|
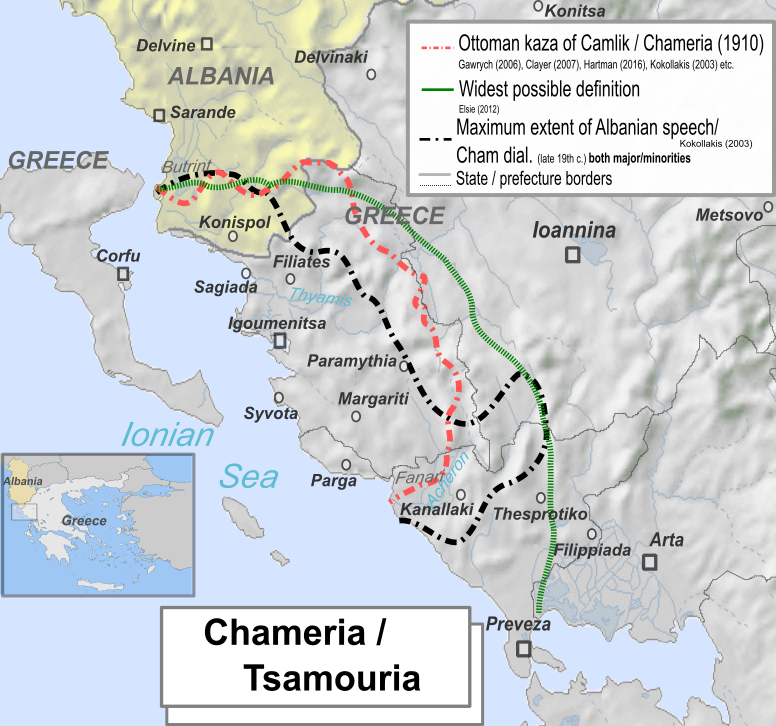
รamรซria
Chameria ( sq, รamรซria; el, ฮคฯฮฑฮผฮฟฯ ฯฮนฮฌ, ''Tsamouriรก''; tr, รamlฤฑk) is a term used today mostly by Albanians to refer to parts of the coastal region of Epirus in southern Albania and Greece, traditionally associated with the Albanian ethnic subgroup of the Chams.Elsie, Robert and Bejtullah D. Destani (2012). ''The Cham Albanians of Greece: A Documentary History''. IB Tauris. . p. XXIX. "Chameria is a mountainous region of the southwestern Balkan Peninsula that now straddles the Greek-Albanian border. Most of Chameria is in the Greek Province of Epirus, corresponding largely to the prefectures of Thesprotia and Preveza, but it also includes the southernmost part of Albania, the area around Konispol. It is approximately 10,000 square kilometres in size and has a current, mostly Greek-speaking population of about 150,000. As an historical region, Chameria, also spelled Chamuria, Chamouria or Tsiamouria, is sometimes confused with Epirus which is in fact a much larger ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cham Albanians
Cham Albanians or Chams ( sq, รamรซ; el, ฮคฯฮฌฮผฮทฮดฮตฯ, ''Tsรกmidhes''), are a sub-group of Albanians who originally resided in the western part of the region of Epirus in northwestern Greece, an area known among Albanians as Chameria. The Chams have their own particular cultural identity, which is a mixture of Albanian and Greek influences as well as many specifically Cham elements.See Hasluk, 'Christianity and Islam under the Sultans', London, 1927. A number of Chams contributed to the Albanian national identity and played an important role in starting the renaissance of the Albanian culture in the 19th century. The Chams speak their own dialect of the Albanian language, the Cham Albanian dialect, which is a Southern Tosk Albanian dialect and one of the two most conservative ones; the other being Arvanitika. During the late 1930s Chams suffered from intimidation and persecution under the dictatorship of General Metaxas. Following the Italian occupation of Albania in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albanian Irredentism
Greater Albania is an irredentist and nationalist concept that seeks to unify the lands that many Albanians consider to form their national homeland. It is based on claims on the present-day or historical presence of Albanian populations in those areas. In addition to the existing Albania, the term incorporates claims to regions in the neighbouring states, the areas include Kosovo, the Preลกevo Valley of Serbia, territories in southern Montenegro, northwestern Greece (the Greek regional units of Thesprotia and Preveza, referred by Albanians as Chameria, and other territories that were part of the Vilayet of Yanina during the Ottoman Empire),. and a western part of North Macedonia. The unification of an even larger area into a single territory under Albanian authority had been theoretically conceived by the League of Prizren, an organization of the 19th century whose goal was to unify the Albanian inhabited lands (and other regions, mostly from the regions of Macedonia and Epir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latium
Latium ( , ; ) is the region of central western Italy in which the city of Rome was founded and grew to be the capital city of the Roman Empire. Definition Latium was originally a small triangle of fertile, volcanic soil (Old Latium) on which resided the tribe of the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins or Latians. It was located on the left bank (east and south) of the Tiber, River Tiber, extending northward to the Aniene, River Anio (a left-bank tributary of the Tiber) and southeastward to the Pomptina Palus (Pontine Marshes, now the Pontine Fields) as far south as the Cape Circeo, Circeian promontory. The right bank of the Tiber was occupied by the Etruscan city of Veii, and the other borders were occupied by Ancient Italic people, Italic tribes. Subsequently, Rome defeated Veii and then its Italic neighbours, expanding its dominions over Southern Etruria and to the south, in a partly marshy and partly mountainous region. The latter saw the creation of numerous Roman and Latin co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konispol
Konispol ( sq-definite, Konispoli) is the southernmost town in Albania. It sits one kilometer away from the Border crossings of Albania, Albanian-Greek border. The settlement is inhabited by Muslim Cham Albanians. Konispol is the modern centre of the Cham Albanian community in Albania. The main economic interests of Konispol are agriculture and viticulture. The town is the seat of the southernmost administrative unit in Albania, the Municipality of Konispol ( sq, Bashkia Konispol). It was formed during the 2015 local government reform by the merger of the former municipalities of Konispol, Markat and Xarrรซ. The total population is 8,245 (2011 census), in a total area of 226.26 km2. The population of the former Konispol municipality at the 2011 census was 2,123. The former Konispol municipal unit (pre-2015) consisted of the town Konispol and the village รiflik. The new larger municipality of Konispol contains settlements that are inhabited by Albanians who form the majority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bistricรซ (river)
Bistricรซ (definite: Bistrica) is a river in southwestern Albania. It ends in the Ionian Sea. Etymology The name Bistrica comes from Slavic, meaning "clear (water)". Other toponyms including "Bistrica" in Balkan countries indicate the Slavic origin of the toponym. Geography Bistricรซ starts from Mali i Gjerรซ (also known as ''Sopot'') in Finiq municipality directing initially versus south-west. The main source is near Krongj ( "The Blue Eye" source), also gathering other sources from the nearby villages of Pecรซ, Kardhikaq, Velahovรซ, and other smaller brooks. It passes through Mesopotam and Finiq municipalities, parallel with the Sarandรซ-Gjirokastรซr road. Initially the river ended in Lake Butrint, which connects with the Ionian sea through the Vivar channel. In 1958, it was deviated to รukรซ channel. The river is 25 km long. Economy and tourism The river is not navigable. There is an artificial lake with the same name ( sq, Liqeni i Bistricรซs) built on its basin, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christoforos Perraivos
Christoforos Perraivos ( el, ฮงฯฮนฯฯฯฯฮฟฯฮฟฯ ฮ ฮตฯฯฮฑฮนฮฒฯฯ) was a Greek officer of the Greek War of Independence, member of the Filiki Eteria and author. In non-Greek sources his name is usually found as ''Per(r)evo(s).'' Biography Perraivos was born on 3 April 1773 in the village of Palioi Poroi, Pieria. His family name was Hatzivasiliou (ฮงฮฑฯฮถฮทฮฒฮฑฯฮนฮปฮตฮฏฮฟฯ ), but adopted the nickname โPerraivosโ alluding to the Perrhaebi, an ancient Greek tribe of Thessaly. It is believed that he was an illegitimate son of a certain monk Hieronymos, an official at the Metropolis of Larissa. In 1793, with the help of the said Hieronymos, he left Greece to study at the Greek School in Bucharest and in 1796 to study medicine in Vienna. There he met the Greek humanist and revolutionary Rigas Feraios and entered an underground revolutionary organization. In 1797 Perraivos was arrested with Rigas and others by the Austrian authorities in Trieste but, unlike Rigas Feraios w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Markat
Markat is a village and a former municipality in Vlorรซ County, southern Albania. In the 2015 local government reform, it became a subdivision of the municipality Konispol. The population in the 2011 census was 1,859.2011 census results The municipal unit consists of the villages Dishat, Vรซrvรซ, , Markat, Ninat and Janjar [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butrint
Butrint ( el, ฮฮฟฯ ฮธฯฯฯฯฮฝ and ฮฮฟฯ ฮธฯฯฯฯฯ, ''Bouthrลtรณn'', la, Buthrลtum) was an ancient Greek and later Roman city and bishopric in Epirus. "Speakers of these various Greek dialects settled different parts of Greece at different times during the Middle Bronze Age, with one group, the 'northwest' Greeks, developing their own dialect and peopling central Epirus. This was the origin of the Molossian or Epirotic tribes." " ..a proper dialect of Greek, like the dialects spoken by Dorians and Molossians." "The western mountains were peopled by the Molossians (the western Greeks of Epirus)." "That the Molossians... spoke Illyrian or another barbaric tongue was nowhere suggested, although Aeschylus and Pindar wrote of Molossian lands. That they in fact spoke greek was implied by Herodotus' inclusion of Molossi among the Greek colonists of Asia Minor, but became demonstrable only when D. Evangelides published two long inscriptions of the Molossian State, set up p. 369 BC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acheron River
The Acheron (; grc, แผฯฮญฯฯฮฝ ''Acheron'' or แผฯฮตฯฮฟฯฯฮนฮฟฯ ''Acherousios''; ell, ฮฯฮญฯฮฟฮฝฯฮฑฯ ''Acherontas'') is a river located in the Epirus region of northwest Greece. It is long, and its drainage area is . Its source is near the village Zotiko, in the southwestern part of the Ioannina regional unit, and it flows into the Ionian Sea in Ammoudia, near Parga. The Acheron also features prominently in Greek mythology, where it is often depicted as the entrance to the Greek Underworld where souls must be ferried across by Charon (although some later sources, such as Roman poets, assign this role to the river Styx). Mythology Ancient Greek mythology saw the Acheron, sometimes known as the "river of woe", as one of the five rivers of the Greek underworld. The name is of uncertain etymology. Most classical accounts, including Pausanias (10.28) and later Dante's ''Inferno'' (3.78), portray the Acheron as the entrance to the Underworld and depict Charon ferry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyamis
The Thyamis ( el, ฮฯฮฑฮผฮนฯ), also known as Glykys (ฮฮปฯ ฮบฯฯ) or Kalamas (ฮฮฑฮปฮฑฮผฮฌฯ), is a river in the Epirus region of Greece. It flows into the Ionian Sea. It is long, and its drainage area is about , over 99% of which on Greek territory. The names of the Chameria region (''Tsamouria'' in Greek), as well as the Chams, derive from the river's name. Thyamis in ancient Greece was mentioned by Pausanias as forming the boundary between Thesprotis and Kestrine. In addition, Suda and Ptolemaeus mentioned it. Some Renaissance scholars believed that the English River Thames owed its name to the River Thyamis, as early Celtic tribes were thought to have migrated from the Epirus region to England. While this belief influenced the modern spelling of the English river's name, it is no longer regarded as credible. Geography The source of the river is near the village Kalpaki, in the northwestern part of the Ioannina regional unit. It flows south at first, and turns southwes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic period (), and the Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form approaches Medieval Greek. There were several regional dialects of Ancient Greek, of which Attic Greek developed into Koine. Dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |