy, was a key figure in the planning of the 9/11 attacks. Intercepts were also obtained that revealed conversations that took place days before September 11 between bin Laden and an associate in Pakistan. In those conversations, the two referred to "an incident that would take place in America on, or around, September 11" and they discussed potential repercussions. In another conversation with an associate in Afghanistan, bin Laden discussed the "scale and effects of a forthcoming operation." These conversations did not specifically mention the World Trade Center, the Pentagon, or other specifics.
The FBI did not record the 2,977 deaths from the attacks in their annual violent crime index for 2001. In a disclaimer, the FBI stated that "the number of deaths is so great that combining it with the traditional crime statistics
Crime statistics refer to systematic, quantitative results about crime, as opposed to crime news or anecdotes. Notably, crime statistics can be the result of two rather different processes:
* scientific research, such as criminological studies, vi ...
will have an outlier
In statistics, an outlier is a data point that differs significantly from other observations. An outlier may be due to a variability in the measurement, an indication of novel data, or it may be the result of experimental error; the latter are ...
effect that falsely skews all types of measurements in the program's analyses." New York City also did not include the deaths in their annual crime statistics for 2001.
CIA
In 2004,John L. Helgerson
John L. Helgerson is a retired career intelligence officer who spent 38 years at the Central Intelligence Agency, his final role was CIA Inspector General from 2002 until his retirement in 2009. He was responsible for investigating CIA interrogati ...
, the Inspector General of the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), conducted an internal review of the agency's pre-9/11 performance and was harshly critical of senior CIA officials for not doing everything possible to confront terrorism. According to Philip Giraldi
Philip Giraldi (born c. 1946) is an American columnist, commentator and security consultant. He is the Executive Director of the Council for the National Interest, a role he has held since 2010. He was previously employed as an intelligence offic ...
in '' The American Conservative'', Helgerson criticized their failure to stop two of the 9/11 hijackers, Nawaf al-Hazmi and Khalid al-Mihdhar, as they entered the United States and their failure to share information on the two men with the FBI.
In May 2007, senators from both major U.S. political parties drafted legislation to make the review public. One of the backers, Senator Ron Wyden
Ronald Lee Wyden (; born May 3, 1949) is an American politician and retired educator serving as the Seniority in the United States Senate, senior United States Senate, United States senator from Oregon, a seat he has held since 1996 United Stat ...
said, "The American people have a right to know what the Central Intelligence Agency was doing in those critical months before 9/11." The report was released in 2009 by President Barack Obama.
Congressional inquiry
In February 2002, the Senate Select Committee on Intelligence and the House Permanent Select Committee on Intelligence formed a joint inquiry into the performance of theU.S. Intelligence Community
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
. Their 832-page report released in December 2002 detailed failings of the FBI and CIA to use available information, including about terrorists the CIA knew were in the United States, in order to disrupt the plots. The joint inquiry developed its information about possible involvement of Saudi Arabian government officials from non-classified sources. Nevertheless, the Bush administration demanded 28 related pages remain classified. In December 2002, the inquiry's chair Bob Graham
Daniel Robert "Bob" Graham (born November 9, 1936) is an American lawyer, author, and politician who served as the 38th governor of Florida from 1979 to 1987 and a United States senator from Florida from 1987 to 2005. He is a member of the Dem ...
(D-FL) revealed in an interview that there was "evidence that there were foreign governments involved in facilitating the activities of at least some of the terrorists in the United States." September 11 victim families were frustrated by the unanswered questions and redacted material from the congressional inquiry and demanded an independent commission. September 11 victim families, members of Congress and the Saudi Arabian government are still seeking release of the documents. In June 2016, CIA chief John Brennan John Brennan may refer to:
Public officials
* Jack Brennan (born 1937), U.S. Marine officer and aide of Richard Nixon
* John Brennan (CIA officer) (born 1955), former CIA Director
* John P. Brennan (1864–1943), Democratic politician in the U. ...
said that he believes 28 redacted pages of a congressional inquiry into 9/11 will soon be made public, and that they will prove that the government of Saudi Arabia had no involvement in the September 11 attacks.
In September 2016, the Congress passed the Justice Against Sponsors of Terrorism Act that would allow relatives of victims of the September 11 attacks to sue Saudi Arabia for its government's alleged role in the attacks.
9/11 Commission
The National Commission on Terrorist Attacks Upon the United States (9/11 Commission), chaired by Thomas Kean andLee H. Hamilton
Lee Herbert Hamilton (born April 20, 1931) is an American politician and lawyer from Indiana. He is a former member of the United States House of Representatives and a former member of the U.S. Homeland Security Advisory Council. A member of the ...
, was formed in late 2002 to prepare a thorough account of the circumstances surrounding the attacks, including preparedness for and the immediate response to the attacks. On July 22, 2004, the Commission issued the '' 9/11 Commission Report''. The report detailed the events of 9/11, found the attacks were carried out by members of al-Qaeda, and examined how security and intelligence agencies were inadequately coordinated to prevent the attacks.
Formed from an independent bipartisan group of mostly former senators, representatives, and governors, the commissioners explained, "We believe the 9/11 attacks revealed four kinds of failures: in imagination, policy, capabilities, and management." The Commission made numerous recommendations on how to prevent future attacks, and in 2011 was dismayed that several of its recommendations had yet to be implemented.
National Institute of Standards and Technology
 The U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
The U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)