β Cells on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Beta cells (β-cells) are a type of
 In beta cells, insulin release is stimulated primarily by glucose present in the blood. As circulating glucose levels rise such as after ingesting a meal, insulin is secreted in a dose-dependent fashion. This system of release is commonly referred to as glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS). There are four key pieces to the triggering pathway of GSIS:
In beta cells, insulin release is stimulated primarily by glucose present in the blood. As circulating glucose levels rise such as after ingesting a meal, insulin is secreted in a dose-dependent fashion. This system of release is commonly referred to as glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS). There are four key pieces to the triggering pathway of GSIS:
cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
found in pancreatic islets
The pancreatic islets or islets of Langerhans are the regions of the pancreas that contain its endocrine (hormone-producing) cells, discovered in 1869 by German pathological anatomist Paul Langerhans. The pancreatic islets constitute 1–2% of ...
that synthesize and secrete insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism o ...
and amylin
Amylin, or islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP), is a 37-residue peptide hormone
Peptide hormones or protein hormones are hormones whose molecules are peptide, or proteins, respectively. The latter have longer amino acid chain lengths than the forme ...
. Beta cells make up 50–70% of the cells in human islets. In patients with Type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes (T1D), formerly known as juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune disease that originates when cells that make insulin (beta cells) are destroyed by the immune system. Insulin is a hormone required for the cells to use blood sugar for ...
, beta-cell mass and function are diminished, leading to insufficient insulin secretion and hyperglycemia.
Function
The primary function of a beta cell is to produce and releaseinsulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism o ...
and amylin
Amylin, or islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP), is a 37-residue peptide hormone
Peptide hormones or protein hormones are hormones whose molecules are peptide, or proteins, respectively. The latter have longer amino acid chain lengths than the forme ...
. Both are hormone
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required ...
s which reduce blood glucose
Glycaemia, also known as blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, or blood glucose level is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood of humans or other animals. Approximately 4 grams of glucose, a simple sugar, is present in the blo ...
levels by different mechanisms. Beta cells can respond quickly to spikes in blood glucose concentrations by secreting some of their stored insulin and amylin while simultaneously producing more. Primary cilia
The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike projecti ...
on beta cells regulate their function and energy metabolism. Cilia deletion can lead to islet dysfunction and type 2 diabetes.
Insulin synthesis
Beta cells are the only site of insulin synthesis in mammals. As glucose stimulates insulin secretion, it simultaneously increases proinsulin biosynthesis, mainly through translational control. Theinsulin gene
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism o ...
is first transcribed into mRNA and translated into preproinsulin. After translation, the preproinsulin precursor contains an N-terminal signal peptide that allows translocation into the rough endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum ( ...
(RER). Inside the RER, the signal peptide is cleaved to form proinsulin. Then, folding of proinsulin occurs forming three disulfide bonds. Subsequent to protein folding, proinsulin is transported to the Golgi apparatus and enters immature insulin granules where proinsulin is cleaved to form insulin and C-peptide
The connecting peptide, or C-peptide, is a short 31-amino-acid polypeptide that connects insulin, insulin's A-chain to its B-chain in the proinsulin molecule. In the context of diabetes or hypoglycemia, a measurement of C-peptide blood serum lev ...
. After maturation, these secretory vesicles hold insulin, C-peptide, and amylin until calcium triggers exocytosis of the granule contents.
Through translational processing, insulin is encoded as a 110 amino acid precursor but is secreted as a 51 amino acid protein.
Insulin secretion
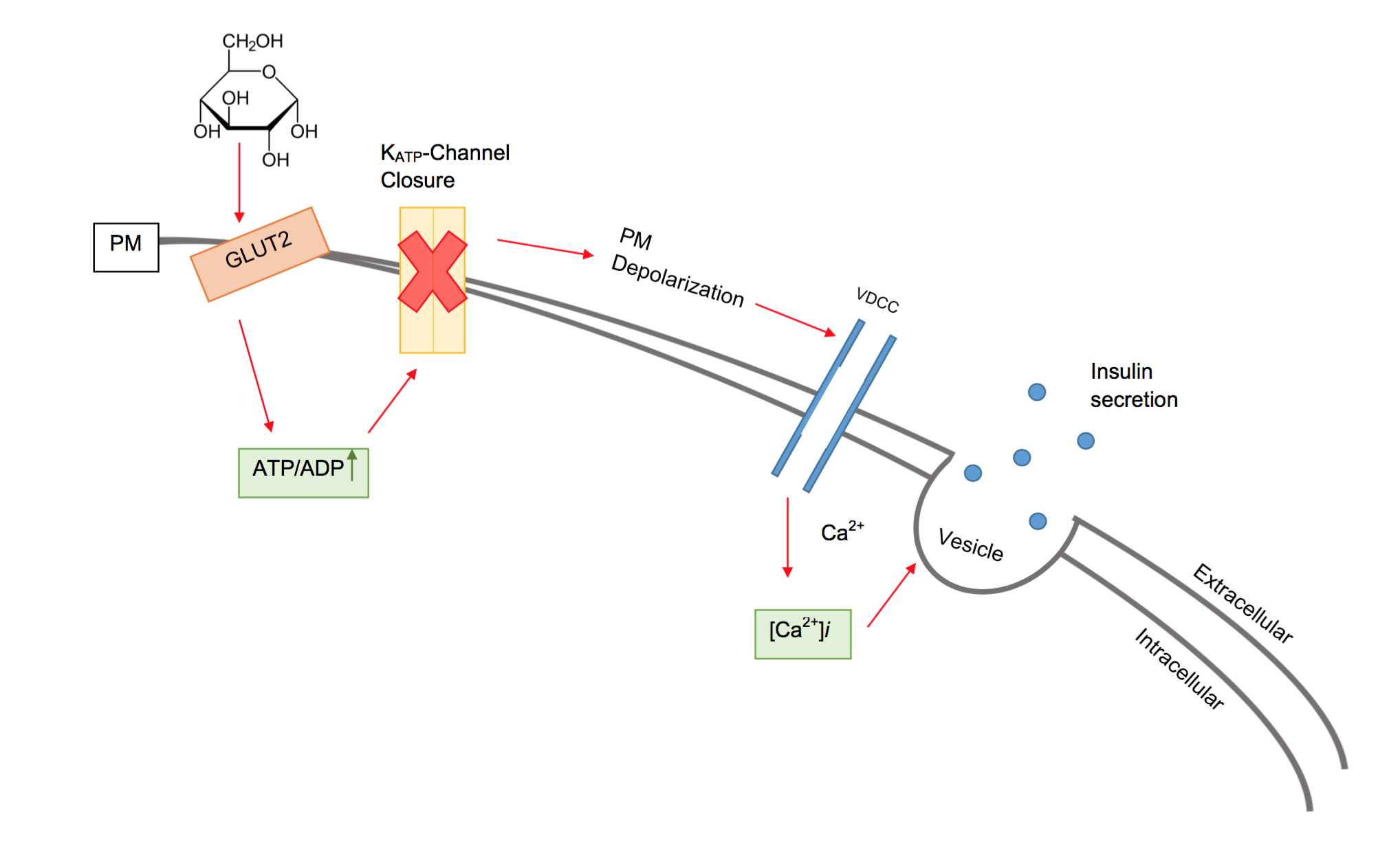
 In beta cells, insulin release is stimulated primarily by glucose present in the blood. As circulating glucose levels rise such as after ingesting a meal, insulin is secreted in a dose-dependent fashion. This system of release is commonly referred to as glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS). There are four key pieces to the triggering pathway of GSIS:
In beta cells, insulin release is stimulated primarily by glucose present in the blood. As circulating glucose levels rise such as after ingesting a meal, insulin is secreted in a dose-dependent fashion. This system of release is commonly referred to as glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS). There are four key pieces to the triggering pathway of GSIS: GLUT2
Glucose transporter 2 (GLUT2) also known as solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 2 (SLC2A2) is a transmembrane carrier protein that enables protein facilitated glucose movement across cell membranes. It is the principa ...
dependent glucose uptake, glucose metabolism, KATP channel closure, and the opening of voltage gated calcium channels causing insulin granule fusion and exocytosis.
Voltage-gated calcium channels
Voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs), also known as voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs), are a group of voltage-gated ion channels found in the membrane of excitable cells (''e.g.'', muscle, glial cells, neurons, etc.) with a permeabili ...
and ATP-sensitive potassium ion channels are embedded in the plasma membrane of beta cells. These ATP-sensitive potassium ion channels are normally open and the calcium ion channels are normally closed. Potassium ions diffuse out of the cell, down their concentration gradient, making the inside of the cell more negative with respect to the outside (as potassium ions carry a positive charge). At rest, this creates a potential difference
Voltage, also known as electric pressure, electric tension, or (electric) potential difference, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a static electric field, it corresponds to the work needed per unit of charge to m ...
across the cell surface membrane of -70mV.
When the glucose concentration outside the cell is high, glucose molecules move into the cell by facilitated diffusion
Facilitated diffusion (also known as facilitated transport or passive-mediated transport) is the process of spontaneous passive transport (as opposed to active transport) of molecules or ions across a biological membrane via specific transmembra ...
, down its concentration gradient through the GLUT2
Glucose transporter 2 (GLUT2) also known as solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 2 (SLC2A2) is a transmembrane carrier protein that enables protein facilitated glucose movement across cell membranes. It is the principa ...
transporter. Since beta cells use glucokinase
Glucokinase () is an enzyme that facilitates phosphorylation of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate. Glucokinase occurs in cells in the liver and pancreas of humans and most other vertebrates. In each of these organs it plays an important role in ...
to catalyze the first step of glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose () into pyruvate (). The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH ...
, metabolism only occurs around physiological blood glucose
Glycaemia, also known as blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, or blood glucose level is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood of humans or other animals. Approximately 4 grams of glucose, a simple sugar, is present in the blo ...
levels and above. Metabolism of the glucose produces ATP, which increases the ATP to ADP ratio.
The ATP-sensitive potassium ion channels close when this ratio rises. This means that potassium ions can no longer diffuse out of the cell. As a result, the potential difference across the membrane becomes more positive (as potassium ions accumulate inside the cell). This change in potential difference opens the voltage-gated calcium channels
Voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs), also known as voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs), are a group of voltage-gated ion channels found in the membrane of excitable cells (''e.g.'', muscle, glial cells, neurons, etc.) with a permeabili ...
, which allows calcium ions from outside the cell to diffuse in down their concentration gradient. When the calcium ions enter the cell, they cause vesicles
Vesicle may refer to:
; In cellular biology or chemistry
* Vesicle (biology and chemistry), a supramolecular assembly of lipid molecules, like a cell membrane
* Synaptic vesicle
; In human embryology
* Vesicle (embryology), bulge-like features o ...
containing insulin to move to, and fuse with, the cell surface membrane, releasing insulin by exocytosis
Exocytosis () is a form of active transport and bulk transport in which a cell transports molecules (e.g., neurotransmitters and proteins) out of the cell ('' exo-'' + ''cytosis''). As an active transport mechanism, exocytosis requires the use o ...
into the hepatic portal vein.
In addition to the triggering pathway, the amplifying pathway can cause increased insulin secretion without a further increase in intracellular calcium levels. The amplifying pathway is modulated by byproducts of glucose metabolism along with various intracellular signaling pathways.
Other hormones secreted
*C-peptide
The connecting peptide, or C-peptide, is a short 31-amino-acid polypeptide that connects insulin, insulin's A-chain to its B-chain in the proinsulin molecule. In the context of diabetes or hypoglycemia, a measurement of C-peptide blood serum lev ...
, which is secreted into the bloodstream in equimolar quantities to insulin. C-peptide helps to prevent neuropathy and other vascular deterioration related symptoms of diabetes mellitus
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
. A practitioner would measure the levels of C-peptide to obtain an estimate for the viable beta cell mass.
* Amylin
Amylin, or islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP), is a 37-residue peptide hormone
Peptide hormones or protein hormones are hormones whose molecules are peptide, or proteins, respectively. The latter have longer amino acid chain lengths than the forme ...
, also known as islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP). The function of amylin is to slow the rate of glucose entering the bloodstream. Amylin can be described as a synergistic partner to insulin, where insulin regulates long term food intake and amylin regulates short term food intake.
Clinical significance
Type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes mellitus
Type 1 diabetes (T1D), formerly known as juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune disease that originates when cells that make insulin (beta cells) are destroyed by the immune system. Insulin is a hormone required for the cells to use blood sugar for ...
, also known as insulin-dependent diabetes, is believed to be caused by an auto-immune mediated destruction of the insulin-producing beta cells in the body. The process of beta-cell destruction begins with insulitis activating antigen-presenting cells (APCs). APCs then trigger activation of CD4+ helper-T cells and chemokines/cytokines release. Then, the cytokines activate CD8+ cytotoxic–T cells which leads to beta-cell destruction. The destruction of these cells reduces the body's ability to respond to glucose levels in the body, therefore making it nearly impossible to properly regulate glucose and glucagon levels in the bloodstream. The body destroys 70–80% of beta cells, leaving only 20–30% of functioning cells. This can cause the patient to experience hyperglycemia, which leads to other adverse short-term and long-term conditions. The symptoms of diabetes can potentially be controlled with methods such as regular doses of insulin and sustaining a proper diet. However, these methods can be tedious and cumbersome to continuously perform on a daily basis.
Type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes, formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, ...
, also known as non insulin dependent diabetes and as chronic hyperglycemia, is caused primarily by genetics and the development of metabolic syndrome. The beta cells can still secrete insulin but the body has developed a resistance and its response to insulin has declined. It is believed to be due to the decline of specific receptors on the surface of the liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for ...
, adipose
Adipose tissue, body fat, or simply fat is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. In addition to adipocytes, adipose tissue contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular ...
, and muscle cells
A muscle cell is also known as a myocyte when referring to either a cardiac muscle cell (cardiomyocyte), or a smooth muscle cell as these are both small cells. A skeletal muscle cell is long and threadlike with many nuclei and is called a muscle ...
which lose their ability to respond to insulin that circulates in the blood. In an effort to secrete enough insulin to overcome the increasing insulin resistance, the beta cells increase their function, size and number. Increased insulin secretion leads to hyperinsulinemia, but blood glucose levels remain within their normal range due to the decreased efficacy of insulin signaling. However, the beta cells can become overworked and exhausted from being overstimulated, leading to a 50% reduction in function along with a 40% decrease in beta-cell volume. At this point, not enough insulin can be produced and secreted to keep blood glucose levels within their normal range, causing overt type 2 diabetes.
Insulinoma
Insulinoma
An insulinoma is a tumour of the pancreas that is derived from beta cells and secretes insulin. It is a rare form of a neuroendocrine tumour. Most insulinomas are benign in that they grow exclusively at their origin within the pancreas, but a min ...
is a rare tumor derived from the neoplasia of beta cells. Insulinomas are usually benign
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse.
Malignancy is most familiar as a characterization of cancer. A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous benign tumor, ''benign'' tumor in that a malign ...
, but may be medically significant and even life-threatening due to recurrent and prolonged attacks of hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia, also called low blood sugar, is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal, typically below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Whipple's triad is used to properly identify hypoglycemic episodes. It is defined as blood glucose belo ...
.
Medications
Many drugs to combat diabetes are aimed at modifying the function of the beta cell. * Sulfonylureas are insulin secretagogues that act by closing the ATP-sensitive potassium channels, thereby causing insulin release. These drugs are known to cause hypoglycemia and can lead to beta-cell failure due to overstimulation. Second-generation versions of sulfonylureas are shorter acting and less likely to cause hypoglycemia. * GLP-1 receptor agonists stimulate insulin secretion by simulating activation of the body's endogenous incretin system. The incretin system acts as an insulin secretion amplifying pathway. * DPP-4 inhibitors block DPP-4 activity which increases postprandial incretin hormone concentration, therefore increasing insulin secretion.Research
Experimental techniques
Many researchers around the world are investigating the pathogenesis of diabetes and beta-cell failure. Tools used to study beta-cell function are expanding rapidly with technology. For instance, transcriptomics have allowed researchers to comprehensively analyze gene transcription in beta-cells to look for genes linked to diabetes. A more common mechanism of analyzing cellular function is calcium imaging. Fluorescent dyes bind to calcium and allow ''in vitro'' imaging of calcium activity which correlates directly with insulin release. A final tool used in beta-cell research are ''in vivo'' experiments. Diabetes mellitus can be experimentally induced ''in vivo'' for research purposes bystreptozotocin
Streptozotocin or streptozocin (INN, USP) (STZ) is a naturally occurring alkylating antineoplastic agent that is particularly toxic to the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas in mammals. It is used in medicine for treating certain canc ...
or alloxan
Alloxan, sometimes referred to as ''alloxan hydrate'', is the name of the organic compound with the formula OC(N(H)CO)2C(OH)2. It is classified as a derivative of pyrimidine. The anhydrous derivative OC(N(H)CO)2CO is also known, as well as a dime ...
, which are specifically toxic to beta cells. Mouse and rat models of diabetes also exist including ob/ob and db/db mice which are a type 2 diabetes model, and non-obese diabetic mice (NOD) which are a model for type 1 diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes
Research has shown that beta cells can be differentiated from human pancreas progenitor cells. These differentiated beta cells, however, often lack much of the structure and markers that beta cells need to perform their necessary functions. Examples of the anomalies that arise from beta cells differentiated from progenitor cells include a failure to react to environments with high glucose concentrations, an inability to produce necessary beta cell markers, and abnormal expression of glucagon along with insulin. In order to successfully re-create functional insulin producing beta cells, studies have shown that manipulating cell-signal pathways in early stem cell development will lead to those stem cells differentiating into viable beta cells. Two key signal pathways have been shown to play a vital role in the differentiation of stem cells into beta cells: the BMP4 pathway and the kinase C. Targeted manipulation of these two pathways has shown that it is possible to induce beta cell differentiation from stem cells. These variations of artificial beta cells have shown greater levels of success in replicating the functionality of natural beta cells, although the replication has not been perfectly re-created yet. Studies have shown that it is possible to regenerate beta cells ''in vivo'' in some animal models. Research in mice has shown that beta cells can often regenerate to the original quantity number after the beta cells have undergone some sort of stress test, such as the intentional destruction of the beta cells in the mice subject or once the auto-immune response has concluded. While these studies have conclusive results in mice, beta cells in human subjects may not possess this same level of versatility. Investigation of beta cells following acute onset of Type 1 diabetes has shown little to no proliferation of newly synthesized beta cells, suggesting that human beta cells might not be as versatile as rat beta cells, but there is actually no comparison that can be made here because healthy (non-diabetic) rats were used to prove that beta cells can proliferate after intentional destruction of beta cells, while diseased (type-1 diabetic) humans were used in the study which was attempted to use as evidence against beta cells regenerating. It appears that much work has to be done in the field of regenerating beta cells. Just as in the discovery of creating insulin through the use of recombinant DNA, the ability to artificially create stem cells that would differentiate into beta cells would prove to be an invaluable resource to patients with Type 1 diabetes. An unlimited amount of beta cells produced artificially could potentially provide therapy to many of the patients who are affected by Type 1 diabetes.Type 2 diabetes
Research focused on non insulin dependent diabetes encompasses many areas of interest. Degeneration of the beta cell as diabetes progresses has been a broadly reviewed topic. Another topic of interest for beta-cell physiologists is the mechanism of insulin pulsatility which has been well investigated. Many genome studies have been completed and are advancing the knowledge of beta-cell function exponentially. Indeed, the area of beta-cell research is very active yet many mysteries remain.See also
*Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor
The gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (GIP-R), also known as the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GIPR'' gene. GIP-R is a member of the 7-transmembrane protein family, a ...
* List of terms associated with diabetes
* Guangxitoxin
Guangxitoxin, also known as GxTX, is a peptide toxin found in the venom of the tarantula '' Plesiophrictus guangxiensis''. It primarily inhibits outward voltage-gated Kv2.1 potassium channel currents, which are prominently expressed in pancreati ...
* Alpha cell
Alpha cells (α cells) are endocrine cells that are found in the Islets of langerhans, Islets of Langerhans in the pancreas. Alpha cells secrete the peptide hormone glucagon in order to increase glucose levels in the blood stream.
Discovery
Isle ...
* Pancreatic development
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e. it has both an endocri ...
* Islets of Langerhans
The pancreatic islets or islets of Langerhans are the regions of the pancreas that contain its endocrine (hormone-producing) cells, discovered in 1869 by German pathological anatomist Paul Langerhans. The pancreatic islets constitute 1–2% of ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Beta Cell Peptide hormone secreting cells