|
Xplico
Xplico is a network forensics analysis tool (NFAT), which is a software that reconstructs the contents of acquisitions performed with a packet sniffer (e.g. Wireshark, tcpdump, Netsniff-ng). Unlike the protocol analyzer, whose main characteristic is not the reconstruction of the data carried by the protocols, Xplico was born expressly with the aim to reconstruct the protocol's application data and it is able to recognize the protocols with a technique named Port Independent Protocol Identification (PIPI). The name "xplico" refers to the Latin verb explico and its significance. Xplico is free and open-source software, subject to the requirements of the GNU General Public License (GPL), version 2. Overview To clarify what Xplico does we can imagine to have the raw data (Ethernet or PPP) of a web navigation (HTTP protocol), in this case Xplico is able to extract and reconstruct all the Web pages and contents (images, files, cookies, and so on). Similarly Xplico is able to reconst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netsniff-ng
netsniff-ng is a free Linux network analyzer and networking toolkit originally written by Daniel Borkmann. Its gain of performance is reached by zero-copy mechanisms for network packets (RX_RING, TX_RING), so that the Linux kernel does not need to copy packets from kernel space to user space via system calls such as recvmsg(). libpcap, starting with release 1.0.0, also supports the zero-copy mechanism on Linux for capturing (RX_RING), so programs using libpcap also use that mechanism on Linux. Overview netsniff-ng was initially created as a network sniffer with support of the Linux kernel packet-mmap interface for network packets, but later on, more tools have been added to make it a useful toolkit such as the iproute2 suite, for instance. Through the kernel's zero-copy interface, efficient packet processing can be reached even on commodity hardware. For instance, Gigabit Ethernet wire-speed has been reached with netsniff-ng's trafgen. The netsniff-ng toolkit does not depend on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Packet Sniffer
A packet analyzer, also known as packet sniffer, protocol analyzer, or network analyzer, is a computer program or computer hardware such as a packet capture appliance, that can intercept and log traffic that passes over a computer network or part of a network. Packet capture is the process of intercepting and logging traffic. As data streams flow across the network, the analyzer captures each packet and, if needed, decodes the packet's raw data, showing the values of various fields in the packet, and analyzes its content according to the appropriate RFC or other specifications. A packet analyzer used for intercepting traffic on wireless networks is known as a wireless analyzer or WiFi analyzer. While a packet analyzer can also be referred to as a network analyzer or protocol analyzer these terms can also have other meanings. Protocol analyzer can technically be a broader, more general class that includes packet analyzers/sniffers. However, the terms are frequently used interch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Packet Analyzer
A packet analyzer, also known as packet sniffer, protocol analyzer, or network analyzer, is a computer program or computer hardware such as a packet capture appliance, that can intercept and log traffic that passes over a computer network or part of a network. Packet capture is the process of intercepting and logging traffic. As data streams flow across the network, the analyzer captures each packet and, if needed, decodes the packet's raw data, showing the values of various fields in the packet, and analyzes its content according to the appropriate RFC or other specifications. A packet analyzer used for intercepting traffic on wireless networks is known as a wireless analyzer or WiFi analyzer. While a packet analyzer can also be referred to as a network analyzer or protocol analyzer these terms can also have other meanings. Protocol analyzer can technically be a broader, more general class that includes packet analyzers/sniffers. However, the terms are frequently used interch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C (programming Language)
C (''pronounced like the letter c'') is a General-purpose language, general-purpose computer programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie, and remains very widely used and influential. By design, C's features cleanly reflect the capabilities of the targeted CPUs. It has found lasting use in operating systems, device drivers, protocol stacks, though decreasingly for application software. C is commonly used on computer architectures that range from the largest supercomputers to the smallest microcontrollers and embedded systems. A successor to the programming language B (programming language), B, C was originally developed at Bell Labs by Ritchie between 1972 and 1973 to construct utilities running on Unix. It was applied to re-implementing the kernel of the Unix operating system. During the 1980s, C gradually gained popularity. It has become one of the measuring programming language popularity, most widely used programming languages, with C compilers avail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VoIP
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), also called IP telephony, is a method and group of technologies for the delivery of voice communications and multimedia sessions over Internet Protocol (IP) networks, such as the Internet. The terms Internet telephony, broadband telephony, and broadband phone service specifically refer to the provisioning of communications services (voice, fax, SMS, voice-messaging) over the Internet, rather than via the public switched telephone network (PSTN), also known as plain old telephone service (POTS). Overview The steps and principles involved in originating VoIP telephone calls are similar to traditional digital telephony and involve signaling, channel setup, digitization of the analog voice signals, and encoding. Instead of being transmitted over a circuit-switched network, the digital information is packetized and transmission occurs as IP packets over a packet-switched network. They transport media streams using special media delivery protocols t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real-time Transport Protocol
The Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) is a network protocol for delivering audio and video over IP networks. RTP is used in communication and entertainment systems that involve streaming media, such as telephony, video teleconference applications including WebRTC, television services and web-based push-to-talk features. RTP typically runs over User Datagram Protocol (UDP). RTP is used in conjunction with the RTP Control Protocol (RTCP). While RTP carries the media streams (e.g., audio and video), RTCP is used to monitor transmission statistics and quality of service (QoS) and aids synchronization of multiple streams. RTP is one of the technical foundations of Voice over IP and in this context is often used in conjunction with a signaling protocol such as the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) which establishes connections across the network. RTP was developed by the Audio-Video Transport Working Group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) and first published in 1996 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Session Initiation Protocol
The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is a signaling protocol used for initiating, maintaining, and terminating communication sessions that include voice, video and messaging applications. SIP is used in Internet telephony, in private IP telephone systems, as well as mobile phone calling over LTE (VoLTE). The protocol defines the specific format of messages exchanged and the sequence of communications for cooperation of the participants. SIP is a text-based protocol, incorporating many elements of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP). A call established with SIP may consist of multiple media streams, but no separate streams are required for applications, such as text messaging, that exchange data as payload in the SIP message. SIP works in conjunction with several other protocols that specify and carry the session media. Most commonly, media type and parameter negotiation and media setup are performed with the Session Description ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SSH File Transfer Protocol
In computing, the SSH File Transfer Protocol (also known as Secure File Transfer Protocol or SFTP) is a network protocol that provides file access, file transfer, and file management over any reliable data stream. It was designed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) as an extension of the Secure Shell protocol (SSH) version 2.0 to provide secure file transfer capabilities. The IETF Internet Draft states that, even though this protocol is described in the context of the SSH-2 protocol, it could be used in a number of different applications, such as secure file transfer over Transport Layer Security (TLS) and transfer of management information in VPN applications. This protocol assumes that it is run over a secure channel, such as SSH, that the server has already authenticated the client, and that the identity of the client user is available to the protocol. Capabilities Compared to the SCP protocol, which only allows file transfers, the SFTP protocol allows for a range of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lawful Interception
Lawful interception (LI) refers to the facilities in telecommunications and telephone networks that allow law enforcement agencies with court orders or other legal authorization to selectively wiretap individual subscribers. Most countries require licensed telecommunications operators to provide their networks with Legal Interception gateways and nodes for the interception of communications. The interfaces of these gateways have been standardized by telecommunication standardization organizations. As with many law enforcement tools, LI systems may be subverted for illicit purposes. With the legacy public switched telephone network (PSTN), wireless, and cable systems, lawful interception (LI) was generally performed by accessing the mechanical or digital switches supporting the targets' calls. The introduction of packet switched networks, softswitch technology, and server-based applications during the past two decades fundamentally altered how LI is undertaken. Lawful interception ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
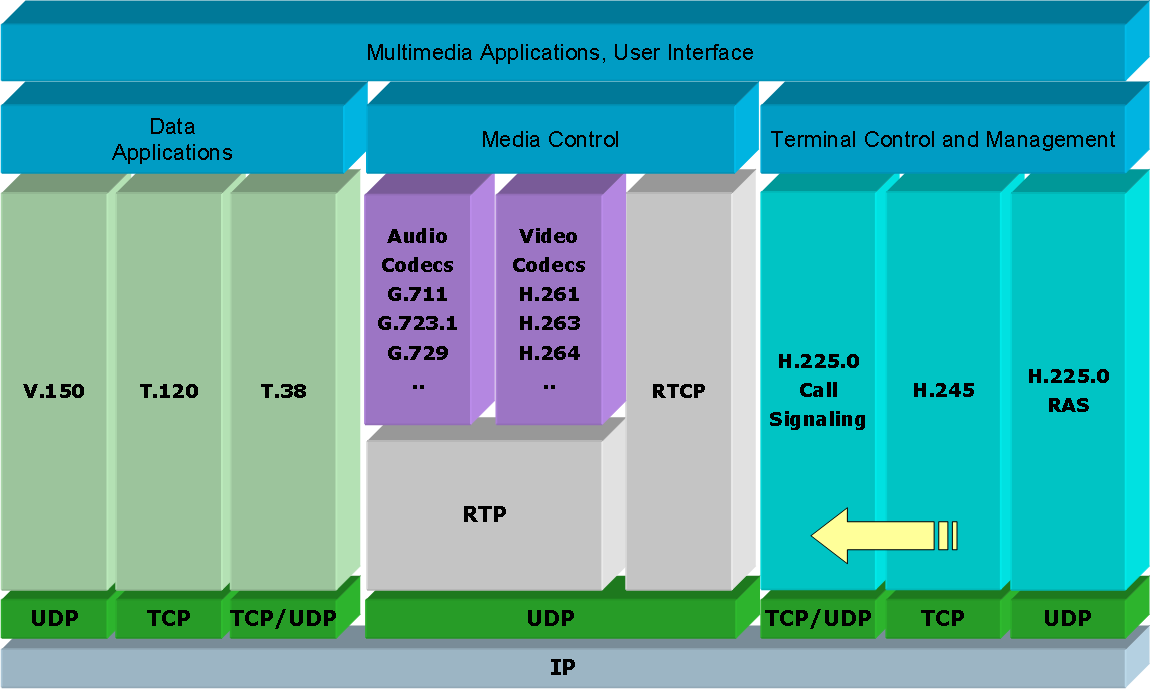
H323
H.323 is a recommendation from the ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) that defines the protocols to provide audio-visual communication sessions on any packet network. The H.323 standard addresses call signaling and control, multimedia transport and control, and bandwidth control for point-to-point and multi-point conferences. It is widely implemented by voice and videoconferencing equipment manufacturers, is used within various Internet real-time applications such as GnuGK and NetMeeting and is widely deployed worldwide by service providers and enterprises for both voice and video services over IP networks. It is a part of the ITU-T H.32x series of protocols, which also address multimedia communications over ISDN, the PSTN or SS7, and 3G mobile networks. H.323 call signaling is based on the ITU-T Recommendation Q.931 protocol and is suited for transmitting calls across networks using a mixture of IP, PSTN, ISDN, and QSIG over ISDN. A call model, similar to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post Office Protocol
In computing, the Post Office Protocol (POP) is an application-layer Internet standard protocol used by e-mail clients to retrieve e-mail from a mail server. POP version 3 (POP3) is the version in common use, and along with IMAP the most common protocols for email retrieval. Purpose The Post Office Protocol provides access via an Internet Protocol (IP) network for a user client application to a mailbox (''maildrop'') maintained on a mail server. The protocol supports download and delete operations for messages. POP3 clients connect, retrieve all messages, store them on the client computer, and finally delete them from the server. This design of POP and its procedures was driven by the need of users having only temporary Internet connections, such as dial-up access, allowing these users to retrieve e-mail when connected, and subsequently to view and manipulate the retrieved messages when offline. POP3 clients also have an option to leave mail on the server after download. By contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Media Gateway Control Protocol
The Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP) is a signaling and call control communication protocol used in voice over IP (VoIP) telecommunication systems. It implements the media gateway control protocol architecture for controlling media gateways connected to the public switched telephone network (PSTN).RFC 2805, Media Gateway Control Protocol Architecture and Requirements, N. Greene, M. Ramalho, B. Rosen, IETF, April 2000 The media gateways provide conversion of traditional electronic media to the Internet Protocol (IP) network. The protocol is a successor to the Simple Gateway Control Protocol (SGCP), which was developed by Bellcore and Cisco, and the Internet Protocol Device Control (IPDC). The methodology of MGCP reflects the structure of the PSTN with the power of the network residing in a call control center softswitch which is analogous to the central office in the telephone network. The endpoints are low-intelligence devices, mostly executing control commands from a call ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |