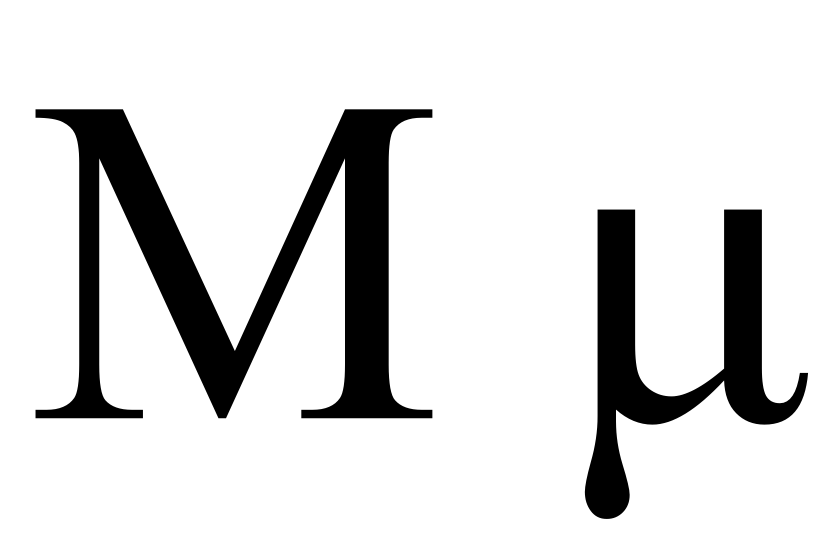|
ê§å
Mem (also spelled Meem, Meme, or Mim) is the thirteenth letter of the Semitic abjads, including Hebrew mƒìm , Aramaic Mem , Syriac mƒ´m а, Arabic mƒ´m and Phoenician mƒìm . Its sound value is . The Phoenician letter gave rise to the Greek mu (Œú), Etruscan , Latin M, and Cyrillic –ú. Origins Mem is believed to derive from the Egyptian hieroglyphic symbol for water, N35 which had been simplified by the Phoenicians and named after their word for ‚Äúwater‚Äù, ''mem'' (), ultimately coming from Proto-Semitic *ma æ-/*may-. Hebrew Mem Hebrew spelling: Hebrew pronunciation Mem represents a bilabial nasal . Variations on written form/pronunciation In Hebrew, Mem, like Kaph, Nun, Pe, and Tzadi, has a final form, used at the end of words: its shape changes from to . Significance In gematria, Mem represents the number 40 in both the Standard and Mispar Gadol Methods of Gematria; However, (mem sofit) final mem's value is 40 in the Standard Method and 600 in the Misp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their history, and they possessed several enclaves such as Arwad and Tell Sukas (modern Syria). The core region in which the Phoenician culture developed and thrived stretched from Tripoli and Byblos in northern Lebanon to Mount Carmel in modern Israel. At their height, the Phoenician possessions in the Eastern Mediterranean stretched from the Orontes River mouth to Ashkelon. Beyond its homeland, the Phoenician civilization extended to the Mediterranean from Cyprus to the Iberian Peninsula. The Phoenicians were a Semitic-speaking people of somewhat unknown origin who emerged in the Levant around 3000 BC. The term ''Phoenicia'' is an ancient Greek exonym that most likely described one of their most famous exports, a dye also known as Tyrian purpl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syriac Alphabet
The Syriac alphabet ( ) is a writing system primarily used to write the Syriac language since the 1st century AD. It is one of the Semitic abjads descending from the Aramaic alphabet through the Palmyrene alphabet, and shares similarities with the Phoenician, Hebrew, Arabic and Sogdian, the precursor and a direct ancestor of the traditional Mongolian scripts. Syriac is written from right to left in horizontal lines. It is a cursive script where most—but not all—letters connect within a word. There is no letter case distinction between upper and lower case letters, though some letters change their form depending on their position within a word. Spaces separate individual words. All 22 letters are consonants, although there are optional diacritic marks to indicate vowels and other features. In addition to the sounds of the language, the letters of the Syriac alphabet can be used to represent numbers in a system similar to Hebrew and Greek numerals. Apart from Classical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenician Alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet is an alphabet (more specifically, an abjad) known in modern times from the Canaanite and Aramaic inscriptions found across the Mediterranean region. The name comes from the Phoenician civilization. The Phoenician alphabet is also called the Early Linear script (in a Semitic languages, Semitic context, not connected to Minoan writing systems), because it is an early development of the Proto-Sinaitic script, Proto- or Old Canaanite or Proto-Sinaitic Writing system, script, into a Writing system#Graphic classification, linear, purely alphabetic script, also marking the transfer from a multi-directional writing system, where a variety of writing directions occurred, to a regulated horizontal, right-to-left script. Its immediate predecessor, the Proto-Canaanite, Old Canaanite or Proto-Sinaitic script, used in the final stages of the Late Bronze Age, first in either Egypt or Canaan and then in the Syro-Hittite states, Syro-Hittite kingdoms, is the oldest fully ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mu (letter)
Mu (uppercase Œú, lowercase Œº; Ancient Greek , ell, ŒºŒπ or ŒºœÖ‚Äîboth ) is the 12th letter of the Greek alphabet, representing the voiced bilabial nasal . In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 40. Mu was derived from the Egyptian hieroglyphic symbol for water, which had been simplified by the Phoenicians and named after their word for water, to become ê§å (mem). Letters that derive from mu include the Roman M and the Cyrillic –ú. Names Ancient Greek In Ancient Greek, the name of the letter was written and pronounced Modern Greek In Modern Greek, the letter is spelled and pronounced . In polytonic orthography, it is written with an acute accent: . Use as symbol The lowercase letter mu (Œº) is used as a special symbol in many academic fields. Uppercase mu is not used, because it appears identical to Latin M. Measurement *the SI prefix ''micro-'', which represents one millionth, or 10−6. Lowercase letter "u" is often substituted for "Œº" w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aramaic Alphabet
The ancient Aramaic alphabet was adapted by Arameans from the Phoenician alphabet and became a distinct script by the 8th century BC. It was used to write the Aramaic languages spoken by ancient Aramean pre-Christian tribes throughout the Fertile Crescent. It was also adopted by other peoples as their own alphabet when empires and their subjects underwent linguistic Aramaization during a language shift for governing purposes —a precursor to Arabization centuries later— including among Assyrians who permanently replaced their Akkadian language and its cuneiform script with Aramaic and its script, and among Jews (but not Samaritans), who adopted the Aramaic language as their vernacular and started using the Aramaic alphabet even for writing Hebrew, displacing the former Paleo-Hebrew alphabet. (The modern Hebrew alphabet derives from the Aramaic alphabet, in contrast to the modern Samaritan alphabet, which derives from Paleo-Hebrew). The letters in the Aramaic alphabet all re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Alphabet
The Hebrew alphabet ( he, wikt:אלפבית, אָלֶף־בֵּית עִבְרִי, ), known variously by scholars as the Ktav Ashuri, Jewish script, square script and block script, is an abjad script used in the writing of the Hebrew language and other Jewish languages, most notably Yiddish, Judaeo-Spanish, Ladino, Judeo-Arabic languages, Judeo-Arabic, and Judeo-Persian. It is also used informally in Israel to write Levantine Arabic, especially among Druze in Israel, Druze. It is an offshoot of the Aramaic alphabet, Imperial Aramaic alphabet, which flourished during the Achaemenid Empire and which itself derives from the Phoenician alphabet. Historically, two separate abjad scripts have been used to write Hebrew. The original, old Hebrew script, known as the paleo-Hebrew alphabet, has been largely preserved in a variant form as the Samaritan alphabet. The present "Jewish script" or "square script", on the contrary, is a stylized form of the Aramaic alphabet and was technicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Letter Mem-final Handwriting
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved throughout history as the main liturgical language of Judaism (since the Second Temple period) and Samaritanism. Hebrew is the only Canaanite language still spoken today, and serves as the only truly successful example of a dead language that has been revived. It is also one of only two Northwest Semitic languages still in use, with the other being Aramaic. The earliest examples of written Paleo-Hebrew date back to the 10th century BCE. Nearly all of the Hebrew Bible is written in Biblical Hebrew, with much of its present form in the dialect that scholars believe flourished around the 6th century BCE, during the time of the Babylonian captivity. For this reason, Hebrew has been referred to by Jews as ''Lashon Hakodesh'' (, ) since ancient t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Letter Mem-nonfinal Rashi
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved throughout history as the main liturgical language of Judaism (since the Second Temple period) and Samaritanism. Hebrew is the only Canaanite language still spoken today, and serves as the only truly successful example of a dead language that has been revived. It is also one of only two Northwest Semitic languages still in use, with the other being Aramaic. The earliest examples of written Paleo-Hebrew date back to the 10th century BCE. Nearly all of the Hebrew Bible is written in Biblical Hebrew, with much of its present form in the dialect that scholars believe flourished around the 6th century BCE, during the time of the Babylonian captivity. For this reason, Hebrew has been referred to by Jews as ''Lashon Hakodesh'' (, ) since ancient t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Letter Mem Handwriting
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved throughout history as the main Sacred language, liturgical language of Judaism (since the Second Temple period) and Samaritanism. Hebrew is the only Canaanite languages, Canaanite language still spoken today, and serves as the only truly successful example of a Extinct language, dead language that has been language revitalization, revived. It is also one of only two Northwest Semitic languages still in use, with the other being Aramaic. The earliest examples of written Paleo-Hebrew alphabet, Paleo-Hebrew date back to the 10th century BCE. Nearly all of the Hebrew Bible is written in Biblical Hebrew, with much of its present form in the dialect that scholars believe flourished around the 6th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Semitic Language
Proto-Semitic is the hypothetical reconstructed proto-language ancestral to the Semitic languages. There is no consensus regarding the location of the Proto-Semitic ''Urheimat''; scholars hypothesize that it may have originated in the Levant (most likely), the Sahara, or the Horn of Africa, and the view that it arose in the Arabian Peninsula has also been common historically. The Semitic language family is considered part of the broader macro-family of Afroasiatic languages. Dating The earliest attestations of a Semitic language are in Akkadian, dating to around the 24th to 23rd centuries BC (see Sargon of Akkad) and the Eblaite language, but earlier evidence of Akkadian comes from personal names in Sumerian texts from the first half of the third millennium BC. One of the earliest known Akkadian inscriptions was found on a bowl at Ur, addressed to the very early pre-Sargonic king Meskiagnunna of Ur (c. 2485–2450 BC) by his queen Gan-saman, who is thought to have been from A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monospaced Font
A monospaced font, also called a fixed-pitch, fixed-width, or non-proportional font, is a font whose letters and characters each occupy the same amount of horizontal space. This contrasts with variable-width fonts, where the letters and spacings have different widths. Monospaced fonts are customary on typewriters and for typesetting computer code. Monospaced fonts were widely used in early computers and computer terminals, which often had extremely limited graphical capabilities. Hardware implementation was simplified by using a text mode where the screen layout was addressed as a regular grid of tiles, each of which could be set to display a character by indexing into the hardware's character map. Some systems allowed colored text to be displayed by varying the foreground and background color for each tile. Other effects included reverse video and blinking text. Nevertheless, these early systems were typically limited to a single console font. Even though computers can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sans-serif
In typography and lettering, a sans-serif, sans serif, gothic, or simply sans letterform is one that does not have extending features called "serifs" at the end of strokes. Sans-serif typefaces tend to have less stroke width variation than serif typefaces. They are often used to convey simplicity and modernity or minimalism. Sans-serif typefaces have become the most prevalent for display of text on computer screens. On lower-resolution digital displays, fine details like serifs may disappear or appear too large. The term comes from the French word , meaning "without" and "serif" of uncertain origin, possibly from the Dutch word meaning "line" or pen-stroke. In printed media, they are more commonly used for display use and less for body text. Before the term "sans-serif" became common in English typography, a number of other terms had been used. One of these outmoded terms for sans-serif was gothic, which is still used in East Asian typography and sometimes seen in typeface na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |