1.96 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 The use of this number in applied statistics can be traced to the influence of
The use of this number in applied statistics can be traced to the influence of
 In
In probability
Probability is the branch of mathematics concerning numerical descriptions of how likely an event is to occur, or how likely it is that a proposition is true. The probability of an event is a number between 0 and 1, where, roughly speakin ...
and statistics, the 97.5th percentile point of the standard normal distribution
In statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is
:
f(x) = \frac e^
The parameter \mu ...
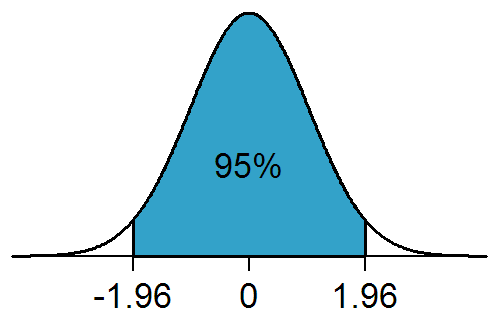
is a number commonly used for statistical calculations. The approximate value of this number is 1.96, meaning that 95% of the area under a normal curve lies within approximately 1.96 standard deviations of the mean
There are several kinds of mean in mathematics, especially in statistics. Each mean serves to summarize a given group of data, often to better understand the overall value (magnitude and sign) of a given data set.
For a data set, the '' ari ...
. Because of the central limit theorem
In probability theory, the central limit theorem (CLT) establishes that, in many situations, when independent random variables are summed up, their properly normalized sum tends toward a normal distribution even if the original variables themsel ...
, this number is used in the construction of approximate 95% confidence intervals. Its ubiquity is due to the arbitrary but common convention of using confidence intervals with 95% probability in science and frequentist statistics, though other probabilities (90%, 99%, etc.) are sometimes used.
This convention seems particularly common in medical statistics,
but is also common in other areas of application, such as earth sciences,
social sciences and business research.
There is no single accepted name for this number; it is also commonly referred to as the "standard normal deviate", "normal score The term normal score is used with two different meanings in statistics. One of them relates to creating a single value which can be treated as if it had arisen from a standard normal distribution (zero mean, unit variance). The second one relates t ...
" or "Z score
In statistics, the standard score is the number of standard deviations by which the value of a raw score (i.e., an observed value or data point) is above or below the mean value of what is being observed or measured. Raw scores above the mean ...
" for the 97.5 percentile point, the .975 point, or just its approximate value, 1.96.
If ''X'' has a standard normal distribution, i.e. ''X'' ~ N(0,1),
:
:
and as the normal distribution is symmetric,
:
One notation for this number is ''z''.975.
From the probability density function
In probability theory, a probability density function (PDF), or density of a continuous random variable, is a function whose value at any given sample (or point) in the sample space (the set of possible values taken by the random variable) ca ...
of the standard normal distribution, the exact value of ''z''.975 is determined by
:
History
Ronald Fisher
Sir Ronald Aylmer Fisher (17 February 1890 – 29 July 1962) was a British polymath who was active as a mathematician, statistician, biologist, geneticist, and academic. For his work in statistics, he has been described as "a genius who ...
's classic textbook, Statistical Methods for Research Workers, first published in 1925:
In Table 1 of the same work, he gave the more precise value 1.959964.
In 1970, the value truncated to 20 decimal places was calculated to be
:1.95996 39845 40054 23552...
The commonly used approximate value of 1.96 is therefore accurate to better than one part in 50,000, which is more than adequate for applied work.
Some people even use the value of 2 in the place of 1.96, reporting a 95.4% confidence interval as a 95% confidence interval. This is not recommended but is occasionally seen.
Software functions
The inverse of the standard normal CDF can be used to compute the value. The following is a table of function calls that return 1.96 in some commonly used applications:See also
*Margin of error
The margin of error is a statistic expressing the amount of random sampling error in the results of a survey. The larger the margin of error, the less confidence one should have that a poll result would reflect the result of a census of the e ...
*Probit
In probability theory and statistics, the probit function is the quantile function associated with the standard normal distribution. It has applications in data analysis and machine learning, in particular exploratory statistical graphics and s ...
*Reference range
In medicine and health-related fields, a reference range or reference interval is the range or the interval of values that is deemed normal for a physiological measurement in healthy persons (for example, the amount of creatinine in the blood, o ...
*Standard error (statistics)
The standard error (SE) of a statistic (usually an estimate of a parameter) is the standard deviation of its sampling distribution or an estimate of that standard deviation. If the statistic is the sample mean, it is called the standard error of ...
* 68–95–99.7 rule
References
Further reading
*{{Citation , editor-last=Gardner , editor-first=Martin J , editor2-last=Altman , editor2-first=Douglas G , editor2-link=Doug Altman , title=Statistics with confidence , publisher=BMJ Books , year=1989 , isbn=978-0-7279-0222-1 , url=https://archive.org/details/statisticswithco0000unse Estimation theory Normal distribution Mathematical constants