Äesko SlovenskÃĄ SuperStar 2009 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Czech Republic, also known as Czechia, and historically known as Bohemia, is a
 There were peasant uprisings influenced by famine. Serfdom was abolished between 1781 and 1848. Several battles of the Napoleonic Wars took place on the current territory of the Czech Republic.
The end of the
There were peasant uprisings influenced by famine. Serfdom was abolished between 1781 and 1848. Several battles of the Napoleonic Wars took place on the current territory of the Czech Republic.
The end of the
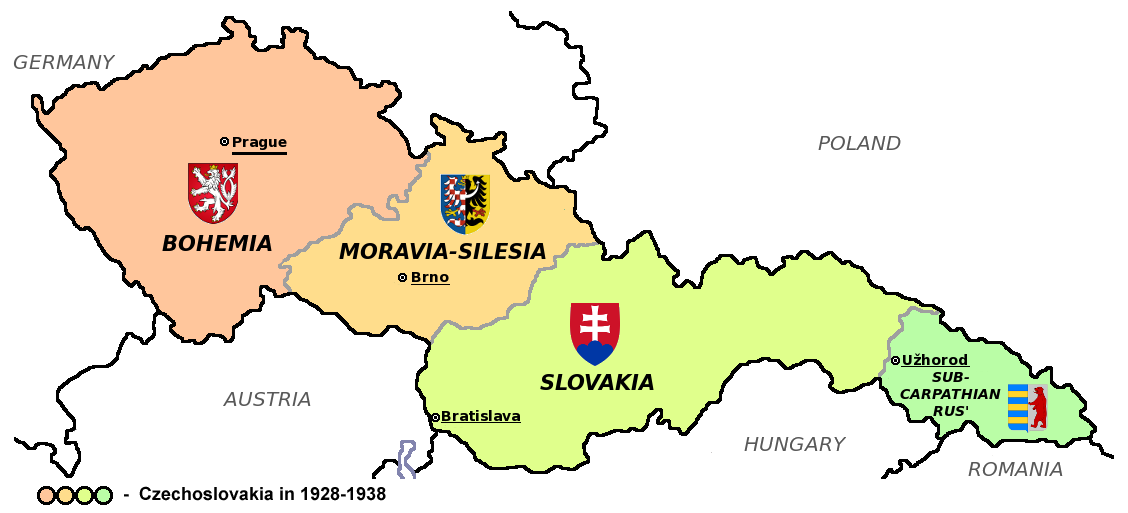 In 1918, during the collapse of the
In 1918, during the collapse of the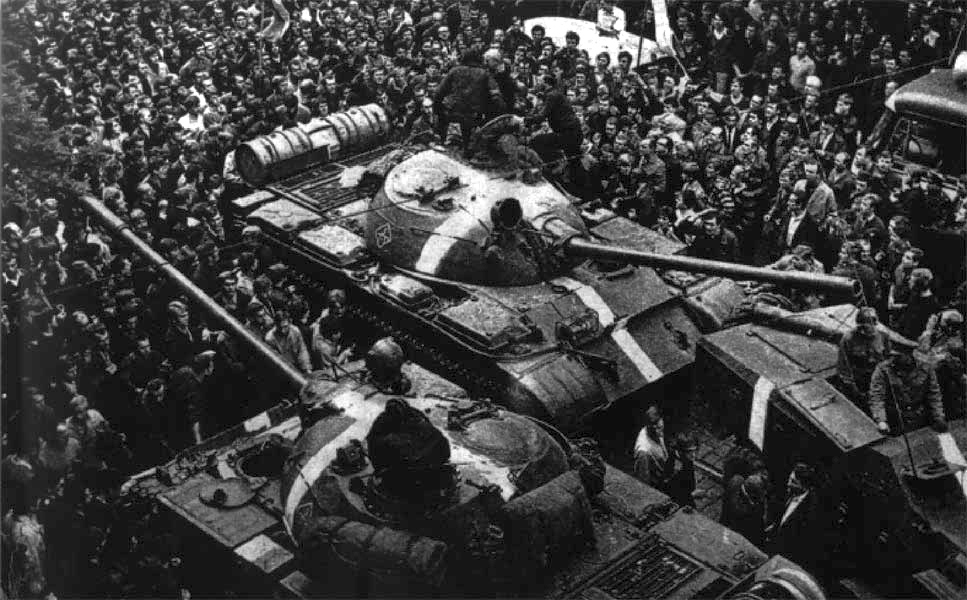  In the Czechoslovakian parliamentary election, 1946, 1946 elections, the Communist Party of Czechoslovakia, Communist Party gained 38% of the votes and became the largest party in the Czechoslovak parliament, formed a coalition with other parties, and consolidated power. A
In the Czechoslovakian parliamentary election, 1946, 1946 elections, the Communist Party of Czechoslovakia, Communist Party gained 38% of the votes and became the largest party in the Czechoslovak parliament, formed a coalition with other parties, and consolidated power. A
 The Czech Republic lies mostly between latitudes 48th parallel north, 48° and 51st parallel north, 51° N and longitudes 12th meridian east, 12° and 19th meridian east, 19° E.
Bohemia, to the west, consists of a basin drained by the Elbe () and the Vltava rivers, surrounded by mostly low mountains, such as the Giant Mountains range () of the Sudetes. The highest point in the country, SnÄÅūka at , is located here. Moravia, the eastern part of the country, is also hilly. It is drained mainly by the Morava (river), Morava River, but it also contains the source of the Oder River ().
Water from the Czech Republic flows to three different seas: the North Sea, Baltic Sea, and Black Sea. The Czech Republic also leases the Moldauhafen, a lot (real estate), lot in the middle of the Hamburg Docks, which was awarded to Czechoslovakia by Article 363 of the Treaty of Versailles, to allow the landlocked country a place where goods transported down river could be transferred to seagoing ships. The territory reverts to Germany in 2028.
Phytogeography, Phytogeographically, the Czech Republic belongs to the Central European province of the Circumboreal Region, within the Boreal Kingdom. According to the World Wide Fund for Nature, the territory of the Czech Republic can be subdivided into four ecoregions: the Western European broadleaf forests, Central European mixed forests, Pannonian mixed forests, and Carpathian montane conifer forests.
There are four national parks in the Czech Republic. The oldest is KrkonoÅĄe National Park (Man and the Biosphere Programme, Biosphere Reserve), and the others are Å umava National Park (Biosphere Reserve), Podyjà National Park, and Bohemian Switzerland.
The three historical lands of the Czech Republic (formerly some countries of the Bohemian Crown) correspond with the river basins of the Elbe and the Vltava basin for Bohemia, the Morava one for Moravia, and the Oder river basin for Czech Silesia (in terms of the Czech territory).
The Czech Republic lies mostly between latitudes 48th parallel north, 48° and 51st parallel north, 51° N and longitudes 12th meridian east, 12° and 19th meridian east, 19° E.
Bohemia, to the west, consists of a basin drained by the Elbe () and the Vltava rivers, surrounded by mostly low mountains, such as the Giant Mountains range () of the Sudetes. The highest point in the country, SnÄÅūka at , is located here. Moravia, the eastern part of the country, is also hilly. It is drained mainly by the Morava (river), Morava River, but it also contains the source of the Oder River ().
Water from the Czech Republic flows to three different seas: the North Sea, Baltic Sea, and Black Sea. The Czech Republic also leases the Moldauhafen, a lot (real estate), lot in the middle of the Hamburg Docks, which was awarded to Czechoslovakia by Article 363 of the Treaty of Versailles, to allow the landlocked country a place where goods transported down river could be transferred to seagoing ships. The territory reverts to Germany in 2028.
Phytogeography, Phytogeographically, the Czech Republic belongs to the Central European province of the Circumboreal Region, within the Boreal Kingdom. According to the World Wide Fund for Nature, the territory of the Czech Republic can be subdivided into four ecoregions: the Western European broadleaf forests, Central European mixed forests, Pannonian mixed forests, and Carpathian montane conifer forests.
There are four national parks in the Czech Republic. The oldest is KrkonoÅĄe National Park (Man and the Biosphere Programme, Biosphere Reserve), and the others are Å umava National Park (Biosphere Reserve), Podyjà National Park, and Bohemian Switzerland.
The three historical lands of the Czech Republic (formerly some countries of the Bohemian Crown) correspond with the river basins of the Elbe and the Vltava basin for Bohemia, the Morava one for Moravia, and the Oder river basin for Czech Silesia (in terms of the Czech territory).
 The Czech Republic has ranked as Global Peace Index, one of the safest or most peaceful countries for the past few decades. It is a member of the United Nations, the
The Czech Republic has ranked as Global Peace Index, one of the safest or most peaceful countries for the past few decades. It is a member of the United Nations, the  The Prime Minister of the Czech Republic, Prime Minister and Minister of Foreign Affairs of the Czech Republic, Minister of Foreign Affairs have primary roles in setting foreign policy, although the President of the Czech Republic, President also has influence and represents the country abroad. Membership in the European Union and NATO is central to the Czech Republic's foreign policy. The Office for Foreign Relations and Information (ÃZSI) serves as the foreign intelligence agency responsible for espionage and foreign policy briefings, as well as protection of Czech Republic's embassies abroad.
The Czech Republic has ties with
The Prime Minister of the Czech Republic, Prime Minister and Minister of Foreign Affairs of the Czech Republic, Minister of Foreign Affairs have primary roles in setting foreign policy, although the President of the Czech Republic, President also has influence and represents the country abroad. Membership in the European Union and NATO is central to the Czech Republic's foreign policy. The Office for Foreign Relations and Information (ÃZSI) serves as the foreign intelligence agency responsible for espionage and foreign policy briefings, as well as protection of Czech Republic's embassies abroad.
The Czech Republic has ties with

 The Czech Republic has a IMF advanced economy list, developed,
The Czech Republic has a IMF advanced economy list, developed,
. The Atlas of Economic Complexity. Access date 3 October 2017. The industrial sector accounts for 37.5% of the economy, while services account for 60% and agriculture for 2.5%. The largest trading partner for both export and import is
 the List of companies of the Czech Republic#Largest by revenue, largest companies by revenue in the Czech Republic were: automobile manufacturer Å koda Auto, utility company ÄEZ Group, conglomerate Agrofert, energy trading company EnergetickÃ― a prÅŊmyslovÃ― holding, EPH, oil processing company Unipetrol, electronics manufacturer Foxconn CZ and steel producer TÅinec Iron and Steel Works, Moravia Steel. Other Czech transportation companies include: Å koda Transportation (tramways, trolleybuses, metro), Tatra (company), Tatra (heavy trucks, the second oldest car maker in the world), Avia Motors, Avia (medium trucks), Karosa and SOR Libchavy (buses), Aero Vodochody (military aircraft), Let Kunovice (civil aircraft), Zetor (tractors), Jawa Moto (motorcycles) and ÄeskÃĄ zbrojovka Strakonice, Äezeta (electric scooters).
Å koda Transportation is the fourth largest tram producer in the world; nearly one third of all trams in the world come from Czech factories. The Czech Republic is also the world's largest Phonograph record, vinyl records manufacturer, with GZ Media producing about 6 million pieces annually in LodÄnice (Beroun District), LodÄnice. ÄeskÃĄ zbrojovka UherskÃ― Brod, ÄeskÃĄ zbrojovka is among the ten largest firearms producers in the world and five who produce automatic weapons.
In the food industry, Czech companies include Agrofert, Kofola and HamÃĐ (company), HamÃĐ.
the List of companies of the Czech Republic#Largest by revenue, largest companies by revenue in the Czech Republic were: automobile manufacturer Å koda Auto, utility company ÄEZ Group, conglomerate Agrofert, energy trading company EnergetickÃ― a prÅŊmyslovÃ― holding, EPH, oil processing company Unipetrol, electronics manufacturer Foxconn CZ and steel producer TÅinec Iron and Steel Works, Moravia Steel. Other Czech transportation companies include: Å koda Transportation (tramways, trolleybuses, metro), Tatra (company), Tatra (heavy trucks, the second oldest car maker in the world), Avia Motors, Avia (medium trucks), Karosa and SOR Libchavy (buses), Aero Vodochody (military aircraft), Let Kunovice (civil aircraft), Zetor (tractors), Jawa Moto (motorcycles) and ÄeskÃĄ zbrojovka Strakonice, Äezeta (electric scooters).
Å koda Transportation is the fourth largest tram producer in the world; nearly one third of all trams in the world come from Czech factories. The Czech Republic is also the world's largest Phonograph record, vinyl records manufacturer, with GZ Media producing about 6 million pieces annually in LodÄnice (Beroun District), LodÄnice. ÄeskÃĄ zbrojovka UherskÃ― Brod, ÄeskÃĄ zbrojovka is among the ten largest firearms producers in the world and five who produce automatic weapons.
In the food industry, Czech companies include Agrofert, Kofola and HamÃĐ (company), HamÃĐ.
 Production of Czech electricity exceeds consumption by about 10 Kilowatt hour, TWh per year, the excess being exported. Nuclear power presently provides about 30 percent of the total power needs, its share is projected to increase to 40 percent. In 2005, 65.4 percent of electricity was produced by steam and combustion power plants (mostly coal); 30 percent by nuclear plants; and 4.6 percent came from renewable sources, including hydropower. The largest Czech power resource is TemelÃn Nuclear Power Station, with another nuclear power plant in Dukovany Nuclear Power Station, Dukovany.
The Czech Republic is reducing its dependence on highly polluting low-grade Lignite, brown coal as a source of energy. Natural gas is purchased from Norway, Norwegian companies and as liquefied gas LNG from the Netherlands and Belgium. In the past, three-quarters of gas supplies came from Russia, but after the start of the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, the government gradually stopped these supplies. Gas consumption (approx. 100 TWh in 2003â2005) is almost double electricity consumption. South Moravia has small Oil and gas deposits in the Czech Republic, oil and gas deposits.
Production of Czech electricity exceeds consumption by about 10 Kilowatt hour, TWh per year, the excess being exported. Nuclear power presently provides about 30 percent of the total power needs, its share is projected to increase to 40 percent. In 2005, 65.4 percent of electricity was produced by steam and combustion power plants (mostly coal); 30 percent by nuclear plants; and 4.6 percent came from renewable sources, including hydropower. The largest Czech power resource is TemelÃn Nuclear Power Station, with another nuclear power plant in Dukovany Nuclear Power Station, Dukovany.
The Czech Republic is reducing its dependence on highly polluting low-grade Lignite, brown coal as a source of energy. Natural gas is purchased from Norway, Norwegian companies and as liquefied gas LNG from the Netherlands and Belgium. In the past, three-quarters of gas supplies came from Russia, but after the start of the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, the government gradually stopped these supplies. Gas consumption (approx. 100 TWh in 2003â2005) is almost double electricity consumption. South Moravia has small Oil and gas deposits in the Czech Republic, oil and gas deposits.
 The Czech lands have a long and well-documented history of scientific innovation. Today, the Czech Republic has a highly sophisticated, developed, high-performing, innovation-oriented scientific community supported by the government, industry, and leading Czech Universities, universities. Czech scientists are embedded members of the global scientific community. They contribute annually to multiple international academic journals and collaborate with their colleagues across boundaries and fields. The Czech Republic was ranked 24th in the Global Innovation Index in 2020 and 2021, up from 26th in 2019.
Historically, the Czech lands, especially
The Czech lands have a long and well-documented history of scientific innovation. Today, the Czech Republic has a highly sophisticated, developed, high-performing, innovation-oriented scientific community supported by the government, industry, and leading Czech Universities, universities. Czech scientists are embedded members of the global scientific community. They contribute annually to multiple international academic journals and collaborate with their colleagues across boundaries and fields. The Czech Republic was ranked 24th in the Global Innovation Index in 2020 and 2021, up from 26th in 2019.
Historically, the Czech lands, especially
Press Release
. 2012. secularpolicyinstitute.net The Czech people have been historically characterized as "tolerant and even indifferent towards religion". The religious identity of the country has changed drastically since the first half of the 20th century, when more than 90% of Czechs were Christians.
Christianization in the 9th and 10th centuries introduced Christianity. After the Bohemian Reformation, most Czechs became Hussites, followers of Jan Hus, Petr ChelÄickÃ― and other regional Protestant Reformers. Taborites and Utraquists were Hussite groups. Towards the end of the Hussite Wars, the Utraquists changed sides and allied with the Roman Catholic Church. Following the joint UtraquistâRoman Catholic victory, Utraquism was accepted as a distinct form of Christianity to be practiced in Kingdom of Bohemia, Bohemia by the Roman Catholic Church while all remaining Hussite groups were prohibited. After the Reformation, some Bohemians went with the Lutheranism, teachings of Martin Luther, especially Sudeten Germans. In the wake of the Reformation, Utraquist Hussites took a renewed increasingly anti-Catholic stance, while some of the defeated Hussite factions were revived. After the Habsburgs regained control of Bohemia, the whole population was forcibly converted to Roman Catholicismâeven the Utraquist Hussites. Going forward, Czechs have become more wary and pessimistic of religion as such. A history of resistance to the Roman Catholic Church followed. It suffered a schism with the neo-Hussite Czechoslovak Hussite Church in 1920, lost the bulk of its adherents during the Communist era and continues to lose in the modern, ongoing secularization. Protestantism never recovered after the Counter-Reformation was introduced by the Habsburg monarchy, Austrian Habsburgs in 1620. Prior to the Holocaust, the Czech Republic had a sizable Jewish community of around 100,000. There are many historically important and culturally relevant Synagogues in the Czech Republic such as Europe's oldest active Synagogue, Old New Synagogue, The Old New Synagogue and the second largest Synagogue in Europe, the Great Synagogue (PlzeÅ). The Holocaust decimated Czech Jewry and the Jewish population as of 2021 is 3,900.
According to the 2011 census, 34% of the population stated they had no religion, 10.3% were Roman Catholic, 0.8% were Protestant (0.5% Evangelical Church of Czech Brethren, Czech Brethren and 0.4% Czechoslovak Hussite Church, Hussite), and 9% followed other forms of religion both denominational or not (of which 863 people answered they are Neopaganism, Pagan). 45% of the population did not answer the question about religion. From 1991 to 2001 and further to 2011 the adherence to Roman Catholicism decreased from 39% to 27% and then to 10%; Protestantism similarly declined from 3.7% to 2% and then to 0.8%. The Muslim population is estimated to be 20,000 representing 0.2% of the population.
The proportion of religious believers varies significantly across the country, from 55% in ZlÃn Region to 16% in Ãstà nad Labem Region.
 The earliest preserved stone buildings in Bohemia and Moravia date back to the time of the Christianization in the 9th and 10th centuries. Since the Middle Ages, the Czech lands have been using the same architectural styles as most of Western Europe, Western and Central Europe. The oldest still standing churches were built in the Romanesque architecture, Romanesque style. During the 13th century, it was replaced by the Czech Gothic architecture, Gothic style. In the 14th century, Emperor Charles IV invited architects from France and Germany, Matthias of Arras and Peter Parler, to his court in Prague. During the Middle Ages, some fortified castles were built by the king and aristocracy, as well as some monasteries.
The Renaissance architecture, Renaissance style penetrated the Bohemian Crown in the late 15th century when the older Gothic style started to be mixed with Renaissance elements. An example of pure Renaissance architecture in Bohemia is the Queen Anne's Summer Palace, which was situated in the garden of Prague Castle. Evidence of the general reception of the Renaissance in Bohemia, involving an influx of Italian architects, can be found in spacious chateaus with arcade courtyards and geometrically arranged gardens. Emphasis was placed on comfort, and buildings that were built for entertainment purposes also appeared.
In the 17th century, the Baroque style spread throughout the Crown of Bohemia.
In the 18th century, Bohemia produced an architectural peculiarity â the ''Baroque Gothic style'', a synthesis of the Gothic and Baroque styles.
The earliest preserved stone buildings in Bohemia and Moravia date back to the time of the Christianization in the 9th and 10th centuries. Since the Middle Ages, the Czech lands have been using the same architectural styles as most of Western Europe, Western and Central Europe. The oldest still standing churches were built in the Romanesque architecture, Romanesque style. During the 13th century, it was replaced by the Czech Gothic architecture, Gothic style. In the 14th century, Emperor Charles IV invited architects from France and Germany, Matthias of Arras and Peter Parler, to his court in Prague. During the Middle Ages, some fortified castles were built by the king and aristocracy, as well as some monasteries.
The Renaissance architecture, Renaissance style penetrated the Bohemian Crown in the late 15th century when the older Gothic style started to be mixed with Renaissance elements. An example of pure Renaissance architecture in Bohemia is the Queen Anne's Summer Palace, which was situated in the garden of Prague Castle. Evidence of the general reception of the Renaissance in Bohemia, involving an influx of Italian architects, can be found in spacious chateaus with arcade courtyards and geometrically arranged gardens. Emphasis was placed on comfort, and buildings that were built for entertainment purposes also appeared.
In the 17th century, the Baroque style spread throughout the Crown of Bohemia.
In the 18th century, Bohemia produced an architectural peculiarity â the ''Baroque Gothic style'', a synthesis of the Gothic and Baroque styles.
 During the 19th century stands the Revival architecture, revival architectural styles. Some churches were restored to their presumed medieval appearance and there were constructed buildings in the Romanesque Revival architecture, Neo-Romanesque, Gothic Revival architecture, Neo-Gothic and Renaissance Revival architecture, Neo-Renaissance styles. At the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries, the new art style appeared in the Czech lands â Art Nouveau.
Bohemia contributed an unusual style to the world's architectural heritage when Czech architects attempted to transpose the Cubism of painting and sculpture into architecture.
Between World Wars I and II, Functionalism (architecture), Functionalism, with its sober, progressive forms, took over as the main architectural style.
After World War II and the Communist coup in 1948, art in Czechoslovakia became Soviet-influenced. The Czechoslovak avant-garde artistic movement is known as the ''Brussels style came up'' in the time of political liberalization of Czechoslovakia in the 1960s. Brutalism dominated in the 1970s and 1980s.
The Czech Republic is not shying away from the more modern trends of international architecture, an example is the TanÄÃcà dÅŊm, Dancing House (TanÄÃcà dÅŊm) in Prague, Golden Angel in Prague or Congress Centre in ZlÃn.
During the 19th century stands the Revival architecture, revival architectural styles. Some churches were restored to their presumed medieval appearance and there were constructed buildings in the Romanesque Revival architecture, Neo-Romanesque, Gothic Revival architecture, Neo-Gothic and Renaissance Revival architecture, Neo-Renaissance styles. At the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries, the new art style appeared in the Czech lands â Art Nouveau.
Bohemia contributed an unusual style to the world's architectural heritage when Czech architects attempted to transpose the Cubism of painting and sculpture into architecture.
Between World Wars I and II, Functionalism (architecture), Functionalism, with its sober, progressive forms, took over as the main architectural style.
After World War II and the Communist coup in 1948, art in Czechoslovakia became Soviet-influenced. The Czechoslovak avant-garde artistic movement is known as the ''Brussels style came up'' in the time of political liberalization of Czechoslovakia in the 1960s. Brutalism dominated in the 1970s and 1980s.
The Czech Republic is not shying away from the more modern trends of international architecture, an example is the TanÄÃcà dÅŊm, Dancing House (TanÄÃcà dÅŊm) in Prague, Golden Angel in Prague or Congress Centre in ZlÃn.
 The literature from the area of today's Czech Republic was mostly written in Czech, but also in
The literature from the area of today's Czech Republic was mostly written in Czech, but also in
 The musical tradition of the Czech lands arose from the first church hymns, whose first evidence is suggested at the break of the 10th and 11th centuries. Some pieces of Czech music include two chorales, which in their time performed the function of anthems: "Hospodine pomiluj ny, Lord, Have Mercy on Us" and the hymn "Saint Wenceslaus" or "Saint Wenceslas Chorale, Saint Wenceslaus Chorale". The authorship of the anthem "Lord, Have Mercy on Us" is ascribed by some historians to Saint Adalbert of Prague (sv.VojtÄch), bishop of
The musical tradition of the Czech lands arose from the first church hymns, whose first evidence is suggested at the break of the 10th and 11th centuries. Some pieces of Czech music include two chorales, which in their time performed the function of anthems: "Hospodine pomiluj ny, Lord, Have Mercy on Us" and the hymn "Saint Wenceslaus" or "Saint Wenceslas Chorale, Saint Wenceslaus Chorale". The authorship of the anthem "Lord, Have Mercy on Us" is ascribed by some historians to Saint Adalbert of Prague (sv.VojtÄch), bishop of
 In the 1960s, the hallmark of Czechoslovak New Wave's films were improvised dialogues, Black comedy, black and absurdity, absurd humor and the occupation of non-actors. Directors are trying to preserve natural atmosphere without refinement and artificial arrangement of scenes. A personality of the 1960s and the beginning of the 1970s with original manuscript and psychological impact is FrantiÅĄek VlÃĄÄil. Another international author is Jan Å vankmajer, a filmmaker and artist whose work spans several media. He is a self-labeled surrealism, surrealist known for animations and features.
The Barrandov Studios in Prague are the largest film studios with film locations in the country. Filmmakers have come to
In the 1960s, the hallmark of Czechoslovak New Wave's films were improvised dialogues, Black comedy, black and absurdity, absurd humor and the occupation of non-actors. Directors are trying to preserve natural atmosphere without refinement and artificial arrangement of scenes. A personality of the 1960s and the beginning of the 1970s with original manuscript and psychological impact is FrantiÅĄek VlÃĄÄil. Another international author is Jan Å vankmajer, a filmmaker and artist whose work spans several media. He is a self-labeled surrealism, surrealist known for animations and features.
The Barrandov Studios in Prague are the largest film studios with film locations in the country. Filmmakers have come to
ct24.cz
As of 2020, it is the most watched broadcaster, followed by the private TV Nova (Czech Republic), TV Nova and Prima televize, Prima TV. However, TV Nova features the most watched main news program and prime time program. Other public media services include the Czech Radio and the Czech News Agency. The best-selling daily national newspapers in 2020/21 are Blesk (average 703,000 daily readers), MladÃĄ fronta DNES (average 461,000 daily readers), PrÃĄvo (average 182,000 daily readers), LidovÃĐ noviny (average 163,000 daily readers) and HospodÃĄÅskÃĐ noviny (average 162,000 daily readers). Most Czechs (87%) read their news online, with Seznam.cz, iDNES.cz, Novinky.cz, Prima televize, iPrima.cz and Seznam ZprÃĄvy, Seznam ZprÃĄvy.cz being the most visited as of 2021.
 Czech cuisine is marked by an emphasis on meat dishes with pork, beef, and chicken. Goose, duck, rabbit, and venison are served. Fish is less common, with the occasional exception of fresh trout and carp, which is served at Christmas. One popular Czech menu item is ''smaÅūenÃ― vepÅovÃ― ÅÃzek'' (fried breaded pork filet), served with boiled potatoes.
There is a variety of local sausages, wurst, pÃĒtÃĐs, and smoked and cured meats. Czech desserts include a variety of whipped cream, chocolate, and fruit pastries and tarts, crÊpes, creme desserts and cheese, poppy-seed-filled and other types of traditional cakes such as ''Buchteln, buchty'', ''Kolach (cake), kolÃĄÄe'' and Apple strudel, ''ÅĄtrÚdl''.
Beer in the Czech Republic, Czech beer has a history extending more than a millennium; the earliest known brewery existed in 993. Today, the Czech Republic has the highest List of countries by beer consumption per capita, beer consumption per capita in the world. The pilsner style beer (pils) originated in
Czech cuisine is marked by an emphasis on meat dishes with pork, beef, and chicken. Goose, duck, rabbit, and venison are served. Fish is less common, with the occasional exception of fresh trout and carp, which is served at Christmas. One popular Czech menu item is ''smaÅūenÃ― vepÅovÃ― ÅÃzek'' (fried breaded pork filet), served with boiled potatoes.
There is a variety of local sausages, wurst, pÃĒtÃĐs, and smoked and cured meats. Czech desserts include a variety of whipped cream, chocolate, and fruit pastries and tarts, crÊpes, creme desserts and cheese, poppy-seed-filled and other types of traditional cakes such as ''Buchteln, buchty'', ''Kolach (cake), kolÃĄÄe'' and Apple strudel, ''ÅĄtrÚdl''.
Beer in the Czech Republic, Czech beer has a history extending more than a millennium; the earliest known brewery existed in 993. Today, the Czech Republic has the highest List of countries by beer consumption per capita, beer consumption per capita in the world. The pilsner style beer (pils) originated in
 The most watched and most attended sport in the Czech Republic are Association football, football and ice hockey. The most watched sporting events are the Ice hockey at the Olympic Games and the Ice Hockey World Championships. The most popular sports in the Czech Republic according to the size of the membership base of sports clubs are: football, tennis, ice hockey, volleyball, floorball, golf, ball hockey, Sport of athletics, athletics, basketball and skiing.
The country has won 15 gold medals in the Summer Olympic Games, Summer Olympics and nine in the Winter Olympic Games, Winter Games. (See All-time Olympic Games medal table, Olympic history.) The Czech Republic men's national ice hockey team, Czech ice hockey team won the gold medal at the 1998 Winter Olympics and has won (along with the Czechoslovakia men's national ice hockey team, Czechoslovakian team) thirteen gold medals at the IHWC, World Championships, including three straight from 1999 Men's World Ice Hockey Championships, 1999 to 2001 Men's World Ice Hockey Championships, 2001.
The Å koda Motorsport is engaged in Motorsport, competition racing since 1901 and has gained a number of titles with various vehicles around the world. MTX (automobile), MTX automobile company was formerly engaged in the manufacture of Auto racing, racing and Formula racing, formula cars since 1969.
Hiking is a popular sport. The word for 'tourist' in Czech, ''turista'', also means 'trekker' or 'hiker'. For hikers, thanks to the more than 120-year-old tradition, there is the Czech Hiking Markers System of trail blazing, that has been adopted by countries worldwide. There is a network of around 40,000 km of marked short- and long-distance trails crossing the whole country and all the Czech mountains.
The most watched and most attended sport in the Czech Republic are Association football, football and ice hockey. The most watched sporting events are the Ice hockey at the Olympic Games and the Ice Hockey World Championships. The most popular sports in the Czech Republic according to the size of the membership base of sports clubs are: football, tennis, ice hockey, volleyball, floorball, golf, ball hockey, Sport of athletics, athletics, basketball and skiing.
The country has won 15 gold medals in the Summer Olympic Games, Summer Olympics and nine in the Winter Olympic Games, Winter Games. (See All-time Olympic Games medal table, Olympic history.) The Czech Republic men's national ice hockey team, Czech ice hockey team won the gold medal at the 1998 Winter Olympics and has won (along with the Czechoslovakia men's national ice hockey team, Czechoslovakian team) thirteen gold medals at the IHWC, World Championships, including three straight from 1999 Men's World Ice Hockey Championships, 1999 to 2001 Men's World Ice Hockey Championships, 2001.
The Å koda Motorsport is engaged in Motorsport, competition racing since 1901 and has gained a number of titles with various vehicles around the world. MTX (automobile), MTX automobile company was formerly engaged in the manufacture of Auto racing, racing and Formula racing, formula cars since 1969.
Hiking is a popular sport. The word for 'tourist' in Czech, ''turista'', also means 'trekker' or 'hiker'. For hikers, thanks to the more than 120-year-old tradition, there is the Czech Hiking Markers System of trail blazing, that has been adopted by countries worldwide. There is a network of around 40,000 km of marked short- and long-distance trails crossing the whole country and all the Czech mountains.
Prague: Belonging and the Modern City
'. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. . * Hochman, JiÅÃ (1998)
''Historical Ddictionary of the Czech State''
Lanham, Md. and London: The Scarecrow Press. .
Governmental website
Presidential website
Senate
Portal of the Public Administration
#VisitCzechia
â official tourist portal of the Czech Republic * * {{Coord, 49, 45, N, 15, 30, E, type:country_region:CZ_scale:9000000, display=title Czech Republic, Central Europe Countries in Europe Landlocked countries Member states of NATO Member states of the European Union Member states of the United Nations Member states of the Three Seas Initiative Republics Member states of the Council of Europe OECD members States and territories established in 1993
landlocked country
A landlocked country is a country that has no territory connected to an ocean or whose coastlines lie solely on endorheic basins. Currently, there are 44 landlocked countries, two of them doubly landlocked (Liechtenstein and Uzbekistan), and t ...
in Central Europe
Central Europe is a geographical region of Europe between Eastern Europe, Eastern, Southern Europe, Southern, Western Europe, Western and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Central Europe is known for its cultural diversity; however, countries in ...
. The country is bordered by Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
to the south, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
to the west, Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
to the northeast, and Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's m ...
to the southeast. The Czech Republic has a hilly landscape that covers an area of with a mostly temperate continental
Continental may refer to:
Places
* Continental, Arizona, a small community in Pima County, Arizona, US
* Continental, Ohio, a small town in Putnam County, US
Arts and entertainment
* ''Continental'' (album), an album by Saint Etienne
* Continen ...
and oceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate or maritime climate, is the temperate climate sub-type in KÃķppen climate classification, KÃķppen classification represented as ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of co ...
. The capital and largest city is Prague
Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its P ...
; other major cities and urban areas include Brno
Brno ( , ; ) is a Statutory city (Czech Republic), city in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. Located at the confluence of the Svitava (river), Svitava and Svratka (river), Svratka rivers, Brno has about 403,000 inhabitants, making ...
, Ostrava
Ostrava (; ; ) is a city in the north-east of the Czech Republic and the capital of the Moravian-Silesian Region. It has about 283,000 inhabitants. It lies from the border with Poland, at the confluences of four rivers: Oder, Opava (river), Opa ...
, PlzeÅ
PlzeÅ (), also known in English and German as Pilsen (), is a city in the Czech Republic. It is the Statutory city (Czech Republic), fourth most populous city in the Czech Republic with about 188,000 inhabitants. It is located about west of P ...
and Liberec
Liberec (; ) is a city in the Czech Republic. It has about 108,000 inhabitants, making it the fifth largest city in the country. It lies on the Lusatian Neisse River, in a basin surrounded by mountains. The city centre is well preserved and is pr ...
.
The Duchy of Bohemia
The Duchy of Bohemia, also later referred to in English as the Czech Duchy, (Old Czech: ) was a monarchy and a Princes of the Holy Roman Empire, principality of the Holy Roman Empire in Central Europe during the Early Middle Ages, Early and High M ...
was founded in the late 9th century under Great Moravia
Great Moravia (; , ''MeghÃĄlÄŦ MoravÃa''; ; ; , ), or simply Moravia, was the first major state that was predominantly West Slavic to emerge in the area of Central Europe, possibly including territories which are today part of the Czech Repub ...
. It was formally recognized as an Imperial Estate
An Imperial Estate (; , plural: ') was an entity or an individual of the Holy Roman Empire with representation and the right to vote in the Imperial Diet (Holy Roman Empire), Imperial Diet ('). Rulers of these Estates were able to exercise signi ...
of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
in 1002 and became a kingdom in 1198. Following the Battle of MohÃĄcs
The Battle of MohÃĄcs (; , ) took place on 29 August 1526 near MohÃĄcs, in the Kingdom of Hungary. It was fought between the forces of Hungary, led by King Louis II of Hungary, Louis II, and the invading Ottoman Empire, commanded by Suleima ...
in 1526, all of the Lands of the Bohemian Crown
The Lands of the Bohemian Crown were the states in Central Europe during the Middle Ages, medieval and early modern periods with feudalism, feudal obligations to the List of Bohemian monarchs, Bohemian kings. The crown lands primarily consisted o ...
were gradually integrated into the Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
. Nearly a hundred years later, the Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
Bohemian Revolt
The Bohemian Revolt (; ; 1618â1620) was an uprising of the Kingdom of Bohemia, Bohemian Estates of the realm, estates against the rule of the Habsburg dynasty that began the Thirty Years' War. It was caused by both religious and power dispu ...
led to the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine ...
. After the Battle of White Mountain
The Battle of White Mountain (; ) was an important battle in the early stages of the Thirty Years' War. It led to the defeat of the Bohemian Revolt and ensured Habsburg control for the next three hundred years.
It was fought on 8 November 16 ...
, the Habsburgs consolidated their rule. With the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806, the Crown lands became part of the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a Multinational state, multinational European Great Powers, great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the Habsburg monarchy, realms of the Habsburgs. Duri ...
.
During the 19th century, the Czech lands
The Czech lands or the Bohemian lands (, ) is a historical-geographical term which denotes the three historical regions of Bohemia, Moravia, and Czech Silesia out of which Czechoslovakia, and later the Czech Republic and Slovakia, were formed. ...
underwent significant industrialization. Following the collapse of Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, also referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Dual Monarchy or the Habsburg Monarchy, was a multi-national constitutional monarchy in Central Europe#Before World War I, Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. A military ...
after World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 â 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, most of the region became part of the First Czechoslovak Republic
The First Czechoslovak Republic, often colloquially referred to as the First Republic, was the first Czechoslovakia, Czechoslovak state that existed from 1918 to 1938, a union of ethnic Czechs and Slovaks. The country was commonly called Czechosl ...
in 1918. Czechoslovakia was the only country in Central and Eastern Europe to remain a parliamentary democracy
A parliamentary system, or parliamentary democracy, is a form of government where the head of government (chief executive) derives their democratic legitimacy from their ability to command the support ("confidence") of a majority of the legisl ...
during the entirety of the interwar period
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period, also known as the interbellum (), lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days) â from the end of World War I (WWI) to the beginning of World War II ( ...
.Timothy Garton Ash '' The Uses of Adversity'' Granta Books, 1991 p. 60 After the Munich Agreement
The Munich Agreement was reached in Munich on 30 September 1938, by Nazi Germany, the United Kingdom, the French Third Republic, French Republic, and the Kingdom of Italy. The agreement provided for the Occupation of Czechoslovakia (1938â194 ...
in 1938, Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
systematically took control over the Czech lands. Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia ( ; Czech language, Czech and , ''Äesko-Slovensko'') was a landlocked country in Central Europe, created in 1918, when it declared its independence from Austria-Hungary. In 1938, after the Munich Agreement, the Sudetenland beca ...
was restored in 1945 and three years later became an Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc (Combloc), the Socialist Bloc, the Workers Bloc, and the Soviet Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of communist states of Central and Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America that were a ...
communist
Communism () is a sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology within the socialist movement, whose goal is the creation of a communist society, a socioeconomic order centered on common ownership of the means of production, di ...
state following a coup d'ÃĐtat
A coup d'ÃĐtat (; ; ), or simply a coup
, is typically an illegal and overt attempt by a military organization or other government elites to unseat an incumbent leadership. A self-coup is said to take place when a leader, having come to powe ...
in 1948. Attempts to liberalize the government and economy were suppressed by a Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
-led invasion of the country during the Prague Spring
The Prague Spring (; ) was a period of liberalization, political liberalization and mass protest in
the Czechoslovak Socialist Republic. It began on 5 January 1968, when reformist Alexander DubÄek was elected Secretary (title), First Secre ...
in 1968. In November 1989, the Velvet Revolution
The Velvet Revolution () or Gentle Revolution () was a non-violent transition of power in what was then Czechoslovakia, occurring from 17 November to 28 November 1989. Popular demonstrations against the one-party government of the Communist Pa ...
ended communist rule in the country and restored democracy
Democracy (from , ''dÄmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which political power is vested in the people or the population of a state. Under a minimalist definition of democracy, rulers are elected through competitiv ...
. On 31 December 1992, Czechoslovakia was peacefully dissolved, with its constituent states becoming the independent states of the Czech Republic and Slovakia.
The Czech Republic is a unitary
Unitary may refer to:
Mathematics
* Unitary divisor
* Unitary element
* Unitary group
* Unitary matrix
* Unitary morphism
* Unitary operator
* Unitary transformation
* Unitary representation
* Unitarity (physics)
* ''E''-unitary inverse semigr ...
parliamentary republic
A parliamentary republic is a republic that operates under a parliamentary system of government where the Executive (government), executive branch (the government) derives its legitimacy from and is accountable to the legislature (the parliament). ...
and developed country
A developed country, or advanced country, is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy, and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations. Most commonly, the criteria for eval ...
with an advanced
The Advanced Party (), otherwise known as the Advanced Association () was a liberal and centrist Zionist political association in Mandatory Palestine founded by several urban liberal Zionists. The party was founded in order to represent the voice ...
, high-income
A high-income economy is defined by the World Bank as a country with a gross national income per capita of US$14,005 or more in 2023, calculated using the Atlas method. While the term "high-income" is often used interchangeably with "First World" ...
social market economy
The social market economy (SOME; ), also called Rhine capitalism, Rhine-Alpine capitalism, the Rhenish model, and social capitalism, is a socioeconomic model combining a free-market capitalist economic system with social policies and enough re ...
. It is a welfare state
A welfare state is a form of government in which the State (polity), state (or a well-established network of social institutions) protects and promotes the economic and social well-being of its citizens, based upon the principles of equal oppor ...
with a European social model
The European social model is a concept that emerged in the discussion of economic globalisation and typically contrasts the degree of employment regulation and social protection in European countries to conditions in the United States. It is ...
, universal health care
Universal health care (also called universal health coverage, universal coverage, or universal care) is a health care system in which all residents of a particular country or region are assured access to health care. It is generally organized a ...
and free-tuition university education
Tertiary education (higher education, or post-secondary education) is the educational level following the completion of secondary education.
The World Bank defines tertiary education as including universities, colleges, and vocational school ...
. It ranks 32nd in the Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistical composite index of life expectancy, Education Index, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income i ...
. The Czech Republic is a member of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
, NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO ; , OTAN), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental Transnationalism, transnational military alliance of 32 Member states of NATO, member s ...
, the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
, the OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; , OCDE) is an international organization, intergovernmental organization with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and international trade, wor ...
, the OSCE
The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) is a regional security-oriented intergovernmental organization comprising member states in Europe, North America, and Asia. Its mandate includes issues such as arms control, the pr ...
, the Council of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; , CdE) is an international organisation with the goal of upholding human rights, democracy and the Law in Europe, rule of law in Europe. Founded in 1949, it is Europe's oldest intergovernmental organisation, represe ...
and the VisegrÃĄd Group
The VisegrÃĄd Group (also known as the VisegrÃĄd Four or the V4) is a cultural and political alliance of four Central European countries: the Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, and Slovakia. The alliance aims to advance co-operation in military, e ...
.
Etymology
The traditional English name "Bohemia" derives fromLatin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
''Boiohaemum'', which means "home of the Boii
The Boii (Latin language, Latin plural, singular ''Boius''; ) were a Celts, Celtic tribe of the later Iron Age, attested at various times in Cisalpine Gaul (present-day Northern Italy), Pannonia (present-day Austria and Hungary), present-day Ba ...
" (a Gallic tribe). The current English name ultimately comes from the Czech word . The name comes from the Slavic tribe () and, according to legend, their leader Äech
Äech (feminine ÄechovÃĄ) is a Czech surname meaning Czech. It was used to distinguish an inhabitant of Bohemia from Slovaks, Moravians and other ethnic groups. Notable people with the surname include:
* Dana ÄechovÃĄ (born 1983), Czech tab ...
, who brought them to Bohemia, to settle on ÅÃp
ÅÃp (; ) is a high solitary hill in the Lower OhÅe Table in the Czech Republic. It is located southeast of LitomÄÅice. According to national legend, it is the place where the first Czechs settled. The mountain and the rotunda on its top a ...
Mountain. The etymology of the word is uncertain, but according to the most common derivation can be traced back to the Proto-Slavic
Proto-Slavic (abbreviated PSl., PS.; also called Common Slavic or Common Slavonic) is the unattested, reconstructed proto-language of all Slavic languages. It represents Slavic speech approximately from the 2nd millennium BC through the 6th ...
root , meaning 'member of the people; kinsman', thus making it Cognate (linguistics), cognate to the Czech word 'person'.
The country has been traditionally divided into three lands, namely Bohemia () in the west, Moravia () in the east, and Czech Silesia (; the smaller, south-eastern part of historical Silesia, most of which is located within modern Poland) in the northeast. Known as the ''lands of the Bohemian Crown'' since the 14th century, a number of other names for the country have been used, including ''Czech/Bohemian lands'', ''Bohemian Crown'', ''Czechia'', and the ''lands of the Crown of Wenceslaus I, Duke of Bohemia, Saint Wenceslaus''. When the country regained its independence after the dissolution of the Austria-Hungary, Austro-Hungarian empire in 1918, the new name of ''Czechoslovakia'' was coined to reflect the union of the Czech and Slovak nations within one country.
After Czechoslovakia dissolved on the last day of 1992, was adopted as the Czech short name for the new state and the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Czech Republic), Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Czech Republic recommended ''Czechia'' for the English-language equivalent. This form was not widely adopted at the time, leading to the long name ''Czech Republic'' being used in English in nearly all circumstances. The Czech government Name of the Czech Republic#Adoption of Czechia, directed use of ''Czechia'' as the official English short name in 2016. The short name has been listed by the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
and is used by other organizations such as the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
, NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO ; , OTAN), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental Transnationalism, transnational military alliance of 32 Member states of NATO, member s ...
, the Central Intelligence Agency, CIA, Google Maps, and the European Broadcasting Union. In 2022, the American ''AP Stylebook'' stated in its entry on the country that "both [Czechia and the Czech Republic] are acceptable. The shorter name Czechia is preferred by the Czech government. If using Czechia, clarify in the story that the country is more widely known in English as the Czech Republic."
History
Prehistory
Archaeological evidence indicates that the area now known as the Czech Republic has been inhabited since the Paleolithic, Paleolithic era. Notably, the Venus of Dolnà VÄstonice, a ceramic figurine dated to approximately 29,000â25,000 BCE, was discovered in this region. This artifact is considered the oldest known ceramic figurine in the world. In the Classical antiquity, classical era, as a result of the 3rd century BC Celts, Celtic migrations, Bohemia became associated with theBoii
The Boii (Latin language, Latin plural, singular ''Boius''; ) were a Celts, Celtic tribe of the later Iron Age, attested at various times in Cisalpine Gaul (present-day Northern Italy), Pannonia (present-day Austria and Hungary), present-day Ba ...
. The Boii founded an oppidum near the site of modern Prague. Later in the 1st century, the Germanic tribes of the Marcomanni and Quadi settled there.
Slavs from the Black SeaâCarpathian Mountains, Carpathian region settled in the area (their migration was pushed by an invasion of peoples from Siberia and Eastern Europe into their area: Huns, Pannonian Avars, Avars, Bulgars and Hungarians, Magyars). In the sixth century, the Huns had moved westwards into Bohemia, Moravia, and some of present-day Austria and Germany.
During the 7th century, the Frankish merchant Samo, supporting the Slavs fighting against nearby settled Pannonian Avars, Avars, became the ruler of the first documented Slavic state in Central Europe, Samo's Empire. The principality of Great Moravia
Great Moravia (; , ''MeghÃĄlÄŦ MoravÃa''; ; ; , ), or simply Moravia, was the first major state that was predominantly West Slavic to emerge in the area of Central Europe, possibly including territories which are today part of the Czech Repub ...
, controlled by Moymirid dynasty, Moymir dynasty, arose in the 8th century. It reached its zenith in the 9th (during the reign of Svatopluk I of Moravia), holding off the influence of the Franks. Great Moravia was Christianized, with a role being played by the Byzantine Empire, Byzantine mission of Cyril and Methodius. They codified the Old Church Slavonic language, the first literary and liturgical language of the Slavs, and the Glagolitic script.
Bohemia
TheDuchy of Bohemia
The Duchy of Bohemia, also later referred to in English as the Czech Duchy, (Old Czech: ) was a monarchy and a Princes of the Holy Roman Empire, principality of the Holy Roman Empire in Central Europe during the Early Middle Ages, Early and High M ...
emerged in the late 9th century when it was unified by the PÅemyslid dynasty. Bohemia was from 1002 until 1806 an Imperial Estate
An Imperial Estate (; , plural: ') was an entity or an individual of the Holy Roman Empire with representation and the right to vote in the Imperial Diet (Holy Roman Empire), Imperial Diet ('). Rulers of these Estates were able to exercise signi ...
of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
.
In 1212, Ottokar I of Bohemia, PÅemysl Ottokar I extracted the Golden Bull of Sicily from the emperor, confirming Ottokar and his descendants' royal status; the Duchy of Bohemia was raised to a Realm, Kingdom. Germans, German immigrants settled in the Bohemian periphery in the 13th century. The Mongol Empire, Mongols in the Mongol invasion of Europe, invasion of Europe carried their raids into Moravia but were defensively defeated at Olomouc.
After a series of dynastic wars, the House of Luxembourg gained the Bohemian throne.
Efforts for a Bohemian Reformation, reform of the church in Bohemia started already in the late 14th century. Jan Hus' followers seceded from some practices of the Catholic Church, Roman Church and in the Hussite Wars (1419â1434) defeated five crusades organized against them by Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor, Sigismund. During the next two centuries, 90% of the population in Bohemia and Moravia were considered Hussites. The pacifist thinker Petr ChelÄickÃ― inspired the movement of the Unity of the Brethren (Czech Republic), Moravian Brethren (by the middle of the 15th century) that completely separated from the Roman Catholic Church.
On 21 December 1421, Jan Å―iÅūka, a successful military commander and mercenary, led his group of forces in the Battle of KutnÃĄ Hora, resulting in a victory for the Hussites. He is honoured to this day as a Hero (title), national hero.
After 1526, Bohemia came increasingly under House of Habsburg, Habsburg control as the Habsburgs became first the elected and then in 1627 the hereditary rulers of Bohemia. Between 1583 and 1611 Prague was the official seat of the Holy Roman Emperor Rudolf II, Holy Roman Emperor, Rudolf II and his court.
The Defenestrations of Prague, Defenestration of Prague and subsequent revolt against the Habsburgs in 1618 marked the start of the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine ...
. In 1620, the rebellion in Bohemia was crushed at the Battle of White Mountain
The Battle of White Mountain (; ) was an important battle in the early stages of the Thirty Years' War. It led to the defeat of the Bohemian Revolt and ensured Habsburg control for the next three hundred years.
It was fought on 8 November 16 ...
and the ties between Bohemia and the Habsburgs' hereditary lands in Austria were strengthened. The leaders of the Bohemian Revolt
The Bohemian Revolt (; ; 1618â1620) was an uprising of the Kingdom of Bohemia, Bohemian Estates of the realm, estates against the rule of the Habsburg dynasty that began the Thirty Years' War. It was caused by both religious and power dispu ...
were Old Town Square execution, executed in 1621. The nobility and the middle class Protestants had to either convert to Catholicism or leave the country.
The following era of 1620 to the late 18th century became known as the "Dark Age". During the Thirty Years' War, the population of the Czech lands
The Czech lands or the Bohemian lands (, ) is a historical-geographical term which denotes the three historical regions of Bohemia, Moravia, and Czech Silesia out of which Czechoslovakia, and later the Czech Republic and Slovakia, were formed. ...
declined by a third through the expulsion of Czech Protestants as well as due to the war, disease and Famines in the Czech lands, famine. The Habsburgs prohibited all Christian confessions other than Catholic Church, Catholicism. The flowering of Czech Baroque architecture, Baroque culture shows the ambiguity of this historical period.
Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Turks and Crimean Khanate, Tatars invaded Moravia in 1663. In 1679â1680 the Czech lands faced the Great Plague of Vienna and an uprising of serfs.
 There were peasant uprisings influenced by famine. Serfdom was abolished between 1781 and 1848. Several battles of the Napoleonic Wars took place on the current territory of the Czech Republic.
The end of the
There were peasant uprisings influenced by famine. Serfdom was abolished between 1781 and 1848. Several battles of the Napoleonic Wars took place on the current territory of the Czech Republic.
The end of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
in 1806 led to degradation of the political status of Bohemia which lost its position of an Prince-elector, electorate of the Holy Roman Empire as well as its own political representation in the Imperial Diet (Holy Roman Empire), Imperial Diet. Bohemian lands became part of the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a Multinational state, multinational European Great Powers, great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the Habsburg monarchy, realms of the Habsburgs. Duri ...
. During the 18th and 19th century the Czech National Revival began its rise, with the purpose to revive Czech language, culture, and national identity. The Revolutions of 1848 in the Austrian Empire, Revolution of 1848 in Prague, striving for liberal reforms and autonomy of the Bohemian Crown within the Austrian Empire, was suppressed.
It seemed that some concessions would be made also to Bohemia, but in the end, the Emperor Franz Joseph I of Austria, Franz Joseph I affected a compromise with Hungary only. The Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867 and the never realized coronation of Franz Joseph as King of Bohemia led to a disappointment of some Czech politicians. The Bohemian Crown lands became part of the so-called Cisleithania.
The Czech Social Democratic and progressive politicians started the fight for universal suffrage. The first elections under Universal suffrage, universal male suffrage were held in 1907.
Czechoslovakia
 In 1918, during the collapse of the
In 1918, during the collapse of the Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
at the end of World War I, the independent republic of Czechoslovakia, which joined the winning Allied powers, was created, with TomÃĄÅĄ Garrigue Masaryk in the lead. This new country incorporated the Bohemian Crown.
The First Czechoslovak Republic
The First Czechoslovak Republic, often colloquially referred to as the First Republic, was the first Czechoslovakia, Czechoslovak state that existed from 1918 to 1938, a union of ethnic Czechs and Slovaks. The country was commonly called Czechosl ...
comprised only 27% of the population of the former Austria-Hungary, but nearly 80% of the industry, which enabled it to compete with Western industrial states.Stephen J. Lee. ''Aspects of European History 1789â1980''. Page 107. Chapter "Austria-Hungary and the successor states". Routledge. 28 January 2008. In 1929 compared to 1913, the gross domestic product increased by 52% and industrial production by 41%. In 1938 Czechoslovakia held 10th place in the world industrial production. Czechoslovakia was the only country in Central and Eastern Europe to remain a liberal democracy throughout the entire
interwar period. Although the First Czechoslovak Republic was a unitary state, it provided certain rights to its minorities, the largest being Germans in Czechoslovakia (1918â1938), Germans (23.6% in 1921), Hungarians in Slovakia, Hungarians (5.6%) and Rusyns and Ukrainians in Czechoslovakia (1918â1938), Ukrainians (3.5%).
Western Czechoslovakia was German occupation of Czechoslovakia, occupied by Nazi Germany, which placed most of the region into the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia. The Protectorate was proclaimed part of the Third Reich, and the president and prime minister were subordinated to Nazi Germany's ''Protector (title), Reichsprotektor''. Theresienstadt concentration camp, One Nazi concentration camp was located within the Czech territory at TerezÃn, north of Prague. The vast majority of the Protectorate's Jews were murdered in Nazi concentration camps, Nazi-run concentration camps. The Nazi called for the extermination, expulsion, Germanization or enslavement of most or all Czechs for the purpose of providing more Lebensraum, living space for the German people. There was Resistance in German-occupied Czechoslovakia, Czechoslovak resistance to Nazi occupation as well as German war crimes, reprisals against the Czechoslovaks for their anti-Nazi resistance. The German occupation ended on 9 May 1945, with the arrival of the Soviet and American armies and the Prague uprising. Most of Czechoslovakia's German-speakers were forcibly Expulsion of Germans from Czechoslovakia, expelled from the country, first as a result of local acts of violence and then under the aegis of an "organized transfer" confirmed by the Soviet Union, the United States, and Great Britain at the Potsdam Conference.
 In the Czechoslovakian parliamentary election, 1946, 1946 elections, the Communist Party of Czechoslovakia, Communist Party gained 38% of the votes and became the largest party in the Czechoslovak parliament, formed a coalition with other parties, and consolidated power. A
In the Czechoslovakian parliamentary election, 1946, 1946 elections, the Communist Party of Czechoslovakia, Communist Party gained 38% of the votes and became the largest party in the Czechoslovak parliament, formed a coalition with other parties, and consolidated power. A coup d'ÃĐtat
A coup d'ÃĐtat (; ; ), or simply a coup
, is typically an illegal and overt attempt by a military organization or other government elites to unseat an incumbent leadership. A self-coup is said to take place when a leader, having come to powe ...
came in 1948 and a single-party government was formed. For the History of Czechoslovakia (1948â1989), next 41 years, the Czechoslovak Communist state conformed to Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc (Combloc), the Socialist Bloc, the Workers Bloc, and the Soviet Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of communist states of Central and Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America that were a ...
economic and political features. The Prague Spring
The Prague Spring (; ) was a period of liberalization, political liberalization and mass protest in
the Czechoslovak Socialist Republic. It began on 5 January 1968, when reformist Alexander DubÄek was elected Secretary (title), First Secre ...
political liberalization was stopped by the 1968 Warsaw Pact invasion of Czechoslovakia. Analysts believe that the invasion caused the communist movement to fracture, ultimately leading to the Revolutions of 1989.
Czech Republic
In November 1989, Czechoslovakia again became a liberal democracy through theVelvet Revolution
The Velvet Revolution () or Gentle Revolution () was a non-violent transition of power in what was then Czechoslovakia, occurring from 17 November to 28 November 1989. Popular demonstrations against the one-party government of the Communist Pa ...
. However, Slovak national aspirations strengthened (Hyphen War) and on 31 December 1992, the Dissolution of Czechoslovakia, country peacefully split into the independent country, countries of the Czech Republic and Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's m ...
. Both countries went through economic reforms and privatizations, with the intention of creating a market economy, as they have been trying to do since 1990, when Czechs and Slovaks still shared the common state. This process was largely successful; in 2006 the Czech Republic was recognized by the World Bank as a "developed country", and in 2009 the Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistical composite index of life expectancy, Education Index, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income i ...
ranked it as a nation of "Very High Human Development".
From 1991, the Czech Republic, originally as part of Czechoslovakia and since 1993 in its own right, has been a member of the VisegrÃĄd Group
The VisegrÃĄd Group (also known as the VisegrÃĄd Four or the V4) is a cultural and political alliance of four Central European countries: the Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, and Slovakia. The alliance aims to advance co-operation in military, e ...
and from 1995, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, OECD. The Czech Republic joined NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO ; , OTAN), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental Transnationalism, transnational military alliance of 32 Member states of NATO, member s ...
on 12 March 1999 and the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
on 1 May 2004. On 21 December 2007 the Czech Republic joined the Schengen Area.
Until 2017, either the centre-left Czech Social Democratic Party or the centre-right Civic Democratic Party (Czech Republic), Civic Democratic Party led the governments of the Czech Republic. In October 2017, the populist movement ANO 2011, led by the country's second-richest man, Andrej BabiÅĄ, won the 2017 Czech legislative election, elections with three times more votes than its closest rival, the Civic Democrats. In December 2017, Czech president MiloÅĄ Zeman appointed Andrej BabiÅĄ as the new prime minister.
In the 2021 Czech legislative election, 2021 elections, ANO 2011 was narrowly defeated and Petr Fiala became the new prime minister. He formed a government coalition of the alliance Spolu (Czech Republic), SPOLU (Civic Democratic Party (Czech Republic), Civic Democratic Party, KDU-ÄSL and TOP 09) and the alliance of Pirates and Mayors. In January 2023, retired general Petr Pavel won the 2023 Czech presidential election, presidential election, becoming new Czech president to succeed MiloÅĄ Zeman. Following the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, the country took in half a million 2022â2023 Ukrainian refugee crisis, Ukrainian refugees, the largest number per capita in the world.
Geography
Climate
The Czech Republic has a temperate climate, situated in the transition zone between the oceanic climate, oceanic and continental climate types, with warm summers and cold, cloudy and snowy winters. The temperature difference between summer and winter is due to the landlocked geographical position. Temperatures vary depending on the elevation. In general, at higher altitudes, the temperatures decrease and precipitation (meteorology), precipitation increases. The wettest area in the Czech Republic is found around BÃlÃ― Potok (Liberec District), BÃlÃ― Potok in Jizera Mountains and the driest region is the Louny District to the northwest ofPrague
Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its P ...
. Another factor is the distribution of the mountains.
At the highest peak of SnÄÅūka (), the average temperature is , whereas in the lowlands of the South Moravian Region, the average temperature is as high as . The country's capital, Prague, has a similar average temperature, although this is influenced by urban factors.
The coldest month is usually January, followed by February and December. During these months, there is snow in the mountains and sometimes in the cities and lowlands. During March, April, and May, the temperature usually increases, especially during April, when the temperature and weather tends to vary during the day. Spring is also characterized by higher water levels in the rivers, due to melting snow with occasional flooding.
The warmest month of the year is July, followed by August and June. On average, summer temperatures are about higher than during winter. Summer is also characterized by rain and storms.
Autumn generally begins in September, which is still warm and dry. During October, temperatures usually fall below or and deciduous trees begin to shed their leaves. By the end of November, temperatures usually range around the freezing point.
The coldest temperature ever measured was in LitvÃnovice near ÄeskÃĐ BudÄjovice in 1929, at and the hottest measured, was at in DobÅichovice in 2012.
Most rain falls during the summer. Sporadic rainfall is throughout the year (in Prague, the average number of days per month experiencing at least of rain varies from 12 in September and October to 16 in November) but concentrated rainfall (days with more than per day) are more frequent in the months of May to August (average around two such days per month). Severe thunderstorms, producing damaging straight-line winds, hail, and occasional tornadoes occur, especially during the summer period.
Biodiversity and conservation
As of 2020, the Czech Republic ranks as the 21st most environmentally conscious country in the world in Environmental Performance Index. It had a 2018 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 1.71/10, ranking it 160th globally out of 172 countries. The Czech Republic has four National Parks (Å umava National Park, KrkonoÅĄe National Park, ÄeskÃĐ Å vÃ―carsko National Park, Podyjà National Park) and 25 Protected Landscape Areas. The fauna of the Czech Republic includes a wide variety of animal species. Some species (especially Endangered species, endangered ones) are bred in Game reserve, reserves. Among the rare animals are, for example, eagles, ospreys, bustards, and storks.Government and politics
The Czech Republic is a pluralist multi-party parliamentary democracy, parliamentary representative democracy. The Parliament of the Czech Republic, Parliament (''Parlament ÄeskÃĐ republiky'') is bicameral, with the Chamber of Deputies of the Czech Republic, Chamber of Deputies (, 200 members) and the Senate of the Czech Republic, Senate (, 81 members). The Member of Parliament#Czech Republic, members of the Chamber of Deputies are elected for a four-year term by proportional representation, with a 5% election threshold. There are 14 voting districts, identical to the country's administrative regions. The Chamber of Deputies, the successor to the Czech National Council, has the powers and responsibilities of the now defunct federal parliament of the former Czechoslovakia. The members of the Senate are elected in single-seat electoral district, constituencies by two-round Two-round system, runoff voting for a six-year term, with one-third elected every even year in the autumn. This arrangement is modeled on the United States Senate, U.S. Senate, but each constituency is roughly the same size and the voting system used is a two-round runoff. The president is a formal head of state with limited and specific powers, who appoints the prime minister, as well the other members of the cabinet on a proposal by the prime minister. From 1993 until 2012, the President of the Czech Republic was selected by a joint session of the parliament for a five-year term, with no more than two consecutive terms (VÃĄclav Havel and VÃĄclav Klaus were both elected twice). Since 2013, the president has been elected directly. Some commentators have argued that, with the introduction of direct election of the President, the Czech Republic has moved away from the parliamentary system and towards a Semi-presidential system, semi-presidential one. The Government of the Czech Republic, Government's exercise of executive power derives from the Constitution of the Czech Republic, Constitution. The members of the government are the Prime Minister of the Czech Republic, Prime Minister, Deputy prime ministers and other ministers. The Government is responsible to the Chamber of Deputies of the Czech Republic, Chamber of Deputies. The Prime Minister of the Czech Republic, Prime Minister is the head of government and wields powers such as the right to set the agenda for most foreign and domestic policy and choose government ministers. , President of the Czech Republic, President , Petr Pavel , Independent politician, Independent , 9 March 2023 , - , President of the Senate of the Czech Republic, President of the Senate , MiloÅĄ VystrÄil , Civic Democratic Party (Czech Republic), ODS , 19 February 2020 , - , President of the Chamber of Deputies (Czech Republic), President of the Chamber of Deputies , MarkÃĐta PekarovÃĄ AdamovÃĄ , TOP 09 , 10 November 2021 , - , Prime Minister of the Czech Republic, Prime Minister , Petr Fiala , Civic Democratic Party (Czech Republic), ODS , 28 November 2021Law
The Czech Republic is a unitary state, with a Civil law (legal system), civil law system based on the continental type, rooted in Germanic legal culture. The basis of the legal system is the Constitution of the Czech Republic adopted in 1993. The Criminal code, Penal Code is effective from 2010. A new Civil code became effective in 2014. The court system includes district, county, and supreme courts and is divided into civil, criminal, and administrative branches. The Czech judiciary has a triumvirate of supreme courts. The Constitutional Court of the Czech Republic, Constitutional Court consists of 15 constitutional judges and oversees violations of the Constitution of the Czech Republic, Constitution by either the legislature or by the Government of the Czech Republic, government. The Supreme Court of the Czech Republic, Supreme Court is formed of 67 judges and is the court of highest appeal for most legal cases heard in the Czech Republic. The Supreme Administrative Court of the Czech Republic, Supreme Administrative Court decides on issues of procedural and administrative propriety. It also has jurisdiction over certain political matters, such as the formation and closure of political parties, jurisdictional boundaries between government entities, and the eligibility of persons to stand for public office. The Supreme Court and the Supreme Administrative Court are both based inBrno
Brno ( , ; ) is a Statutory city (Czech Republic), city in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. Located at the confluence of the Svitava (river), Svitava and Svratka (river), Svratka rivers, Brno has about 403,000 inhabitants, making ...
, as is the Supreme Public Prosecutor's Office.
Foreign relations
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
, NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO ; , OTAN), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental Transnationalism, transnational military alliance of 32 Member states of NATO, member s ...
, OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; , OCDE) is an international organization, intergovernmental organization with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and international trade, wor ...
, Council of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; , CdE) is an international organisation with the goal of upholding human rights, democracy and the Law in Europe, rule of law in Europe. Founded in 1949, it is Europe's oldest intergovernmental organisation, represe ...
and is an observer to the Organization of American States. The embassies of most countries with diplomatic relations with the Czech Republic are located in Prague
Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its P ...
, while Consul (representative), consulates are located across the country.
The Czech passport is Visa requirements for Czech citizens, restricted by visas. According to the 2018 Henley & Partners Visa Restrictions Index, Czech citizens have visa-free access to 173 countries, which ranks them 7th along with Malta and New Zealand. The World Tourism Organization ranks the Czech passport 24th. The US Visa Waiver Program applies to Czech nationals.
 The Prime Minister of the Czech Republic, Prime Minister and Minister of Foreign Affairs of the Czech Republic, Minister of Foreign Affairs have primary roles in setting foreign policy, although the President of the Czech Republic, President also has influence and represents the country abroad. Membership in the European Union and NATO is central to the Czech Republic's foreign policy. The Office for Foreign Relations and Information (ÃZSI) serves as the foreign intelligence agency responsible for espionage and foreign policy briefings, as well as protection of Czech Republic's embassies abroad.
The Czech Republic has ties with
The Prime Minister of the Czech Republic, Prime Minister and Minister of Foreign Affairs of the Czech Republic, Minister of Foreign Affairs have primary roles in setting foreign policy, although the President of the Czech Republic, President also has influence and represents the country abroad. Membership in the European Union and NATO is central to the Czech Republic's foreign policy. The Office for Foreign Relations and Information (ÃZSI) serves as the foreign intelligence agency responsible for espionage and foreign policy briefings, as well as protection of Czech Republic's embassies abroad.
The Czech Republic has ties with Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's m ...
, Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
and Hungary as a member of the VisegrÃĄd Group
The VisegrÃĄd Group (also known as the VisegrÃĄd Four or the V4) is a cultural and political alliance of four Central European countries: the Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, and Slovakia. The alliance aims to advance co-operation in military, e ...
, as well as with Germany, Israel, the United States and the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
and its Members of the European Union, members. After 2020, relations with Asian democratic states, such as Taiwan, are being strengthened. Conversely, the Czech Republic has long had bad relations with Russia; from 2021, the Czech Republic appears on Russia's official list of enemy countries. The Czech Republic also has problematic relations with China.
Czech officials have supported dissenters in Belarus, Moldova, Myanmar and Cuba.
Famous Czech diplomats of the past included Jaroslav Lev of RoÅūmitÃĄl, Humprecht Jan Czernin, Count Philip Kinsky of Wchinitz and Tettau, Wenzel Anton, Prince of Kaunitz-Rietberg, Prince Karl Philipp, Prince of Schwarzenberg, Karl Philipp Schwarzenberg, Alois Lexa von Aehrenthal, Ottokar Czernin, Edvard BeneÅĄ, Jan Masaryk, JiÅÃ HÃĄjek, JiÅÃ Dienstbier, Michael Å―antovskÃ―, Petr KolÃĄÅ, Alexandr Vondra, Prince Karel Schwarzenberg and Petr Pavel.
Military
The Army of the Czech Republic, Czech armed forces consist of the Czech Land Forces, the Czech Air Force and of specialized support units. The armed forces are managed by the Ministry of Defence (Czech Republic), Ministry of Defence. The President of the Czech Republic is Commander-in-chief of the armed forces. In 2004 the army transformed itself into a fully professional organization and compulsory military service was abolished. The country has been a member ofNATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO ; , OTAN), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental Transnationalism, transnational military alliance of 32 Member states of NATO, member s ...
since 12 March 1999. Defence spending is approximately 1.28% of the GDP (2021). The armed forces are charged with protecting the Czech Republic and its allies, promoting global security interests, and contributing to NATO.
Currently, as a member of NATO, the Czech military are participating in the Resolute Support Mission, Resolute Support and Kosovo Force, KFOR operations and have soldiers in Afghanistan, Mali, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Kosovo, Egypt, Israel and Operation Atalanta, Somalia. The Czech Air Force also served in the Baltic states and Iceland. The main equipment of the Czech military includes Saab JAS 39 Gripen, JAS 39 Gripen multi-role fighters, Aero L-159 Alca combat aircraft, Bell AH-1Z Viper, AH-1Z Viper attack helicopters, armored vehicles (Pandur II, BMP-2, BVP-2) and tanks (T-72M4CZ and Leopard 2A4).
Human rights
Human rights in the Czech Republic are guaranteed by the Charter of Fundamental Rights and Freedoms and international treaties on human rights. Nevertheless, there were cases of human rights violations such as discrimination against Roma children, for which the European Commission asked the Czech Republic to provide an explanation, or the illegal sterilization of Roma women, for which the government apologized. People of the same sex can enter into a "registered partnership" in the Czech Republic. Conducting same-sex marriage is not legal under current Czech law.Administrative divisions
Since 2000, the Czech Republic has been divided into Regions of the Czech Republic, thirteen regions (Czech language, Czech: wikt:en:kraj#Czech, ''kraje'', singular ''kraj'') and the capital city ofPrague
Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its P ...
. Every region has its own elected regional assembly and a regional governor. In Prague, the assembly and presidential powers are executed by the city council and the mayor.
The older seventy-six Districts of the Czech Republic, districts (''okresy'', singular ''okres'') including three "statutory cities" (without Prague, which had special status) lost most of their importance in 1999 in an administrative reform; they remain as territorial divisions and seats of various branches of state administration.
The smallest administrative units are Obec, ''obce'' (municipalities). As of 2021, the Czech Republic is divided into 6,254 municipalities. Cities and towns are also municipalities. The capital city of Prague is a region and municipality at the same time.
Economy
high-income
A high-income economy is defined by the World Bank as a country with a gross national income per capita of US$14,005 or more in 2023, calculated using the Atlas method. While the term "high-income" is often used interchangeably with "First World" ...
Trading nation, export-oriented social market economy
The social market economy (SOME; ), also called Rhine capitalism, Rhine-Alpine capitalism, the Rhenish model, and social capitalism, is a socioeconomic model combining a free-market capitalist economic system with social policies and enough re ...
based in services, manufacturing and innovation, that maintains a welfare state
A welfare state is a form of government in which the State (polity), state (or a well-established network of social institutions) protects and promotes the economic and social well-being of its citizens, based upon the principles of equal oppor ...
and the European social model
The European social model is a concept that emerged in the discussion of economic globalisation and typically contrasts the degree of employment regulation and social protection in European countries to conditions in the United States. It is ...
. The Czech Republic participates in the European Single Market as a member of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
and is therefore a part of the economy of the European Union, but uses its own currency, the Czech koruna, instead of the euro. It has a per capita GDP rate that is 91% of the EU average and is a member of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, OECD. Monetary policy is conducted by the Czech National Bank, whose independence is guaranteed by the Constitution of the Czech Republic, Constitution. The Czech Republic ranks 12th in the United Nations Development Programme, UN List of countries by inequality-adjusted HDI, inequality-adjusted human development and 24th in World Bank Human Capital Index. It was described by ''The Guardian'' as "one of Europe's most flourishing economies".
, the country's GDP per capita at purchasing power parity is $51,329 and $29,856 at Real versus nominal value (economics), nominal value. According to Allianz A.G., in 2024 the country was an MWC (mean wealth country), ranking 24th in net financial assets. The country experienced a 4.5% Economic growth, GDP growth in 2017. The 2016 unemployment rate was the lowest in the EU at 2.4%, and the 2016 poverty rate was the second lowest of OECD members. 30th in the 2024 Global Innovation Index, 29th in the Global Competitiveness Report, and 25th in the Global Enabling Trade Report. The Czech Republic has a diverse economy that List of countries by economic complexity, ranks 7th in the 2016 Economic Complexity Index.Economic Complexity Rankings (ECI). The Atlas of Economic Complexity. Access date 3 October 2017. The industrial sector accounts for 37.5% of the economy, while services account for 60% and agriculture for 2.5%. The largest trading partner for both export and import is
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
and the EU in general. Dividends worth CZK 270 billion were paid to the Foreign ownership, foreign owners of Czech companies in 2017, which has become a political issue. The country has been a member of the Schengen Area since 1 May 2004, having abolished border controls, completely opening its borders with all of its neighbors on 21 December 2007.
Industry
 the List of companies of the Czech Republic#Largest by revenue, largest companies by revenue in the Czech Republic were: automobile manufacturer Å koda Auto, utility company ÄEZ Group, conglomerate Agrofert, energy trading company EnergetickÃ― a prÅŊmyslovÃ― holding, EPH, oil processing company Unipetrol, electronics manufacturer Foxconn CZ and steel producer TÅinec Iron and Steel Works, Moravia Steel. Other Czech transportation companies include: Å koda Transportation (tramways, trolleybuses, metro), Tatra (company), Tatra (heavy trucks, the second oldest car maker in the world), Avia Motors, Avia (medium trucks), Karosa and SOR Libchavy (buses), Aero Vodochody (military aircraft), Let Kunovice (civil aircraft), Zetor (tractors), Jawa Moto (motorcycles) and ÄeskÃĄ zbrojovka Strakonice, Äezeta (electric scooters).
Å koda Transportation is the fourth largest tram producer in the world; nearly one third of all trams in the world come from Czech factories. The Czech Republic is also the world's largest Phonograph record, vinyl records manufacturer, with GZ Media producing about 6 million pieces annually in LodÄnice (Beroun District), LodÄnice. ÄeskÃĄ zbrojovka UherskÃ― Brod, ÄeskÃĄ zbrojovka is among the ten largest firearms producers in the world and five who produce automatic weapons.
In the food industry, Czech companies include Agrofert, Kofola and HamÃĐ (company), HamÃĐ.
the List of companies of the Czech Republic#Largest by revenue, largest companies by revenue in the Czech Republic were: automobile manufacturer Å koda Auto, utility company ÄEZ Group, conglomerate Agrofert, energy trading company EnergetickÃ― a prÅŊmyslovÃ― holding, EPH, oil processing company Unipetrol, electronics manufacturer Foxconn CZ and steel producer TÅinec Iron and Steel Works, Moravia Steel. Other Czech transportation companies include: Å koda Transportation (tramways, trolleybuses, metro), Tatra (company), Tatra (heavy trucks, the second oldest car maker in the world), Avia Motors, Avia (medium trucks), Karosa and SOR Libchavy (buses), Aero Vodochody (military aircraft), Let Kunovice (civil aircraft), Zetor (tractors), Jawa Moto (motorcycles) and ÄeskÃĄ zbrojovka Strakonice, Äezeta (electric scooters).
Å koda Transportation is the fourth largest tram producer in the world; nearly one third of all trams in the world come from Czech factories. The Czech Republic is also the world's largest Phonograph record, vinyl records manufacturer, with GZ Media producing about 6 million pieces annually in LodÄnice (Beroun District), LodÄnice. ÄeskÃĄ zbrojovka UherskÃ― Brod, ÄeskÃĄ zbrojovka is among the ten largest firearms producers in the world and five who produce automatic weapons.
In the food industry, Czech companies include Agrofert, Kofola and HamÃĐ (company), HamÃĐ.
Energy
 Production of Czech electricity exceeds consumption by about 10 Kilowatt hour, TWh per year, the excess being exported. Nuclear power presently provides about 30 percent of the total power needs, its share is projected to increase to 40 percent. In 2005, 65.4 percent of electricity was produced by steam and combustion power plants (mostly coal); 30 percent by nuclear plants; and 4.6 percent came from renewable sources, including hydropower. The largest Czech power resource is TemelÃn Nuclear Power Station, with another nuclear power plant in Dukovany Nuclear Power Station, Dukovany.
The Czech Republic is reducing its dependence on highly polluting low-grade Lignite, brown coal as a source of energy. Natural gas is purchased from Norway, Norwegian companies and as liquefied gas LNG from the Netherlands and Belgium. In the past, three-quarters of gas supplies came from Russia, but after the start of the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, the government gradually stopped these supplies. Gas consumption (approx. 100 TWh in 2003â2005) is almost double electricity consumption. South Moravia has small Oil and gas deposits in the Czech Republic, oil and gas deposits.
Production of Czech electricity exceeds consumption by about 10 Kilowatt hour, TWh per year, the excess being exported. Nuclear power presently provides about 30 percent of the total power needs, its share is projected to increase to 40 percent. In 2005, 65.4 percent of electricity was produced by steam and combustion power plants (mostly coal); 30 percent by nuclear plants; and 4.6 percent came from renewable sources, including hydropower. The largest Czech power resource is TemelÃn Nuclear Power Station, with another nuclear power plant in Dukovany Nuclear Power Station, Dukovany.
The Czech Republic is reducing its dependence on highly polluting low-grade Lignite, brown coal as a source of energy. Natural gas is purchased from Norway, Norwegian companies and as liquefied gas LNG from the Netherlands and Belgium. In the past, three-quarters of gas supplies came from Russia, but after the start of the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, the government gradually stopped these supplies. Gas consumption (approx. 100 TWh in 2003â2005) is almost double electricity consumption. South Moravia has small Oil and gas deposits in the Czech Republic, oil and gas deposits.
Transportation infrastructure
the road network in the Czech Republic is long, out of which are motorways. The Speed limits by country, speed limit is within towns, outside of towns and on motorways. The Czech Republic has one of the List of countries by rail transport network size, densest rail networks in the world. the country has of lines. Of that number, is electrified, are single-line tracks and are double and multiple-line tracks. The length of tracks is , out of which is electrified. ÄeskÃĐ drÃĄhy (the Czech Railways) is the main railway operator in the country, with about 180 million passengers carried yearly. Maximum speed is limited to . VÃĄclav Havel Airport Prague, VÃĄclav Havel Airport in Prague is the main international airport in the country. In 2019, it handled 17.8 million passengers. In total, the Czech Republic has List of airports in the Czech Republic, 91 airports, six of which provide international air services. The public international airports are in Brno-TuÅany Airport, Brno, Karlovy Vary Airport, Karlovy Vary, Mnichovo HradiÅĄtÄ Airport, Mnichovo HradiÅĄtÄ, LeoÅĄ JanÃĄÄek Airport Ostrava, MoÅĄnov (nearOstrava
Ostrava (; ; ) is a city in the north-east of the Czech Republic and the capital of the Moravian-Silesian Region. It has about 283,000 inhabitants. It lies from the border with Poland, at the confluences of four rivers: Oder, Opava (river), Opa ...
), Pardubice Airport, Pardubice and Prague. The non-public international airports capable of handling airliners are in Kunovice Airport, Kunovice and Vodochody Airport, Vodochody.
Russia (via pipelines through Ukraine) and, to a lesser extent, Norway (via pipelines through Germany) supply the Czech Republic with liquid and natural gas.
Communications and IT
The Czech Republic ranks in the top 10 countries worldwide with the fastest average internet speed. By the beginning of 2008, there were over 800 mostly local Wireless Internet service provider, WISPs, with about 350,000 subscribers in 2007. Plans based on either General Packet Radio Service, GPRS, Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution, EDGE, Universal Mobile Telecommunications System, UMTS or CDMA2000 are being offered by all three mobile phone operators (T-Mobile Czech Republic, T-Mobile, O2 Czech Republic, O2, Vodafone) and internet provider U:fon. Government-owned ÄeskÃ― Telecom slowed down broadband penetration. At the beginning of 2004, local-loop unbundling began and alternative operators started to offer ADSL and also Symmetric digital subscriber line, SDSL. This and later privatization of ÄeskÃ― Telecom helped drive down prices. On 1 July 2006, ÄeskÃ― Telecom was acquired by globalized company (Spain-owned) TelefÃģnica group and adopted the new name TelefÃģnica O2 Czech Republic. , VDSL and ADSL2+ are offered in variants, with download speeds of up to 50 Mbit/s and upload speeds of up to 5 Mbit/s. Cable internet is gaining more popularity with its higher download speeds ranging from 50 Mbit/s to 1 Gbit/s. Two computer security companies, Avast and AVG Technologies, AVG, were founded in the Czech Republic. In 2016, Avast led by Pavel BaudiÅĄ bought rival AVG for United States dollar, US$1.3 billion, together at the time, these companies had a user base of about 400 million people and 40% of the consumer market outside of China. Avast is the leading provider of antivirus software, with a 20.5% market share.Tourism
Prague
Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its P ...
is the fifth most visited city in Europe after London, Paris, Istanbul and Rome. In 2001, the total earnings from tourism reached 118 billion Czech koruna, CZK, making up 5.5% of the country's Measures of national income and output, GNP and 9% of its overall export earnings. The industry employs more than 110,000 people â over 1% of the population.
Guidebooks and tourists reporting overcharging by taxi drivers and pickpocketing problems talk mainly about Prague, though the situation has improved recently. Since 2005, Prague's mayor, Pavel BÃĐm, has worked to improve this reputation by cracking down on petty crime and, aside from these problems, Prague is a "safe" city. The Czech Republic's crime rate is described by the United States State department as "low".
The Czech Republic boasts List of World Heritage Sites in the Czech Republic, 17 UNESCO World Heritage Sites, 3 of them being transnational. , further 13 sites are on the tentative list.
Architectural heritage is an object of interest to visitors â it includes List of castles in the Czech Republic, castles and chÃĒteaux from different historical epochs, namely KarlÅĄtejn Castle, ÄeskÃ― Krumlov and the LedniceâValtice Cultural Landscape. There are 12 List of cathedrals in the Czech Republic, cathedrals and 15 churches elevated to the rank of Minor basilica, basilica by the Pope, as well as many monasteries.
Away from the towns, areas such as Bohemian Paradise, Bohemian Forest and the Giant Mountains attract visitors seeking outdoor pursuits.
The country is also known for its various List of museums in the Czech Republic, museums, puppeteer, puppetry and marionette exhibitions that take part within larger puppet theatre festival, festivals, and beer festivals. Aquapalace Prague in Äestlice is the largest water park in the country.
Science
 The Czech lands have a long and well-documented history of scientific innovation. Today, the Czech Republic has a highly sophisticated, developed, high-performing, innovation-oriented scientific community supported by the government, industry, and leading Czech Universities, universities. Czech scientists are embedded members of the global scientific community. They contribute annually to multiple international academic journals and collaborate with their colleagues across boundaries and fields. The Czech Republic was ranked 24th in the Global Innovation Index in 2020 and 2021, up from 26th in 2019.
Historically, the Czech lands, especially
The Czech lands have a long and well-documented history of scientific innovation. Today, the Czech Republic has a highly sophisticated, developed, high-performing, innovation-oriented scientific community supported by the government, industry, and leading Czech Universities, universities. Czech scientists are embedded members of the global scientific community. They contribute annually to multiple international academic journals and collaborate with their colleagues across boundaries and fields. The Czech Republic was ranked 24th in the Global Innovation Index in 2020 and 2021, up from 26th in 2019.
Historically, the Czech lands, especially Prague
Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its P ...
, have been the seat of scientific discovery going back to early modern times, including Tycho Brahe, Nicolaus Copernicus, and Johannes Kepler. In 1784 the scientific community was first formally organized under the charter of the Royal Czech Society of Sciences. Currently, this organization is known as the Czech Academy of Sciences. Similarly, the Czech lands have a well-established history of scientists, including Nobel laureates biochemists Gerty Cori, Gerty and Carl Ferdinand Cori, chemists Jaroslav HeyrovskÃ― (inventor of polarography, Analytical chemistry, electroanalytical chemistry and recipient of the Nobel Prize) and Otto Wichterle (chemists responsible for the invention of the modern contact lens and silon-synthetic fiber), physicists Ernst Mach (physicist and critic of Newton's theories of space and time, foreshadowing Einstein's theory of relativity) and Peter GrÞnberg, physiologist Jan Evangelista PurkynÄ and chemist AntonÃn HolÃ― (scientist and chemist, in 2009 was involved in creation of the most effective drug in the treatment of AIDS), Sigmund Freud, the founder of psychoanalysis, was born in PÅÃbor, Gregor Mendel, the founder of genetics, was born in HynÄice (VraÅūnÃĐ), HynÄice and spent most of his life in Brno
Brno ( , ; ) is a Statutory city (Czech Republic), city in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. Located at the confluence of the Svitava (river), Svitava and Svratka (river), Svratka rivers, Brno has about 403,000 inhabitants, making ...
, logician and mathematician Kurt GÃķdel was born in Brno.
Other famous Czech scientists include: Stanislav Brebera (inventor of the plastic explosive Semtex), VÃĄclav Prokop DiviÅĄ (inventor of the first grounded lightning rod), Jakub HusnÃk (improved the process of photolithography), Jan JanskÃ― (serologist and neurologist, discovered the ABO blood groups), Karel KlÃÄ (painter and photographer, inventor of the photogravure), FrantiÅĄek KÅiÅūÃk (electrical engineer, inventor of the arc lamp), Jan Marek Marci (mathematician, physicist and imperial physician, one of the founders of spectroscopy), VladimÃr Remek (the first person outside of the Soviet Union and the United States to go into space), Jakub KryÅĄtof Rad (inventor of sugar cubes), Josef Ressel (inventor of the propeller, screw propeller and Protractor compass, modern compass).. Czech.cz. Retrieved 3 March 2009.
Historically, most scientific research was recorded in Latin, but from the 18th century onwards increasingly in German and Czech, archived in libraries supported and managed by religious groups and other denominations as evidenced by historical locations of international renown and heritage such as the Strahov Monastery and the Clementinum in Prague
Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its P ...
. Increasingly, Czech scientists publish their work and that of their history in English.
The current important scientific institution is the already mentioned Czech Academy of Sciences, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, the Central European Institute of Technology, CEITEC Institute in Brno
Brno ( , ; ) is a Statutory city (Czech Republic), city in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. Located at the confluence of the Svitava (river), Svitava and Svratka (river), Svratka rivers, Brno has about 403,000 inhabitants, making ...
or the HiLASE and Eli Beamlines centers with the most powerful laser in the world in Dolnà BÅeÅūany. Prague is the seat of the administrative center of the GSA Agency operating the European navigation system Galileo (satellite navigation), Galileo and the European Union Agency for the Space Programme.
Demographics
The total fertility rate (TFR) in 2020 was estimated at 1.71 children per woman, which is below the replacement rate of 2.1. The Czech Republic's population has an average age of 43.3 years. The life expectancy in 2021 was estimated to be 79.5 years (76.55 years male, 82.61 years female). About 77,000 people immigrate to the Czech Republic annually. Vietnamese people in the Czech Republic, Vietnamese immigrants began settling in the country during the Communist period, when they were invited as guest workers by the Czechoslovak government. In 2009, there were about 70,000 Vietnamese in the Czech Republic. Most have decided to stay in the country permanently. According to results of the 2021 census, the majority of the inhabitants of the Czech Republic are Czechs (57.3%), followed by Moravians (ethnic group), Moravians (3.4%), Slovaks (0.9%), Ukrainians (0.7%), Vietnamese people, Viets (0.3%), Polish people, Poles (0.3%), Russians (0.2%), Silesians (0.1%) and Germans (0.1%). Another 4.0% declared a combination of two nationalities (3.6% combination of Czech and other nationality). As the 'nationality' was an optional item, a number of people left this field blank (31.6%). According to some estimates, there are about 250,000 Romani people in the Czech Republic. The Polish minority in the Czech Republic, Polish minority resides mainly in the Trans-Olza region. There were 658,564 foreigners residing in the country in 2021, according to the Czech Statistical Office, with the largest groups being Ukrainians in the Czech Republic, Ukrainian (22%), Slovaks in the Czech Republic, Slovak (22%), Vietnamese people in the Czech Republic, Vietnamese (12%), Russians, Russian (7%) and Germans in the Czech Republic, German (4%). Most of the foreign population lives in Prague (37.3%) and Central Bohemia Region (13.2%). The History of the Jews in the Czech Republic, Jewish population of Bohemia and Moravia, 118,000 according to the 1930 census, was nearly annihilated by the Nazi Germans during the Holocaust. There were approximately 3,900 Jews in the Czech Republic in 2021. The former Czech prime minister, Jan Fischer (politician), Jan Fischer, is of Jewish faith. Nationality of residents, who answered the question in the Census 2021:Largest cities
Religion
About 75% to 79% of residents of the Czech Republic do not declare having any religion or faith in surveys, and the proportion of convinced Atheism, atheists (30%) is the third highest in the world behind those of China (47%) and Japan (31%).Global Index of Religion and Atheism. 2012. secularpolicyinstitute.net
Education and health care
Education in the Czech Republic is compulsory for nine years and citizens have access to a free-tuition Tertiary education in the Czech Republic, university education, while the average number of years of education is 13.1. Additionally, the Czech Republic has a "relatively equal" educational system in comparison with other countries in Europe. Founded in 1348, Charles University was the first university inCentral Europe
Central Europe is a geographical region of Europe between Eastern Europe, Eastern, Southern Europe, Southern, Western Europe, Western and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Central Europe is known for its cultural diversity; however, countries in ...
. Other major universities in the country are Masaryk University, Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Technical University, PalackÃ― University, Olomouc, PalackÃ― University, Academy of Performing Arts in Prague, Academy of Performing Arts and University of Economics, Prague, University of Economics.
The Programme for International Student Assessment, coordinated by the OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; , OCDE) is an international organization, intergovernmental organization with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and international trade, wor ...
, currently ranks the Czech education system as the 15th most successful in the world, higher than the OECD average. The UN Education Index ranks the Czech Republic 10th (positioned behind Denmark and ahead of South Korea).
Health care in the Czech Republic is similar in quality to that of other developed nations. The Czech universal health care system is based on a Health insurance mandate, compulsory insurance model, with fee-for-service care funded by mandatory employment-related insurance plans. According to the 2016 Euro health consumer index, a comparison of healthcare in Europe, the Czech healthcare is 13th, ranked behind Sweden and two positions ahead of the United Kingdom.
Culture
Art
Venus of Dolnà VÄstonice is an important example of prehistoric art unearthed in the Czech Republic. Theodoric of Prague was a painter in the Gothic era who decorated the castle KarlÅĄtejn. In the Baroque era, there were painters Wenceslaus Hollar, Jan KupeckÃ―, Karel Å krÃĐta, Anton Raphael Mengs and Petr Brandl and sculptors Matthias Braun and Ferdinand Brokoff. In the first half of the 19th century, Josef MÃĄnes joined the romantic movement. In the second half the so-called "National Theatre generation" rose to prominence: sculptor Josef VÃĄclav Myslbek and painters MikolÃĄÅĄ AleÅĄ, VÃĄclav BroÅūÃk, VojtÄch Hynais and Julius MaÅÃĄk. At the end of the century came Art Nouveau, with Alphonse Mucha, Alfons Mucha becoming its main representative. He is known for his Art Nouveau posters and a cycle of 20 large canvases named the Slav Epic, which depicts the history of Czechs and other Slavs. , it can be seen in the VeletrÅūnà Palace of the National Gallery in Prague, which manages the largest collection of art in the Czech Republic. Max Å vabinskÃ― was another Art Nouveau painter. The 20th century brought an avant-garde revolution, represented in the Czech lands mainly by expressionists and cubists: Josef Äapek, Emil Filla, Bohumil KubiÅĄta or Jan ZrzavÃ―. Surrealism emerged particularly through the work of Toyen, Josef Å Ãma and Karel Teige. In the world, however, the most well-known Czech avant-garde artist might be FrantiÅĄek Kupka, a pioneer of abstract painting. Illustrators and cartoonists to gain fame in the first half of the 20th century include Josef Lada, ZdenÄk Burian or Emil OrlÃk. Art photography became a new field represented by FrantiÅĄek Drtikol, Josef Sudek, later Jan Saudek and Josef Koudelka. The Czech Republic is also known for its individually made, mouth-blown, and decorated Bohemian glass.Architecture
 The earliest preserved stone buildings in Bohemia and Moravia date back to the time of the Christianization in the 9th and 10th centuries. Since the Middle Ages, the Czech lands have been using the same architectural styles as most of Western Europe, Western and Central Europe. The oldest still standing churches were built in the Romanesque architecture, Romanesque style. During the 13th century, it was replaced by the Czech Gothic architecture, Gothic style. In the 14th century, Emperor Charles IV invited architects from France and Germany, Matthias of Arras and Peter Parler, to his court in Prague. During the Middle Ages, some fortified castles were built by the king and aristocracy, as well as some monasteries.
The Renaissance architecture, Renaissance style penetrated the Bohemian Crown in the late 15th century when the older Gothic style started to be mixed with Renaissance elements. An example of pure Renaissance architecture in Bohemia is the Queen Anne's Summer Palace, which was situated in the garden of Prague Castle. Evidence of the general reception of the Renaissance in Bohemia, involving an influx of Italian architects, can be found in spacious chateaus with arcade courtyards and geometrically arranged gardens. Emphasis was placed on comfort, and buildings that were built for entertainment purposes also appeared.
In the 17th century, the Baroque style spread throughout the Crown of Bohemia.
In the 18th century, Bohemia produced an architectural peculiarity â the ''Baroque Gothic style'', a synthesis of the Gothic and Baroque styles.
The earliest preserved stone buildings in Bohemia and Moravia date back to the time of the Christianization in the 9th and 10th centuries. Since the Middle Ages, the Czech lands have been using the same architectural styles as most of Western Europe, Western and Central Europe. The oldest still standing churches were built in the Romanesque architecture, Romanesque style. During the 13th century, it was replaced by the Czech Gothic architecture, Gothic style. In the 14th century, Emperor Charles IV invited architects from France and Germany, Matthias of Arras and Peter Parler, to his court in Prague. During the Middle Ages, some fortified castles were built by the king and aristocracy, as well as some monasteries.
The Renaissance architecture, Renaissance style penetrated the Bohemian Crown in the late 15th century when the older Gothic style started to be mixed with Renaissance elements. An example of pure Renaissance architecture in Bohemia is the Queen Anne's Summer Palace, which was situated in the garden of Prague Castle. Evidence of the general reception of the Renaissance in Bohemia, involving an influx of Italian architects, can be found in spacious chateaus with arcade courtyards and geometrically arranged gardens. Emphasis was placed on comfort, and buildings that were built for entertainment purposes also appeared.
In the 17th century, the Baroque style spread throughout the Crown of Bohemia.
In the 18th century, Bohemia produced an architectural peculiarity â the ''Baroque Gothic style'', a synthesis of the Gothic and Baroque styles.
 During the 19th century stands the Revival architecture, revival architectural styles. Some churches were restored to their presumed medieval appearance and there were constructed buildings in the Romanesque Revival architecture, Neo-Romanesque, Gothic Revival architecture, Neo-Gothic and Renaissance Revival architecture, Neo-Renaissance styles. At the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries, the new art style appeared in the Czech lands â Art Nouveau.
Bohemia contributed an unusual style to the world's architectural heritage when Czech architects attempted to transpose the Cubism of painting and sculpture into architecture.
Between World Wars I and II, Functionalism (architecture), Functionalism, with its sober, progressive forms, took over as the main architectural style.
After World War II and the Communist coup in 1948, art in Czechoslovakia became Soviet-influenced. The Czechoslovak avant-garde artistic movement is known as the ''Brussels style came up'' in the time of political liberalization of Czechoslovakia in the 1960s. Brutalism dominated in the 1970s and 1980s.
The Czech Republic is not shying away from the more modern trends of international architecture, an example is the TanÄÃcà dÅŊm, Dancing House (TanÄÃcà dÅŊm) in Prague, Golden Angel in Prague or Congress Centre in ZlÃn.
During the 19th century stands the Revival architecture, revival architectural styles. Some churches were restored to their presumed medieval appearance and there were constructed buildings in the Romanesque Revival architecture, Neo-Romanesque, Gothic Revival architecture, Neo-Gothic and Renaissance Revival architecture, Neo-Renaissance styles. At the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries, the new art style appeared in the Czech lands â Art Nouveau.
Bohemia contributed an unusual style to the world's architectural heritage when Czech architects attempted to transpose the Cubism of painting and sculpture into architecture.
Between World Wars I and II, Functionalism (architecture), Functionalism, with its sober, progressive forms, took over as the main architectural style.
After World War II and the Communist coup in 1948, art in Czechoslovakia became Soviet-influenced. The Czechoslovak avant-garde artistic movement is known as the ''Brussels style came up'' in the time of political liberalization of Czechoslovakia in the 1960s. Brutalism dominated in the 1970s and 1980s.
The Czech Republic is not shying away from the more modern trends of international architecture, an example is the TanÄÃcà dÅŊm, Dancing House (TanÄÃcà dÅŊm) in Prague, Golden Angel in Prague or Congress Centre in ZlÃn.
Literature
 The literature from the area of today's Czech Republic was mostly written in Czech, but also in
The literature from the area of today's Czech Republic was mostly written in Czech, but also in Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
and German or even Old Church Slavonic. Franz Kafka, although a competent user of Czech, wrote in his mother tongue, German. His works include ''The Trial'' and ''The Castle (novel), The Castle''.
In the second half of the 13th century, the royal court in Prague became one of the centers of German Minnesang and courtly literature. The Czech German-language literature can be seen in the first half of the 20th century.
Bible translations into Czech, Bible translations played a role in the development of Czech literature. The oldest Czech translation of the Psalms originated in the late 13th century and the first complete Czech translation of the Bible was finished around 1360. The first complete printed Czech Bible was published in 1488. The first complete Czech Bible translation from the original languages was published between 1579 and 1593. The Codex Gigas from the 12th century is the largest extant medieval manuscript in the world.
Czech-language literature can be divided into several periods: the Middle Ages; the Hussite period; the Renaissance humanism; the Baroque period; the Enlightenment and Czech reawakening in the first half of the 19th century, modern literature in the second half of the 19th century; the avant-garde of the interwar period; the years under Communism; and the Czech Republic.
The antiwar comedy novel ''The Good Soldier Å vejk'' is the most translated Czech book in history.
The international literary award the Franz Kafka Prize is awarded in the Czech Republic.
The Czech Republic has the densest network of libraries in Europe.
Czech literature and culture played a role on at least two occasions when Czechs lived under oppression and political activity was suppressed. On both of these occasions, in the early 19th century and then again in the 1960s, the Czechs used their cultural and literary effort to strive for political freedom, establishing a confident, politically aware nation.
Music
 The musical tradition of the Czech lands arose from the first church hymns, whose first evidence is suggested at the break of the 10th and 11th centuries. Some pieces of Czech music include two chorales, which in their time performed the function of anthems: "Hospodine pomiluj ny, Lord, Have Mercy on Us" and the hymn "Saint Wenceslaus" or "Saint Wenceslas Chorale, Saint Wenceslaus Chorale". The authorship of the anthem "Lord, Have Mercy on Us" is ascribed by some historians to Saint Adalbert of Prague (sv.VojtÄch), bishop of
The musical tradition of the Czech lands arose from the first church hymns, whose first evidence is suggested at the break of the 10th and 11th centuries. Some pieces of Czech music include two chorales, which in their time performed the function of anthems: "Hospodine pomiluj ny, Lord, Have Mercy on Us" and the hymn "Saint Wenceslaus" or "Saint Wenceslas Chorale, Saint Wenceslaus Chorale". The authorship of the anthem "Lord, Have Mercy on Us" is ascribed by some historians to Saint Adalbert of Prague (sv.VojtÄch), bishop of Prague
Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its P ...
, living between 956 and 997.
The wealth of musical culture lies in the classical music tradition during all historical periods, especially in the Baroque music, Baroque, Classical period (music), Classicism, Romantic, Modernism (music), modern classical music and in the traditional music, traditional folk music of Bohemia, Moravia and Silesia. Since the early era of artificial music, Czech musicians and composers have been influenced the folk music of the region and dance.
Czech music can be considered to have been "beneficial" in both the European and worldwide context, several times co-determined or even determined a newly arriving era in musical art, above all of Classical period (music), Classical era, as well as by original attitudes in Baroque (music), Baroque, Romantic (music), Romantic and modern classical music. Some Czech musical works are ''The Bartered Bride'', ''New World Symphony'', ''Sinfonietta (JanÃĄÄek), Sinfonietta'' and ''JenÅŊfa''.
A music festival in the country is Prague Spring International Music Festival of classical music, a permanent showcase for performing artists, symphony orchestras and chamber music ensembles of the world.
Theatre
The roots of Czech theatre can be found in the Middle Ages, especially in the cultural life of the Gothic period. In the 19th century, the theatre played a role in the national awakening movement and later, in the 20th century, it became a part of modern European theatre art. The original Czech cultural phenomenon came into being at the end of the 1950s. This project called Laterna magika, resulting in productions that combined theater, dance, and film in a poetic manner, considered the first multimedia art project in an international context. One drama is Karel Äapek's play ''R.U.R.'', which introduced the word "robot". The country has a tradition of Puppetry, puppet theater. In 2016, Puppetry#Czech Republic and Slovakia, Czech and Slovak Puppetry was included on the UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage Lists.Film
The tradition of Czech cinematography started in the second half of the 1890s. Peaks of the production in the era of silent movies include the historical drama ''The Builder of the Temple'' and the social and erotic drama ''Erotikon'' directed by Gustav MachatÃ―. The early Czech sound film era was productive, above all in mainstream genres, with the comedies of Martin FriÄ or Karel LamaÄ. There were dramatic movies sought internationally. HermÃna TÃ―rlovÃĄ was a prominent Czech animator, screenwriter, and film director. She was often called the mother of Czech animation. Over the course of her career, she produced over 60 animated children's short films using puppets and the technique of stop motion animation. Before the German occupation, in 1933, filmmaker and animator established the first Czech animation studio "IRE Film" with her husband Karel Dodal. After the period of Nazi occupation and early communist official dramaturgy of socialist realism in movies at the turn of the 1940s and 1950s with fewer exceptions such as ''Krakatit'' or ''Men without wings'' (awarded by in 1946), an era of the Czech film began with animated films, performed in anglophone countries under the name "The Fabulous World of Jules Verne" from 1958, which combined acted drama with animation, and JiÅÃ Trnka, the founder of the modern puppet film. This began a tradition of animated films (''Mole (ZdenÄk Miler character), Mole'' etc.). In the 1960s, the hallmark of Czechoslovak New Wave's films were improvised dialogues, Black comedy, black and absurdity, absurd humor and the occupation of non-actors. Directors are trying to preserve natural atmosphere without refinement and artificial arrangement of scenes. A personality of the 1960s and the beginning of the 1970s with original manuscript and psychological impact is FrantiÅĄek VlÃĄÄil. Another international author is Jan Å vankmajer, a filmmaker and artist whose work spans several media. He is a self-labeled surrealism, surrealist known for animations and features.
The Barrandov Studios in Prague are the largest film studios with film locations in the country. Filmmakers have come to
In the 1960s, the hallmark of Czechoslovak New Wave's films were improvised dialogues, Black comedy, black and absurdity, absurd humor and the occupation of non-actors. Directors are trying to preserve natural atmosphere without refinement and artificial arrangement of scenes. A personality of the 1960s and the beginning of the 1970s with original manuscript and psychological impact is FrantiÅĄek VlÃĄÄil. Another international author is Jan Å vankmajer, a filmmaker and artist whose work spans several media. He is a self-labeled surrealism, surrealist known for animations and features.
The Barrandov Studios in Prague are the largest film studios with film locations in the country. Filmmakers have come to Prague
Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its P ...
to shoot scenery no longer found in Berlin, Paris and Vienna. The city of Karlovy Vary was used as a location for the 2006 James Bond film Casino Royale.
The Czech Lion is the highest Czech award for film achievement. Karlovy Vary International Film Festival is one of the film festivals that have been given competitive status by the FIAPF. Other film festivals held in the country include Febiofest, Jihlava International Documentary Film Festival, One World Film Festival, ZlÃn Film Festival and Fresh Film Festival.
Media
Czech journalists and media enjoy a degree of Freedom of the press, freedom. There are restrictions against writing in support of Nazism, racism or violating Czech law. The Czech press was ranked as the 40th most free press in the World Press Freedom Index by Reporters Without Borders in 2021. Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty has its headquarters in Prague. Czech Television is the country's national public television broadcaster. It operates a number of channels, including ÄT1, ÄT2, and the 24-hour news channel ÄT24, as well as the news websitct24.cz
As of 2020, it is the most watched broadcaster, followed by the private TV Nova (Czech Republic), TV Nova and Prima televize, Prima TV. However, TV Nova features the most watched main news program and prime time program. Other public media services include the Czech Radio and the Czech News Agency. The best-selling daily national newspapers in 2020/21 are Blesk (average 703,000 daily readers), MladÃĄ fronta DNES (average 461,000 daily readers), PrÃĄvo (average 182,000 daily readers), LidovÃĐ noviny (average 163,000 daily readers) and HospodÃĄÅskÃĐ noviny (average 162,000 daily readers). Most Czechs (87%) read their news online, with Seznam.cz, iDNES.cz, Novinky.cz, Prima televize, iPrima.cz and Seznam ZprÃĄvy, Seznam ZprÃĄvy.cz being the most visited as of 2021.
Cuisine
 Czech cuisine is marked by an emphasis on meat dishes with pork, beef, and chicken. Goose, duck, rabbit, and venison are served. Fish is less common, with the occasional exception of fresh trout and carp, which is served at Christmas. One popular Czech menu item is ''smaÅūenÃ― vepÅovÃ― ÅÃzek'' (fried breaded pork filet), served with boiled potatoes.
There is a variety of local sausages, wurst, pÃĒtÃĐs, and smoked and cured meats. Czech desserts include a variety of whipped cream, chocolate, and fruit pastries and tarts, crÊpes, creme desserts and cheese, poppy-seed-filled and other types of traditional cakes such as ''Buchteln, buchty'', ''Kolach (cake), kolÃĄÄe'' and Apple strudel, ''ÅĄtrÚdl''.
Beer in the Czech Republic, Czech beer has a history extending more than a millennium; the earliest known brewery existed in 993. Today, the Czech Republic has the highest List of countries by beer consumption per capita, beer consumption per capita in the world. The pilsner style beer (pils) originated in
Czech cuisine is marked by an emphasis on meat dishes with pork, beef, and chicken. Goose, duck, rabbit, and venison are served. Fish is less common, with the occasional exception of fresh trout and carp, which is served at Christmas. One popular Czech menu item is ''smaÅūenÃ― vepÅovÃ― ÅÃzek'' (fried breaded pork filet), served with boiled potatoes.
There is a variety of local sausages, wurst, pÃĒtÃĐs, and smoked and cured meats. Czech desserts include a variety of whipped cream, chocolate, and fruit pastries and tarts, crÊpes, creme desserts and cheese, poppy-seed-filled and other types of traditional cakes such as ''Buchteln, buchty'', ''Kolach (cake), kolÃĄÄe'' and Apple strudel, ''ÅĄtrÚdl''.
Beer in the Czech Republic, Czech beer has a history extending more than a millennium; the earliest known brewery existed in 993. Today, the Czech Republic has the highest List of countries by beer consumption per capita, beer consumption per capita in the world. The pilsner style beer (pils) originated in PlzeÅ
PlzeÅ (), also known in English and German as Pilsen (), is a city in the Czech Republic. It is the Statutory city (Czech Republic), fourth most populous city in the Czech Republic with about 188,000 inhabitants. It is located about west of P ...
, where the world's first blond lager Pilsner Urquell is still produced. It has served as the inspiration for more than two-thirds of the beer produced in the world today. The city of ÄeskÃĐ BudÄjovice has similarly lent its name to its beer, known as Budweiser Budvar.
The South Moravian region has been producing Czech wine, wine since the Middle Ages; about 94% of vineyards in the Czech Republic are Moravian. Aside from beer, slivovitz and wine, the Czech Republic also produces two liquors, Fernet Stock and Becherovka. Kofola is a non-alcoholic domestic cola soft drink which competes with Coca-Cola and Pepsi.
Sport
 The most watched and most attended sport in the Czech Republic are Association football, football and ice hockey. The most watched sporting events are the Ice hockey at the Olympic Games and the Ice Hockey World Championships. The most popular sports in the Czech Republic according to the size of the membership base of sports clubs are: football, tennis, ice hockey, volleyball, floorball, golf, ball hockey, Sport of athletics, athletics, basketball and skiing.
The country has won 15 gold medals in the Summer Olympic Games, Summer Olympics and nine in the Winter Olympic Games, Winter Games. (See All-time Olympic Games medal table, Olympic history.) The Czech Republic men's national ice hockey team, Czech ice hockey team won the gold medal at the 1998 Winter Olympics and has won (along with the Czechoslovakia men's national ice hockey team, Czechoslovakian team) thirteen gold medals at the IHWC, World Championships, including three straight from 1999 Men's World Ice Hockey Championships, 1999 to 2001 Men's World Ice Hockey Championships, 2001.
The Å koda Motorsport is engaged in Motorsport, competition racing since 1901 and has gained a number of titles with various vehicles around the world. MTX (automobile), MTX automobile company was formerly engaged in the manufacture of Auto racing, racing and Formula racing, formula cars since 1969.
Hiking is a popular sport. The word for 'tourist' in Czech, ''turista'', also means 'trekker' or 'hiker'. For hikers, thanks to the more than 120-year-old tradition, there is the Czech Hiking Markers System of trail blazing, that has been adopted by countries worldwide. There is a network of around 40,000 km of marked short- and long-distance trails crossing the whole country and all the Czech mountains.
The most watched and most attended sport in the Czech Republic are Association football, football and ice hockey. The most watched sporting events are the Ice hockey at the Olympic Games and the Ice Hockey World Championships. The most popular sports in the Czech Republic according to the size of the membership base of sports clubs are: football, tennis, ice hockey, volleyball, floorball, golf, ball hockey, Sport of athletics, athletics, basketball and skiing.
The country has won 15 gold medals in the Summer Olympic Games, Summer Olympics and nine in the Winter Olympic Games, Winter Games. (See All-time Olympic Games medal table, Olympic history.) The Czech Republic men's national ice hockey team, Czech ice hockey team won the gold medal at the 1998 Winter Olympics and has won (along with the Czechoslovakia men's national ice hockey team, Czechoslovakian team) thirteen gold medals at the IHWC, World Championships, including three straight from 1999 Men's World Ice Hockey Championships, 1999 to 2001 Men's World Ice Hockey Championships, 2001.
The Å koda Motorsport is engaged in Motorsport, competition racing since 1901 and has gained a number of titles with various vehicles around the world. MTX (automobile), MTX automobile company was formerly engaged in the manufacture of Auto racing, racing and Formula racing, formula cars since 1969.
Hiking is a popular sport. The word for 'tourist' in Czech, ''turista'', also means 'trekker' or 'hiker'. For hikers, thanks to the more than 120-year-old tradition, there is the Czech Hiking Markers System of trail blazing, that has been adopted by countries worldwide. There is a network of around 40,000 km of marked short- and long-distance trails crossing the whole country and all the Czech mountains.
See also
* List of Czech Republic-related topics * Outline of the Czech RepublicExplanatory notes
References
Further reading
* * Bryant, Chad (2021).Prague: Belonging and the Modern City
'. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. . * Hochman, JiÅÃ (1998)
''Historical Ddictionary of the Czech State''
Lanham, Md. and London: The Scarecrow Press. .
External links
Governmental website
Presidential website
Senate
Portal of the Public Administration
#VisitCzechia
â official tourist portal of the Czech Republic * * {{Coord, 49, 45, N, 15, 30, E, type:country_region:CZ_scale:9000000, display=title Czech Republic, Central Europe Countries in Europe Landlocked countries Member states of NATO Member states of the European Union Member states of the United Nations Member states of the Three Seas Initiative Republics Member states of the Council of Europe OECD members States and territories established in 1993