α-thujone on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Thujone () is a
/ref> Thujone acts on the
File:(-)-alpha-Thujon.svg, (−)-α-thujone
File:Alpha-(+)-Thujon.svg, (+)-α-thujone
File:Beta-(+)-Thujon.svg, (+)-β-thujone
File:Beta-(-)-Thujon.svg, (−)-β-thujone
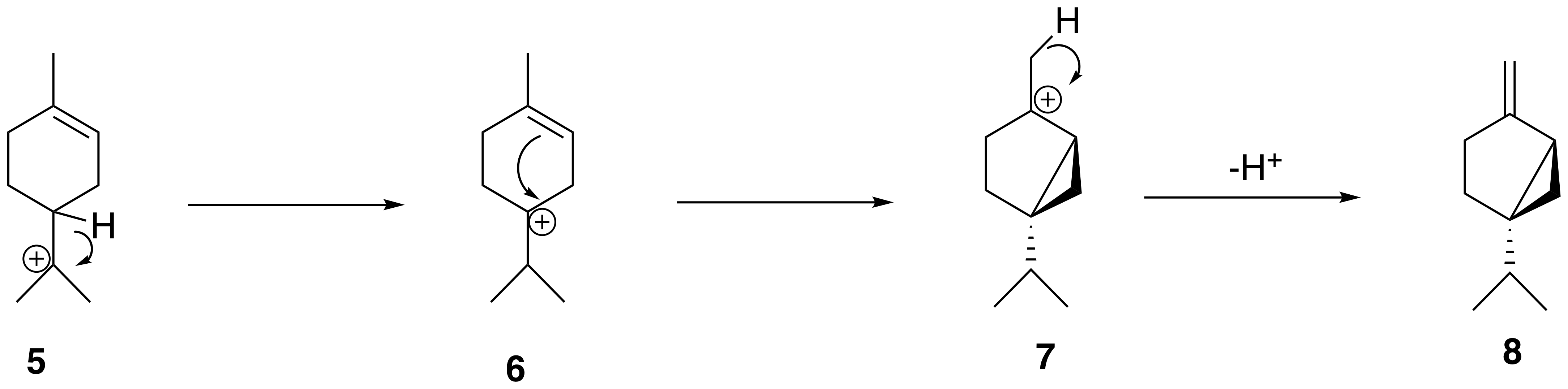
 The α-terpinyl cation (5) then undergoes a 1,2 hydride shift via a Wagner-Meerwein rearrangement, Wagner–Meerwein rearrangement, leading to the formation of the terpinen-4-yl cation (6). This cation undergoes a second cyclization to form the thujyl cation intermediate (7) before loss of a proton to form the thujone precursor, Sabinene, (+)-sabinene (8).
The α-terpinyl cation (5) then undergoes a 1,2 hydride shift via a Wagner-Meerwein rearrangement, Wagner–Meerwein rearrangement, leading to the formation of the terpinen-4-yl cation (6). This cation undergoes a second cyclization to form the thujyl cation intermediate (7) before loss of a proton to form the thujone precursor, Sabinene, (+)-sabinene (8).
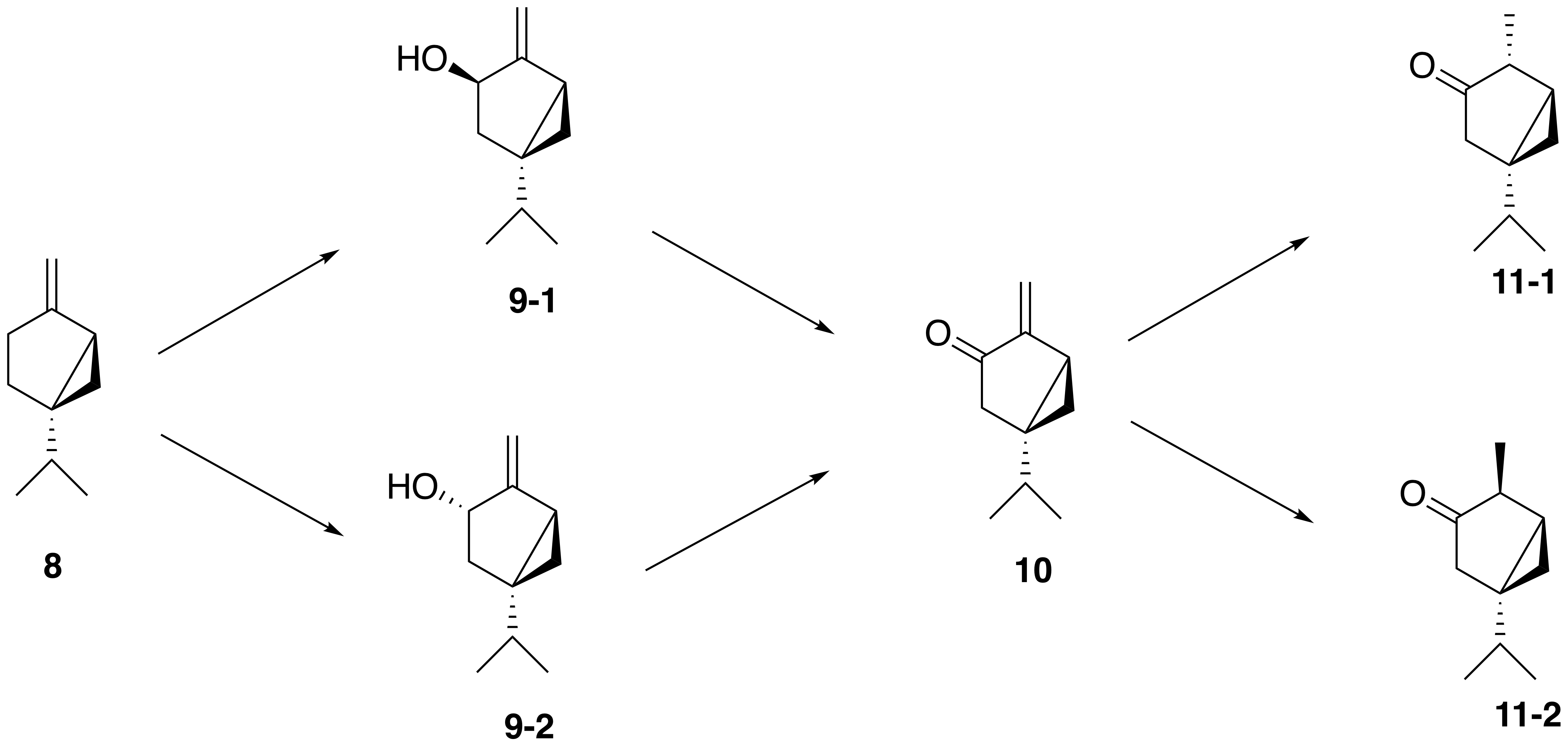
 From Sabinene, (+)-sabinene (8), the proposed biosynthetic route to generate thujone follows a three-step pathway: Sabinene, (+)-sabinene is first oxidized to an isomer of (+)-sabinol (9-1,2) by a Cytochrome P450, cytochrome P450 enzyme, followed by conversion to (+)-sabinone (10) via a dehydrogenase. Finally, a reductase mediates the conversion to α-thujone (11-1) and β-thujone (11-2). The isomerism of the (+)-sabinol intermediate varies among thujone-producing plants; for instance, in the western redcedar (''Thuja plicata''), thujone is derived exclusively from the (+)-''trans''-sabinol intermediate (9-1) whereas in the Garden sage, common garden sage ('' Salvia officinalis''), thujone is formed from the (+)-''cis''-sabinol intermediate (9-2).
From Sabinene, (+)-sabinene (8), the proposed biosynthetic route to generate thujone follows a three-step pathway: Sabinene, (+)-sabinene is first oxidized to an isomer of (+)-sabinol (9-1,2) by a Cytochrome P450, cytochrome P450 enzyme, followed by conversion to (+)-sabinone (10) via a dehydrogenase. Finally, a reductase mediates the conversion to α-thujone (11-1) and β-thujone (11-2). The isomerism of the (+)-sabinol intermediate varies among thujone-producing plants; for instance, in the western redcedar (''Thuja plicata''), thujone is derived exclusively from the (+)-''trans''-sabinol intermediate (9-1) whereas in the Garden sage, common garden sage ('' Salvia officinalis''), thujone is formed from the (+)-''cis''-sabinol intermediate (9-2).
 Based on studies that looked only at molecular shape, for many years thujone was thought to act similarly to Tetrahydrocannabinol, THC on the cannabinoid receptors;Barnaby Conrad III, Conrad III, Barnaby; (1988). ''Absinthe: History in a Bottle.'' Chronicle Books. p. 152 however, this has since been proven false. Thujone is a gamma-aminobutyric acid, GABAA receptor antagonist and more specifically, a GABAA receptor, GABAA receptor competitive antagonist. By inhibiting GABA receptor activation, neurons may fire more easily, which can cause muscle spasms and convulsions. This interaction with the GABAA receptor, GABAA receptor is specific to alpha-thujone. Thujone is also a 5-HT3 antagonist, 5-HT3 antagonist.
The median lethal dose, or LD50, of alpha-thujone, the more active of the two isomers, in mice, is around 45 mg/kg, with 0% mortality rate at 30 mg/kg and 100% at 60 mg/kg. Mice exposed to the higher dose have convulsions that lead to death within 1 minute. From 30 to 45 mg/kg, the mice experience muscle spasms in the legs, which progress to general convulsions until death or recovery. These effects are in line with other GABA antagonists. Also, alpha-thujone is metabolized quickly in the liver in mice. Pretreatment with GABA positive allosteric modulators like diazepam, phenobarbital, or 1 g/kg of ethanol protects against a lethal dose of 100 mg/kg.
Attention performance has been tested with low and high doses of thujone in alcohol. The high dose had a short-term negative effect on attention performance. The lower dose showed no noticeable effect.
Thujone is reported to be toxic to brain, kidney, and liver cells and could cause convulsions if used in too high a dose. Other thujone-containing plants such as the tree ''
Based on studies that looked only at molecular shape, for many years thujone was thought to act similarly to Tetrahydrocannabinol, THC on the cannabinoid receptors;Barnaby Conrad III, Conrad III, Barnaby; (1988). ''Absinthe: History in a Bottle.'' Chronicle Books. p. 152 however, this has since been proven false. Thujone is a gamma-aminobutyric acid, GABAA receptor antagonist and more specifically, a GABAA receptor, GABAA receptor competitive antagonist. By inhibiting GABA receptor activation, neurons may fire more easily, which can cause muscle spasms and convulsions. This interaction with the GABAA receptor, GABAA receptor is specific to alpha-thujone. Thujone is also a 5-HT3 antagonist, 5-HT3 antagonist.
The median lethal dose, or LD50, of alpha-thujone, the more active of the two isomers, in mice, is around 45 mg/kg, with 0% mortality rate at 30 mg/kg and 100% at 60 mg/kg. Mice exposed to the higher dose have convulsions that lead to death within 1 minute. From 30 to 45 mg/kg, the mice experience muscle spasms in the legs, which progress to general convulsions until death or recovery. These effects are in line with other GABA antagonists. Also, alpha-thujone is metabolized quickly in the liver in mice. Pretreatment with GABA positive allosteric modulators like diazepam, phenobarbital, or 1 g/kg of ethanol protects against a lethal dose of 100 mg/kg.
Attention performance has been tested with low and high doses of thujone in alcohol. The high dose had a short-term negative effect on attention performance. The lower dose showed no noticeable effect.
Thujone is reported to be toxic to brain, kidney, and liver cells and could cause convulsions if used in too high a dose. Other thujone-containing plants such as the tree ''
/ref> A 2005 study recreated three 1899 high-wormwood recipes and tested with GC-MS, and found that the highest contained 4.3 mg/L thujone. GC-MS testing is important in this capacity, because gas chromatography alone may record an inaccurately high reading of thujone as other compounds may interfere with and add to the apparent measured amount.
European Commission. *0.5 mg/kg in food prepared with Artemisia (genus), ''Artemisia'' species, excluding those prepared with common sage, sage and non alcoholic beverages *10 mg/kg in alcoholic beverages not prepared with ''Artemisia'' species *25 mg/kg in food prepared with common sage, sage *35 mg/kg in alcoholic beverages prepared with ''Artemisia'' species
October 17, 2007. Retrieved May 5, 2009 Other herbs that contain thujone have no restrictions. For example, Common sage, sage and sage oil (which can be up to 50% thujone) are on the Food and Drug Administration's list of generally recognized as safe (GRAS) substances. Absinthe offered for sale in the United States must be thujone-free by the same standard that applies to other beverages containing Artemisia, so absinthe with small amounts of thujone may be legally imported.
Absinthe absolved
, ''Cern Courier'', July 8, 2008
Thujone.Info
— Databank of peer reviewed articles on thujone, absinthe, absinthism, and independent thujone ratings of some commercial brands.
The Shaky History of Thujone
– Wormwood Society article on thujone and its history. {{Convulsants Absinthe GABAA receptor negative allosteric modulators Convulsants Monoterpenes 5-HT3 antagonists Ketones Perfume ingredients Bicyclic compounds Cyclopentanes Cyclopropanes Isopropyl compounds Neurotoxins Plant toxins
ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure R–C(=O)–R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group –C(=O)– (which contains a carbon-oxygen double bo ...
and a monoterpene that occurs predominantly in two diastereomeric ( epimeric) forms: (−)-α-thujone and (+)-β-thujone.
Though it is best known as a chemical compound in the spirit absinthe
Absinthe (, ) is an anise-flavoured spirit derived from several plants, including the flowers and leaves of ''Artemisia absinthium'' ("grand wormwood"), together with green anise, sweet fennel, and other medicinal and culinary herbs. Historical ...
, it is unlikely to be responsible for absinthe's alleged stimulant and psychoactive effects due to the small quantities present.Absinthe Myths Finally Laid To Rest/ref> Thujone acts on the
neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neuro ...
gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) as an antagonist (opposite to the effects of alcohol). As a competitive antagonist of GABA, thujone alone is considered to be convulsant A convulsant is a drug which induces convulsions and/or epileptic seizures, the opposite of an anticonvulsant. These drugs generally act as stimulants at low doses, but are not used for this purpose due to the risk of convulsions and consequent exc ...
, though by interfering with the inhibitory transmitter GABA, it may convey stimulating, mood-elevating effects at low doses. It is also used in perfumery as a component of several essential oils.
In addition to the naturally occurring (−)-α-thujone and (+)-β-thujone, two other forms are possible: (+)-α-thujone and (−)-β-thujone. In 2016, they were found in nature as well, in '' Salvia officinalis''.
Sources
Thujone is found in a number of plants, such asarborvitae
''Thuja'' ( ) is a genus of coniferous tree or shrub in the Cupressaceae (cypress family). There are five species in the genus, two native to North America and three native to eastern Asia. The genus is monophyletic and sister to '' Thujopsis''. ...
(genus ''Thuja'', hence the derivation of the name), Nootka cypress
''Callitropsis nootkatensis'', formerly known as ''Cupressus nootkatensis'' ( syn. ''Xanthocyparis nootkatensis'') is a species of trees in the cypress family native to the coastal regions of northwestern North America. This species goes by many ...
, some junipers, mugwort, oregano, common sage, tansy, and Artemisia (plant), wormwood, most notably grand wormwood (''Artemisia absinthium''), usually as a mix of isomers in a 1:2 ratio. It is also found in various species of ''Mentha'' (mint).
Biosynthesis
The biosynthesis of thujone is similar to the synthesis of other monoterpenes and begins with the formation of geranyl diphosphate (Geranyl diphosphate, GPP) from Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate, DMAPP) and isopentenyl diphosphate (Isopentenyl diphosphate, IPP), catalyzed by the enzyme geranyl diphosphate synthase. Quantitative 13CNMR spectroscopic analysis has demonstrated that the Isoprene rule, isoprene units used to form thujone in plants are derived from the MEP pathway, methylerythritol phosphate pathway (MEP pathway, MEP). The reactions that generate the thujone skeleton in sabinene from Geranyl diphosphate, GPP are mediated by the enzyme (+)-sabinene synthase, sabinene synthase which has Geranyl diphosphate, GPP as its substrate. Geranyl diphosphate, GPP (1) first isomerizes to linalyl diphosphate (LPP) (2) and neryl diphosphate (NPP) (3). LPP preferentially forms a delocalized allylic cation-diphosphate (4). The ion-pair intermediate then cyclizes in an electrophilic addition to yield the α-terpinyl tertiary cation (5). The α-terpinyl cation (5) then undergoes a 1,2 hydride shift via a Wagner-Meerwein rearrangement, Wagner–Meerwein rearrangement, leading to the formation of the terpinen-4-yl cation (6). This cation undergoes a second cyclization to form the thujyl cation intermediate (7) before loss of a proton to form the thujone precursor, Sabinene, (+)-sabinene (8).
The α-terpinyl cation (5) then undergoes a 1,2 hydride shift via a Wagner-Meerwein rearrangement, Wagner–Meerwein rearrangement, leading to the formation of the terpinen-4-yl cation (6). This cation undergoes a second cyclization to form the thujyl cation intermediate (7) before loss of a proton to form the thujone precursor, Sabinene, (+)-sabinene (8).
 From Sabinene, (+)-sabinene (8), the proposed biosynthetic route to generate thujone follows a three-step pathway: Sabinene, (+)-sabinene is first oxidized to an isomer of (+)-sabinol (9-1,2) by a Cytochrome P450, cytochrome P450 enzyme, followed by conversion to (+)-sabinone (10) via a dehydrogenase. Finally, a reductase mediates the conversion to α-thujone (11-1) and β-thujone (11-2). The isomerism of the (+)-sabinol intermediate varies among thujone-producing plants; for instance, in the western redcedar (''Thuja plicata''), thujone is derived exclusively from the (+)-''trans''-sabinol intermediate (9-1) whereas in the Garden sage, common garden sage ('' Salvia officinalis''), thujone is formed from the (+)-''cis''-sabinol intermediate (9-2).
From Sabinene, (+)-sabinene (8), the proposed biosynthetic route to generate thujone follows a three-step pathway: Sabinene, (+)-sabinene is first oxidized to an isomer of (+)-sabinol (9-1,2) by a Cytochrome P450, cytochrome P450 enzyme, followed by conversion to (+)-sabinone (10) via a dehydrogenase. Finally, a reductase mediates the conversion to α-thujone (11-1) and β-thujone (11-2). The isomerism of the (+)-sabinol intermediate varies among thujone-producing plants; for instance, in the western redcedar (''Thuja plicata''), thujone is derived exclusively from the (+)-''trans''-sabinol intermediate (9-1) whereas in the Garden sage, common garden sage ('' Salvia officinalis''), thujone is formed from the (+)-''cis''-sabinol intermediate (9-2).

Pharmacology
 Based on studies that looked only at molecular shape, for many years thujone was thought to act similarly to Tetrahydrocannabinol, THC on the cannabinoid receptors;Barnaby Conrad III, Conrad III, Barnaby; (1988). ''Absinthe: History in a Bottle.'' Chronicle Books. p. 152 however, this has since been proven false. Thujone is a gamma-aminobutyric acid, GABAA receptor antagonist and more specifically, a GABAA receptor, GABAA receptor competitive antagonist. By inhibiting GABA receptor activation, neurons may fire more easily, which can cause muscle spasms and convulsions. This interaction with the GABAA receptor, GABAA receptor is specific to alpha-thujone. Thujone is also a 5-HT3 antagonist, 5-HT3 antagonist.
The median lethal dose, or LD50, of alpha-thujone, the more active of the two isomers, in mice, is around 45 mg/kg, with 0% mortality rate at 30 mg/kg and 100% at 60 mg/kg. Mice exposed to the higher dose have convulsions that lead to death within 1 minute. From 30 to 45 mg/kg, the mice experience muscle spasms in the legs, which progress to general convulsions until death or recovery. These effects are in line with other GABA antagonists. Also, alpha-thujone is metabolized quickly in the liver in mice. Pretreatment with GABA positive allosteric modulators like diazepam, phenobarbital, or 1 g/kg of ethanol protects against a lethal dose of 100 mg/kg.
Attention performance has been tested with low and high doses of thujone in alcohol. The high dose had a short-term negative effect on attention performance. The lower dose showed no noticeable effect.
Thujone is reported to be toxic to brain, kidney, and liver cells and could cause convulsions if used in too high a dose. Other thujone-containing plants such as the tree ''
Based on studies that looked only at molecular shape, for many years thujone was thought to act similarly to Tetrahydrocannabinol, THC on the cannabinoid receptors;Barnaby Conrad III, Conrad III, Barnaby; (1988). ''Absinthe: History in a Bottle.'' Chronicle Books. p. 152 however, this has since been proven false. Thujone is a gamma-aminobutyric acid, GABAA receptor antagonist and more specifically, a GABAA receptor, GABAA receptor competitive antagonist. By inhibiting GABA receptor activation, neurons may fire more easily, which can cause muscle spasms and convulsions. This interaction with the GABAA receptor, GABAA receptor is specific to alpha-thujone. Thujone is also a 5-HT3 antagonist, 5-HT3 antagonist.
The median lethal dose, or LD50, of alpha-thujone, the more active of the two isomers, in mice, is around 45 mg/kg, with 0% mortality rate at 30 mg/kg and 100% at 60 mg/kg. Mice exposed to the higher dose have convulsions that lead to death within 1 minute. From 30 to 45 mg/kg, the mice experience muscle spasms in the legs, which progress to general convulsions until death or recovery. These effects are in line with other GABA antagonists. Also, alpha-thujone is metabolized quickly in the liver in mice. Pretreatment with GABA positive allosteric modulators like diazepam, phenobarbital, or 1 g/kg of ethanol protects against a lethal dose of 100 mg/kg.
Attention performance has been tested with low and high doses of thujone in alcohol. The high dose had a short-term negative effect on attention performance. The lower dose showed no noticeable effect.
Thujone is reported to be toxic to brain, kidney, and liver cells and could cause convulsions if used in too high a dose. Other thujone-containing plants such as the tree ''arborvitae
''Thuja'' ( ) is a genus of coniferous tree or shrub in the Cupressaceae (cypress family). There are five species in the genus, two native to North America and three native to eastern Asia. The genus is monophyletic and sister to '' Thujopsis''. ...
'' (''Thuja occidentalis'') are used in herbal medicine, mainly for their immune-system stimulating effects. Side effects from the essential oil of this plant include anxiety, sleeplessness, and convulsions, which confirms the central nervous system effects of thujone.
In absinthe
Thujone is most famous for being a compound in the spiritabsinthe
Absinthe (, ) is an anise-flavoured spirit derived from several plants, including the flowers and leaves of ''Artemisia absinthium'' ("grand wormwood"), together with green anise, sweet fennel, and other medicinal and culinary herbs. Historical ...
. In the past, absinthe was thought to contain up to 260–350 mg/L thujone, but modern tests have shown this estimate to be far too high. A 2008 study of 13 pre-ban (1895–1910) bottles using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) found that the bottles had between 0.5 and 48.3 mg/L and averaged 25.4 mg/L Absinthe Myths Finally Laid To Rest/ref> A 2005 study recreated three 1899 high-wormwood recipes and tested with GC-MS, and found that the highest contained 4.3 mg/L thujone. GC-MS testing is important in this capacity, because gas chromatography alone may record an inaccurately high reading of thujone as other compounds may interfere with and add to the apparent measured amount.
History
The compound was discovered after absinthe became popular in the mid-19th century. Valentin Magnan, Dr. Valentin Magnan, who studied alcoholism, tested pure wormwood oil on animals and discovered it caused Non-epileptic seizure, seizures independent from the effects of alcohol. Based on this, absinthe, which contains a small amount of wormwood oil, was assumed to be more dangerous than ordinary alcohol. Eventually, thujone was isolated as the cause of these reactions. Magnan went on to study 250 abusers of alcohol and noted that those who drank absinthe had seizures and hallucinations. The seizures are caused by the (+)-α-thujone interacting with the GABA receptors, causing epileptic activity. In light of modern evidence, these conclusions are questionable, as they are based on a poor understanding of other compounds and diseases, and clouded by Magnan's belief that alcohol and absinthe were degenerating the French race. After absinthe was banned, research dropped off until the 1970s, when the British scientific journal ''Nature (journal), Nature'' published an article comparing the molecular shape of thujone to tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive substance found in cannabis (drug), cannabis, and hypothesized it would act the same way on the brain, sparking the myth that thujone was a cannabinoid. More recently, following European Council Directive No. 88/388/EEC (1988) allowing certain levels of thujone in foodstuffs in the EU, the studies described above were conducted and found only minute levels of thujone in absinthe.Regulations
European Union
Maximum thujone levels in the EU are:Regulation (EC) No 1334/2008 of the European Parliament and Council of 16 December 2008European Commission. *0.5 mg/kg in food prepared with Artemisia (genus), ''Artemisia'' species, excluding those prepared with common sage, sage and non alcoholic beverages *10 mg/kg in alcoholic beverages not prepared with ''Artemisia'' species *25 mg/kg in food prepared with common sage, sage *35 mg/kg in alcoholic beverages prepared with ''Artemisia'' species
United States
In the United States, the addition of pure thujone to foods is not permitted. Foods or beverages that contain ''Artemisia (plant), Artemisia'' species, white cedar, oak moss, tansy, or yarrow, must be thujone-free, which in practice means that they contain less than 10 parts per million thujone.Department of the Treasury Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau Industry Circular 2007-5October 17, 2007. Retrieved May 5, 2009 Other herbs that contain thujone have no restrictions. For example, Common sage, sage and sage oil (which can be up to 50% thujone) are on the Food and Drug Administration's list of generally recognized as safe (GRAS) substances. Absinthe offered for sale in the United States must be thujone-free by the same standard that applies to other beverages containing Artemisia, so absinthe with small amounts of thujone may be legally imported.
Canada
In Canada, liquor laws are the domain of the provincial governments. Alberta, Ontario, and Nova Scotia allow 10 mg/kg thujone; Quebec allows 15 mg per kg; Manitoba allows 6–8 mg thujone per litre; British Columbia adheres to the same levels as Ontario. However, in Saskatchewan and Quebec, one can purchase any liquor available in the world upon the purchase of a maximum of one case, usually 12 750-ml bottles or 9 L. The individual liquor boards must approve each product before it may be sold on shelves.Chemical spectra of α-thujone
1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3)
δ [ppm] = 2.54 (ddd, J = 18.8, 2.3, 1.1 Hz, 1H, H-2), 2.21 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H, H-4), 2.07 (d, J = 18.8 Hz, 1H, H-2'), 1.36 (hept, J = 6.8 Hz, 1H, H-7), 1.15 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 3H, H-9), 1.08 (dd, J = 8.1, 4.0 Hz, 1H, H-5), 1.00 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, 3H, H-8), 0.95 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, 3H, H-8') 0.76 (ddd, J = 8.1, 5.6, 2.5 Hz, 1H, H-6), 0.12 (dd, J = 5.6, 4.1 Hz, 1H, H-6').13C NMR (91 MHz, CDCl3)
δ [ppm] = 221.7 (C=O, C-3), 47.5 (CH, C-4), 39.9 (CH2, C-2), 33.1 (CH, C-7), 29.8 (C, C-1), 25.7 (CH, C-5), 20.1 (CH3, C-8), 19.9 (CH3, C-8') 18.9 (CH3, C-9), 18.4 (CH2, C-6).Mass spectrometry
m/z: 81(100), 110(96.58), 109(59.88), 95(58.97), 67(57.37). The www.webbook.nist.gov website lists the m/z ratios for Thujone as: 110(100), 81(~89), 95(~71); 67(~69), 109(~44).IR
cm−1: 3020, 2961, 1733, 1602, 1455, 1219, 1096, 1014.See also
* ''Piołunówka'' – Polish alcoholic preparation with thujone content higher than in absintheReferences
Further reading
*External links
Absinthe absolved
, ''Cern Courier'', July 8, 2008
Thujone.Info
— Databank of peer reviewed articles on thujone, absinthe, absinthism, and independent thujone ratings of some commercial brands.
The Shaky History of Thujone
– Wormwood Society article on thujone and its history. {{Convulsants Absinthe GABAA receptor negative allosteric modulators Convulsants Monoterpenes 5-HT3 antagonists Ketones Perfume ingredients Bicyclic compounds Cyclopentanes Cyclopropanes Isopropyl compounds Neurotoxins Plant toxins