|
Zirconium Alloy
Zirconium alloys are solid solutions of zirconium or other metals, a common subgroup having the trade mark Zircaloy. Zirconium has very low absorption cross-section of thermal neutrons, high hardness, ductility and corrosion resistance. One of the main uses of zirconium alloys is in nuclear technology, as cladding of fuel rods in nuclear reactors, especially water reactors. A typical composition of nuclear-grade zirconium alloys is more than 95 weight percent zirconium and less than 2% of tin, niobium, iron, chromium, nickel and other metals, which are added to improve mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. The water cooling of reactor zirconium alloys elevates requirement for their resistance to oxidation-related nodular corrosion. Furthermore, oxidative reaction of zirconium with water releases hydrogen gas, which partly diffuses into the alloy and forms zirconium hydrides. The hydrides are less dense and are weaker mechanically than the alloy; their formation resul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid Solution
A solid solution, a term popularly used for metals, is a homogenous mixture of two different kinds of atoms in solid state and have a single crystal structure. Many examples can be found in metallurgy, geology, and solid-state chemistry. The word "solution" is used to describe the intimate mixing of components at the atomic level and distinguishes these homogeneous materials from physical mixtures of components. Two terms are mainly associated with solid solutions - ''solvents'' and ''solutes,'' depending on the relative abundance of the atomic species. In general if two compounds are isostructural then a solid solution will exist between the end members (also known as parents). For example sodium chloride and potassium chloride have the same cubic crystal structure so it is possible to make a pure compound with any ratio of sodium to potassium (Na1-xKx)Cl by dissolving that ratio of NaCl and KCl in water and then evaporating the solution. A member of this family is sold under t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nodular Corrosion
Galvanic corrosion (also called bimetallic corrosion or dissimilar metal corrosion) is an electrochemical process in which one metal corrodes preferentially when it is in electrical contact with another, in the presence of an electrolyte. A similar galvanic reaction is exploited in primary cells to generate a useful electrical voltage to power portable devices. This phenomenon is named after Italian physician Luigi Galvani (1737-1798). Overview Dissimilar metals and alloys have different electrode potentials, and when two or more come into contact in an electrolyte, one metal (that's more reactive) acts as anode and the other (that's less reactive) as cathode. The electropotential difference between the reactions at the two electrodes is the driving force for an accelerated attack on the anode metal, which dissolves into the electrolyte. This leads to the metal at the anode corroding more quickly than it otherwise would and corrosion at the cathode being inhibited. The presence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VVER
The water-water energetic reactor (WWER), or VVER (from russian: водо-водяной энергетический реактор; transliterates as ; ''water-water power reactor'') is a series of pressurized water reactor designs originally developed in the Soviet Union, and now Russia, by OKB Gidropress. The idea of such a reactor was proposed at the Kurchatov Institute by Savely Moiseevich Feinberg. VVER were originally developed before the 1970s, and have been continually updated. As a result, the name VVER is associated with a wide variety of reactor designs spanning from generation I reactors to modern generation III+ reactor designs. Power output ranges from 70 to 1300 MWe, with designs of up to 1700 MWe in development. The first prototype VVER-210 was built at the Novovoronezh Nuclear Power Plant. VVER power stations have mostly been installed in Russia and the former Soviet Union, but also in China, the Czech Republic, Finland, Germany, Hungary, Slovakia, Bulgaria, Indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourth-largest country in the Americas, and the eighth-largest country in the world. It shares the bulk of the Southern Cone with Chile to the west, and is also bordered by Bolivia and Paraguay to the north, Brazil to the northeast, Uruguay and the South Atlantic Ocean to the east, and the Drake Passage to the south. Argentina is a federal state subdivided into twenty-three provinces, and one autonomous city, which is the federal capital and largest city of the nation, Buenos Aires. The provinces and the capital have their own constitutions, but exist under a federal system. Argentina claims sovereignty over the Falkland Islands, South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands, and a part of Antarctica. The earliest recorded human prese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westinghouse Electric Company
Westinghouse Electric Company LLC is an American nuclear power company formed in 1999 from the nuclear power division of the original Westinghouse Electric Corporation. It offers nuclear products and services to utilities internationally, including nuclear fuel, service and maintenance, instrumentation, control and design of nuclear power plants. Westinghouse's world headquarters are located in the Pittsburgh suburb of Cranberry Township, Pennsylvania. Brookfield Business Partners, a Canadian private equity fund and a subsidiary of Brookfield Asset Management is the majority owner of Westinghouse. On March 24, 2017, parent company Toshiba announced that Westinghouse Electric Company would file for Chapter 11 bankruptcy because of US$9 billion of losses from nuclear reactor construction projects. The projects responsible for this loss are mostly the construction of four AP1000 reactors at Vogtle in Georgia and the Virgil C. Summer plant in South Carolina. Westinghouse filed fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressurized Water Reactor
A pressurized water reactor (PWR) is a type of light-water reactor, light-water nuclear reactor. PWRs constitute the large majority of the world's nuclear power plants (with notable exceptions being the UK, Japan and Canada). In a PWR, the primary nuclear reactor coolant, coolant (water) is pumped under high pressure to the reactor core where it is heated by the energy released by the Nuclear fission, fission of atoms. The heated, high pressure water then flows to a Water-tube boiler, steam generator, where it transfers its thermal energy to lower pressure water of a secondary system where steam is generated. The steam then drives turbines, which spin an electric generator. In contrast to a boiling water reactor (BWR), pressure in the primary coolant loop prevents the water from boiling within the reactor. All light-water reactors use ordinary water as both coolant and neutron moderator. Most use anywhere from two to four vertically mounted steam generators; VVER reactors use horizo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CANDU Reactor
The CANDU (Canada Deuterium Uranium) is a Canadian pressurized heavy-water reactor design used to generate electric power. The acronym refers to its deuterium oxide ( heavy water) moderator and its use of (originally, natural) uranium fuel. CANDU reactors were first developed in the late 1950s and 1960s by a partnership between Atomic Energy of Canada Limited (AECL), the Hydro-Electric Power Commission of Ontario, Canadian General Electric, and other companies. There have been two major types of CANDU reactors, the original design of around 500 MWe that was intended to be used in multi-reactor installations in large plants, and the rationalized CANDU 6 in the 600 MWe class that is designed to be used in single stand-alone units or in small multi-unit plants. CANDU 6 units were built in Quebec and New Brunswick, as well as Pakistan, Argentina, South Korea, Romania, and China. A single example of a non-CANDU 6 design was sold to India. The multi-unit design was used o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boiling Water Reactor
A boiling water reactor (BWR) is a type of light water nuclear reactor used for the generation of electrical power. It is a design different from a Soviet graphite-moderated RBMK. It is the second most common type of electricity-generating nuclear reactor after the pressurized water reactor (PWR), which is also a type of light water nuclear reactor. The main difference between a BWR and PWR is that in a BWR, the reactor core heats water, which turns to steam and then drives a steam turbine. In a PWR, the reactor core heats water, which does not boil. This hot water then exchanges heat with a lower pressure system, which turns water into steam that drives the turbine. The BWR was developed by the Argonne National Laboratory and General Electric (GE) in the mid-1950s. The main present manufacturer is GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy, which specializes in the design and construction of this type of reactor. Overview A boiling water reactor uses demineralized water as a coolant and neu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niobium
Niobium is a chemical element with chemical symbol Nb (formerly columbium, Cb) and atomic number 41. It is a light grey, crystalline, and ductile transition metal. Pure niobium has a Mohs hardness rating similar to pure titanium, and it has similar ductility to iron. Niobium oxidizes in Earth's atmosphere very slowly, hence its application in jewelry as a hypoallergenic alternative to nickel. Niobium is often found in the minerals pyrochlore and columbite, hence the former name "columbium". Its name comes from Greek mythology: Niobe, daughter of Tantalus, the namesake of tantalum. The name reflects the great similarity between the two elements in their physical and chemical properties, which makes them difficult to distinguish. English chemist Charles Hatchett reported a new element similar to tantalum in 1801 and named it columbium. In 1809, English chemist William Hyde Wollaston wrongly concluded that tantalum and columbium were identical. German chemist Heinrich Rose determin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
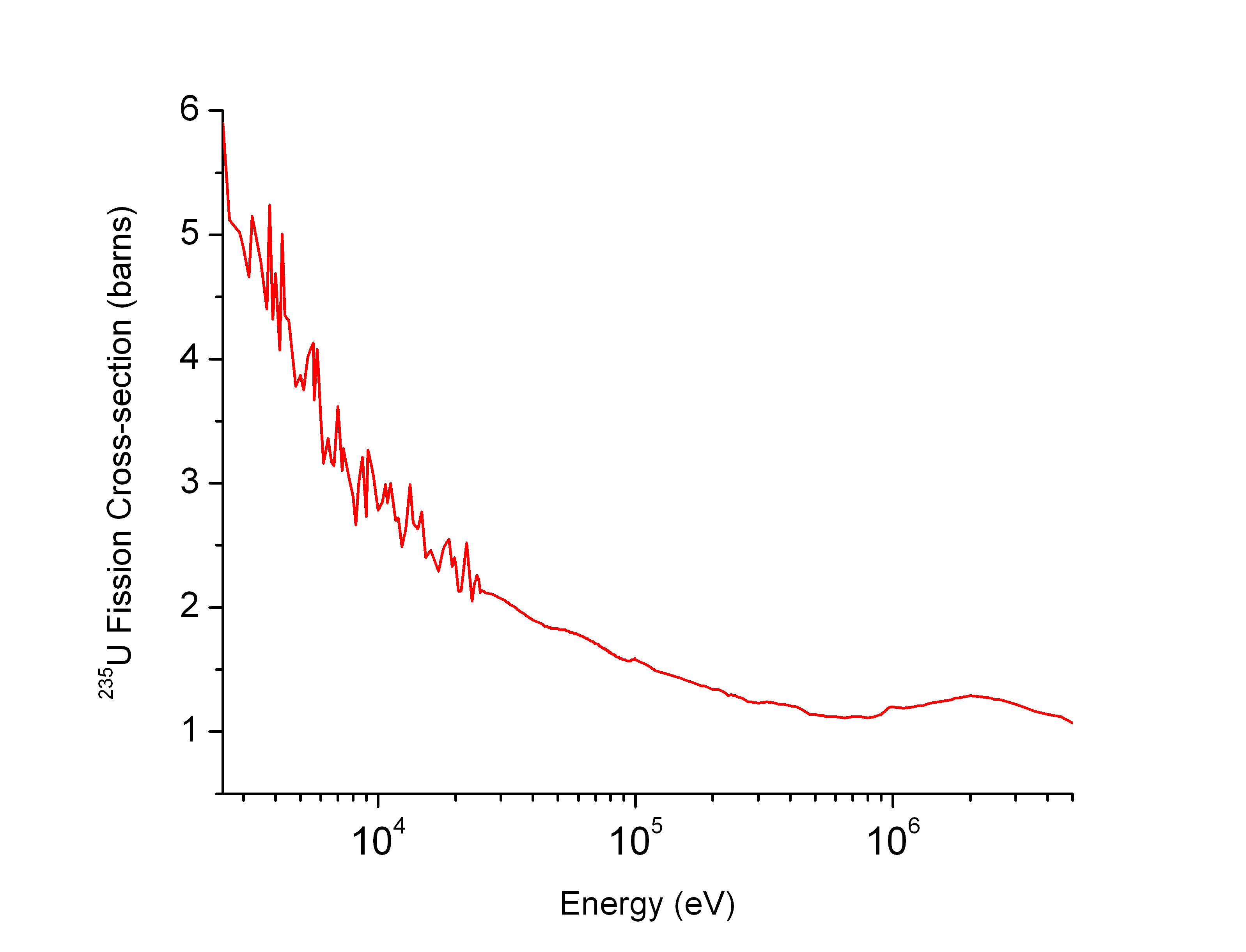
Barn (unit)
A barn (symbol: b) is a metric unit of area equal to (100 fm2). Originally used in nuclear physics for expressing the cross sectional area of nuclei and nuclear reactions, today it is also used in all fields of high-energy physics to express the cross sections of any scattering process, and is best understood as a measure of the probability of interaction between small particles. A barn is approximately the cross-sectional area of a uranium nucleus. The barn is also the unit of area used in nuclear quadrupole resonance and nuclear magnetic resonance to quantify the interaction of a nucleus with an electric field gradient. While the barn never was an SI unit, the SI standards body acknowledged it in the 8th SI Brochure (superseded in 2019) due to its use in particle physics. Etymology During Manhattan Project research on the atomic bomb during World War II, American physicists at Purdue University needed a secretive name for a unit with which to quantify the cross-secti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron Cross Section
In nuclear physics, the concept of a neutron cross section is used to express the likelihood of interaction between an incident neutron and a target nucleus. The neutron cross section σ can be defined as the area in cm2 for which the number of neutron-nuclei reactions taking place is equal to the product of the number of incident neutrons that would pass through the area and the number of target nuclei. In conjunction with the neutron flux, it enables the calculation of the reaction rate, for example to derive the thermal power of a nuclear power plant. The standard unit for measuring the cross section is the barn, which is equal to 10−28 m2 or 10−24 cm2. The larger the neutron cross section, the more likely a neutron will react with the nucleus. An isotope (or nuclide) can be classified according to its neutron cross section and how it reacts to an incident neutron. Nuclides that tend to absorb a neutron and either decay or keep the neutron in its nucleus are neutron absor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hafnium
Hafnium is a chemical element with the symbol Hf and atomic number 72. A lustrous, silvery gray, tetravalent transition metal, hafnium chemically resembles zirconium and is found in many zirconium minerals. Its existence was predicted by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, though it was not identified until 1923, by Dirk Coster and George de Hevesy, making it the penultimate stable element to be discovered (the last being rhenium in 1925). Hafnium is named after , the Latin name for Copenhagen, where it was discovered. Hafnium is used in filaments and electrodes. Some semiconductor fabrication processes use its oxide for integrated circuits at 45 nanometers and smaller feature lengths. Some superalloys used for special applications contain hafnium in combination with niobium, titanium, or tungsten. Hafnium's large neutron capture cross section makes it a good material for neutron absorption in control rods in nuclear power plants, but at the same time requires that it be removed from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |