|
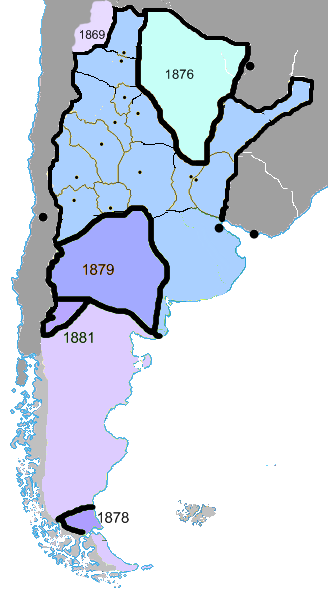
Zanja De Alsina
Zanja de Alsina (, '' Alsina's trench'') were a system of trenches and wooden watchtowers (''mangrullos'') built in the central and southern parts of Buenos Aires Province to defend the territories of the federal government against indigenous Mapuche '' malones''. The -wide trench was reinforced with 80 small strongholds and garrisons, called ''fortines''. The defensive line was named after Adolfo Alsina, Argentine Minister of War under President Nicolás Avellaneda Nicolás Remigio Aurelio Avellaneda Silva (3 October 1837 – 24 November 1885) was an Argentine politician and journalist, and President of Argentina from 1874 to 1880. Avellaneda's main projects while in office were banking and education ... who planned the building of the trench in the 1870s. The trench's purpose was denounced when it became clear that it was unable to stop large-scale incursions between 1876 and 1877. Conquest of the Desert Fortification lines Forts in Argentina Buildings and structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mapa ARGENTINA Frontera
Mapa or MAPA may refer to: People * Alec Mapa (born 1965), American actor, comedian and writer * Dennis Mapa (born 1969), Filipino economist and statistician * Jao Mapa (born 1976), Filipino actor * Placido Mapa Jr. (born 1932), Filipino businessman, economist, and government official * Suraj Mapa (born 1980), Sri Lankan actor * Victorino Mapa (1855–1927), Filipino chief justice and government official Other uses * "Mapa" (song), a 2021 song by SB19 * Mexican American Political Association * Mapa (publisher), an Israeli subsidiary of Ituran * Mapa Group, a Turkish conglomerate * Mapa, a company producing latex gloves that merged with Hutchinson SA in 1973 * Most Affected People and Areas, a climate justice concept See also * * Mappa (other) * Mapah (other) Mapah may refer to: * ''Ha-Mapah'' (Hebrew: "the tablecloth"), a commentary on the Shulchan Aruch by Moses Isserles * The Mapah, title of the French mystic Simon Ganneau Simon Ganneau (born circa 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
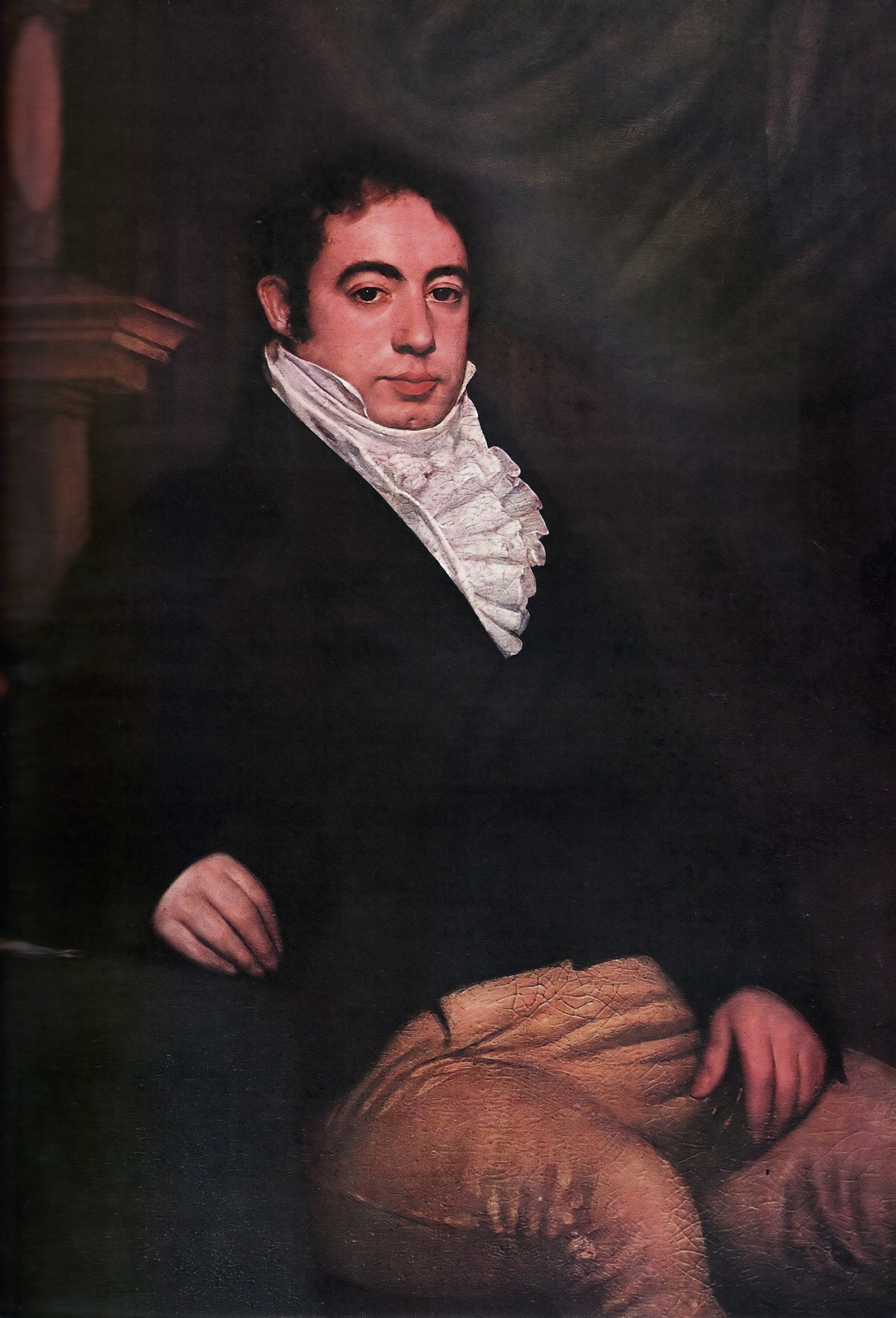
Adolfo Alsina
Adolfo Alsina Maza (January 4, 1829 – December 29, 1877) was an Argentine lawyer and Unitarian politician, who was one of the founders of the Autonomist Party and the National Autonomist Party.Ione S. Wright and Lisa M. Nekhom, ''Historical Dictionary of Argentina'' (1978) p 24 Biography Alsina was born in Buenos Aires, the son of Unitarian politician Valentín Alsina and Antonia Maza (daughter of Manuel Vicente Maza). He moved to Montevideo, Uruguay when Juan Manuel de Rosas became Governor of Buenos Aires Province for the second time, in 1835. In the neighbouring country Alsina started his law studies. After the Battle of Caseros in 1852, his family returned to Argentina, and his father was named a Minister by president Vicente López y Planes. Adolfo finished law school and joined the Unitarian army in the civil war. In 1860, after the Battle of Pavón and the National Union Pact, he took part in the commission responsible for the constitution reform of 1860. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trench
A trench is a type of excavation or in the ground that is generally deeper than it is wide (as opposed to a wider gully, or ditch), and narrow compared with its length (as opposed to a simple hole or pit). In geology, trenches result from erosion by rivers or by geological movement of tectonic plates. In civil engineering, trenches are often created to install underground utilities such as gas, water, power and communication lines. In construction, trenches are dug for foundations of buildings, retaining walls and dams, and for cut-and-cover construction of tunnels. In archaeology, the "trench method" is used for searching and excavating ancient ruins or to dig into strata of sedimented material. In geotechnical engineering, trenches serve for locating faults and investigating deep soil properties. In trench warfare, soldiers occupy trenches to protect them against weapons fire. Trenches are dug by use of manual tools such as shovels and pickaxes, or by heavy equipment such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buenos Aires Province
Buenos Aires (), officially the Buenos Aires Province (''Provincia de Buenos Aires'' ), is the largest and most populous Argentine province. It takes its name from the city of Buenos Aires, the capital of the country, which used to be part of the province and the province's capital until it was federalized in 1880. Since then, in spite of bearing the same name, the province does not include Buenos Aires proper, though it does include all other parts of the Greater Buenos Aires metropolitan area. The capital of the province is the city of La Plata, founded in 1882. It is bordered by the provinces of Entre Ríos to the northeast, Santa Fe to the north, Córdoba to the northwest, La Pampa to the west, Río Negro to the south and west and the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires to the northeast. Uruguay is just across the Rio de la Plata to the northeast, and both are on the coast of the Atlantic Ocean to the east. Almost the entire province is part of the Pampas geographical regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mapuche
The Mapuche ( (Mapuche & Spanish: )) are a group of indigenous inhabitants of south-central Chile and southwestern Argentina, including parts of Patagonia. The collective term refers to a wide-ranging ethnicity composed of various groups who shared a common social, religious, and economic structure, as well as a common linguistic heritage as Mapudungun speakers. Their habitat once extended from Aconcagua Valley to Chiloé Archipelago and later spread eastward to Puelmapu, a land comprising part of the Argentine pampa and Patagonia. Today the collective group makes up over 80% of the indigenous peoples in Chile, and about 9% of the total Chilean population. The Mapuche are particularly concentrated in the Araucanía region. Many have migrated from rural areas to the cities of Santiago and Buenos Aires for economic opportunities. The Mapuche traditional economy is based on agriculture; their traditional social organization consists of extended families, under the direction of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malón
''Malón'' (from the Mapudungun ''maleu,'' to inflict damage to the enemy) is the name given to plunder raids carried out by Mapuche warriors, who rode horses into Spanish, Chilean and Argentine territories from the 17th to the 19th centuries, as well as to their attacks on rival Mapuche factions. Historian Juan Ignacio Molina said the Mapuche considered the malón to be a means of obtaining justice: Leaders such as Lientur used the malón against European colonists: it consisted of a fast surprise attack by a number of mounted Mapuche warriors against the white (''huinca'') populations, ranches, settlements and fortifications in Chile and Argentina, with the aim of obtaining horses, cattle, provisions, and captives, often young women. The rapid attack without formal order did not give the targets time to organize a defense, and it left behind a devastated population unable to retaliate or pursue. In Chile, the Spaniards responded with a system of fortifications known as ''La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
President Of Argentina
The president of Argentina ( es, Presidente de Argentina), officially known as the president of the Argentine Nation ( es, Presidente de la Nación Argentina), is both head of state and head of government of Argentina. Under Constitution of Argentina, the national constitution, the president is also the Head of government, chief executive of the Government of Argentina, federal government and commander-in-chief of the Armed Forces of the Argentine Republic, armed forces. Throughout Argentine history, the List of heads of state of Argentina, office of head of state has undergone many changes, both in its title as in its features and powers. Current president Alberto Fernández was sworn into office on 10 December 2019. He succeeded Mauricio Macri. The constitution of Argentina, along with several constitutional amendments, establishes the requirements, powers, and responsibilities of the president and term of office and the method of election. History The origins of Argentina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicolás Avellaneda
Nicolás Remigio Aurelio Avellaneda Silva (3 October 1837 – 24 November 1885) was an Argentine politician and journalist, and President of Argentina from 1874 to 1880. Avellaneda's main projects while in office were banking and education reform, leading to Argentina's economic growth. The most important events of his government were the Conquest of the Desert and the transformation of the Buenos Aires into a federal district. His grandson was José Domingo Molina Gómez, who took presidency when Juan Perón was captured. Biography Born in San Miguel de Tucumán, his mother moved with him to Bolivia after the death of his father, Marco Avellaneda, during a revolt against Juan Manuel de Rosas. He studied law at Córdoba, without graduating. Back at Tucumán he founded '' El Eco del Norte'', and moved to Buenos Aires in 1857, becoming director of the ''El Nacional'' and editor of '' El Comercio de la Plata''. He finished his studies at Buenos Aires, meeting Domingo Faus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conquest Of The Desert
The Conquest of the Desert ( es, Conquista del desierto) was an Argentine military campaign directed mainly by General Julio Argentino Roca in the 1870s with the intention of establishing dominance over the Patagonian Desert, inhabited primarily by indigenous peoples. The Conquest of the Desert extended Argentine territories into Patagonia and ended Chilean expansion in the region. Argentine troops killed more than 1,000 Mapuche, displaced over 15,000 more from their traditional lands and enslaved a portion of the remaining natives. Settlers of European descent moved in and developed the lands through irrigation for agriculture, turning the territory into a breadbasket that contributed to the emergence of Argentina as an agricultural superpower in the early 20th century.''The Argentine Military and the Boundary Dispute With Chile, 1870-1902,'' George V. Rauch, p. 47, Greenwood Publishing Group, 1999 The conquest was paralleled by a similar campaign in Chile called the Occupati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fortification Lines
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ("to make"). From very early history to modern times, defensive walls have often been necessary for cities to survive in an ever-changing world of invasion and conquest. Some settlements in the Indus Valley civilization were the first small cities to be fortified. In ancient Greece, large stone walls had been built in Mycenaean Greece, such as the ancient site of Mycenae (famous for the huge stone blocks of its 'cyclopean' walls). A Greek '' phrourion'' was a fortified collection of buildings used as a military garrison, and is the equivalent of the Roman castellum or English fortress. These constructions mainly served the purpose of a watch tower, to guard certain roads, passes, and borders. Though smaller than a real fortress, they act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forts In Argentina
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ("to make"). From very early history to modern times, defensive walls have often been necessary for cities to survive in an ever-changing world of invasion and conquest. Some settlements in the Indus Valley civilization were the first small cities to be fortified. In ancient Greece, large stone walls had been built in Mycenaean Greece, such as the ancient site of Mycenae (famous for the huge stone blocks of its 'cyclopean' walls). A Greek '' phrourion'' was a fortified collection of buildings used as a military garrison, and is the equivalent of the Roman castellum or English fortress. These constructions mainly served the purpose of a watch tower, to guard certain roads, passes, and borders. Though smaller than a real fortress, they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |