|
≈Ýilutƒó
≈Ýilutƒó (, previously ''≈Ýilokarƒçiama'', german: link=no, Heydekrug), is a city in the south of the Klaipƒóda County, Lithuania. The city was part of the Klaipƒóda Region and ethnographic Lithuania Minor. ≈Ýilutƒó was the interwar capital of ≈Ýilutƒó County and is currently the capital of ≈Ýilutƒó District Municipality. Name ≈Ýilutƒó's origin dates to an inn (Krug, locally ''karƒçema'') catering to travelers and their horses which was located halfway between Memel (Klaipƒóda) and Tilsit (Til≈æƒó). The German name of ''Heydekrug'' referred to a ''Krug'' (an archaic word for inn) in the ''Heide'' (heathland). The inn was known for being in the region where most people spoke the Memelland-Samogitian dialect ''≈Ýilokarƒçema''. History A famous fish market was opened in ≈Ýilutƒó almost 500 years ago, when Georg Tallat purchased the inn together with the land and fishing rights in 1511. The town was a gathering place for peasants from nearby Samogitia and Curonian and Prussian fis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
≈Ýilutƒó District Municipality
≈Ýilutƒó (, previously ''≈Ýilokarƒçiama'', german: link=no, Heydekrug), is a city in the south of the Klaipƒóda County, Lithuania. The city was part of the Klaipƒóda Region and ethnographic Lithuania Minor. ≈Ýilutƒó was the interwar period, interwar capital of ≈Ýilutƒó County and is currently the capital of ≈Ýilutƒó District Municipality. Name ≈Ýilutƒó's origin dates to an Public house#Inns, inn (Krug, locally ''karƒçema'') catering to travelers and their horses which was located halfway between Klaipƒóda, Memel (Klaipƒóda) and Sovetsk, Kaliningrad Oblast, Tilsit (Til≈æƒó). The German name of ''Heydekrug'' referred to a ''Krug'' (an archaic word for inn) in the ''Heide'' (heathland). The inn was known for being in the region where most people spoke the Memelland-Samogitian dialect ''≈Ýilokarƒçema''. History A famous fish market was opened in ≈Ýilutƒó almost 500 years ago, when Georg Tallat purchased the inn together with the land and fishing rights in 1511. The town was a gather ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
≈Ýilutƒó District Municipality
≈Ýilutƒó (, previously ''≈Ýilokarƒçiama'', german: link=no, Heydekrug), is a city in the south of the Klaipƒóda County, Lithuania. The city was part of the Klaipƒóda Region and ethnographic Lithuania Minor. ≈Ýilutƒó was the interwar period, interwar capital of ≈Ýilutƒó County and is currently the capital of ≈Ýilutƒó District Municipality. Name ≈Ýilutƒó's origin dates to an Public house#Inns, inn (Krug, locally ''karƒçema'') catering to travelers and their horses which was located halfway between Klaipƒóda, Memel (Klaipƒóda) and Sovetsk, Kaliningrad Oblast, Tilsit (Til≈æƒó). The German name of ''Heydekrug'' referred to a ''Krug'' (an archaic word for inn) in the ''Heide'' (heathland). The inn was known for being in the region where most people spoke the Memelland-Samogitian dialect ''≈Ýilokarƒçema''. History A famous fish market was opened in ≈Ýilutƒó almost 500 years ago, when Georg Tallat purchased the inn together with the land and fishing rights in 1511. The town was a gather ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
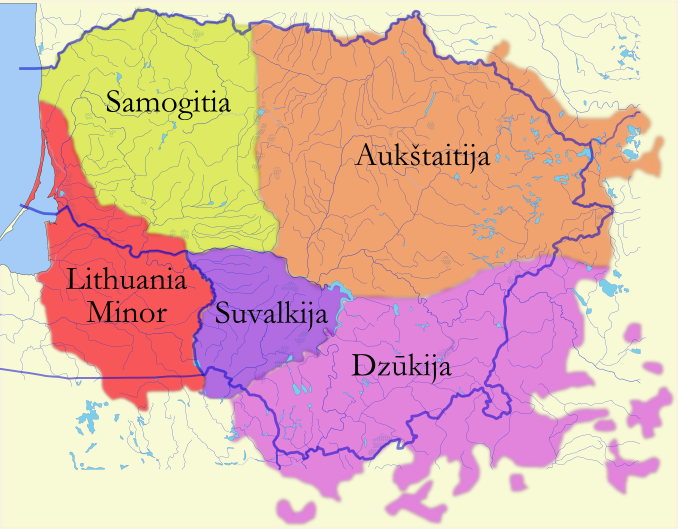
Lithuania Minor
Lithuania Minor ( lt, Mažoji Lietuva; german: Kleinlitauen; pl, Litwa Mniejsza; russian: Ма́лая Литва́), or Prussian Lithuania ( lt, Prūsų Lietuva; german: Preußisch-Litauen, pl, Litwa Pruska), is a historical ethnographic region of Prussia, where Prussian Lithuanians (or Lietuvininkai) lived, now located in Lithuania and the Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia. Lithuania Minor encompassed the northeastern part of the region and got its name from the territory's substantial Lithuanian-speaking population. Prior to the invasion of the Teutonic Knights in the 13th century, the main part of the territory later known as Lithuania Minor was inhabited by the tribes of Skalvians and Nadruvians. The land depopulated during the incessant war between Lithuania and the Teutonic Order. The war ended with the Treaty of Melno and the land was repopulated by Lithuanian newcomers, returning refugees, and the remaining indigenous Baltic peoples; the term Lithuania Minor appeared for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rusnƒó
Rusnƒó (german: Ru√ü) is a border town in ≈Ýilutƒó district, Lithuania, located on the Rusnƒó Island in the Nemunas Delta, 9 km south-west from ≈Ýilutƒó. History Rusnƒó was first mentioned in historical sources in the 14th century. In 1419 the first church was built in Rusnƒó, and in 1553 a Lithuanian parish school was established. Accessed September 16, 2006 In 1863 the Rusnƒó synagogue opened. In 1946 Rusnƒó received municipal rights, and in 1967 the whole Island of Rusnƒó was given this status. Geography Some parts of the town of Rusnƒó near are located below the sea level and are the lowest in Lithuan ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klaipƒóda County
Klaipėda County ( lt, Klaipėdos apskritis) is one of ten counties in Lithuania, bordering Tauragė County to the southeast, Telšiai County to the northeast, Kurzeme in Latvia to the north, and Kaliningrad Oblast in Russia to the south. To the west is the Baltic Sea. It lies in the west of the country and is the only county to have a coastline and not landlocked. Its capital is Klaipėda. On 1 July 2010, the county administration was abolished, and since that date, Klaipėda County remains as the territorial and statistical unit. Geography The topography of Klaipėda County is divided into three regions, the highest in the east and lowest in the west: the Western Zemaičiai Plateau in the east, the Western Zemaičiai Plain in the center, and the Pajurys Lowland in the west and on the Baltic coast. Klaipėda County borders Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia, to the south via the Nemunas, which drains into the Curonian Lagoon. The Curonian Spit, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is split ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Municipalities Of Lithuania
__NOTOC__ Lithuania is divided into three layers of administrative divisions. The first-level division consists of 10 counties ( Lithuanian: singular – ''apskritis'', plural – ''apskritys''). These are sub-divided into 60 municipalities (Lithuanian: plural – ''savivaldybės'', singular – ''savivaldybė''), which in turn are further sub-divided into over 500 smaller groups, known as elderships (Lithuanian: plural – ''seniūnijos'', singular – ''seniūnija''). At the end of its tenure as a Soviet Socialist Republic, Lithuania's administrative divisions consisted of 44 regions, 12 cities, 80 towns, 19 settlements, and 426 rural districts. The reform of this system was an immediate concern for the new government. The Constitution of Lithuania, ratified in 1992, delegated the power of establishing future administrative units to the Lithuanian Parliament (Seimas). Accordingly, the Seimas passed two fundamental laws: a 1993 law on government representation and a 1994 law ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klaipƒóda
Klaipėda (; ; german: Memel; pl, Kłajpeda; russian: Клайпеда; sgs, Klaipieda) is a city in Lithuania on the Baltic Sea coast. The capital of the eponymous county, it is the third largest city and the only major seaport in Lithuania. The city has a complex recorded history, partially due to the combined regional importance of the usually ice-free Port of Klaipėda at the mouth of the river . Located in the region of Lithuania Minor, at various times, it was a part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Prussia and Germany until the 1919 Treaty of Versailles. As a result of the 1923 Klaipėda Revolt it was annexed by Lithuania and has remained with Lithuania to this day, except between 1939 and 1945 when it was occupied by Germany following the 1939 German ultimatum to Lithuania. The population has migrated from the city to its suburbs and hinterland. The number of inhabitants of Klaipėda city shrank from 202,929 in 1989 to 162,360 in 2011, but the urban zone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samogitia
Samogitia or ≈Ωemaitija ( Samogitian: ''≈Ωemaitƒójƒó''; see below for alternative and historical names) is one of the five cultural regions of Lithuania and formerly one of the two core administrative divisions of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania alongside Lithuania proper. ≈Ωemaitija is located in northwestern Lithuania. Its largest city is ≈Ýiauliai. ≈Ωemaitija has a long and distinct cultural history, reflected in the existence of the Samogitian language. Etymology and alternative names Ruthenian sources mentioned the region as –∂–µ–º–æ—Ç—å—Å–∫–∞—è –∑–µ–º–ª—è, ''≈Ωemot'skaja zemlja''; this gave rise to its Polish form, , and probably to the Middle High German . In Latin texts, the name is usually written as etc. The area has long been known to its residents and to other Lithuanians exclusively as ≈Ωemaitija (the name Samogitia is no longer in use within Lithuania and has not been used for at least two centuries); ≈Ωemaitija means "lowlands" in Lithuanian. The region is also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counties Of Lithuania
The territory of Lithuania is divided into 10 counties (Lithuanian language, Lithuanian: singular ''apskritis'', plural ''apskritys''), all named after their capitals. The counties are divided into Municipalities of Lithuania, 60 municipalities (Lithuanian: singular ''savivaldybė'', plural ''savivaldybės''): 9 city municipalities, 43 district municipalities and 8 municipalities. Each municipality is then divided into elderates (Lithuanian: singular ''seniūnija'', plural ''seniūnijos''). This division was created in 1994 and slightly modified in 2000. Until 2010, the counties were administered by county governors (Lithuanian: singular – ''apskrities viršininkas'', plural – ''apskrities viršininkai'') appointed by the central government in Vilnius. Their primary duty was to ensure that the municipalities obey the laws and the Constitution of Lithuania. They did not have great powers vested in them, and so it was suggested that 10 counties are too much for Lithuania as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curonians
:''The Kursenieki are also sometimes known as Curonians.'' The Curonians or Kurs ( lv, kurši; lt, kuršiai; german: Kuren; non, Kúrir; orv, кърсь) were a Baltic tribe living on the shores of the Baltic Sea in what are now the western parts of Latvia and Lithuania from the 5th to the 16th centuries, when they merged with other Baltic tribes. They gave their name to the region of Courland (''Kurzeme''), and they spoke the Curonian language. Curonian lands were conquered by the Livonian Order in 1266 and they eventually merged with other Baltic tribes contributing to the ethnogenesis of Lithuanians and Latvians. Origin The ethnic origin of the Curonians has been disputed in the past. Some researchers place the Curonians in the eastern Baltic group.Östen Dahl (ed.) 2001, ''The Circum-Baltic Languages: Typology and Contact,'' vol. 1 Others hold that the Curonians were related to Old Prussians who belonged in the western Baltic group. History The Curonians were known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klaipƒóda Region
The Klaipėda Region ( lt, Klaipėdos kraštas) or Memel Territory (german: Memelland or ''Memelgebiet'') was defined by the 1919 Treaty of Versailles in 1920 and refers to the northernmost part of the German province of East Prussia, when as Memelland it was put under the administration of the Entente's Council of Ambassadors. The Memel Territory, together with other areas severed from Germany (the Saar and Danzig) was to remain under the control of the League of Nations until a future day when the people of these regions would be allowed to vote on whether the land would return to Germany or not. Today, the former Memel Territory is controlled by Lithuania as part of Klaipėda and Tauragė counties. Historical overview In 1226 Duke Konrad I of Masovia requested assistance against the Prussians and other Baltic tribes, including the Skalvians who lived along the Neman (Memel) River. In March 1226, Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II issued the Golden Bull of Rimini, which p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landkreis Heydekrug
Landkreis Heydekrug (1818–1945) was an administrative territorial entity of East Prussia, located in Lithuania Minor. It was part of Regierungsbezirk Gumbinnen. The seat was in Heydekrug (modern ≈Ýilutƒó). In 1913, Karkeln and surrounding inland towns (those south of the yellow line in the map) were administratively transferred to Kreis Niederung.Maria Sator - Heirat (Marriage) Landesarchiv Berlin; Berlin, Deutschland; Personenstandsregister 1876-1945; laufendenummer: 28697. Source Information ‚Äì Ancestry.com. Eastern Prussian Provinces, Germany oland Selected Civil Vitals, 1874-1945 (database on-line). Provo, UT, USA: Ancestry.com Operations, Inc., 2016. Original data: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |